FRONT HUB DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.G Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1998, Model line: RAM 1500, Model: DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.GPages: 2627
Page 282 of 2627

Position the micrometer approximately 25.4 mm (1
in.) from the rotor outer circumference for each mea-
surement.
Thickness should notvaryby more than 0.015 mm
(0.0059 in.) from point-to-point on the rotor. Machine
or replace the rotor if necessary.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - FRONT
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove the wheel and tire assembly.
(3) Remove the caliper from the steering knuckle,
(Refer to 5 - BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/DISC BRAKE CALIPERS - REMOVAL) and remove
caliper adapter assembly (Fig. 58).
NOTE: Do not allow brake hose to support caliper
adapter assembly.
(4) Remove the rotor from the hub/bearing wheel
studs (Fig. 59) or (Fig. 60).
Fig. 56 Checking Rotor Runout And Thickness
Variation
1 - DIAL INDICATOR
Fig. 57 Measuring Rotor Thickness
1 - MICROMETER
2 - ROTOR
Fig. 58 Caliper Adapter Assembly
1 - KNUCKLE
2 - CALIPER
3 - ROTOR
Fig. 59 FRONT ROTOR
1 - ROTOR
2 - HUB/BEARING
DRBRAKES - BASE 5 - 33
ROTORS (Continued)
Page 283 of 2627

REMOVAL - REAR
(1) Raise and support the vehicle
(2) Remove the tire and wheel assembly.
(3) Remove the disc brake caliper, (Refer to 5 -
BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/DISC
BRAKE CALIPERS - REMOVAL).
(4) Remove the caliper adapter bolts (Fig.
61).(Refer to 5 - BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANI-
CAL/DISC BRAKE CALIPER ADAPTER -
REMOVAL)
(5) Remove the retaining clips and rotor assembly
(Fig. 61).
REMOVAL - REAR DUAL WHEELS
(1) Raise and support the vehicle
(2) Remove the tire and wheel assembly.
(3) Remove the disc brake caliper, (Refer to 5 -
BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/DISC
BRAKE CALIPERS - REMOVAL).
(4) Remove the caliper adapter bolts.
(5) Remove the rear axle shaft from the housing
on dual rear wheels, (Refer to 3 - DIFFERENTIAL &
DRIVELINE/REAR AXLE - 286RBI/AXLE SHAFTS -
REMOVAL).
(6) Remove the hub and rotor assembly (C3500
only) (Fig. 62).
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - FRONT
(1) On models with all-wheel antilock system
(ABS), check condition of tone wheel on hub/bearing.
If teeth on wheel are damaged, hub/bearing assembly
will have to be replaced (tone wheel is not serviced
separately).
(2) Install the rotor onto the hub/bearing wheel
studs.
(3) Install the caliper adapter assembly,(Refer to 5
- BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/DISC
BRAKE CALIPERS - INSTALLATION) and tighten
adapter bolts to:
(4) Install the wheel and tire assembly, (Refer to
22 - TIRES/WHEELS/WHEELS - STANDARD PRO-
CEDURE) and lower the vehicle.
(5) Apply the brakes several times to seat brake
pads. Be sure to obtain firm pedal before moving
vehicle.
INSTALLATION - REAR
(1) Install the rotor to the axleshaft (Fig. 61).
Fig. 60 8 LUG ROTOR ASSEMBLY
1 - SPRING
2 - SHOCK
3 - UPPER AND LOWER SUSPENSION ARMS
4 - DISC BRAKE CALIPER
5 - DISC BRAKE CALIPER ADAPTER
6 - ROTOR
Fig. 61 REAR ROTOR
1 - ROTOR
2 - CALIPER ADAPTER
3 - CALIPER
Fig. 62 ROTOR / HUB REMOVAL
5 - 34 BRAKES - BASEDR
ROTORS (Continued)
Page 296 of 2627

FRONT WHEEL SPEED
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The ABS brake system uses 3 wheel speed sensors.
A sensor is mounted to each front hub/bearings. The
third sensor is mounted on top of the rear axle dif-
ferential housing.
OPERATION
The Wheel Speed Sensor consists of a magnet sur-
rounded by windings from a single strand of wire.
The sensor sends a small AC signal to the CAB. This
signal is generated by magnetic induction. The mag-
netic induction is created when a toothed sensor ring
(exciter ring or tone wheel) passes the stationary
magnetic WSS.
When the ring gear is rotated, the exciter ring
passes the tip of the WSS. As the exciter ring tooth
approaches the tip of the WSS, the magnetic lines of
force expand, causing the magnetic field to cut across
the sensor's windings. This, in turn causes current to
flow through the WSS circuit (Fig. 1) in one direc-
tion. When the exciter ring tooth moves away from
the sensor tip, the magnetic lines of force collapse
cutting the winding in the opposite direction. This
causes the current to flow in the opposite direction.
Every time a tooth of the exciter ring passes the tip
of the WSS, an AC signal is generated. Each AC sig-
nal (positive to negative signal or sinewave) is inter-
preted by the CAB. It then compares the frequency of
the sinewave to a time value to calculate vehicle
speed. The CAB continues to monitor the frequency
to determine a deceleration rate that would indicate
a possible wheel-locking tendency.
The signal strength of any magnetic induction sen-
sor is directly affected by:
²Magnetic field strength; the stronger the mag-
netic field, the stronger the signal
²Number of windings in the sensor; more wind-
ings provide a stronger signal
²Exciter ring speed; the faster the exciter ring/
tone wheel rotates, the stronger the signal will be
²Distance between the exciter ring teeth and
WSS; the closer the WSS is to the exciter ring/tone
wheel, the stronger the signal will be
The rear WSS is not adjustable. A clearance speci-
fication has been established for manufacturing toler-
ances. If the clearance is not within these
specifications, then either the WSS or other compo-
nents may be damaged. The clearance between the
WSS and the exciter ring is 0.005 ± 0.050 in.
The assembly plant performs a ªRolls Testº on
every vehicle that leaves the assembly plant. One of
the test performed is a test of the WSS. To properlytest the sensor, the assembly plant connects test
equipment to the Data Link Connector (DLC). This
connector is located to the right of the steering col-
umn and attached to the lower portion of the instru-
ment panel (Fig. 2). The rolls test terminal is spliced
to the WSS circuit. The vehicle is then driven on a
set of rollers and the WSS output is monitored for
proper operation.
Fig. 1 Operation of the Wheel Speed Sensor
1 - MAGNETIC CORE
2 - CAB
3 - AIR GAP
4 - EXCITER RING
5 - COIL
Fig. 2 Data Link Connector - Typical
1 - 16±WAY DATA LINK CONNECTOR
DRBRAKES - ABS 5 - 47
Page 297 of 2627

REMOVAL
(1) Remove the front rotor (Refer to 5 - BRAKES/
HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/ROTORS -
REMOVAL).
(2) Remove the wheel speed sensor mounting bolt
from the hub. (Fig. 3)
(3) Remove the wheel speed sensor from the hub.
(4) Remove the wiring from the clips and discon-
nect the electrical connector.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the wiring to the clips and Reconnect
the electrical connector.
(2) Install the wheel speed sensor to the hub.
(3) Install the wheel speed sensor mounting bolt to
the hub. Tighten the bolt to 21 N´m (190 in. lbs.).
(4) Install the front rotor and brake caliper assem-
bly (Refer to 5 - BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANI-
CAL/ROTORS - INSTALLATION).
REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REAR WHEEL
ANTILOCK
Diagnosis of base brake conditions which are
mechanical in nature should be performed first. This
includes brake noise, lack of power assist, parking
brake, or vehicle vibration during normal braking.
The RWAL brake system performs several self-
tests every time the ignition switch is turned on and
the vehicle is driven. The CAB monitors the system
inputs and outputs circuits to verify the system is
operating properly. If the CAB senses a malfunction
in the system it will set a DTC into memory and trig-
ger the warning lamp.NOTE: The MDS or DRB III scan tool is used to
diagnose the RWAL system. For test procedures
refer to the Chassis Diagnostic Manual.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise the vehicle on a hoist.
(2) Remove the brake line mounting nut and
remove the brake line from the sensor stud.
(3) Remove the mounting stud from the sensor and
shield (Fig. 4).
(4) Remove the sensor and shield from the differ-
ential housing.
(5) Disconnect the sensor wire harness and remove
the sensor.
INSTALLATION
(1) Connect the harness to the sensor.Be sure
the seal is securely in place between the sensor
and the wiring connector.
(2) Install the O-ring on the sensor (if removed).
(3) Insert the sensor in the differential housing.
(4) Install the sensor shield.
(5) Install the sensor mounting stud and tighten to
24 N´m (200 in. lbs.).
(6) Install the brake line on the sensor stud and
install the nut.
(7) Lower the vehicle.
Fig. 3 WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
1 - WHEEL SPEED SENSOR MOUNTING BOLT
2 - WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
3 - HUB/BEARINGFig. 4 REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
1 - WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
2 - MOUNTING BOLT
3 - AXLE HOUSING
5 - 48 BRAKES - ABSDR
FRONT WHEEL SPEED SENSOR (Continued)
Page 304 of 2627
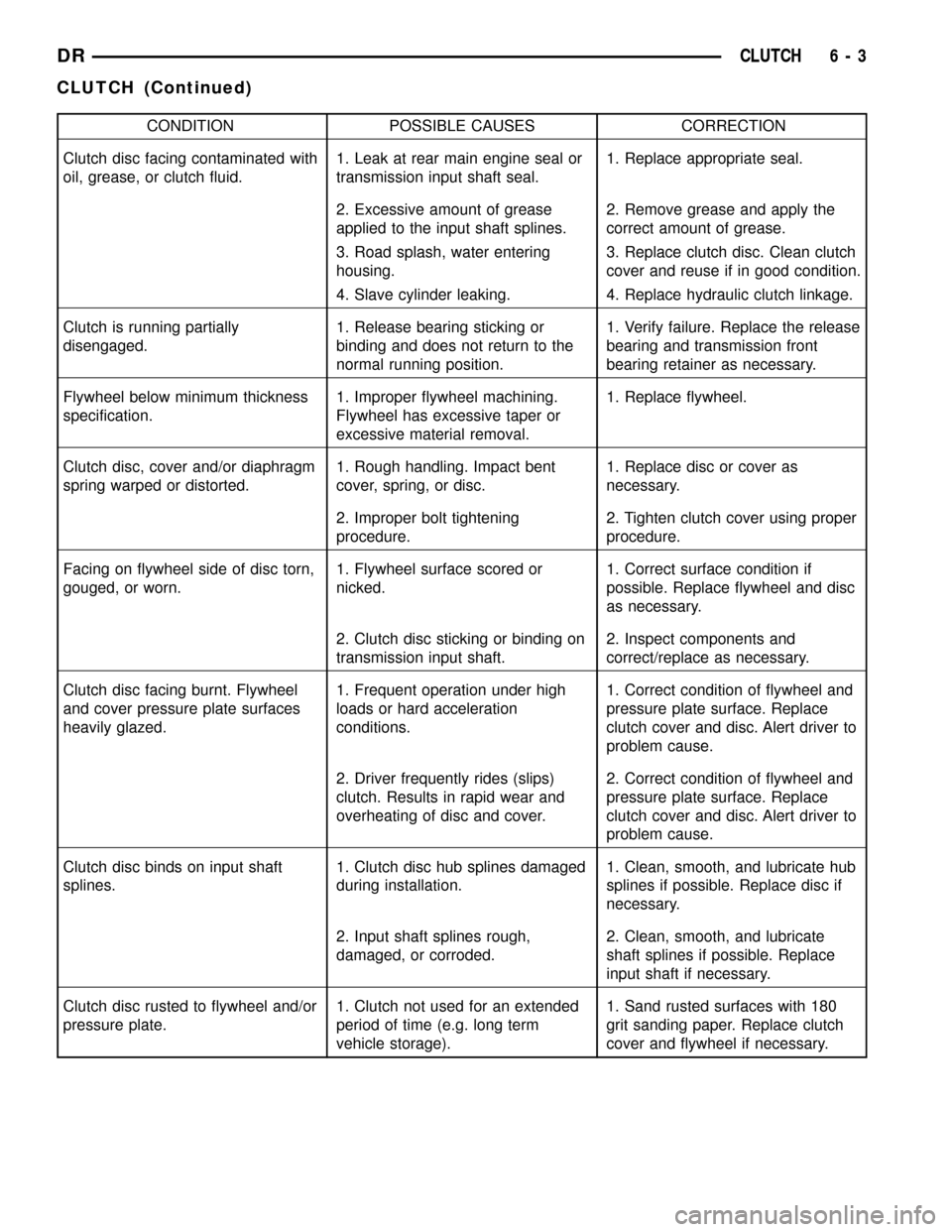
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
Clutch disc facing contaminated with
oil, grease, or clutch fluid.1. Leak at rear main engine seal or
transmission input shaft seal.1. Replace appropriate seal.
2. Excessive amount of grease
applied to the input shaft splines.2. Remove grease and apply the
correct amount of grease.
3. Road splash, water entering
housing.3. Replace clutch disc. Clean clutch
cover and reuse if in good condition.
4. Slave cylinder leaking. 4. Replace hydraulic clutch linkage.
Clutch is running partially
disengaged.1. Release bearing sticking or
binding and does not return to the
normal running position.1. Verify failure. Replace the release
bearing and transmission front
bearing retainer as necessary.
Flywheel below minimum thickness
specification.1. Improper flywheel machining.
Flywheel has excessive taper or
excessive material removal.1. Replace flywheel.
Clutch disc, cover and/or diaphragm
spring warped or distorted.1. Rough handling. Impact bent
cover, spring, or disc.1. Replace disc or cover as
necessary.
2. Improper bolt tightening
procedure.2. Tighten clutch cover using proper
procedure.
Facing on flywheel side of disc torn,
gouged, or worn.1. Flywheel surface scored or
nicked.1. Correct surface condition if
possible. Replace flywheel and disc
as necessary.
2. Clutch disc sticking or binding on
transmission input shaft.2. Inspect components and
correct/replace as necessary.
Clutch disc facing burnt. Flywheel
and cover pressure plate surfaces
heavily glazed.1. Frequent operation under high
loads or hard acceleration
conditions.1. Correct condition of flywheel and
pressure plate surface. Replace
clutch cover and disc. Alert driver to
problem cause.
2. Driver frequently rides (slips)
clutch. Results in rapid wear and
overheating of disc and cover.2. Correct condition of flywheel and
pressure plate surface. Replace
clutch cover and disc. Alert driver to
problem cause.
Clutch disc binds on input shaft
splines.1. Clutch disc hub splines damaged
during installation.1. Clean, smooth, and lubricate hub
splines if possible. Replace disc if
necessary.
2. Input shaft splines rough,
damaged, or corroded.2. Clean, smooth, and lubricate
shaft splines if possible. Replace
input shaft if necessary.
Clutch disc rusted to flywheel and/or
pressure plate.1. Clutch not used for an extended
period of time (e.g. long term
vehicle storage).1. Sand rusted surfaces with 180
grit sanding paper. Replace clutch
cover and flywheel if necessary.
DRCLUTCH 6 - 3
CLUTCH (Continued)
Page 348 of 2627

OPERATION
Coolant flows through the engine block absorbing
the heat from the engine, then flows to the radiator
where the cooling fins in the radiator transfers the
heat from the coolant to the atmosphere. During cold
weather the ethylene-glycol or propylene-glycol cool-
ant prevents water present in the cooling system
from freezing within temperatures indicated by mix-
ture ratio of coolant to water.
COOLANT RECOVERY
CONTAINER- GAS ENGINES
DESCRIPTION
The coolant reserve/overflow tank is mounted on
top of the fan shroud, and is made of high tempera-
ture plastic (Fig. 1).
OPERATION
The coolant reserve/overflow system works in con-
junction with the radiator pressure cap. It utilizes
thermal expansion and contraction of coolant to keep
coolant free of trapped air. It provides a volume for
expansion and contraction of coolant. It also provides
a convenient and safe method for checking coolant
level and adjusting level at atmospheric pressure.
This is done without removing the radiator pressure
cap. The system also provides some reserve coolantto the radiator to cover minor leaks and evaporation
or boiling losses.
As the engine cools, a vacuum is formed in the
cooling system of both the radiator and engine. Cool-
ant will then be drawn from the coolant tank and
returned to a proper level in the radiator.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove recovery hose from radiator.
(2) Remove the coolant container to fan shroud
mounting bolt.
(3) Tilt the container backward towards the engine
to disengage the mounting pin locking features and
lift the container away from the fan shroud (Fig. 1).
INSTALLATION
(1) Align the coolant container mounting pins into
the slots on the fan shroud and push the container
onto the fan shroud.
(2) Secure the container to the fan shroud with the
bolt. Tighten to 8.5N´m (75 in-lbs).
NOTE: Ensure that the locking feature on the
mounting pins has engaged.
(3) Connect the recovery hose to the radiator (Fig.
1).
RADIATOR FAN - GAS
ENGINES
REMOVAL
CAUTION: If the viscous fan drive is replaced
because of mechanical damage, the cooling fan
blades should also be inspected. Inspect for fatigue
cracks, loose blades, or loose rivets that could
have resulted from excessive vibration. Replace fan
blade assembly if any of these conditions are
found. Also inspect water pump bearing and shaft
assembly for any related damage due to a viscous
fan drive malfunction.
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable from battery.
(2) Remove coolant reserve/overflow container from
fan shroud and lay aside.Do Notdisconnect the
hoses or drain coolant from the container.
(3) The thermal viscous fan drive/fan blade assem-
bly is attached (threaded) to the water pump hub
shaft (Fig. 3). Remove the fan blade/viscous fan drive
assembly from the water pump by turning the
mounting nut counterclockwise as viewed from the
front. Threads on the viscous fan drive areRIGHT-
HAND.A 36 MM Fan Wrench should be used to pre-
vent pulley from rotating (Fig. 2).
Fig. 1 Coolant Recovery Bottle - Gas Engine
1 - SCREW
2 - COOLANT RECOVERY CONTAINER
3 - RADIATOR/RADIATOR CAP
4 - FAN SHROUD
DRENGINE 7 - 33
COOLANT (Continued)
Page 366 of 2627

²Engine loads and temperatures are high such as
when towing a trailer.
²Cool silicone fluid within the fan drive unit is
being redistributed back to its normal disengaged
(warm) position. This can occur during the first 15
seconds to one minute after engine start-up on a cold
engine.
LEAKS
Viscous fan drive operation is not affected by small
oil stains near the drive bearing. If leakage appears
excessive, replace the fan drive unit.
VISCOUS DRIVE
If the fan assembly free-wheels without drag (the
fan blades will revolve more than five turns when
spun by hand), replace the fan drive. This spin test
must be performed when the engine is cool.
For the following test, the cooling system must be
in good condition. It also will ensure against exces-
sively high coolant temperature.
WARNING: BE SURE THAT THERE IS ADEQUATE
FAN BLADE CLEARANCE BEFORE DRILLING.
(1) Drill a 3.18-mm (1/8-in) diameter hole in the
top center of the fan shroud.
(2) Obtain a dial thermometer with an 8 inch stem
(or equivalent). It should have a range of -18É-to-
105ÉC (0É-to-220É F). Insert thermometer through the
hole in the shroud. Be sure that there is adequate
clearance from the fan blades.
(3) Connect a tachometer and an engine ignition
timing light. The timing light is to be used as a
strobe light. This step cannot be used on the diesel
engine.(4) Block the air flow through the radiator. Secure
a sheet of plastic in front of the radiator. Use tape at
the top to secure the plastic and be sure that the air
flow is blocked.
(5) Be sure that the air conditioner (if equipped)
and blowe fan is turned off.
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE
ENGINE IS OPERATING. DO NOT STAND IN A
DIRECT LINE WITH THE FAN. DO NOT PUT YOUR
HANDS NEAR THE PULLEYS, BELTS OR FAN. DO
NOT WEAR LOOSE CLOTHING.
(6) Start the engine and operate at 2400 rpm.
Within ten minutes the air temperature (indicated on
the dial thermometer) should be up to 88É C (190É F).
Fan driveengagementshould start to occur at/be-
tween:
²3.7L Automatic - 93É C - 99ÉC (200É F - 210É F)
²3.7L Manual/4.7L Automatic/5.9L - 85É - 91É C
(185É - 195É F)
²4.7L Manual - 74É - 79É C (165É - 175É F)
²5.7L
²5.9L
²Engagement is distinguishable by a definite
increasein fan flow noise (roaring). The timing light
also will indicate an increase in the speed of the fan.
(7) When viscous drive engagement is verified,
remove the plastic sheet. Fan drivedisengagement
should start to occur at or between:
²3.7L Automatic - 76ÉC - 81ÉC (168É F - 178É F)
²3.7L Manual/4.7L Auto/ 5.9L - 67ÉC - 73ÉC (153É
F - 163É F)
²4.7L Manual - 56ÉC - 62ÉC (133É F - 143É F)
²5.7L
²5.9L
²8.0L engine - 93É to 101É C (190É - 205É F) Min-
imum 73ÉC (163ÉF). A definitedecreaseof fan flow
noise (roaring) should be noticed. If not, replace the
defective viscous fan drive unit.
CAUTION: Some engines equipped with serpentine
drive belts have reverse rotating fans and viscous
fan drives. They are marked with the word
REVERSE to designate their usage. Installation of
the wrong fan or viscous fan drive can result in
engine overheating.
Fig. 32 Viscous Fan Drive - Typical
1 - VISCOUS FAN DRIVE
2 - THERMOSTATIC SPRING
3 - MOUNTING NUT TO WATER PUMP HUB
DRENGINE 7 - 51
FAN DRIVE VISCOUS CLUTCH-GAS ENGINES (Continued)
Page 379 of 2627

REMOVAL
NOTE:
The water pump on all models can be removed
without discharging the air conditioning system (if
equipped).
The water pump on all gas powered engines is
bolted directly to the engine timing chain case/
cover.
On the 8.0L V-10 engine, a rubber o-ring (instead of
a gasket) is used as a seal between the water pump
and timing chain case/cover.
If water pump is replaced because of bearing/shaft
damage or leaking shaft seal, the mechanical cooling
fan assembly should also be inspected. Inspect for
fatigue cracks, loose blades or loose rivets that could
have resulted from excessive vibration. Replace fan if
any of these conditions are found. Also check condi-
tion of the thermal viscous fan drive (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ENGINE/FAN DRIVE VISCOUS
CLUTCH - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable from battery.
(2) Drain cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
Do not waste reusable coolant. If solution is clean,
drain coolant into a clean container for reuse.
(3) Remove windshield washer reservoir tank from
radiator fan shroud.
(4) Remove the four fan shroud mounting bolts at
the radiator (Fig. 51). Do not attempt to remove
shroud from vehicle at this time.
WARNING: CONSTANT TENSION HOSE CLAMPS
ARE USED ON MOST COOLING SYSTEM HOSES.WHEN REMOVING OR INSTALLING, USE ONLY
TOOLS DESIGNED FOR SERVICING THIS TYPE OF
CLAMP, SUCH AS SPECIAL CLAMP TOOL NUMBER
6094. ALWAYS WEAR SAFETY GLASSES WHEN
SERVICING CONSTANT TENSION CLAMPS.
CAUTION: A number or letter is stamped into the
tongue of constant tension clamps. If replacement
is necessary, use only an original equipment clamp
with a matching number or letter.
(5) Remove radiator upper hose at radiator.
(6) The thermal viscous fan drive is threaded on to
the water pump hub shaft (Fig. 53). Remove the fan/
fan drive assembly from water pump by turning the
mounting nut counterclockwise (as viewed from
front). Threads on the fan drive areRIGHT-HAND.
A 36 MM fan wrench can be used with Tool 6958
Spanner Wrench and Adapter Pins 8346 (Fig. 52) to
prevent the pulley from rotating.
(7) If water pump is being replaced, do not unbolt
fan blade assembly (Fig. 53) from the thermal control
fan drive.
(8) Remove fan blade/fan drive and fan shroud as
an assembly from vehicle.
After removing fan blade/fan drive assembly,do
notplace the thermal viscous fan drive in the hori-
zontal position. If stored horizontally, the silicone
Fig. 51 Typical Fan Shroud Mounting
1 - RADIATOR SUPPORT
2 - RADIATOR
3 - BOLTS (4)
4 - FAN SHROUD
Fig. 52 Using Special Tool 6958 Spanner Wrench
and Adapter Pins 8346
1 - SPECIAL TOOL 6958 SPANNER WRENCH WITH ADAPTER
PINS 8346
2-FAN
7 - 64 ENGINEDR
WATER PUMP - 8.0L (Continued)
Page 641 of 2627

WARNING: TO AVOID PERSONAL INJURY OR
DEATH, ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIRBAGS,
DISABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYS-
TEM BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING
WHEEL, STEERING COLUMN, AIRBAG, SEAT BELT
TENSIONER, IMPACT SENSOR, OR INSTRUMENT
PANEL COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE.
DISCONNECT AND ISOLATE THE BATTERY NEGA-
TIVE (GROUND) CABLE, THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES
FOR THE SYSTEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE
BEFORE PERFORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR
SERVICE. THIS IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DIS-
ABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYSTEM.
FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRECAUTIONS
COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOY-
MENT.
NOTE: Before starting this procedure, be certain
that the front wheels are still in the straight-ahead
position.
(1) While holding the centered clockspring rotor
and case stationary in relation to each other, care-
fully slide the clockspring down over the steering col-
umn upper shaft.
(2) Align and seat the hole in the locating tab at
the eleven o'clock position on the clockspring case
over the locating pin on the multi-function switch
mounting housing (Fig. 20).
(3) Install and tighten the two screws that secure
the clockspring to the multi-function switch mount-
ing housing. Tighten the screws to 2 N´m (20 in.
lbs.).
(4) Reconnect the two instrument panel wire har-
ness connectors for the clockspring to the two connec-
tor receptacles below the steering column on the back
of the clockspring housing.
(5) Position the lower shroud onto the steering col-
umn.
(6) From below the steering column, install and
tighten the one center screw that secures the lower
shroud to the steering column lock housing. Tighten
the screw to 2 N´m (20 in. lbs.).(7) Position the upper shroud onto the steering col-
umn. If the vehicle is equipped with an automatic
transmission, be certain to engage the gearshift lever
gap hider into the openings in the right side of the
upper and lower shrouds.
(8) Align the snap features on the upper shroud
with the receptacles on the lower shroud and apply
hand pressure to snap them together.
(9) From below the steering column, install and
tighten the two screws that secure the upper shroud
to the lower shroud. Tighten the screws to 2 N´m (20
in. lbs.).
(10) If the vehicle is equipped with the optional tilt
steering column, align the steering column tilt knob
with the tilt adjuster mechanism lever located on the
left side of the column just below the multi-function
switch control stalk and, using hand pressure, push
the knob firmly onto the lever.
(11) Reinstall the steering column opening cover
onto the instrument panel. (Refer to 23 - BODY/IN-
STRUMENT PANEL/STEERING COLUMN OPEN-
ING COVER - INSTALLATION).
(12) If a new clockspring has been installed,
remove the plastic locking pin that is securing the
clockspring rotor to the clockspring case to maintain
clockspring centering.
NOTE: When reinstalling the steering wheel, be cer-
tain to index the yellow rubber booted engagement
dowel on the upper surface of the clockspring rotor
between the two fins cast into the lower surface of
the steering wheel armature hub.
(13) Reinstall the steering wheel onto the steering
column. (Refer to 19 - STEERING/COLUMN/STEER-
ING WHEEL - INSTALLATION).
(14) Reconnect the steering wheel wire harness
connectors to the upper clockspring connector recep-
tacles. Be certain that the steering wheel wire har-
ness is routed between the steering wheel back trim
cover and the steering wheel armature.
(15) Reinstall the driver airbag onto the steering
wheel. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/RESTRAINTS/
DRIVER AIRBAG - INSTALLATION).
8O - 22 RESTRAINTSDR
CLOCKSPRING (Continued)
Page 1230 of 2627
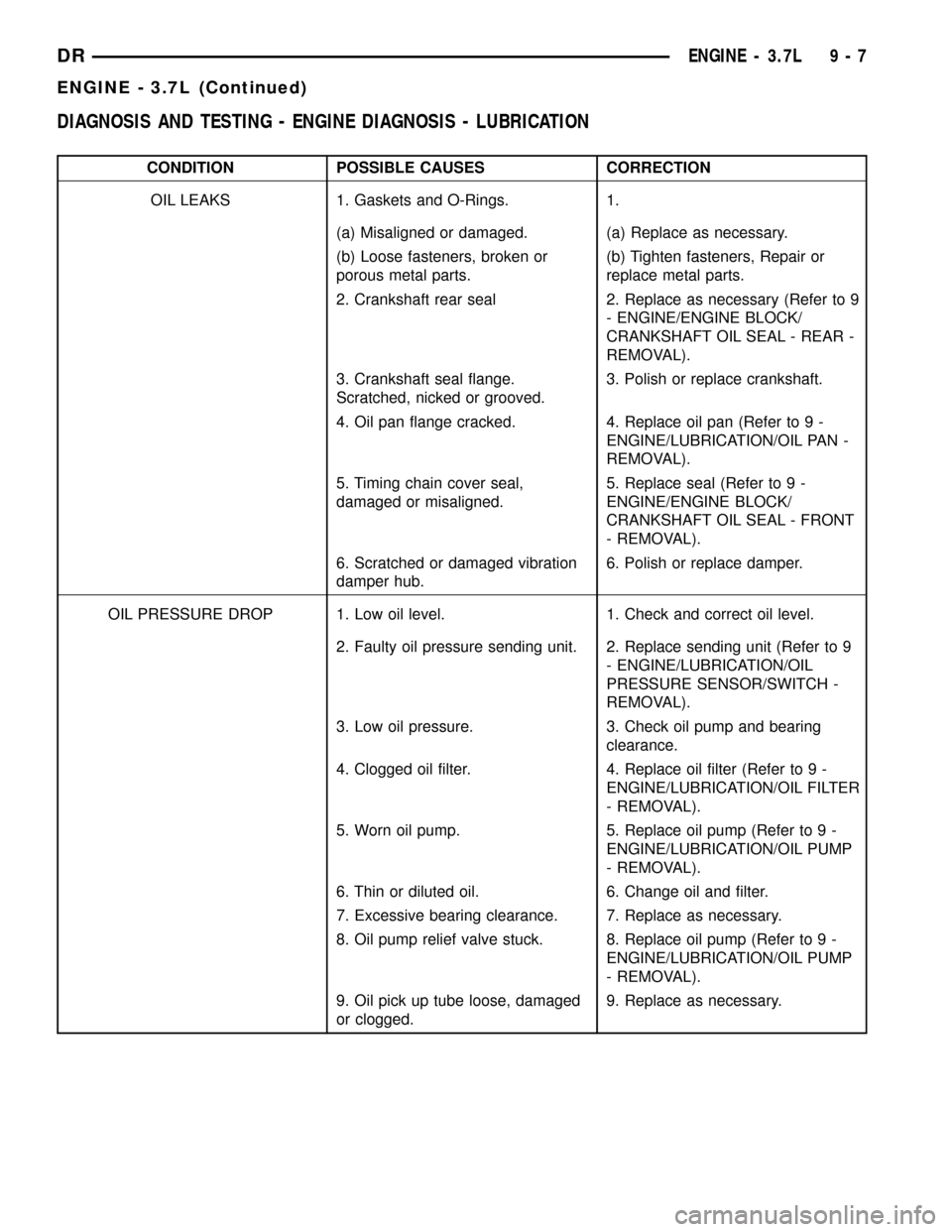
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE DIAGNOSIS - LUBRICATION
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
OIL LEAKS 1. Gaskets and O-Rings. 1.
(a) Misaligned or damaged. (a) Replace as necessary.
(b) Loose fasteners, broken or
porous metal parts.(b) Tighten fasteners, Repair or
replace metal parts.
2. Crankshaft rear seal 2. Replace as necessary (Refer to 9
- ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/
CRANKSHAFT OIL SEAL - REAR -
REMOVAL).
3. Crankshaft seal flange.
Scratched, nicked or grooved.3. Polish or replace crankshaft.
4. Oil pan flange cracked. 4. Replace oil pan (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PAN -
REMOVAL).
5. Timing chain cover seal,
damaged or misaligned.5. Replace seal (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/
CRANKSHAFT OIL SEAL - FRONT
- REMOVAL).
6. Scratched or damaged vibration
damper hub.6. Polish or replace damper.
OIL PRESSURE DROP 1. Low oil level. 1. Check and correct oil level.
2. Faulty oil pressure sending unit. 2. Replace sending unit (Refer to 9
- ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL
PRESSURE SENSOR/SWITCH -
REMOVAL).
3. Low oil pressure. 3. Check oil pump and bearing
clearance.
4. Clogged oil filter. 4. Replace oil filter (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL FILTER
- REMOVAL).
5. Worn oil pump. 5. Replace oil pump (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PUMP
- REMOVAL).
6. Thin or diluted oil. 6. Change oil and filter.
7. Excessive bearing clearance. 7. Replace as necessary.
8. Oil pump relief valve stuck. 8. Replace oil pump (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PUMP
- REMOVAL).
9. Oil pick up tube loose, damaged
or clogged.9. Replace as necessary.
DRENGINE - 3.7L 9 - 7
ENGINE - 3.7L (Continued)