Cooling DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1998, Model line: RAM 1500, Model: DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.GPages: 2627
Page 2492 of 2627
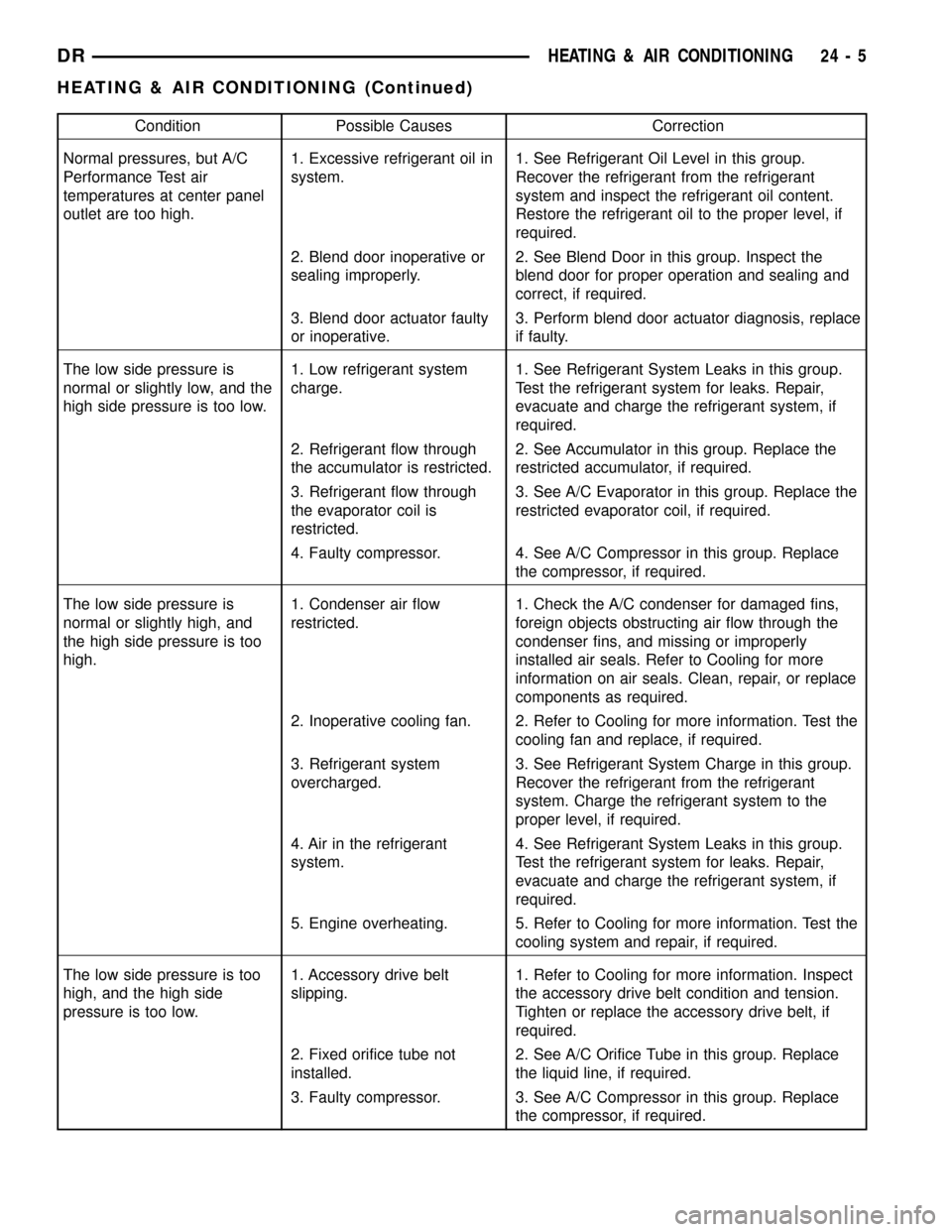
Condition Possible Causes Correction
Normal pressures, but A/C
Performance Test air
temperatures at center panel
outlet are too high.1. Excessive refrigerant oil in
system.1. See Refrigerant Oil Level in this group.
Recover the refrigerant from the refrigerant
system and inspect the refrigerant oil content.
Restore the refrigerant oil to the proper level, if
required.
2. Blend door inoperative or
sealing improperly.2. See Blend Door in this group. Inspect the
blend door for proper operation and sealing and
correct, if required.
3. Blend door actuator faulty
or inoperative.3. Perform blend door actuator diagnosis, replace
if faulty.
The low side pressure is
normal or slightly low, and the
high side pressure is too low.1. Low refrigerant system
charge.1. See Refrigerant System Leaks in this group.
Test the refrigerant system for leaks. Repair,
evacuate and charge the refrigerant system, if
required.
2. Refrigerant flow through
the accumulator is restricted.2. See Accumulator in this group. Replace the
restricted accumulator, if required.
3. Refrigerant flow through
the evaporator coil is
restricted.3. See A/C Evaporator in this group. Replace the
restricted evaporator coil, if required.
4. Faulty compressor. 4. See A/C Compressor in this group. Replace
the compressor, if required.
The low side pressure is
normal or slightly high, and
the high side pressure is too
high.1. Condenser air flow
restricted.1. Check the A/C condenser for damaged fins,
foreign objects obstructing air flow through the
condenser fins, and missing or improperly
installed air seals. Refer to Cooling for more
information on air seals. Clean, repair, or replace
components as required.
2. Inoperative cooling fan. 2. Refer to Cooling for more information. Test the
cooling fan and replace, if required.
3. Refrigerant system
overcharged.3. See Refrigerant System Charge in this group.
Recover the refrigerant from the refrigerant
system. Charge the refrigerant system to the
proper level, if required.
4. Air in the refrigerant
system.4. See Refrigerant System Leaks in this group.
Test the refrigerant system for leaks. Repair,
evacuate and charge the refrigerant system, if
required.
5. Engine overheating. 5. Refer to Cooling for more information. Test the
cooling system and repair, if required.
The low side pressure is too
high, and the high side
pressure is too low.1. Accessory drive belt
slipping.1. Refer to Cooling for more information. Inspect
the accessory drive belt condition and tension.
Tighten or replace the accessory drive belt, if
required.
2. Fixed orifice tube not
installed.2. See A/C Orifice Tube in this group. Replace
the liquid line, if required.
3. Faulty compressor. 3. See A/C Compressor in this group. Replace
the compressor, if required.
DRHEATING & AIR CONDITIONING 24 - 5
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)
Page 2493 of 2627

Condition Possible Causes Correction
The low side pressure is too
low, and the high side
pressure is too high.1. Restricted refrigerant flow
through the refrigerant lines.1. See Liquid, Suction, and Discharge Line in this
group. Inspect the refrigerant lines for kinks, tight
bends or improper routing. Correct the routing or
replace the refrigerant line, if required.
2. Restricted refrigerant flow
through the fixed orifice tube.2. See A/C Orifice Tube in this group. Replace
the liquid line, if required.
3. Restricted refrigerant flow
through the condenser.3. See A/C Condenser in this group. Replace the
restricted condenser, if required.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HEATER
PERFORMANCE TEST
Review Safety Warnings and Cautions before per-
forming this procedure (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - WARNING) and
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - CAUTION).
Check the coolant level, drive belt tension, vacuum
line connections, radiator air flow and fan operation.
Start engine and allow to warm up to normal tem-
perature.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE RADIATOR CAP
WHEN ENGINE IS HOT, PERSONAL INJURY CAN
RESULT.
If vehicle has been run recently, wait 15 minutes
before removing cap. Place a rag over the cap andturn it to the first safety stop. Allow pressure to
escape through the overflow tube. When the system
stabilizes, remove the cap completely.
MAXIMUM HEATER OUTPUT: TEST AND ACTION
Engine coolant is provided to the heater system by
two heater hoses. With the engine idling at normal
operating temperature, set the temperature control
to maximum heat, the mode control to the floor posi-
tion, and the blower in the highest speed position.
Using a test thermometer, check the temperature of
the air being discharged from the floor outlets. Com-
pare the test thermometer reading to the Tempera-
ture Reference chart.
TEMPERATURE REFERENCE CHART
Ambient Air Temperature15.5É C
(60É F)21.1É C
(70É F)26.6É C
(80É F)32.2É C
(90É F)
Minimum Air Temperature at
Floor Outlet62.2É C
(144É F)63.8É C
(147É F)65.5É C
(150É F)67.2É C
(153É F)
Both of the heater hoses should be HOT to the
touch (coolant return hose should be slightly cooler
than the supply hose). If the coolant return hose is
much cooler than the supply hose, locate and repair
the engine coolant flow obstruction in the heater sys-
tem. If both heater hoses are cool to the touch,
inspect the engine cooling system (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
OBSTRUCTED COOLANT FLOW Possible loca-
tions or causes of obstructed coolant flow are as fol-
lows:
²Pinched or kinked heater hoses.
²Improper heater hose routing.
²Plugged heater hoses or supply and return ports
at the cooling system connections.
²Plugged heater core.If proper coolant flow through the cooling system is
verified, and heater outlet air temperature is insuffi-
cient, a mechanical problem may exist.
MECHANICAL PROBLEMS Possible causes of
insufficient heat due to mechanical problems are as
follows:
²Obstructed cowl air intake.
²Obstructed heater system outlets.
²Blend door not functioning properly.
TEMPERATURE CONTROL
If the heater outlet air temperature cannot be
adjusted with the temperature control knob on the
A/C-heater control, the following could require ser-
vice:
²Blend door binding.
²Faulty blend door motor.
24 - 6 HEATING & AIR CONDITIONINGDR
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)
Page 2495 of 2627
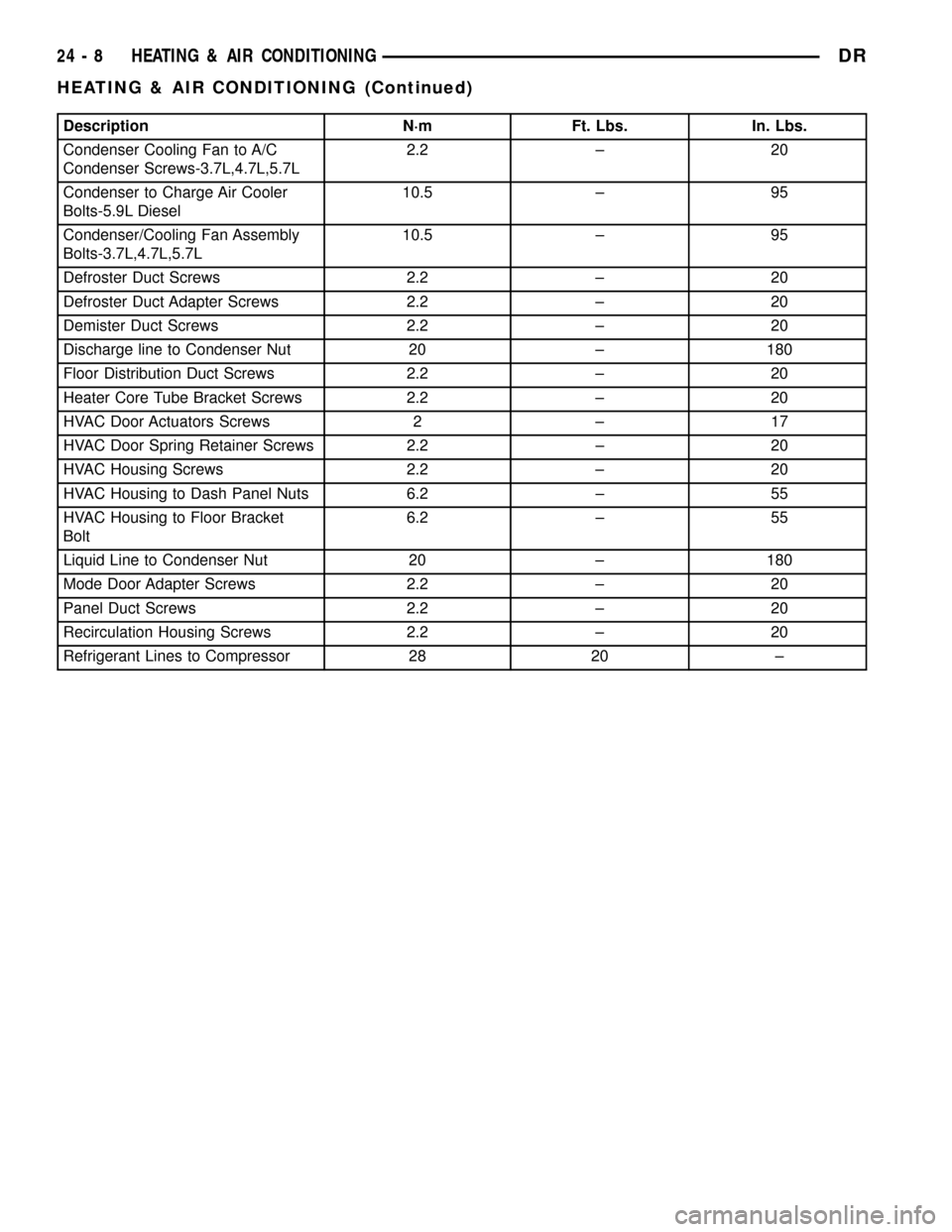
Description N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Condenser Cooling Fan to A/C
Condenser Screws-3.7L,4.7L,5.7L2.2 ± 20
Condenser to Charge Air Cooler
Bolts-5.9L Diesel10.5 ± 95
Condenser/Cooling Fan Assembly
Bolts-3.7L,4.7L,5.7L10.5 ± 95
Defroster Duct Screws 2.2 ± 20
Defroster Duct Adapter Screws 2.2 ± 20
Demister Duct Screws 2.2 ± 20
Discharge line to Condenser Nut 20 ± 180
Floor Distribution Duct Screws 2.2 ± 20
Heater Core Tube Bracket Screws 2.2 ± 20
HVAC Door Actuators Screws 2 ± 17
HVAC Door Spring Retainer Screws 2.2 ± 20
HVAC Housing Screws 2.2 ± 20
HVAC Housing to Dash Panel Nuts 6.2 ± 55
HVAC Housing to Floor Bracket
Bolt6.2 ± 55
Liquid Line to Condenser Nut 20 ± 180
Mode Door Adapter Screws 2.2 ± 20
Panel Duct Screws 2.2 ± 20
Recirculation Housing Screws 2.2 ± 20
Refrigerant Lines to Compressor 28 20 ±
24 - 8 HEATING & AIR CONDITIONINGDR
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)
Page 2497 of 2627

and coil are the only serviced parts on the compres-
sor.
A/C compressor clutch engagement is controlled by
several components: the A/C-heater control, A/C pres-
sure transducer, A/C compressor clutch relay, evapo-
rator temperature sensor and the powertrain control
module (PCM). The PCM may delay compressor
clutch engagement for up to thirty seconds (Refer to
8 - ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL MOD-
ULES/POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE -
DESCRIPTION).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C COMPRESSOR
CLUTCH COIL
For circuit descriptions and diagrams, (Refer to
Appropriate Wiring Information). The battery must
be fully-charged before performing the following
tests. Refer to Battery for more information.
(1) Connect an ammeter (0 to 10 ampere scale) in
series with the clutch coil terminal. Use a voltmeter
(0 to 20 volt scale) with clip-type leads for measuring
the voltage across the battery and the compressor
clutch coil.
(2) With the A/C-heater controls in any A/C mode,
and the blower motor switch in the lowest speed
position, start the engine and run it at normal idle.
(3) The compressor clutch coil voltage should read
within 0.2 volts of the battery voltage. If there is
voltage at the clutch coil, but the reading is not
within 0.2 volts of the battery voltage, test the clutch
coil feed circuit for excessive voltage drop and repair
as required. If there is no voltage reading at the
clutch coil, use a DRB IIItscan tool and (Refer to
Appropriate Diagnostic Information) for testing of thecompressor clutch circuit and PCM control. The fol-
lowing components must be checked and repaired as
required before you can complete testing of the clutch
coil:
²Fuses in the junction block and the power distri-
bution center (PDC)
²A/C-heater control
²A/C compressor clutch relay
²A/C pressure transducer
²Evaporator temperature sensor
²Powertrain control module (PCM)
(4) The compressor clutch coil is acceptable if the
current draw measured at the clutch coil is within
specifications with the electrical system voltage at
11.5 to 12.5 volts (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING - SPECIFICATIONS). This should
only be checked with the work area temperature at
21É C (70É F). If system voltage is more than 12.5
volts, add electrical loads by turning on electrical
accessories until the system voltage drops below 12.5
volts.
(a) If the clutch coil current reading is above
specifications, the coil is shorted and should be
replaced.
(b) If the clutch coil current reading is zero, the
coil is open and should be replaced.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - A/C COMPRESSOR
CLUTCH BREAK-IN
After a new compressor clutch has been installed,
cycle the compressor clutch approximately twenty
times (five seconds on, then five seconds off). During
this procedure, set the A/C-heater control to the
Recirculation Mode, the blower motor switch in the
highest speed position, and the engine speed at 1500
to 2000 rpm. This procedure (burnishing) will seat
the opposing friction surfaces and provide a higher
compressor clutch torque capability.
REMOVAL
The refrigerant system can remain fully-charged
during compressor clutch, rotor, or coil replacement.
The compressor clutch can be serviced in the vehicle.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the serpentine drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
(3) Disconnect the compressor clutch coil wire har-
ness connector.
(4) Remove the bolts that secure the compressor to
the mounting bracket.
(5) Remove the compressor from the mounting
bracket. Support the compressor in the engine com-
partment while servicing the clutch.
Fig. 1 Compressor Clutch - Typical
1 - CLUTCH PLATE
2 - SHAFT KEY (not used on KJ)
3 - ROTOR
4 - COIL
5 - CLUTCH SHIMS
6 - SNAP RING
7 - SNAP RING
24 - 10 CONTROLSDR
A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH/COIL (Continued)
Page 2521 of 2627

INSTALLATION
(1) Install the floor distribution duct onto the bot-
tom of the HVAC housing.
(2) Install the five screws that secure the floor dis-
tribution duct to the HVAC housing. Tighten the
screws to 2.2 N´m (20 in. lbs.).
(3) Install the HVAC housing (Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/DISTRIBUTION/HVAC
HOUSING - INSTALLATION).
HVAC HOUSING
REMOVAL
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN AN ACCIDENTAL
AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
NOTE: The HVAC housing must be removed from
the vehicle and the two halves of the housing sep-
arated for service access of the heater core, evap-
orator coil, defrost door, blend door(s) and the
recirculation door.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Drain the engine cooling system (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(3) Recover the refrigerant from the refrigerant
system (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITION-
ING/PLUMBING - STANDARD PROCEDURE -
REFRIGERANT RECOVERY).
(4) Disconnect the liquid refrigerant line fitting
from the evaporator inlet tube (Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/REFRIG-
ERANT LINE COUPLER - REMOVAL). Discard the
O-ring seal and install plugs in, or tape over the
opened liquid refrigerant line fitting and evaporator
inlet tube.
(5) Remove the accumulator (Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/ACCU-
MULATOR - REMOVAL). Discard the O-ring seals
and install plugs in, or tape over the opened refrig-
erant line fittings and evaporator outlet tube.(6) Disconnect the heater hoses from the heater
core tubes. Install plugs in, or tape over the opened
heater core tubes.
(7) Remove the powertrain control module (PCM)
from the engine compartment to gain access to the
HVAC housing retaining nuts (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES/POWER-
TRAIN CONTROL MODULE - REMOVAL).
(8) Remove the two nuts from the HVAC housing
mounting studs in the engine compartment.
(9) Remove the instrument panel from the vehicle
(Refer to 23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL -
REMOVAL).
(10) Remove the bolt that secures the HVAC hous-
ing to the floor bracket located in the center of the
vehicle (Fig. 9).
(11) Remove the two nuts from the HVAC housing
mounting studs in the passenger compartment.
(12) Remove the HVAC housing from inside the
vehicle. Take care not to allow any remaining coolant
to drain onto the vehicles interior.
Fig. 9 HVAC Housing - Dual Zone Shown, Single
Zone Typical
1 - NUT
2 - PASSENGER BLEND DOOR ACTUATOR
3 - NUT
4 - INLET BAFFLE
5 - RECIRCULATION DOOR ACTUATOR
6 - RECIRCULATION DOOR
7 - DRIVER SIDE BLEND DOOR ACTUATOR
8 - HVAC HOUSING
9 - BOLT
10 - DEFROSTER DOOR ACTUATOR
11 - MODE DOOR ACTUATOR
24 - 34 DISTRIBUTIONDR
FLOOR DISTRIBUTION DUCT (Continued)
Page 2523 of 2627

ING/CONTROLS/BLOWER MOTOR RESISTOR
BLOCK - INSTALLATION).
(5) If removed, install the blower motor (Refer to
24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/DISTRIBU-
TION/BLOWER MOTOR - INSTALLATION).
(6) Install the HVAC wire harness. Make sure the
wires are routed through all wiring retainers.
(7) Connect the wire harness to the blower motor,
blower motor resistor block, evaporator temperature
sensor and each actuator.
(8) Install the HVAC housing (Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/DISTRIBUTION/HVAC
HOUSING - INSTALLATION).
INSTALLATION
WARNING: IF THE VEHICLE IS EQUIPPED WITH AIR
CONDITIONING, REVIEW THE WARNINGS AND
CAUTIONS IN PLUMBING BEFORE PERFORMING
THE FOLLOWING OPERATION. (Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - WARNING)
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - CAUTION) (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - CAUTION -
REFRIGERANT HOSES/LINES/TUBES PRECAU-
TIONS)
(1) Position the HVAC housing into the vehicle. Be
certain that the evaporator condensate drain tube
and the housing mounting studs are inserted into
their correct locations.
(2) Install the two nuts that secure the HVAC
housing to the mounting studs in the passenger com-
partment. Tighten the nuts to 6.2 N´m (55 in. lbs.).
(3) Install the bolt that secures the HVAC housing
to the floor bracket in the passenger compartment.
Tighten the bolt to 6.2 N´m (55 in. lbs.).
(4) Install the instrument panel (Refer to 23 -
BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL - INSTALLATION).
(5) Install the two nuts that secure the HVAC
housing to the mounting studs in the engine com-
partment. Tighten the nuts to 6.2 N´m (55 in. lbs.).
(6) Install the powertrain control module (PCM)
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CON-
TROL MODULES/POWERTRAIN CONTROL MOD-
ULE - INSTALLATION).
(7) Unplug or remove the tape from the heater
core tubes and connect the heater hoses to the heater
core tubes.
(8) Unplug or remove the tape from the opened
refrigerant line fittings and the evaporator outlet
tube and install the accumulator (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/AC-
CUMULATOR - INSTALLATION).
(9) Unplug or remove the tape from the liquid line
and the evaporator inlet tube fittings. Connect the
liquid line coupler to the evaporator inlet tube (Referto 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMB-
ING - STANDARD PROCEDURE - A/C LINE COU-
PLERS).
(10) Evacuate the refrigerant system (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYS-
TEM EVACUATE).
(11) Charge the refrigerant system (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYS-
TEM CHARGE).
(12) Fill the engine cooling system (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ENGINE - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(13) Connect the battery negative cable.
(14) Start the engine and check for proper opera-
tion of the heating and air conditioning systems.
INSTRUMENT PANEL
DEMISTER DUCTS
REMOVAL
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
(1) Remove the defroster ducts (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/DISTRIBUTION/
DEFROSTER DUCTS - REMOVAL).
(2) Remove the two screws that secure the center
distribution duct to the instrument panel support.
(3) Remove the center distribution duct from
instrument panel support, panel ducts and demister
ducts.
(4) Remove the right side panel duct adapter (Fig.
11).
(5) Remove the right side intermediate demister
duct.
(6) Remove the left side intermediate demister
duct.
(7) Remove the left side panel duct adapter.
(8) Remove the instrument panel cover (Refer to
23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/INSTRUMENT
PANEL TOP COVER - REMOVAL).
24 - 36 DISTRIBUTIONDR
HVAC HOUSING (Continued)
Page 2528 of 2627

PLUMBING
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
PLUMBING
DESCRIPTION - REFRIGERANT LINE.......42
OPERATION- REFRIGERANT LINES........42
WARNING
ENGINE COOLING SYSTEM.............42
A/C SYSTEM.........................43
CAUTION
A/C SYSTEM.........................43
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REFRIGERANT
SYSTEM LEAKS......................44
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - HANDLING
TUBING AND FITTINGS.................45
STANDARD PROCEDURE - DIODE
REPLACEMENT.......................45
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT
SYSTEM SERVICE EQUIPMENT..........46
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT
RECOVERY..........................47
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT
SYSTEM EVACUATE...................47
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT
SYSTEM CHARGE.....................47
A/C COMPRESSOR
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - A/C COMPRESSOR.......48
DESCRIPTION - HIGH PRESSURE RELIEF
VALVE..............................48
OPERATION
OPERATION - A/C COMPRESSOR........48
OPERATION - HIGH PRESSURE RELIEF
VALVE..............................48
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C
COMPRESSOR.......................49
REMOVAL.............................49
INSTALLATION.........................51
A/C CONDENSER
DESCRIPTION.........................52
OPERATION...........................52
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 3.7, 4.7 AND 5.7L ENGINES....52
REMOVAL - 5.9L DIESEL ENGINE.........53
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 3.7, 4.7 AND 5.7L ENGINES . 53
INSTALLATION - 5.9L DIESEL ENGINE.....54
A/C CONDENSER FAN
REMOVAL - 3.7, 4.7 and 5.7L ENGINES......55
INSTALLATION - 3.7, 4.7 and 5.7L ENGINES . . . 55A/C DISCHARGE LINE
DESCRIPTION.........................56
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 5.9L DIESEL ENGINE.........56
REMOVAL - 3.7L/4.7L AND 5.7L HEMI
ENGINE.............................57
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 5.9L DIESEL ENGINE.....58
INSTALLATION - 3.7L/4.7L AND 5.7L HEMI
ENGINE.............................59
A/C EVAPORATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................59
OPERATION...........................59
REMOVAL.............................60
INSTALLATION.........................60
A/C ORIFICE TUBE
DESCRIPTION.........................60
OPERATION...........................60
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C ORIFICE
TUBE...............................61
ACCUMULATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................61
OPERATION...........................61
REMOVAL.............................61
INSTALLATION.........................62
HEATER CORE
DESCRIPTION.........................63
OPERATION...........................63
REMOVAL.............................63
INSTALLATION.........................63
HEATER INLET HOSE
REMOVAL.............................64
INSTALLATION.........................64
HEATER RETURN HOSE
REMOVAL.............................64
INSTALLATION.........................65
LIQUID LINE
DESCRIPTION.........................65
REMOVAL.............................65
INSTALLATION.........................66
REFRIGERANT
DESCRIPTION.........................67
OPERATION...........................67
REFRIGERANT LINE COUPLER
DESCRIPTION.........................67
OPERATION...........................67
REMOVAL.............................68
INSTALLATION.........................68
DRPLUMBING 24 - 41
Page 2529 of 2627

REFRIGERANT OIL
DESCRIPTION.........................68
OPERATION...........................69
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT
OIL LEVEL...........................69
SERVICE PORT VALVE CORE
DESCRIPTION.........................70
REMOVAL - SERVICE PORT VALVE CORES . . 70
INSTALLATION.........................70
SUCTION LINE
DESCRIPTION.........................70REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 5.9L DIESEL ENGINE.........70
REMOVAL - 3.7L/4.7L AND 5.7L HEMI
ENGINE.............................71
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 5.9L DIESEL ENGINE.....72
INSTALLATION - 3.7L/4.7L AND 5.7L HEMI
ENGINE.............................73
PLUMBING
DESCRIPTION - REFRIGERANT LINE
The refrigerant lines and hoses are used to carry
the refrigerant between the various air conditioning
system components. A barrier hose design with a
nylon tube, which is sandwiched between rubber lay-
ers, is used for the R-134a air conditioning system on
this vehicle. This nylon tube helps to further contain
the R-134a refrigerant, which has a smaller molecu-
lar structure than R-12 refrigerant. The ends of the
refrigerant hoses are made from lightweight alumi-
num or steel, and commonly use braze-less fittings.
Any kinks or sharp bends in the refrigerant plumb-
ing will reduce the capacity of the entire air condi-
tioning system. Kinks and sharp bends reduce the
flow of refrigerant in the system. A good rule for the
flexible hose refrigerant lines is to keep the radius of
all bends at least ten times the diameter of the hose.
In addition, the flexible hose refrigerant lines should
be routed so they are at least 80 millimeters (3
inches) from an exhaust manifold.
OPERATION- REFRIGERANT LINES
High pressures are produced in the refrigerant sys-
tem when the air conditioning compressor is operat-
ing. Extreme care must be exercised to make sure
that each of the refrigerant system connections is
pressure-tight and leak free. It is a good practice to
inspect all flexible hose refrigerant lines at least once
a year to make sure they are in good condition and
properly routed.
The refrigerant lines and hoses are coupled with
other components of the HVAC system with either
O-rings or dual plane seals.
The refrigerant lines and hoses cannot be repaired
and, if faulty or damaged, they must be replaced.
WARNING
ENGINE COOLING SYSTEM
WARNING: THE ENGINE COOLING SYSTEM IS
DESIGNED TO DEVELOP INTERNAL PRESSURES
OF 97 TO 123 KILOPASCALS (14 TO 18 POUNDS
PER SQUARE INCH). DO NOT REMOVE OR
LOOSEN THE COOLANT PRESSURE CAP, CYLIN-
DER BLOCK DRAIN PLUGS, RADIATOR DRAIN,
RADIATOR HOSES, HEATER HOSES, OR HOSE
CLAMPS WHILE THE ENGINE COOLING SYSTEM IS
HOT AND UNDER PRESSURE. FAILURE TO
OBSERVE THIS WARNING CAN RESULT IN SERI-
OUS BURNS FROM THE HEATED ENGINE COOL-
ANT. ALLOW THE VEHICLE TO COOL FOR A
MINIMUM OF 15 MINUTES BEFORE OPENING THE
COOLING SYSTEM FOR SERVICE.
24 - 42 PLUMBINGDR
Page 2531 of 2627

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REFRIGERANT
SYSTEM LEAKS
WARNING: R-134a SERVICE EQUIPMENT OR VEHI-
CLE A/C SYSTEM SHOULD NOT BE PRESSURE
TESTED OR LEAK TESTED WITH COMPRESSED
AIR. MIXTURE OF AIR and R-134a CAN BE COM-
BUSTIBLE AT ELEVATED PRESSURES. THESE MIX-
TURES ARE POTENTIALLY DANGEROUS AND MAY
RESULT IN FIRE OR EXPLOSION CAUSING INJURY
OR PROPERTY DAMAGE.
AVOID BREATHING A/C REFRIGERANT AND LUBRI-
CANT VAPOR OR MIST. EXPOSURE MAY IRRITATE
EYES, NOSE AND THROAT. USE ONLY APPROVED
SERVICE EQUIPMENT MEETING SAE REQUIRE-
MENTS TO DISCHARGE R-134a SYSTEM. IF ACCI-
DENTAL SYSTEM DISCHARGE OCCURS,
VENTILATE WORK AREA BEFORE RESUMING SER-
VICE.
NOTE: The refrigerant system does come from the
factory with a yellow tracer dye already installed to
aid in detection of leaks.
If the A/C system is not cooling properly, determine
if the refrigerant system is fully charged with
R-134a. This is accomplished by performing a system
Charge Level-Check or Fill. If while performing this
test A/C liquid line pressure is less than 345 kPa (50
psi) proceed to System Empty procedure. If liquid
line pressure is greater than 345 kPa (50 psi) proceed
to System Low procedure. If the refrigerant system is
empty or low in refrigerant charge, a leak at any line
fitting or component seal is likely. A review of the fit-
tings, lines and components for oily residue is an
indication of the leak location. To detect a leak in the
refrigerant system, perform one of the following pro-
cedures as indicated by the symptoms.
SYSTEM EMPTY
(1) Evacuate the refrigerant system to the lowest
degree of vacuum possible (approx. 28 in Hg.). Deter-
mine if the system holds a vacuum for 15 minutes. If
vacuum is held, a leak is probably not present. If sys-
tem will not maintain vacuum level, proceed with
this procedure.(2) Prepare a 0.284 Kg. (10 oz.) refrigerant charge
to be injected into the system.
(3) Connect and dispense 0.284 Kg. (10 oz.) of
refrigerant into the evacuated refrigerant system.
(4) Proceed to Step 2 of System Low procedure.
SYSTEM LOW
(1) Determine if there is any (R-134a) refrigerant
in the system.
(2) Position the vehicle in a wind free work area.
This will aid in detecting small leaks.
(3) Bring the refrigerant system up to operating
temperature and pressure. This is done by allowing
the engine to run for five minutes with the system
set to the following:
²Transmission in Park or Neutral with parking
brake set
²Engine idling at 700 rpm
²A/C controls set in 100 percent outside air
²Blower switch in the high A/C position
²A/C in the ON position
²Open all windows
CAUTION: A leak detector designed for R-12 refrig-
erant (only) will not detect leaks in a R-134a refrig-
erant system.
(4) Shut off the vehicle and wait 2 to 7 minutes.
Then use an Electronic Leak Detector that is
designed to detect R-134a type refrigerant and search
for leaks. Fittings, lines, or components that appear
to be oily usually indicates a refrigerant leak. To
inspect the evaporator core for leaks, insert the leak
detector probe into the drain tube opening or a heat
duct. A R-134a dye is available to aid in leak detec-
tion, use only DaimlerChrysler approved refrigerant
dye.
24 - 44 PLUMBINGDR
PLUMBING (Continued)
Page 2536 of 2627

when a minimum discharge pressure of 2756 kPa
(400 psi) is reached.
The high pressure relief valve vents only enough
refrigerant to reduce the system pressure, and then
re-seats itself. The majority of the refrigerant is con-
served in the system. If the valve vents refrigerant, it
does not mean that the valve is faulty.
The high pressure relief valve is a factory-cali-
brated unit. The valve cannot be adjusted or
repaired, and must not be removed or otherwise dis-
turbed. The valve is only serviced as a part of the
compressor assembly.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C COMPRESSOR
When investigating an air conditioning related
noise, you must first know the conditions under
which the noise occurs. These conditions include:
weather, vehicle speed, transmission in gear or neu-
tral, engine speed, engine temperature, and any
other special conditions. Noises that develop during
air conditioning operation can often be misleading.
For example: What sounds like a failed front bearing
or connecting rod, may be caused by loose bolts, nuts,
mounting brackets, or a loose compressor clutch
assembly.
Drive belts are speed sensitive. At different engine
speeds and depending upon belt tension, belts can
develop noises that are mistaken for a compressor
noise. Improper belt tension can cause a misleading
noise when the compressor clutch is engaged, which
may not occur when the compressor clutch is disen-
gaged. Check the serpentine drive belt condition and
tension as described in Cooling before beginning this
procedure.
(1) Select a quiet area for testing. Duplicate the
complaint conditions as much as possible. Switch the
compressor on and off several times to clearly iden-
tify the compressor noise. Listen to the compressor
while the clutch is engaged and disengaged. Probe
the compressor with an engine stethoscope or a long
screwdriver with the handle held to your ear to bet-
ter localize the source of the noise.
(2) Loosen all of the compressor mounting hard-
ware and retighten. Tighten the compressor clutch
mounting nut. Be certain that the clutch coil is
mounted securely to the compressor, and that the
clutch plate and rotor are properly aligned and have
the correct air gap (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING/CONTROLS/A/C COMPRESSOR
CLUTCH - INSTALLATION).
(3) To duplicate a high-ambient temperature condi-
tion (high head pressure), restrict the air flow
through the condenser. Install a manifold gauge set
or a DRBIIItscan tool to be certain that the dis-
charge pressure does not exceed 2760 kPa (400 psi).(4) Check the refrigerant system plumbing for
incorrect routing, rubbing or interference, which can
cause unusual noises. Also check the refrigerant lines
for kinks or sharp bends that will restrict refrigerant
flow, which can cause noises (Refer to 24 - HEATING
& AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
(5) If the noise is from opening and closing of the
high pressure relief valve, recover, evacuate and
recharge the refrigerant system (Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE), (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - STANDARD
PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM EVACU-
ATE) and (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDI-
TIONING/PLUMBING - STANDARD PROCEDURE -
REFRIGERANT SYSTEM CHARGE). If the high
pressure relief valve still does not seat properly,
replace the compressor (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/A/C COMPRES-
SOR - REMOVAL).
(6) If the noise is from liquid slugging on the suc-
tion line, replace the accumulator (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/AC-
CUMULATOR - REMOVAL) and check the refriger-
ant oil level and the refrigerant system charge (Refer
to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMB-
ING/REFRIGERANT OIL - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE) (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/ACCUMULATOR -
REMOVAL). If after replacing the accumulator the
slugging condition still exists then replace the com-
pressor.(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITION-
ING/PLUMBING/A/C COMPRESSOR - REMOVAL).
(7) If the liquid slugging condition continues fol-
lowing accumulator replacement, replace the com-
pressor and repeat Step 1.
REMOVAL
WARNING: REVIEW THE WARNINGS AND CAU-
TIONS IN THE FRONT OF THIS SECTION BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION (Refer
to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
WARNING) and (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CON-
DITIONING/PLUMBING - CAUTION).
NOTE: The A/C compressor may be removed and
repositioned without disconnecting the refrigerant
lines or discharging the refrigerant system. Dis-
charging is not necessary if servicing the compres-
sor clutch, clutch coil, engine, engine cylinder head
or the generator.
(1) Recover the refrigerant from the refrigerant
system (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITION-
DRPLUMBING 24 - 49
A/C COMPRESSOR (Continued)