Coil DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.G Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1998, Model line: RAM 1500, Model: DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.GPages: 2627
Page 296 of 2627

FRONT WHEEL SPEED
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The ABS brake system uses 3 wheel speed sensors.
A sensor is mounted to each front hub/bearings. The
third sensor is mounted on top of the rear axle dif-
ferential housing.
OPERATION
The Wheel Speed Sensor consists of a magnet sur-
rounded by windings from a single strand of wire.
The sensor sends a small AC signal to the CAB. This
signal is generated by magnetic induction. The mag-
netic induction is created when a toothed sensor ring
(exciter ring or tone wheel) passes the stationary
magnetic WSS.
When the ring gear is rotated, the exciter ring
passes the tip of the WSS. As the exciter ring tooth
approaches the tip of the WSS, the magnetic lines of
force expand, causing the magnetic field to cut across
the sensor's windings. This, in turn causes current to
flow through the WSS circuit (Fig. 1) in one direc-
tion. When the exciter ring tooth moves away from
the sensor tip, the magnetic lines of force collapse
cutting the winding in the opposite direction. This
causes the current to flow in the opposite direction.
Every time a tooth of the exciter ring passes the tip
of the WSS, an AC signal is generated. Each AC sig-
nal (positive to negative signal or sinewave) is inter-
preted by the CAB. It then compares the frequency of
the sinewave to a time value to calculate vehicle
speed. The CAB continues to monitor the frequency
to determine a deceleration rate that would indicate
a possible wheel-locking tendency.
The signal strength of any magnetic induction sen-
sor is directly affected by:
²Magnetic field strength; the stronger the mag-
netic field, the stronger the signal
²Number of windings in the sensor; more wind-
ings provide a stronger signal
²Exciter ring speed; the faster the exciter ring/
tone wheel rotates, the stronger the signal will be
²Distance between the exciter ring teeth and
WSS; the closer the WSS is to the exciter ring/tone
wheel, the stronger the signal will be
The rear WSS is not adjustable. A clearance speci-
fication has been established for manufacturing toler-
ances. If the clearance is not within these
specifications, then either the WSS or other compo-
nents may be damaged. The clearance between the
WSS and the exciter ring is 0.005 ± 0.050 in.
The assembly plant performs a ªRolls Testº on
every vehicle that leaves the assembly plant. One of
the test performed is a test of the WSS. To properlytest the sensor, the assembly plant connects test
equipment to the Data Link Connector (DLC). This
connector is located to the right of the steering col-
umn and attached to the lower portion of the instru-
ment panel (Fig. 2). The rolls test terminal is spliced
to the WSS circuit. The vehicle is then driven on a
set of rollers and the WSS output is monitored for
proper operation.
Fig. 1 Operation of the Wheel Speed Sensor
1 - MAGNETIC CORE
2 - CAB
3 - AIR GAP
4 - EXCITER RING
5 - COIL
Fig. 2 Data Link Connector - Typical
1 - 16±WAY DATA LINK CONNECTOR
DRBRAKES - ABS 5 - 47
Page 338 of 2627

INSTALLATION
(1) Install tensioner on to the mounting bracket.
Tighten bolt to 41 N´m (30 ft. lbs.).
(2) Install tensioner and bracket assembly
(3) Install accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS - INSTAL-
LATION).
BELT TENSIONER - 5.9L
DIESEL
DESCRIPTION
Drive belts on all engines are equipped with a
spring loaded automatic belt tensioner (Fig. 4). This
tensioner maintains constant belt tension at all times
and requires no maintenance or adjustment.
CAUTION: Do not attempt to check belt tension with
a belt tension gauge on vehicles equipped with an
automatic belt tensioner.
OPERATION
WARNING: THE AUTOMATIC BELT TENSIONER
ASSEMBLY IS SPRING LOADED. DO NOT ATTEMPT
TO DISASSEMBLE THE TENSIONER ASSEMBLY.
The automatic belt tensioner maintains correct belt
tension using a coiled spring within the tensioner
housing. The spring applies pressure to the tensioner
arm pressing the arm into the belt, tensioning the
belt.
REMOVAL
WARNING: BECAUSE OF HIGH SPRING PRES-
SURE, DO NOT ATTEMPT TO DISASSEMBLE AUTO-
MATIC TENSIONER. UNIT IS SERVICED AS AN
ASSEMBLY.
(1) Remove accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
(2) Remove tensioner mounting bolt (Fig. 5) and
remove tensioner.
Fig. 4 Accessory Drive Belt - 5.9L Diesel
1 - GENERATOR
2 - WATER PUMP
3 - IDLER
4 - POWER STEERING PUMP
5 - RADIATOR FAN PULLEY
6 - CRANKSHAFT
7 - AUTOMATIC TENSIONER
8 - A/C COMPRESSOR
Fig. 5 AUTOMATIC BELT TENSIONER 5.9L DIESEL
ENGINE
1 - GENERATOR
2 - WATER PUMP
3 - IDLER
4 - POWER STEERING PUMP
5 - RADIATOR FAN PULLEY
6 - CRANKSHAFT
7 - AUTOMATIC TENSIONER
8 - A/C COMPRESSOR
DRACCESSORY DRIVE 7 - 23
BELT TENSIONER-5.7L (Continued)
Page 352 of 2627

REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the battery negative cable.
(2) Drain the coolant (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(3) Remove the power cord from the heater by
unplugging (Fig. 7).
(4) Loosen (but do not completely remove) the
screw at center of block heater (Fig. 7).
(5) Remove the block heater by carefully prying
from side-to-side. Note the direction of the heating
element coil (up or down). The element coil must be
installed correctly to prevent damage.
INSTALLATION
(1) Clean and inspect the block heater hole.
(2) Install the new O-ring seal(s) to heater.
(3) Insert the block heater into cylinder block and
position the element properly.
(4) With the heater fully seated, tighten center
screw to 2 N´m (17 in. lbs.).
(5) Fill the cooling system with the recommended
coolant. (Refer to 7 - COOLING - STANDARD PRO-
CEDURE).
(6) Start and warm the engine.
(7) Check the block heater for leaks.
ENGINE BLOCK HEATER - 5.9L
DIESEL
DESCRIPTION
WARNING: DO NOT OPERATE ENGINE UNLESS
BLOCK HEATER CORD HAS BEEN DISCONNECTED
FROM POWER SOURCE AND SECURED IN PLACE.
THE POWER CORD MUST BE SECURED IN ITS
RETAINING CLIPS AND ROUTED AWAY FROM
EXHAUST MANIFOLDS AND MOVING PARTS.
An optional engine block heater is available on all
models. The heater is equipped with a power cord.
The heater is mounted in a threaded hole of the
engine cylinder block with the heating element
immersed in engine coolant. The cord is attached to
an engine compartment component with tie-straps.
The 5.9L diesel engine has the block heater located
on the right side of the engine below the exhaust
manifold next to the oil cooler (Fig. 8).
Fig. 6 Engine Block Heater - 3.7L/4.7L
1 - ENGINE BLOCK HEATER
Fig. 7 Engine Block Heater
1 - FREEZE PLUG HOLE
2 - BLOCK HEATER
3 - SCREW
4 - POWER CORD (120V AC)
5 - HEATING COIL
6 - OIL FILTER
DRENGINE 7 - 37
ENGINE BLOCK HEATER (Continued)
Page 365 of 2627

(9) Install support rod.
(10) Fill cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(11) Connect negative battery cable to battery.
(12) Start and warm engine. Check for leaks.
FAN DRIVE VISCOUS CLUTCH-
GAS ENGINES
DESCRIPTION
The thermal viscous fan drive (Fig. 31) is a sili-
cone-fluid- filled coupling used to connect the fan
blades to the water pump shaft. The coupling allows
the fan to be driven in a normal manner. This is
done at low engine speeds while limiting the top
speed of the fan to a predetermined maximum level
at higher engine speeds.
OPERATION
A thermostatic bimetallic spring coil is located on
the front face of the viscous fan drive unit (a typical
viscous unit is shown in (Fig. 32). This spring coilreacts to the temperature of the radiator discharge
air. It engages the viscous fan drive for higher fan
speed if the air temperature from the radiator rises
above a certain point. Until additional engine cooling
is necessary, the fan will remain at a reduced rpm
regardless of engine speed.
Only when sufficient heat is present, will the vis-
cous fan drive engage. This is when the air flowing
through the radiator core causes a reaction to the
bimetallic coil. It then increases fan speed to provide
the necessary additional engine cooling.
Once the engine has cooled, the radiator discharge
temperature will drop. The bimetallic coil again
reacts and the fan speed is reduced to the previous
disengaged speed.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - VISCOUS FAN
DRIVE
NOISE
NOTE: It is normal for fan noise to be louder (roar-
ing) when:
²The underhood temperature is above the engage-
ment point for the viscous drive coupling. This may
occur when ambient (outside air temperature) is very
high.
Fig. 30 Thermostat - 8.0L V-10 Engine
1 - COOLANT TEMP. SENSOR (FOR PCM)
2 - HEATER SUPPLY FITTING
3 - BOLTS (6)
4 - HOUSING WITH INTEGRAL SEAL
5 - THERMOSTAT
6 - RUBBER LIP SEAL
7 - TEMP. GAUGE SENDING UNIT
Fig. 31 Viscous Fan
1 - WATER PUMP BYPASS HOSE
2 - FAN BLADE ASSEMBLY
3 - VISCOUS FAN DRIVE
4 - WATER PUMP AND PULLEY
5 - Bolts (4)
7 - 50 ENGINEDR
ENGINE COOLANT THERMOSTAT - 8.0L (Continued)
Page 398 of 2627

(1) Install remote radio switch to the steering
wheel.
(2) Connect the wire harness to the remote radio
switch.
(3) Install the speed control switches (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/SPEED CONTROL/SWITCH -
INSTALLATION).
(4) Install the driver airbag
(5) Connect the battery negative cable.
SPEAKER
DESCRIPTION
STANDARD
The standard equipment speaker system includes
speakers in four locations. One 15.2 X 22.8 centime-
ter (6 X 9 inch) full-range speaker is located in each
front door. There is also one full-range 13.3 centime-
ter (5.25 inch) diameter full-range speaker located in
each rear door.
PREMIUM
The optional premium speaker system features
eleven Premium model speakers in seven locations.
Each of the standard speakers is replaced with Pre-
mium model speakers. One 8.8 centimeter (3.50 inch)
diameter speaker is located on each end of the
instrument panel top pad. One 6.3 centimeter (2.50
inch) diameter speaker is located in the center of the
instrument panel top pad. One 15.2 X 22.8 centime-
ter (6 X 9 inch) Premium speaker is located in each
front door. There is also one coaxial 13.3 centimeter
(5.25 inch) diameter Premium full-range speaker
located in each rear door. The premium speaker sys-
tem also includes a power amplifier mounted behind
the glove box. The total available power of the pre-
mium speaker system is 240 watts.
OPERATION
Two wires connected to each speaker, one feed cir-
cuit (+) and one return circuit (±), allow the audio
output signal electrical current to flow through the
voice coil. For complete circuit diagrams, refer to the
appropriate wiring information. The wiring informa-
tion includes wiring diagrams, proper wire and con-
nector repair procedures, details of wire harness
routing and retention, connector pin-out information
and location views for the various wire harness con-
nectors, splices and grounds.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SPEAKER
Any diagnosis of the Audio system should
begin with the use of the DRB IIItdiagnostic
tool. For information on the use of the
DRB IIIt, refer to the appropriate Diagnostic
Service Manual.
Refer to the appropriate wiring information.
WARNING: DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM
BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL,
STEERING COLUMN, SEAT BELT TENSIONER, SIDE
AIRBAG, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
CAUTION: The speaker output of the radio is a
ªfloating groundº system. Do not allow any speaker
lead to short to ground, as damage to the radio
and/or amplifier may result.
(1) If all speakers are inoperative, check the fuses
in the Integrated Power Module (IPM). If OK, go to
Step 2. If not OK, repair the shorted circuit or com-
ponent as required and replace the faulty fuse.
(2) Check the amplifier fuse (if equipped) in the
IPM. If OK, go to Step 3. If not OK, repair the
shorted circuit or component as required and replace
the faulty fuse.
(3) Turn the ignition switch to the ON position.
Turn the radio receiver ON. Adjust the balance and
fader control controls to check the performance of
each individual speaker. Note the speaker locations
that are not performing correctly. Go to Step 4.
(4) Turn the radio receiver OFF. Turn the ignition
OFF. Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable. If vehicle isnotequipped with a amplifier,
remove the radio receiver. If vehicle is equipped with
an amplifier. disconnect wire harness connector at
output side of amplifier. Go to Step 5.
(5) Check both the speaker feed (+) circuit and
return (-) circuit cavities for the inoperative speaker
at the radio receiver wire harness connector for con-
tinuity to ground. There should be no continuity. If
OK, go to Step 6. If not OK, repair the shorted
speaker feed (+) and/or return (-) circuits(s) to the
speaker as required.
DRAUDIO/VIDEO 8A - 13
REMOTE SWITCHES (Continued)
Page 416 of 2627

IDLE MODE
When the engine is at operating temperature, this
is a Closed Loop mode. At idle speed, the PCM
receives inputs from:
²Air conditioning select signal (if equipped)
²Air conditioning request signal (if equipped)
²Battery voltage
²Crankshaft position sensor
²Engine coolant temperature sensor
²Intake manifold air temperature sensor
²Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor
²Throttle position sensor (TPS)
²Camshaft position sensor signal
²Battery voltage
²Park/neutral switch (gear indicator signalÐauto.
trans. only)
²Oxygen sensors
Based on these inputs, the following occurs:
²Voltage is applied to the fuel injectors with the
ASD relay via the PCM. The PCM will then control
injection sequence and injector pulse width by turn-
ing the ground circuit to each individual injector on
and off.
²The PCM monitors the O2S sensor input and
adjusts air-fuel ratio by varying injector pulse width.
It also adjusts engine idle speed through the idle air
control (IAC) motor.
²The PCM adjusts ignition timing by increasing
and decreasing spark advance.
²The PCM operates the A/C compressor clutch
through the A/C compressor clutch relay. This is done
if A/C has been selected by the vehicle operator and
specified pressures are met at the high and low±pres-
sure A/C switches. Refer to Heating and Air Condi-
tioning for additional information.
CRUISE MODE
When the engine is at operating temperature, this
is a Closed Loop mode. At cruising speed, the PCM
receives inputs from:
²Air conditioning select signal (if equipped)
²Air conditioning request signal (if equipped)
²Battery voltage
²Engine coolant temperature sensor
²Crankshaft position sensor
²Intake manifold air temperature sensor
²Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor
²Throttle position sensor (TPS)
²Camshaft position sensor signal
²Park/neutral switch (gear indicator signalÐauto.
trans. only)²Oxygen (O2S) sensors
Based on these inputs, the following occurs:
²Voltage is applied to the fuel injectors with the
ASD relay via the PCM. The PCM will then adjust
the injector pulse width by turning the ground circuit
to each individual injector on and off.
²The PCM monitors the O2S sensor input and
adjusts air-fuel ratio. It also adjusts engine idle
speed through the idle air control (IAC) motor.
²The PCM adjusts ignition timing by turning the
ground path to the coil(s) on and off.
²The PCM operates the A/C compressor clutch
through the clutch relay. This happens if A/C has
been selected by the vehicle operator and requested
by the A/C thermostat.
ACCELERATION MODE
This is an Open Loop mode. The PCM recognizes
an abrupt increase in throttle position or MAP pres-
sure as a demand for increased engine output and
vehicle acceleration. The PCM increases injector
pulse width in response to increased throttle opening.
DECELERATION MODE
When the engine is at operating temperature, this
is an Open Loop mode. During hard deceleration, the
PCM receives the following inputs.
²Air conditioning select signal (if equipped)
²Air conditioning request signal (if equipped)
²Battery voltage
²Engine coolant temperature sensor
²Crankshaft position sensor
²Intake manifold air temperature sensor
²Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor
²Throttle position sensor (TPS)
²Camshaft position sensor signal
²Park/neutral switch (gear indicator signalÐauto.
trans. only)
²Vehicle speed
If the vehicle is under hard deceleration with the
proper rpm and closed throttle conditions, the PCM
will ignore the oxygen sensor input signal. The PCM
will enter a fuel cut-off strategy in which it will not
supply a ground to the injectors. If a hard decelera-
tion does not exist, the PCM will determine the
proper injector pulse width and continue injection.
Based on the above inputs, the PCM will adjust
engine idle speed through the idle air control (IAC)
motor.
The PCM adjusts ignition timing by turning the
ground path to the coil on and off.
DRELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES 8E - 9
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 417 of 2627

WIDE OPEN THROTTLE MODE
This is an Open Loop mode. During wide open
throttle operation, the PCM receives the following
inputs.
²Battery voltage
²Crankshaft position sensor
²Engine coolant temperature sensor
²Intake manifold air temperature sensor
²Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor
²Throttle position sensor (TPS)
²Camshaft position sensor signal
During wide open throttle conditions, the following
occurs:
²Voltage is applied to the fuel injectors with the
ASD relay via the PCM. The PCM will then control
the injection sequence and injector pulse width by
turning the ground circuit to each individual injector
on and off. The PCM ignores the oxygen sensor input
signal and provides a predetermined amount of addi-
tional fuel. This is done by adjusting injector pulse
width.
²The PCM adjusts ignition timing by turning the
ground path to the coil(s) on and off.
IGNITION SWITCH OFF MODE
When ignition switch is turned to OFF position,
the PCM stops operating the injectors, ignition coil,
ASD relay and fuel pump relay.
DESCRIPTION - 5 VOLT SUPPLIES
Two different Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
five volt supply circuits are used; primary and sec-
ondary.
DESCRIPTION - IGNITION CIRCUIT SENSE
This circuit ties the ignition switch to the Power-
train Control Module (PCM).
DESCRIPTION - POWER GROUNDS
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) has 2 main
grounds. Both of these grounds are referred to as
power grounds. All of the high-current, noisy, electri-
cal devices are connected to these grounds as well as
all of the sensor returns. The sensor return comes
into the sensor return circuit, passes through noise
suppression, and is then connected to the power
ground.
The power ground is used to control ground cir-
cuits for the following PCM loads:
²Generator field winding
²Fuel injectors
²Ignition coil(s)
²Certain relays/solenoids
²Certain sensors
DESCRIPTION - SENSOR RETURN
The Sensor Return circuits are internal to the Pow-
ertrain Control Module (PCM).
Sensor Return provides a low±noise ground refer-
ence for all engine control system sensors. Refer to
Power Grounds for more information.
OPERATION
OPERATION - PCM
The PCM operates the fuel system. The PCM is a
pre-programmed, triple microprocessor digital com-
puter. It regulates ignition timing, air-fuel ratio,
emission control devices, charging system, certain
transmission features, speed control, air conditioning
compressor clutch engagement and idle speed. The
PCM can adapt its programming to meet changing
operating conditions.
The PCM receives input signals from various
switches and sensors. Based on these inputs, the
PCM regulates various engine and vehicle operations
through different system components. These compo-
nents are referred to as Powertrain Control Module
(PCM) Outputs. The sensors and switches that pro-
vide inputs to the PCM are considered Powertrain
Control Module (PCM) Inputs.
The PCM adjusts ignition timing based upon
inputs it receives from sensors that react to: engine
rpm, manifold absolute pressure, engine coolant tem-
perature, throttle position, transmission gear selec-
tion (automatic transmission), vehicle speed, power
steering pump pressure, and the brake switch.
The PCM adjusts idle speed based on inputs it
receives from sensors that react to: throttle position,
vehicle speed, transmission gear selection, engine
coolant temperature and from inputs it receives from
the air conditioning clutch switch and brake switch.
Based on inputs that it receives, the PCM adjusts
ignition coil dwell. The PCM also adjusts the gener-
ator charge rate through control of the generator
field and provides speed control operation.
NOTE: PCM Inputs:
²ABS module (if equipped)
²A/C request (if equipped with factory A/C)
²A/C select (if equipped with factory A/C)
²A/C pressure transducer
²Auto shutdown (ASD) sense
²Battery temperature sensor
²Battery voltage
²Brake switch
²J1850 bus (+) circuits
²J1850 bus (-) circuits
²Camshaft position sensor signal
²Crankshaft position sensor
8E - 10 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESDR
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 418 of 2627

²Data link connection for DRB scan tool
²EATX module (if equipped)
²Engine coolant temperature sensor
²Fuel level (through J1850 circuitry)
²Generator (battery voltage) output
²Ignition circuit sense (ignition switch in on/off/
crank/run position)
²Intake manifold air temperature sensor
²Knock sensors (2 on 3.7L engine)
²Leak detection pump (switch) sense (if equipped)
²Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor
²Oil pressure
²Oxygen sensors
²Park/neutral switch (auto. trans. only)
²Power ground
²Power steering pressure switch (if equipped)
²Sensor return
²Signal ground
²Speed control multiplexed single wire input
²Throttle position sensor
²Transfer case switch (4WD range position)
²Vehicle speed signal
NOTE: PCM Outputs:
²A/C clutch relay
²Auto shutdown (ASD) relay
²J1850 bus (+/-) circuits for: speedometer, voltme-
ter, fuel gauge, oil pressure gauge/lamp, engine temp.
gauge and speed control warn. lamp
²Data link connection for DRB scan tool
²EGR valve control solenoid (if equipped)
²EVAP canister purge solenoid
²Five volt sensor supply (primary)
²Five volt sensor supply (secondary)
²Fuel injectors
²Fuel pump relay
²Generator field driver (-)
²Generator field driver (+)
²Idle air control (IAC) motor
²Ignition coil(s)
²Leak detection pump (if equipped)
²Malfunction indicator lamp (Check engine lamp).
Driven through J1850 circuits.²Oxygen sensor heater relays
²Oxygen sensors (pulse width modulated)
²Radiator cooling fan relay (pulse width modu-
lated)
²Speed control vacuum solenoid
²Speed control vent solenoid
²Tachometer (if equipped). Driven through J1850
circuits.
²Transmission convertor clutch circuit. Driven
through J1850 circuits.
OPERATION - 5 VOLT SUPPLIES
Primary 5±volt supply:
²supplies the required 5 volt power source to the
Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor.
²supplies the required 5 volt power source to the
Camshaft Position (CMP) sensor.
²supplies a reference voltage for the Manifold
Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor.
²supplies a reference voltage for the Throttle
Position Sensor (TPS) sensor.
Secondary 5±volt supply:
²supplies the required 5 volt power source to the
oil pressure sensor.
²supplies the required 5 volt power source for the
Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS) (if equipped).
²supplies the 5 volt power source to the transmis-
sion pressure sensor (certain automatic transmis-
sions).
OPERATION - IGNITION CIRCUIT SENSE
The ignition circuit sense input tells the PCM the
ignition switch has energized the ignition circuit.
Battery voltage is also supplied to the PCM
through the ignition switch when the ignition is in
the RUN or START position. This is referred to as
the9ignition sense9circuit and is used to9wake up9
the PCM. Voltage on the ignition input can be as low
as 6 volts and the PCM will still function. Voltage is
supplied to this circuit to power the PCM's 8-volt reg-
ulator and to allow the PCM to perform fuel, ignition
and emissions control functions.
DRELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES 8E - 11
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 452 of 2627
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Generator (short)
Horizontal Mounting Bolt -
3.7L / 4.7L Engines74 55 -
Generator B+ Output
Cable Terminal Nut12 - 108
BATTERY TEMPERATURE
SENSOR
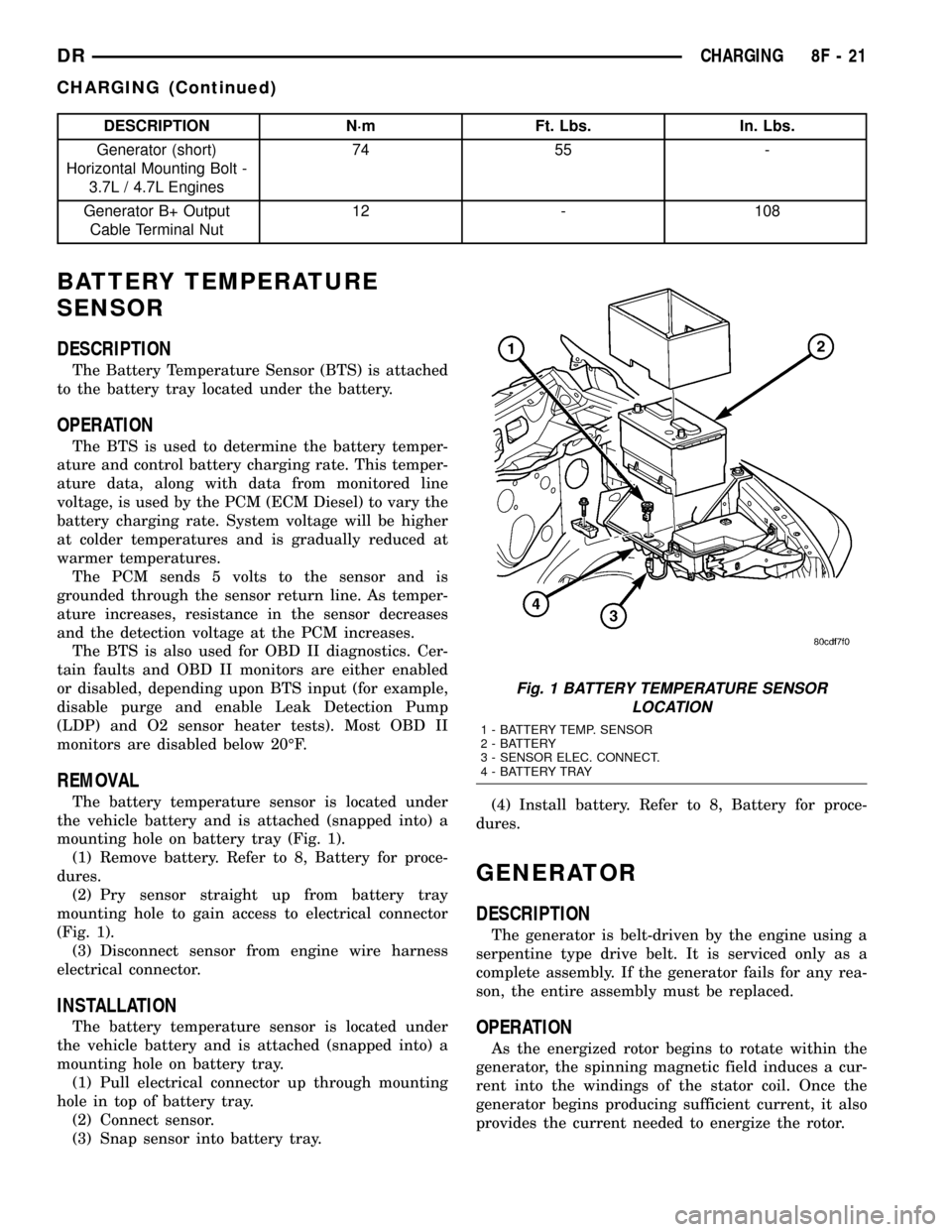
DESCRIPTION
The Battery Temperature Sensor (BTS) is attached
to the battery tray located under the battery.
OPERATION
The BTS is used to determine the battery temper-
ature and control battery charging rate. This temper-
ature data, along with data from monitored line
voltage, is used by the PCM (ECM Diesel) to vary the
battery charging rate. System voltage will be higher
at colder temperatures and is gradually reduced at
warmer temperatures.
The PCM sends 5 volts to the sensor and is
grounded through the sensor return line. As temper-
ature increases, resistance in the sensor decreases
and the detection voltage at the PCM increases.
The BTS is also used for OBD II diagnostics. Cer-
tain faults and OBD II monitors are either enabled
or disabled, depending upon BTS input (for example,
disable purge and enable Leak Detection Pump
(LDP) and O2 sensor heater tests). Most OBD II
monitors are disabled below 20ÉF.
REMOVAL
The battery temperature sensor is located under
the vehicle battery and is attached (snapped into) a
mounting hole on battery tray (Fig. 1).
(1) Remove battery. Refer to 8, Battery for proce-
dures.
(2) Pry sensor straight up from battery tray
mounting hole to gain access to electrical connector
(Fig. 1).
(3) Disconnect sensor from engine wire harness
electrical connector.
INSTALLATION
The battery temperature sensor is located under
the vehicle battery and is attached (snapped into) a
mounting hole on battery tray.
(1) Pull electrical connector up through mounting
hole in top of battery tray.
(2) Connect sensor.
(3) Snap sensor into battery tray.(4) Install battery. Refer to 8, Battery for proce-
dures.
GENERATOR
DESCRIPTION
The generator is belt-driven by the engine using a
serpentine type drive belt. It is serviced only as a
complete assembly. If the generator fails for any rea-
son, the entire assembly must be replaced.
OPERATION
As the energized rotor begins to rotate within the
generator, the spinning magnetic field induces a cur-
rent into the windings of the stator coil. Once the
generator begins producing sufficient current, it also
provides the current needed to energize the rotor.
Fig. 1 BATTERY TEMPERATURE SENSOR
LOCATION
1 - BATTERY TEMP. SENSOR
2 - BATTERY
3 - SENSOR ELEC. CONNECT.
4 - BATTERY TRAY
DRCHARGING 8F - 21
CHARGING (Continued)
Page 457 of 2627

STARTING
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
STARTING
DESCRIPTION.........................26
OPERATION...........................26
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - STARTING
SYSTEM............................27
SPECIFICATIONS
STARTING SYSTEM...................31
SPECIFICATIONS - TORQUE - STARTING
SYSTEM............................32
STARTER MOTOR
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - STARTER
MOTOR .............................32REMOVAL.............................33
INSTALLATION.........................34
STARTER MOTOR RELAY
DESCRIPTION.........................35
OPERATION...........................36
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - STARTER RELAY . 36
REMOVAL.............................37
INSTALLATION.........................37
STARTING
DESCRIPTION
The starting system consists of:
²Starter relay
²Starter motor (including an integral starter sole-
noid)
Other components to be considered as part of start-
ing system are:
²Battery
²Battery cables
²Ignition switch and key lock cylinder
²Clutch pedal position switch (manual transmis-
sion)
²Park/neutral position switch (automatic trans-
mission)
²Wire harnesses and connections.
The Battery, Starting, and Charging systems oper-
ate in conjunction with one another, and must be
tested as a complete system. For correct operation of
starting/charging systems, all components used in
these 3 systems must perform within specifications.
When attempting to diagnose any of these systems, it
is important that you keep their interdependency in
mind.
The diagnostic procedures used in each of these
groups include the most basic conventional diagnostic
methods, to the more sophisticated On-Board Diag-
nostics (OBD) built into the Powertrain Control Mod-
ule (PCM). Use of an induction-type milliampere
ammeter, volt/ohmmeter, battery charger, carbon pile
rheostat (load tester), and 12-volt test lamp may be
required.Certain starting system components are monitored
by the PCM and may produce a Diagnostic Trouble
Code (DTC). Refer to Diagnostic Trouble Codes in
Emission Control for a list of codes.
OPERATION
The starting system components form two separate
circuits. A high-amperage feed circuit that feeds the
starter motor between 150 and 350 amperes (700
amperes - diesel engine), and a low-amperage control
circuit that operates on less than 20 amperes. The
high-amperage feed circuit components include the
battery, the battery cables, the contact disc portion of
the starter solenoid, and the starter motor. The low-
amperage control circuit components include the igni-
tion switch, the clutch pedal position switch (manual
transmission), the park/neutral position switch (auto-
matic transmission), the starter relay, the electro-
magnetic windings of the starter solenoid, and the
connecting wire harness components.
If the vehicle is equipped with a manual transmis-
sion, it has a clutch pedal position switch installed in
series between the ignition switch and the coil bat-
tery terminal of the starter relay. This normally open
switch prevents the starter relay from being ener-
gized when the ignition switch is turned to the Start
position, unless the clutch pedal is depressed. This
feature prevents starter motor operation while the
clutch disc and the flywheel are engaged. The starter
relay coil ground terminal is always grounded on
vehicles with a manual transmission.
8F - 26 STARTINGDR