RELAY CONNECTORS DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.G User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1998, Model line: RAM 1500, Model: DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.GPages: 2627
Page 735 of 2627

²Ohmmeter - Used to check the resistance
between two points of a circuit. Low or no resistance
in a circuit means good continuity.
CAUTION: Most of the electrical components used
in today's vehicles are Solid State. When checking
resistance in these circuits use a meter with a 10 -
megohm or greater impedance rating. In addition,
make sure the power is disconnected from the cir-
cuit. Circuits that are powered up by the vehicle's
electrical system can cause damage to the equip-
ment and provide false readings.
²Probing Tools - These tools are used for probing
terminals in connectors (Fig. 5). Select the proper
size tool from Special Tool Package 6807, and insert
it into the terminal being tested. Use the other end
of the tool to insert the meter probe.
INTERMITTENT AND POOR CONNECTIONS
Most intermittent electrical problems are caused
by faulty electrical connections or wiring. It is also
possible for a sticking component or relay to cause a
problem. Before condemning a component or wiring
assembly, check the following items.
²Connectors are fully seated
²Spread terminals, or terminal push out
²
Terminals in the wiring assembly are fully seated
into the connector/component and locked into position
²Dirt or corrosion on the terminals. Any amount
of corrosion or dirt could cause an intermittent prob-
lem
²Damaged connector/component casing exposing
the item to dirt or moisture
²Wire insulation that has rubbed through causing
a short to ground
²Some or all of the wiring strands broken inside
of the insulation
²Wiring broken inside of the insulation
TROUBLESHOOTING WIRING PROBLEMS
When troubleshooting wiring problems there are
six steps which can aid in the procedure. The steps
are listed and explained below. Always check for non-factory items added to the vehicle before doing any
diagnosis. If the vehicle is equipped with these items,
disconnect them to verify these add-on items are not
the cause of the problem.
(1) Verify the problem.
(2) Verify any related symptoms. Do this by per-
forming operational checks on components that are
in the same circuit. Refer to the wiring diagrams.
(3) Analyze the symptoms. Use the wiring dia-
grams to determine what the circuit is doing, where
the problem most likely is occurring and where the
diagnosis will continue.
(4) Isolate the problem area.
(5) Repair the problem area.
(6) Verify the proper operation. For this step,
check for proper operation of all items on the
repaired circuit. Refer to the wiring diagrams.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ELECTROSTATIC
DISCHARGE (ESD) SENSITIVE DEVICES
All ESD sensitive components are solid state and a
symbol (Fig. 6) is used to indicate this. When han-
dling any component with this symbol, comply with
the following procedures to reduce the possibility of
electrostatic charge build up on the body and inad-
vertent discharge into the component. If it is not
known whether the part is ESD sensitive, assume
that it is.
(1) Always touch a known good ground before han-
dling the part. This should be repeated while han-
dling the part and more frequently after sliding
across a seat, sitting down from a standing position,
or walking a distance.
(2) Avoid touching electrical terminals of the part,
unless instructed to do so by a written procedure.
(3) When using a voltmeter, be sure to connect the
ground lead first.
(4) Do not remove the part form it's protective
packing until it is time to install the part.
(5) Before removing the part from it's pakage,
ground the pakage to a known good ground on the
vehicle.
Fig. 5 PROBING TOOL
1 - SPECIAL TOOL 6801
2 - PROBING END
Fig. 6 ELECTROSTATIC DISCHARGE SYMBOL
8W - 01 - 8 8W-01 WIRING DIAGRAM INFORMATIONDR
WIRING DIAGRAM INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 745 of 2627

Component Page
Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor........ 8W-30
Mode Door Actuators................... 8W-42
Multi-Function Switch............ 8W-40, 52, 53
Natural Vacuum Leak Detection Assembly . . 8W-30
Output Speed Sensor................... 8W-31
Overhead Map/Reading Lamp......... 8W-44, 49
Oxygen Sensor Downstream Relay........ 8W-30
Oxygen Sensors....................... 8W-30
Park Brake Switch.................... 8W-40
Park Lamp Relay................... 8W-50, 52
Park/Turn Signal Lamps............. 8W-50, 52
Power Mirrors........................ 8W-62
Power Outlets........................ 8W-41
Power Seat Motors.................... 8W-63
Power Seat Switches................... 8W-63
Power Steering Pressure Switch.......... 8W-30
Power Window Circuit Breaker........... 8W-10
Power Window Motors.................. 8W-60
Power Window Switches................ 8W-60
Powertrain Control Module.............. 8W-30
PTCS............................... 8W-10
PTO Switch.......................... 8W-30
Radio............................... 8W-47
Rear Window Defogger Relay............ 8W-48
Recirculation Door Actuator............. 8W-42
Remote Radio Switches................. 8W-47
Seat Belt Pretensioners................. 8W-43
Seat Belt Switch-Driver................ 8W-40
Seat Belt Tensioner Reducer............. 8W-40
Seat Heater Interface Module............ 8W-63
Sentry Key Immobilizer Module.......... 8W-39
Side Impact Sensors................... 8W-43
Speakers............................ 8W-47Component Page
Speed Control Servo................... 8W-33
Speed Control Switches................. 8W-33
Splices.............................. 8W-70
Starter Motor........................ 8W-21
Starter Motor Relay................... 8W-21
Tail/Stop Lamp....................... 8W-52
Tail/Stop/Turn Signal Lamps.......... 8W-51, 52
Tail/Turn Lamp....................... 8W-52
Tailgate Lamp........................ 8W-51
Throttle Position Sensor................ 8W-30
Tow/Haul Overdrive Switch........... 8W-30, 31
Trailer Tow Connectors................. 8W-54
Trailer Tow Relays.................... 8W-54
Transfer Case Control Module............ 8W-31
Transfer Case Mode Sensor.............. 8W-31
Transfer Case Selector Switch............ 8W-31
Transfer Case Shift Motor............... 8W-31
Transmission Control Relay............. 8W-31
Transmission Range Sensor.............. 8W-31
Transmission Solenoid Assembly.......... 8W-31
Transmission Solenoid/TRS Assembly...... 8W-31
Underhood Lamp...................... 8W-44
Vacuum Pump........................ 8W-30
Vistronic Fan Drive................. 8W-30, 70
Washer Fluid Level Switch.............. 8W-53
Washer Pump Motor-Front.............. 8W-53
Water In Fuel Sensor.................. 8W-30
Wheel Speed Sensors................... 8W-35
Wiper High/Low Relay................. 8W-53
Wiper Motor-Front.................... 8W-53
Wiper On/Off Relay.................... 8W-53
8W - 02 - 2 8W-02 COMPONENT INDEXDR
Page 1218 of 2627

INTEGRATED POWER MODULE
DESCRIPTION
The Integrated Power Module (IPM) (Fig. 1) is a
combination of the Power Distribution Center (PDC)
and the Front Control Module (FCM). The IPM is
located in the engine compartment, next to the bat-
tery on this model. The power distribution center
mates directly with the Front Control Module (FCM)
to form the Integrated Power Module Fuse and Relay
Center. The power distribution center (PDC) is a
printed circuit board based module that contains
fuses and relays, while the front control module con-
tains the electronics controlling the integrated power
module and other functions. This integrated power
module connects directly to the battery positive via a
stud located on top of the unit. The ground connec-
tion is via electrical connectors. The integrated power
module provides the primary means of voltage distri-
bution and protection for the entire vehicle.
The molded plastic integrated power module hous-
ing includes a base and cover. The integrated power
module cover is easily opened or removed for service
access by unscrewing the cover retaining nut and has
a fuse and relay layout map integral to the inside
surface of the cover. This integrated power module
housing base and cover are secured in place via bolts
to the left front fender support assembly.
Replaceable components of the integrated power
module assembly are broken down into the followingcomponents: the Power Distribution Center (PDC),
the integrated power module cover, the Front Control
Module (FCM) and the Integrated Power Module
Assembly which includes the power distribution cen-
ter, the cover and FCM.Refer to the Front Con-
trol Module in the Electronic Control Module
sectionof this service manual for information on the
front control module.
OPERATION
All of the current from the battery and the gener-
ator output enters the integrated power module via a
stud on the top of the module. The integrated power
module cover is removed to access the fuses or relays.
Internal connections of all of the power distribution
center circuits is accomplished by a combination of
bus bars and a printed circuit board. Refer to the
Wiring section of the service manual for complete
integrated power module circuit schematics.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the negative and positive battery
cables.
(2) Unsnap cover and remove the B+ terminal nut
from the integrated power module B+ terminal.
Remove the B+ cable from the integrated power mod-
ule.
(3) Disconnect the gray connector from the inte-
grated power module.
Fig. 1 DR INTEGRATED POWER MODULE
1 - POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER HOUSING
2 - FRONT CONTROL MODULE ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
Fig. 2 DR INTEGRATED POWER MODULE
1 - COVER RETAINING BOLT
2 - INTEGRATED POWER MODULE RETAINING BOLT
3 - RETAINING SCREW
4 - INTEGRATED POWER MODULE COVER
DR8W-97 POWER DISTRIBUTION 8W - 97 - 3
Page 1220 of 2627

(3) Connect the electrical connectors by pushing
straight on and rotating the connector arm inboard,
until the connector is firmly locked in place on the
module assembly.
(4) Grasp the integrated power module with two
hands and install the assembly on the battery tray
(Fig. 5).
(5) Install the integrated power module retaining
bolt and screw.
(6) Connect the gray connector on the integrated
power module housing.
(7) Install the B+ terminal cable and nut on the
integrated power module B+ terminal. Snap the
cover in place.
(8) Connect the negative and positive battery
cables.
FRONT CONTROL MODULE
DESCRIPTION
The Front Control Module (FCM) is a micro con-
troller based module located in the left front corner
of the engine compartment. On this model the inte-
grated power module must be positioned aside in
order to access the front control module. The front
control module mates to the power distribution cen-
ter to form the Integrated Power Module (IPM). Theintegrated power module connects directly to the bat-
tery and provides the primary means of circuit pro-
tection and power distribution for all vehicle
electrical systems. The front control module controls
power to some of these vehicle systems electrical and
electromechanical loads based on inputs received
from hard wired switch inputs and data received on
the PCI bus circuit (J1850).
For information on theIntegrated Power Mod-
ule Refer to the Power Distribution Sectionof
the service manual.
OPERATION
As messages are sent over the PCI bus circuit, the
front control module reads these messages and con-
trols power to some of the vehicles electrical systems
by completing the circuit to ground (low side driver)
or completing the circuit to 12 volt power (high side
driver). The following functions areControlledby
the Front Control Module:
²Headlamp Power with Voltage Regulation
²Windshield Wiper ªON/OFFº Relay Actuation
²Windshield Wiper ªHI/LOº Relay Actuation
²Windshield Washer Pump Motor
²Fog Lamp Relay Actuation
²Park Lamp Relay Actuation
²Horn Relay Actuation
The following inputs areReceived/Monitoredby
the Front Control Module:
²B+ Connection Detection
²Power Ground
²Ambient Temperature Sensing
²Ignition Switch Run
²Washer Fluid Level Switch
²Windshield Wiper Park Switch
²PCI Bus Circuit
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FRONT CONTROL
MODULE
The front control module is a printed circuit board
based module with a on-board micro-processor. The
front control module interfaces with other electronic
modules in the vehicle via the Programmable Com-
munications Interface (PCI) data bus (J1850). In
order to obtain conclusive testing the Programmable
Communications Interface (PCI) data bus network
and all of the electronic modules that provide inputs
to, or receive outputs from the front control module
must be checked. All PCI (J1850) communication
faults must be resolved prior to further diagnosing
any front control module related issues.
The front control module was designed to be diag-
nosed with an appropriate diagnostic scan tool, such
as the DRB IIIt. The most reliable, efficient, and
accurate means to diagnose the front control module
Fig. 5 INTEGRATED POWER MODULE MOUNTING
TABS
1 - INTEGRATED POWER MODULE MOUNTING HOLES
2 - BATTERY TRAY ASSEMBLY
3 - FRONT CONTROL MODULE
DR8W-97 POWER DISTRIBUTION 8W - 97 - 5
INTEGRATED POWER MODULE (Continued)
Page 1464 of 2627

(10) Drain engine oil. Remove and discard the oil
filter (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL FIL-
TER - REMOVAL).
(11) Install the drain plug. Tighten the plug to 50
N´m (37 ft. lbs.) torque.
(12) Install a new oil filter (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
LUBRICATION/OIL FILTER - INSTALLATION).
(13) Fill engine crankcase with the specified
amount and grade of oil (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/FLUID TYPES - SPECIFICA-
TIONS).
(14) Connect the negative cable(s) to the battery.
(15) Start the engine and check for any leaks.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - ENGINE
(1) Disconnect both battery negative cables.
(2) Disconnect engine grid heater harness at grid
heater relays.
(3) Disconnect electrical connections from rear of
alternator.
(4) Recover A/C refrigerant. (Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE).
(5) Raise vehicle on a hoist.
(6) Drain engine coolant (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(7) Remove engine oil drain plug and drain engine
oil.
(8) Reinstall drain plug. Tighten to 50N´m (37 ft.
lbs.) torque.
(9) Lower the vehicle.
(10) Remove fan/drive assembly. Refer to Section 7
± Fan/Drive Removal
(11) Remove radiator upper hose.
(12) Remove upper fan shroud mounting bolts.
(13) Disconnect the coolant recovery bottle hose
from the radiator fill neck and remove bottle.
(14) Using a 36mm wrench, remove viscous fan/
drive assembly. (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/RA-
DIATOR FAN - REMOVAL).
(15) Remove cooling fan and shroud together.
(16) Disconnect heater core supply and return
hoses from the cylinder head fitting and coolant pipe.
(17) Raise vehicle on a hoist.
(18) Remove transmission and transfer case (if
equipped).
(19) Disconnect exhaust pipe from turbocharger
extension pipe.
(20) Disconnect engine harness to vehicle harness
connectors.
(21) Remove starter motor (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/STARTING/STARTER MOTOR - REMOVAL).(22) Remove flywheel/flexplate.
(23) Remove transmission adapter
(24) Disconnect A/C suction/discharge hose from
the rear of the A/C compressor.
(25) Lower vehicle.
(26) Disconnect lower radiator hose from radiator
outlet.
(27) Automatic transmission models:
(28) Disconnect transmission oil cooler lines from
in front of radiator using special tool #6931
(29) Remove radiator. (Refer to 7 - COOLING/EN-
GINE/RADIATOR - REMOVAL).
(30) If A/C equipped, disconnect A/C condenser
refrigerant lines.
(31) Disconnect charge air cooler piping.
(32) Remove charge air cooler mounting bolts.
(33) Remove charge air cooler (and A/C condenser
if equipped) from vehicle.
(34) Remove damper and speed indicator ring from
front of engine.
(35) Disconnect engine block heater connector.
(36) Disconnect A/C compressor and pressure sen-
sor electrical connectors.
(37) Remove the passenger battery ground cable
from the engine block. Remove the driver side bat-
tery ground cable from the engine block.
(38) Remove power steering pump from engine by
removing 3 bolts.
(39) Remove accelerator linkage cover.
(40) Disconnect cables from on-engine APPS.
(41) Disconnect the ECM power connector.
(42) Disconnect the ECM ground wire from the
hydroform screw.
(43) Disconnect the fuel supply and return hoses.
(44) Remove the cylinder head cover. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(45) Disconnect the 3 injector harness connectors
at the rocker housing. Disconnect the wire harnesses
from the injectors.
(46) Remove the rear engine lift bracket.
(47) Remove cylinder #4, #5, and #6 intake and
exhaust rocker arms, pedestals, and push tubes. Note
the original location for re-assembly.
(48) Loosen #6 fuel line shield bolts and rotate
shield out of the way.
(49) Remove cylinder #5 and #6 high pressure fuel
lines. Remove the fuel connector tube nut and fuel
connector tube. Remove cylinder #5 and #6 fuel injec-
tor.
(50) Remove rocker housing.
DRENGINE 5.9L DIESEL 9 - 241
ENGINE 5.9L DIESEL (Continued)
Page 1466 of 2627

(8) Replace injector o-ring and sealing washer on
injectors #5 and #6. Install injectors and torque using
the following steps:
²Step 1ÐInstall injector hold-down capscrews
and torque to 5 N´m (44 in. lbs.) torque.
²Step 2ÐLoosen injector hold-down capscrews.
²Step 3ÐInstall HPC connector tube and nut.
Torque nut to 15 N´m (11 ft. lbs.) torque.
²Step 4ÐTorque injector hold-down capscrews to
10 N´m (89 in. lbs.) torque.
²Step 5ÐTorque HPC connector tube nut to 50
N´m (37 ft. lbs.) torque.
(9) Install #5 and #6 high pressure fuel lines. Fol-
low correct torque sequence per section 14. Torque
fuel line fittings to 30 N-m (22 ft-lb). Torque brace
capscrew to 24 N-m (18 ft-lb).
(10) Install rear engine lift bracket. Torque to 77
N-m (57 ft-lb).
(11) Install push tubes, rocker arms, and pedestals
for cylinders #4, #5, and #6. Torque the mounting
bolts to 36 N-m (27 ft-lbs).
(12) Reset valve lash on cylinders #4, #5, and #6.
Torque adjusting nuts to 24 N-m (18 ft-lbs).
(13) Install cylinder head cover. Torque to 24 N-m
(18 ft-lbs).(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD -
INSTALLATION).
(14) Connect breather tube and lube oil drain tube
to breather housing cover. Install breather housing.
Torque capscrews to 24 N-m (18 ft-lbs)
(15) Connect fuel supply and return hoses.
(16) Connect ECM ground to hydroform screw.
Connect ECM power connector.
(17) Install the APPS cable(s) to the APPS. Install
the throttle linkage cover.
(18) Install the power steering pump.
(19) Install the damper and speed indicator ring.
Torque to 40 N-m (30 ft-lb) plus 60 degrees.
(20) Connect the engine block heater connection.
(21) Connect the A/C compressor and pressure sen-
sor connectors
(22) Install the charge air cooler and a/c condenser
(if equipped). Install and tighten the charge air
cooler mounting bolts to 2 N-m (17 in-lbs).
(23) Connect the charge air cooler piping. Torque
all clamps to 8 N-m (72 in-lbs).
(24) Connect the a/c refrigerant lines to the a/c
condenser (if equipped).
(25) Install the radiator upper support panel.
(26) Install radiator.
(27) Connect the transmission quick-connect oil
cooler lines.(28) Raise vehicle.
(29) Connect a/c compressor suction/discharge hose
(if equipped).
(30) Install the radiator lower hose and clamps.
(31) Install the battery negative cables to the
engine block on the driver and passenger side.
(32) Install the transmission adapter with a new
camshaft rectangular ring seal. Torque to 77 N-m (57
ft-lb).
(33) Install the flywheel/flexplate. Torque to 137
N-m (101 ft-lb).
(34) Install the starter motor. Torque to 43 N-m
(32 ft-lb). (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/STARTING/
STARTER MOTOR - INSTALLATION).
(35) Connect engine to vehicle harness connectors.
(36) Install transmission and transfer case (if
equipped).
(37) Connect the exhaust pipe to the turbocharger
elbow.
(38) Connect the transmission auxiliary oil cooler
lines (if equipped).
(39) Lower the vehicle.
(40) Connect the heater core supply and return
hoses.
(41) Install the cooling fan and upper fan shroud
at the same time. (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/
RADIATOR FAN - INSTALLATION).
(42) Install the coolant recovery bottle.
(43) Install the windshield washer bottle.
(44) Install the upper radiator hose and clamps.
(45) Raise vehicle.
(46) Connect electronically controlled fan drive
wire harness. Install lower radiator fan shroud.
(47) Change oil filter and install new engine oil.
(48) Fill the cooling system with coolant. (Refer to
7 - COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(49) Connect grid heater harness at grid heater
relays.
(50) Connect electrical connections to rear of alter-
nator.
(51) Start the engine and inspect for engine oil,
coolant, and fuel leaks.
INSTALLATIONÐCRANKCASE BREATHER
(1) Install a new o-ring onto the breather element.
(2) Lubricate o-ring and install into cylinder head
cover. Torque capscrews to 10 N´m (89 in. lbs.).
(3) Connect breather tube and lube oil drain tube.
(4) Install breather cover (Fig. 4). Torque to 24
N´m (18 ft. lbs.)
(5) Install oil fill cap.
DRENGINE 5.9L DIESEL 9 - 243
ENGINE 5.9L DIESEL (Continued)
Page 1651 of 2627

INTAKE AIR HEATER RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The 2 intake manifold air heater relays are located
in the engine compartment. They are attached to a
common bracket. This bracket is attached to the
right battery tray (Fig. 29).
OPERATION
The Engine Control Module (ECM) operates the 2
heating elements through the 2 intake manifold air
heater relays.
Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures for an
electrical operation and complete description of the
intake heaters, including pre-heat and post-heat
cycles.
REMOVAL
The 2 intake manifold air heater relays are located
in the engine compartment. They are attached to a
common bracket. This bracket is attached to the
right battery tray (Fig. 29).
The mounting bracket and both relays are replaced
as an assembly.
(1) Disconnect both negative battery cables at both
batteries.
(2) Disconnect four relay trigger wires at both
relays. Note position of wiring before removing.
(3) Lift four rubber shields from all 4 cables.(4) Remove four nuts at cable connectors. Note
position of wiring before removing.
(5) Remove relay mounting bracket bolts and
remove relay assembly.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install relay assembly to battery tray. Tighten
mounting bolts to 4.5 N´m (40 in. lbs.) torque.
(2) Connect eight electrical connectors to relays.
(3) Connect battery cables to both batteries.
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE
SENSOR/MAP SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The combination, dual function Intake Manifold
Air Temperature Sensor/MAP Sensor is installed into
the top of the intake manifold.
OPERATION
The combination, dual function Intake Manifold
Air Temperature Sensor/MAP Sensor is installed into
the top of the intake manifold with the sensor ele-
ment extending into the air stream.
The IAT portion of the sensor provides an input
voltage to the Engine Control Module (ECM) indicat-
ing intake manifold air temperature. The MAP por-
tion of the sensor provides an input voltage to the
ECM indicating turbocharger boost pressure.
REMOVAL
The combination, dual function Intake Manifold
Air Temperature Sensor/MAP (IAT/MAP) sensor is
installed into the top of the intake manifold (Fig. 30).
(1) Clean area around sensor.
(2) Disconnect electrical connector from IAT/MAP
sensor.
(3) Remove two T-15 Torx headed screws.
(4) Remove sensor from intake manifold.
(5) Check condition of sensor o-ring (Fig. 31).
INSTALLATION
(1) Check condition of sensor o-ring.
(2) Lubricate sensor o-ring with clean engine oil.
(3) Clean sensor mounting area at intake mani-
fold.
(4) Position sensor into intake manifold.
(5) Install and tighten 2 sensor mounting screws
to 1 N´m (9 in. lbs.) torque.
(6) Connect electrical connector to sensor.
Fig. 29 INTAKE MANIFOLD AIR HEATER RELAYS
1 - BATTERY
2 - CABLES TO INTAKE HEATERS
3 - RELAY TRIGGER WIRES
4 - INTAKE AIR HEATER RELAYS (2)
14 - 82 FUEL INJECTION - DIESELDR
Page 1858 of 2627
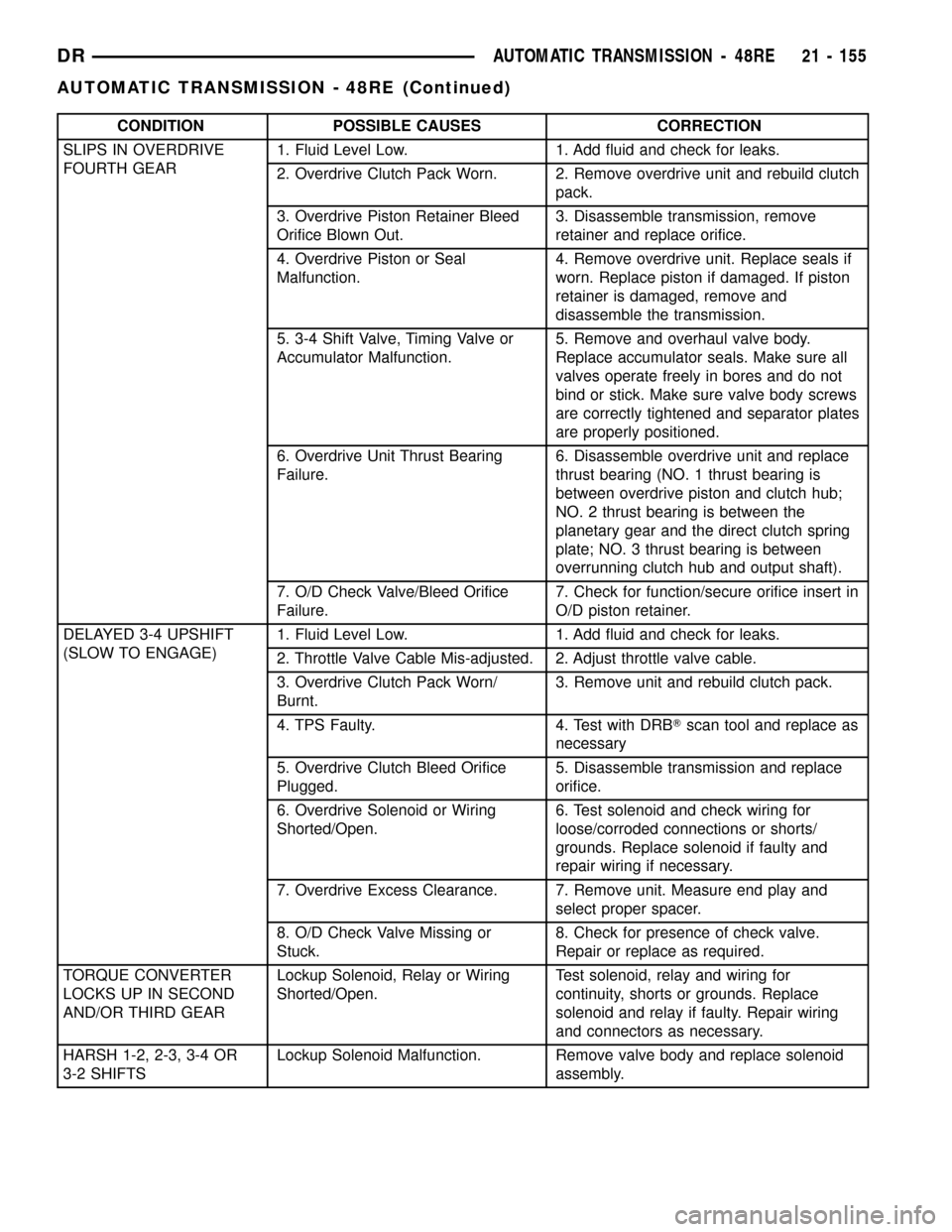
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
SLIPS IN OVERDRIVE
FOURTH GEAR1. Fluid Level Low. 1. Add fluid and check for leaks.
2. Overdrive Clutch Pack Worn. 2. Remove overdrive unit and rebuild clutch
pack.
3. Overdrive Piston Retainer Bleed
Orifice Blown Out.3. Disassemble transmission, remove
retainer and replace orifice.
4. Overdrive Piston or Seal
Malfunction.4. Remove overdrive unit. Replace seals if
worn. Replace piston if damaged. If piston
retainer is damaged, remove and
disassemble the transmission.
5. 3-4 Shift Valve, Timing Valve or
Accumulator Malfunction.5. Remove and overhaul valve body.
Replace accumulator seals. Make sure all
valves operate freely in bores and do not
bind or stick. Make sure valve body screws
are correctly tightened and separator plates
are properly positioned.
6. Overdrive Unit Thrust Bearing
Failure.6. Disassemble overdrive unit and replace
thrust bearing (NO. 1 thrust bearing is
between overdrive piston and clutch hub;
NO. 2 thrust bearing is between the
planetary gear and the direct clutch spring
plate; NO. 3 thrust bearing is between
overrunning clutch hub and output shaft).
7. O/D Check Valve/Bleed Orifice
Failure.7. Check for function/secure orifice insert in
O/D piston retainer.
DELAYED 3-4 UPSHIFT
(SLOW TO ENGAGE)1. Fluid Level Low. 1. Add fluid and check for leaks.
2. Throttle Valve Cable Mis-adjusted. 2. Adjust throttle valve cable.
3. Overdrive Clutch Pack Worn/
Burnt.3. Remove unit and rebuild clutch pack.
4. TPS Faulty. 4. Test with DRBTscan tool and replace as
necessary
5. Overdrive Clutch Bleed Orifice
Plugged.5. Disassemble transmission and replace
orifice.
6. Overdrive Solenoid or Wiring
Shorted/Open.6. Test solenoid and check wiring for
loose/corroded connections or shorts/
grounds. Replace solenoid if faulty and
repair wiring if necessary.
7. Overdrive Excess Clearance. 7. Remove unit. Measure end play and
select proper spacer.
8. O/D Check Valve Missing or
Stuck.8. Check for presence of check valve.
Repair or replace as required.
TORQUE CONVERTER
LOCKS UP IN SECOND
AND/OR THIRD GEARLockup Solenoid, Relay or Wiring
Shorted/Open.Test solenoid, relay and wiring for
continuity, shorts or grounds. Replace
solenoid and relay if faulty. Repair wiring
and connectors as necessary.
HARSH 1-2, 2-3, 3-4 OR
3-2 SHIFTSLockup Solenoid Malfunction. Remove valve body and replace solenoid
assembly.
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 155
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE (Continued)