water pump DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.G User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1998, Model line: RAM 1500, Model: DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.GPages: 2627
Page 318 of 2627

DESCRIPTION - COOLING SYSTEM FLOW -
5.9L DIESEL
The diesel engine cooling system consists of :
²Cross-flow radiator
²Belt driven water pump
²Cooling fan (attached to the electronic viscous
fan drive)
²Belt driven Electronic viscous fan drive
²Two piece fan shroud
²Radiator pressure cap
²Vertically mounted thermostat
²Coolant reserve/recovery system
²Transmission oil cooler
²Coolant
Coolant flow circuits for the 5.9L diesel engine are
shown in (Fig. 3).
DESCRIPTION - HOSE CLAMPS
The cooling system utilizes spring type hose
clamps. If a spring type clamp replacement is neces-
sary, replace with the original Mopartequipment
spring type clamp.
CAUTION: A number or letter is stamped into the
tongue of constant tension clamps. If replacement
is necessary, use only a original equipment clamp
with matching number or letter and ensure the
clamp has the same size width (Fig. 4).
Fig. 2 5.7L Engine Coolant System Flow
1 - LH CYLINDER HEAD
2 - TO RADIATOR3 - FROM RADIATOR
4 - TO RH CYLINDER HEAD
DRCOOLING 7 - 3
COOLING (Continued)
Page 320 of 2627

OPERATION
OPERATION - COOLING SYSTEM
The cooling system regulates engine operating tem-
perature. It allows the engine to reach normal oper-
ating temperature as quickly as possible. It also
maintains normal operating temperature and pre-
vents overheating.
The cooling system also provides a means of heat-
ing the passenger compartment and cooling the auto-
matic transmission fluid (if equipped). The cooling
system is pressurized and uses a centrifugal water
pump to circulate coolant throughout the system.
All engines utilize an ambient overflow bottle for
coolant recovery/reserve.
An optional factory installed maximum duty cool-
ing package is available on most models. This pack-
age will provide additional cooling capacity for
vehicles used under extreme conditions such as
trailer towing in high ambient temperatures.
OPERATION - HOSE CLAMPS
The spring type hose clamp applies constant ten-
sion on a hose connection. To remove a spring type
hose clamp, only use constant tension clamp pliers
designed to compress the hose clamp.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐON-BOARD
DIAGNOSTICS (OBD)
COOLING SYSTEM RELATED DIAGNOSTICS
The Engine Control Module (ECM) has been pro-
grammed to monitor certain cooling system compo-
nents:
²If the engine has remained cool for too long a
period, such as with a stuck open thermostat, a Diag-
nostic Trouble Code (DTC) can be set.
²If an open or shorted condition has developed in
the electronically controlled viscous fan clutch circuit,
a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) can be set.
²If fan speed is not detected a DTC will be set.
²Coolant temperature sensor circuit problems can
set a DTC.
If the problem is sensed in a monitored circuit
often enough to indicated an actual problem, a DTC
is stored. The DTC will be stored in the ECM mem-
ory for eventual display to the service technician.
(Refer to 25 - EMISSIONS CONTROL - DESCRIP-
TION).
ACCESSING DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
To read DTC's and to obtain cooling system data,
(Refer to 25 - EMISSIONS CONTROL - DESCRIP-
TION).
ERASING TROUBLE CODES
After the problem has been repaired, use the
DRBIIItscan tool to erase a DTC. Refer to the
appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures ser-
vice information for operation of the DRBIIItscan
tool.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COOLING SYSTEM
- TESTING FOR LEAKS
ULTRAVIOLET LIGHT METHOD
A leak detection additive is available through the
parts department that can be added to cooling sys-
tem. The additive is highly visible under ultraviolet
light (black light). Pour one ounce of additive into
cooling system. Place heater control unit in HEAT
position. Start and operate the engine until the radi-
ator upper hose is warm to the touch. Aim the com-
mercially available black light tool at the components
to be checked. If leaks are present, the black light
will cause the additive to glow a bright green color.
The black light can be used in conjunction with a
pressure tester to determine if any external leaks
exist (Fig. 5).
Fig. 4 Spring Clamp Size Location
1 - SPRING CLAMP SIZE LOCATION
DRCOOLING 7 - 5
COOLING (Continued)
Page 321 of 2627

PRESSURE TESTER METHOD
The engine should be at normal operating temper-
ature. Recheck the system cold if the cause of coolant
loss is not located during the warm engine examina-
tion.
WARNING: HOT, PRESSURIZED COOLANT CAN
CAUSE INJURY BY SCALDING.
Carefully remove the radiator pressure cap from
the filler neck and check the coolant level. Push
down on the cap to disengage it from the stop tabs.
Wipe the inside of the filler neck and examine the
lower inside sealing seat for nicks, cracks, paint, dirt
and solder residue. Inspect the radiator-to- reserve/
overflow tank hose for internal obstructions. Insert a
wire through the hose to be sure it is not obstructed.
Inspect the cams on the outside of the filler neck.
If the cams are damaged, seating of the pressure cap
valve and tester seal will be affected.
Attach pressure tester (7700 or an equivalent) to
radiator filler neck.
Operate the tester pump to apply 103.4 kPa (15
psi) pressure to the system. If the hoses enlarge
excessively or bulges while testing, replace as neces-
sary. Observe the gauge pointer and determine the
condition of the cooling system according to following
criteria:
Holds Steady:If the pointer remains steady for
two minutes, serious coolant leaks are not present in
system. However, there could be an internal leakthat does not appear with normal system test pres-
sure. If it is certain that coolant is being lost and
leaks cannot be detected, inspect for interior leakage
or perform Internal Leakage Test. Refer to INTER-
NAL LEAKAGE INSPECTION.
Drops Slowly:Indicates a small leak or seepage
is occurring. Examine all of the connections for seep-
age or slight leakage with a flashlight. Inspect the
radiator, hoses, gasket edges and heater. Seal the
small leak holes with a Sealer Lubricant (or equiva-
lent). Repair the leak holes and inspect the system
again with pressure applied.
Drops Quickly:Indicates that serious leakage is
occurring. Examine the system for external leakage.
If leaks are not visible, inspect for internal leakage.
Large radiator leak holes should be repaired by a
reputable radiator repair shop.
INTERNAL LEAKAGE INSPECTION
Remove the engine oil pan drain plug and drain a
small amount of engine oil. If coolant is present in
the pan, it will drain first because it is heavier than
oil. An alternative method is to operate engine for a
short period to churn the oil. After this is done,
remove the engine dipstick and inspect for water
globules. Also inspect the transmission dipstick for
water globules and transmission fluid cooler for leak-
age.
WARNING: WITH RADIATOR PRESSURE TESTER
TOOL INSTALLED ON RADIATOR, DO NOT ALLOW
PRESSURE TO EXCEED 145 kPa (21 PSI). PRES-
SURE WILL BUILD UP QUICKLY IF A COMBUSTION
LEAK IS PRESENT. TO RELEASE PRESSURE,
ROCK TESTER FROM SIDE TO SIDE. WHEN
REMOVING TESTER, DO NOT TURN TESTER MORE
THAN 1/2 TURN IF SYSTEM IS UNDER PRESSURE.
Operate the engine without the pressure cap on
the radiator until the thermostat opens. Attach a
Pressure Tester to the filler neck. If pressure builds
up quickly it indicates a combustion leak exists. This
is usually the result of a cylinder head gasket leak or
crack in engine. Repair as necessary.
If there is not an immediate pressure increase,
pump the Pressure Tester. Do this until indicated
pressure is within system range of 110 kPa (16 psi).
Fluctuation of the gauge pointer indicates compres-
sion or combustion leakage into cooling system.
Because the vehicle is equipped with a catalytic
converter,do notshort out cylinders to isolate com-
pression leak.
If the needle on dial of the pressure tester does not
fluctuate, race engine a few times to check for an
abnormal amount of coolant or steam. This would be
emitting from exhaust pipe. Coolant or steam from
Fig. 5 Leak Detection Using Black Light - Typical
1 - TYPICAL BLACK LIGHT TOOL
7 - 6 COOLINGDR
COOLING (Continued)
Page 323 of 2627

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
TEMPERATURE GAUGE READS
HIGH. COOLANT MAY OR MAY
NOT BE LEAKING FROM SYSTEM1. Vehicle overloaded, high ambient
(outside) temperatures with A/C
turned on, stop and go driving or
prolonged operation at idle speeds.1. Temporary condition, repair not
required. Notify customer of vehicle
operation instructions located in
Owners Manual.
NOTE: Information on dash cluster
is displayed based on broadcast
information from ECM. DTC will be
set for engine sensor circuit
concern.2. Temperature gauge not
functioning correctly.2. Check cluster (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/INSTRUMENT
CLUSTER - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING)
3. Air trapped in cooling system 3. Drain cooling system (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - STANDARD
PROCEDURE) and refill (Refer to 7
- COOLING - STANDARD
PROCEDURE)
4. Radiator cap faulty. 4. Replace radiator cap.
5. Plugged A/C or radiator cooling
fins.5. Clean all debris away from A/C
and radiator cooling fins.
6. Coolant mixture incorrect. 6. Drain cooling system (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - STANDARD
PROCEDURE) refill with correct
mixture (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
7. Thermostat stuck shut. 7. Inspect and test thermostat.
Replace thermostat if necessary.
8. Bug screen or winter front being
used.8. Remove bug screen or winter
front.
9. Electronically controlled viscous
fan drive not operating properly.9. Check viscous fan (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ENGINE/FAN DRIVE
VISCOUS CLUTCH - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING)
10. Cylinder head gasket leaking. 10. Check for leaking head gaskets
(Refer to 7 - COOLING -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
11. Heater core leaking. 11. Replace heater core.
12. Cooling system hoses leaking. 12. Tighten clamps or Replace
hoses.
13. Brakes dragging. 13. Check brakes. (Refer to 5 -
BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/
MECHANICAL - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING)
14. Accessory drive belt. 14. Inspect. Replace as necessary.
15. Water Pump. 15. Inspect and replace as
necessary.
16. Engine sensor stuck in range. 16. Monitor sensor with DRBIII to
verify sensor reading changes
increase in temperature.
17. Temperature sensor failed out
of range.17. A DTC will be set.
7 - 8 COOLINGDR
COOLING (Continued)
Page 324 of 2627
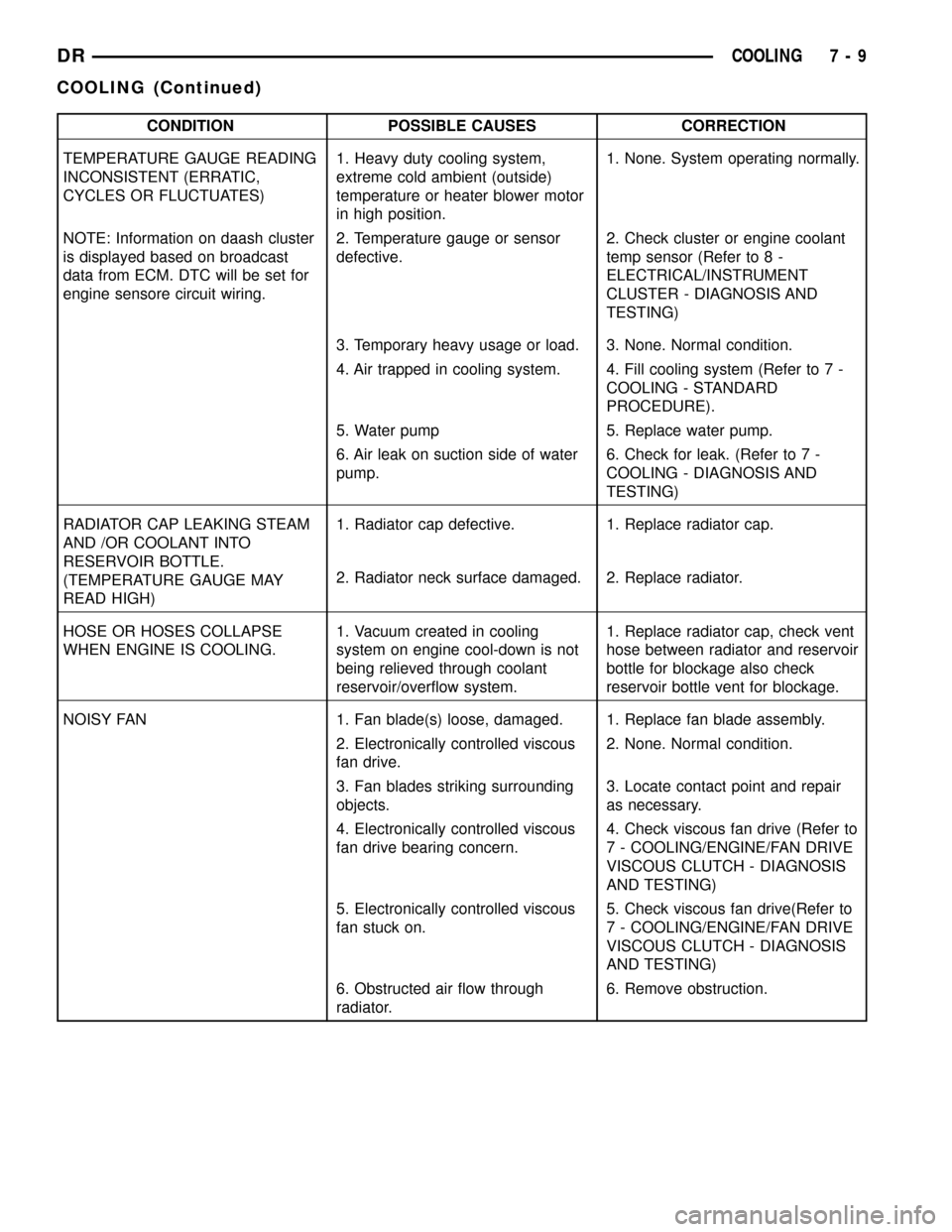
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
TEMPERATURE GAUGE READING
INCONSISTENT (ERRATIC,
CYCLES OR FLUCTUATES)1. Heavy duty cooling system,
extreme cold ambient (outside)
temperature or heater blower motor
in high position.1. None. System operating normally.
NOTE: Information on daash cluster
is displayed based on broadcast
data from ECM. DTC will be set for
engine sensore circuit wiring.2. Temperature gauge or sensor
defective.2. Check cluster or engine coolant
temp sensor (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/INSTRUMENT
CLUSTER - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING)
3. Temporary heavy usage or load. 3. None. Normal condition.
4. Air trapped in cooling system. 4. Fill cooling system (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
5. Water pump 5. Replace water pump.
6. Air leak on suction side of water
pump.6. Check for leak. (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING)
RADIATOR CAP LEAKING STEAM
AND /OR COOLANT INTO
RESERVOIR BOTTLE.
(TEMPERATURE GAUGE MAY
READ HIGH)1. Radiator cap defective. 1. Replace radiator cap.
2. Radiator neck surface damaged. 2. Replace radiator.
HOSE OR HOSES COLLAPSE
WHEN ENGINE IS COOLING.1. Vacuum created in cooling
system on engine cool-down is not
being relieved through coolant
reservoir/overflow system.1. Replace radiator cap, check vent
hose between radiator and reservoir
bottle for blockage also check
reservoir bottle vent for blockage.
NOISY FAN 1. Fan blade(s) loose, damaged. 1. Replace fan blade assembly.
2. Electronically controlled viscous
fan drive.2. None. Normal condition.
3. Fan blades striking surrounding
objects.3. Locate contact point and repair
as necessary.
4. Electronically controlled viscous
fan drive bearing concern.4. Check viscous fan drive (Refer to
7 - COOLING/ENGINE/FAN DRIVE
VISCOUS CLUTCH - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING)
5. Electronically controlled viscous
fan stuck on.5. Check viscous fan drive(Refer to
7 - COOLING/ENGINE/FAN DRIVE
VISCOUS CLUTCH - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING)
6. Obstructed air flow through
radiator.6. Remove obstruction.
DRCOOLING 7 - 9
COOLING (Continued)
Page 325 of 2627
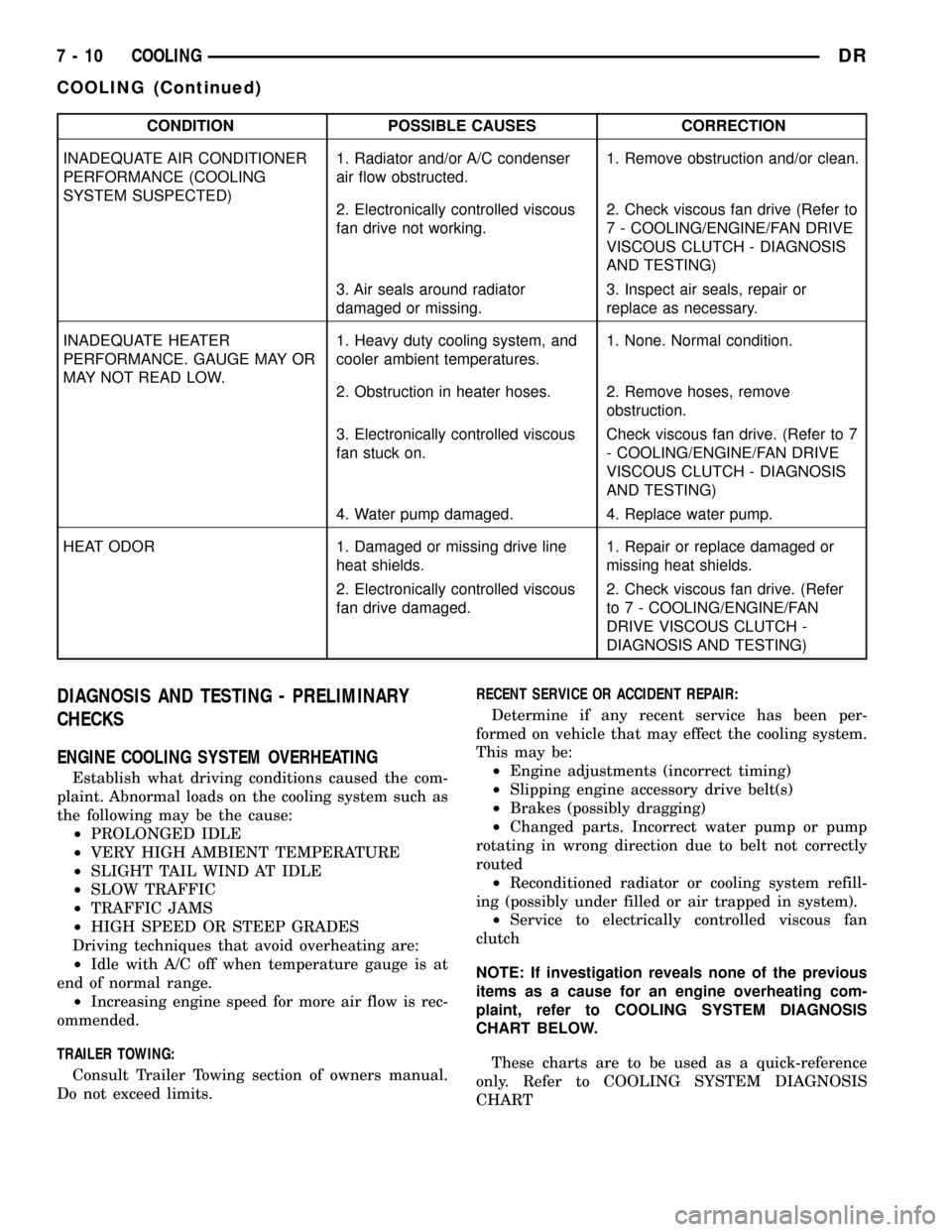
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
INADEQUATE AIR CONDITIONER
PERFORMANCE (COOLING
SYSTEM SUSPECTED)1. Radiator and/or A/C condenser
air flow obstructed.1. Remove obstruction and/or clean.
2. Electronically controlled viscous
fan drive not working.2. Check viscous fan drive (Refer to
7 - COOLING/ENGINE/FAN DRIVE
VISCOUS CLUTCH - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING)
3. Air seals around radiator
damaged or missing.3. Inspect air seals, repair or
replace as necessary.
INADEQUATE HEATER
PERFORMANCE. GAUGE MAY OR
MAY NOT READ LOW.1. Heavy duty cooling system, and
cooler ambient temperatures.1. None. Normal condition.
2. Obstruction in heater hoses. 2. Remove hoses, remove
obstruction.
3. Electronically controlled viscous
fan stuck on.Check viscous fan drive. (Refer to 7
- COOLING/ENGINE/FAN DRIVE
VISCOUS CLUTCH - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING)
4. Water pump damaged. 4. Replace water pump.
HEAT ODOR 1. Damaged or missing drive line
heat shields.1. Repair or replace damaged or
missing heat shields.
2. Electronically controlled viscous
fan drive damaged.2. Check viscous fan drive. (Refer
to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/FAN
DRIVE VISCOUS CLUTCH -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING)
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PRELIMINARY
CHECKS
ENGINE COOLING SYSTEM OVERHEATING
Establish what driving conditions caused the com-
plaint. Abnormal loads on the cooling system such as
the following may be the cause:
²PROLONGED IDLE
²VERY HIGH AMBIENT TEMPERATURE
²SLIGHT TAIL WIND AT IDLE
²SLOW TRAFFIC
²TRAFFIC JAMS
²HIGH SPEED OR STEEP GRADES
Driving techniques that avoid overheating are:
²Idle with A/C off when temperature gauge is at
end of normal range.
²Increasing engine speed for more air flow is rec-
ommended.
TRAILER TOWING:
Consult Trailer Towing section of owners manual.
Do not exceed limits.RECENT SERVICE OR ACCIDENT REPAIR:
Determine if any recent service has been per-
formed on vehicle that may effect the cooling system.
This may be:
²Engine adjustments (incorrect timing)
²Slipping engine accessory drive belt(s)
²Brakes (possibly dragging)
²Changed parts. Incorrect water pump or pump
rotating in wrong direction due to belt not correctly
routed
²Reconditioned radiator or cooling system refill-
ing (possibly under filled or air trapped in system).
²Service to electrically controlled viscous fan
clutch
NOTE: If investigation reveals none of the previous
items as a cause for an engine overheating com-
plaint, refer to COOLING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
CHART BELOW.
These charts are to be used as a quick-reference
only. Refer to COOLING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
CHART
7 - 10 COOLINGDR
COOLING (Continued)
Page 329 of 2627

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
Temperature gauge reading is
inconsistent (fluctuates, cycles or is
erratic)1. During cold weather operation,
with the heater blower in the high
position, the gauge reading may
drop slightly.1. A normal condition. No correction
necessary.
2. Temperature gauge or engine
mounted gauge sensor defective or
shorted. Also, corroded or loose
wiring in this circuit.2. Check operation of gauge and
repair if necessary. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/INSTRUMENT
CLUSTER - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
3. Gauge reading rises when
vehicle is brought to a stop after
heavy use (engine still running)3. A normal condition. No correction
is necessary. Gauge should return
to normal range after vehicle is
driven.
4. Gauge reading high after
re-starting a warmed up (hot)
engine.4. A normal condition. No correction
is necessary. The gauge should
return to normal range after a few
minutes of engine operation.
5. Coolant level low in radiator (air
will build up in the cooling system
causing the thermostat to open
late).5. Check and correct coolant leaks.
(Refer to 7 - COOLING -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
6. Cylinder head gasket leaking
allowing exhaust gas to enter
cooling system causing a
thermostat to open late.6. (a) Check for cylinder head
gasket leaks. (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
(b) Check for coolant in the engine
oil. Inspect for white steam emitting
from the exhaust system. Repair as
necessary.
7. Water pump impeller loose on
shaft.7. Check water pump and replace
as necessary. (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ENGINE/WATER PUMP -
REMOVAL).
8. Loose accessory drive belt.
(water pump slipping)8. (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS
- DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
Check and correct as necessary.
9. Air leak on the suction side of
the water pump allows air to build
up in cooling system causing
thermostat to open late.9. Locate leak and repair as
necessary.
PRESSURE CAP IS BLOWING
OFF STEAM AND/OR COOLANT
TO COOLANT TANK.
TEMPERATURE GAUGE READING
MAY BE ABOVE NORMAL BUT
NOT HIGH. COOLANT LEVEL MAY
BE HIGH IN COOLANT RESERVE/
OVERFLOW TANK1. Pressure relief valve in radiator
cap is defective.1. Check condition of radiator cap
and cap seals. (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ENGINE/RADIATOR
PRESSURE CAP - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING). Replace cap as
necessary.
7 - 14 COOLINGDR
COOLING (Continued)
Page 330 of 2627
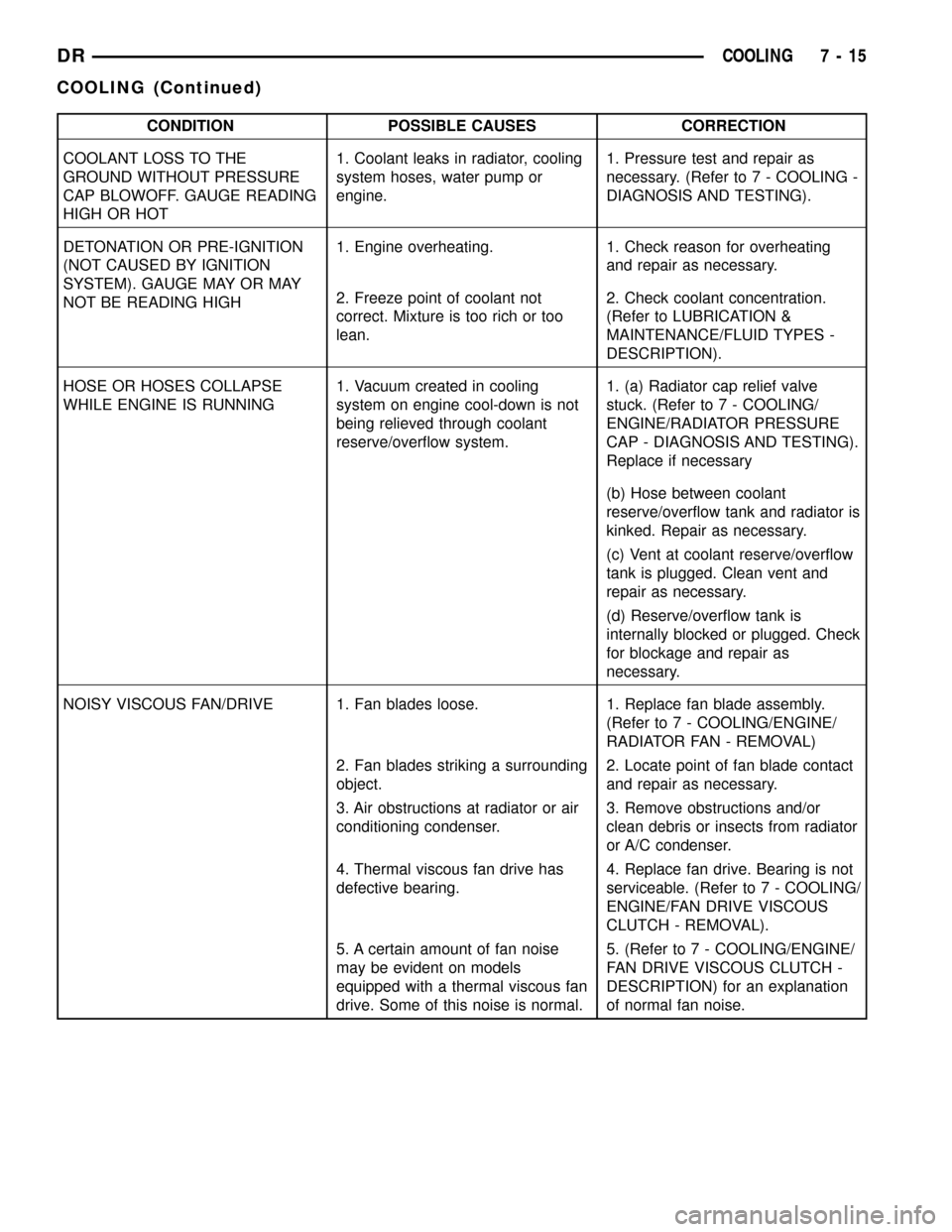
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
COOLANT LOSS TO THE
GROUND WITHOUT PRESSURE
CAP BLOWOFF. GAUGE READING
HIGH OR HOT1. Coolant leaks in radiator, cooling
system hoses, water pump or
engine.1. Pressure test and repair as
necessary. (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
DETONATION OR PRE-IGNITION
(NOT CAUSED BY IGNITION
SYSTEM). GAUGE MAY OR MAY
NOT BE READING HIGH1. Engine overheating. 1. Check reason for overheating
and repair as necessary.
2. Freeze point of coolant not
correct. Mixture is too rich or too
lean.2. Check coolant concentration.
(Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/FLUID TYPES -
DESCRIPTION).
HOSE OR HOSES COLLAPSE
WHILE ENGINE IS RUNNING1. Vacuum created in cooling
system on engine cool-down is not
being relieved through coolant
reserve/overflow system.1. (a) Radiator cap relief valve
stuck. (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ENGINE/RADIATOR PRESSURE
CAP - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
Replace if necessary
(b) Hose between coolant
reserve/overflow tank and radiator is
kinked. Repair as necessary.
(c) Vent at coolant reserve/overflow
tank is plugged. Clean vent and
repair as necessary.
(d) Reserve/overflow tank is
internally blocked or plugged. Check
for blockage and repair as
necessary.
NOISY VISCOUS FAN/DRIVE 1. Fan blades loose. 1. Replace fan blade assembly.
(Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/
RADIATOR FAN - REMOVAL)
2. Fan blades striking a surrounding
object.2. Locate point of fan blade contact
and repair as necessary.
3. Air obstructions at radiator or air
conditioning condenser.3. Remove obstructions and/or
clean debris or insects from radiator
or A/C condenser.
4. Thermal viscous fan drive has
defective bearing.4. Replace fan drive. Bearing is not
serviceable. (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ENGINE/FAN DRIVE VISCOUS
CLUTCH - REMOVAL).
5. A certain amount of fan noise
may be evident on models
equipped with a thermal viscous fan
drive. Some of this noise is normal.5. (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/
FAN DRIVE VISCOUS CLUTCH -
DESCRIPTION) for an explanation
of normal fan noise.
DRCOOLING 7 - 15
COOLING (Continued)
Page 331 of 2627
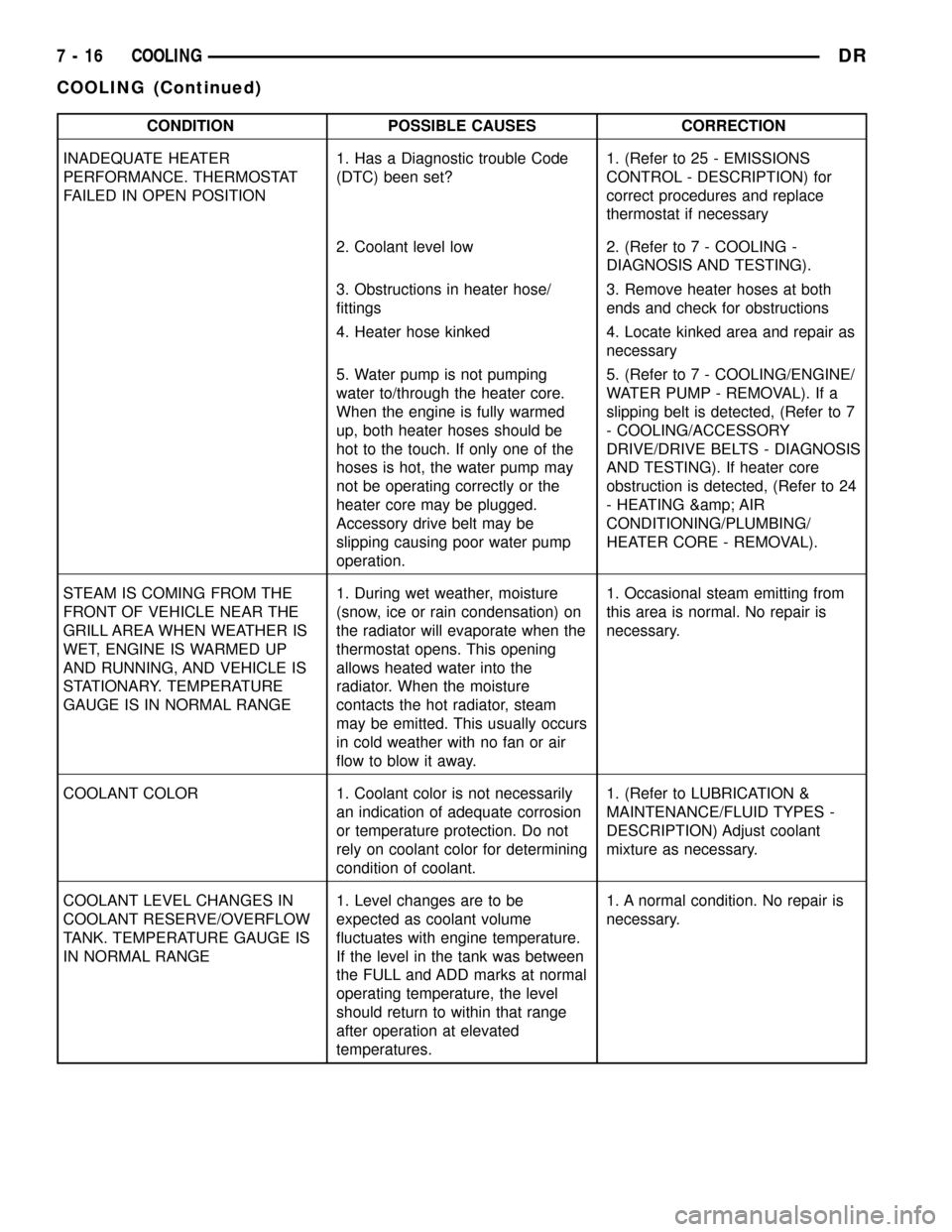
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
INADEQUATE HEATER
PERFORMANCE. THERMOSTAT
FAILED IN OPEN POSITION1. Has a Diagnostic trouble Code
(DTC) been set?1. (Refer to 25 - EMISSIONS
CONTROL - DESCRIPTION) for
correct procedures and replace
thermostat if necessary
2. Coolant level low 2. (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
3. Obstructions in heater hose/
fittings3. Remove heater hoses at both
ends and check for obstructions
4. Heater hose kinked 4. Locate kinked area and repair as
necessary
5. Water pump is not pumping
water to/through the heater core.
When the engine is fully warmed
up, both heater hoses should be
hot to the touch. If only one of the
hoses is hot, the water pump may
not be operating correctly or the
heater core may be plugged.
Accessory drive belt may be
slipping causing poor water pump
operation.5. (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/
WATER PUMP - REMOVAL). If a
slipping belt is detected, (Refer to 7
- COOLING/ACCESSORY
DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING). If heater core
obstruction is detected, (Refer to 24
- HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/
HEATER CORE - REMOVAL).
STEAM IS COMING FROM THE
FRONT OF VEHICLE NEAR THE
GRILL AREA WHEN WEATHER IS
WET, ENGINE IS WARMED UP
AND RUNNING, AND VEHICLE IS
STATIONARY. TEMPERATURE
GAUGE IS IN NORMAL RANGE1. During wet weather, moisture
(snow, ice or rain condensation) on
the radiator will evaporate when the
thermostat opens. This opening
allows heated water into the
radiator. When the moisture
contacts the hot radiator, steam
may be emitted. This usually occurs
in cold weather with no fan or air
flow to blow it away.1. Occasional steam emitting from
this area is normal. No repair is
necessary.
COOLANT COLOR 1. Coolant color is not necessarily
an indication of adequate corrosion
or temperature protection. Do not
rely on coolant color for determining
condition of coolant.1. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/FLUID TYPES -
DESCRIPTION) Adjust coolant
mixture as necessary.
COOLANT LEVEL CHANGES IN
COOLANT RESERVE/OVERFLOW
TANK. TEMPERATURE GAUGE IS
IN NORMAL RANGE1. Level changes are to be
expected as coolant volume
fluctuates with engine temperature.
If the level in the tank was between
the FULL and ADD marks at normal
operating temperature, the level
should return to within that range
after operation at elevated
temperatures.1. A normal condition. No repair is
necessary.
7 - 16 COOLINGDR
COOLING (Continued)
Page 332 of 2627

STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - COOLANT LEVEL
CHECK
NOTE: Do not remove radiator cap for routine cool-
ant level inspections. The coolant level can be
checked at coolant recovery bottle or the coolant
degas bottle.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE OR LOOSEN THE
RADIATOR CAP WITH THE COOLING SYSTEM HOT
AND UNDER PRESSURE. SERIOUS BURNS FROM
COOLANT OR HIGH PRESSURE STEAM CAN
OCCUR.
The coolant reserve/overflow system provides a
quick method for determining the coolant level with-
out removing the radiator pressure cap. With the
engine at normal operating temperature and idling,
observe the level of the coolant on the external level
indicator on the side of the coolant reserve / overflow
bottle. The coolant level should be between the MIN
and MAX marks. If the coolant is below the MIN
mark, add a 50/50 mixture of antifreeze and water to
the bottle until the level reaches the MIN mark.Do
Not Overfill the bottle by adding fluid above
the MAX line.This may cause coolant to spill onto
the ground during subsequent vehicle operation.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - COOLING SYSTEM
CLEANING/REVERSE FLUSHING
CLEANING
Drain the cooling system and refill with water. Run
the engine with the radiator cap installed until the
upper radiator hose is hot. Stop the engine and drain
the water from system. If the water is dirty, fill the
system with water, run the engine and drain the sys-
tem. Repeat this procedure until the water drains
clean.
REVERSE FLUSHING
Reverse flushing of the cooling system is the forc-
ing of water through the cooling system. This is done
using air pressure in the opposite direction of normal
coolant flow. It is usually only necessary with very
dirty systems with evidence of partial plugging.
REVERSE FLUSHING RADIATOR
Disconnect the radiator hoses from the radiator
inlet and outlet. Attach a section of the radiator hose
to the radiator bottom outlet fitting and insert the
flushing gun. Connect a water supply hose and air
supply hose to the flushing gun.CAUTION: Internal radiator pressure must not
exceed 138 kPa (20 psi) as damage to radiator may
result.
Allow the radiator to fill with water. When the
radiator is filled, apply air in short blasts. Allow the
radiator to refill between blasts. Continue this
reverse flushing until clean water flows out through
the rear of the radiator cooling tube passages.
REVERSE FLUSHING ENGINE
Drain the cooling system. Remove the thermostat
housing and thermostat. Install the thermostat hous-
ing. Disconnect the radiator upper hose from the
radiator and attach the flushing gun to the hose. Dis-
connect the radiator lower hose from the water pump
and attach a lead-away hose to the water pump inlet
fitting.
CAUTION: On vehicles equipped with a heater water
control valve, be sure the heater control valve is
closed (heat off). This will prevent coolant flow with
scale and other deposits from entering the heater
core.
Connect the water supply hose and air supply hose
to flushing gun. Allow the engine to fill with water.
When the engine is filled, apply air in short blasts,
allowing the system to fill between air blasts. Con-
tinue until clean water flows through the lead away
hose.
Remove the lead away hose, flushing gun, water
supply hose and air supply hose. Remove the thermo-
stat housing and install the thermostat. Install the
thermostat housing with a replacement gasket. Refer
to Thermostat Replacement. Connect the radiator
hoses. Refill the cooling system with the correct anti-
freeze/water mixture. Refer to Refilling the Cooling
System.
CHEMICAL CLEANING
In some instances, use a radiator cleaner (Mopart
Radiator Kleen or equivalent) before flushing. This
will soften scale and other deposits and aid flushing
operation.
CAUTION: Follow manufacturers instructions when
using these products.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - DRAINING COOLING
SYSTEM - ALL GAS ENGINES
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE CYLINDER BLOCK
DRAIN PLUGS OR LOOSEN RADIATOR DRAIN-
COCK WITH SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER PRESSURE.
SERIOUS BURNS FROM COOLANT CAN OCCUR.
DRCOOLING 7 - 17
COOLING (Continued)