DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.G Workshop Manual
Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1998, Model line: RAM 1500, Model: DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.GPages: 2627
Page 1501 of 2627

(5) Make sure the provided seal pilot is installed
into the new crankshaft seal. Use the alignment/in-
stallation tool and press the seal onto the crankshaft
(Fig. 75). Alternately drive the seal at the 12, 3, 6
and 9 o'clock positions.
(6) Remove the alignment tool and trim the
retainer gasket even with the oil pan mounting sur-
face (Fig. 76).
(7) Remove the seal pilot.
(8) Apply a small amount of MopartSilicone Rub-
ber Adhesive Sealant to the oil pan rail T-joints.
(9) Install the four (4) oil pan rear mounting bolts
and torque to 28 N´m (21 ft. lbs.).
(10) Install new rectangular ring seal for cam bore.
(11) Install the flywheel housing and bolts. Torque
bolts to 77 N´m (57 ft. lbs.).
(12) Install the flywheel or converter drive plate.
Tighten bolts to 137 N´m (101 ft. lbs.).
(13) Install the starter motor Refer to (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/STARTING/STARTER MOTOR -
INSTALLATION).
(14) Install the transmission and transfer case (if
equipped).
(15) Lower vehicle.(16) Fill the crankcase with new engine oil.
(17) Connect the battery negative cables.
(18) Start engine and check for oil leaks.
Fig. 74 Aligning Seal Retainer with Alignment/
Installation Tool
1 - ALIGNMENT / INSTALLATION TOOL
2 - SEAL RETAINER
Fig. 75 Installing Seal Using Alignment Tool and
Hammer
1 - SEAL PILOT TOOL
2 - INSTALLATION TOOL
3 - SEAL
4 - RETAINER
Fig. 76 Trimming Excess Gasket Material
1 - GASKET
9 - 278 ENGINE 5.9L DIESELDR
CRANKSHAFT REAR OIL SEAL RETAINER (Continued)
Page 1502 of 2627

SOLID LIFTERS/TAPPETS
REMOVAL
NOTE: This procedure requires use of Miller Tool
8502 Tappet Replacement Kit.
(1) Remove camshaft (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/EN-
GINE BLOCK/CAMSHAFT & BEARINGS (IN
BLOCK) - REMOVAL).
(2) Insert the trough (provided with tool kit) the
full length of the camshaft bore (Fig. 77). Make sure
the cap end goes in first and the open side faces up
(towards tappets).
(3)Remove only one tappet at a time.Remove
rubber band from one cylinder pair and attach tappet
dowel not being removed to the next cylinder pair
(Fig. 78).
(4) Raise dowel rod (disengage from tappet) and
allow tappet to fall into trough (Fig. 79).
(5) Carefully remove trough(do not rotate)and
tappet. If the tappet is not being replaced, mark it so
it can be installed in its original location.
(6) Re-install trough and repeat procedure on
remaining tappets.
CLEANING
Clean tappet with a suitable solvent. Rinse in hot
water and blow dry with a clean shop rag or com-
pressed air.
INSPECTION
(1) Visually inspect the tappet the tappet socket,
stem, and face for excessive wear, cracks, or obvious
damage (Fig. 80).
(2) Measure the tappet stem diameter. Replace the
tappet if it falls below the minimum size (Fig. 80).
Fig. 77 Inserting the Trough - Typical
1 - TROUGH
Fig. 78 Secure Dowel/Tappet to Adjacent Cylinder -
typical
Fig. 79 Lift Dowel Rod to Disengage from Tappet -
typical
Fig. 80 Tappet Inspection
TAPPET STEM DIAMETER
15.936 mm (0.627 in.) MIN.
15.977 mm (0.629 in.) MAX.
DRENGINE 5.9L DIESEL 9 - 279
Page 1503 of 2627
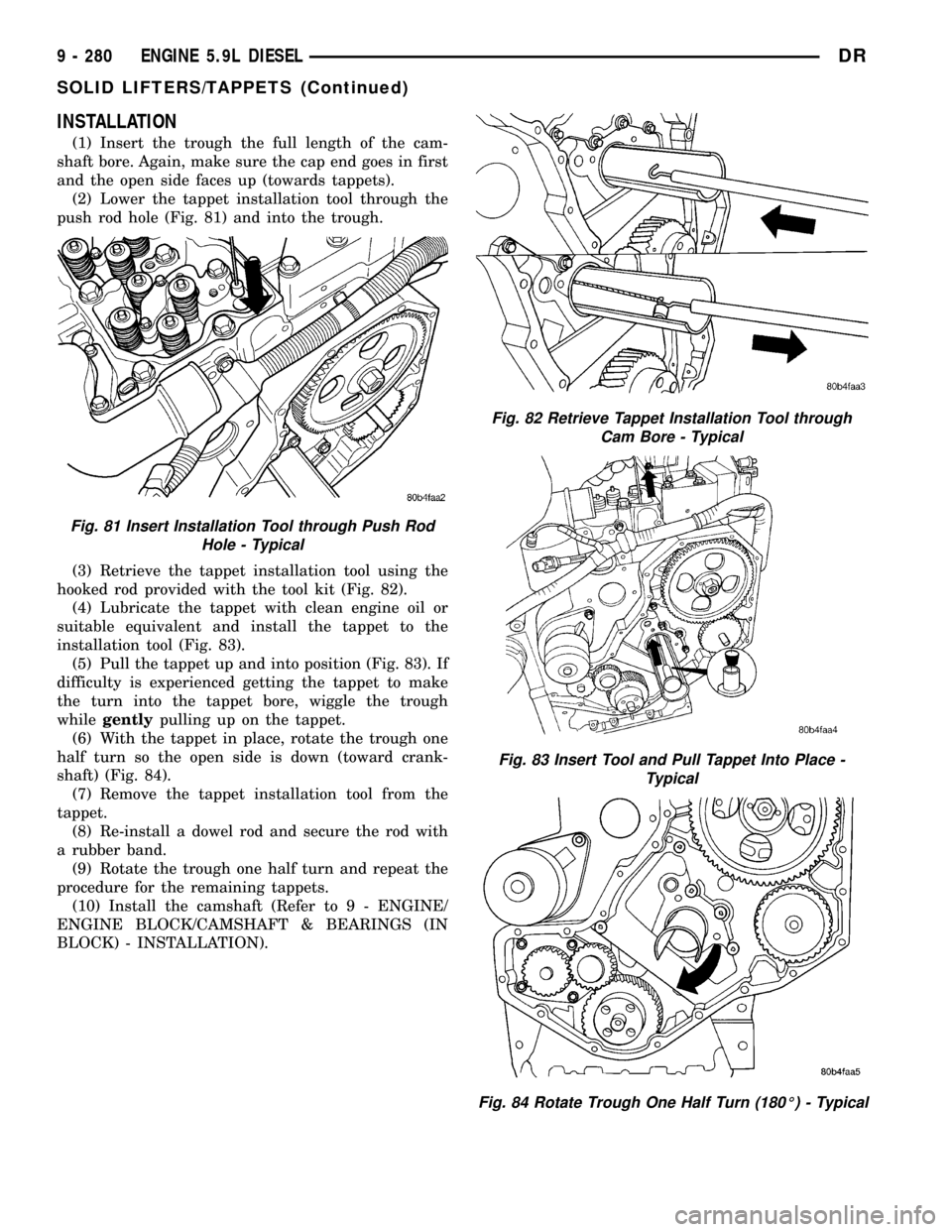
INSTALLATION
(1) Insert the trough the full length of the cam-
shaft bore. Again, make sure the cap end goes in first
and the open side faces up (towards tappets).
(2) Lower the tappet installation tool through the
push rod hole (Fig. 81) and into the trough.
(3) Retrieve the tappet installation tool using the
hooked rod provided with the tool kit (Fig. 82).
(4) Lubricate the tappet with clean engine oil or
suitable equivalent and install the tappet to the
installation tool (Fig. 83).
(5) Pull the tappet up and into position (Fig. 83). If
difficulty is experienced getting the tappet to make
the turn into the tappet bore, wiggle the trough
whilegentlypulling up on the tappet.
(6) With the tappet in place, rotate the trough one
half turn so the open side is down (toward crank-
shaft) (Fig. 84).
(7) Remove the tappet installation tool from the
tappet.
(8) Re-install a dowel rod and secure the rod with
a rubber band.
(9) Rotate the trough one half turn and repeat the
procedure for the remaining tappets.
(10) Install the camshaft (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
ENGINE BLOCK/CAMSHAFT & BEARINGS (IN
BLOCK) - INSTALLATION).
Fig. 81 Insert Installation Tool through Push Rod
Hole - Typical
Fig. 82 Retrieve Tappet Installation Tool through
Cam Bore - Typical
Fig. 83 Insert Tool and Pull Tappet Into Place -
Typical
Fig. 84 Rotate Trough One Half Turn (180É) - Typical
9 - 280 ENGINE 5.9L DIESELDR
SOLID LIFTERS/TAPPETS (Continued)
Page 1504 of 2627
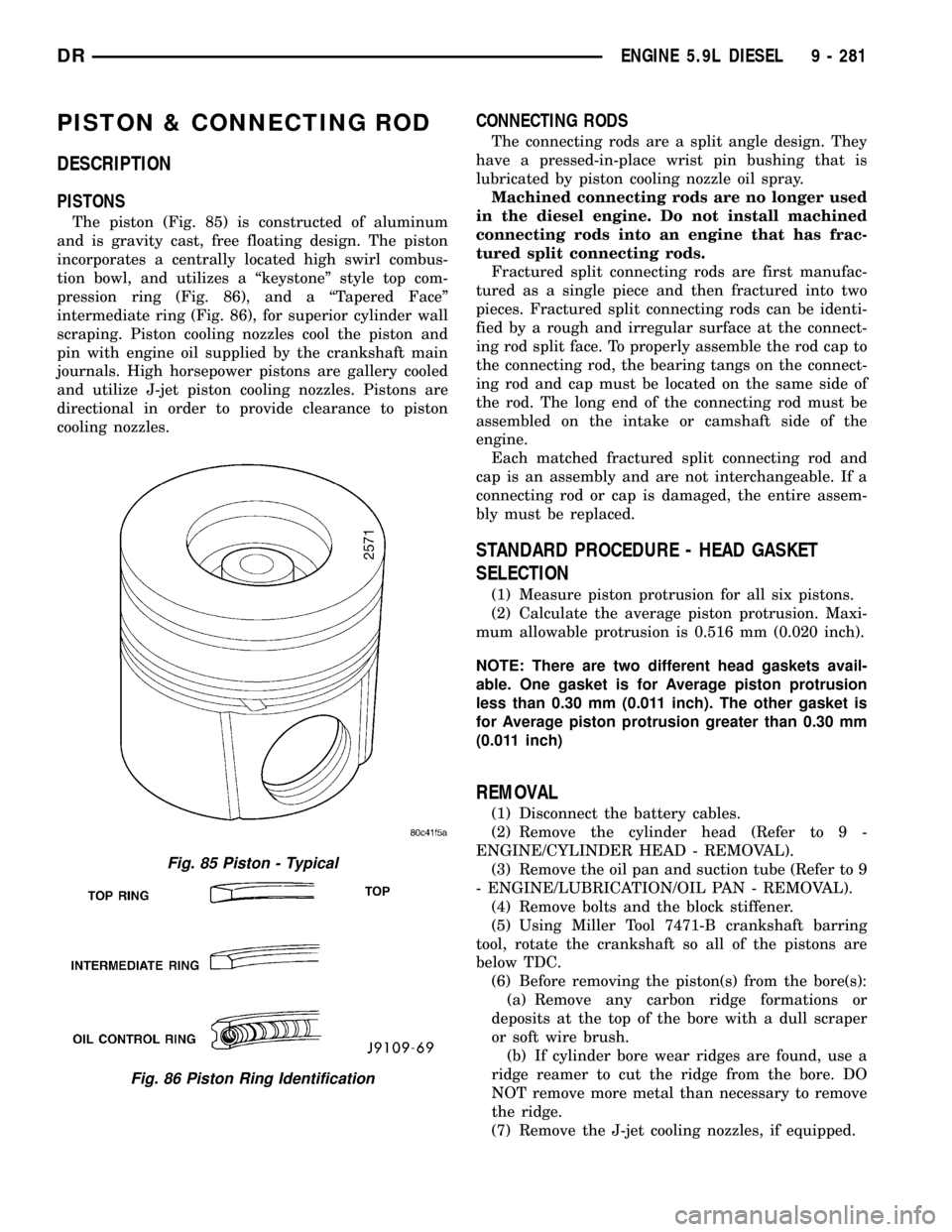
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD
DESCRIPTION
PISTONS
The piston (Fig. 85) is constructed of aluminum
and is gravity cast, free floating design. The piston
incorporates a centrally located high swirl combus-
tion bowl, and utilizes a ªkeystoneº style top com-
pression ring (Fig. 86), and a ªTapered Faceº
intermediate ring (Fig. 86), for superior cylinder wall
scraping. Piston cooling nozzles cool the piston and
pin with engine oil supplied by the crankshaft main
journals. High horsepower pistons are gallery cooled
and utilize J-jet piston cooling nozzles. Pistons are
directional in order to provide clearance to piston
cooling nozzles.
CONNECTING RODS
The connecting rods are a split angle design. They
have a pressed-in-place wrist pin bushing that is
lubricated by piston cooling nozzle oil spray.
Machined connecting rods are no longer used
in the diesel engine. Do not install machined
connecting rods into an engine that has frac-
tured split connecting rods.
Fractured split connecting rods are first manufac-
tured as a single piece and then fractured into two
pieces. Fractured split connecting rods can be identi-
fied by a rough and irregular surface at the connect-
ing rod split face. To properly assemble the rod cap to
the connecting rod, the bearing tangs on the connect-
ing rod and cap must be located on the same side of
the rod. The long end of the connecting rod must be
assembled on the intake or camshaft side of the
engine.
Each matched fractured split connecting rod and
cap is an assembly and are not interchangeable. If a
connecting rod or cap is damaged, the entire assem-
bly must be replaced.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - HEAD GASKET
SELECTION
(1) Measure piston protrusion for all six pistons.
(2) Calculate the average piston protrusion. Maxi-
mum allowable protrusion is 0.516 mm (0.020 inch).
NOTE: There are two different head gaskets avail-
able. One gasket is for Average piston protrusion
less than 0.30 mm (0.011 inch). The other gasket is
for Average piston protrusion greater than 0.30 mm
(0.011 inch)
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the battery cables.
(2) Remove the cylinder head (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - REMOVAL).
(3) Remove the oil pan and suction tube (Refer to 9
- ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PAN - REMOVAL).
(4) Remove bolts and the block stiffener.
(5) Using Miller Tool 7471-B crankshaft barring
tool, rotate the crankshaft so all of the pistons are
below TDC.
(6) Before removing the piston(s) from the bore(s):
(a) Remove any carbon ridge formations or
deposits at the top of the bore with a dull scraper
or soft wire brush.
(b) If cylinder bore wear ridges are found, use a
ridge reamer to cut the ridge from the bore. DO
NOT remove more metal than necessary to remove
the ridge.
(7) Remove the J-jet cooling nozzles, if equipped.
Fig. 85 Piston - Typical
Fig. 86 Piston Ring Identification
DRENGINE 5.9L DIESEL 9 - 281
Page 1505 of 2627

NOTE: If cylinders have ridges, the cylinders are
oversize and will more than likely need boring.
(8) Using a hammer and steel stamp, stamp the
cylinder number in the top of each piston. The front
of the piston is identified by a stamping on the top of
the piston. DO NOT stamp in the outside 5 mm (.197
in.) of the piston diameter. DO NOT stamp over the
piston pin.
(9) Mark the connecting rod and cap with the cor-
responding cylinder numbers.
(10) Remove the connecting rod bolts and rod caps.
Use care so the cylinder bores and connecting rods
are not damaged.
(11) Use a hammer handle or similar object to
push the piston and connecting rod through the cyl-
inder bore.
(12) Store the piston/rod assemblies in a rack.
CLEANINGÐPISTON AND CONNECTING ROD
CAUTION: DO NOT use bead blast to clean the pis-
tons. DO NOT clean the pistons and rods in an acid
tank.
PISTON
Clean the pistons and pins in a suitable solvent,
rinse in hot water and blow dry with compressed air.
Soaking the pistons over night will loosen most of the
carbon build up. De-carbon the ring grooves with a
broken piston ring and again clean the pistons in sol-
vent. Rinse in hot water and blow dry with com-
pressed air.
CONNECTING ROD
Clean the connecting rods in a suitable solvent,
rinse in hot water and blow dry with compressed air.
INSPECTION
INSPECTION - PISTONS
Inspect the pistons for damage and excessive wear.
Check top of the piston, ring grooves, skirt and pin
bore. Measure the piston skirt diameter. If the piston
is out of limits, replace the piston.
PISTON SKIRT DIAMETER (MIN.)
101.775 mm (4.006 in. )The upper groove only needs to be inspected for
damage. Use a new piston ring to measure the clear-
ance in the intermediate ring groove (Fig. 87). Mini-
mum clearance is 0.045 mm (0.0018 inch), maximum
clearance is 0.095 mm (.0037 inch). If the clearance
of the intermediate ring exceeds specifications,
replace the piston.
Use a new oil ring to measure the clearance in the
oil groove (Fig. 87). Minimum clearance is 0.040 mm
(0.0016 inch), maximum clearance is 0.085 mm
(.0033 inch). If the clearance exceeds specifications,
replace the piston.
Measure the pin bore (Fig. 88). The maximum
diameter is 40.012 mm (1.5753 inch), Minimum is
40.006 mm (1.575 inch). If the bore is over limits,
replace the piston.
Fig. 87 Intermediate and Oil Ring Clearances
1 - FEELER GAUGE
2 - RING
3 - PISTON
Fig. 88 Piston Pin Bore
1 - PISTON
2 - PIN BORE
9 - 282 ENGINE 5.9L DIESELDR
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD (Continued)
Page 1506 of 2627

Inspect the piston pin for nicks, gouges and exces-
sive wear. Measure the pin diameter (Fig. 89). The
minimum diameter is 39.990 mm (1.5744 inch), max-
imum 40.003 mm (1.5749 inch). If the diameter is out
of limits, replace the pin.
INSPECTIONÐCONNECTING ROD
Inspect the connecting rod for damage and wear.
The I-Beam section of the connecting rod cannot have
dents or other damage. Damage to this part can
cause stress risers which will progress to breakage.
Measure the connecting rod pin bore (Fig. 90). The
maximum diameter is 40.042 mm (1.5765 inch), min-
imum diameter is 40.019 mm (1.5756 inch). If out of
limits, replace the connecting rod.
INSTALLATION
(1) Lubricate the cylinder bores with clean engine
oil.
(2) Generously lubricate the rings and piston
skirts with clean engine oil.(3) Orientate the rings on the piston (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/PISTON RINGS - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE).
(4) Compress the rings using a piston ring com-
pressor tool (Fig. 91). If using a strap-type ring com-
pressor, make sure the inside end of the strap does
not hook on a ring gap and break the ring.
(5) Bar the crankshaft so the rod journal for the
piston to be installed is at BDC (Bottom Dead Cen-
ter) - (Fig. 92).
(6) Make sure the front of the piston is oriented
properly according to the marking on the top of the
piston and the connecting rod is oriented properly.
(7) Position the piston and rod assembly into the
cylinder bore with the front of the piston oriented
properly according to the stamping in the top of the
piston. Use care when you install the piston and con-
necting rod so the cylinder bore is not damaged. The
long side of the connecting rod must be installed on
the intake side of the engine.
(8) Push the piston into the bore until the top of
the piston is approximately 50 mm (2 inch) below the
top of the block. Carefully pull the connecting rod
onto the crankshaft journal.
(9) Use clean engine oil to lubricate the threads
and under the heads of the connecting rod bolts.
Fig. 89 Piston Pin Diameter
1 - PISTON PIN
Fig. 90 Connecting Rod Pin Bore
1 - CONNECTING ROD
Fig. 91 Piston Ring Compressor Tool
1 - PISTON RING COMPRESSOR TOOL
Fig. 92 Piston/Rod Assembly at BDC
DRENGINE 5.9L DIESEL 9 - 283
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD (Continued)
Page 1507 of 2627
(10)For fractured/split type connecting rods,
the long end of the rod must be installed towards the
intake side of the engine.
(a) The connecting rod split/face must face
toward the same side as the piston notch feature
on the skirt. The split face will face toward the
exhaust side of the engine if properly installed.
(11) Install the rod cap and bolts to the connecting
rod. Tighten the connecting rod bolts evenly in 3
steps.
²Tighten the bolts to 30 N´m (22 ft. lbs.) torque.
²Tighten the bolts to 60 N´m (44 ft. lbs.) torque.
²Rotate 60É clockwise.
(12) The crankshaft must rotate freely. Check for
freedom of rotation as the caps are installed. If the
crankshaft does not rotate freely, check the installa-
tion of the rod bearing and the bearing size.
(13) Measure the side clearance between the con-
necting rod and the crankshaft. DO NOT measure
the clearance between the cap and crankshaft.
(14) Install J-jet piston cooling nozzles if equipped.
(15) Install block stiffener. Torque to 43 N´m (32 ft.
lbs.).
(16) Install the suction tube and oil pan (Refer to 9
- ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PAN - INSTALLA-
TION).
(17) Install the cylinder head onto the engine
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - INSTAL-
LATION).
(18) Install a new filter and fill the crankcase with
new engine oil.Prefill the filter with clean oil.
(19) Connect the battery negative cables and start
engine.
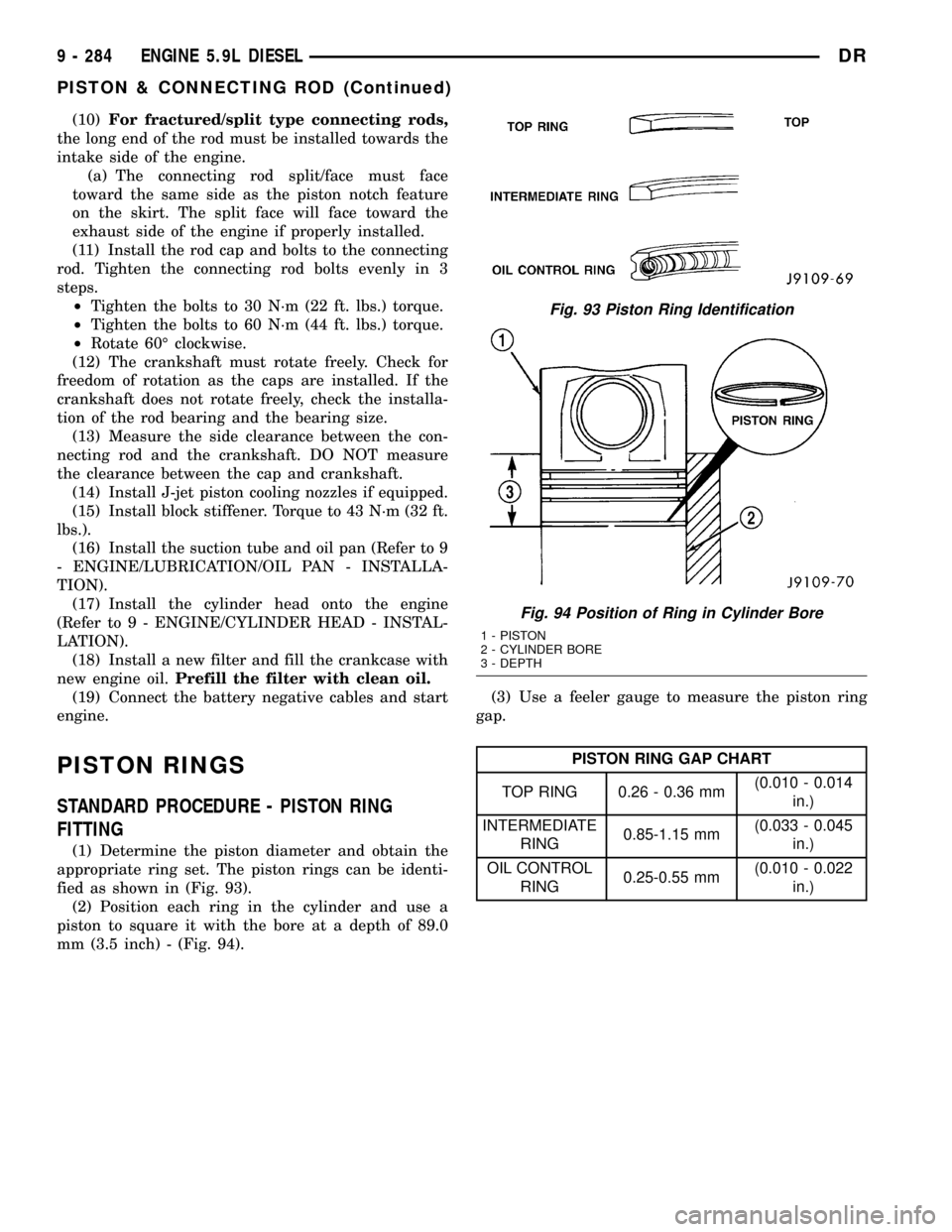
PISTON RINGS
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PISTON RING
FITTING
(1) Determine the piston diameter and obtain the
appropriate ring set. The piston rings can be identi-
fied as shown in (Fig. 93).
(2) Position each ring in the cylinder and use a
piston to square it with the bore at a depth of 89.0
mm (3.5 inch) - (Fig. 94).(3) Use a feeler gauge to measure the piston ring
gap.
PISTON RING GAP CHART
TOP RING 0.26 - 0.36 mm(0.010 - 0.014
in.)
INTERMEDIATE
RING0.85-1.15 mm(0.033 - 0.045
in.)
OIL CONTROL
RING0.25-0.55 mm(0.010 - 0.022
in.)
Fig. 93 Piston Ring Identification
Fig. 94 Position of Ring in Cylinder Bore
1 - PISTON
2 - CYLINDER BORE
3 - DEPTH
9 - 284 ENGINE 5.9L DIESELDR
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD (Continued)
Page 1508 of 2627

(4) The top surface of all of the rings are identified
with the word TOP or the supplier's MARK. Assem-
ble the rings with the word TOP or the supplier's
MARK up.
(5) Position the oil ring expander in the oil control
ring groove (bottom groove).
(6) Install the oil control ring with the end gap
OPPOSITE the ends on the expander (Fig. 95).
(7) Install the intermediate piston ring in the sec-
ond groove.
(8) Install the top piston ring in the top groove
(Fig. 96).
(9) Position the rings as shown in (Fig. 97).
VIBRATION DAMPER
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).(2) Remove the four (4) damper to crankshaft bolts
and remove damper and speed indicator ring.
INSPECTION
(1) Inspect the damper hub for cracks and replace
if any are found.
(2) Inspect the index lines on the damper hub and
the inertia member (Fig. 98). If the lines are more
than 1.59 mm (1/16 in.) out of alignment, replace the
damper.
(3) Inspect the rubber member for deterioration or
missing segments (Fig. 99).Fig. 95 Oil Control Ring/Expander Location in
Groove
1 - OIL CONTROL RING
2 - EXPANDER
3 - PISTON
Fig. 96 Piston Ring Installation Tool
1 - PISTON RING INSTALLATION TOOL
Fig. 97 Piston Ring Orientation
1 - TOP RING
2 - INTERMEDIATE RING
3 - OIL CONTROL RING
Fig. 98 Inspect Index Lines for Alignment
1 - INDEX LINES
2 - HUB
3 - INERTIA MEMBER
DRENGINE 5.9L DIESEL 9 - 285
PISTON RINGS (Continued)
Page 1509 of 2627

INSTALLATION
(1) Install speed indicator ring.
NOTE: The speed indicator ring is located over a
dowel pin.
(2) Install the crankshaft damper and bolts.
Tighten bolts to 40 N´m (30 ft. lbs.) torque, plus an
additional 60É.
NOTE: The damper must be installed so the hole is
located over the dowel pin.
(3) Install the accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
INSTALLATION).
FRONT MOUNT
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the battery negative cables.
(2) Remove the viscous fan/drive assembly (Refer
to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/RADIATOR FAN -
REMOVAL).
(3) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(4) Install engine support fixture tool# 8534 and
steel bracket tool # 8534A
(5) Loosen the thru-bolt and nut.
(6) Lift the engine SLIGHTLY and remove the
insulator to block bolts (Fig. 101) (Fig. 100).
(7) Remove the insulator from the vehicle.
Fig. 99 Inspect Damper Rubber Member
Fig. 100 RH Insulator
1 - Mount
2 - Insulator
3 - Bolt
Fig. 101 LH Insulator
1 - Bolt
2 - Insulator
3 - Mount
9 - 286 ENGINE 5.9L DIESELDR
VIBRATION DAMPER (Continued)
Page 1510 of 2627

INSTALLATION
(1) With engine raised SLIGHTLY, position the
insulator to the mount (Fig. 102) (Fig. 103). Install
the bolts and torque to specification.
(2) Lower the engine using tool # 8534, while guid-
ing the mount and thru-bolt into the frame mounted
support cushion brackets.
(3) Install the thru-bolt nut and tighten the nut to
95 N´m (70 ft. lbs.) torque.(4) Remove the engine support fixture tool #8534.
(5) Lower the vehicle.
(6) Install the viscous fan/drive assembly (Refer to
7 - COOLING/ENGINE/RADIATOR FAN - INSTAL-
LATION).
(7) Connect the battery negative cables.
Fig. 102 LH Insulator
1 - Bolt
2 - Insulator
3 - Mount
Fig. 103 RH Insulator
1 - Mount
2 - Insulator
3 - Bolt
DRENGINE 5.9L DIESEL 9 - 287
FRONT MOUNT (Continued)