steering wheel DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.G Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1998, Model line: RAM 1500, Model: DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.GPages: 2627
Page 68 of 2627

(6) Position the hub spacer (Fig. 8) and brake
shield (Fig. 9) on bolts just installed in knuckle.
NOTE: If the vehicle is equipped with a wheel speed
sensor the brake shield must be positioned on the
hub bearing (Fig. 10).
(7) Align the rotor hub with the drive shaft and
start the shaft into the rotor hub splines.NOTE: Position wheel speed sensor wire at the top
of the knuckle if equipped.
(8) Align the bolt holes in the hub bearing flange
with the bolts installed in the knuckle. Then thread
the bolts into the bearing flange far enough to hold
the assembly in place.
(9) Install the remaining bolts. Tighten the hub/
bearing bolts to 202 N´m (149 ft. lbs.
(10) Install the washer and axle nut and tighten a
beginning torque of 179 N´m (132 ft. lbs.).
(11) Rotate the axle 5 to 10 times to seat the hub
bearing.
(12) Tighten to a final torque of 356 N´m (263 ft.
lbs.).
(13) Align the axle nut to the next forward cotter
pin hole and install a new cotter pin in the axle nut.
(14) Install the brake caliper, (Refer to 5 -
BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/DISC
BRAKE CALIPERS - INSTALLATION).
(15) Install the sensor wire to the steering knuckle
and frame and if equipped. Connect the wheel speed
sensor wire under the hood.
(16) Install the wheel and tire assemblies, (Refer
to 22 - TIRES/WHEELS/WHEELS - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
(17) Remove the support and lower the vehicle.
(18) Apply the brakes several times to seat the
brake shoes and caliper piston. Do not move the vehi-
cle until a firm brake pedal is obtained.
Fig. 8 Hub Spacer
1 - ROTOR HUB BOLTS
2 - HUB SPACER (POSITION FLAT TO REAR)
3 - APPLY ANTI-SEIZE COMPOUND TO SPLINES
Fig. 9 Brake Shield
1 - BRAKE SHIELD
2 - HUB BEARING BOLTS
3 - STEERING KNUCKLE
Fig. 10 Brake Shield With Wheel Speed Sensor
1 - WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
2 - HUB BEARING
3 - SHIELD
DRFRONT - LINK/COIL 2 - 33
HUB / BEARING (Continued)
Page 101 of 2627

HALF SHAFT
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
HALF SHAFT
CAUTION.............................20
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING................20
REMOVAL.............................20
INSTALLATION.........................21
SPECIFICATIONS.......................21
SPECIAL TOOLS.......................21CV JOINT-OUTER
REMOVAL.............................22
INSTALLATION.........................23
CV JOINT-INNER
REMOVAL.............................25
INSTALLATION.........................25
HALF SHAFT
CAUTION
CAUTION:: Never grasp half shaft assembly by the
boots. This may cause the boot to pucker or crease
and reduce the service life of the boot.
Avoid over angulating or stroking the C/V joints
when handling the half shaft.
Half shafts exposed to battery acid, transmission
fluid, brake fluid, differential fluid or gasoline may
cause the boots to deteriorate. Failure to heed cau-
tion may result in damage.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
Check inboard and outboard C/V joint for leaking
grease. This is a sign of boot or boot clamp damage.
NOISE/VIBRATION IN TURNS
A clicking noise or vibration in turns could be
caused by a damaged outer C/V or inner tripod joint
seal boot or seal boot clamps. This will result in the
loss/contamination of the joint grease, resulting in
inadequate lubrication of the joint. Noise could also
be caused by another component of the vehicle com-
ing in contact with the half shafts.
CLUNKING NOISE DURING ACCELERATION
This noise may be a damaged or worn C/V joint. A
torn boot or loose/missing clamp on the inner/outer
joint which has allowed the grease to be lost will
damage the C/V joint.
SHUDDER/VIBRATION DURING ACCELERATION
This could be a worn/damaged inner tripod joint or
a sticking tripod joint. Improper wheel alignment
may also cause a shudder or vibration.
VIBRATION AT HIGHWAY SPEEDS
This problem could be a result of out of balance
front tires or tire/wheel runout. Foreign material
(mud, etc.) packed on the backside of the wheel(s)
will also cause a vibration.
REMOVAL
(1) With vehicle in neutral, position vehicle on
hoist.
(2) Remove half shaft hub nut.
(3) Remove brake caliper and rotor.
(4) Position hydraulic jack under lower suspension
arm and raise jack to unload rebound bumper.
(5) Remove lower shock absorber bolt.
(6) Remove upper ball joint nut and seperate ball
with Remover 8677 (Fig. 1).
(7) Disengage inner C/V joint from axle shaft with
two pry bars between the C/V housing and axle hous-
ing.
Fig. 1 UPPER BALL JOINT SEPARATION
1 - UPPER CONTROL ARM
2 - REMOVER
3 - STEERING KNUCKLE
3 - 20 HALF SHAFTDR
Page 138 of 2627
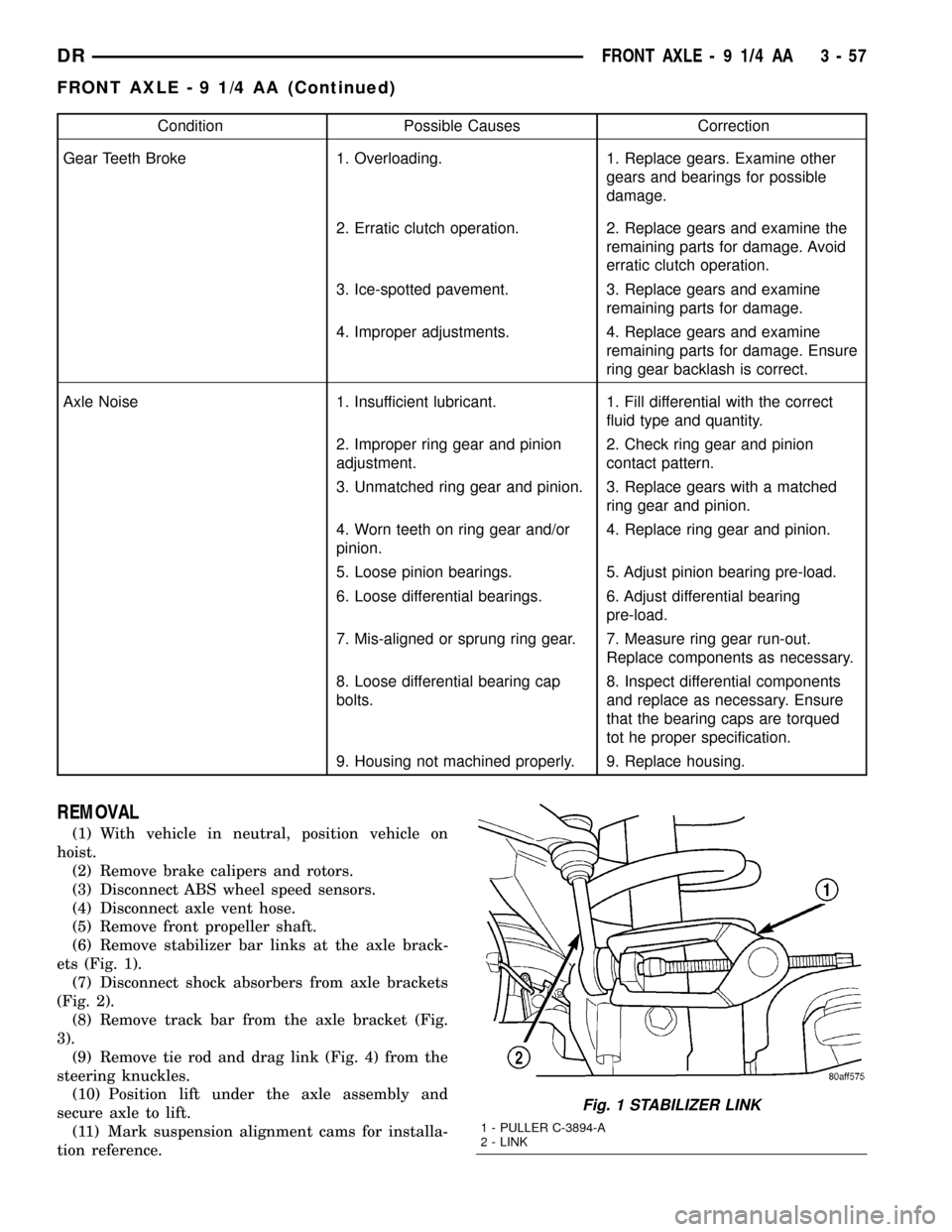
Condition Possible Causes Correction
Gear Teeth Broke 1. Overloading. 1. Replace gears. Examine other
gears and bearings for possible
damage.
2. Erratic clutch operation. 2. Replace gears and examine the
remaining parts for damage. Avoid
erratic clutch operation.
3. Ice-spotted pavement. 3. Replace gears and examine
remaining parts for damage.
4. Improper adjustments. 4. Replace gears and examine
remaining parts for damage. Ensure
ring gear backlash is correct.
Axle Noise 1. Insufficient lubricant. 1. Fill differential with the correct
fluid type and quantity.
2. Improper ring gear and pinion
adjustment.2. Check ring gear and pinion
contact pattern.
3. Unmatched ring gear and pinion. 3. Replace gears with a matched
ring gear and pinion.
4. Worn teeth on ring gear and/or
pinion.4. Replace ring gear and pinion.
5. Loose pinion bearings. 5. Adjust pinion bearing pre-load.
6. Loose differential bearings. 6. Adjust differential bearing
pre-load.
7. Mis-aligned or sprung ring gear. 7. Measure ring gear run-out.
Replace components as necessary.
8. Loose differential bearing cap
bolts.8. Inspect differential components
and replace as necessary. Ensure
that the bearing caps are torqued
tot he proper specification.
9. Housing not machined properly. 9. Replace housing.
REMOVAL
(1) With vehicle in neutral, position vehicle on
hoist.
(2) Remove brake calipers and rotors.
(3) Disconnect ABS wheel speed sensors.
(4) Disconnect axle vent hose.
(5) Remove front propeller shaft.
(6) Remove stabilizer bar links at the axle brack-
ets (Fig. 1).
(7) Disconnect shock absorbers from axle brackets
(Fig. 2).
(8) Remove track bar from the axle bracket (Fig.
3).
(9) Remove tie rod and drag link (Fig. 4) from the
steering knuckles.
(10) Position lift under the axle assembly and
secure axle to lift.
(11) Mark suspension alignment cams for installa-
tion reference.
Fig. 1 STABILIZER LINK
1 - PULLER C-3894-A
2 - LINK
DRFRONT AXLE - 9 1/4 AA 3 - 57
FRONT AXLE - 9 1/4 AA (Continued)
Page 140 of 2627

(7) Connect track bar to the axle bracket and
install the bolt. Do not tighten at this time.
(8) Install shock absorber and tighten bolts to 121
N´m (89 ft. lbs.).
(9) Install stabilizer bar link to the axle bracket.
Tighten the nut to 68 N´m (50 ft. lbs.).
(10) Install drag link and tie rod to the steering
knuckles and tighten the nuts to 108 N´m (80 ft.
lbs.).
(11) Install ABS wheel speed sensors.
(12) Install rotors and brake calipers.
(13) Connect the axle vent hose.
(14) Install front propeller shaft.
(15) With vehicle on the ground, tighten upper
suspension arm nuts at axle to 149 N´m (110 ft. lbs.).
Tighten upper suspension arm nuts at frame to 149
N´m (110 ft. lbs.).
(16) With vehicle on the ground, tighten lower sus-
pension arm nuts at axle to 190 N´m (140 ft. lbs.).
Tighten the lower suspension arm nuts at frame to
190 N´m (140 ft. lbs.).
(17) Tighten track bar bolt at the axle bracket to
176 N´m (130 ft. lbs.).
(18) Check front wheel alignment.
ADJUSTMENTS
Ring and pinion gears are supplied as matched
sets. Compensation for pinion depth variance is
achieved with a select shim. located between the rear
pinion bearing and pinion gear head.
PINION DEPTH MEASUREMENT AND ADJUSTMENT
Measurements are taken with pinion bearing cups
and pinion bearings installed in the housing. Take
measurements with Pinion Gauge Set and Dial Indi-
cator C-3339 (Fig. 6).
(1) Assemble Pinion Height Block 6739, Pinion
Block 8878 and rear pinion bearing onto Screw 6741
(Fig. 6).
(2) Insert assembled height gauge components,
rear bearing and screw into the housing through pin-
ion bearing cups (Fig. 7).
(3) Install front pinion bearing and Cone-Nut 6740
onto the screw. Tighten cone-nut until Torque To
Rotate the screw is 1.7-2.26 N´m (15-20 in. lbs.).
(4) Place Arbor Disc 8289 on Arbor D-115-3 in posi-
tion in the housing side bearing cradles (Fig. 8).
(5) Install differential bearing caps on arbor discs
and snug the bearing cap bolts. Then cross tighten
cap bolts to 85 N´m (63 ft. lbs.).
NOTE: Arbor should rotate freely in the arbor disc.
(6) Assemble Dial Indicator C-3339 into Scooter
Block D-115-2 and secure set screw.(7) Position Scooter Block/Dial Indicator flush on
the pinion height block. Hold scooter block and zero
the dial indicator.
Fig. 6 PINION GEAR DEPTH GAUGE TOOLS
1 - DIAL INDICATOR
2 - ARBOR
3 - PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
4 - CONE
5 - SCREW
6 - PINION BLOCK
7 - SCOOTER BLOCK
8 - ARBOR DISC
Fig. 7 PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
1. PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
2. PINION BLOCK
DRFRONT AXLE - 9 1/4 AA 3 - 59
FRONT AXLE - 9 1/4 AA (Continued)
Page 148 of 2627

AXLE SHAFTS
REMOVAL
(1) With the vehicle in neutral, position vehicle on
hoist.
(2) Remove brake caliper, rotor and ABS wheel
speed sensor if equipped.
(3) Remove axle shaft cotter pin, hub nut and
washer (Fig. 19).(4) Remove four hub bearing bolts (Fig. 20) from
the back of the steering knuckle.
PINION INSTALLER 8982
FLANGE PULLER 8992
BRIDGE 938
Fig. 19 AXLE NUT
1 - AXLE NUT
2 - AXLE
3 - COTTER PIN
Fig. 20 HUB BEARING BOLTS
1 - STUB SHAFT
2 - BEARING BOLTS
3 - AXLE SHAFT
DRFRONT AXLE - 9 1/4 AA 3 - 67
FRONT AXLE - 9 1/4 AA (Continued)
Page 150 of 2627

ASSEMBLY
(1) Pack the bearing caps 1/3 full of wheel bearing
lubricant. Apply extreme pressure (EP), lithium-base
lubricant to aid in installation.
(2) Position the spider in the yoke. Insert the seals
and bearings. Tap the bearing caps into the yoke
bores far enough to hold the spider in position.
(3) Place the socket (driver) against one bearing
cap. Position the yoke with the socket in a vise.
(4) Tighten the vise to force the bearing caps into
the yoke. Force the caps enough to install the retain-
ing clips.
(5) Install the bearing cap retaining clips.
(6) Install axle shaft.
INSTALLATION
(1) Clean axle shaft and apply a thin film of
Mopar Wheel Bearing Grease to the shaft splines
and hub bore.
(2) Install axle shaft through the steering knuckle
and into the differential side gears (Fig. 24).
(3) Install hub bearing in the knuckle.
(4) Install hub bearing bolts and tighten to 202
N´m (149 ft. lbs.).
(5) Install ABS wheel speed sensor, brake rotor
and caliper.
(6) Install axle washer and nut. Tighten axle nut
to 179 N´m (132 ft. lbs.).
(7) Rotate axle several 5 to 10 times to seat the
wheel bearing.
(8) Tighten axle nut to final torque of 356 N´m
(263 ft. lbs.).
(9) Align nut to next cotter pin hole and install
new cotter pin.
AXLE SHAFT SEALS
REMOVAL
(1) Remove hub bearings and axle shafts.
(2) Remove differential from differential housing.
(3) Remove differential bearing adjusters (Fig. 25).
(4) Remove axle seals (Fig. 26) located behind
adjusters with Receiver 8498 and Extractor 6310.
(5) Install Receiver 8498 into the adjuster bore.
Fig. 24 AXLE SHAFT
1 - AXLE YOKE
2 - AXLE SHAFT
3 - KNUCKLE
Fig. 25 ADJUSTERS
1 - DIFFERENTIAL CASE BEARING ADJUSTERS
2 - DIFFERENTIAL HOUSING
Fig. 26 AXLE SHAFT SEAL
1 - ADJUSTER THREADS
2 - SEAL
DRFRONT AXLE - 9 1/4 AA 3 - 69
AXLE SHAFTS (Continued)
Page 251 of 2627

FLUID RESERVOIR
REMOVAL.............................23
INSTALLATION.........................24
BRAKE JUNCTION BLOCK
REMOVAL.............................24
INSTALLATION.........................24
MASTER CYLINDER
DESCRIPTION.........................24
OPERATION...........................25
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - MASTER
CYLINDER/POWER BOOSTER...........25
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MASTER
CYLINDER BLEEDING..................26
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - ALL EXCEPT HYDROBOOST . . . 26
REMOVAL - HYDROBOOST.............26
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - ALL EXCEPT
HYDROBOOST.......................27
INSTALLATION - HYDROBOOST..........27
PEDAL
DESCRIPTION.........................28
OPERATION...........................28
REMOVAL.............................28
INSTALLATION.........................28
POWER BRAKE BOOSTER
DESCRIPTION.........................29
OPERATION...........................29
REMOVAL.............................29
INSTALLATION.........................29
HYDRO-BOOST BRAKE BOOSTER
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC
BOOSTER...........................30
STANDARD PROCEDURE - BLEEDING......31
REMOVAL.............................31
INSTALLATION.........................32
ROTORS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DISC BRAKE ROTOR..................32
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - FRONT....................33
REMOVAL - REAR.....................34REMOVAL - REAR DUAL WHEELS........34
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - FRONT................34
INSTALLATION - REAR.................34
INSTALLATION - REAR DUAL WHEELS....35
SUPPORT PLATE
REMOVAL.............................35
INSTALLATION.........................36
PARKING BRAKE
DESCRIPTION.........................36
OPERATION...........................36
CABLES
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - FRONT PARKING BRAKE
CABLE..............................36
REMOVAL - REAR PARK BRAKE CABLE . . . 37
REMOVAL - RIGHT REAR CABLE.........37
REMOVAL - LEFT REAR CABLE..........38
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - FRONT PARKING BRAKE
CABLE..............................38
INSTALLATION - REAR PARK BRAKE
CABLE..............................38
INSTALLATION - RIGHT REAR CABLE.....38
INSTALLATION - LEFT REAR CABLE......39
SHOES
REMOVAL.............................39
CLEANING - REAR DRUM IN HAT BRAKE....39
INSPECTION - REAR DRUM IN HAT BRAKE . . 39
INSTALLATION.........................40
ADJUSTMENTS
ADJUSTMENT - PARKING BRAKE SHOES . . 41
ADJUSTMENT - WITH ADJUSTING TOOL . . . 42
PEDAL
REMOVAL.............................42
INSTALLATION.........................42
CABLE TENSIONER
ADJUSTMENTS
ADJUSTMENT........................43
RELEASE HANDLE
REMOVAL.............................44
INSTALLATION.........................44
BRAKES - BASE
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BASE BRAKE
SYSTEM
Base brake components consist of the brake pads,
calipers, brake drum in hat rotor in the rear, rotors,
brake lines, master cylinder, booster, and parking
brake components.
Brake diagnosis involves determining if the prob-
lem is related to a mechanical, hydraulic, or vacuum
operated component.
The first diagnosis step is the preliminary check.
PRELIMINARY BRAKE CHECK
(1) Check condition of tires and wheels. Damaged
wheels and worn, damaged, or underinflated tires
can cause pull, shudder, vibration, and a condition
similar to grab.
(2) If complaint was based on noise when braking,
check suspension components. Jounce front and rear
of vehicle and listen for noise that might be caused
by loose, worn or damaged suspension or steering
components.
(3) Inspect brake fluid level and condition. Note
that the brake reservoir fluid level will decrease in
proportion to normal lining wear.Also note that
brake fluid tends to darken over time. This is
5 - 2 BRAKES - BASEDR
Page 254 of 2627

of chatter are out-of-tolerance rotors, brake lining not
securely attached to the shoes, loose wheel bearings
and contaminated brake lining.
THUMP/CLUNK NOISE
Thumping or clunk noises during braking are fre-
quentlynotcaused by brake components. In many
cases, such noises are caused by loose or damaged
steering, suspension, or engine components. However,
calipers that bind on the slide surfaces can generate
a thump or clunk noise.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MANUAL BLEEDING
Use Mopar brake fluid, or an equivalent quality
fluid meeting SAE J1703-F and DOT 3 standards
only. Use fresh, clean fluid from a sealed container at
all times.
(1) Remove reservoir filler caps and fill reservoir.
(2) If calipers were overhauled, open all caliper
bleed screws. Then close each bleed screw as fluid
starts to drip from it. Top off master cylinder reser-
voir once more before proceeding.
(3) Attach one end of bleed hose to bleed screw
and insert opposite end in glass container partially
filled with brake fluid (Fig. 1). Be sure end of bleed
hose is immersed in fluid.
NOTE: Bleed procedure should be in this order (1)
Right rear (2) Left rear (3) Right front (4) Left front.(4) Open up bleeder, then have a helper press
down the brake pedal. Once the pedal is down close
the bleeder. Repeat bleeding until fluid stream is
clear and free of bubbles. Then move to the next
wheel.
(5) Before moving the vehicle verify the pedal is
firm and not mushy.
(6) Top off the brake fluid and install the reservoir
cap.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PRESSURE
BLEEDING
Use Mopar brake fluid, or an equivalent quality
fluid meeting SAE J1703-F and DOT 3 standards
only. Use fresh, clean fluid from a sealed container at
all times.
Follow the manufacturers instructions carefully
when using pressure equipment. Do not exceed the
tank manufacturers pressure recommendations. Gen-
erally, a tank pressure of 15-20 psi is sufficient for
bleeding.
Fill the bleeder tank with recommended fluid and
purge air from the tank lines before bleeding.
Do not pressure bleed without a proper master cyl-
inder adapter. The wrong adapter can lead to leak-
age, or drawing air back into the system.
SPECIAL TOOLS
BASE BRAKES
Fig. 1 Bleed Hose Setup
1 - BLEED HOSE
2 - FLUID CONTAINER PARTIALLY FILLED WITH FLUID
INSTALLER, BRAKE CALIPER DUST BOOT C-4340
INSTALLER, BRAKE CALIPER DUST BOOT
C-3716-A
DRBRAKES - BASE 5 - 5
BRAKES - BASE (Continued)
Page 255 of 2627

ADJUSTABLE PEDAL SWITCH
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the lower drivers side bezel (Refer to
23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/INSTRUMENT
PANEL DR SIDE BEZEL - REMOVAL).
(2) Disconnect the electrical connector from the
adjustable pedal switch.
(3) Remove the switch from the lower drivers side
bezel by squeezing the retaining clips together and
pushing the switch outwards (Fig. 2).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the switch to the lower drivers side
bezel by pushing the switch inwards seating the
retaining clips to the lower drivers side bezel.
(2) Reconnect the electrical connector to the
adjustable pedal switch.
(3) Install the lower drivers side bezel (Fig. 2)
(Refer to 23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/IN-
STRUMENT PANEL DR SIDE BEZEL - INSTALLA-
TION).
ADJUSTABLE PEDAL MOTOR
DESCRIPTION
The Adjustable Pedals System (APS) is designed to
enable the fore and aft repositioning of the brake and
accelerator pedals. This results in improved ergonom-
ics in relation to the steering wheel for taller and
shorter drivers. Being able to adjust the pedal posi-
tions also allows the driver to set steering wheel tilt
and seat position to the most comfortable position.
The position of the brake and accelerator pedals can
be adjusted without compromising safety or comfort
in actuating the pedals.
Change of pedal position is accomplished by means
of a motor driven screw. Operating the adjustable
pedal switch activates the pedal drive motor (Fig. 3).
The pedal drive motor turns a screw that changes
the position of the brake and accelerator pedals. The
pedal can be moved rearward (closer to the driver) or
forward (away from driver). The brake pedal is
moved on its drive screw to a position where the
driver feels most comfortable.
The accelerator pedal is moved at the same time
and the same distance as the brake pedal.
Neither the pedal drive motor (Fig. 3) nor drive
mechanism are subject to the mechanical stress of
brake or accelerator application.
²SYSTEM FEATURES:
²Range of Adjustment: The pedals may be
adjusted up to 3 in. (75 mm)
²Pedal Adjustment Speed: 0.5 in./sec (12.5
mm/sec)
HANDLE C-4171
CAP, MASTER CYLINDER PRESSURE BLEED 6921
GAUGE, BRAKE SAFE-SET C-3919
Fig. 2 LOWER DRIVERS SIDE BEZEL
1 - SCREWS (2)
2 - ADJUSTABLE PEDAL SWITCH (if equipped)
3 - PEDAL SWITCH ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
4 - BEZEL
5 - 6 BRAKES - BASEDR
BRAKES - BASE (Continued)
Page 262 of 2627

INSTALLATION - REAR TUBE / HOSE
ASSEMBLY
(1) Install the hose.
(2) Install the banjo bolt at the caliper (Fig. 9) and
tighten fitting bolt to 27 N´m (245 in. lbs.).
(3) Install the mounting bolt for the brake hose at
the axle (Fig. 9).
(4) Install the brake line located at the axle.
(5) Lower the vehicle and remove the support.
(6) Remove the prop rod.
(7) Bleed the brake system (Refer to 5 - BRAKES -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
INSTALLATION - FRONT BRAKE HOSE
(1) Install the hose.
(2) Install the mounting bolt for the brake hose at
the frame (Fig. 11).
(3) Install the brake hose banjo bolt at the caliper
(Fig. 10).
(4) Reinstall the wheel speed sensor wire to the
brake hose (Fig. 10).
(5) Remove the support and lower the vehicle.
(6) Remove the prop rod from the brake pedal.
(7) Bleed the brake system (Refer to 5 - BRAKES -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
BRAKE PADS/SHOES
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - FRONT
(1) Raise and support vehicle.
(2) Remove the wheel and tire assemblies.(3) Compress the caliper.
(4) Remove the caliper, (Refer to 5 - BRAKES/HY-
DRAULIC/MECHANICAL/DISC BRAKE CALIPERS
- REMOVAL).
(5) Remove the caliper by tilting the top up and off
the caliper adapter (Fig. 12).
NOTE: Do not allow brake hose to support caliper
assembly.
(6) Support and hang the caliper. (Fig. 13)
(7) Remove the inboard brake shoe from the cali-
per adapter (Fig. 14).
Fig. 11 BRAKE HOSE MOUNT DRIVERS SIDE
1 - MOUNTING BOLT
2 - WHEEL SPEED SENSOR WIRE
3 - BRAKE HOSE
Fig. 12 Caliper
1 - CALIPER
2 - CALIPER ADAPTER
Fig. 13 DISC BRAKE CALIPER - FRONT
1 - STEERING KNUCKLE
2 - DISC BRAKE CALIPER
3 - CALIPER MOUNTING ADAPTER
4 - DISC BRAKE ROTOR
DRBRAKES - BASE 5 - 13
BRAKE LINES (Continued)