Egr DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1998, Model line: RAM 1500, Model: DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.GPages: 2627
Page 2531 of 2627

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REFRIGERANT
SYSTEM LEAKS
WARNING: R-134a SERVICE EQUIPMENT OR VEHI-
CLE A/C SYSTEM SHOULD NOT BE PRESSURE
TESTED OR LEAK TESTED WITH COMPRESSED
AIR. MIXTURE OF AIR and R-134a CAN BE COM-
BUSTIBLE AT ELEVATED PRESSURES. THESE MIX-
TURES ARE POTENTIALLY DANGEROUS AND MAY
RESULT IN FIRE OR EXPLOSION CAUSING INJURY
OR PROPERTY DAMAGE.
AVOID BREATHING A/C REFRIGERANT AND LUBRI-
CANT VAPOR OR MIST. EXPOSURE MAY IRRITATE
EYES, NOSE AND THROAT. USE ONLY APPROVED
SERVICE EQUIPMENT MEETING SAE REQUIRE-
MENTS TO DISCHARGE R-134a SYSTEM. IF ACCI-
DENTAL SYSTEM DISCHARGE OCCURS,
VENTILATE WORK AREA BEFORE RESUMING SER-
VICE.
NOTE: The refrigerant system does come from the
factory with a yellow tracer dye already installed to
aid in detection of leaks.
If the A/C system is not cooling properly, determine
if the refrigerant system is fully charged with
R-134a. This is accomplished by performing a system
Charge Level-Check or Fill. If while performing this
test A/C liquid line pressure is less than 345 kPa (50
psi) proceed to System Empty procedure. If liquid
line pressure is greater than 345 kPa (50 psi) proceed
to System Low procedure. If the refrigerant system is
empty or low in refrigerant charge, a leak at any line
fitting or component seal is likely. A review of the fit-
tings, lines and components for oily residue is an
indication of the leak location. To detect a leak in the
refrigerant system, perform one of the following pro-
cedures as indicated by the symptoms.
SYSTEM EMPTY
(1) Evacuate the refrigerant system to the lowest
degree of vacuum possible (approx. 28 in Hg.). Deter-
mine if the system holds a vacuum for 15 minutes. If
vacuum is held, a leak is probably not present. If sys-
tem will not maintain vacuum level, proceed with
this procedure.(2) Prepare a 0.284 Kg. (10 oz.) refrigerant charge
to be injected into the system.
(3) Connect and dispense 0.284 Kg. (10 oz.) of
refrigerant into the evacuated refrigerant system.
(4) Proceed to Step 2 of System Low procedure.
SYSTEM LOW
(1) Determine if there is any (R-134a) refrigerant
in the system.
(2) Position the vehicle in a wind free work area.
This will aid in detecting small leaks.
(3) Bring the refrigerant system up to operating
temperature and pressure. This is done by allowing
the engine to run for five minutes with the system
set to the following:
²Transmission in Park or Neutral with parking
brake set
²Engine idling at 700 rpm
²A/C controls set in 100 percent outside air
²Blower switch in the high A/C position
²A/C in the ON position
²Open all windows
CAUTION: A leak detector designed for R-12 refrig-
erant (only) will not detect leaks in a R-134a refrig-
erant system.
(4) Shut off the vehicle and wait 2 to 7 minutes.
Then use an Electronic Leak Detector that is
designed to detect R-134a type refrigerant and search
for leaks. Fittings, lines, or components that appear
to be oily usually indicates a refrigerant leak. To
inspect the evaporator core for leaks, insert the leak
detector probe into the drain tube opening or a heat
duct. A R-134a dye is available to aid in leak detec-
tion, use only DaimlerChrysler approved refrigerant
dye.
24 - 44 PLUMBINGDR
PLUMBING (Continued)
Page 2548 of 2627

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C ORIFICE TUBE
WARNING: THE LIQUID LINE BETWEEN THE CON-
DENSER OUTLET AND THE A/C ORIFICE TUBE
CAN BECOME HOT ENOUGH TO BURN THE SKIN.
USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN PERFORMING THE
FOLLOWING TEST.
NOTE: The A/C orifice tube can be checked for
proper operation using the following procedure.
However, the A/C orifice tube is only serviced as a
part of the liquid line. If the results of this test indi-
cate that the A/C orifice tube is obstructed or miss-
ing, the liquid line must be replaced.
(1) Confirm that the refrigerant system is properly
charged. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDI-
TIONING - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C PER-
FORMANCE)
(2) Start the engine. Turn on the air conditioning
system and confirm that the compressor clutch is
engaged.
(3) Allow the air conditioning system to operate for
five minutes.
(4) Lightly and cautiously touch the liquid line
near the condenser outlet at the front of the engine
compartment. The liquid line should be hot to the
touch.
(5) Touch the liquid line near the evaporator inlet
at the rear of the engine compartment. The liquid
line should be cold to the touch.
(6) If there is a distinct temperature differential
between the two ends of the liquid line, the A/C ori-
fice tube is in good condition. If there is little or no
detectable temperature differential between the two
ends of the liquid line, the A/C orifice tube is
obstructed or missing and the liquid line must be
replaced.
ACCUMULATOR
DESCRIPTION
The accumulator (Fig. 21) is mounted in the engine
compartment between the evaporator outlet and the
compressor suction port. An integral mounting
bracket is used to secure the accumulator to the dash
panel.
The accumulator cannot be repaired and, if faulty
or damaged, it must be replaced. The rubber O-rings
are available for service replacement.
OPERATION
Refrigerant enters the accumulator canister as a
low pressure vapor through the inlet tube. Any liq-
uid, oil-laden refrigerant falls to the bottom of thecanister, which acts as a separator. A desiccant bag is
mounted inside the accumulator canister to absorb
any moisture which may have entered and become
trapped within the refrigerant system.
REMOVAL
WARNING: REVIEW THE WARNINGS AND CAU-
TIONS IN THE FRONT OF THIS SECTION BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION (Refer
to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
WARNING) and (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CON-
DITIONING/PLUMBING - CAUTION).
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Recover the refrigerant from the refrigerant
system (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITION-
Fig. 21 Accumulator - Typical
1 - A/C LOW PRESSURE SWITCH (IF EQUIPPED)
2 - PRESSURE SWITCH FITTING
3 - OUTLET TO COMPRESSOR
4 - ANTI-SIPHON HOLE
5 - DESICCANT BAG
6 - OIL RETURN ORIFICE FILTER
7 - VAPOR RETURN TUBE
8 - ACCUMULATOR DOME
9 - O-RING SEAL
10 - INLET FROM EVAPORATOR
DRPLUMBING 24 - 61
A/C ORIFICE TUBE (Continued)
Page 2565 of 2627

O2S is used to detect the amount of oxygen in the
exhaust gas before the gas enters the catalytic con-
verter. The PCM calculates the A/F mixture from the
output of the O2S. A low voltage indicates high oxy-
gen content (lean mixture). A high voltage indicates a
low content of oxygen (rich mixture).
When the upstream O2S detects a lean condition,
there is an abundance of oxygen in the exhaust gas.
A functioning converter would store this oxygen so it
can use it for the oxidation of HC and CO. As the
converter absorbs the oxygen, there will be a lack of
oxygen downstream of the converter. The output of
the downstream O2S will indicate limited activity in
this condition.
As the converter loses the ability to store oxygen,
the condition can be detected from the behavior of
the downstream O2S. When the efficiency drops, no
chemical reaction takes place. This means the con-
centration of oxygen will be the same downstream as
upstream. The output voltage of the downstream
O2S copies the voltage of the upstream sensor. The
only difference is a time lag (seen by the PCM)
between the switching of the O2S's.
To monitor the system, the number of lean-to-rich
switches of upstream and downstream O2S's is
counted. The ratio of downstream switches to
upstream switches is used to determine whether the
catalyst is operating properly. An effective catalyst
will have fewer downstream switches than it has
upstream switches i.e., a ratio closer to zero. For a
totally ineffective catalyst, this ratio will be one-to-
one, indicating that no oxidation occurs in the device.
The system must be monitored so that when cata-
lyst efficiency deteriorates and exhaust emissions
increase to over the legal limit, the MIL will be illu-
minated.
DESCRIPTION - TRIP DEFINITION
The term ªTripº has different meanings depending
on what the circumstances are. If the MIL (Malfunc-
tion Indicator Lamp) is OFF, a Trip is defined as
when the Oxygen Sensor Monitor and the Catalyst
Monitor have been completed in the same drive cycle.
When any Emission DTC is set, the MIL on the
dash is turned ON. When the MIL is ON, it takes 3
good trips to turn the MIL OFF. In this case, it
depends on what type of DTC is set to know what a
ªTripº is.
For the Fuel Monitor or Mis-Fire Monitor (contin-
uous monitor), the vehicle must be operated in the
ªSimilar Condition Windowº for a specified amount of
time to be considered a Good Trip.If a Non-Contiuous OBDII Monitor fails twice in a
row and turns ON the MIL, re-running that monitor
which previously failed, on the next start-up and
passing the monitor, is considered to be a Good Trip.
These will include the following:
²Oxygen Sensor
²Catalyst Monitor
²Purge Flow Monitor
²Leak Detection Pump Monitor (if equipped)
²EGR Monitor (if equipped)
²Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor
If any other Emission DTC is set (not an OBDII
Monitor), a Good Trip is considered to be when the
Oxygen Sensor Monitor and Catalyst Monitor have
been completed; or 2 Minutes of engine run time if
the Oxygen Sensor Monitor or Catalyst Monitor have
been stopped from running.
It can take up to 2 Failures in a row to turn on the
MIL. After the MIL is ON, it takes 3 Good Trips to
turn the MIL OFF. After the MIL is OFF, the PCM
will self-erase the DTC after 40 Warm-up cycles. A
Warm-up cycle is counted when the ECT (Engine
Coolant Temperature Sensor) has crossed 160ÉF and
has risen by at least 40ÉF since the engine has been
started.
DESCRIPTION - COMPONENT MONITORS
There are several components that will affect vehi-
cle emissions if they malfunction. If one of these com-
ponents malfunctions the Malfunction Indicator
Lamp (MIL) will illuminate.
Some of the component monitors are checking for
proper operation of the part. Electrically operated
components now have input (rationality) and output
(functionality) checks. Previously, a component like
the Throttle Position sensor (TPS) was checked by
the PCM for an open or shorted circuit. If one of
these conditions occurred, a DTC was set. Now there
is a check to ensure that the component is working.
This is done by watching for a TPS indication of a
greater or lesser throttle opening than MAP and
engine rpm indicate. In the case of the TPS, if engine
vacuum is high and engine rpm is 1600 or greater,
and the TPS indicates a large throttle opening, a
DTC will be set. The same applies to low vacuum if
the TPS indicates a small throttle opening.
All open/short circuit checks, or any component
that has an associated limp-in, will set a fault after 1
trip with the malfunction present. Components with-
out an associated limp-in will take two trips to illu-
minate the MIL.
25 - 4 EMISSIONS CONTROLDR
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2567 of 2627

For example, when the MIL is illuminated for an
Oxygen Sensor fault, the Task Manager does not run
the Catalyst Monitor until the Oxygen Sensor fault is
remedied. Since the Catalyst Monitor is based on sig-
nals from the Oxygen Sensor, running the test would
produce inaccurate results.
²Conflict
There are situations when the Task Manager does
not run a test if another monitor is in progress. In
these situations, the effects of another monitor run-
ning could result in an erroneous failure. If thiscon-
flictis present, the monitor is not run until the
conflicting condition passes. Most likely the monitor
will run later after the conflicting monitor has
passed.
For example, if the Fuel System Monitor is in
progress, the Task Manager does not run the EGR
Monitor. Since both tests monitor changes in air/fuel
ratio and adaptive fuel compensation, the monitors
will conflict with each other.
²Suspend
Occasionally the Task Manager may not allow a two
trip fault to mature. The Task Manager willsus-
pendthe maturing of a fault if a condition exists
that may induce an erroneous failure. This prevents
illuminating the MIL for the wrong fault and allows
more precis diagnosis.
For example, if the PCM is storing a one trip fault
for the Oxygen Sensor and the EGR monitor, the
Task Manager may still run the EGR Monitor but
will suspend the results until the Oxygen Sensor
Monitor either passes or fails. At that point the Task
Manager can determine if the EGR system is actu-
ally failing or if an Oxygen Sensor is failing.
MIL Illumination
The PCM Task Manager carries out the illumina-
tion of the MIL. The Task Manager triggers MIL illu-
mination upon test failure, depending on monitor
failure criteria.
The Task Manager Screen shows both a Requested
MIL state and an Actual MIL state. When the MIL is
illuminated upon completion of a test for a third trip,
the Requested MIL state changes to OFF. However,
the MIL remains illuminated until the next key
cycle. (On some vehicles, the MIL will actually turn
OFF during the third key cycle) During the key cycle
for the third good trip, the Requested MIL state is
OFF, while the Actual MILL state is ON. After the
next key cycle, the MIL is not illuminated and both
MIL states read OFF.
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
With OBD II, different DTC faults have different
priorities according to regulations. As a result, the
priorities determine MIL illumination and DTC era-sure. DTCs are entered according to individual prior-
ity. DTCs with a higher priority overwrite lower
priority DTCs.
Priorities
²Priority 0 ÐNon-emissions related trouble codes
²Priority 1 Ð One trip failure of a two trip fault
for non-fuel system and non-misfire.
²Priority 2 Ð One trip failure of a two trip fault
for fuel system (rich/lean) or misfire.
²Priority3ÐTwotrip failure for a non-fuel sys-
tem and non-misfire or matured one trip comprehen-
sive component fault.
²Priority4ÐTwotrip failure or matured fault
for fuel system (rich/lean) and misfire or one trip cat-
alyst damaging misfire.
Non-emissions related failures have no priority.
One trip failures of two trip faults have low priority.
Two trip failures or matured faults have higher pri-
ority. One and two trip failures of fuel system and
misfire monitor take precedence over non-fuel system
and non-misfire failures.
DTC Self Erasure
With one trip components or systems, the MIL is
illuminated upon test failure and DTCs are stored.
Two trip monitors are components requiring failure
in two consecutive trips for MIL illumination. Upon
failure of the first test, the Task Manager enters a
maturing code. If the component fails the test for a
second time the code matures and a DTC is set.
After three good trips the MIL is extinguished and
the Task Manager automatically switches the trip
counter to a warm-up cycle counter. DTCs are auto-
matically erased following 40 warm-up cycles if the
component does not fail again.
For misfire and fuel system monitors, the compo-
nent must pass the test under a Similar Conditions
Window in order to record a good trip. A Similar Con-
ditions Window is when engine RPM is within 375
RPM and load is within 10% of when the fault
occurred.
NOTE: It is important to understand that a compo-
nent does not have to fail under a similar window of
operation to mature. It must pass the test under a
Similar Conditions Window when it failed to record
a Good Trip for DTC erasure for misfire and fuel
system monitors.
DTCs can be erased anytime with a DRB III. Eras-
ing the DTC with the DRB III erases all OBD II
information. The DRB III automatically displays a
warning that erasing the DTC will also erase all
OBD II monitor data. This includes all counter infor-
mation for warm-up cycles, trips and Freeze Frame.
25 - 6 EMISSIONS CONTROLDR
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2568 of 2627

Trip Indicator
TheTripis essential for running monitors and
extinguishing the MIL. In OBD II terms, a trip is a
set of vehicle operating conditions that must be met
for a specific monitor to run. All trips begin with a
key cycle.
Good Trip
The Good Trip counters are as follows:
²Specific Good Trip
²Fuel System Good Trip
²Misfire Good Trip
²Alternate Good Trip (appears as a Global Good
Trip on DRB III)
²Comprehensive Components
²Major Monitor
²Warm-Up Cycles
Specific Good Trip
The term Good Trip has different meanings
depending on the circumstances:
²If the MIL is OFF, a trip is defined as when the
Oxygen Sensor Monitor and the Catalyst Monitor
have been completed in the same drive cycle.
²If the MIL is ON and a DTC was set by the Fuel
Monitor or Misfire Monitor (both continuous moni-
tors), the vehicle must be operated in the Similar
Condition Window for a specified amount of time.
²If the MIL is ON and a DTC was set by a Task
Manager commanded once-per-trip monitor (such as
the Oxygen Sensor Monitor, Catalyst Monitor, Purge
Flow Monitor, Leak Detection Pump Monitor, EGR
Monitor or Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor), a good
trip is when the monitor is passed on the next start-
up.
²If the MIL is ON and any other emissions DTC
was set (not an OBD II monitor), a good trip occurs
when the Oxygen Sensor Monitor and Catalyst Mon-
itor have been completed, or two minutes of engine
run time if the Oxygen Sensor Monitor and Catalyst
Monitor have been stopped from running.
Fuel System Good Trip
To count a good trip (three required) and turn off
the MIL, the following conditions must occur:
²Engine in closed loop
²Operating in Similar Conditions Window
²Short Term multiplied by Long Term less than
threshold
²Less than threshold for a predetermined time
If all of the previous criteria are met, the PCM will
count a good trip (three required) and turn off the
MIL.
Misfire Good Trip
If the following conditions are met the PCM will
count one good trip (three required) in order to turn
off the MIL:
²Operating in Similar Condition Window
²1000 engine revolutions with no misfireWarm-Up Cycles
Once the MIL has been extinguished by the Good
Trip Counter, the PCM automatically switches to a
Warm-Up Cycle Counter that can be viewed on the
DRB III. Warm-Up Cycles are used to erase DTCs
and Freeze Frames. Forty Warm-Up cycles must
occur in order for the PCM to self-erase a DTC and
Freeze Frame. A Warm-Up Cycle is defined as fol-
lows:
²Engine coolant temperature must start below
and rise above 160É F
²Engine coolant temperature must rise by 40É F
²No further faults occur
Freeze Frame Data Storage
Once a failure occurs, the Task Manager records
several engine operating conditions and stores it in a
Freeze Frame. The Freeze Frame is considered one
frame of information taken by an on-board data
recorder. When a fault occurs, the PCM stores the
input data from various sensors so that technicians
can determine under what vehicle operating condi-
tions the failure occurred.
The data stored in Freeze Frame is usually
recorded when a system fails the first time for two
trip faults. Freeze Frame data will only be overwrit-
ten by a different fault with a higher priority.
CAUTION: Erasing DTCs, either with the DRB III or
by disconnecting the battery, also clears all Freeze
Frame data.
Similar Conditions Window
The Similar Conditions Window displays informa-
tion about engine operation during a monitor. Abso-
lute MAP (engine load) and Engine RPM are stored
in this window when a failure occurs. There are two
different Similar conditions Windows: Fuel System
and Misfire.
FUEL SYSTEM
²Fuel System Similar Conditions WindowÐ
An indicator that 'Absolute MAP When Fuel Sys Fail'
and 'RPM When Fuel Sys Failed' are all in the same
range when the failure occurred. Indicated by switch-
ing from 'NO' to 'YES'.
²Absolute MAP When Fuel Sys FailÐ The
stored MAP reading at the time of failure. Informs
the user at what engine load the failure occurred.
²Absolute MAPÐ A live reading of engine load
to aid the user in accessing the Similar Conditions
Window.
²RPM When Fuel Sys FailÐ The stored RPM
reading at the time of failure. Informs the user at
what engine RPM the failure occurred.
DREMISSIONS CONTROL 25 - 7
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2569 of 2627

²Engine RPMÐ A live reading of engine RPM
to aid the user in accessing the Similar Conditions
Window.
²Adaptive Memory FactorÐ The PCM utilizes
both Short Term Compensation and Long Term Adap-
tive to calculate the Adaptive Memory Factor for
total fuel correction.
²Upstream O2S VoltsÐ A live reading of the
Oxygen Sensor to indicate its performance. For
example, stuck lean, stuck rich, etc.
²SCW Time in Window (Similar Conditions
Window Time in Window)Ð A timer used by the
PCM that indicates that, after all Similar Conditions
have been met, if there has been enough good engine
running time in the SCW without failure detected.
This timer is used to increment a Good Trip.
²Fuel System Good Trip CounterÐATrip
Counter used to turn OFF the MIL for Fuel System
DTCs. To increment a Fuel System Good Trip, the
engine must be in the Similar Conditions Window,
Adaptive Memory Factor must be less than cali-
brated threshold and the Adaptive Memory Factor
must stay below that threshold for a calibrated
amount of time.
²Test Done This TripÐ Indicates that the
monitor has already been run and completed during
the current trip.
MISFIRE
²Same Misfire Warm-Up StateÐ Indicates if
the misfire occurred when the engine was warmed up
(above 160É F).
²In Similar Misfire WindowÐ An indicator
that 'Absolute MAP When Misfire Occurred' and
'RPM When Misfire Occurred' are all in the same
range when the failure occurred. Indicated by switch-
ing from 'NO' to 'YES'.
²Absolute MAP When Misfire OccurredÐ
The stored MAP reading at the time of failure.
Informs the user at what engine load the failure
occurred.
²Absolute MAPÐ A live reading of engine load
to aid the user in accessing the Similar Conditions
Window.
²RPM When Misfire OccurredÐ The stored
RPM reading at the time of failure. Informs the user
at what engine RPM the failure occurred.
²Engine RPMÐ A live reading of engine RPM
to aid the user in accessing the Similar Conditions
Window.
²Adaptive Memory FactorÐ The PCM utilizes
both Short Term Compensation and Long Term Adap-
tive to calculate the Adaptive Memory Factor for
total fuel correction.
²200 Rev CounterÐ Counts 0±100 720 degree
cycles.²SCW Cat 200 Rev CounterÐ Counts when in
similar conditions.
²SCW FTP 1000 Rev CounterÐ Counts 0±4
when in similar conditions.
²Misfire Good Trip CounterÐ Counts up to
three to turn OFF the MIL.
²Misfire DataÐ Data collected during test.
²Test Done This TripÐ Indicates YES when the
test is done.
OPERATION - NON-MONITORED CIRCUITS
The PCM does not monitor the following circuits,
systems and conditions that could have malfunctions
causing driveability problems. The PCM might not
store diagnostic trouble codes for these conditions.
However, problems with these systems may cause the
PCM to store diagnostic trouble codes for other sys-
tems or components.EXAMPLE:a fuel pressure
problem will not register a fault directly, but could
cause a rich/lean condition or misfire. This could
cause the PCM to store an oxygen sensor or misfire
diagnostic trouble code
FUEL PRESSURE
The fuel pressure regulator controls fuel system
pressure. The PCM cannot detect a clogged fuel
pump inlet filter, clogged in-line fuel filter, or a
pinched fuel supply or return line. However, these
could result in a rich or lean condition causing the
PCM to store an oxygen sensor or fuel system diag-
nostic trouble code.
SECONDARY IGNITION CIRCUIT
The PCM cannot detect an inoperative ignition coil,
fouled or worn spark plugs, ignition cross firing, or
open spark plug cables.
CYLINDER COMPRESSION
The PCM cannot detect uneven, low, or high engine
cylinder compression.
EXHAUST SYSTEM
The PCM cannot detect a plugged, restricted or
leaking exhaust system, although it may set a fuel
system fault.
FUEL INJECTOR MECHANICAL MALFUNCTIONS
The PCM cannot determine if a fuel injector is
clogged, the needle is sticking or if the wrong injector
is installed. However, these could result in a rich or
lean condition causing the PCM to store a diagnostic
trouble code for either misfire, an oxygen sensor, or
the fuel system.
25 - 8 EMISSIONS CONTROLDR
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2582 of 2627

REMOVAL
3.7L V-6 / 4.7L V-8
The PCV valve is located on the oil filler tube (Fig.
22). Two locating tabs are located on the side of the
valve (Fig. 22). These 2 tabs fit into a cam lock in the
oil filler tube. An o-ring seals the valve to the filler
tube.
(1) Disconnect PCV line/hose (Fig. 22) by discon-
necting rubber hose at PCV valve fitting.
(2) Remove PCV valve at oil filler tube by rotating
PCV valve downward (counter-clockwise) until locat-
ing tabs have been freed at cam lock (Fig. 22). After
tabs have cleared, pull valve straight out from filler
tube.To prevent damage to PCV valve locating
tabs, valve must be pointed downward for
removal. Do not force valve from oil filler tube.
(3) After valve is removed, check condition of valve
o-ring (Fig. 22).
5.7L V-8
The PCV valve is mounted into the top of the
intake manifold, located to the right / rear of the
throttle body (Fig. 12). The PCV valve is sealed to
the intake manifold with 2 o-rings (Fig. 13).
(1) Remove PCV valve by rotating counter-clock-
wise 90 degrees until locating tabs have been freed.
After tabs have cleared, pull valve straight up from
intake manifold.(2) After valve is removed, check condition of 2
valve o-rings.
INSTALLATION
3.7L V6 / 4.7L V-8
The PCV valve is located on the oil filler tube. Two
locating tabs are located on the side of the valve.
These 2 tabs fit into a cam lock in the oil filler tube.
An o-ring seals the valve to the filler tube.
(1) Return PCV valve back to oil filler tube by
placing valve locating tabs into cam lock. Press PCV
valve in and rotate valve upward. A slight click will
be felt when tabs have engaged cam lock. Valve
should be pointed towards rear of vehicle.
(2) Connect PCV line/hose and rubber hose to PCV
valve.
Fig. 21 CHECK VALVES - PCV SYSTEM - 3.7L V-6 /
4.7L V-8
1 - CONNECTING HOSES
2 - CHECK VALVES
Fig. 22 PCV VALVE/OIL FILLER TUBE LOCATION -
3.7L V-6 / 4.7L V-8
1 - O-RING
2 - LOCATING TABS
3 - CAM LOCK
4 - OIL FILLER TUBE
5 - PCV LINE/HOSE
6 - P C V VA LV E
DREVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS 25 - 21
PCV VALVE (Continued)
Page 2583 of 2627
5.7L V-8
(1) Clean out intake manifold opening.
(2) Check condition of 2 o-rings on PCV valve.
(3) Apply engine oil to 2 o-rings.
(4) Place PCV valve into intake manifold and
rotate 90 degrees clockwise for installation.
VACUUM LINES
DESCRIPTION
A vacuum schematic for emission related items can
be found on the vehicles VECI label. Refer to Vehicle
Emission Control Information (VECI) Label for label
location.
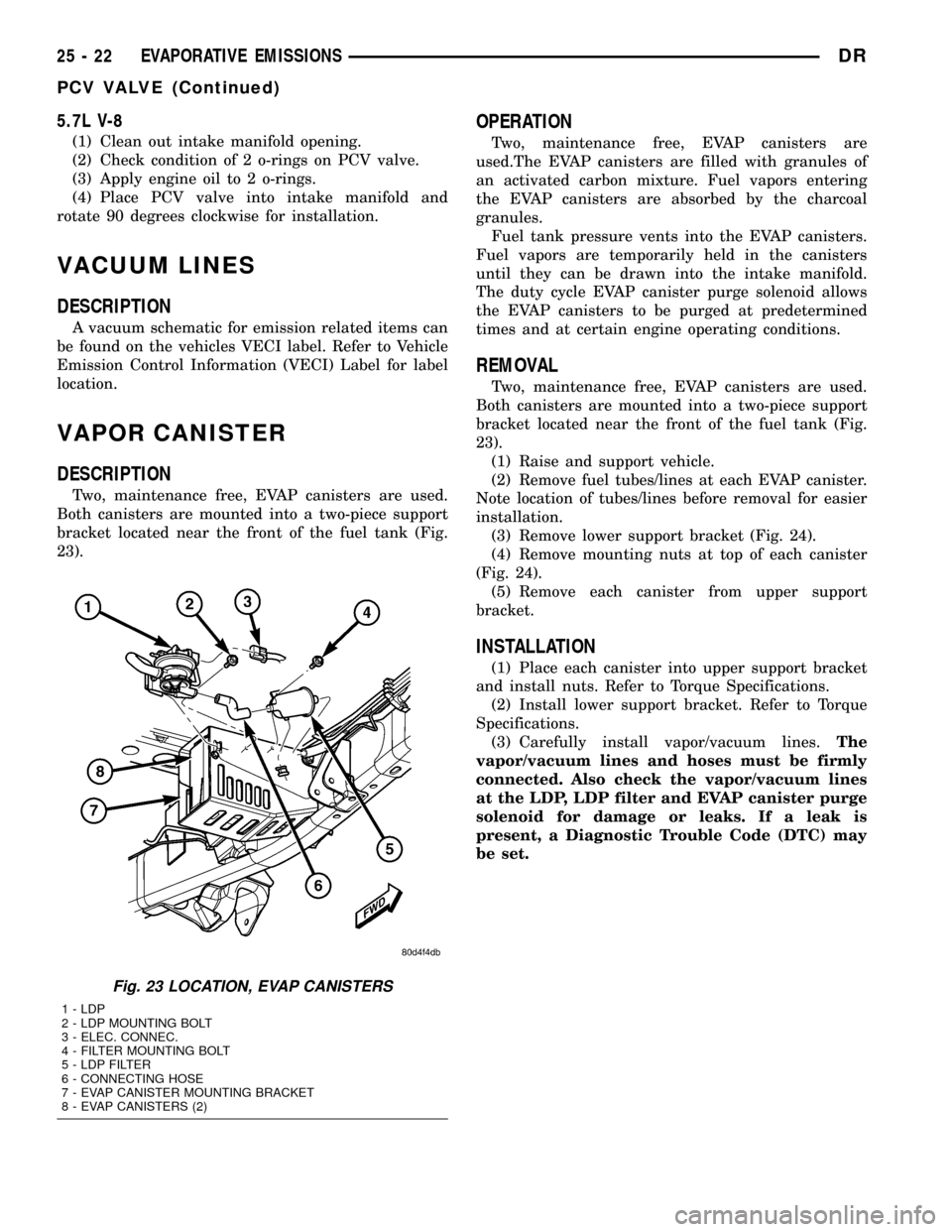
VAPOR CANISTER
DESCRIPTION
Two, maintenance free, EVAP canisters are used.
Both canisters are mounted into a two-piece support
bracket located near the front of the fuel tank (Fig.
23).
OPERATION
Two, maintenance free, EVAP canisters are
used.The EVAP canisters are filled with granules of
an activated carbon mixture. Fuel vapors entering
the EVAP canisters are absorbed by the charcoal
granules.
Fuel tank pressure vents into the EVAP canisters.
Fuel vapors are temporarily held in the canisters
until they can be drawn into the intake manifold.
The duty cycle EVAP canister purge solenoid allows
the EVAP canisters to be purged at predetermined
times and at certain engine operating conditions.
REMOVAL
Two, maintenance free, EVAP canisters are used.
Both canisters are mounted into a two-piece support
bracket located near the front of the fuel tank (Fig.
23).
(1) Raise and support vehicle.
(2) Remove fuel tubes/lines at each EVAP canister.
Note location of tubes/lines before removal for easier
installation.
(3) Remove lower support bracket (Fig. 24).
(4) Remove mounting nuts at top of each canister
(Fig. 24).
(5) Remove each canister from upper support
bracket.
INSTALLATION
(1) Place each canister into upper support bracket
and install nuts. Refer to Torque Specifications.
(2) Install lower support bracket. Refer to Torque
Specifications.
(3) Carefully install vapor/vacuum lines.The
vapor/vacuum lines and hoses must be firmly
connected. Also check the vapor/vacuum lines
at the LDP, LDP filter and EVAP canister purge
solenoid for damage or leaks. If a leak is
present, a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) may
be set.
Fig. 23 LOCATION, EVAP CANISTERS
1 - LDP
2 - LDP MOUNTING BOLT
3 - ELEC. CONNEC.
4 - FILTER MOUNTING BOLT
5 - LDP FILTER
6 - CONNECTING HOSE
7 - EVAP CANISTER MOUNTING BRACKET
8 - EVAP CANISTERS (2)
25 - 22 EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONSDR
PCV VALVE (Continued)
Page 2605 of 2627
INTAKE AIR HEATER - OPERATION.......14-80
INTAKE AIR HEATER - REMOVAL........14-80
INTAKE AIR HEATER RELAY -
DESCRIPTION.......................14-82
INTAKE AIR HEATER RELAY -
INSTALLATION.......................14-82
INTAKE AIR HEATER RELAY -
OPERATION.........................14-82
INTAKE AIR HEATER RELAY - REMOVAL . . 14-82
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR -
DESCRIPTION.......................14-30
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR -
INSTALLATION.......................14-31
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR -
OPERATION.........................14-30
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR -
REMOVAL..........................14-30
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR/
MAP SENSOR - DESCRIPTION..........14-82
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR/
MAP SENSOR - INSTALLATION..........14-82
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR/
MAP SENSOR - OPERATION............14-82
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR/
MAP SENSOR - REMOVAL.............14-82
INTAKE MANIFOLD - CLEANING....9-160,9-226,
9-297
INTAKE MANIFOLD - DESCRIPTION . 9-159,9-225,
9-72
INTAKE MANIFOLD - INSPECTION . . 9-160,9-226,
9-297
INTAKE MANIFOLD - INSTALLATION.....9-160,
9-226,9-298,9-73
INTAKE MANIFOLD - REMOVAL....9-159,9-226,
9-297,9-73
INTAKE MANIFOLD LEAKAGE -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING........9-159,9-225
INTAKE MANIFOLD LEAKS - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING........................9-72
INTAKE SYSTEM - INSTALLATION, AIR....9-199
INTAKE SYSTEM - REMOVAL, AIR.......9-199
INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES & SEATS -
DESCRIPTION..............9-123,9-256,9-28
INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES & SEATS -
INSTALLATION...................9-124,9-30
INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES & SEATS -
REMOVAL......................9-124,9-29
INTEGRATED POWER MODULE -
DESCRIPTION.....................8W-97-3
INTEGRATED POWER MODULE -
INSTALLATION....................8W-97-4
INTEGRATED POWER MODULE -
OPERATION.......................8W-97-3
INTEGRATED POWER MODULE -
REMOVAL........................8W-97-3
INTERIOR - CAUTION.................23-62
INTERLOCK - ADJUSTMENTS, BRAKE
TRANSMISSION SHIFT.........21-196,21-365
INTERLOCK - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
BRAKE TRANSMISSION SHIFT . . . 21-196,21-364
INTERLOCK SYSTEM - DESCRIPTION,
BRAKE TRANSMISSION SHIFT . . . 21-196,21-364
INTERLOCK SYSTEM - OPERATION,
BRAKE TRANSMISSION SHIFT . . . 21-196,21-364
INTERNATIONAL SYMBOLS -
DESCRIPTION......................Intro.-5
INVERTED FLARING - STANDARD
PROCEDURE, DOUBLE.................5-10
IOD FUSE - DESCRIPTION...........8W-97-6
IOD FUSE - INSTALLATION...........8W-97-7
IOD FUSE - OPERATION.............8W-97-6
IOD FUSE - REMOVAL..............8W-97-7
ISO FLARING - STANDARD PROCEDURE
. . . 5-11
ISOLATORS - INSTALLATION, BODY
......23-37
ISOLATORS - REMOVAL, BODY
.........23-36
JOINT - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
LOWER BALL
....................2-19,2-34
JOINT - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
UPPER BALL
.....................2-27,2-36
JOINT - INSTALLATION, LOWER BALL
. 2-20,2-35
JOINT - INSTALLATION, UPPER BALL
.....2-36
JOINT - REMOVAL, LOWER BALL
.....2-19,2-35
JOINT - REMOVAL, UPPER BALL
.........2-36
JOINT-INNER - INSTALLATION, CV
........3-25
JOINT-INNER - REMOVAL, CV
............3-25
JOINT-OUTER - INSTALLATION, CV
........3-23
JOINT-OUTER - REMOVAL, CV
...........3-22JOINTS - ASSEMBLY, DOUBLE CARDAN
UNIVERSAL..........................3-17
JOINTS - DISASSEMBLY, DOUBLE
CARDAN UNIVERSAL..................3-16
JOUNCE BUMPER - INSTALLATION.......2-43
JOUNCE BUMPER - REMOVAL...........2-43
JOURNAL CLEARANCE - STANDARD
PROCEDURE, CONNECTING ROD
BEARING AND CRANKSHAFT...........9-272
JUMP STARTING - STANDARD
PROCEDURE.........................0-19
JUNCTION BLOCK - INSTALLATION,
BRAKE..............................5-24
JUNCTION BLOCK - REMOVAL, BRAKE....5-24
KEY CYLINDER - INSTALLATION.........19-12
KEY CYLINDER - REMOVAL............19-12
KEY IMMOBILIZER MODULE -
DESCRIPTION, SENTRY................8E-13
KEY IMMOBILIZER MODULE -
INSTALLATION, SENTRY...............8E-15
KEY IMMOBILIZER MODULE -
OPERATION, SENTRY.................8E-13
KEY IMMOBILIZER MODULE - REMOVAL,
SENTRY............................8E-15
KEY IMMOBILIZER MODULE (SKIM) -
DESCRIPTION, SENTRY................8Q-1
KEY IMMOBILIZER MODULE (SKIM) -
OPERATION, SENTRY..................8Q-2
KEY IMMOBILIZER SYSTEM INDICATOR
LAMP - DESCRIPTION, SENTRY..........8Q-5
KEY IMMOBILIZER SYSTEM INDICATOR
LAMP - OPERATION, SENTRY...........8Q-5
KEY IMMOBILIZER SYSTEM
INITIALIZATION, STANDARD
PROCEDURE - SENTRY................8Q-3
KEY IMMOBILIZER SYSTEM (SKIS) -
DESCRIPTION, SENTRY................8Q-1
KEY IMMOBILIZER SYSTEM (SKIS) -
OPERATION, SENTRY..................8Q-2
KEY IMMOBILIZER SYSTEM
TRANSPONDER PROGRAMMING,
STANDARD PROCEDURE - SENTRY.......8Q-4
KEY LOCK CYLINDER - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, IGNITION SWITCH............19-11
KEY-IN IGNITION SWITCH -
DESCRIPTION.......................19-11
KEYLESS ENTRY MODULE -
DESCRIPTION, REMOTE................8N-7
KEYLESS ENTRY MODULE - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING, REMOTE................8N-7
KEYLESS ENTRY MODULE -
INSTALLATION, REMOTE...............8N-8
KEYLESS ENTRY MODULE - OPERATION,
REMOTE............................8N-7
KEYLESS ENTRY MODULE - REMOVAL,
REMOTE............................8N-7
KEYLESS ENTRY TRANSMITTER -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING, REMOTE......8N-8
KEYLESS ENTRY TRANSMITTER -
SPECIFICATIONS, REMOTE..............8N-9
KNOB RELEASE - INSTALLATION, TILT
LEVER.............................19-16
KNOB RELEASE - REMOVAL, TILT LEVER . . 19-16
KNOCK SENSOR - DESCRIPTION.........8I-14
KNOCK SENSOR - INSTALLATION........8I-15
KNOCK SENSOR - OPERATION..........8I-14
KNOCK SENSOR - REMOVAL............8I-15
KNUCKLE - DESCRIPTION...............2-18
KNUCKLE - INSTALLATION..........2-19,2-37
KNUCKLE - OPERATION................2-18
KNUCKLE - REMOVAL..............2-18,2-37
LABEL - DESCRIPTION, VEHICLE
CERTIFICATION....................Intro.-11
LAMP - DESCRIPTION, DOME...........8L-26
LAMP - DESCRIPTION, READING........8L-28
LAMP - DESCRIPTION, SENTRY KEY
IMMOBILIZER SYSTEM INDICATOR.......8Q-5
LAMP - INSTALLATION, CAB CLEARANCE . 8L-12
LAMP - INSTALLATION, CENTER HIGH
MOUNTED STOP.....................8L-11
LAMP - INSTALLATION, DOME..........8L-26
LAMP - INSTALLATION, FENDER
MARKER
...........................8L-18
LAMP - INSTALLATION, FOG
............8L-12
LAMP - INSTALLATION, LICENSE PLATE
. . 8L-17
LAMP - INSTALLATION, PARK/TURN
SIGNAL
............................8L-21
LAMP - INSTALLATION, READING
........8L-29LAMP - INSTALLATION, TAILGATE
MARKER...........................8L-18
LAMP - INSTALLATION, UNDERHOOD....8L-25
LAMP - OPERATION, DOME............8L-26
LAMP - OPERATION, READING..........8L-28
LAMP - OPERATION, SENTRY KEY
IMMOBILIZER SYSTEM INDICATOR.......8Q-5
LAMP - REMOVAL, CAB CLEARANCE.....8L-11
LAMP - REMOVAL, CENTER HIGH
MOUNTED STOP.....................8L-11
LAMP - REMOVAL, DOME..............8L-26
LAMP - REMOVAL, FENDER MARKER....8L-17
LAMP - REMOVAL, FOG...............8L-12
LAMP - REMOVAL, LICENSE PLATE......8L-17
LAMP - REMOVAL, PARK/TURN SIGNAL . . 8L-21
LAMP - REMOVAL, READING...........8L-28
LAMP - REMOVAL, TAILGATE MARKER . . . 8L-18
LAMP - REMOVAL, UNDERHOOD........8L-25
LAMP INDICATOR - DESCRIPTION,
CARGO.............................8J-20
LAMP INDICATOR - OPERATION, CARGO . . 8J-20
LAMP (MIL) - DESCRIPTION,
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR.............8J-31
LAMP (MIL) - OPERATION,
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR.............8J-31
LAMP OUT INDICATOR - DESCRIPTION . . . 8J-29
LAMP OUT INDICATOR - OPERATION.....8J-29
LAMP RELAY - DESCRIPTION, FOG......8L-12
LAMP RELAY - DESCRIPTION, PARK.....8L-20
LAMP RELAY - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, PARK......................8L-20
LAMP RELAY - INSTALLATION, FOG......8L-13
LAMP RELAY - INSTALLATION, PARK.....8L-21
LAMP RELAY - OPERATION, FOG........8L-13
LAMP RELAY - OPERATION, PARK.......8L-20
LAMP RELAY - REMOVAL, FOG.........8L-13
LAMP RELAY - REMOVAL, PARK........8L-21
LAMP REPLACEMENT - STANDARD
PROCEDURE, MODULE................8M-3
LAMP REPLACEMENT - STANDARD
PROCEDURE, READING/COURTESY.......8M-3
LAMP SWITCH - DESCRIPTION, BACKUP . . . 8L-8
LAMP SWITCH - DESCRIPTION, BRAKE....8L-9
LAMP SWITCH - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, BACKUP.....................8L-8
LAMP SWITCH - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, BRAKE.....................8L-10
LAMP SWITCH - INSTALLATION, BRAKE . . 8L-11
LAMP SWITCH - OPERATION, BACKUP....8L-8
LAMP SWITCH - OPERATION, BRAKE......8L-9
LAMP SWITCH - REMOVAL, BRAKE......8L-10
LAMP UNIT - INSTALLATION, CENTER
HIGH MOUNTED STOP................8L-11
LAMP UNIT - INSTALLATION, LICENSE
PLATE .............................8L-17
LAMP UNIT - INSTALLATION,
UNDERHOOD........................8L-25
LAMP UNIT - REMOVAL, CENTER HIGH
MOUNTED STOP.....................8L-11
LAMP UNIT - REMOVAL, LICENSE PLATE . . 8L-17
LAMP UNIT - REMOVAL, UNDERHOOD . . . 8L-25
LAMPS, SPECIFICATIONS - EXTERIOR.....8L-7
LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR -
DESCRIPTION........................8L-2
LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING..............8L-3
LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR -
OPERATION..........................8L-2
LAMP/SWITCH - INSTALLATION, GLOVE
BOX ...............................8L-28
LAMP/SWITCH - REMOVAL, GLOVE BOX . . 8L-27
LASH ADJUSTER - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, HYDRAULIC.............9-125,9-32
LASH ADJUSTMENT AND VERIFICATION
- STANDARD PROCEDURE, VALVE.......9-259
LATCH - INSTALLATION.....23-16,23-23,23-32,
23-47
LATCH - INSTALLATION, GLOVE BOX.....23-52
LATCH - INSTALLATION, UNDER SEAT
STORAGE BIN.......................23-80
LATCH - REMOVAL
....23-16,23-23,23-32,23-47
LATCH - REMOVAL, GLOVE BOX
.........23-52
LATCH - REMOVAL, UNDER SEAT
STORAGE BIN
.......................23-80
LATCH RELEASE CABLE/HANDLE
ASSEMBLY - INSTALLATION
............23-47
LATCH RELEASE CABLE/HANDLE
ASSEMBLY - REMOVAL
................23-47
18 INDEXDR
Description Group-Page Description Group-Page Description Group-Page
Page 2607 of 2627
LUBRICATION - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, ENGINE DIAGNOSIS.......9-187,9-7
LUBRICATION - OPERATION . . . 9-150,9-289,9-61
LUBRICATION - STANDARD PROCEDURE . . 19-34
LUBRICATION - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
BODY...............................23-3
LUMBAR CONTROL SWITCH -
DESCRIPTION.......................8N-17
LUMBAR CONTROL SWITCH -
OPERATION.........................8N-18
LUMBAR CONTROL SWITCH - REMOVAL . 8N-18
LUMBAR MOTOR - DESCRIPTION.......8N-18
LUMBAR MOTOR - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING...........................8N-18
LUMBAR MOTOR - OPERATION.........8N-18
LUMBAR SUPPORT HANDLE/BEZEL -
INSTALLATION.......................23-82
LUMBAR SUPPORT HANDLE/BEZEL -
REMOVAL..........................23-82
MAIN BEARING - FITTING - STANDARD
PROCEDURE, CRANKSHAFT.......9-134,9-207
MAIN BEARING CLEARANCE -
STANDARD PROCEDURE...............9-274
MAIN BEARING FITTING, STANDARD
PROCEDURE.........................9-44
MAIN BEARINGS - INSPECTION,
CRANKSHAFT..................9-135,9-208
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES, 24-VALVE
CUMMINS TURBO DIESEL..............0-12
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR LAMP (MIL) -
DESCRIPTION.......................8J-31
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR LAMP (MIL) -
OPERATION.........................8J-31
MANAGER - DESCRIPTION, TASK.........25-1
MANAGER - OPERATION, TASK..........25-5
MANIFOLD - CLEANING, EXHAUST . 9-163,9-226,
9-298
MANIFOLD - CLEANING, INTAKE . . . 9-160,9-226,
9-297
MANIFOLD - DESCRIPTION, EXHAUST . . . 9-161,
9-226,9-74
MANIFOLD - DESCRIPTION, INTAKE.....9-159,
9-225,9-72
MANIFOLD - INSPECTION, EXHAUST.....9-163,
9-227,9-298
MANIFOLD - INSPECTION, INTAKE . 9-160,9-226,
9-297
MANIFOLD - INSTALLATION, EXHAUST . . . 9-164,
9-227,9-298,9-74
MANIFOLD - INSTALLATION, INTAKE.....9-160,
9-226,9-298,9-73
MANIFOLD - OPERATION, EXHAUST......9-226
MANIFOLD - REMOVAL, EXHAUST . . 9-161,9-226,
9-298,9-74
MANIFOLD - REMOVAL, INTAKE . . . 9-159,9-226,
9-297,9-73
MANIFOLD LEAKAGE - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, INTAKE...............9-159,9-225
MANIFOLD LEAKS - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, INTAKE.....................9-72
MANUAL - INSTALLATION, WINDOW
REGULATOR...................23-27,23-35
MANUAL - REMOVAL, WINDOW
REGULATOR...................23-26,23-35
MANUAL BLEEDING - STANDARD
PROCEDURE..........................5-5
MANUAL TRANSMISSION -
DESCRIPTION.........................0-4
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV3500 -
ASSEMBLY..........................21-17
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV3500 -
CLEANING..........................21-15
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV3500 -
DESCRIPTION........................21-1
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV3500 -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING..............21-3
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV3500 -
DISASSEMBLY........................21-4
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV3500 -
INSPECTION
........................21-16
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV3500 -
INSTALLATION
.......................21-39
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV3500 -
OPERATION
..........................21-1
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV3500 -
REMOVAL
...........................21-3
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV3500 -
SPECIAL TOOLS
.....................21-40MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV3500 -
SPECIFICATIONS.....................21-40
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV4500 -
ASSEMBLY..........................21-63
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV4500 -
CLEANING..........................21-62
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV4500 -
DESCRIPTION.......................21-43
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV4500 -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.............21-44
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV4500 -
DISASSEMBLY.......................21-46
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV4500 -
INSPECTION........................21-62
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV4500 -
INSTALLATION.......................21-80
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV4500 -
OPERATION.........................21-43
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV4500 -
REMOVAL..........................21-44
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV4500 -
SPECIAL TOOLS.....................21-81
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV4500 -
SPECIFICATIONS.....................21-81
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV5600 -
ASSEMBLY.........................21-106
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV5600 -
DESCRIPTION.......................21-88
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV5600 -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.............21-90
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV5600 -
DISASSEMBLY.......................21-91
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV5600 -
INSPECTION.........................21-106
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV5600 -
INSTALLATION......................21-121
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV5600 -
OPERATION.........................21-90
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV5600 -
REMOVAL..........................21-90
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV5600 -
SPECIAL TOOLS....................21-123
MAP SENSOR - DESCRIPTION.....14-32,14-83
MAP SENSOR - INSTALLATION..........14-34
MAP SENSOR - OPERATION............14-32
MAP SENSOR - REMOVAL.............14-33
MARKER LAMP - INSTALLATION,
FENDER............................8L-18
MARKER LAMP - INSTALLATION,
TAILGATE...........................8L-18
MARKER LAMP - REMOVAL, FENDER....8L-17
MARKER LAMP - REMOVAL, TAILGATE . . . 8L-18
MASTER CYLINDER - DESCRIPTION......5-24
MASTER CYLINDER - OPERATION........5-25
MASTER CYLINDER BLEEDING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE................5-26
MASTER CYLINDER/POWER BOOSTER -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING..............5-25
MATCH MOUNTING - STANDARD
PROCEDURE.........................22-3
MATCHING TIRE - DESCRIPTION, FULL
SIZE, SPARE WHEEL WITH.............22-15
MATS - INSTALLATION, CARPETS AND
FLOOR.............................23-65
MATS - REMOVAL, CARPETS AND
FLOOR.............................23-65
MEASUREMENT - 4WD (LD) -
STANDARD PROCEDURE, HEIGHT.........2-3
MEASURING TIMING CHAIN WEAR -
STANDARD PROCEDURE...............9-167
MEASURING TIMING CHAIN WEAR,
STANDARD PROCEDURE................9-77
MECHANICAL - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, ENGINE DIAGNOSIS.....9-185,9-188,
9-233,9-6,9-92
MECHANISM - DESCRIPTION, SHIFT....21-252,
21-398
MECHANISM - INSTALLATION, SHIFT.....21-87
MECHANISM - OPERATION, SHIFT......21-252,
21-398
MECHANISM - REMOVAL, SHIFT
........21-86
METRIC SYSTEM - DESCRIPTION
......Intro.-8
MICRO 420 BATTERY TESTER -
STANDARD PROCEDURE, USING
........8F-12
MILE, SPECIFICATIONS - TIRE
REVOLUTIONS PER
...................22-10
MINI-TRIP COMPUTER - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING, COMPASS
..............8M-6MIRROR - DESCRIPTION, AUTOMATIC
DAY / NIGHT........................8N-11
MIRROR - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
AUTOMATIC DAY / NIGHT..............8N-11
MIRROR - INSTALLATION, SIDE VIEW....23-42
MIRROR - OPERATION, AUTOMATIC DAY
/ NIGHT............................8N-11
MIRROR - REMOVAL, AUTOMATIC DAY /
NIGHT.............................8N-12
MIRROR - REMOVAL, REAR VIEW.......23-69
MIRROR - REMOVAL, SIDE VIEW........23-41
MIRROR - REMOVAL, SIDEVIEW........8N-12
MIRROR FLAG - INSTALLATION, SIDE
VIEW..............................23-27
MIRROR FLAG - REMOVAL, SIDE VIEW . . . 23-27
MIRROR GLASS - INSTALLATION, SIDE
VIEW..............................23-43
MIRROR GLASS - REMOVAL, SIDE VIEW . . 23-42
MIRROR SUPPORT BRACKET -
INSTALLATION, REAR VIEW............23-70
MIRROR SWITCH - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, POWER....................8N-12
MIRROR SWITCH - REMOVAL, POWER . . . 8N-12
MIRRORS - DESCRIPTION, HEATED.......8G-6
MIRRORS - DESCRIPTION, POWER......8N-10
MIRRORS - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
POWER............................8N-10
MIRRORS - OPERATION, HEATED........8G-6
MIRRORS - OPERATION, POWER........8N-10
MODE - DESCRIPTION, CIRCUIT
ACTUATION TEST.....................25-1
MODE - DESCRIPTION, STATE DISPLAY
TEST...............................25-1
MODE DOOR - INSTALLATION..........24-38
MODE DOOR - REMOVAL..............24-38
MODE DOOR ACTUATOR - DESCRIPTION . . 24-23
MODE DOOR ACTUATOR -
INSTALLATION.......................24-23
MODE DOOR ACTUATOR - OPERATION . . . 24-23
MODE DOOR ACTUATOR - REMOVAL.....24-23
MODE SENSOR - DESCRIPTION . . 21-509,21-538,
21-573
MODE SENSOR - OPERATION . . . 21-509,21-539,
21-573
MODES OF OPERATION - DESCRIPTION....8E-7
MODES, STANDARD PROCEDURE -
CONFIGURING A NEW MODULE /
SWITCH OPERATING...................8Q-3
MODULE - DESCRIPTION, AIRBAG
CONTROL..........................8O-11
MODULE - DESCRIPTION, DRIVER DOOR . . 8N-5
MODULE - DESCRIPTION, FRONT
CONTROL........................8W-97-5
MODULE - DESCRIPTION, FRONT
CONTROL...........................8E-5
MODULE - DESCRIPTION, FUEL PUMP....14-11
MODULE - DESCRIPTION, FUEL TANK....14-63
MODULE - DESCRIPTION, HEATED SEAT . . . 8E-6
MODULE - DESCRIPTION, HEATED SEAT . . 8G-13
MODULE - DESCRIPTION, INTEGRATED
POWER..........................8W-97-3
MODULE - DESCRIPTION, REMOTE
KEYLESS ENTRY......................8N-7
MODULE - DESCRIPTION, SENTRY KEY
IMMOBILIZER.......................8E-13
MODULE - DESCRIPTION, TRANSFER
CASE CONTROL......................8E-16
MODULE - DESCRIPTION,
TRANSMISSION CONTROL.............8E-20
MODULE - DESCRIPTION, WIPER.......8R-22
MODULE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
DRIVER DOOR.......................8N-6
MODULE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
FRONT CONTROL..................8W-97-5
MODULE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
FRONT CONTROL.....................8E-5
MODULE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
HEATED SEAT ........................8E-6
MODULE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
HEATED SEAT
.......................8G-14
MODULE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
REMOTE KEYLESS ENTRY
..............8N-7
MODULE - INSTALLATION, AIRBAG
CONTROL
..........................8O-13
MODULE - INSTALLATION, DRIVER
DOOR
..............................8N-7
MODULE - INSTALLATION, ENGINE
CONTROL
...........................8E-4
20 INDEXDR
Description Group-Page Description Group-Page Description Group-Page