service DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.G User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1998, Model line: RAM 1500, Model: DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.GPages: 2627
Page 23 of 2627
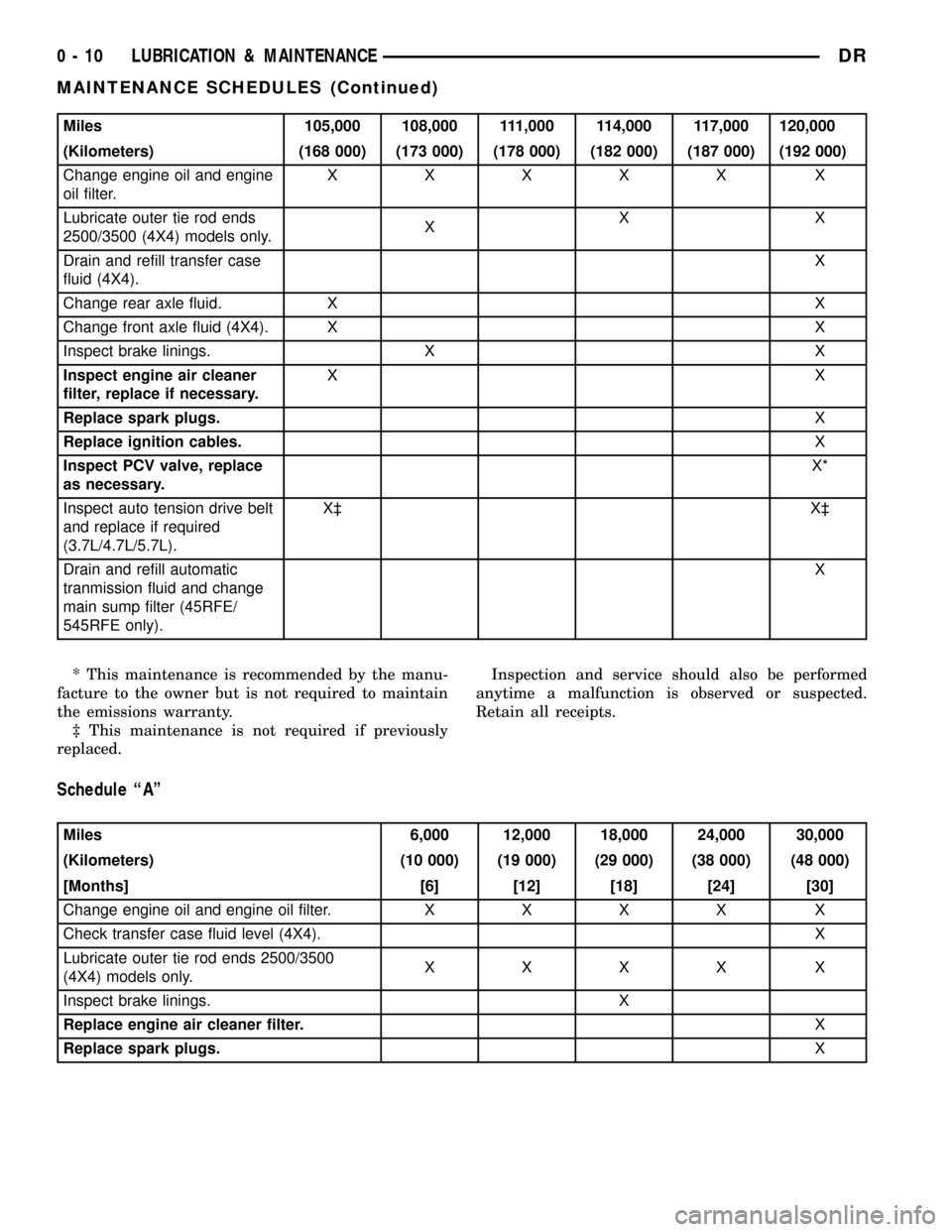
Miles 105,000 108,000 111,000 114,000 117,000 120,000
(Kilometers) (168 000) (173 000) (178 000) (182 000) (187 000) (192 000)
Change engine oil and engine
oil filter.XXXXX X
Lubricate outer tie rod ends
2500/3500 (4X4) models only.XXX
Drain and refill transfer case
fluid (4X4).X
Change rear axle fluid. X X
Change front axle fluid (4X4). X X
Inspect brake linings. X X
Inspect engine air cleaner
filter, replace if necessary.XX
Replace spark plugs.X
Replace ignition cables.X
Inspect PCV valve, replace
as necessary.X*
Inspect auto tension drive belt
and replace if required
(3.7L/4.7L/5.7L).X³ X³
Drain and refill automatic
tranmission fluid and change
main sump filter (45RFE/
545RFE only).X
* This maintenance is recommended by the manu-
facture to the owner but is not required to maintain
the emissions warranty.
³ This maintenance is not required if previously
replaced.Inspection and service should also be performed
anytime a malfunction is observed or suspected.
Retain all receipts.
Schedule ªAº
Miles 6,000 12,000 18,000 24,000 30,000
(Kilometers) (10 000) (19 000) (29 000) (38 000) (48 000)
[Months] [6] [12] [18] [24] [30]
Change engine oil and engine oil filter.XXXX X
Check transfer case fluid level (4X4). X
Lubricate outer tie rod ends 2500/3500
(4X4) models only.XXXX X
Inspect brake linings. X
Replace engine air cleaner filter.X
Replace spark plugs.X
0 - 10 LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCEDR
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES (Continued)
Page 25 of 2627
![DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.G User Guide Miles 102,000 108,000 114,000 120,000
(Kilometers) (163 000) (173 000) (182 000) (192 000)
[Months] [102] [108] [114] [120]
Change engine oil and engine oil filter. X X X X
Drain and refill transfer c DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.G User Guide Miles 102,000 108,000 114,000 120,000
(Kilometers) (163 000) (173 000) (182 000) (192 000)
[Months] [102] [108] [114] [120]
Change engine oil and engine oil filter. X X X X
Drain and refill transfer c](/img/12/5702/w960_5702-24.png)
Miles 102,000 108,000 114,000 120,000
(Kilometers) (163 000) (173 000) (182 000) (192 000)
[Months] [102] [108] [114] [120]
Change engine oil and engine oil filter. X X X X
Drain and refill transfer case fluid (4X4). X
Flush and replace engine coolant, if not done at 60 mos. X
Lubricate outer tie rod ends 2500/3500 (4X4) models
only.XXX X
Inspect brake linings. X
Inspect auto tension drive belt and replace if required
(3.7L/4.7L/5.7L).X³X³
Replace ignition cables.X
Replace engine air cleaner filter.X
Replace spark plugs.X
Inspect PCV Valve, replace as necessary X*
* This maintenance is recommended by the manu-
facture to the owner but is not required to maintain
the emissions warranty.
³ This maintenance is not required if previously
replaced.
Inspection and service should also be performed
anytime a malfunction is observed or suspected.
WARNING: You can be badly injured working on or
around a motor vehicle. Do only that service work
for which you have the knowledge and the right
equipment. If you have any doubt about your ability
to perform a service job, take your vehicle to a
competent mechanic.
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES Ð 24±VALVE
CUMMINS TURBO DIESEL
There are two maintenance schedules that show
therequiredservice for your vehicle.
First is ScheduleªBº. It is for vehicles that are
operated under the conditions that are listed below
and at the beginning of the schedule.
²Day or night temperatures are below 0É C (32É
F).
²Stop and go driving.
²Extensive engine idling.
²Driving in dusty conditions.
²Short trips of less than 16 km (10 miles).
²More than 50% of your driving is at sustained
high speeds during hot weather, above 32É C (90É F).²Trailer towing.
²Taxi, police, or delivery service (commercial ser-
vice).
²Off-road or desert operation.
NOTE: Most vehicles are operated under the condi-
tions listed for Schedule(B(.
Second is ScheduleªAº. It is for vehicles that are
not operated under any of the conditions listed under
Schedule9B9.
Use the schedule that best describes your driving
conditions. Where time and mileage are listed, follow
the interval that occurs first.
CAUTION: Failure to perform the required mainte-
nance items may result in damage to the vehicle.At Each Stop for Fuel
²Check the engine oil level about 15 minutes
after a fully warmed engine is shut off. Checking the
oil level while the vehicle is on level ground will
improve the accuracy of the oil level reading. Add oil
only when the level is at or below the ADD or MIN
mark.
²Check the windshield washer solvent and add if
required.
²Drain water from the fuel filter.
0 - 12 LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCEDR
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES (Continued)
Page 26 of 2627
Once a Month
²Check tire pressure and look for unusual wear
or damage.
²Inspect the batteries and clean and tighten the
terminals as required.
²Check the fluid levels of coolant reservoir, brake
master cylinder, power steering and transmission
and transfer case (if equipped), add as needed.
²Check Filter MinderŸ. Replace air cleaner
filter element if necessary.
²Check all lights and all other electrical items for
correct operation.
At Each Oil Change
²Change the engine oil filter.
²Inspect the exhaust system.
²Inspect the brake hoses.
²Inspect the CV joints (if equipped) and front sus-
pension components.
²Check the automatic transmission fluid level.
²Check the manual transmission fluid level.
²Check the coolant level, hoses, and clamps.
Tire Rotation
²Rotate the tires every 7,500 miles (12 000 km).
Engine Oil Change Chart Notes
²LTier 1 EPA (250 hp or 305 hp) Engines Only
(see engine data label for your engine type)
²² California LEV (235 hp) Engines Only (see
engine data label for your engine type)
Schedule ªBº
Follow schedule ªBº if you usually operate your
vehicle under one or more of the following conditions.
²Day or night temperatures are below 0É C (32É
F).
²Stop and go driving.
²Extensive engine idling.
²Driving in dusty conditions.
²Short trips of less than 16 km (10 miles).
²More than 50% of your driving is at sustained
high speeds during hot weather, above 32É C (90É F).
²Trailer towing.
²Taxi, police, or delivery service (commercial ser-
vice).
²Off-road or desert operation.
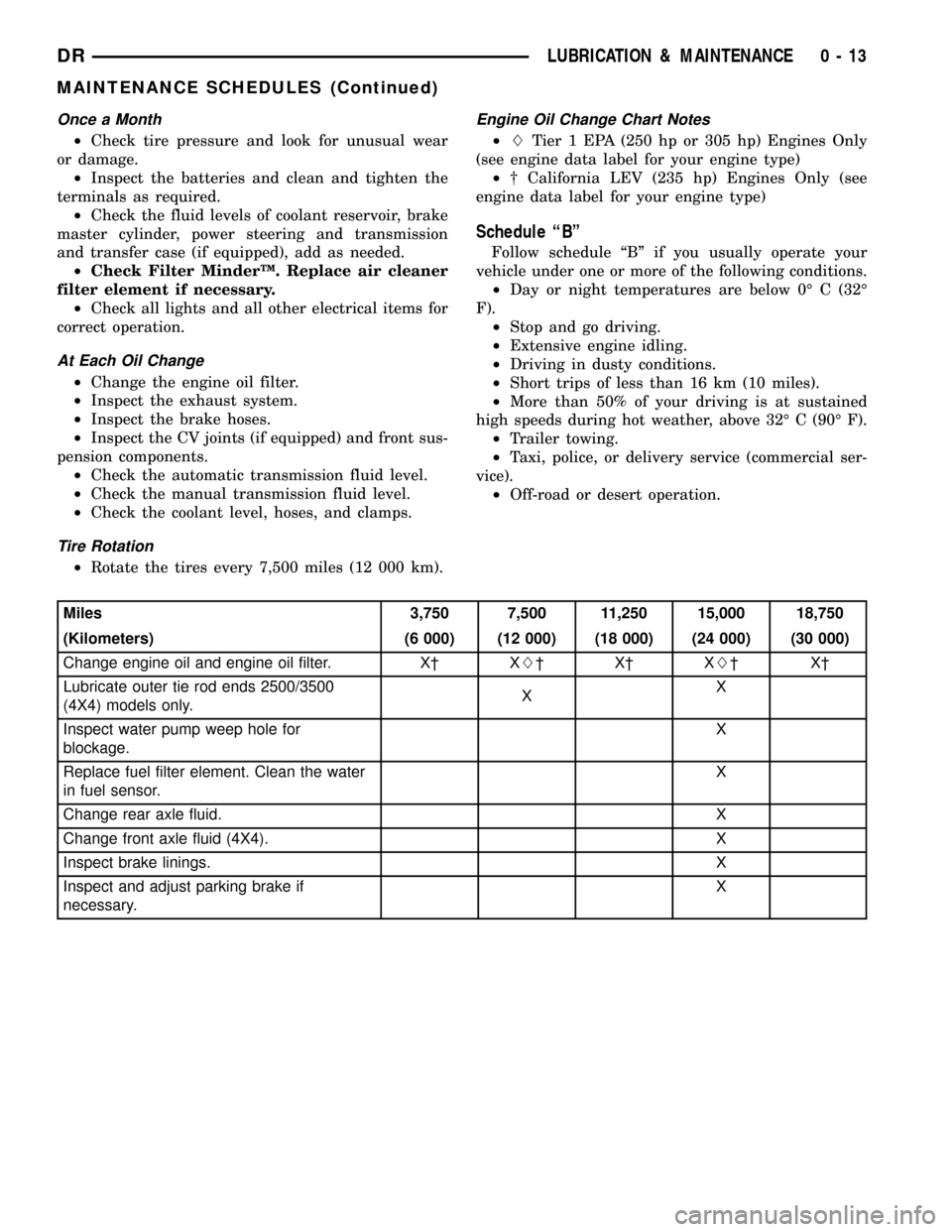
Miles 3,750 7,500 11,250 15,000 18,750
(Kilometers) (6 000) (12 000) (18 000) (24 000) (30 000)
Change engine oil and engine oil filter. X² XL²X²XL²X²
Lubricate outer tie rod ends 2500/3500
(4X4) models only.XX
Inspect water pump weep hole for
blockage.X
Replace fuel filter element. Clean the water
in fuel sensor.X
Change rear axle fluid. X
Change front axle fluid (4X4). X
Inspect brake linings.X
Inspect and adjust parking brake if
necessary.X
DRLUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE 0 - 13
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES (Continued)
Page 30 of 2627
²LTier 1 EPA (250 hp or 305 hp) Engines Only
(see engine data label for your engine type)
²² California LEV (235 hp) Engines Only (see
engine data label for your engine type)Inspection and service should also be performed
anytime a malfunction is observed or suspected.
Schedule ªAº
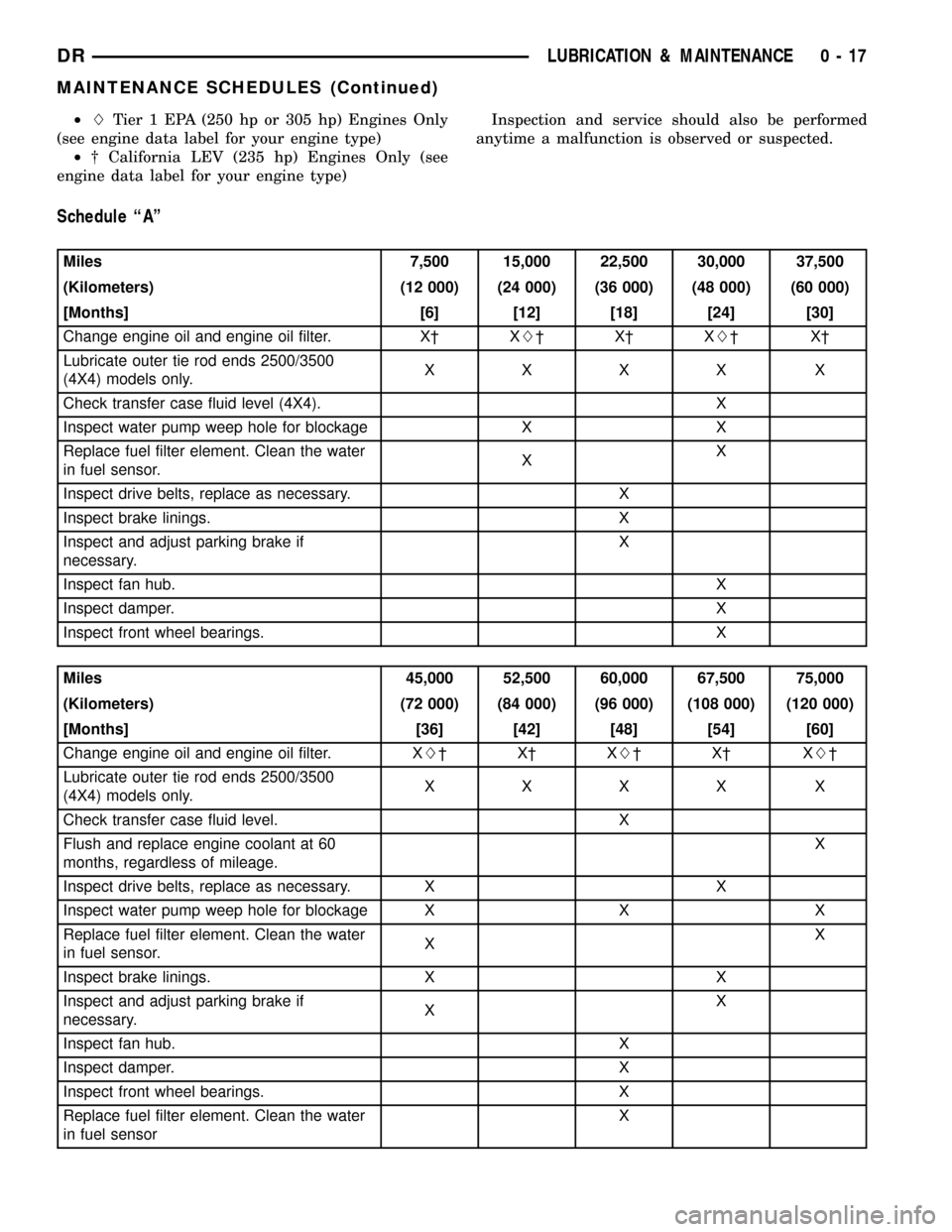
Miles 7,500 15,000 22,500 30,000 37,500
(Kilometers) (12 000) (24 000) (36 000) (48 000) (60 000)
[Months] [6] [12] [18] [24] [30]
Change engine oil and engine oil filter. X² XL²X²XL²X²
Lubricate outer tie rod ends 2500/3500
(4X4) models only.XXXX X
Check transfer case fluid level (4X4). X
Inspect water pump weep hole for blockage X X
Replace fuel filter element. Clean the water
in fuel sensor.XX
Inspect drive belts, replace as necessary. X
Inspect brake linings. X
Inspect and adjust parking brake if
necessary.X
Inspect fan hub.X
Inspect damper.X
Inspect front wheel bearings. X
Miles 45,000 52,500 60,000 67,500 75,000
(Kilometers) (72 000) (84 000) (96 000) (108 000) (120 000)
[Months] [36] [42] [48] [54] [60]
Change engine oil and engine oil filter. XL²X²XL²X² XL²
Lubricate outer tie rod ends 2500/3500
(4X4) models only.XXXX X
Check transfer case fluid level. X
Flush and replace engine coolant at 60
months, regardless of mileage.X
Inspect drive belts, replace as necessary. X X
Inspect water pump weep hole for blockage X X X
Replace fuel filter element. Clean the water
in fuel sensor.XX
Inspect brake linings. X X
Inspect and adjust parking brake if
necessary.XX
Inspect fan hub. X
Inspect damper. X
Inspect front wheel bearings. X
Replace fuel filter element. Clean the water
in fuel sensorX
DRLUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE 0 - 17
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES (Continued)
Page 32 of 2627
![DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.G User Guide Miles 112,500 120,000 127,500 135,000 142,500 150,000
(Kilometers) (181 000) (193 000) (205 000) (217 000) (229 000) (241 000)
[Months] [90] [96] [102] [108] [114] [150]
Inspect front wheel bearings. DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.G User Guide Miles 112,500 120,000 127,500 135,000 142,500 150,000
(Kilometers) (181 000) (193 000) (205 000) (217 000) (229 000) (241 000)
[Months] [90] [96] [102] [108] [114] [150]
Inspect front wheel bearings.](/img/12/5702/w960_5702-31.png)
Miles 112,500 120,000 127,500 135,000 142,500 150,000
(Kilometers) (181 000) (193 000) (205 000) (217 000) (229 000) (241 000)
[Months] [90] [96] [102] [108] [114] [150]
Inspect front wheel bearings. X X
Inspect brake linings. X X
Inspect and adjust parking
brake if necessary.XX
Adjust valve lash clearance.X
²LTier 1 EPA (250 hp or 305 hp) Engines Only
(see engine data label for your engine type)
²² California LEV (235 hp) Engines Only (see
engine data label for your engine type)
Inspection and service should also be performed
anytime a malfunction is observed or suspected.
WARNING: You can be badly injured working on or
around a motor vehicle. Do only that service work
for which you have the knowledge and the right
equipment. If you have any doubt about your ability
to perform a service job, take your vehicle to a
competent mechanic.
JUMP STARTING
STANDARD PROCEDURE - JUMP STARTING
WARNING: REVIEW ALL SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
AND WARNINGS IN THE BATTERY SYSTEM SEC-
TION OF THE SERVICE MANUAL. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/BATTERY SYSTEM/BATTERY - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE)
²DO NOT JUMP START A FROZEN BATTERY,
PERSONAL INJURY CAN RESULT.
²IF EQUIPPED, DO NOT JUMP START WHEN
MAINTENANCE FREE BATTERY INDICATOR DOT IS
YELLOW OR BRIGHT COLOR.
²DO NOT JUMP START A VEHICLE WHEN THE
BATTERY FLUID IS BELOW THE TOP OF LEAD
PLATES.
²DO NOT ALLOW JUMPER CABLE CLAMPS TO
TOUCH EACH OTHER WHEN CONNECTED TO A
BOOSTER SOURCE.
²DO NOT USE OPEN FLAME NEAR BATTERY.
²REMOVE METALLIC JEWELRY WORN ON
HANDS OR WRISTS TO AVOID INJURY BY ACCI-
DENTAL ARCING OF BATTERY CURRENT.
²WHEN USING A HIGH OUTPUT BOOSTING
DEVICE, DO NOT ALLOW BATTERY VOLTAGE TO
EXCEED 16 VOLTS. REFER TO INSTRUCTIONS
PROVIDED WITH DEVICE BEING USED.FAILURE TO FOLLOW THESE INSTRUCTIONS MAY
RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY.
CAUTION: When using another vehicle as a
booster, do not allow vehicles to touch. Electrical
systems can be damaged on either vehicle.
TO JUMP START A DISABLED VEHICLE:
(1) Raise hood on disabled vehicle and visually
inspect engine compartment for:
²Battery cable clamp condition, clean if necessary.
²Frozen battery.
²Yellow or bright color test indicator, if equipped.
²Low battery fluid level.
²Generator drive belt condition and tension.
²Fuel fumes or leakage, correct if necessary.
CAUTION: If the cause of starting problem on dis-
abled vehicle is severe, damage to booster vehicle
charging system can result.
(2) When using another vehicle as a booster
source, park the booster vehicle within cable reach.
Turn off all accessories, set the parking brake, place
the automatic transmission in PARK or the manual
transmission in NEUTRAL and turn the ignition
OFF.
(3) On disabled vehicle, place gear selector in park
or neutral and set park brake. Turn off all accesso-
ries.
(4) Connect jumper cables to booster battery. RED
clamp to positive terminal (+). BLACK clamp to neg-
ative terminal (-). DO NOT allow clamps at opposite
end of cables to touch, electrical arc will result.
Review all warnings in this procedure.
(5) On disabled vehicle, connect RED jumper cable
clamp to positive (+) terminal. Connect BLACK
jumper cable clamp to engine ground as close to the
ground cable attaching point as possible.
(6) Start the engine in the vehicle which has the
booster battery, let the engine idle a few minutes,
then start the engine in the vehicle with the dis-
charged battery.
DRLUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE 0 - 19
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES (Continued)
Page 60 of 2627

ends of the bar mount to the lower suspension arm.
All mounting points of the stabilizer bar are isolated
by bushings (Fig. 28).
OPERATION
The stabilizer bar is used to minimize vehicle front
sway during turns. The bar helps to maintain a flat
attitude to the road surface.
REMOVAL
NOTE: To service the stabilizer bar the vehicle
should be on a drive on hoist. The vehicle suspen-
sion must be at curb height for stabilizer bar instal-
lation.
(1) Remove the stabilizer bar link upper nuts and
remove the retainers and grommets (Fig. 29).
(2) Remove the stabilizer bar retainer, bolts and
retainers from the frame crossmember (Fig. 29) and
remove the bar.
(3) If necessary, remove the bushings from the sta-
bilizer barDo not cut the old bushings off the
stabilizer bar use a mixture of soapy water in
order to aid in sliding the bushing off.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: To service the stabilizer bar the vehicle must
be on a drive on hoist. The vehicle suspension
must be at curb height for stabilizer bar installation.
(1) If removed, Install the bushings on the stabi-
lizer bar using a mixture of soapy water or equiva-
lent in order to slide the bushing over the bar with
easeDo not cut the new bushing for installa-
tion.
(2) Position the stabilizer bar on the frame cross-
member brackets and install the bracket and bolts
finger-tight (Fig. 29).NOTE: Check the alignment of the bar to ensure
there is no interference with the either frame rail or
chassis component. Spacing should be equal on
both sides.
(3) Install the stabilizer bar to the stabilizer link
and install the grommets and retainers.
(4) Install the nuts to the stabilizer link and
tighten to 38 N´m (27 ft. lbs.).
(5) Tighten the brackets to the frame to 61 N´m
(45 ft. lbs.).
STABILIZER LINK
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 4X4
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove the lower nut (Fig. 29).
(3) Remove the upper nut, retainers and grommets
(Fig. 29).
(4) Remove the stabilizer link from the vehicle
(Fig. 29).
REMOVAL - 4X2
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove the lower nut (Fig. 29).
(3) Remove the upper nut, retainer and grommets
(Fig. 29).
(4) Remove the stabilizer link from the vehicle
(Fig. 29).
Fig. 28 STABILIZER BAR
Fig. 29 STABILIZER LINK
1 - STABILIZER LINK
2 - SWAY BAR BRACKET
DRFRONT - INDEPENDENT FRONT SUSPENSION 2 - 25
STABILIZER BAR (Continued)
Page 101 of 2627

HALF SHAFT
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
HALF SHAFT
CAUTION.............................20
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING................20
REMOVAL.............................20
INSTALLATION.........................21
SPECIFICATIONS.......................21
SPECIAL TOOLS.......................21CV JOINT-OUTER
REMOVAL.............................22
INSTALLATION.........................23
CV JOINT-INNER
REMOVAL.............................25
INSTALLATION.........................25
HALF SHAFT
CAUTION
CAUTION:: Never grasp half shaft assembly by the
boots. This may cause the boot to pucker or crease
and reduce the service life of the boot.
Avoid over angulating or stroking the C/V joints
when handling the half shaft.
Half shafts exposed to battery acid, transmission
fluid, brake fluid, differential fluid or gasoline may
cause the boots to deteriorate. Failure to heed cau-
tion may result in damage.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
Check inboard and outboard C/V joint for leaking
grease. This is a sign of boot or boot clamp damage.
NOISE/VIBRATION IN TURNS
A clicking noise or vibration in turns could be
caused by a damaged outer C/V or inner tripod joint
seal boot or seal boot clamps. This will result in the
loss/contamination of the joint grease, resulting in
inadequate lubrication of the joint. Noise could also
be caused by another component of the vehicle com-
ing in contact with the half shafts.
CLUNKING NOISE DURING ACCELERATION
This noise may be a damaged or worn C/V joint. A
torn boot or loose/missing clamp on the inner/outer
joint which has allowed the grease to be lost will
damage the C/V joint.
SHUDDER/VIBRATION DURING ACCELERATION
This could be a worn/damaged inner tripod joint or
a sticking tripod joint. Improper wheel alignment
may also cause a shudder or vibration.
VIBRATION AT HIGHWAY SPEEDS
This problem could be a result of out of balance
front tires or tire/wheel runout. Foreign material
(mud, etc.) packed on the backside of the wheel(s)
will also cause a vibration.
REMOVAL
(1) With vehicle in neutral, position vehicle on
hoist.
(2) Remove half shaft hub nut.
(3) Remove brake caliper and rotor.
(4) Position hydraulic jack under lower suspension
arm and raise jack to unload rebound bumper.
(5) Remove lower shock absorber bolt.
(6) Remove upper ball joint nut and seperate ball
with Remover 8677 (Fig. 1).
(7) Disengage inner C/V joint from axle shaft with
two pry bars between the C/V housing and axle hous-
ing.
Fig. 1 UPPER BALL JOINT SEPARATION
1 - UPPER CONTROL ARM
2 - REMOVER
3 - STEERING KNUCKLE
3 - 20 HALF SHAFTDR
Page 110 of 2627
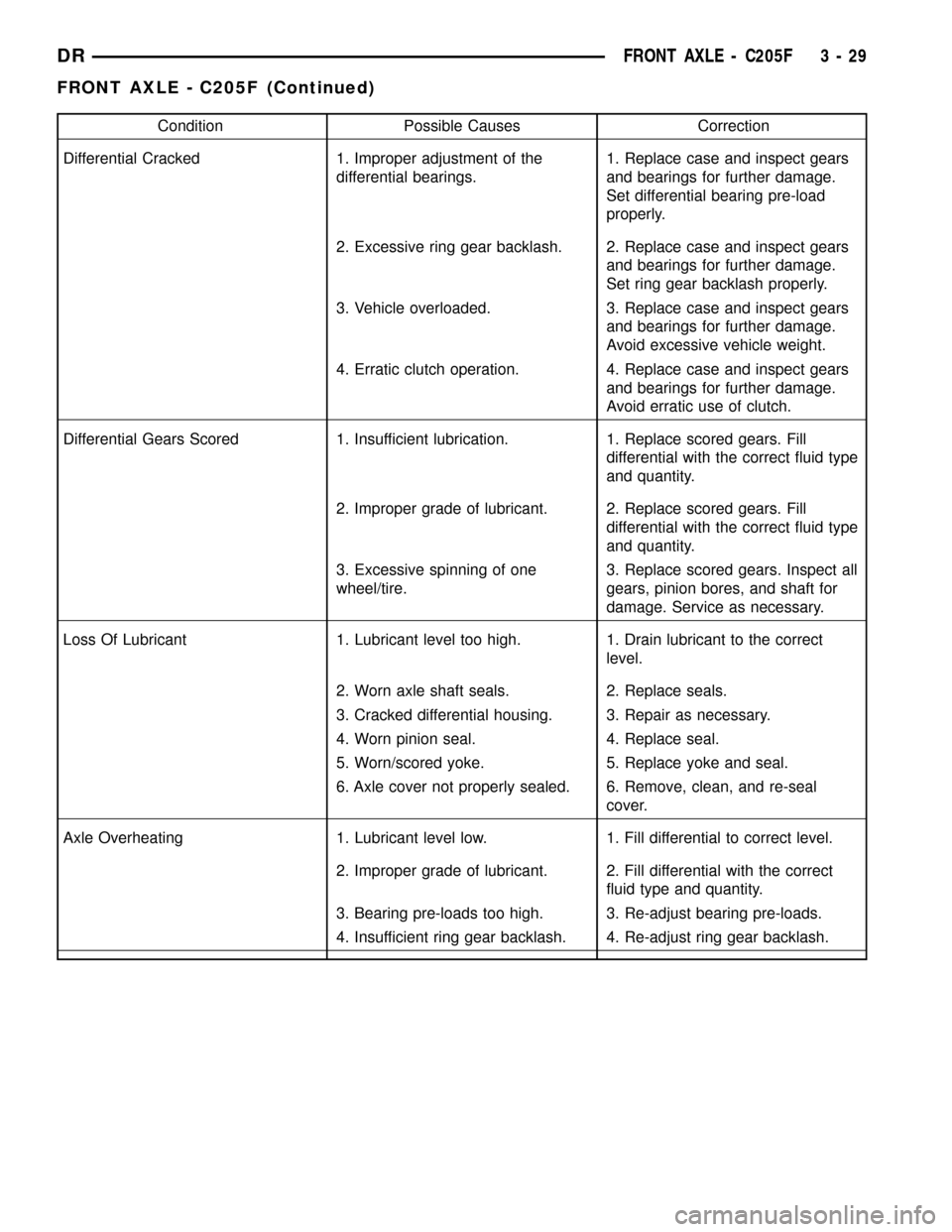
Condition Possible Causes Correction
Differential Cracked 1. Improper adjustment of the
differential bearings.1. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Set differential bearing pre-load
properly.
2. Excessive ring gear backlash. 2. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Set ring gear backlash properly.
3. Vehicle overloaded. 3. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Avoid excessive vehicle weight.
4. Erratic clutch operation. 4. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Avoid erratic use of clutch.
Differential Gears Scored 1. Insufficient lubrication. 1. Replace scored gears. Fill
differential with the correct fluid type
and quantity.
2. Improper grade of lubricant. 2. Replace scored gears. Fill
differential with the correct fluid type
and quantity.
3. Excessive spinning of one
wheel/tire.3. Replace scored gears. Inspect all
gears, pinion bores, and shaft for
damage. Service as necessary.
Loss Of Lubricant 1. Lubricant level too high. 1. Drain lubricant to the correct
level.
2. Worn axle shaft seals. 2. Replace seals.
3. Cracked differential housing. 3. Repair as necessary.
4. Worn pinion seal. 4. Replace seal.
5. Worn/scored yoke. 5. Replace yoke and seal.
6. Axle cover not properly sealed. 6. Remove, clean, and re-seal
cover.
Axle Overheating 1. Lubricant level low. 1. Fill differential to correct level.
2. Improper grade of lubricant. 2. Fill differential with the correct
fluid type and quantity.
3. Bearing pre-loads too high. 3. Re-adjust bearing pre-loads.
4. Insufficient ring gear backlash. 4. Re-adjust ring gear backlash.
DRFRONT AXLE - C205F 3 - 29
FRONT AXLE - C205F (Continued)
Page 130 of 2627

PINION GEAR/RING GEAR
REMOVAL
NOTE: The ring gear and pinion are serviced in a
matched set. Never replace one without replacing
the other.
(1) Remove differential from housing.
(2) Place differential case in a vise with soft jaw
(Fig. 44).
(3) Remove bolts holding ring gear to differential
case.
(4) Drive ring gear from differential case with a
soft hammer (Fig. 44).
(5) Mark companion yoke and companion flange
for installation reference.
(6) Remove companion flange bolts and tie the pro-
peller shaft to the vehicle underbody.
(7) Rotate companion flange three or four times
and verify flange rotates smoothly.
(8) Record pinion rotating torque an inch pound
torque wrench for installation reference (Fig. 45).
(9) Install bolts into two of the threaded holes in
the companion flange 180É apart.
(10) Position Holder 6719 against the companion
flange and install a bolt and washer into one of the
remaining threaded holes. Tighten the bolts so that
the Holder 6719 is held to the flange.(11) Remove the pinion nut.
(12) Remove the companion flange with Remover
C-452 (Fig. 46).
(13) Remove pinion from differential housing.
(14) Remove pinion seal with a pry tool or a slide
hammer mounted screw.
(15) Remove oil slinger, if equipped and front pin-
ion bearing.
(16) Remove front pinion bearing cup with
Remover 8831 and Handle C-4171 (Fig. 47).
Fig. 43 DIFFERENTIAL CASE BEARINGS
1 - HANDLE
2 - DIFFERENTIAL
3 - BEARING
4 - INSTALLER
Fig. 44 RING GEAR
1 - DIFFERENTIAL CASE
2 - RING GEAR
3 - HAMMER
Fig. 45 PINION ROTATING TORQUE
1 - PINION COMPANION FLANGE
2 - TORQUE WRENCH
DRFRONT AXLE - C205F 3 - 49
DIFFERENTIAL CASE BEARINGS (Continued)
Page 132 of 2627

INSTALLATION
NOTE: The ring gear and pinion are serviced in a
matched set. Never replace one gear without replac-
ing the other matching gear. If ring and pinion
gears or bearings are replaced, Refer to Adjust-
ments for Pinion Gear Depth Setting.
(1) Apply Mopar Door Ease or equivalent lubricant
to outside surface of the bearing cups.
(2) Install rear pinion bearing cup with Installer
8692 and Driver Handle C-4171 (Fig. 51).
(3) Install front pinion bearing cup with Installer
8693 and Handle C-4171.
(4) Lubricate front pinion bearing and install bear-
ing in the housing.
(5) Apply a light coating of gear lubricant on the
lip of pinion seal.
(6) Install pinion seal with Installer 8695 and
Handle C-4171 (Fig. 52).
Fig. 50 REAR PINION BEARING
1 - PULLER
2 - VISE
3 - ADAPTERS
4 - DRIVE PINION GEAR SHAFTFig. 51 REAR PINION BEARING CUP
1 - HOUSING
2 - INSTALLER
3 - HANDLE
Fig. 52 PINION SEAL
1 - HANDLE
2 - INSTALLER
DRFRONT AXLE - C205F 3 - 51
PINION GEAR/RING GEAR (Continued)