relay DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.G Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1998, Model line: RAM 1500, Model: DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.GPages: 2627
Page 492 of 2627
IGNITION COIL RESISTANCE - 3.7L V-6
PRIMARY RESISTANCE
21-27ÉC (70-80ÉF)SECONDARY
RESISTANCE 21-27ÉC
(70-80ÉF)
0.6 - 0.9 Ohms 6,000 - 9,000 Ohms
IGNITION COIL RESISTANCE - 4.7L V-8
PRIMARY
RESISTANCE 21-27ÉC
(70-80ÉF)SECONDARY
RESISTANCE 21-27ÉC
(70-80ÉF)
0.6 - 0.9 Ohms 6,000 - 9,000 Ohms
IGNITION COIL RESISTANCE - 5.7L V-8
PRIMARY RESISTANCE @ 21-27ÉC (70-80ÉF)
0.558 - 0.682 Ohms
(Plus or Minus 10% @ 70-80É F)
IGNITION TIMING
Ignition timing is not adjustable on any engine.
AUTOMATIC SHUT DOWN
RELAY
DESCRIPTION - PCM OUTPUT
The 5±pin, 12±volt, Automatic Shutdown (ASD)
relay is located in the Power Distribution Center
(PDC). Refer to label on PDC cover for relay location.
OPERATION
OPERATION - PCM OUTPUT
The ASD relay supplies battery voltage (12+ volts)
to the fuel injectors and ignition coil(s). With certain
emissions packages it also supplies 12±volts to the
oxygen sensor heating elements.
The ground circuit for the coil within the ASD
relay is controlled by the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM). The PCM operates the ASD relay by switch-
ing its ground circuit on and off.
The ASD relay will be shut±down, meaning the
12±volt power supply to the ASD relay will be de-ac-
tivated by the PCM if:
²the ignition key is left in the ON position. This
is if the engine has not been running for approxi-
mately 1.8 seconds.
²there is a crankshaft position sensor signal to
the PCM that is lower than pre-determined values.
OPERATION - ASD SENSE - PCM INPUT
A 12 volt signal at this input indicates to the PCM
that the ASD has been activated. The relay is used to
connect the oxygen sensor heater element, ignition
coil and fuel injectors to 12 volt + power supply.
This input is used only to sense that the ASD relay
is energized. If the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM) does not see 12 volts at this input when the
ASD should be activated, it will set a Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ASD AND FUEL
PUMP RELAYS
The following description of operation and
tests apply only to the Automatic Shutdown
(ASD) and fuel pump relays. The terminals on the
bottom of each relay are numbered. Two different
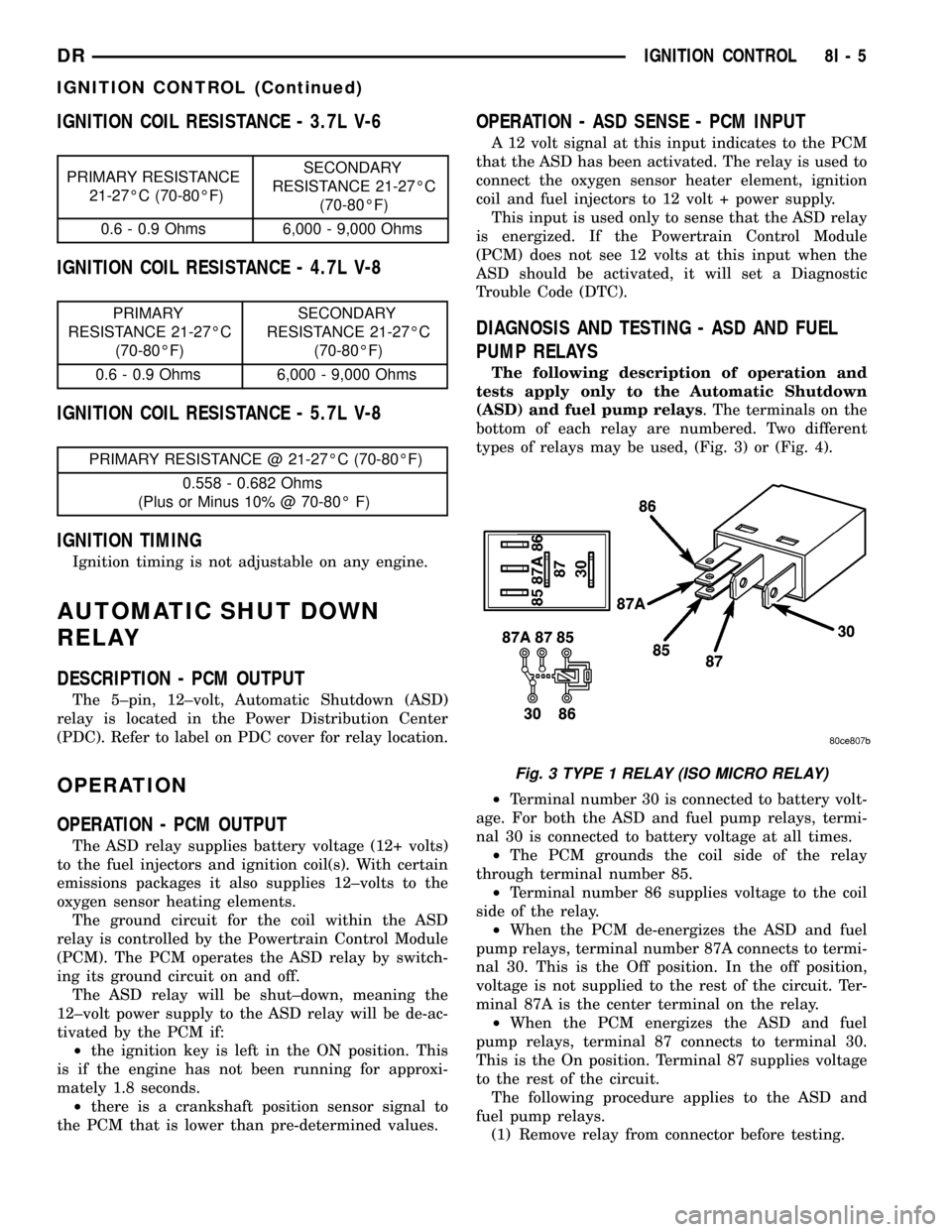
types of relays may be used, (Fig. 3) or (Fig. 4).
²Terminal number 30 is connected to battery volt-
age. For both the ASD and fuel pump relays, termi-
nal 30 is connected to battery voltage at all times.
²The PCM grounds the coil side of the relay
through terminal number 85.
²Terminal number 86 supplies voltage to the coil
side of the relay.
²When the PCM de-energizes the ASD and fuel
pump relays, terminal number 87A connects to termi-
nal 30. This is the Off position. In the off position,
voltage is not supplied to the rest of the circuit. Ter-
minal 87A is the center terminal on the relay.
²When the PCM energizes the ASD and fuel
pump relays, terminal 87 connects to terminal 30.
This is the On position. Terminal 87 supplies voltage
to the rest of the circuit.
The following procedure applies to the ASD and
fuel pump relays.
(1) Remove relay from connector before testing.
Fig. 3 TYPE 1 RELAY (ISO MICRO RELAY)
DRIGNITION CONTROL 8I - 5
IGNITION CONTROL (Continued)
Page 493 of 2627

(2) With the relay removed from the vehicle, use
an ohmmeter to check the resistance between termi-
nals 85 and 86. The resistance should be 75 ohms +/-
5 ohms.
(3) Connect the ohmmeter between terminals 30
and 87A. The ohmmeter should show continuity
between terminals 30 and 87A.
(4) Connect the ohmmeter between terminals 87
and 30. The ohmmeter should not show continuity at
this time.
(5) Connect one end of a jumper wire (16 gauge or
smaller) to relay terminal 85. Connect the other end
of the jumper wire to the ground side of a 12 volt
power source.
(6) Connect one end of another jumper wire (16
gauge or smaller) to the power side of the 12 volt
power source.Do not attach the other end of the
jumper wire to the relay at this time.
WARNING: DO NOT ALLOW OHMMETER TO CON-
TACT TERMINALS 85 OR 86 DURING THIS TEST.
DAMAGE TO OHMMETER MAY RESULT.
(7) Attach the other end of the jumper wire to
relay terminal 86. This activates the relay. The ohm-
meter should now show continuity between relay ter-
minals 87 and 30. The ohmmeter should not show
continuity between relay terminals 87A and 30.
(8) Disconnect jumper wires.(9) Replace the relay if it did not pass the continu-
ity and resistance tests. If the relay passed the tests,
it operates properly. Check the remainder of the ASD
and fuel pump relay circuits. Refer to 8, Wiring Dia-
grams.
REMOVAL
The ASD relay is located in the Power Distribution
Center (PDC) (Fig. 5). Refer to label on PDC cover
for relay location.
(1) Remove PDC cover.
(2) Remove relay from PDC.
(3) Check condition of relay terminals and PDC
connector terminals for damage or corrosion. Repair
if necessary before installing relay.
(4) Check for pin height (pin height should be the
same for all terminals within the PDC connector).
Repair if necessary before installing relay.
INSTALLATION
The ASD relay is located in the Power Distribution
Center (PDC) (Fig. 5). Refer to label on PDC cover
for relay location.
(1) Install relay to PDC.
(2) Install cover to PDC.
Fig. 4 ASD AND FUEL PUMP RELAY TERMINALSÐ
TYPE 2
TERMINAL LEGEND
NUMBER IDENTIFICATION
30 COMMON FEED
85 COIL GROUND
86 COIL BATTERY
87 NORMALLY OPEN
87A NORMALLY CLOSED
Fig. 5 PDC LOCATION
1 - BATTERY
2 - INTEGRATED POWER MODULE (IPM)
8I - 6 IGNITION CONTROLDR
AUTOMATIC SHUT DOWN RELAY (Continued)
Page 499 of 2627

OPERATION
3.7L V-6
Battery voltage is supplied to the 6 individual igni-
tion coils from the ASD relay. The Powertrain Con-
trol Module (PCM) opens and closes each ignition coil
ground circuit at a determined time for ignition coil
operation.
Base ignition timing is not adjustable.By con-
trolling the coil ground circuit, the PCM is able to set
the base timing and adjust the ignition timing
advance. This is done to meet changing engine oper-
ating conditions.
The ignition coil is not oil filled. The windings are
embedded in an epoxy compound. This provides heat
and vibration resistance that allows the ignition coil
to be mounted on the engine.
Because of coil design, spark plug cables (second-
ary cables) are not used with the 3.7L V-6 engine.
4.7L V-8
Battery voltage is supplied to the 8 individual igni-
tion coils from the ASD relay. The Powertrain Con-
trol Module (PCM) opens and closes each ignition coil
ground circuit at a determined time for ignition coil
operation.
Fig. 17 IGNITION COIL LOCATION - 4.7L V-8
1 - IGNITION COIL
2 - COIL ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
3 - COIL MOUNTING STUD/NUT
Fig. 18 IGNITION COIL - 5.7L V-8
1 - IGNITION COIL
2 - MOUNTING BOLTS (2)
3 - BOOT TO SPARK PLUG
Fig. 19 IGNITION COIL R/I Ð 5.7L V-8
1 - SLIDE LOCK (SLIDE OUTWARD TO UNLOCK)
2 - SPARK PLUG CABLE (TO OPPOSITE CYLINDER BANK
SPARK PLUG)
3 - RELEASE LOCK / TAB (PUSH HERE)
4 - ELEC. CONNECTOR
5 - IGNITION COIL
6 - COIL MOUNTING BOLTS (2)
7 - SPARK PLUG CABLE (TO OPPOSITE CYLINDER BANK
IGNITION COIL)
8I - 12 IGNITION CONTROLDR
IGNITION COIL (Continued)
Page 500 of 2627

Base ignition timing is not adjustable.By con-
trolling the coil ground circuit, the PCM is able to set
the base timing and adjust the ignition timing
advance. This is done to meet changing engine oper-
ating conditions.
The ignition coil is not oil filled. The windings are
embedded in an epoxy compound. This provides heat
and vibration resistance that allows the ignition coil
to be mounted on the engine.
Because of coil design, spark plug cables (second-
ary cables) are not used with the 4.7L V-8 engine.
5.7L V-8
The ignition system is controlled by the Powertrain
Control Module (PCM) on all engines.
A ªwasted sparkº system is used on the 5.7L
engine combining paired, or dual-firing coils, and 2
spark plugs per cylinder. The coils and spark plugs
are connected with paired, secondary high-voltage
cables.
Each cylinder is equipped with 1 dual-output coil.
Meaning one coil mounts directly over one of the
dual spark plugs for 1 high-voltage output. A second
high-voltage output is supplied directly from the
same coil (using a plug cable) to one of the dual
spark plugs on a corresponding (paired) cylinder on
the opposite cylinder bank.
Each coil fires 2 spark plugs simultaneously on
each of the cylinder banks (one cylinder on compres-
sion stroke and one cylinder on exhaust stroke).
EXAMPLE :When the #1 cylinder is on compression
stroke and ready for spark, the #1 coil will fire one of
the dual spark plugs on the #1 cylinder (directly
below the coil). The other dual spark plug on the #1
cylinder will be fired by the #6 coil. At the same
time, the #1 coil will fire a ªwasted sparkº to one of
the dual spark plugs at the #6 cylinder as coil #6 also
fires a ªwasted sparkº to one of the dual spark plugs
at the #6 cylinder.
The firing order is paired at cylinders 1/6, 2/3, 4/7,
5/8. Basic cylinder firing order is 1±8±4±3±6±5±7±2.
Battery voltage is supplied to all of the ignition
coils positive terminals from the ASD relay. If the
PCM does not see a signal from the crankshaft and
camshaft sensors (indicating the ignition key is ON
but the engine is not running), it will shut down the
ASD circuit.
Base ignition timing is not adjustable on the
5.7L V-8 engine.By controlling the coil ground cir-
cuits, the PCM is able to set the base timing and
adjust the ignition timing advance. This is done to
meet changing engine operating conditions.
The PCM adjusts ignition timing based on inputs it
receives from:
²The engine coolant temperature sensor
²The crankshaft position sensor (engine speed)²The camshaft position sensor (crankshaft posi-
tion)
²The manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor
²The throttle position sensor
²Transmission gear selection
REMOVAL
3.7L V-6
An individual ignition coil is used for each spark
plug (Fig. 15). The coil fits into machined holes in the
cylinder head. A mounting stud/nut secures each coil
to the top of the intake manifold (Fig. 16). The bot-
tom of the coil is equipped with a rubber boot to seal
the spark plug to the coil. Inside each rubber boot is
a spring. The spring is used for a mechanical contact
between the coil and the top of the spark plug. These
rubber boots and springs are a permanent part of the
coil and are not serviced separately. An o-ring (Fig.
15) is used to seal the coil at the opening into the cyl-
inder head.
(1) Depending on which coil is being removed, the
throttle body air intake tube or intake box may need
to be removed to gain access to coil.
(2) Disconnect electrical connector from coil by
pushing downward on release lock on top of connec-
tor and pull connector from coil.
(3) Clean area at base of coil with compressed air
before removal.
(4) Remove coil mounting nut from mounting stud
(Fig. 16).
(5) Carefully pull up coil from cylinder head open-
ing with a slight twisting action.
(6) Remove coil from vehicle.
4.7L V-8
An individual ignition coil is used for each spark
plug (Fig. 15). The coil fits into machined holes in the
cylinder head. A mounting stud/nut secures each coil
to the top of the intake manifold (Fig. 17). The bot-
tom of the coil is equipped with a rubber boot to seal
the spark plug to the coil. Inside each rubber boot is
a spring. The spring is used for a mechanical contact
between the coil and the top of the spark plug. These
rubber boots and springs are a permanent part of the
coil and are not serviced separately. An o-ring (Fig.
15) is used to seal the coil at the opening into the cyl-
inder head.
(1) Depending on which coil is being removed, the
throttle body air intake tube or intake box may need
to be removed to gain access to coil.
(2) Disconnect electrical connector (Fig. 17) from
coil by pushing downward on release lock on top of
connector and pull connector from coil.
(3) Clean area at base of coil with compressed air
before removal.
DRIGNITION CONTROL 8I - 13
IGNITION COIL (Continued)
Page 512 of 2627

Sandwiched between the rear cover and the lens,
hood and mask unit is the cluster housing. The
molded plastic cluster housing serves as the carrier
for the cluster circuit board and circuitry, the cluster
connector receptacles, the RKE interface connector,
the gauges, a Light Emitting Diode (LED) for each
cluster indicator, two VFD units, an audible tone
generator, the cluster overlay, the gauge pointers, the
odometer/trip odometer switch and the switch button.
The cluster overlay is a laminated plastic unit. The
dark, visible, outer surface of the overlay is marked
with all of the gauge dial faces and graduations, but
this layer is also translucent. The darkness of this
outer layer prevents the cluster from appearing clut-
tered or busy by concealing the cluster indicators
that are not illuminated, while the translucence of
this layer allows those indicators and icons that are
illuminated to be readily visible. The underlying
layer of the overlay is opaque and allows light from
the LED for each of the various indicators and the
incandescent illumination lamps behind it to be visi-
ble through the outer layer of the overlay only
through predetermined stencil-like cutouts. A rectan-
gular opening in the overlay at the base of both the
speedometer and tachometer dial faces has a smoked
clear lens through which the illuminated VFD units
can be viewed.
Several versions of the EMIC module are offered
on this model. These versions accommodate all of the
variations of optional equipment and regulatory
requirements for the various markets in which the
vehicle will be offered. The microprocessor-based
EMIC utilizes integrated circuitry and information
carried on the Programmable Communications Inter-
face (PCI) data bus network along with several hard
wired analog and multiplexed inputs to monitor sen-
sors and switches throughout the vehicle. In response
to those inputs, the internal circuitry and program-
ming of the EMIC allow it to control and integrate
many electronic functions and features of the vehicle
through both hard wired outputs and the transmis-
sion of electronic message outputs to other electronic
modules in the vehicle over the PCI data bus. (Refer
to 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL
MODULES/COMMUNICATION - DESCRIPTION -
PCI BUS).
Besides typical instrument cluster gauge and indi-
cator support, the electronic functions and features
that the EMIC supports or controls include the fol-
lowing:
²Audible Warnings- The EMIC electronic cir-
cuit board is equipped with an audible tone generator
and programming that allows it to provide various
audible alerts to the vehicle operator, including
chime tones and beep tones. An electromechanical
relay is also soldered onto the circuit board to pro-duce audible clicks that emulate the sound of a con-
ventional turn signal or hazard warning flasher.
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/CHIME/BUZZER -
DESCRIPTION).
²Brake Lamp Control- The EMIC provides
electronic brake lamp request messages to the Front
Control Module (FCM) located on the Integrated
Power Module (IPM) for brake lamp control, exclud-
ing control of the Center High Mounted Stop Lamp
(CHMSL), which remains controlled by a direct hard
wired output of the brake lamp switch.
²Brake Transmission Shift Interlock Control
- The EMIC monitors inputs from the brake lamp
switch, ignition switch, and the Transmission Range
Sensor (TRS), then controls a high-side driver output
to operate the Brake Transmission Shift Interlock
(BTSI) solenoid that locks and unlocks the automatic
transmission gearshift selector lever on the steering
column.
²Cargo Lamp Control- The EMIC provides
direct control of cargo lamp operation with a load
shedding (battery saver) feature which will automat-
ically turn off the cargo lamp if it remains on after a
timed interval.
²Central Locking- The EMIC provides support
for the central locking feature of the power lock sys-
tem. This feature will lock or unlock all doors based
upon the input from the door cylinder lock switch.
Door cylinder lock switches are used only on models
equipped with the optional Vehicle Theft Security
System (VTSS).
²Door Lock Inhibit- The EMIC inhibits locking
of the doors with the power lock switch when the key
is in the ignition switch and the driver side front
door is ajar. However, operation of the door locks is
not inhibited under the same conditions when the
Lock button of the optional RKE transmitter is
depressed.
²Enhanced Accident Response- The EMIC
monitors an input from the Airbag Control Module
(ACM) and, following an airbag deployment, will
immediately disable the power lock output, unlock all
doors by activating the power unlock output, then
enables the power lock output. This feature, like all
other enhanced accident response features, is depen-
dent upon a functional vehicle electrical system fol-
lowing the vehicle impact event.
²Exterior Lighting Control- The EMIC pro-
vides electronic head lamp and/or park lamp request
messages to the Front Control Module (FCM) located
on the Integrated Power Module (IPM) for the appro-
priate exterior lamp control of standard head and
park lamps, as well as optional front fog lamps. This
includes support for headlamp beam selection and
the optical horn feature, also known as flash-to-pass.
DRINSTRUMENT CLUSTER 8J - 3
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER (Continued)
Page 519 of 2627

INPUT AND OUTPUT CIRCUITS
HARD WIRED INPUTS
The hard wired inputs to the EMIC include the fol-
lowing:
²Brake Lamp Switch Output
²Driver Cylinder Lock Switch Sense
²Driver Door Ajar Switch Sense
²Driver Door Lock Switch MUX - with
Power Locks
²Fused B(+) - Ignition-Off Draw
²Fused B(+) - Power Lock Feed - with Power
Locks
²Fused Ignition Switch Output (Accessory-
Run)
²Fused Ignition Switch Output (Off-Run-
Start)
²Fused Ignition Switch Output (Run-Start)
²Headlamp Dimmer Switch MUX
²Headlamp Switch MUX
²Horn Relay Control
²Key-In Ignition Switch Sense
²Left Rear Door Ajar Switch Sense
²Panel Lamps Dimmer Switch Signal
²Park Brake Switch Sense
²Passenger Door Ajar Switch Sense
²Passenger Door Lock Switch MUX - with
Power Locks
²Radio Control MUX
²Right Rear Door Ajar Switch Sense
²RKE Supply - with RKE
²Seat Belt Switch Sense
²Transmission Range Sensor MUX - with
Auto Trans
²Turn/Hazard Switch MUX
²Washer/Beam Select Switch MUX
²Wiper Switch MUX
Refer to the appropriate wiring information for
additional details.
HARD WIRED OUTPUTS
The hard wired outputs of the EMIC include the
following:
²Accessory Switch Bank Illumination Driver
²BTSI Driver - with Auto Trans
²Cargo Lamp Driver
²Dome/Overhead Lamp Driver
²Driver Door Unlock Driver - with Power
Locks
²Headlamp Switch Illumination Driver
²Heated Seat Switch Indicator Driver - with
Heated Seats
²Heater-A/C Control Illumination Driver
²Left Door Lock Driver - with Power Locks
²Left Rear Door Unlock Driver - with Power
Locks²Map/Glove Box Lamp Driver
²Radio Illumination Driver
²Right Door Lock Driver - with Power Locks
²Right Door Unlock Driver - with Power
Locks
²Transfer Case Switch Illumination Driver -
with Four-Wheel Drive
Refer to the appropriate wiring information for
additional details.
GROUNDS
The EMIC receives and supplies a ground path to
several switches and sensors through the following
hard wired circuits:
²Ground - Illumination (2 Circuits)
²Ground - Power Lock - with Power Locks
²Ground - Signal
²Headlamp Switch Return
²Multi-Function Switch Return
²Transmission Range Sensor Return - with
Auto Trans
Refer to the appropriate wiring information for
additional details.
COMMUNICATION
The EMIC has provisions for the following commu-
nication circuits:
²PCI Data Bus
²RKE Program Serial Data - with RKE
²RKE Transmit Serial Data - with RKE
Refer to the appropriate wiring information for
additional details.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - INSTRUMENT
CLUSTER
If all of the instrument cluster gauges and/or indi-
cators are inoperative, refer to PRELIMINARY
DIAGNOSIS. If an individual gauge or Programma-
ble Communications Interface (PCI) data bus mes-
sage-controlled indicator is inoperative, refer to
ACTUATOR TEST. If an individual hard wired indi-
cator is inoperative, refer to the diagnosis and testing
information for that specific indicator.
Refer to the appropriate wiring information. The
wiring information includes wiring diagrams, proper
wire and connector repair procedures, details of wire
harness routing and retention, connector pin-out
information and location views for the various wire
harness connectors, splices and grounds.
8J - 10 INSTRUMENT CLUSTERDR
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER (Continued)
Page 550 of 2627

the upper edge of the instrument cluster, between
the speedometer and the tachometer. Each turn sig-
nal indicator consists of a stencil-like cutout of the
International Control and Display Symbol icon for
ªTurn Warningº in the opaque layer of the instru-
ment cluster overlay. The dark outer layer of the
overlay prevents these icons from being clearly visi-
ble when they are not illuminated. A green Light
Emitting Diode (LED) behind each turn signal indi-
cator cutout in the opaque layer of the overlay causes
the icon to appear in green through the translucent
outer layer of the overlay when the indicator is illu-
minated from behind by the LED, which is soldered
onto the instrument cluster electronic circuit board.
The turn signal indicators are serviced as a unit with
the instrument cluster.
OPERATION
The turn signal indicators give an indication to the
vehicle operator that the turn signal (left or right
indicator flashing) or hazard warning (both left and
right indicators flashing) have been selected and are
operating. These indicators are controlled by transis-
tors on the instrument cluster electronic circuit board
based upon the cluster programming, a hard wired
multiplex input received by the cluster from the turn
signal and hazard warning switch circuitry of the
multi-function switch on the turn/hazard switch mux
circuit, and electronic messages received from the
Front Control Module (FCM) over the Programmable
Communications Interface (PCI) data bus. Each turn
signal indicator Light Emitting Diode (LED) is com-
pletely controlled by the instrument cluster logic cir-
cuit, and that logic will allow this indicator to
operate whenever the instrument cluster receives a
battery current input on the fused B(+) circuit.
Therefore, each LED can be illuminated regardless of
the ignition switch position. The LED only illumi-
nates when it is provided a path to ground by the
instrument cluster transistor. The instrument cluster
will turn on the turn signal indicators for the follow-
ing reasons:
²Turn Signal-On Input- Each time the cluster
detects a turn signal-on input from the turn signal
switch circuitry of the multi-function switch on the
turn/hazard switch mux circuit, the requested turn
signal lamps and turn signal indicator will be flashed
on and off, and an electromechanical relay soldered
onto the cluster electronic circuit board will produce
a clicking sound to emulate a conventional turn sig-
nal flasher. The turn signals and the turn signal
indicators continue to flash on and off until the clus-
ter receives a turn signal-off input from the multi-
function switch, or until the ignition switch is turned
to the Off position, whichever occurs first.²Hazard Warning-On Input- Each time the
cluster detects a hazard warning-on input from the
hazard warning switch circuitry of the multi-function
switch on the turn/hazard switch mux circuit, all of
the turn signal lamps and both turn signal indicators
will be flashed on and off, and an electromechanical
relay soldered onto the cluster electronic circuit
board will produce a clicking sound to emulate a con-
ventional hazard warning flasher. The turn signals
and the turn signal indicators continue to flash on
and off until the cluster receives a hazard warning-
off input from the multi-function switch.
²Lamp Out Mode- The instrument cluster also
sends electronic turn signal on and off messages to
the FCM over the PCI data bus, and the FCM
flashes the appropriate exterior turn signal lamps. If
the FCM detects an inoperative turn signal lamp or
circuit, it increases the flash rate for the remaining
operative turn signals and sends an electronic mes-
sage back to the instrument cluster. The instrument
cluster then increases the flash rate of the turn sig-
nal indicator(s) and the clicking rate of the electro-
mechanical relay to provide an indication of the
problem to the vehicle operator.
²Actuator Test- Each time the cluster is put
through the actuator test, the turn signal indicators
will be turned on, then off again during the bulb
check portion of the test to confirm the functionality
of each LED and the cluster control circuitry.
The instrument cluster continually monitors the
multi-function switch and electronic messages from
the FCM to determine the proper turn signal and
hazard warning system control. For further diagnosis
of the turn signal indicators or the instrument clus-
ter circuitry that controls the indicators, (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/INSTRUMENT CLUSTER - DIAGNO-
SIS AND TESTING). For proper diagnosis of the
turn signal and hazard warning system, the multi-
function switch, the FCM, the PCI data bus, or the
electronic message inputs to the instrument cluster
that control the turn signal indicators, a DRBIIIt
scan tool is required. Refer to the appropriate diag-
nostic information.
UPSHIFT INDICATOR
DESCRIPTION
An upshift indicator is standard equipment on all
instrument clusters (Fig. 33). However, on vehicles
not equipped with a manual transmission, this indi-
Fig. 33 Upshift Indicator
DRINSTRUMENT CLUSTER 8J - 41
TURN SIGNAL INDICATOR (Continued)
Page 556 of 2627
LAMPS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR............... 1LAMPS/LIGHTING - INTERIOR............... 26
LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR
DESCRIPTION..........................2
OPERATION............................2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - LAMPS/
LIGHTING - EXTERIOR..................3
STANDARD PROCEDURE
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS.................7
SPECIFICATIONS
EXTERIOR LAMPS.....................7
BACKUP LAMP
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - WITH CARGO BOX...........7
REMOVAL - WITHOUT CARGO BOX........7
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - WITH CARGO BOX........7
INSTALLATION - WITHOUT CARGO BOX....8
BACKUP LAMP SWITCH
DESCRIPTION..........................8
OPERATION............................8
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BACKUP LAMP
SWITCH.............................8
BRAKE LAMP
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - WITH CARGO BOX...........9
REMOVAL - WITHOUT CARGO BOX........9
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - WITH CARGO BOX........9
INSTALLATION - WITHOUT CARGO BOX....9
BRAKE LAMP SWITCH
DESCRIPTION..........................9
OPERATION............................9
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BRAKE LAMP
SWITCH............................10
REMOVAL.............................10
INSTALLATION.........................11
CENTER HIGH MOUNTED STOP LAMP
REMOVAL.............................11INSTALLATION.........................11
CENTER HIGH MOUNTED STOP LAMP UNIT
REMOVAL.............................11
INSTALLATION.........................11
CAB CLEARANCE LAMP
REMOVAL.............................11
INSTALLATION.........................12
FOG LAMP
REMOVAL.............................12
INSTALLATION.........................12
FOG LAMP RELAY
DESCRIPTION.........................12
OPERATION...........................13
REMOVAL.............................13
INSTALLATION.........................13
HAZARD SWITCH
DESCRIPTION.........................14
OPERATION...........................14
HEADLAMP
REMOVAL.............................14
INSTALLATION.........................14
HEADLAMP SWITCH
DESCRIPTION.........................14
OPERATION...........................14
REMOVAL.............................14
INSTALLATION.........................15
HEADLAMP UNIT
REMOVAL.............................15
INSTALLATION.........................15
ADJUSTMENTS........................16
LICENSE PLATE LAMP
REMOVAL.............................17
INSTALLATION.........................17
LICENSE PLATE LAMP UNIT
REMOVAL.............................17
INSTALLATION.........................17
DRLAMPS 8L - 1
Page 557 of 2627

MARKER LAMP UNIT
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - FENDER MARKER LAMP......17
REMOVAL - TAILGATE MARKER LAMP.....18
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - FENDER MARKER LAMP . . 18
INSTALLATION - TAILGATE MARKER LAMP . 18
MULTI-FUNCTION SWITCH
DESCRIPTION - TURN SIGNAL SYSTEM.....18
OPERATION - TURN SIGNAL SYSTEM.......18
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - MULTI-
FUNCTION SWITCH...................18
REMOVAL.............................19
INSTALLATION.........................19
PARK LAMP RELAY
DESCRIPTION.........................20
OPERATION...........................20
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PARK LAMP
RELAY..............................20
REMOVAL.............................21
INSTALLATION.........................21
PARK/TURN SIGNAL LAMP
REMOVAL.............................21
INSTALLATION.........................21
TAIL LAMP
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - WITH CARGO BOX..........22REMOVAL - WITHOUT CARGO BOX.......22
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - WITH CARGO BOX.......22
INSTALLATION - WITHOUT CARGO BOX . . . 22
TAIL LAMP UNIT
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - WITH CARGO BOX..........22
REMOVAL - WITHOUT CARGO BOX.......23
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - WITH CARGO BOX.......23
INSTALLATION - WITHOUT CARGO BOX . . . 23
TRAILER TOW WIRING
DESCRIPTION.........................24
TURN LAMP
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - WITH CARGO BOX..........24
REMOVAL - WITHOUT CARGO BOX.......24
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - WITH CARGO BOX.......24
INSTALLATION - WITHOUT CARGO BOX . . . 24
UNDERHOOD LAMP
REMOVAL.............................25
INSTALLATION.........................25
UNDERHOOD LAMP UNIT
REMOVAL.............................25
INSTALLATION.........................25
LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR
DESCRIPTION
The exterior lighting system for this model include
the following components:
²Backup Lamps
²Brake Lamps
²Daytime Running Lamps
²Front Fog Lamps
²Hazard Warning Lamps
²Headlamps
²Park Lamps
²Turn Signal Lamps
Other components of the exterior lighting system
for this model include:
²Backup Lamp Switch
²Brake Lamp Switch
²Front Control Module
²Front Fog Lamp Relay
²Hazard Switch
²Multi-Function Switch
²Park Lamp Relay
²Trailer Tow Connectors
Some of the interior and exterior lighting functions
are governed by the front control module. The head-
lamp, dome, and door ajar switchs provide signals to
the instrument cluster. The instrument cluster sends
a J1850 message to the front control module to
enable the necessary components for illumination.Hard wired circuitry connects the exterior lighting
system components to the electrical system of the
vehicle. Refer to the appropriate wiring information.OPERATION
DAYTIME RUNNING LAMPS
Power is reduced using pulse-width modulation to
the high beams, where by the power is switched on
and off rapidly instead of remaining on continuously.
The duration and interval of the power pulses is pro-
grammed into the Front Control Module (FCM).
HEADLAMP SYSTEM
The instrument cluster monitors both the multi-
plexed headlamp and multifunction switches. The
instrument cluster transmits a J1850 bus message to
the front control module (FCM) to activate the head-
lamps. The headlamp system will default to head-
lamps ON position when ignition switch is ON and
when an open or short circuit failure occurs on the
headlamp switch input to the instrument cluster. The
system will return to normal operation when the
open or short is repaired. A fault will be reported by
the Instrument Cluster when a failure occurs on the
dimmer or headlamp switch input.
If the exterior lamps are ON, and the headlamp
switch is in any position other than OFF, with the
ignition switch OFF (LOCK) after 5 minutes, the
8L - 2 LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIORDR
Page 558 of 2627

Instrument Cluster transmits a message via J1850
informing the the FCM. The FCM will then turn off
the headlamps, park lamps and fog lamps. This fea-
ture (load shed) prevents the vehicle battery from
being discharged when the vehicle lights have been
left ON.
HEADLAMP TIME DELAY SYSTEM
The headlamp time delay system is activated by
turning the headlamps ON (high or low beam) while
the engine is running, turning the ignition switch
OFF, and then turning the headlamp switch OFF
within 45 seconds. The system will not activate if
more than 45 seconds elapse between ignition switch
OFF and headlamp switch OFF. The FCM will allow
the headlamps to remain ON for 60 seconds (config-
urable) before they automatically turn off (If the key
is in the ignition during the headlamp time delay
mode, then the headlamps including panel dimming
will be ON).
LAMP OUTAGE
If one or more of the following lamps (Low and/or
High beams, Brake and/or Turn Signal) are out, then
a ªlamps outº indicator located in the cluster will
illuminate.
OPTICAL HORN/HIGH BEAMS
When the multiplexed multifunction switch is
pulled to the first detent (optical horn) signal, the
headlamps are ON, the Instrument Cluster shall
send a message via J1850 to the FCM to turn on the
headlamps drivers to illuminate all four filaments
(Low and High beams). When the multifunction
switch is pulled to the second detent (high beam) sig-
nal and the headlamps are ON, the Instrument Clus-
ter shall send a message via J1850 to the FCM to
turn on the headlamps drivers. The High Beams are
illuminated and the Low Beams and Fog Lamps (if
ON) are extinguished. If the headlamps were in the
high beam configuration when power was removedfrom the headlamps, the headlamps will return to
their last state prior to being shut off.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - LAMPS/LIGHTING
- EXTERIOR
WARNING: EYE PROTECTION SHOULD BE USED
WHEN SERVICING GLASS COMPONENTS. PER-
SONAL INJURY CAN RESULT.
CAUTION: Do not touch the glass of halogen bulbs
with fingers or other possibly oily surface, reduced
bulb life will result. Do not use bulbs other than
those indicated in the Bulb Application table. Dam-
age to lamp and/or Daytime Running Lamp Module
can result. Do not use fuses, circuit breakers or
relays having greater amperage value than indi-
cated on the fuse panel or in the Owners Manual.
When a vehicle experiences problems with the
headlamp system, verify the condition of the battery
connections, fuses, charging system, headlamp bulbs,
wire connectors, relay, multifunction switch, and
headlamp switch. Refer to the appropriate wiring
information.
Each vehicle is equipped with various lamp assem-
blies. A good ground is necessary for proper lighting
operation. Grounding is provided by the lamp socket
when it comes in contact with the metal body, or
through a separate ground wire.
When changing lamp bulbs check the socket for
loose pin connections and corrosion. Repair as neces-
sary.
When it is necessary to remove components to ser-
vice another, it should not be necessary to apply
excessive force or bend a component to remove it.
Before damaging a trim component, verify hidden
fasteners or captured edges are not holding the com-
ponent in place.
DRLAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR 8L - 3
LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR (Continued)