Iod fuse DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.G Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1998, Model line: RAM 1500, Model: DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.GPages: 2627
Page 603 of 2627

tons is depressed to move the selected mirror Up,
Down, Right or Left. The DDM power mirror switch
circuitry controls the battery current and ground
feeds to each of the four (two in each mirror head)
power mirror motors. The Light-Emitting Diode
(LED) in the DDM power mirror switch is connected
to battery current through the power window circuit
breaker in the IPM on a fused ignition switch output
(run-acc) circuit so that the switch directional but-
tons will be illuminated whenever the ignition switch
is in the On or Accessory positions.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - DRIVER DOOR
MODULE
The Light-Emitting Diode (LED) illumination
lamps for all of the Driver Door Module (DDM)
power window, power lock, and power mirror
switches receive battery current through the power
window circuit breaker in the Integrated Power Mod-
ule (IPM). If all of the LEDs are inoperative in the
DDM, be certain to diagnose the power window sys-
tem before replacing the switch unit. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/POWER WINDOWS - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING). If only one LED in the DDM is
inoperative, replace the faulty DDM. If the driver
side front door power window operates in a normal
manner, but the Auto-Down feature is inoperative,
replace the faulty DDM. Refer to the appropriate wir-
ing information.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable. Remove the DDM from the door trim panel.
Disconnect the door wire harness connectors for the
DDM from the DDM connector receptacles.
(2) Test the DDM switch continuity. See the Driver
Door Module Switch Tests chart to determine if the
continuity is correct for the suspect switches in each
switch position (Fig. 2) and/or (Fig. 3). If not OK,
replace the faulty DDM as required.
DRIVER DOOR MODULE SWITCH TESTS
POWER LOCK SWITCH
SWITCH POSITIONRESISTANCE BETWEEN
CONNECTOR C-1 PINS
7&11
NEUTRAL 10 KILOHMS 1%
LOCK 820 OHMS 5%
UNLOCK 330 OHMS 5%
POWER MIRROR SWITCH
SWITCH POSITIONCONTINUITY BETWEEN
PINS OF CONNECTOR
C-2
LEFT MIRROR SELECTED
UP PINS1&3
DOWN PINS2&3
RIGHT PINS2&3
LEFT PINS3&6
RIGHT MIRROR SELECTED
UP PINS3&7
DOWN PINS2&3
RIGHT PINS2&3
LEFT PINS3&4
POWER WINDOW SWITCH
SWITCH POSITION CONTINUITY BETWEEN
PINS OF CONNECTOR
C-1
NEUTRAL PINS1&8,PINS2&8,
PINS3&8,PINS4&8,
PINS5&8,PINS6&8,
PINS 8 & 10, PINS 8 &
12
LEFT FRONT UP PINS5&9
Fig. 2 Driver Door Module Connector C1 Receptacle
Fig. 3 Driver Door Module Connector C2 Receptacle
8N - 6 POWER LOCKSDR
DRIVER DOOR MODULE (Continued)
Page 607 of 2627

POWER MIRRORS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
POWER MIRRORS
DESCRIPTION.........................10
OPERATION...........................10
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER
MIRRORS...........................10
AUTOMATIC DAY / NIGHT MIRROR
DESCRIPTION.........................11
OPERATION...........................11
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AUTOMATIC DAY
/ NIGHT MIRROR......................11REMOVAL.............................12
POWER MIRROR SWITCH
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER MIRROR
SWITCH............................12
REMOVAL.............................12
SIDEVIEW MIRROR
REMOVAL.............................12
POWER MIRRORS
DESCRIPTION
AUTOMATIC DAY/NIGHT MIRROR
The automatic day/night mirror system is able to
automatically change the reflectance of the inside
rear view mirror in order to reduce the glare of head-
lamps approaching the vehicle from the rear. The
automatic day/night rear view mirror receives bat-
tery current through a fuse in the Integrated Power
Module (IPM) only when the ignition switch is in the
On position.
OUTSIDE REAR VIEW MIRROR
The power operated outside rear view mirrors
allow the driver to adjust both outside mirrors elec-
trically from the driver side front seat position by
operating a switch on the driver side front door trim
panel. The power mirrors receive a non-switched bat-
tery feed through a fuse in the Integrated Power
Module (IPM) so that the system will remain opera-
tional, regardless of the ignition switch position.
OPERATION
AUTOMATIC DAY/NIGHT MIRROR
A switch located on the bottom of the automatic
day/night mirror housing allows the vehicle operator
to select whether the automatic dimming feature is
operational. When the automatic day/night mirror is
turned on, the mirror switch is lighted by an integral
Light-Emitting Diode (LED). The mirror will auto-
matically disable its self-dimming feature whenever
the vehicle is being driven in reverse.
OUTSIDE REAR VIEW MIRROR
The heated mirrors include an electric heating grid
behind the mirror glass in each outside mirror, which
can clear the mirror glass of ice, snow, or fog. (Refer
to 8 - ELECTRICAL/HEATED MIRRORS -
DESCRIPTION) for more information.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER MIRRORS
WIRING VOLTAGE TEST
The following wiring test determines whether or
not voltage is continuous through the body harness
to switch.
(1) Remove the power mirror switch (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/POWER LOCKS/DOOR MODULE -
REMOVAL).
(2) Disconnect wire harness connector from back of
power mirror switch.
(3) Connect the clip end of a 12 volt test light to
Pin 5 in the mirror switch harness connector. Touch
the test light probe to Pin 3.
If the test light illuminates, the wiring circuit
between the battery and switch is OK.
If the lamp does not illuminate, first check fuse in
the Integrated Power Module (IPM). If fuse is OK,
then check for a broken wire.
Refer to the appropriate wiring information.
POWER MIRROR MOTOR TEST
If the power mirror switch is receiving proper cur-
rent and ground and mirrors do not operate, proceed
with power mirror motor test. Refer to the appropri-
ate wiring information.
(1) Remove the power mirror switch (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/POWER LOCKS/DOOR MODULE -
REMOVAL).
8N - 10 POWER MIRRORSDR
Page 617 of 2627
(5) Momentarily touch the Positive (+) jumper
probe to the other motor connector terminal.
When positive probe is connected the motor should
rotate in one direction to either move window up or
down. If window is all the way up or down the motor
will grunt and the inner door panel will flex when
actuated in that one direction.
(6) Reverse jumper probes at the motor connector
terminals and window should now move in opposite
direction. If window does not move or grunt, replace
the motor.
If window moved completely up or down, reverse
the jumper probes and cycle window to the opposite
position to verify full operation.
If motor grunts and does not move, verify that reg-
ulator is not binding.
WINDOW MOTOR
REMOVAL
The window motor is serviced with the window
regulator (Refer to 23 - BODY/DOOR - FRONT/WIN-
DOW REGULATOR - REMOVAL) or (Refer to 23 -
BODY/DOORS - REAR/WINDOW REGULATOR -
REMOVAL).
WINDOW SWITCH
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - WINDOW SWITCH
The Light-Emitting Diode (LED) illumination
lamps for all of the power window and lock switch
and bezel unit switch paddles receive battery current
through the power window circuit breaker in the
junction block. If all of the LEDs are inoperative in
both the power window and lock switch units and the
power windows are inoperative, (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/POWER WINDOWS - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING). If the power windows operate, but any or
all of the LEDs are inoperative, the power window
and lock switch units with the inoperative LED(s) is
faulty and must be replaced. For complete circuit dia-
grams, refer to the appropriate wiring information.
(1) Check the fuse in the Integrated Power Module
(IPM) and the circuit breaker located near the park
brake pedal. If OK, go to Step 2. If not OK, replace
the faulty fuse or circuit breaker.
(2) Turn the ignition switch to the On position.
Check for battery voltage at the fuse in the Inte-
grated Power Module (IPM). If OK, turn the ignition
switch to the Off position and go to Step 3. If not OK,
check circuit breaker and repair the circuit to the
ignition switch as required.
(3) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable. Remove the power window switch unit fromthe door trim panel (passenger doors). The drivers
door switch is included with the Driver Door Module
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/POWER LOCKS/DOOR
MODULE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING) for service
procedures. Unplug the wire harness connector from
the switch unit.
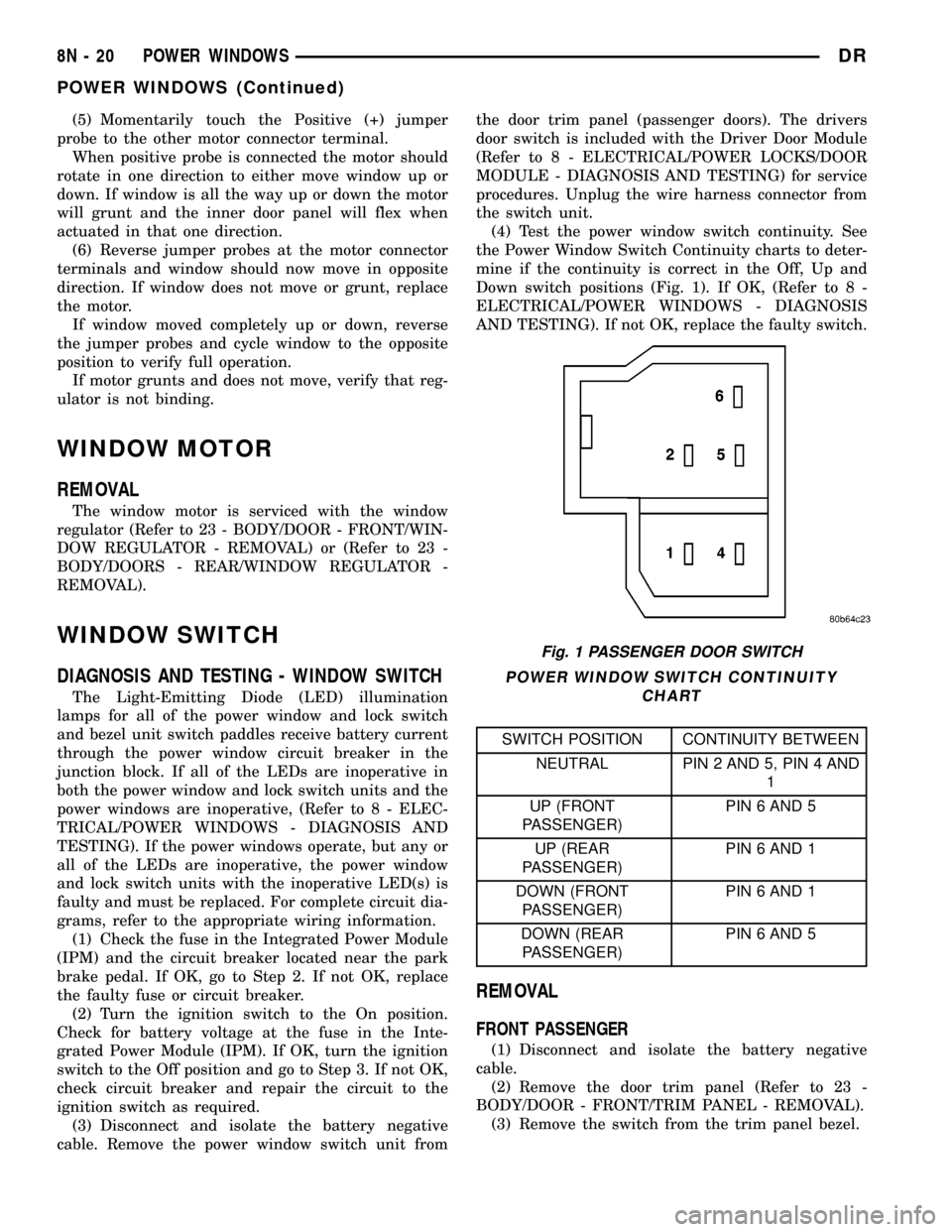
(4) Test the power window switch continuity. See
the Power Window Switch Continuity charts to deter-
mine if the continuity is correct in the Off, Up and
Down switch positions (Fig. 1). If OK, (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/POWER WINDOWS - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING). If not OK, replace the faulty switch.
POWER WINDOW SWITCH CONTINUITY
CHART
SWITCH POSITION CONTINUITY BETWEEN
NEUTRAL PIN 2 AND 5, PIN 4 AND
1
UP (FRONT
PASSENGER)PIN 6 AND 5
UP (REAR
PASSENGER)PIN 6 AND 1
DOWN (FRONT
PASSENGER)PIN 6 AND 1
DOWN (REAR
PASSENGER)PIN 6 AND 5
REMOVAL
FRONT PASSENGER
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the door trim panel (Refer to 23 -
BODY/DOOR - FRONT/TRIM PANEL - REMOVAL).
(3) Remove the switch from the trim panel bezel.
Fig. 1 PASSENGER DOOR SWITCH
8N - 20 POWER WINDOWSDR
POWER WINDOWS (Continued)
Page 728 of 2627

8W-01 WIRING DIAGRAM INFORMATION
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
WIRING DIAGRAM INFORMATION
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - HOW TO USE WIRING
DIAGRAMS...........................1
DESCRIPTION - CIRCUIT INFORMATION....5
DESCRIPTION - CIRCUIT FUNCTIONS......6
DESCRIPTION - SECTION IDENTIFICATION
AND INFORMATION....................6
DESCRIPTION - CONNECTOR, GROUND
AND SPLICE INFORMATION..............7
WARNING
WARNINGS - GENERAL.................7
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - WIRING
HARNESS............................7
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE -
ELECTROSTATIC DISCHARGE (ESD)
SENSITIVE DEVICES...................8
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TESTING OF
VOLTAGE POTENTIAL...................9
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TESTING FOR
CONTINUITY..........................9STANDARD PROCEDURE - TESTING FOR A
SHORT TO GROUND...................9
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TESTING FOR A
SHORT TO GROUND ON FUSES
POWERING SEVERAL LOADS...........10
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TESTING FOR A
VOLTAGE DROP......................10
SPECIAL TOOLS
WIRING/TERMINAL....................10
CONNECTOR
REMOVAL.............................11
INSTALLATION.........................11
DIODE
REMOVAL.............................14
INSTALLATION.........................14
TERMINAL
REMOVAL.............................14
INSTALLATION.........................14
WIRE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - WIRE SPLICING . . 15
WIRING DIAGRAM
INFORMATION
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - HOW TO USE WIRING
DIAGRAMS
DaimlerChrysler Corporation wiring diagrams are
designed to provide information regarding the vehi-
cles wiring content. In order to effectively use the
wiring diagrams to diagnose and repair
DaimlerChrysler Corporation vehicles, it is important
to understand all of their features and characteris-
tics.
Diagrams are arranged such that the power (B+)
side of the circuit is placed near the top of the page,
and the ground (B-) side of the circuit is placed near
the bottom of the page (Fig. 1).
All switches, components, and modules are shown
in the at rest position with the doors closed and the
key removed from the ignition (Fig. 2).Components are shown two ways. A solid line
around a component indicates that the component is
complete. A dashed line around the component indi-
cates that the component is being shown is not com-
plete. Incomplete components have a reference
number to indicate the page where the component is
shown complete.
It is important to realize that no attempt is made
on the diagrams to represent components and wiring
as they appear on the vehicle. For example, a short
piece of wire is treated the same as a long one. In
addition, switches and other components are shown
as simply as possible, with regard to function only.
SYMBOLS
International symbols are used throughout the wir-
ing diagrams. These symbols are consistent with
those being used around the world (Fig. 3).
DR8W-01 WIRING DIAGRAM INFORMATION 8W - 01 - 1
Page 1109 of 2627

ENGINE CONTROL MODULE C2 (DIESEL) - 50 WAY
CAV CIRCUIT FUNCTION
1- -
2- -
3 K615 18VT/WT INLET AIR TEMPERATURE SENSE
3 K615 18BR/WT (M/T) INLET AIR TEMPERATURE SENSE
4 V35 18VT/OR (A/T) S/C VENT CONTROL
5 K176 18BR/OR INTAKE AIR HEATER RELAY NO 2 CONTROL
6 K174 18BR/YL INTAKE AIR HEATER RELAY NO 1 CONTROL
7 V32 18VT/YL (A/T) SPEED CONTROL SUPPLY
8- -
9 T41 18YL/DB (A/T) PARK/NEUTRAL POSITION SWITCH SENSE (T41)
10 K161 18BR/LB FAN SPEED SENSOR
11 B22 18DG/YL VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR SIGNAL NO. 1
12 G6 18VT/GY OIL PRESSURE SIGNAL
13 T6 18DG (A/T) TOW/HAUL OVERDRIVE OFF SWITCH SENSE
14 T118 18DG (A/T) GOVERNOR PRESSURE SOLENOID CONTROL
15 T9 18DG/TN (A/T) 3-4 SOLENIOD CONTROL
16 D21 18WT/BR SCI TRANSMIT (PCM)
16 D21 18PK (M/T) SCI TRANSMIT
17 - -
18 T38 18YL/BR (A/T) GOVERNOR PRESSURE SENSOR SIGNAL
19 D20 18WT/LG SCI RECEIVE (PCM)
20 A209 16RD FUSED B(+)
21 Z902 16BK GROUND
22 - -
23 F856 18YL/PK 5 VOLT SUPPLY
24 K900 18DB/DG SENSOR GROUND
25 T75 18YL/LB (A/T) TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH SOLENOID CONTROL
26 N4 18DB/WT FUEL LEVEL SENSOR SIGNAL
27 - -
28 D25 18WT/VT PCI BUS
29 T54 18DG/OR (A/T) TRANSMISSION TEMPERATURE SENSOR SIGNAL
30 A209 16RD FUSED B(+)
31 T515 18YL/DB (A/T) TRANSMISSION CONTROL RELAY CONTROL
32 F202 18PK/GY FUSED IGNITION SWITCH OUTPUT (RUN-START)
33 K854 18VT/BR (M/T) 5 VOLT SUPPLY
34 V36 18VT/YL (A/T) S/C VACUUM CONTROL
35 K616 18BR/YL INLET AIR PRESSURE SENSE
36 V32 18VT/YL (M/T) SPEED CONTROL SUPPLY
37 B29 18DG/WT BRAKE SWITCH SIGNAL
38 - -
39 - -
40 A209 16RD FUSED B(+)
41 C13 18LB/OR A/C CLUTCH RELAY CONTROL
42 - -
43 K160 18BR/OR PARK LOCKOUT SOLENOID CONTROL
44 T14 18DG/BR (A/T) OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR SIGNAL
45 T13 18DG/VT (A/T) SENSOR GROUND
46 V37 18VT S/C SWITCH NO. 1 SIGNAL
47 K25 18DB/VT BATT TEMP SIGNAL
48 K400 18BR/VT (M/T) APPS NO.2 RETURN
49 Z902 16BK GROUND
50 Z902 16BK GROUND
8W - 80 - 60 8W-80 CONNECTOR PIN-OUTSDR
Page 1151 of 2627

TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR-6WAY
CAV CIRCUIT FUNCTION
1 L10 18WT/GY FUSED IGNITION SWITCH OUTPUT (RUN)
2 T117 20DG/YL TRANS RANGE SENSOR ELECTRONIC CLUSTER 5
VOLT SUPPLY
3- -
4 L1 18WT/LG BACKUP LAMP FEED
5 T917 20YL/TN TRANS RANGE SENSOR ELECTRONIC CLUSTER MUX
6 T41 20YL/DB PARK NEUTRAL POSITION SWITCH SENSE (T41)
6 T41 18YL/DB PARK NEUTRAL POSITION SWITCH SENSE (T41)
TRANSMISSION SOLENOID ASSEMBLY (48RE)-8WAY
CAV CIRCUIT FUNCTION
1 T16 18YL/OR TRANSMISSION CONTROL RELAY OUTPUT
2 F856 18YL/PK 5 VOLT SUPPLY
3 K900 20DB/DG SENSOR GROUND
3 K900 18DB/DG SENSOR GROUND
4 T38 18YL/BR GOVERNOR PRESSURE SENSOR SIGNAL
5 T118 18DG GOVERNOR PRESSURE SOLENOID CONTROL
6 T9 18DG/TN 3-4 SHIFT SOLENOID
7 T75 18YL/LB TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH SOLENOID CONTROL
8 T54 18DG/OR TRANSMISSION TEMPERATURE SENSOR SIGNAL
TRANSMISSION SOLENOID/TRS ASSEMBLY (NGC) - 23 WAY
CAV CIRCUIT FUNCTION
1 L10 18WT/GY FUSED IGNITION SWITCH OUTPUT (RUN)
2 T20 18DG/WT L/R SOLENOID CONTROL
3- -
4 T41 20YL/DB TRS T41 SENSE
5 T42 18DG/YL TRS T42 SENSE
6 L1 18WT/LG BACKUP LAMP FEED
7 T60 18YL/GY OVERDRIVE SOLENOID CONTROL
8 T3 18DG/DB TRS T3 SENSE
9 T1 18DG/LB TRS T1 SENSE
10 T16 18YL/OR TRANSMISSION CONTROL RELAY OUTPUT
11 T48 18BR/YL 4C PRESSURE SWITCH SENSE
12 T140 18YL/GY PRESSURE CONTROL SOLENIOD CONTROL
13 T4 18DG/LB TRS T2 SENSE
14 T50 18YL/TN LOW/REVERSE PRESSURE SWITCH SENSE
15 T147 18DG/YL 2C PRESSURE SWITCH SENSE
16 T9 18DG/TN OVERDRIVE PRESSURE SWITCH SENSE
17 T59 18YL/LB UNDERDRIVE SOLENOID CONTROL
18 T29 18YL/WT UNDERDRIVE PRESSURE SWITCH SENSE
19 T259 18YL/DG 4C SOLENOID CONTROL
20 T219 18YL/LG 2C SOLENOID CONTROL
21 T118 18DG MS SOLENOID CONTROL
22 K900 18DB/DG SENSOR GROUND
23 T54 18DG/OR TRANSMISSION TEMPERATURE SENSOR SIGNAL
8W - 80 - 102 8W-80 CONNECTOR PIN-OUTSDR
Page 1216 of 2627

8W-97 POWER DISTRIBUTION
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
POWER DISTRIBUTION
DESCRIPTION..........................1
OPERATION............................1
SPECIAL TOOLS
POWER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS.........2
CIGAR LIGHTER OUTLET
DESCRIPTION..........................2
OPERATION............................2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CIGAR LIGHTER
OUTLET.............................2
INTEGRATED POWER MODULE
DESCRIPTION..........................3
OPERATION............................3
REMOVAL.............................3
INSTALLATION..........................4
FRONT CONTROL MODULE
DESCRIPTION..........................5OPERATION............................5
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FRONT
CONTROL MODULE....................5
REMOVAL.............................6
INSTALLATION..........................6
IOD FUSE
DESCRIPTION..........................6
OPERATION............................6
REMOVAL.............................7
INSTALLATION..........................7
POWER OUTLET
DESCRIPTION..........................7
OPERATION............................7
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER
OUTLET.............................7
REMOVAL.............................8
INSTALLATION..........................8
POWER DISTRIBUTION
DESCRIPTION
This group covers the various standard and
optional power distribution components used on this
model. The power distribution system for this vehicle
consists of the following components:
²Integrated Power Module (IPM)
²Front Control Module (FCM)
²Power Distribution Center (PDC)
²Power Outlets
²Cigar Lighter Outlets
²Relays
Refer to Wiring Diagrams for complete circuit sche-
matics.
The power distribution system also incorporates
various types of circuit control and protection fea-
tures, including:
²Automatic resetting circuit breakers
²Blade-type fuses
²Cartridge fuses
²Relays
Following are general descriptions of the major
components in the power distribution system. See the
owner's manual in the vehicle glove box for more
information on the features and use of all of the
power distribution system components.
OPERATION
The power distribution system for this vehicle is
designed to provide safe, reliable, and centralized dis-
tribution points for the electrical current required to
operate all of the many standard and optional facto-
ry-installed electrical and electronic powertrain,
chassis, safety, security, comfort and convenience sys-
tems. At the same time, the power distribution sys-
tem was designed to provide ready access to these
electrical distribution points for the vehicle techni-
cian to use when conducting diagnosis and repair of
faulty circuits. The power distribution system can
also prove useful for the sourcing of additional elec-
trical circuits that may be required to provide the
electrical current needed to operate many accessories
that the vehicle owner may choose to have installed
in the aftermarket.
DR8W-97 POWER DISTRIBUTION 8W - 97 - 1
Page 1221 of 2627

requires the use of a DRB IIItscan tool and the
proper Body Diagnostic Procedures manual.
Before any testing of the front control module is
attempted, the battery should be fully charged and
all wire harness and ground connections inspected
around the affected areas on the vehicle.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the positive and negative battery
cables from the battery.
(2) Partially remove the integrated power module
from the engine compartment (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/POWER DISTRIBUTION/INTEGRATED
POWER MODULE - REMOVAL).
(3) Remove the front control module retaining
screws.
(4) Using both hands, pull the front control module
straightfrom the integrated power module assembly
to disconnect the 49-way electrical connector and
remove the front control module from the vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the front control module on the inte-
grated power module assembly by pushing the
49-way electrical connector straight in.
(2) Install the front control module retaining
screws. Torque the screws to 7 in. lbs.
(3) Install the integrated power module (Refer to 8
- ELECTRICAL/POWER DISTRIBUTION/INTE-
GRATED POWER MODULE - INSTALLATION).
(4) Connect the positive and negative battery
cables.
IOD FUSE
DESCRIPTION
All vehicles are equipped with an Ignition-Off
Draw (IOD) fuse that is disconnected within the Inte-
grated Power Module when the vehicle is shipped
from the factory. Dealer personnel are to reconnect
the IOD fuse in the Integrated Power Module as part
of the preparation procedures performed just prior to
new vehicle delivery.
A laser printed fuse layout map is integral to the
Integrated Power Module cover to ensure proper fuse
identification. The IOD fuse is a 20 ampere mini
blade-type fuse, located in fuse cavity # 51 (Fig. 6).
The fuse is secured within a black molded plastic
fuse holder and puller unit that serves both as a tool
for disconnecting and reconnecting the fuse in its
Integrated Power Module cavity, and as a fuse holder
that conveniently stores the fuse in the same Inte-
grated Power Module cavity after it has been discon-
nected.
CIRCUITS INCLUDED WITH IOD FUSE
²Cluster (CCN)
²Diagnostic Connector
²Map Lamps
²Glove Box Lamp
²Courtesy Lamps
²Radio
²Underhood Lamp
OPERATION
The term ignition-off draw identifies a normal con-
dition where power is being drained from the battery
with the ignition switch in the Off position. The IOD
fuse feeds the memory and sleep mode functions for
some of the electronic modules in the vehicle as well
as various other accessories that require battery cur-
rent when the ignition switch is in the Off position.
The only reason the IOD fuse is disconnected is to
reduce the normal IOD of the vehicle electrical sys-
tem during new vehicle transportation and pre-deliv-
ery storage to reduce battery depletion, while still
allowing vehicle operation so that the vehicle can be
loaded, unloaded and moved as needed by both vehi-
cle transportation company and dealer personnel.
The IOD fuse is disconnected from Integrated
Power Module fuse cavity # 51 when the vehicle is
shipped from the assembly plant. Dealer personnel
must reconnect the IOD fuse when the vehicle is
being prepared for delivery in order to restore full
electrical system operation. Once the vehicle is pre-
pared for delivery, the IOD function of this fuse
Fig. 6 IOD FUSE LOCATION
1 - IOD FUSE
8W - 97 - 6 8W-97 POWER DISTRIBUTIONDR
FRONT CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 1222 of 2627

becomes transparent and the fuse that has been
assigned the IOD designation becomes only another
Fused B(+) circuit fuse.
The IOD fuse can be used by the vehicle owner as
a convenient means of reducing battery depletion
when a vehicle is to be stored for periods not to
exceed about thirty days. However, it must be
remembered that disconnecting the IOD fuse will not
eliminate IOD, but only reduce this normal condition.
If a vehicle will be stored for more than about thirty
days, the battery negative cable should be discon-
nected to eliminate normal IOD; and, the battery
should be tested and recharged at regular intervals
during the vehicle storage period to prevent the bat-
tery from becoming discharged or damaged.
REMOVAL
The Ignition-Off Draw (IOD) fuse is disconnected
from Integrated Power Module fuse cavity # 51 when
the vehicle is shipped from the assembly plant.
Dealer personnel must reconnect the IOD fuse when
the vehicle is being prepared for delivery in order to
restore full electrical system operation.
(1) Turn the ignition switch to the Off position.
(2) Remove the Integrated Power Module cover.
(3) Grasp the outer tabs of the IOD fuse holder
unit in fuse cavity # 51 between the thumb and fore-
finger and pull the unit firmly upward.
(4) Install the Integrated Power Module cover.
INSTALLATION
(1) Turn the ignition switch to the Off position.
(2) Remove the Integrated Power Module cover.
(3) To install the IOD fuse, use a thumb to press
the IOD fuse holder unit in fuse cavity # 51 firmly
into the Integrated Power Module.
(4) Install the Integrated Power Module cover.
POWER OUTLET
DESCRIPTION
Two power outlets are utilized on this model. One
in the instrument panel center lower bezel and the
other in the center console. The power outlet bases
are secured by a snap fit within the instrument
panel or trim panel. A plastic protective cap snaps
into the power outlet base when the power outlet is
not being used, and hangs from the power outlet base
mount by an integral bail strap while the power out-
let is in use.The power outlet receptacle unit and the accessory
power outlet protective cap are available for service.
The power outlet receptacle cannot be repaired and,
if faulty or damaged, it must be replaced.
OPERATION
The power outlet base or receptacle shell is con-
nected to ground, and an insulated contact in the
bottom of the shell is connected to battery current.
The power outlet receives battery voltage from a fuse
in the integrated power module at all times.
While the power outlet is very similar to a cigar
lighter base unit, it does not include the two small
spring-clip retainers inside the bottom of the recepta-
cle shell that are used to secure the cigar lighter
heating element to the insulated contact.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER OUTLET
For complete circuit diagrams, refer toWiring
Diagrams.
(1) Check the fused B(+) fuse in the integrated
power module. If OK, go to Step 2. If not OK, repair
the shorted circuit or component as required and
replace the faulty fuse.
(2) Check for battery voltage at the fused B(+) fuse
in the integrated power module. If OK, go to Step 3.
If not OK, repair the open fused B(+) circuit to the
battery as required.
(3) Remove the plastic protective cap from the
power outlet receptacle. Check for continuity between
the inside circumference of the power outlet recepta-
cle and a good ground. There should be continuity. If
OK, go to Step 4. If not OK, go to Step 5.
(4) Check for battery voltage at the insulated con-
tact located at the back of the power outlet recepta-
cle. If not OK, go to Step 5.
(5) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable. Remove the power outlet receptacle from the
instrument panel. Disconnect the wire harness con-
nector from the power outlet receptacle. Check for
continuity between the ground circuit cavity of the
power outlet wire harness connector and a good
ground. There should be continuity. If OK, go to Step
6. If not OK, repair the open ground circuit to ground
as required.
(6) Connect the battery negative cable. Check for
battery voltage at the fused B(+) circuit cavity of the
power outlet wire harness connector. If OK, replace
the faulty power outlet receptacle. If not OK, repair
the open fused B(+) circuit to the integrated power
module fuse as required.
DR8W-97 POWER DISTRIBUTION 8W - 97 - 7
IOD FUSE (Continued)
Page 2500 of 2627

NOTE: The air gap is determined by the spacer
shims. When installing an original, or a new clutch
assembly, try the original shims first. When install-
ing a new clutch onto a compressor that previously
did not have a clutch, use a 1.0, 0.50, and 0.13 mil-
limeter (0.040, 0.020, and 0.005 inch) shims from the
new clutch hardware package that is provided with
the new clutch.
(9) To complete the procedure (Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/A/C COM-
PRESSOR - INSTALLATION).
A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH
RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The A/C compressor clutch relay (Fig. 10) is a
International Standards Organization (ISO) micro-re-
lay. Relays conforming to the ISO specifications have
common physical dimensions, current capacities, ter-
minal patterns, and terminal functions. The ISO
micro-relay terminal functions are the same as a con-
ventional ISO relay. However, the ISO micro-relay
terminal pattern (or footprint) is different, the cur-
rent capacity is lower, and the physical dimensions
are smaller than those of the conventional ISO relay.
The A/C compressor clutch relay is located in the
intergrated power module (IPM) in the engine com-
partment. See the fuse and relay layout label affixed
to the inside surface of the IPM cover for A/C com-
pressor clutch relay identification and location.
The black, molded plastic case is the most visible
component of the A/C compressor clutch relay. Fivemale spade-type terminals extend from the bottom of
the base to connect the relay to the vehicle electrical
system, and the ISO designation for each terminal is
molded into the base adjacent to each terminal. The
ISO terminal designations are as follows:
²30 (Common Feed)- This terminal is con-
nected to the movable contact point of the relay.
²85 (Coil Ground)- This terminal is connected
to the ground feed side of the relay control coil.
²86 (Coil Battery)- This terminal is connected
to the battery feed side of the relay control coil.
²87 (Normally Open)- This terminal is con-
nected to the normally open fixed contact point of the
relay.
²87A (Normally Closed)- This terminal is con-
nected to the normally closed fixed contact point of
the relay.
OPERATION
The A/C compressor clutch relay is an electrome-
chanical switch that uses a low current input from
the powertrain control module (PCM) or engine con-
trol module (ECM) depending on engine application,
to control the high current output to the compressor
clutch electromagnetic coil. The movable common
feed contact point is held against the fixed normally
closed contact point by spring pressure. When the
relay coil is energized, an electromagnetic field is
produced by the coil windings. This electromagnetic
field draws the movable relay contact point away
from the fixed normally closed contact point, and
holds it against the fixed normally open contact
point. When the relay coil is de-energized, spring
pressure returns the movable contact point back
against the fixed normally closed contact point. The
resistor or diode is connected in parallel with the
relay coil in the relay, and helps to dissipate voltage
Fig. 9 Check Clutch Air Gap - Typical
1 - FEELER GAUGE
Fig. 10 A/C Compressor Clutch Micro-Relay
30 - COMMON FEED
85 - COIL GROUND
86 - COIL BATTERY
87 - NORMALLY OPEN
87A - NORMALLY CLOSED
DRCONTROLS 24 - 13
A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH/COIL (Continued)