Coil DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.G Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1998, Model line: RAM 1500, Model: DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.GPages: 2627
Page 458 of 2627

If the vehicle is equipped with an automatic trans-
mission, battery voltage is supplied through the low-
amperage control circuit to the coil battery terminal
of the starter relay when the ignition switch is
turned to the Start position. The park/neutral posi-
tion switch is installed in series between the starter
relay coil ground terminal and ground. This normally
open switch prevents the starter relay from being
energized and the starter motor from operating
unless the automatic transmission gear selector is in
the Neutral or Park positions.
When the starter relay coil is energized, the nor-
mally open relay contacts close. The relay contacts
connect the relay common feed terminal to the relay
normally open terminal. The closed relay contacts
energize the starter solenoid coil windings.
The energized solenoid pull-in coil pulls in the sole-
noid plunger. The solenoid plunger pulls the shift
lever in the starter motor. This engages the starter
overrunning clutch and pinion gear with the starter
ring gear.
As the solenoid plunger reaches the end of its
travel, the solenoid contact disc completes the high-
amperage starter feed circuit and energizes the sole-
noid plunger hold-in coil. Current now flows between
the solenoid battery terminal and the starter motor,
energizing the starter.Once the engine starts, the overrunning clutch pro-
tects the starter motor from damage by allowing the
starter pinion gear to spin faster than the pinion
shaft. When the ignition switch is released to the On
position, the starter relay coil is de-energized. This
causes the relay contacts to open. When the relay
contacts open, the starter solenoid plunger hold-in
coil is de-energized.
When the solenoid plunger hold-in coil is de-ener-
gized, the solenoid plunger return spring returns the
plunger to its relaxed position. This causes the con-
tact disc to open the starter feed circuit, and the shift
lever to disengage the overrunning clutch and pinion
gear from the starter ring gear.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - STARTING
SYSTEM
The battery, starting, and charging systems oper-
ate in conjunction with one another, and must be
tested as a complete system. For correct starting/
charging system operation, all of the components
involved in these 3 systems must perform within
specifications.
Starting System Diagnosis
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
STARTER FAILS TO
OPERATE.1. Battery discharged or
faulty.1. Refer to Battery. Charge or replace battery, if required.
2. Starting circuit wiring
faulty.2. Refer to 8, Wiring Diagrams. Test and repair starter
feed and/or control circuits, if required.
3. Starter relay faulty. 3. Refer to Starter Relay in Diagnosis and Testing.
Replace starter relay if required.
4. Ignition switch faulty. 4. Refer to Ignition Switch and Key Lock Cylinder.
Replace ignition switch if required.
5. Clutch pedal position
switch faulty.5. Refer to Clutch Pedal Position Switch.
6. Park/Neutral position
switch faulty or
misadjusted.6. Refer to Park/Neutral Position Switch. Replace
park/neutral position switch if required.
7. Starter solenoid faulty. 7. Refer to Starter Motor. Replace starter motor assembly
if required.
8. Starter motor faulty. 8. If all other starting system components and circuits test
OK, replace starter motor.
DRSTARTING 8F - 27
STARTING (Continued)
Page 464 of 2627

(6) Note reading on ammeter and compare reading
to free running test maximum amperage draw. Refer
to Specifications for starter motor free running test
maximum amperage draw specifications.
(7) If ammeter reading exceeds maximum amper-
age draw specification, replace faulty starter motor
assembly.
STARTER SOLENOID
This test can only be performed with starter motor
removed from vehicle.
(1) Remove starter motor from vehicle. Refer to
Starter Motor Removal and Installation.
(2) Disconnect wire from solenoid field coil termi-
nal.
(3) Check for continuity between solenoid terminal
and solenoid field coil terminal with a continuity
tester (Fig. 7). There should be continuity. If OK, go
to Step 4. If not OK, replace faulty starter motor
assembly.
(4) Check for continuity between solenoid terminal
and solenoid case (Fig. 8). There should be continuity.
If not OK, replace faulty starter motor assembly.REMOVAL
3.7L / 4.7L
(1) Disconnect and isolate negative battery cable.
(2) Raise and support vehicle.
(3) Note: If equipped with 4WD and certain trans-
missions, a support bracket is used between front
axle and side of transmission. Remove 2 support
bracket bolts at transmission. Pry support bracket
slightly to gain access to lower starter mounting bolt.
(4) Remove 1 bolt and 1 nut if equipped with a
manual transmission (Fig. 9).
(5) Remove 2 bolts if equipped with an automatic
transmission (Fig. 10).
(6) Move starter motor towards front of vehicle far
enough for nose of starter pinion housing to clear
housing. Always support starter motor during this
process, do not let starter motor hang from wire har-
ness.
(7) Tilt nose downwards and lower starter motor
far enough to access and remove nut that secures
battery positive cable wire harness connector eyelet
to solenoid battery terminal stud. Do not let starter
motor hang from wire harness.
(8) Remove battery positive cable wire harness
connector eyelet from solenoid battery terminal stud.
(9) Disconnect battery positive cable wire harness
connector from solenoid terminal connector recepta-
cle.
(10) Remove starter motor.
Fig. 7 CONTINUITY BETWEEN SOLENOID AND
FIELD COIL TERMINALS - TYPICAL
1 - OHMMETER
2 - SOLENOID TERMINAL
3 - FIELD COIL TERMINAL
Fig. 8 CONTINUITY BETWEEN SOLENOID
TERMINAL AND CASE - TYPICAL
1 - SOLENOID TERMINAL
2 - OHMMETER
3 - SOLENOID
Fig. 9 STARTER R/I - 3.7L/4.7L - MAN. TRANS.
1 - EYELET TERMINAL
2 - NUT
3 - BRACKET
4 - STUD
5 - STARTER MOTOR
6 - LOCK WASHER
7 - WIRE HARNESS CONNECTOR
8 - NUT
9 - SCREW AND WASHER (2)
DRSTARTING 8F - 33
STARTER MOTOR (Continued)
Page 466 of 2627

5.7L
(1) Connect solenoid wire to starter motor (snaps
on).
(2) Position battery cable to solenoid stud. Install
and tighten battery cable eyelet nut. Refer to Torque
Specifications. Do not allow starter motor to hang
from wire harness.
(3) Position starter motor to engine.
(4) If equipped with automatic transmission, slide
cooler tube bracket into position.
(5) Install and tighten both mounting bolts. Refer
to Torque Specifications.
(6) Lower vehicle.
(7) Connect negative battery cable.
5.9L Diesel
(1)If Equipped:Position and hold aluminum
spacer to rear of starter while positioning starter to
engine.
(2) Connect solenoid wire to starter motor. Tighten
nut.
(3) Position battery cable to starter stud. Install
and tighten battery cable nut. Refer to Torque Spec-
ifications. Do not allow starter motor to hang from
wire harness.
(4) Position starter motor to transmission.
(5) If equipped with automatic transmission, slide
cooler tube bracket into position.
(6) Install and tighten 3 starter mounting bolts.
Refer to Torque Specifications.
(7) Lower vehicle.
(8) Connect both negative battery cables to both
batteries.
STARTER MOTOR RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The starter relay is an electromechanical device
that switches battery current to the pull-in coil of the
starter solenoid when ignition switch is turned to
Start position. The starter relay is located in the
Power Distribution Center (PDC) in the engine com-
partment. See PDC cover for relay identification and
location.
The starter relay is a International Standards
Organization (ISO) relay. Relays conforming to ISO
specifications have common physical dimensions, cur-
rent capacities, terminal patterns, and terminal func-
tions.
The starter relay cannot be repaired or adjusted. If
faulty or damaged, it must be replaced.
Fig. 12 STARTER R/I - 5.9L DIESEL
1 - MOUNTING BOLTS (3)
2 - STARTER MOTOR
3 - SPACER (CERTAIN TRANSMISSIONS)
Fig. 13 STARTER ELECTRICAL CONNECTORS -
5.9L DIESEL
1 - STARTER MOTOR
2 - BATTERY CABLE NUT
3 - SOLENOID NUT
4 - HARNESS ASSEMBLY
DRSTARTING 8F - 35
STARTER MOTOR (Continued)
Page 467 of 2627

OPERATION
The ISO relay consists of an electromagnetic coil, a
resistor or diode, and three (two fixed and one mov-
able) electrical contacts. The movable (common feed)
relay contact is held against one of the fixed contacts
(normally closed) by spring pressure. When electro-
magnetic coil is energized, it draws the movable con-
tact away from normally closed fixed contact, and
holds it against the other (normally open) fixed con-
tact.
When electromagnetic coil is de-energized, spring
pressure returns movable contact to normally closed
position. The resistor or diode is connected in parallel
with electromagnetic coil within relay, and helps to
dissipate voltage spikes produced when coil is de-en-
ergized.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - STARTER RELAY
The starter relay (Fig. 14) is located in Power Dis-
tribution Center (PDC). Refer to PDC cover for relay
identification and location. For complete starter relay
wiring circuit diagrams, refer to 8, Wiring Diagrams.
(1) Remove starter relay from PDC.
(2) A relay in de-energized position should have
continuity between terminals 87A and 30, and no
continuity between terminals 87 and 30. If OK, go to
Step 3. If not OK, replace faulty relay.
(3) Resistance between terminals 85 and 86 (elec-
tromagnet) should be 75 5 ohms. If OK, go to Step
4. If not OK, replace faulty relay.
(4) Connect 12V battery to terminals 85 and 86.
There should now be continuity between terminals
30 and 87, and no continuity between terminals 87A
and 30. If OK, perform Relay Circuit Test that fol-
lows. If not OK, replace faulty relay.
RELAY CIRCUIT TEST
(1) The relay common feed terminal cavity (30) is
connected to battery voltage and should be hot at all
times. If OK, go to Step 2. If not OK, repair open cir-
cuit to fuse in PDC as required.
(2) The relay normally closed terminal (87A) is
connected to terminal 30 in the de-energized position,
but is not used for this application. Go to Step 3.
(3) The relay normally open terminal (87) is con-
nected to common feed terminal (30) in the energized
position. This terminal supplies battery voltage to
starter solenoid field coils. There should be continu-
ity between cavity for relay terminal 87 and starter
solenoid terminal at all times. If OK, go to Step 4. If
not OK, repair open circuit to starter solenoid as
required.(4) The coil battery terminal (86) is connected to
electromagnet in relay. It is energized when ignition
switch is held in Start position. On vehicles with
manual transmission, clutch pedal must be fully
depressed for this test. Check for battery voltage at
cavity for relay terminal 86 with ignition switch in
Start position, and no voltage when ignition switch is
released to On position. If OK, go to Step 5. If not
OK with automatic transmission, check for open or
short circuit to ignition switch and repair, if required.
If circuit to ignition switch is OK, refer toIgnition
Switch and Key Lock Cylinder. If not OK with a
manual transmission, check circuit between relay
and clutch pedal position switch for open or a short.
If circuit is OK, refer toClutch Pedal Position
Switchin 6 , Clutch.
(5) The coil ground terminal (85) is connected to
the electromagnet in the relay. On vehicles with
manual transmission, it is grounded at all times. On
vehicles with automatic transmission, it is grounded
through park/neutral position switch only when gear-
shift selector lever is in Park or Neutral positions.
Check for continuity to ground at cavity for relay ter-
minal 85. If not OK with manual transmission,
repair circuit to ground as required. If not OK with
automatic transmission, check for pen or short circuit
to park/neutral position switch and repair, if
required. If circuit to park/neutral position switch is
OK, refer toPark/Neutral Position Switchin 21,
Transmission.
Fig. 14 TYPE 1 RELAY
TERMINAL LEGEND
NUMBER IDENTIFICATION
30 COMMON FEED
85 COIL GROUND
86 COIL BATTERY
87 NORMALLY OPEN
87A NORMALLY CLOSED
8F - 36 STARTINGDR
STARTER MOTOR RELAY (Continued)
Page 471 of 2627

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REAR WINDOW
DEFOGGER SYSTEM
For circuit descriptions and diagrams, refer to Rear
Window Defogger in Wiring Diagrams. The operation
of the electrically heated rear window defogger sys-
tem can be confirmed in one of the following man-
ners:
1. Turn the ignition switch to the On position.
While monitoring the instrument panel voltmeter, set
the defogger switch in the On position. When the
defogger switch is turned On, a distinct voltmeter
needle deflection should be noted.
2. Turn the ignition switch to the On position. Set
the defogger switch in the On position. The rear win-
dow defogger operation can be checked by feeling the
rear window or outside rear view mirror glass. A dis-
tinct difference in temperature between the grid lines
and the adjacent clear glass or the mirror glass can
be detected within three to four minutes of operation.
3. Using a 12-volt DC voltmeter, contact the rear
glass heating grid terminal A (right side) with the
negative lead, and terminal B (left side) with the pos-
itive lead (Fig. 1). The voltmeter should read battery
voltage.
The above checks will confirm system operation.
Illumination of the defogger switch indicator lamp
means that there is electrical current available at the
output of the rear window defogger logic and timer
circuitry, but does not confirm that the electrical cur-
rent is reaching the rear glass heating grid lines.
If the defogger system does not operate, the prob-
lem should be isolated in the following manner:(1) Confirm that the ignition switch is in the On
position.
(2) Make sure that the rear glass heating grid feed
and ground wires are connected to the glass. Confirm
that the ground wire has continuity to ground.
(3) Check the fuses in the power distribution cen-
ter (PDC) and in the junction block. The fuses must
be tight in their receptacles and all electrical connec-
tions must be secure.
When the above steps have been completed and the
rear glass heating grid is still inoperative, one or
more of the following could be faulty:
²Rear window switch in the A/C-heater control..
²Rear window grid lines (all grid lines would
have to be broken or one of the feed wires discon-
nected for the entire system to be inoperative).
If setting the defogger switch to the On position
produces a severe voltmeter deflection, check for a
short circuit between the rear window switch defog-
ger relay output and the rear glass heating grid.
REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER
RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The rear window defogger relay (Fig. 2) is a Inter-
national Standards Organization (ISO) micro-relay.
Relays conforming to the ISO specifications have
common physical dimensions, current capacities, ter-
minal patterns, and terminal functions. The ISO
micro-relay terminal functions are the same as a con-
ventional ISO relay. However, the ISO micro-relay
terminal pattern (or footprint) is different, the cur-
rent capacity is lower, and the physical dimensions
are smaller than those of the conventional ISO relay.
The rear window defogger relay is located in the
power distribution center (PDC) in the engine com-
partment. Refer to the PDC label for rear window
defogger relay identification and location.
The black, molded plastic case is the most visible
component of the rear window defogger relay. Five
male spade-type terminals extend from the bottom of
the base to connect the relay to the vehicle electrical
system, and the ISO designation for each terminal is
molded into the base adjacent to each terminal. The
ISO terminal designations are as follows:
²30 (Common Feed)- This terminal is con-
nected to the movable contact point of the relay.
²85 (Coil Ground)- This terminal is connected
to the ground feed side of the relay control coil.
²86 (Coil Battery)- This terminal is connected
to the battery feed side of the relay control coil.
²87 (Normally Open)- This terminal is con-
nected to the normally open fixed contact point of the
relay.
Fig. 1 Grid Line Test - Typical
1 - VIEW FROM INSIDE VEHICLE
2 - REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER
3 - BUS BARS
4 - VOLTAGE FEED (A)
5 - VOLTMETER
6 - MID-POINT (C)
7 - PICK-UP LEADS
8 - GROUND (B)
8G - 2 HEATED GLASSDR
HEATED GLASS (Continued)
Page 472 of 2627

²87A (Normally Closed)- This terminal is con-
nected to the normally closed fixed contact point of
the relay.
The rear window defogger relay cannot be adjusted
or repaired. If the relay is damaged or faulty, it must
be replaced.
OPERATION
The rear window defogger relay is an electrome-
chanical switch that uses a low current input from
the integrated power module (IPM) to control the
high current output to the rear window defogger
grid. The movable common feed contact point is held
against the fixed normally closed contact point by
spring pressure. When the relay coil is energized, an
electromagnetic field is produced by the coil wind-
ings. This electromagnetic field draws the movable
relay contact point away from the fixed normally
closed contact point, and holds it against the fixed
normally open contact point. When the relay coil is
de-energized, spring pressure returns the movable
contact point back against the fixed normally closed
contact point. The resistor or diode is connected in
parallel with the relay coil in the relay, and helps to
dissipate voltage spikes and electromagnetic interfer-
ence that can be generated as the electromagnetic
field of the relay coil collapses.
The rear window defogger relay terminals are con-
nected to the vehicle electrical system through a
receptacle in the IPM. The inputs and outputs of the
rear window defogger relay include:
²The common feed terminal (30) receives a bat-
tery current input from fuse 27 (15 amp) in the IPM
through a fused B(+) circuit at all times.²The coil ground terminal (87) receives a ground
input from the A/C-heater control when the A/C-
heater control electronically pulls the control circuit
to ground.
²The coil battery terminal (85) receives a battery
current input from fuse 36 (10 amp) in the IPM
through a fused B(+) circuit only when the ignition
switch is in the Run position.
²The normally open terminal (86) provides a bat-
tery current output to the rear window defogger and
heated power mirrors (when equipped) through the
relay output circuit only when the rear window
defogger relay coil is energized.
²The normally closed terminal (87A) is not con-
nected to any circuit in this application, but provides
a battery current output only when the rear window
defogger relay coil is de-energized.
The rear window defogger relay cannot be repaired
and, if faulty or damaged, it must be replaced. Refer
to the appropriate wiring information for diagnosis
and testing of the micro-relay and for complete rear
window defogger system wiring diagrams.
REMOVAL
(1)Disconnect and isolate the negative battery cable.
(2) Remove the cover from the integrated power
module (IPM) (Fig. 3).
(3) Refer to the fuse and relay layout map on the
inner surface of the IPM cover for rear window defog-
ger relay identification and location.
(4) Remove the rear window defogger relay from
the IPM.
Fig. 2 Rear Window Defogger Relay
1 - RELAY TERMINALS
2 - RELAY CAVITIES
Fig. 3 Integrated Power Module (IPM)
1 - BATTERY
2 - INTEGRATED POWER MODULE (IPM)
DRHEATED GLASS 8G - 3
REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER RELAY (Continued)
Page 488 of 2627
IGNITION CONTROL
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
IGNITION CONTROL
DESCRIPTION..........................1
SPECIFICATIONS
SPECIFICATIONS - TORQUE - IGNITION....3
ENGINE FIRING ORDER - 3.7L V-6.........4
ENGINE FIRING ORDER ± 4.7L V-8........4
FIRING ORDER / CABLE ROUTING ± 5.7L
V-8 ENGINE...........................4
SPARK PLUG CABLE RESISTANCE........4
SPARK PLUGS........................4
IGNITION COIL RESISTANCE - 3.7L V-6.....5
IGNITION COIL RESISTANCE - 4.7L V-8.....5
IGNITION COIL RESISTANCE - 5.7L V-8.....5
IGNITION TIMING......................5
AUTOMATIC SHUT DOWN RELAY
DESCRIPTION - PCM OUTPUT.............5
OPERATION
OPERATION - PCM OUTPUT.............5
OPERATION - ASD SENSE - PCM INPUT....5
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ASD AND FUEL
PUMP RELAYS........................5
REMOVAL.............................6
INSTALLATION..........................6
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
DESCRIPTION..........................7
OPERATION............................7
REMOVAL.............................9
INSTALLATION.........................10IGNITION COIL
DESCRIPTION.........................11
OPERATION...........................12
REMOVAL.............................13
INSTALLATION.........................14
KNOCK SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................14
OPERATION...........................14
REMOVAL.............................15
INSTALLATION.........................15
SPARK PLUG
DESCRIPTION.........................17
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SPARK PLUG
CONDITIONS.........................17
REMOVAL.............................19
CLEANING
CLEANING AND ADJUSTMENT...........20
INSTALLATION.........................20
IGNITION COIL CAPACITOR
DESCRIPTION.........................21
OPERATION...........................21
REMOVAL.............................21
INSTALLATION.........................21
SPARK PLUG CABLE
DESCRIPTION.........................21
OPERATION...........................21
REMOVAL.............................22
INSTALLATION.........................22
IGNITION CONTROL
DESCRIPTION
The ignition system is controlled by the Powertrain
Control Module (PCM) on all engines.
3.7L V-6 ENGINE
The 3.7L V-6 engine uses a separate ignition coil
for each cylinder. The one-piece coil bolts directly to
the cylinder head. Rubber boots seal the secondary
terminal ends of the coils to the top of all 6 spark
plugs. A separate electrical connector is used for each
coil.
Because of coil design, spark plug cables (second-
ary cables) are not used. A distributor is not used
with the 3.7L engine.
Two knock sensors (one for each cylinder bank) are
used to help control spark knock.The Auto Shutdown (ASD) relay provides battery
voltage to each ignition coil.
The ignition system consists of:
²6 Spark Plugs
²6 Separate Ignition Coils
²2 Knock Sensors
²Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
²Also to be considered part of the ignition system
are certain inputs from the Crankshaft Position,
Camshaft Position, Throttle Position, 2 knock and
MAP Sensors
4.7L V-8 ENGINE
The 4.7L V-8 engine uses a separate ignition coil
for each cylinder. The one-piece coil bolts directly to
the cylinder head. Rubber boots seal the secondary
terminal ends of the coils to the top of all 8 spark
plugs. A separate electrical connector is used for each
coil.
DRIGNITION CONTROL 8I - 1
Page 489 of 2627

Because of coil design, spark plug cables (second-
ary cables) are not used. A distributor is not used
with the 4.7L engine.
Two knock sensors (one for each cylinder bank) are
used to help control spark knock.
The Auto Shutdown (ASD) relay provides battery
voltage to each ignition coil.
The ignition system consists of:
²8 Spark Plugs
²8 Separate Ignition Coils
²2 Knock Sensors
²Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
²Also to be considered part of the ignition system
are certain inputs from the Crankshaft Position,
Camshaft Position, Throttle Position, 2 knock and
MAP Sensors
5.7L V-8 ENGINE
For additional information, also refer to Igni-
tion Coil Description and Operation.
The 5.7L V-8 engine is equipped with 16 spark
plugs. Two plugs are used for each cylinder. The 5.7L
is also equipped with 8 separate and independent
ignition coils. The one-piece coil bolts directly to the
cylinder head cover and attaches the coils secondary
output terminal directly to a spark plug using a rub-
ber boot seal. Each coil is also equipped with a sec-
ond output terminal. This second terminal connects a
conventional spark plug cable directly to a spark
plug on the opposite cylinder bank. A separate pri-
mary electrical connector is used for each coil.
Eight conventional spark plug cables are used with
the 5.7L. These cables connect a coil on one cylinder
bank, directly to a spark plug on the opposite cylin-
der bank. The cables are placed and routed in a spe-
cial plastic loom to keep them separated. This loom is
clipped to the intake manifold. To prevent a miss-
match of cables, a corresponding spark plug / coil
number is displayed on each plug cable: 1/6, 2/3, 4/7
and 5/8. These numbers can also be found on the top
of the intake manifold to the right of the throttle
body (Fig. 1).Two knock sensors (one for each cylinder bank) are
used to help control spark knock.
The 5.7L engine will not use a conventional distrib-
utor.
The ignition system consists of:
²16 Spark Plugs (2 per cylinder)
²8 Separate, Dual-Secondary Output, Ignition
Coils
²2 Knock Sensors
²8 Secondary Ignition Cables
²Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
²Also to be considered part of the ignition system
are certain inputs from the Crankshaft Position,
Camshaft Position, Throttle Position, 2 knock and
MAP Sensors
Fig. 1 FIRING ORDER / CABLE ROUTING - 5.7L V-8
ENGINE
1 - TOP OF INTAKE MANIFOLD
2 - CYLINDER FIRING ORDER (IGNITION COIL NUMBER)
3 - CORRESPONDING SPARK PLUG NUMBER
8I - 2 IGNITION CONTROLDR
IGNITION CONTROL (Continued)
Page 490 of 2627
SPECIFICATIONS
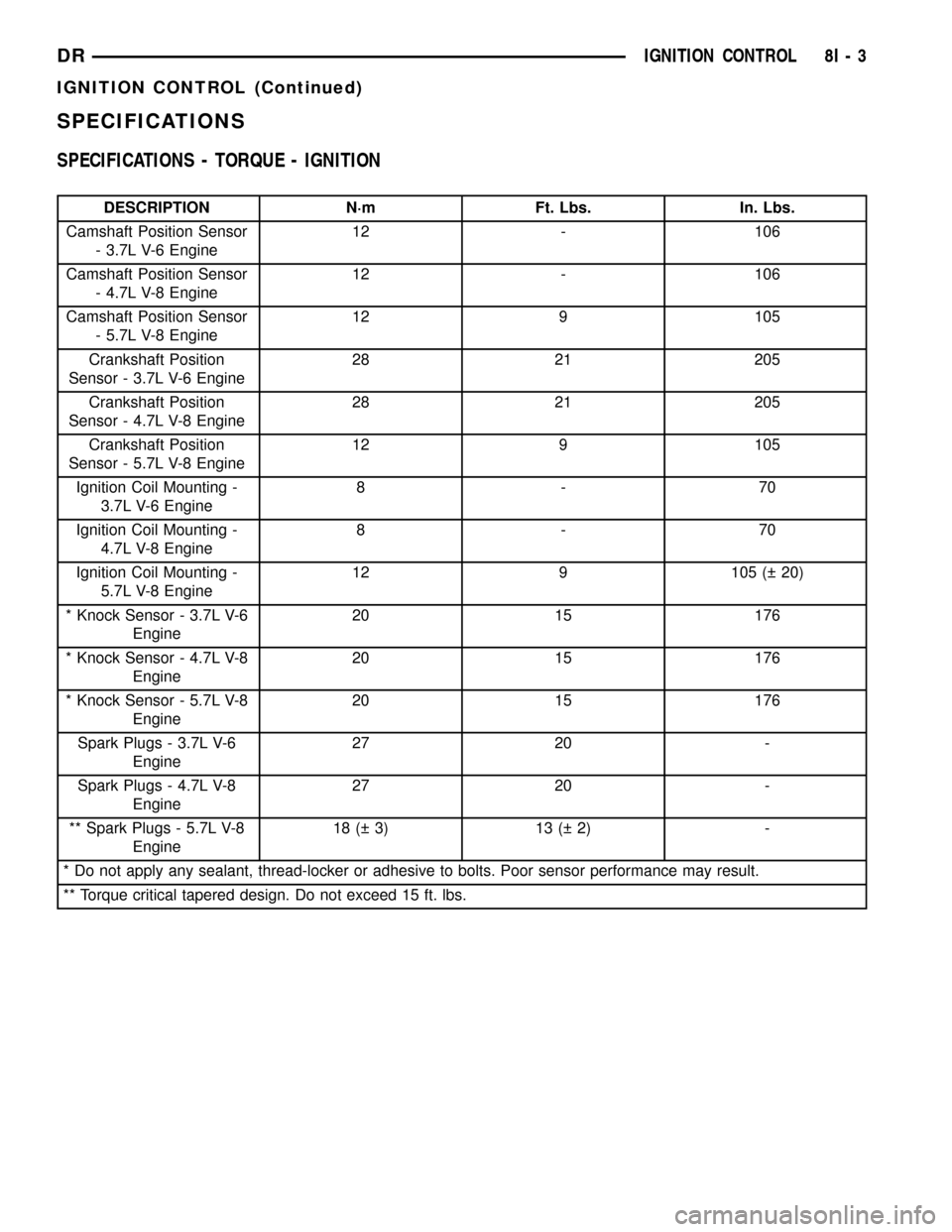
SPECIFICATIONS - TORQUE - IGNITION
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Camshaft Position Sensor
- 3.7L V-6 Engine12 - 106
Camshaft Position Sensor
- 4.7L V-8 Engine12 - 106
Camshaft Position Sensor
- 5.7L V-8 Engine12 9 105
Crankshaft Position
Sensor - 3.7L V-6 Engine28 21 205
Crankshaft Position
Sensor - 4.7L V-8 Engine28 21 205
Crankshaft Position
Sensor - 5.7L V-8 Engine12 9 105
Ignition Coil Mounting -
3.7L V-6 Engine8-70
Ignition Coil Mounting -
4.7L V-8 Engine8-70
Ignition Coil Mounting -
5.7L V-8 Engine12 9 105 ( 20)
* Knock Sensor - 3.7L V-6
Engine20 15 176
* Knock Sensor - 4.7L V-8
Engine20 15 176
* Knock Sensor - 5.7L V-8
Engine20 15 176
Spark Plugs - 3.7L V-6
Engine27 20 -
Spark Plugs - 4.7L V-8
Engine27 20 -
** Spark Plugs - 5.7L V-8
Engine18 ( 3) 13 ( 2) -
* Do not apply any sealant, thread-locker or adhesive to bolts. Poor sensor performance may result.
** Torque critical tapered design. Do not exceed 15 ft. lbs.
DRIGNITION CONTROL 8I - 3
IGNITION CONTROL (Continued)
Page 491 of 2627
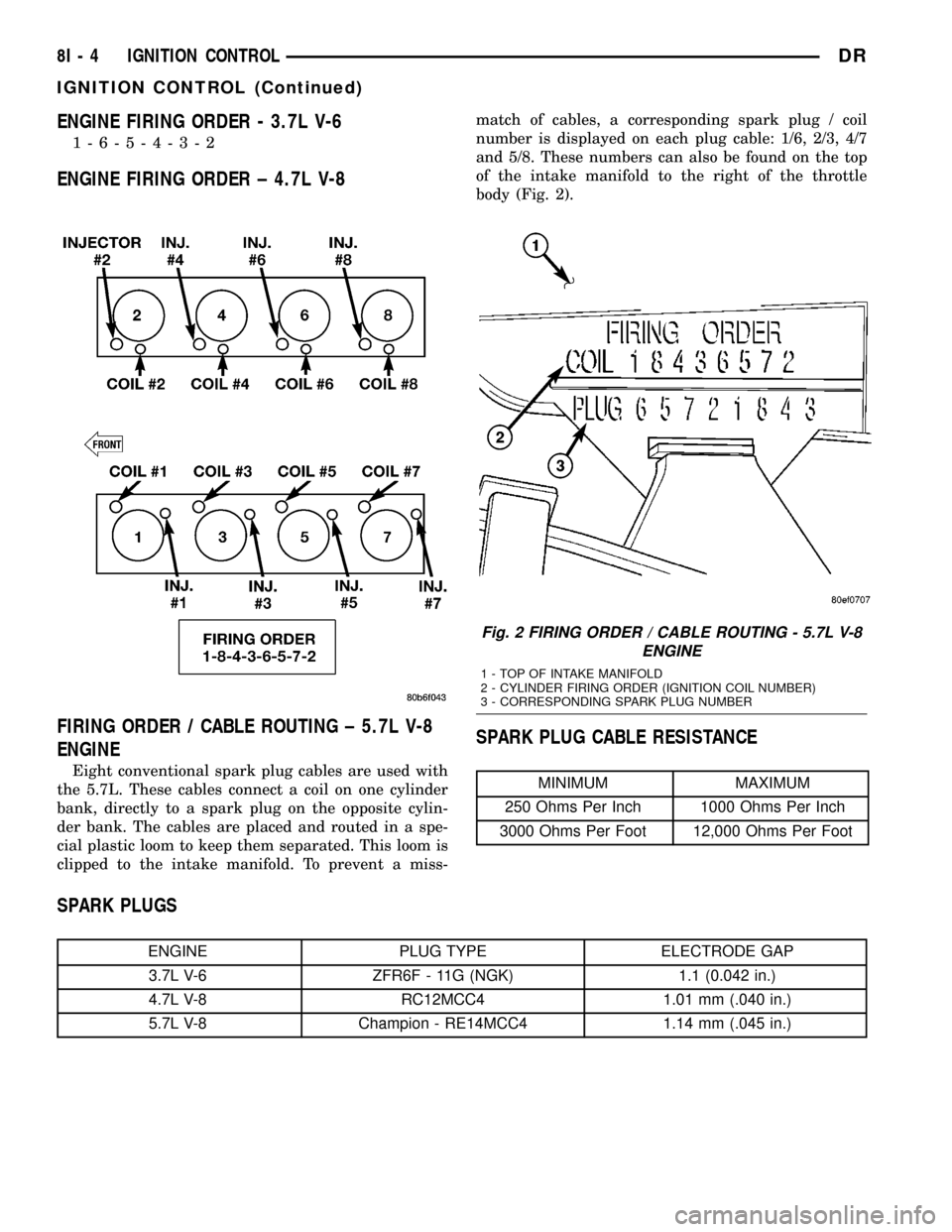
ENGINE FIRING ORDER - 3.7L V-6
1-6-5-4-3-2
ENGINE FIRING ORDER ± 4.7L V-8
FIRING ORDER / CABLE ROUTING ± 5.7L V-8
ENGINE
Eight conventional spark plug cables are used with
the 5.7L. These cables connect a coil on one cylinder
bank, directly to a spark plug on the opposite cylin-
der bank. The cables are placed and routed in a spe-
cial plastic loom to keep them separated. This loom is
clipped to the intake manifold. To prevent a miss-match of cables, a corresponding spark plug / coil
number is displayed on each plug cable: 1/6, 2/3, 4/7
and 5/8. These numbers can also be found on the top
of the intake manifold to the right of the throttle
body (Fig. 2).
SPARK PLUG CABLE RESISTANCE
MINIMUM MAXIMUM
250 Ohms Per Inch 1000 Ohms Per Inch
3000 Ohms Per Foot 12,000 Ohms Per Foot
SPARK PLUGS
ENGINE PLUG TYPE ELECTRODE GAP
3.7L V-6 ZFR6F - 11G (NGK) 1.1 (0.042 in.)
4.7L V-8 RC12MCC4 1.01 mm (.040 in.)
5.7L V-8 Champion - RE14MCC4 1.14 mm (.045 in.)
Fig. 2 FIRING ORDER / CABLE ROUTING - 5.7L V-8
ENGINE
1 - TOP OF INTAKE MANIFOLD
2 - CYLINDER FIRING ORDER (IGNITION COIL NUMBER)
3 - CORRESPONDING SPARK PLUG NUMBER
8I - 4 IGNITION CONTROLDR
IGNITION CONTROL (Continued)