Power control DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1998, Model line: RAM 1500, Model: DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.GPages: 2627
Page 1459 of 2627
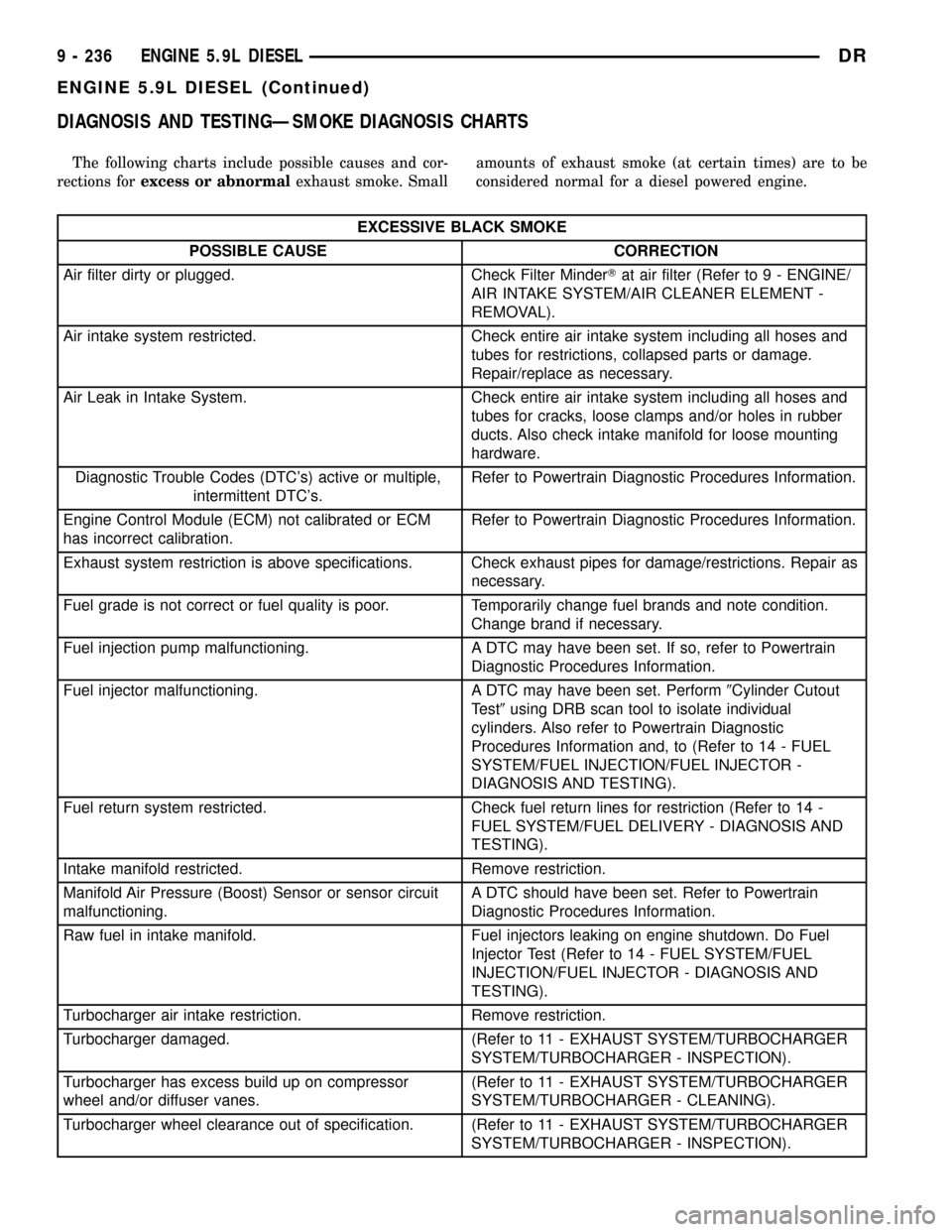
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐSMOKE DIAGNOSIS CHARTS
The following charts include possible causes and cor-
rections forexcess or abnormalexhaust smoke. Smallamounts of exhaust smoke (at certain times) are to be
considered normal for a diesel powered engine.
EXCESSIVE BLACK SMOKE
POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
Air filter dirty or plugged. Check Filter MinderTat air filter (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
AIR INTAKE SYSTEM/AIR CLEANER ELEMENT -
REMOVAL).
Air intake system restricted. Check entire air intake system including all hoses and
tubes for restrictions, collapsed parts or damage.
Repair/replace as necessary.
Air Leak in Intake System. Check entire air intake system including all hoses and
tubes for cracks, loose clamps and/or holes in rubber
ducts. Also check intake manifold for loose mounting
hardware.
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC's) active or multiple,
intermittent DTC's.Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures Information.
Engine Control Module (ECM) not calibrated or ECM
has incorrect calibration.Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures Information.
Exhaust system restriction is above specifications. Check exhaust pipes for damage/restrictions. Repair as
necessary.
Fuel grade is not correct or fuel quality is poor. Temporarily change fuel brands and note condition.
Change brand if necessary.
Fuel injection pump malfunctioning. A DTC may have been set. If so, refer to Powertrain
Diagnostic Procedures Information.
Fuel injector malfunctioning. A DTC may have been set. Perform9Cylinder Cutout
Test9using DRB scan tool to isolate individual
cylinders. Also refer to Powertrain Diagnostic
Procedures Information and, to (Refer to 14 - FUEL
SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/FUEL INJECTOR -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
Fuel return system restricted. Check fuel return lines for restriction (Refer to 14 -
FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
Intake manifold restricted. Remove restriction.
Manifold Air Pressure (Boost) Sensor or sensor circuit
malfunctioning.A DTC should have been set. Refer to Powertrain
Diagnostic Procedures Information.
Raw fuel in intake manifold. Fuel injectors leaking on engine shutdown. Do Fuel
Injector Test (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL
INJECTION/FUEL INJECTOR - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
Turbocharger air intake restriction. Remove restriction.
Turbocharger damaged. (Refer to 11 - EXHAUST SYSTEM/TURBOCHARGER
SYSTEM/TURBOCHARGER - INSPECTION).
Turbocharger has excess build up on compressor
wheel and/or diffuser vanes.(Refer to 11 - EXHAUST SYSTEM/TURBOCHARGER
SYSTEM/TURBOCHARGER - CLEANING).
Turbocharger wheel clearance out of specification. (Refer to 11 - EXHAUST SYSTEM/TURBOCHARGER
SYSTEM/TURBOCHARGER - INSPECTION).
9 - 236 ENGINE 5.9L DIESELDR
ENGINE 5.9L DIESEL (Continued)
Page 1460 of 2627
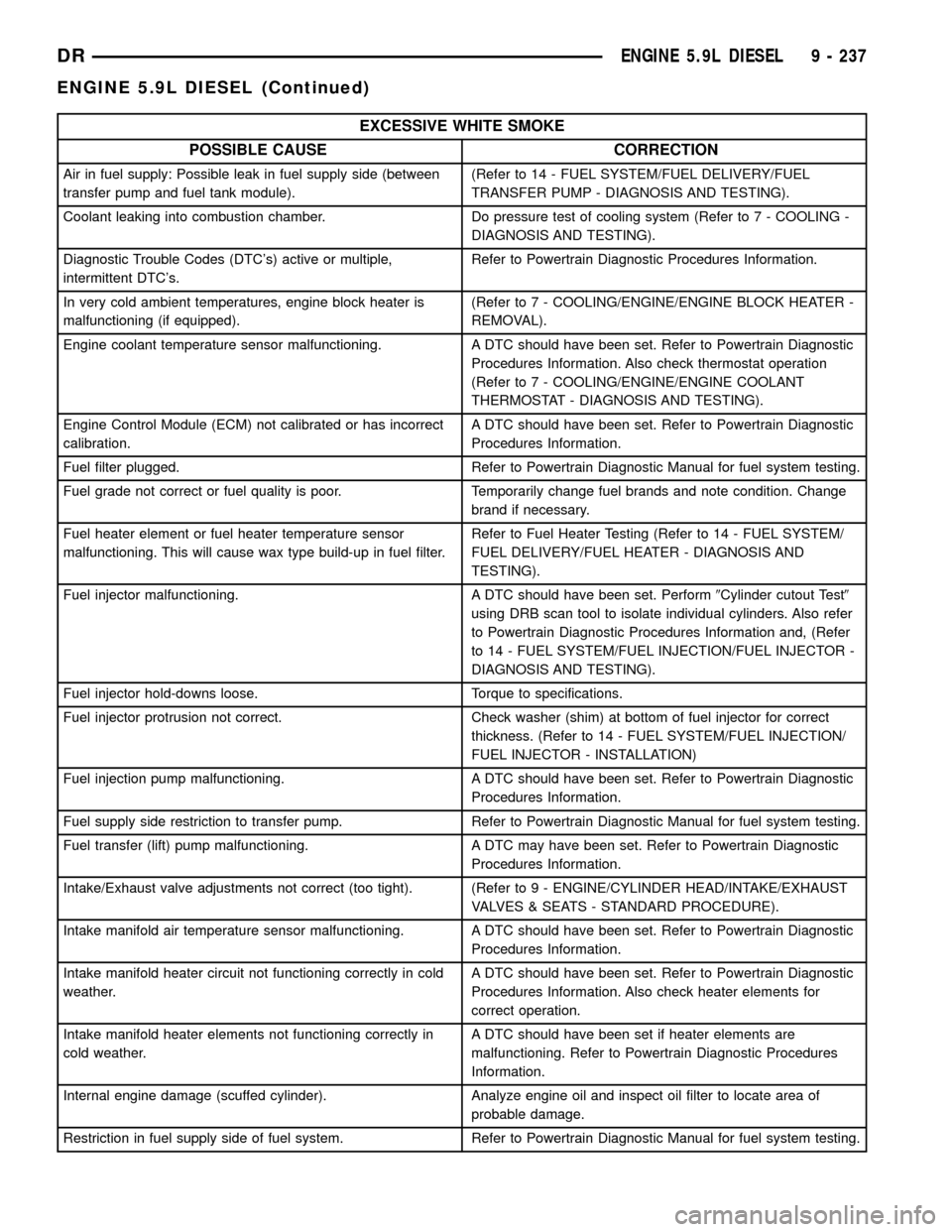
EXCESSIVE WHITE SMOKE
POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
Air in fuel supply: Possible leak in fuel supply side (between
transfer pump and fuel tank module).(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY/FUEL
TRANSFER PUMP - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
Coolant leaking into combustion chamber. Do pressure test of cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC's) active or multiple,
intermittent DTC's.Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures Information.
In very cold ambient temperatures, engine block heater is
malfunctioning (if equipped).(Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK HEATER -
REMOVAL).
Engine coolant temperature sensor malfunctioning. A DTC should have been set. Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic
Procedures Information. Also check thermostat operation
(Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/ENGINE COOLANT
THERMOSTAT - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
Engine Control Module (ECM) not calibrated or has incorrect
calibration.A DTC should have been set. Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic
Procedures Information.
Fuel filter plugged. Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic Manual for fuel system testing.
Fuel grade not correct or fuel quality is poor. Temporarily change fuel brands and note condition. Change
brand if necessary.
Fuel heater element or fuel heater temperature sensor
malfunctioning. This will cause wax type build-up in fuel filter.Refer to Fuel Heater Testing (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/
FUEL DELIVERY/FUEL HEATER - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
Fuel injector malfunctioning. A DTC should have been set. Perform9Cylinder cutout Test9
using DRB scan tool to isolate individual cylinders. Also refer
to Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures Information and, (Refer
to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/FUEL INJECTOR -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
Fuel injector hold-downs loose. Torque to specifications.
Fuel injector protrusion not correct. Check washer (shim) at bottom of fuel injector for correct
thickness. (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/
FUEL INJECTOR - INSTALLATION)
Fuel injection pump malfunctioning. A DTC should have been set. Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic
Procedures Information.
Fuel supply side restriction to transfer pump. Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic Manual for fuel system testing.
Fuel transfer (lift) pump malfunctioning. A DTC may have been set. Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic
Procedures Information.
Intake/Exhaust valve adjustments not correct (too tight). (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/INTAKE/EXHAUST
VALVES & SEATS - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
Intake manifold air temperature sensor malfunctioning. A DTC should have been set. Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic
Procedures Information.
Intake manifold heater circuit not functioning correctly in cold
weather.A DTC should have been set. Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic
Procedures Information. Also check heater elements for
correct operation.
Intake manifold heater elements not functioning correctly in
cold weather.A DTC should have been set if heater elements are
malfunctioning. Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures
Information.
Internal engine damage (scuffed cylinder). Analyze engine oil and inspect oil filter to locate area of
probable damage.
Restriction in fuel supply side of fuel system. Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic Manual for fuel system testing.
DRENGINE 5.9L DIESEL 9 - 237
ENGINE 5.9L DIESEL (Continued)
Page 1466 of 2627

(8) Replace injector o-ring and sealing washer on
injectors #5 and #6. Install injectors and torque using
the following steps:
²Step 1ÐInstall injector hold-down capscrews
and torque to 5 N´m (44 in. lbs.) torque.
²Step 2ÐLoosen injector hold-down capscrews.
²Step 3ÐInstall HPC connector tube and nut.
Torque nut to 15 N´m (11 ft. lbs.) torque.
²Step 4ÐTorque injector hold-down capscrews to
10 N´m (89 in. lbs.) torque.
²Step 5ÐTorque HPC connector tube nut to 50
N´m (37 ft. lbs.) torque.
(9) Install #5 and #6 high pressure fuel lines. Fol-
low correct torque sequence per section 14. Torque
fuel line fittings to 30 N-m (22 ft-lb). Torque brace
capscrew to 24 N-m (18 ft-lb).
(10) Install rear engine lift bracket. Torque to 77
N-m (57 ft-lb).
(11) Install push tubes, rocker arms, and pedestals
for cylinders #4, #5, and #6. Torque the mounting
bolts to 36 N-m (27 ft-lbs).
(12) Reset valve lash on cylinders #4, #5, and #6.
Torque adjusting nuts to 24 N-m (18 ft-lbs).
(13) Install cylinder head cover. Torque to 24 N-m
(18 ft-lbs).(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD -
INSTALLATION).
(14) Connect breather tube and lube oil drain tube
to breather housing cover. Install breather housing.
Torque capscrews to 24 N-m (18 ft-lbs)
(15) Connect fuel supply and return hoses.
(16) Connect ECM ground to hydroform screw.
Connect ECM power connector.
(17) Install the APPS cable(s) to the APPS. Install
the throttle linkage cover.
(18) Install the power steering pump.
(19) Install the damper and speed indicator ring.
Torque to 40 N-m (30 ft-lb) plus 60 degrees.
(20) Connect the engine block heater connection.
(21) Connect the A/C compressor and pressure sen-
sor connectors
(22) Install the charge air cooler and a/c condenser
(if equipped). Install and tighten the charge air
cooler mounting bolts to 2 N-m (17 in-lbs).
(23) Connect the charge air cooler piping. Torque
all clamps to 8 N-m (72 in-lbs).
(24) Connect the a/c refrigerant lines to the a/c
condenser (if equipped).
(25) Install the radiator upper support panel.
(26) Install radiator.
(27) Connect the transmission quick-connect oil
cooler lines.(28) Raise vehicle.
(29) Connect a/c compressor suction/discharge hose
(if equipped).
(30) Install the radiator lower hose and clamps.
(31) Install the battery negative cables to the
engine block on the driver and passenger side.
(32) Install the transmission adapter with a new
camshaft rectangular ring seal. Torque to 77 N-m (57
ft-lb).
(33) Install the flywheel/flexplate. Torque to 137
N-m (101 ft-lb).
(34) Install the starter motor. Torque to 43 N-m
(32 ft-lb). (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/STARTING/
STARTER MOTOR - INSTALLATION).
(35) Connect engine to vehicle harness connectors.
(36) Install transmission and transfer case (if
equipped).
(37) Connect the exhaust pipe to the turbocharger
elbow.
(38) Connect the transmission auxiliary oil cooler
lines (if equipped).
(39) Lower the vehicle.
(40) Connect the heater core supply and return
hoses.
(41) Install the cooling fan and upper fan shroud
at the same time. (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/
RADIATOR FAN - INSTALLATION).
(42) Install the coolant recovery bottle.
(43) Install the windshield washer bottle.
(44) Install the upper radiator hose and clamps.
(45) Raise vehicle.
(46) Connect electronically controlled fan drive
wire harness. Install lower radiator fan shroud.
(47) Change oil filter and install new engine oil.
(48) Fill the cooling system with coolant. (Refer to
7 - COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(49) Connect grid heater harness at grid heater
relays.
(50) Connect electrical connections to rear of alter-
nator.
(51) Start the engine and inspect for engine oil,
coolant, and fuel leaks.
INSTALLATIONÐCRANKCASE BREATHER
(1) Install a new o-ring onto the breather element.
(2) Lubricate o-ring and install into cylinder head
cover. Torque capscrews to 10 N´m (89 in. lbs.).
(3) Connect breather tube and lube oil drain tube.
(4) Install breather cover (Fig. 4). Torque to 24
N´m (18 ft. lbs.)
(5) Install oil fill cap.
DRENGINE 5.9L DIESEL 9 - 243
ENGINE 5.9L DIESEL (Continued)
Page 1467 of 2627
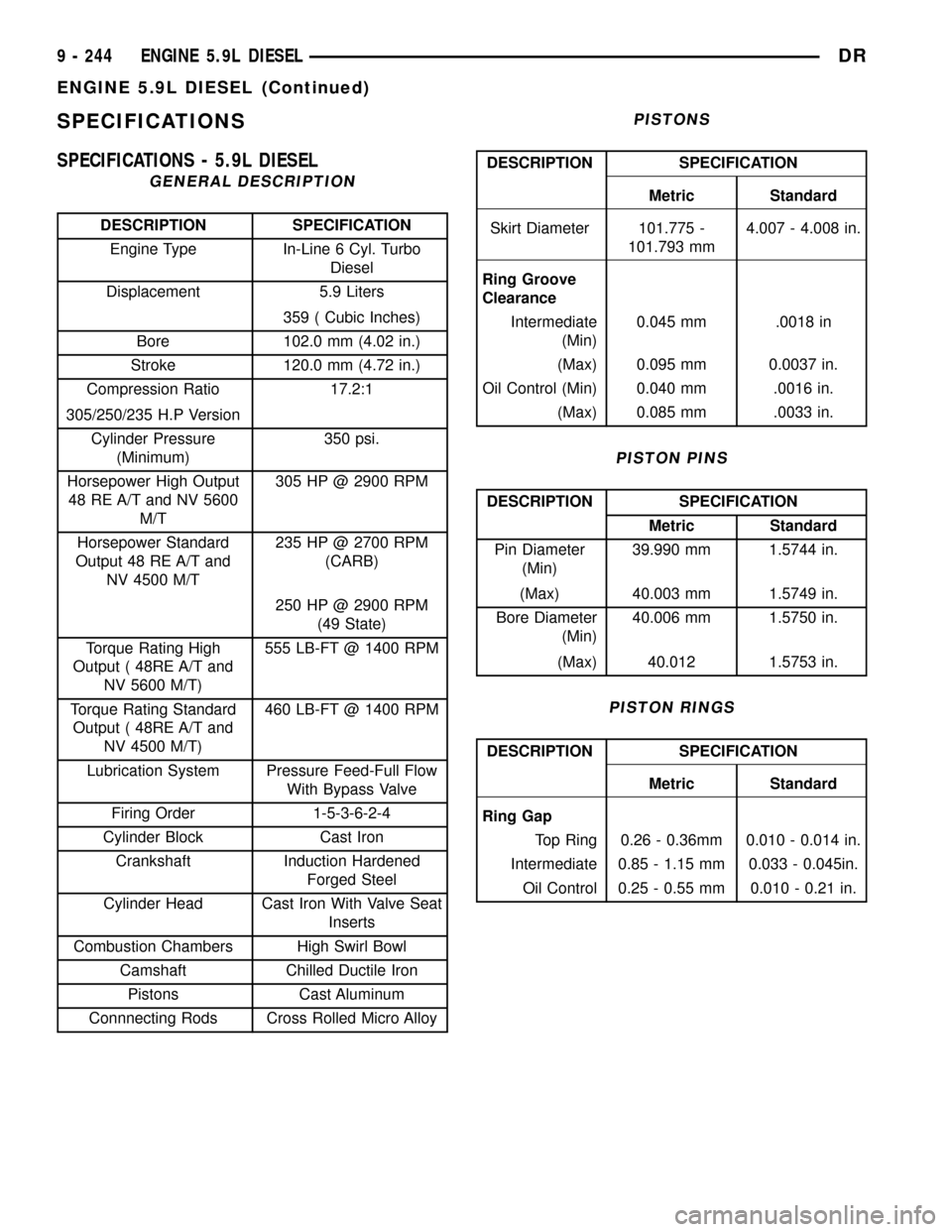
SPECIFICATIONS
SPECIFICATIONS - 5.9L DIESEL
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Engine Type In-Line 6 Cyl. Turbo
Diesel
Displacement 5.9 Liters
359 ( Cubic Inches)
Bore 102.0 mm (4.02 in.)
Stroke 120.0 mm (4.72 in.)
Compression Ratio 17.2:1
305/250/235 H.P Version
Cylinder Pressure
(Minimum)350 psi.
Horsepower High Output
48 RE A/T and NV 5600
M/T305 HP @ 2900 RPM
Horsepower Standard
Output 48 RE A/T and
NV 4500 M/T235 HP @ 2700 RPM
(CARB)
250 HP @ 2900 RPM
(49 State)
Torque Rating High
Output ( 48RE A/T and
NV 5600 M/T)555 LB-FT @ 1400 RPM
Torque Rating Standard
Output ( 48RE A/T and
NV 4500 M/T)460 LB-FT @ 1400 RPM
Lubrication System Pressure Feed-Full Flow
With Bypass Valve
Firing Order 1-5-3-6-2-4
Cylinder Block Cast Iron
Crankshaft Induction Hardened
Forged Steel
Cylinder Head Cast Iron With Valve Seat
Inserts
Combustion Chambers High Swirl Bowl
Camshaft Chilled Ductile Iron
Pistons Cast Aluminum
Connnecting Rods Cross Rolled Micro Alloy
PISTONS
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Metric Standard
Skirt Diameter 101.775 -
101.793 mm4.007 - 4.008 in.
Ring Groove
Clearance
Intermediate
(Min)0.045 mm .0018 in
(Max) 0.095 mm 0.0037 in.
Oil Control (Min) 0.040 mm .0016 in.
(Max) 0.085 mm .0033 in.
PISTON PINS
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Metric Standard
Pin Diameter
(Min)39.990 mm 1.5744 in.
(Max) 40.003 mm 1.5749 in.
Bore Diameter
(Min)40.006 mm 1.5750 in.
(Max) 40.012 1.5753 in.
PISTON RINGS
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Metric Standard
Ring Gap
Top Ring 0.26 - 0.36mm 0.010 - 0.014 in.
Intermediate 0.85 - 1.15 mm 0.033 - 0.045in.
Oil Control 0.25 - 0.55 mm 0.010 - 0.21 in.
9 - 244 ENGINE 5.9L DIESELDR
ENGINE 5.9L DIESEL (Continued)
Page 1471 of 2627
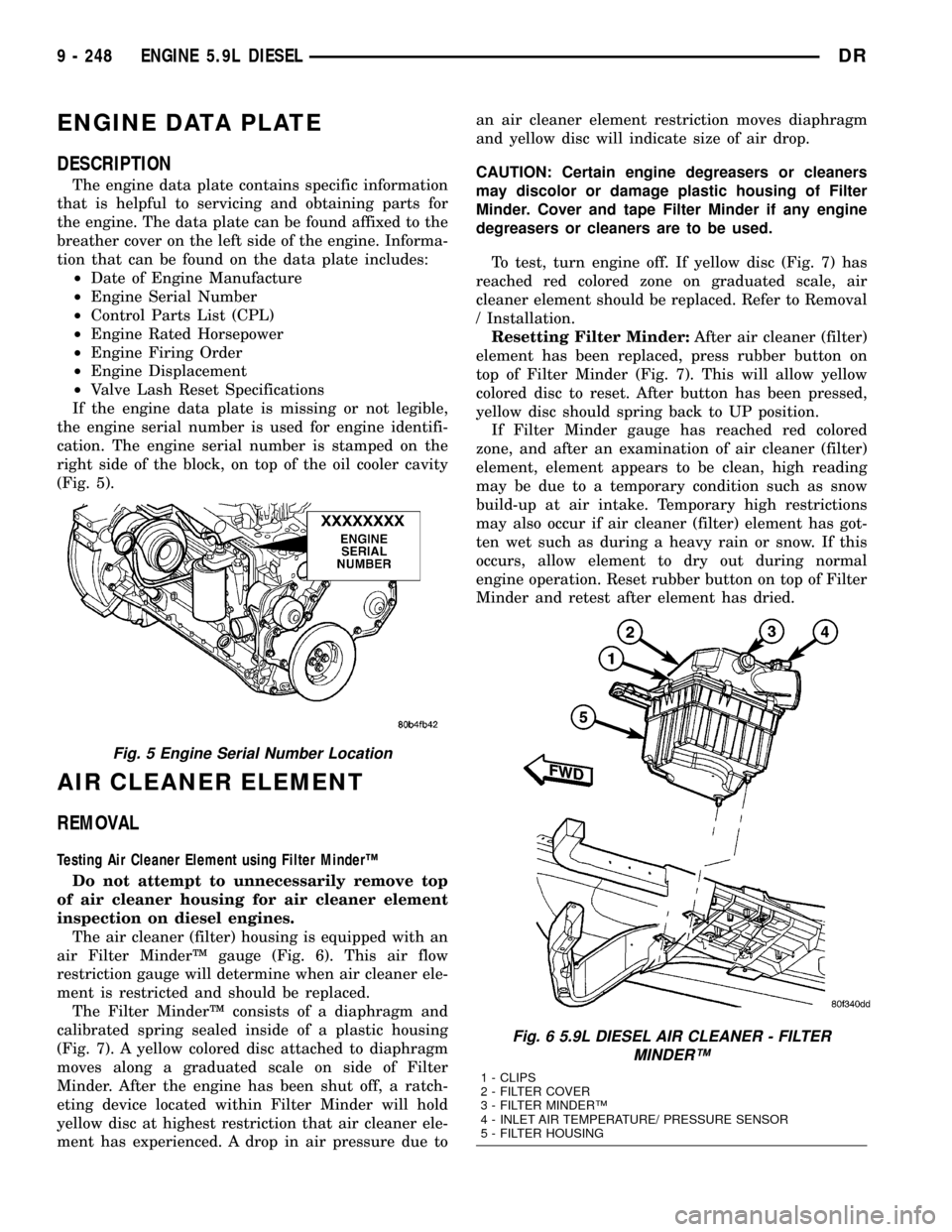
ENGINE DATA PLATE
DESCRIPTION
The engine data plate contains specific information
that is helpful to servicing and obtaining parts for
the engine. The data plate can be found affixed to the
breather cover on the left side of the engine. Informa-
tion that can be found on the data plate includes:
²Date of Engine Manufacture
²Engine Serial Number
²Control Parts List (CPL)
²Engine Rated Horsepower
²Engine Firing Order
²Engine Displacement
²Valve Lash Reset Specifications
If the engine data plate is missing or not legible,
the engine serial number is used for engine identifi-
cation. The engine serial number is stamped on the
right side of the block, on top of the oil cooler cavity
(Fig. 5).
AIR CLEANER ELEMENT
REMOVAL
Testing Air Cleaner Element using Filter MinderŸ
Do not attempt to unnecessarily remove top
of air cleaner housing for air cleaner element
inspection on diesel engines.
The air cleaner (filter) housing is equipped with an
air Filter MinderŸ gauge (Fig. 6). This air flow
restriction gauge will determine when air cleaner ele-
ment is restricted and should be replaced.
The Filter MinderŸ consists of a diaphragm and
calibrated spring sealed inside of a plastic housing
(Fig. 7). A yellow colored disc attached to diaphragm
moves along a graduated scale on side of Filter
Minder. After the engine has been shut off, a ratch-
eting device located within Filter Minder will hold
yellow disc at highest restriction that air cleaner ele-
ment has experienced. A drop in air pressure due toan air cleaner element restriction moves diaphragm
and yellow disc will indicate size of air drop.
CAUTION: Certain engine degreasers or cleaners
may discolor or damage plastic housing of Filter
Minder. Cover and tape Filter Minder if any engine
degreasers or cleaners are to be used.
To test, turn engine off. If yellow disc (Fig. 7) has
reached red colored zone on graduated scale, air
cleaner element should be replaced. Refer to Removal
/ Installation.
Resetting Filter Minder:After air cleaner (filter)
element has been replaced, press rubber button on
top of Filter Minder (Fig. 7). This will allow yellow
colored disc to reset. After button has been pressed,
yellow disc should spring back to UP position.
If Filter Minder gauge has reached red colored
zone, and after an examination of air cleaner (filter)
element, element appears to be clean, high reading
may be due to a temporary condition such as snow
build-up at air intake. Temporary high restrictions
may also occur if air cleaner (filter) element has got-
ten wet such as during a heavy rain or snow. If this
occurs, allow element to dry out during normal
engine operation. Reset rubber button on top of Filter
Minder and retest after element has dried.
Fig. 5 Engine Serial Number Location
Fig. 6 5.9L DIESEL AIR CLEANER - FILTER
MINDERŸ
1 - CLIPS
2 - FILTER COVER
3 - FILTER MINDERŸ
4 - INLET AIR TEMPERATURE/ PRESSURE SENSOR
5 - FILTER HOUSING
9 - 248 ENGINE 5.9L DIESELDR
Page 1495 of 2627
(6) Remove the wooden dowel rods and rubber
bands from the tappets.
(7) Lubricate the push rods with engine oil and
install in their original location.Verify that they
are seated in the tappets.
(8) Lubricate the valve tips with engine oil and
install the crossheads in their original locations.
(9) Lubricate the crossheads and push rod sockets
with engine oil and install the rocker arms and ped-
estals in their original locations. Tighten bolts to 36
N´m (27 ft. lbs.) torque.
(10)Verify valve lash adjustment (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/INTAKE/EXHAUST
VALVES & SEATS - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(11) Install the cylinder head cover and reusable
gasket (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/
CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
(12) Install gear housing cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/GEAR HOUSING COVER
- INSTALLATION). Install front crankshaft dust
seal.
(13) Install the crankshaft damper with the speed
indicator ring (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/ENGINE
BLOCK/VIBRATION DAMPER - INSTALLATION).
(14) Install the fan support/hub assembly Refer to
(Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/RADIATOR FAN -
INSTALLATION).
(15) Install the power steering pump.
(16) Install accessory drive belt tensioner. Torque
bolt to 43 Nm (32 ft. lbs.).
(17) Install the accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
INSTALLATION).
(18) Install the charge air cooler (with a/c con-
denser and auxiliary transmission oil cooler, if
equipped) and tighten the mounting bolts to 2 N´m
(17 in. lbs.) torque.
(19) Connect charge air cooler inlet and outlet
pipes. Tighten clamps to 11 N´m (95 in. lbs.) torque.
(20) Install the radiator upper support panel.
(21) Close radiator petcock and lower the radiator
into the engine compartment. Tighten the mounting
bolts to 11 N´m (95 in. lbs.) torque.
(22) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(23) Connect radiator lower hose and install
clamp.
(24) Connect transmission auxiliary oil cooler lines
(if equipped).
(25) Lower vehicle.
(26) Install the fan shroud and tighten the mount-
ing screws to 6 N´m (50 in. lbs.) torque.
(27) Install the electronically controlled viscous
fan/drive assembly. Connect harness connector.(Refer
to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/RADIATOR FAN -
INSTALLATION).(28) Install the coolant recovery and windshield
washer fluid reservoirs to the fan shroud.
(29) Connect the coolant recovery hose to the radi-
ator filler neck.
(30) Add engine coolant (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(31) Charge A/C system with refrigerant (if A/C
equipped) (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDI-
TIONING/PLUMBING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(32) Connect the battery negative cables.
(33) Start engine and check for engine oil and cool-
ant leaks.
CONNECTING ROD BEARINGS
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CONNECTING ROD
BEARING AND CRANKSHAFT JOURNAL
CLEARANCE
(1) Measure the connecting rod bore with bearings
removedand the bolts tightened to 100 N´m (73 ft.
lbs.) torque..
(2) Measure the connecting rod bore with the bear-
ingsinstalledand the bolts tightened to 100 N´m
(73 ft. lbs.) torque.
Measure within 20É arc from each side of the part-
ing line. Also measure 90É from parting line.
Record the smallest and largest diameter.
Measure the diameter of the rod journal at the
location shown (Fig. 63). Calculate the average diam-
eter for each side of the journal.
Determine minimum bearing clearance by calculat-
ing the differance between the smallest connecting
rod bore diameter with the bearing installed and the
average diameter for each side of the crankshaft jour-
nal.
Determine the maximum bearing clearance by cal-
culating the difference between the largest connect-
ing rod bore diameter and the average diameter with
the bearing installed for each side of the crankshaft
journal.
DESCRIPTION MEASUREMENT
CONNECTING ROD
BORE, BEARINGS
REMOVEDMIN. 72.99 mm (2.874
in.)
MAX. 73.01 mm (2.875
in.)
CONNECTING ROD
BORE, BEARINGS
INSTALLEDMIN. 69.05 mm (2.719
in.)
MAX. 69.10 mm (2.720
in.)
9 - 272 ENGINE 5.9L DIESELDR
CAMSHAFT & BEARINGS (IN BLOCK) (Continued)
Page 1575 of 2627

OPERATION
Fuel Pressure Regulator Operation:The pres-
sure regulator is a mechanical device that is not con-
trolled by engine vacuum or the Powertrain Control
Module (PCM).
The regulator is calibrated to maintain fuel system
operating pressure of approximately 58 2 psi at the
fuel injectors. It contains a diaphragm, calibrated
springs and a fuel return valve. The internal fuel fil-
ter (Fig. 2) is also part of the assembly.
Fuel is supplied to the filter/regulator by the elec-
tric fuel pump through an opening tube at the bot-
tom of filter/regulator (Fig. 2).
The regulator acts as a check valve to maintain
some fuel pressure when the engine is not operating.
This will help to start the engine. A second check
valve is located at the outlet end of the electric fuel
pump.Refer to Fuel Pump - Description and
Operation for more information.
If fuel pressure at the pressure regulator exceeds
approximately 60 psi, an internal diaphragm opens
and excess fuel pressure is routed back into the tank
through the bottom of pressure regulator.
Both fuel filters (at bottom of fuel pump module
and within fuel pressure regulator) are designed for
extended service. They do not require normal sched-
uled maintenance. Filters should only be replaced if
a diagnostic procedure indicates to do so.
FUEL LEVEL SENDING UNIT /
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The fuel gauge sending unit (fuel level sensor) is
attached to the side of the fuel pump module. The
sending unit consists of a float, an arm, and a vari-
able resistor track (card).
OPERATION
The fuel pump module has 4 different circuits
(wires). Two of these circuits are used for the fuel
gauge sending unit for fuel gauge operation, and for
certain OBD II emission requirements. The other 2
wires are used for electric fuel pump operation.
For Fuel Gauge Operation:A constant current
source is supplied to the resistor track on the fuel
gauge sending unit. This is fed directly from the
Powertrain Control Module (PCM).NOTE: For
diagnostic purposes, this 12V power source can
only be verified with the circuit opened (fuel
pump module electrical connector unplugged).
With the connectors plugged, output voltages
will vary from about 0.6 volts at FULL, to about
8.6 volts at EMPTY (about 8.6 volts at EMPTY
for Jeep models, and about 7.0 volts at EMPTY
for Dodge Truck models).The resistor track is
used to vary the voltage (resistance) depending on
fuel tank float level. As fuel level increases, the float
and arm move up, which decreases voltage. As fuel
level decreases, the float and arm move down, which
increases voltage. The varied voltage signal is
returned back to the PCM through the sensor return
circuit.
Both of the electrical circuits between the fuel
gauge sending unit and the PCM are hard-wired (not
multi-plexed). After the voltage signal is sent from
the resistor track, and back to the PCM, the PCM
will interpret the resistance (voltage) data and send
a message across the multi-plex bus circuits to the
instrument panel cluster. Here it is translated into
the appropriate fuel gauge level reading. Refer to
Instrument Panel for additional information.
For OBD II Emission Monitor Requirements:
The PCM will monitor the voltage output sent from
the resistor track on the sending unit to indicate fuel
level. The purpose of this feature is to prevent the
OBD II system from recording/setting false misfire
and fuel system monitor diagnostic trouble codes.
The feature is activated if the fuel level in the tank
is less than approximately 15 percent of its rated
capacity. If equipped with a Leak Detection Pump
(EVAP system monitor), this feature will also be acti-
vated if the fuel level in the tank is more than
approximately 85 percent of its rated capacity.
Fig. 2 SIDE VIEW - FILTER/REGULATOR
1 - INTERNAL FUEL FILTER
2 - FUEL FLOW TO FUEL INJECTORS
3 - FUEL FILTER/FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
4 - EXCESS FUEL BACK TO TANK
5 - FUEL INLET
6 - RUBBER GROMMET
7 - TOP OF PUMP MODULE
14 - 6 FUEL DELIVERY - GASDR
FUEL FILTER/PRESSURE REGULATOR (Continued)
Page 1592 of 2627

(5) Position APPS assembly to bottom of battery
tray and install 3 bolts. Refer to Torque Specifica-
tions.
(6) Install wheelhouse liner. Refer to Body.
(7)The 5.7L V-8 engine is equipped with a
fully electronic accelerator pedal position sen-
sor. If equipped with a 5.7L, also perform the
following 3 steps:
(a) Connect negative battery cable to battery.
(b) Turn ignition switch ON, but do not crank
engine.
(c) Leave ignition switch ON for a minimum of
10 seconds. This will allow PCM to learn electrical
parameters.
(d) The DRB IIItScan Tool may also be used to
learn electrical parameters. Go to the Miscella-
neous menu, and then select ETC Learn.
(8) If the previous step is not performed, a Diag-
nostic Trouble Code (DTC) will be set.
(9) If necessary, use DRB IIItScan Tool to erase
any Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC's) from PCM.
CRANKSHAFT POSITION
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
3.7L V-6
The Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor is mounted
into the right rear side of the cylinder block. It is
positioned and bolted into a machined hole.
4.7L V-8
The Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor is mounted
into the right rear side of the cylinder block. It is
positioned and bolted into a machined hole.
5.7L V-8
The Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor is mounted
into the right rear side of the cylinder block. It is
positioned and bolted into a machined hole.
OPERATION
3.7L V-6
Engine speed and crankshaft position are provided
through the CKP (Crankshaft Position) sensor. The
sensor generates pulses that are the input sent to the
Powertrain Control Module (PCM). The PCM inter-
prets the sensor input to determine the crankshaft
position. The PCM then uses this position, along with
other inputs, to determine injector sequence and igni-
tion timing.
Fig. 3 APPS REMOVE / INSTALL
1 - BOTTOM OF BATTERY TRAY
2 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
3 - APPS
4 - SWING-DOWN DOOR
5 - CABLE (TO PEDAL)
6 - CABLE RELEASE TAB
Fig. 4 APPS CABLE
1 - APPS LEVER
2 - BALL SOCKET
3 - SWING-DOWN DOOR
4 - CABLE CLIP
5 - CABLE
DRFUEL INJECTION - GAS 14 - 23
ACCELERATOR PEDAL POSITION SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1596 of 2627

stream. The spraying action atomizes the fuel, add-
ing it to the air entering the combustion chamber.
The nozzle (outlet) ends of the injectors are posi-
tioned into openings in the intake manifold just
above the intake valve ports of the cylinder head.
The engine wiring harness connector for each fuel
injector is equipped with an attached numerical tag
(INJ 1, INJ 2 etc.). This is used to identify each fuel
injector.
The injectors are energized individually in a
sequential order by the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM). The PCM will adjust injector pulse width by
switching the ground path to each individual injector
on and off. Injector pulse width is the period of time
that the injector is energized. The PCM will adjust
injector pulse width based on various inputs it
receives.
Battery voltage is supplied to the injectors through
the ASD relay.
The PCM determines injector pulse width based on
various inputs.
OPERATION - PCM OUTPUT
The nozzle ends of the injectors are positioned into
openings in the intake manifold just above the intake
valve ports of the cylinder head. The engine wiring
harness connector for each fuel injector is equipped
with an attached numerical tag (INJ 1, INJ 2 etc.).
This is used to identify each fuel injector with its
respective cylinder number.
The injectors are energized individually in a
sequential order by the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM). The PCM will adjust injector pulse width by
switching the ground path to each individual injector
on and off. Injector pulse width is the period of time
that the injector is energized. The PCM will adjust
injector pulse width based on various inputs it
receives.
Battery voltage (12 volts +) is supplied to the injec-
tors through the ASD relay. The ASD relay will shut-
down the 12 volt power source to the fuel injectors if
the PCM senses the ignition is on, but the engine is
not running. This occurs after the engine has not
been running for approximately 1.8 seconds.
The PCM determines injector on-time (pulse width)
based on various inputs.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove fuel rail. Refer to Fuel Injector Rail
Removal.
(2) Disconnect clip(s) that retain fuel injector(s) to
fuel rail (Fig. 12).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install fuel injector(s) into fuel rail assembly
and install retaining clip(s).(2) If same injector(s) is being reinstalled, install
new o-ring(s).
(3) Apply a small amount of clean engine oil to
each injector o-ring. This will aid in installation.
(4) Install fuel rail. Refer to Fuel Rail Installation.
(5) Start engine and check for fuel leaks.
FUEL PUMP RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The 5±pin, 12±volt, fuel pump relay is located in
the Power Distribution Center (PDC). Refer to the
label on the PDC cover for relay location.
OPERATION
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) energizes
the electric fuel pump through the fuel pump relay.
The fuel pump relay is energized by first applying
battery voltage to it when the ignition key is turned
ON, and then applying a ground signal to the relay
from the PCM.
Whenever the ignition key is turned ON, the elec-
tric fuel pump will operate. But, the PCM will shut-
down the ground circuit to the fuel pump relay in
approximately 1±3 seconds unless the engine is oper-
ating or the starter motor is engaged.
Fig. 12 INJECTOR RETAINING CLIP
1 - PLIERS
2 - INJECTOR CLIP
3 - FUEL INJECTOR - TYPICAL
4 - FUEL RAIL - TYPICAL
DRFUEL INJECTION - GAS 14 - 27
FUEL INJECTOR (Continued)
Page 1597 of 2627

REMOVAL
The fuel pump relay is located in the Power Distri-
bution Center (PDC) (Fig. 13). Refer to label on PDC
cover for relay location.
(1) Remove PDC cover.
(2) Remove relay from PDC.
(3) Check condition of relay terminals and PDC
connector terminals for damage or corrosion. Repair
if necessary before installing relay.
(4) Check for pin height (pin height should be the
same for all terminals within the PDC connector).
Repair if necessary before installing relay.
INSTALLATION
The fuel pump relay is located in the Power Distri-
bution Center (PDC). Refer to label on PDC cover for
relay location.
(1) Install relay to PDC.
(2) Install cover to PDC.
IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR
DESCRIPTION
A separate IAC motor is not used with the 5.7L V-8
engine.
The IAC stepper motor is mounted to the throttle
body, and regulates the amount of air bypassing the
control of the throttle plate. As engine loads and
ambient temperatures change, engine rpm changes.
A pintle on the IAC stepper motor protrudes into apassage in the throttle body, controlling air flow
through the passage. The IAC is controlled by the
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) to maintain the
target engine idle speed.
OPERATION
A separate IAC motor is not used with the 5.7L V-8
engine.
At idle, engine speed can be increased by retract-
ing the IAC motor pintle and allowing more air to
pass through the port, or it can be decreased by
restricting the passage with the pintle and diminish-
ing the amount of air bypassing the throttle plate.
The IAC is called a stepper motor because it is
moved (rotated) in steps, or increments. Opening the
IAC opens an air passage around the throttle blade
which increases RPM.
The PCM uses the IAC motor to control idle speed
(along with timing) and to reach a desired MAP dur-
ing decel (keep engine from stalling).
The IAC motor has 4 wires with 4 circuits. Two of
the wires are for 12 volts and ground to supply elec-
trical current to the motor windings to operate the
stepper motor in one direction. The other 2 wires are
also for 12 volts and ground to supply electrical cur-
rent to operate the stepper motor in the opposite
direction.
To make the IAC go in the opposite direction, the
PCM just reverses polarity on both windings. If only
1 wire is open, the IAC can only be moved 1 step
(increment) in either direction. To keep the IAC
motor in position when no movement is needed, the
PCM will energize both windings at the same time.
This locks the IAC motor in place.
In the IAC motor system, the PCM will count
every step that the motor is moved. This allows the
PCM to determine the motor pintle position. If the
memory is cleared, the PCM no longer knows the
position of the pintle. So at the first key ON, the
PCM drives the IAC motor closed, regardless of
where it was before. This zeros the counter. From
this point the PCM will back out the IAC motor and
keep track of its position again.
When engine rpm is above idle speed, the IAC is
used for the following:
²Off-idle dashpot (throttle blade will close quickly
but idle speed will not stop quickly)
²Deceleration air flow control
²A/C compressor load control (also opens the pas-
sage slightly before the compressor is engaged so
that the engine rpm does not dip down when the
compressor engages)
²Power steering load control
The PCM can control polarity of the circuit to con-
trol direction of the stepper motor.
Fig. 13 PDC LOCATION
1 - BATTERY
2 - INTEGRATED POWER MODULE (IPM)
14 - 28 FUEL INJECTION - GASDR
FUEL PUMP RELAY (Continued)