spark DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.G Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1998, Model line: RAM 1500, Model: DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.GPages: 2627
Page 1406 of 2627
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE
DIAGNOSIS - INTRODUCTION
Engine diagnosis is helpful in determining the
causes of malfunctions not detected and remedied by
routine maintenance.
These malfunctions may be classified as either per-
formance (e.g., engine idles rough and stalls) or
mechanical (e.g., a strange noise).
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TEST-
ING) - PERFORMANCE and (Refer to 9 - ENGINE -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING)ÐMECHANICAL for
possible causes and corrections of malfunctions.
(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING) and (Refer to 14 -
FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING) for the fuel system diagnosis.Additional tests and diagnostic procedures may be
necessary for specific engine malfunctions that can
not be isolated with the Service Diagnosis charts.
Information concerning additional tests and diagno-
sis is provided within the following diagnosis:
²Cylinder Compression Pressure Test (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
²Cylinder Combustion Pressure Leakage Test
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TEST-
ING).
²Engine Cylinder Head Gasket Failure Diagnosis
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - DIAGNO-
SIS AND TESTING).
²Intake Manifold Leakage Diagnosis (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE DIAGNOSIS - PERFORMANCE
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
ENGINE WILL NOT START 1. Weak battery 1. Charge or replace as necessary.
2. Corroded or loose battery
connections.2. Clean and tighten battery
connections. Apply a coat of light
mineral grease to the terminals.
3. Faulty starter. 3. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
STARTING - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
4. Faulty coil or control unit. 4. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/IGNITION COIL
- REMOVAL).
5. Incorrect spark plug gap. 5. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/SPARK PLUG -
CLEANING).
6. Dirt or water in fuel system. 6. Clean system and replace fuel
filter.
7. Faulty fuel pump, relay or wiring. 7. Repair or replace as necessary.
DRENGINE - 5.7L 9 - 183
ENGINE - 5.7L (Continued)
Page 1407 of 2627
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
ENGINE STALLS OR ROUGH IDLE 1. Idle speed set to low. 1. (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/
FUEL INJECTION/IDLE AIR
CONTROL MOTOR - REMOVAL).
2. Idle mixture too lean or too rich. 2. Refer to Powertrain Diagnosis
Information.
3. Vacuum leak. 3. Inspect intake manifold and
vacuum hoses, repair or replace as
necessary.
4. Faulty coil. 4. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/IGNITION COIL
- REMOVAL).
5. Incorrect engine timing. 5. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE
TIMING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
1. ENGINE LOSS OF POWER 1. Dirty or incorrectly gapped spark
plugs.1. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/SPARK PLUG -
CLEANING).
2. Dirt or water in fuel system. 2. Clean system and replace fuel
filter.
3. Faulty fuel pump. 3. (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/
FUEL DELIVERY/FUEL PUMP -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
4. Blown cylinder head gasket. 4. Replace cylinder head gasket.
5. Low compression. 5. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
6. Burned, warped or pitted valves. 6. Replace as necessary.
7. Plugged or restricted exhaust
system.7. Inspect and replace as necessary.
8. Faulty coil. 8. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/IGNITION COIL
- REMOVAL).
1. ENGINE MISSES ON
ACCELERATION1. Spark plugs dirty or incorrectly
gapped.1. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/SPARK PLUG -
CLEANING).
2. Dirt in fuel system. 2. Clean fuel system.
3. Burned, warped or pitted valves. 3. Replcae as necessary.
4. Faulty coil. 4. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/IGNITION COIL
- REMOVAL).
1. ENGINE MISSES AT HIGH SPEED 1. Spark plugs dirty or incorrectly
gapped.1. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/SPARK PLUG -
CLEANING).
2. Faulty coil. 2. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/IGNITION COIL
- REMOVAL).
3. Dirt or water in fuel system. 3. Clean system and replace fuel
filter.
9 - 184 ENGINE - 5.7LDR
ENGINE - 5.7L (Continued)
Page 1409 of 2627

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMPRESSION PRESSURE
The results of a cylinder compression pressure test
can be utilized to diagnose several engine malfunc-
tions.
Ensure the battery is completely charged and the
engine starter motor is in good operating condition.
Otherwise the indicated compression pressures may
not be valid for diagnosis purposes.
(1) Clean the spark plug recesses with compressed
air.
(2) Remove the spark plugs.
(3) Disable the fuel system (Refer to 14 - FUEL
SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY - DESCRIPTION).
(4) Remove the ASD relay (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/IGNITION CONTROL/AUTO SHUT DOWN
RELAY - REMOVAL).
(5) Insert a compression pressure gauge and rotate
the engine with the engine starter motor for three
revolutions.
(6) Record the compression pressure on the 3rd
revolution. Continue the test for the remaining cylin-
ders.
(7) (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS) for
the correct engine compression pressures.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE
The combustion pressure leakage test provides an
accurate means for determining engine condition.
Combustion pressure leakage testing will detect:
²Exhaust and intake valve leaks (improper seat-
ing).²Leaks between adjacent cylinders or into water
jacket.
²Any causes for combustion/compression pressure
loss.
(1) Check the coolant level and fill as required. DO
NOT install the radiator cap.
(2) Start and operate the engine until it attains
normal operating temperature, then turn the engine
OFF.
(3) Remove the spark plugs.
(4) Remove the oil filler cap.
(5) Remove the air cleaner hose.
(6) Calibrate the tester according to the manufac-
turer's instructions. The shop air source for testing
should maintain 483 kPa (70 psi) minimum, 1,379
kPa (200 psi) maximum and 552 kPa (80 psi) recom-
mended.
(7) Perform the test procedures on each cylinder
according to the tester manufacturer's instructions.
Set piston of cylinder to be tested at TDC compres-
sion,While testing, listen for pressurized air escaping
through the throttle body, tailpipe and oil filler cap
opening. Check for bubbles in the radiator coolant.
All gauge pressure indications should be equal,
with no more than 25% leakage.
FOR EXAMPLE:At 552 kPa (80 psi) input pres-
sure, a minimum of 414 kPa (60 psi) should be main-
tained in the cylinder.
Refer to CYLINDER COMBUSTION PRESSURE
LEAKAGE DIAGNOSIS CHART.
CYLINDER COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE DIAGNOSIS CHART
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
AIR ESCAPES THROUGH
THROTTLE BODYIntake valve bent, burnt, or not
seated properlyInspect valve and valve seat. Reface
or replace, as necessary. Inspect
valve springs. Replace as necessary.
AIR ESCAPES THROUGH TAILPIPE Exhaust valve bent, burnt, or not
seated properlyInspect valve and valve seat. Reface
or replace, as necessary. Inspect
valve springs. Replace as necessary.
AIR ESCAPES THROUGH
RADIATORHead gasket leaking or cracked
cylinder head or blockRemove cylinder head and inspect.
Replace defective part
MORE THAN 50% LEAKAGE FROM
ADJACENT CYLINDERSHead gasket leaking or crack in
cylinder head or block between
adjacent cylindersRemove cylinder head and inspect.
Replace gasket, head, or block as
necessary
MORE THAN 25% LEAKAGE AND
AIR ESCAPES THROUGH OIL
FILLER CAP OPENING ONLYStuck or broken piston rings; cracked
piston; worn rings and/or cylinder wallInspect for broken rings or piston.
Measure ring gap and cylinder
diameter, taper and out-of-round.
Replace defective part as necessary
9 - 186 ENGINE - 5.7LDR
ENGINE - 5.7L (Continued)
Page 1410 of 2627
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐENGINE DIAGNOSIS - LUBRICATION
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
OIL LEAKS 1. Gaskets and O-Rings. 1.
(a) Misaligned or damaged. (a) Replace as necessary.
(b) Loose fasteners, broken or
porous metal parts.(b) Tighten fasteners, Repair or
replace metal parts.
2. Crankshaft rear seal 2. Replace as necessary.
3. Crankshaft seal flange.
Scratched, nicked or grooved.3. Polish or replace crankshaft.
4. Oil pan flange cracked. 4. Replace oil pan.
5.Front cover seal, damaged or
misaligned.5. Replace seal.
6. Scratched or damaged vibration
damper hub.6. Polish or replace damper.
7. Crankshaft Rear Flange
Microporosity7. Replace Crankshaft
OIL PRESSURE DROP 1. Low oil level. 1. Check and correct oil level.
2. Faulty oil pressure sending unit. 2. Replace sending unit.
3. Low oil pressure. 3. Check pump and bearing
clearance.
4. Clogged oil filter. 4. Replace oil filter.
5. Worn oil pump. 5. Replace as necessary.
6. Thin or diluted oil. 6. Change oil and filter.
7. Excessive bearing clearance. 7. Replace as necessary.
8. Oil pump relief valve stuck. 8. Replace oil pump.
9. Oil pickup tube loose or
damaged.9. Replace as necessary.
OIL PUMPING AT RINGS; SPARK
PLUGS FOULING1. Worn or damaged rings. 1. Hone cylinder bores and replace
rings.
2. Carbon in oil ring slots. 2. Replace rings.
3. Incorrect ring size installed. 3. Replace rings.
4. Worn valve guides. 4. Ream guides and replace valves.
5. Leaking intake gasket. 5. Replace intake gaskets.
6. Leaking valve guide seals. 6. Replace valve guide seals.
DRENGINE - 5.7L 9 - 187
ENGINE - 5.7L (Continued)
Page 1413 of 2627

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
EXCESSIVE OIL CONSUMPTION OR
SPARK PLUGS OIL FOULED1. CCV System malfunction 1. (Refer to 25 - EMISSIONS
CONTROL/EVAPORATIVE
EMISSIONS - DESCRIPTION) for
correct operation
2. Defective valve stem seal(s) 2. Repair or replace seal(s)
3. Worn or broken piston rings 3. Hone cylinder bores. Install new
rings
4. Scuffed pistons/cylinder walls 4. Hone cylinder bores and replace
pistons as required
5. Carbon in oil control ring groove 5. Remove rings and de-carbon piston
6. Worn valve guides 6. Inspect/replace valve guides as
necessary
7. Piston rings fitted too tightly in
grooves7. Remove rings and check ring end
gap and side clearance. Replace if
necessary
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REPAIR DAMAGED
OR WORN THREADS
CAUTION: Be sure that the tapped holes maintain
the original center line.
Damaged or worn threads can be repaired. Essen-
tially, this repair consists of:
²Drilling out worn or damaged threads.
²Tapping the hole with a special Heli-Coil Tap, or
equivalent.
²Installing an insert into the tapped hole to bring
the hole back to its original thread size.
STANDARD PROCEDUREÐHYDROSTATIC
LOCK
CAUTION: DO NOT use the starter motor to rotate
the crankshaft. Severe damage could occur.
When an engine is suspected of hydrostatic lock
(regardless of what caused the problem), follow the
steps below.
(1) Perform the Fuel Pressure Release Procedure
(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(2) Disconnect the negative cable(s) from the bat-
tery.
(3) Inspect air cleaner, induction system, and
intake manifold to ensure system is dry and clear of
foreign material.
(4) Place a shop towel around the spark plugs to
catch any fluid that may possibly be under pressure
in the cylinder head. Remove the spark plugs.(5) With all spark plugs removed, rotate the crank-
shaft using a breaker bar and socket.
(6) Identify the fluid in the cylinders (coolant, fuel,
oil, etc.).
(7) Be sure all fluid has been removed from the
cylinders.
(8) Repair engine or components as necessary to
prevent this problem from occurring again.
(9) Squirt a small amount of engine oil into the
cylinders to lubricate the walls. This will prevent
damage on restart.
(10) Install new spark plugs. Tighten the spark
plugs to 41 N´m (30 ft. lbs.) torque.
(11) Drain engine oil. Remove and discard the oil
filter.
(12) Install the drain plug. Tighten the plug to 34
N´m (25 ft. lbs.) torque.
(13) Install a new oil filter.
(14) Fill engine crankcase with the specified
amount and grade of oil. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE - SPECIFICATIONS).
(15) Connect the negative cable(s) to the battery.
(16) Start the engine and check for any leaks.
REMOVAL
(1) Perform the Fuel System Pressure Release pro-
cedure (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIV-
ERY - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(2) Disconnect the battery negative cable.
(3) Remove the air cleaner resonator and duct
work as an assembly.
(4) Drain cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(5) Remove the accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
9 - 190 ENGINE - 5.7LDR
ENGINE - 5.7L (Continued)
Page 1419 of 2627

DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. In.
Lbs. Lbs.
GeneratorÐMounting Bolt 55 40 Ð
Intake ManifoldÐBolts Refer to Procedure
Lifter Guide Holder 12 Ð 106
Oil Pan Bolts 12 - 105
Oil Dipstick Tube 12 Ð 105
Oil PanÐDrain Plug 34 25 Ð
Oil PumpÐAttaching Bolts 28 Ð 250
Oil Pump Pickup Tube ± Bolt
and Nut28 Ð 250
Rear Seal Retainer Attaching
Bolts15 Ð 132
Rear Insulator to BracketÐ 68 50 Ð
Through-Bolt (2WD)
Rear Insulator to
Crossmember41 30 Ð
Support BracketÐNut (2WD)
Rear Insulator to
CrossmemberÐ68 50 Ð
Nuts (4WD)
Rear Insulator to
TransmissionÐ68 50 Ð
Bolts (4WD)
Rear Insulator BracketÐBolts 68 50 Ð
(4WD Automatic)
Rear Support Bracket to 41 30 Ð
Crossmember FlangeÐNuts
Rear Support Plate to
Transfer41 30 Ð
CaseÐBolts
Rocker ArmÐBolts 22 Ð 195
Spark Plugs Ð Ð Ð
Thermostat HousingÐBolts 28 Ð 250
Throttle BodyÐBolts 12 Ð 105
Transfer Case to Insulator 204 105 Ð
Mounting PlateÐNuts
Transmission Support
BracketÐ68 50 Ð
Bolts (2WD)
Vibration DamperÐBolt 176 129 Ð
Water Pump to Timing Chain 28 Ð 250
Case CoverÐBoltsSPECIAL TOOLS
5.7L ENGINE
CRANKSHAFT DAMPER REMOVER INSERT - 8513-A
Bloc±Chek±Kit C-3685±A
Bore Size Indicator C-119
Puller 8454
Crankshaft Damper Installer 8512
9 - 196 ENGINE - 5.7LDR
ENGINE - 5.7L (Continued)
Page 1424 of 2627
CAUTION: The head gaskets are marked ªTOPº to
indicate which side goes up.
(4) Position cylinder heads onto head gaskets and
cylinder block.
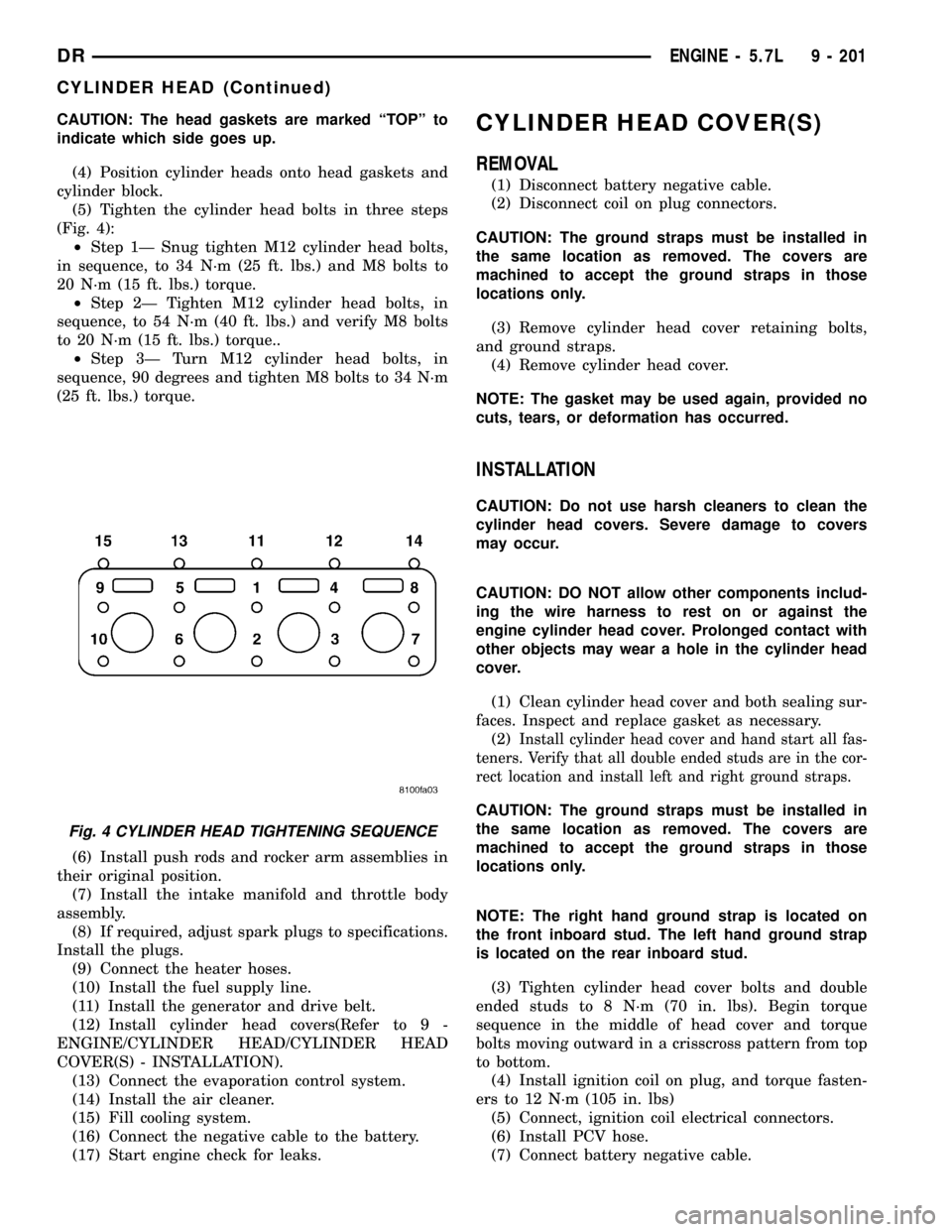
(5) Tighten the cylinder head bolts in three steps
(Fig. 4):
²Step 1Ð Snug tighten M12 cylinder head bolts,
in sequence, to 34 N´m (25 ft. lbs.) and M8 bolts to
20 N´m (15 ft. lbs.) torque.
²Step 2Ð Tighten M12 cylinder head bolts, in
sequence, to 54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.) and verify M8 bolts
to 20 N´m (15 ft. lbs.) torque..
²Step 3Ð Turn M12 cylinder head bolts, in
sequence, 90 degrees and tighten M8 bolts to 34 N´m
(25 ft. lbs.) torque.
(6) Install push rods and rocker arm assemblies in
their original position.
(7) Install the intake manifold and throttle body
assembly.
(8) If required, adjust spark plugs to specifications.
Install the plugs.
(9) Connect the heater hoses.
(10) Install the fuel supply line.
(11) Install the generator and drive belt.
(12) Install cylinder head covers(Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
(13) Connect the evaporation control system.
(14) Install the air cleaner.
(15) Fill cooling system.
(16) Connect the negative cable to the battery.
(17) Start engine check for leaks.CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S)
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Disconnect coil on plug connectors.
CAUTION: The ground straps must be installed in
the same location as removed. The covers are
machined to accept the ground straps in those
locations only.
(3) Remove cylinder head cover retaining bolts,
and ground straps.
(4) Remove cylinder head cover.
NOTE: The gasket may be used again, provided no
cuts, tears, or deformation has occurred.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Do not use harsh cleaners to clean the
cylinder head covers. Severe damage to covers
may occur.
CAUTION: DO NOT allow other components includ-
ing the wire harness to rest on or against the
engine cylinder head cover. Prolonged contact with
other objects may wear a hole in the cylinder head
cover.
(1) Clean cylinder head cover and both sealing sur-
faces. Inspect and replace gasket as necessary.
(2)
Install cylinder head cover and hand start all fas-
teners. Verify that all double ended studs are in the cor-
rect location and install left and right ground straps.
CAUTION: The ground straps must be installed in
the same location as removed. The covers are
machined to accept the ground straps in those
locations only.
NOTE: The right hand ground strap is located on
the front inboard stud. The left hand ground strap
is located on the rear inboard stud.
(3) Tighten cylinder head cover bolts and double
ended studs to 8 N´m (70 in. lbs). Begin torque
sequence in the middle of head cover and torque
bolts moving outward in a crisscross pattern from top
to bottom.
(4) Install ignition coil on plug, and torque fasten-
ers to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs)
(5) Connect, ignition coil electrical connectors.
(6) Install PCV hose.
(7) Connect battery negative cable.
Fig. 4 CYLINDER HEAD TIGHTENING SEQUENCE
DRENGINE - 5.7L 9 - 201
CYLINDER HEAD (Continued)
Page 1427 of 2627

VALVE SPRINGS
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable.
(2) Remove air cleaner assembly.
(3) Remove air intake resonator.
(4) Remove spark plug cables.
(5) Remove ignition coil connectors (Fig. 6).
(6) Remove ignition coils.
(7) Remove one spark plug.
(8) Remove valve cover.
CAUTION: The piston must be at TDC, and both
valves closed on the cylinder to be serviced.
NOTE: If removing intake valve spring, install spe-
cial tool# 9070, pushrod retaining plate, to retain
the intake pushrods.
(9) Remove exhaust/intake rocker arm shafts.
(10) Install spring compressor, special tool# 9065.
NOTE: All valve springs and seals are removed in
the same manner.(11) Charge cylinder with air.
NOTE: Tap the top of the valve spring retainer to
loosen the spring retainers locks.
(12) Compress valve spring and remove valve
retainer locks.
(13) Release spring compressor and remove valve
spring.
NOTE: The valve springs are interchangeable
between intake and exhaust.
(14) Remove valve seal.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install valve seal.
(2) Install valve spring.
(3) Using special tool# 9065, compress valve spring
and install valve spring retainer and locks.
(4) Release air charge in cylinder.
(5) Remove spring compressor tool # 9065.
CAUTION: Verify that the pushrods are fully seated
into lifter and rocker arm. Recheck after rocker arm
shaft has been torqued to specification.
(6) Install rocker arm shaft and pushrods(Refer to
9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/ROCKER ARM /
ADJUSTER ASSY - INSTALLATION).
(7) Tighten the rocker shaft bolts to 22 N´m (195
in. lbs.) torque,using the following sequence:Center,
center-right, center-left, right, left.
(8) Remove special tool# 9070, pushrod retaining
plate, if used.
(9) Install cylinder head cover.
(10) Tighten cylinder head cover bolts and double
ended studs(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER
HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S) - INSTALLA-
TION).
(11) Install spark plugs.
(12) Install ignition coil on plug, and torque fas-
teners to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs)
(13) Install ignition coil connectors.
(14) Install spark plug cables.
(15) Install air intake resonator.
(16) Install air cleaner assembly.
(17) Connect negative battery cable.
Fig. 6 IGNITION COIL R/I Ð 5.7L V-8
1 - SLIDE LOCK (SLIDE OUTWARD TO UNLOCK)
2 - SPARK PLUG CABLE (TO OPPOSITE CYLINDER BANK
SPARK PLUG)
3 - RELEASE LOCK / TAB (PUSH HERE)
4 - ELEC. CONNECTOR
5 - IGNITION COIL
6 - COIL MOUNTING BOLTS (2)
7 - SPARK PLUG CABLE (TO OPPOSITE CYLINDER BANK
IGNITION COIL)
9 - 204 ENGINE - 5.7LDR
Page 1531 of 2627
SPECIAL TOOLS
CATALYTIC CONVERTER
DESCRIPTION - CATALYTIC CONVERTER
WARNING: THE NORMAL OPERATING TEMPERA-
TURE OF THE EXHAUST SYSTEM IS VERY HIGH.
THEREFORE, NEVER WORK AROUND OR ATTEMPT
TO SERVICE ANY PART OF THE EXHAUST SYSTEM
UNTIL IT IS COOLED. SPECIAL CARE SHOULD BE
TAKEN WHEN WORKING NEAR THE CATALYTIC
CONVERTER. THE TEMPERATURE OF THE CON-
VERTER RISES TO A HIGH LEVEL AFTER A SHORT
PERIOD OF ENGINE OPERATION TIME.
CAUTION: DO NOT remove spark plug wires from
plugs or by any other means short out cylinders.
Failure of the catalytic converter can occur due to a
temperature increase caused by unburned fuel
passing through the converter.
The stainless steel catalytic converter body is
designed to last the life of the vehicle. Excessive heat
can result in bulging or other distortion, but exces-
sive heat will not be the fault of the converter. If
unburned fuel enters the converter, overheating may
occur. If a converter is heat-damaged, correct the
cause of the damage at the same time the converter
is replaced. Also, inspect all other components of the
exhaust system for heat damage.
Unleaded gasoline must be used to avoid con-
taminating the catalyst core.
50 State emission vehicles incorporate two mini
catalytic converters located after the exhaust mani-
folds and before the inline catalytic converter.
OPERATION
The catalytic converter captures and burns any
unburned fuel mixture exiting the combustion cham-
bers during the exhaust stroke of the engine. This
process aids in reducing emissions output.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL
WARNING: IF TORCHES ARE USED WHEN WORK-
ING ON THE EXHAUST SYSTEM, DO NOT ALLOW
THE FLAME NEAR THE FUEL LINES.
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Saturate the bolts and nuts with heat valve
lubricant. Allow 5 minutes for penetration.
(3) Remove the bolts from the crossover pipe to the
catalytic converter connection.
(4) Disconnect oxygen sensor wiring.
(5) Loosen the nuts from the clamp that hold the
catalytic converter to the exhaust pipe flange connec-
tion.
NOTE: Do not remove nut from T-Bolt. Only remove
nut far enough, so that the T end can be removed
from the clamp.
(6) Remove the T bolt end of the fastener, from the
clamp.
(7) Spread the clamp, and remove the catalytic
converter from the vehicle.
(8) Discard the clamp.
NOTE: The catalytic converter to exhaust manifold
clamp is not reusable. Always use a new clamp
when reinstalling the catalytic converter.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support vehicle.
(2) Saturate the bolts and nuts with heat valve
lubricant. Allow 5 minutes for penetration.
(3) Remove clamps and nuts.
(4) Remove the catalytic converter.
INSPECTION
Look at the stainless steel body of the converter,
inspect for bulging or other distortion that could be a
result of overheating. If the converter has a heat
shield attached make sure it is not bent or loose.
If you suspect internal damage to the catalyst, tap-
ping the bottom of the catalyst with a rubber mallet
may indicate a damaged core.
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION
NOTE: The catalytic converter to exhaust manifold
clamp is not reusable. Always use a new clamp
when reinstalling the catalytic converter.
TURBOCHARGER TESTER 9022
11 - 6 EXHAUST SYSTEMDR
EXHAUST SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 1584 of 2627

(2) Perform Fuel System Pressure Release Proce-
dure.
(3) Remove negative battery cable at battery.
(4) Remove flex tube (air cleaner housing to
engine).
(5) Remove air resonator box at throttle body.
(6) Disconnect all spark plug cables from all spark
plugs and ignition coils. Do not remove cables from
cable routing tray. Note original cable positions while
removing (Fig. 22).
(7) Remove spark plug cable tray from engine by
releasing 4 retaining clips (Fig. 21). Remove tray and
cables from engine as an assembly.
(8) Disconnect electrical connectors at all 8 igni-
tion coils. Refer to Ignition Coil Removal/Installation.
(9) Disconnect fuel line latch clip and fuel line at
fuel rail. A special tool will be necessary for fuel line
disconnection. Refer to Quick-Connect Fittings.
(10) Disconnect electrical connectors at all 8 fuel
injectors. To remove connector refer to (Fig. 17). Push
red colored slider away from injector (1). While push-
ing slider, depress tab (2) and remove connector (3)
from injector. The factory fuel injection wiring har-
ness is numerically tagged (INJ 1, INJ 2, etc.) for
injector position identification. If harness is not
tagged, note wiring location before removal.
(11) Disconnect electrical connectors at all throttle
body sensors.
(12) Remove 4 fuel rail mounting bolts and hold-
own clamps (Fig. 20).
(13) Gently rock and pullleftside of fuel rail until
fuel injectors just start to clear machined holes in
intake manifold. Gently rock and pullrightside of
rail until injectors just start to clear intake manifold
head holes. Repeat this procedure (left/right) until all
injectors have cleared machined holes.
(14) Remove fuel rail (with injectors attached)
from engine.
(15) If fuel injectors are to be removed, refer to
Fuel Injector Removal/Installation.
INSTALLATION
3.7L V-6
(1) If fuel injectors are to be installed, refer to Fuel
Injector Removal/Installation.
(2) Clean out fuel injector machined bores in
intake manifold.
(3) Apply a small amount of engine oil to each fuel
injector o-ring. This will help in fuel rail installation.
(4) Position fuel rail/fuel injector assembly to
machined injector openings in cylinder head.
(5) Guide each injector into cylinder head. Be care-
ful not to tear injector o-rings.
(6) Pushrightside of fuel rail down until fuel
injectors have bottomed on cylinder head shoulder.Pushleftfuel rail down until injectors have bot-
tomed on cylinder head shoulder.
Fig. 20 5.7L FUEL RAIL
1 - FUEL RAIL
2 - MOUNTING BOLT
3 - HOLDOWN CLAMPS
4 - CONNECTOR TUBE
Fig. 21 5.7L SPARK PLUG CABLE ROUTING TRAY
1 - SPARK PLUG CABLES
2 - RETAINING CLIP
3 - SPARK PLUG CABLE ROUTING TRAY
DRFUEL DELIVERY - GAS 14 - 15
FUEL RAIL (Continued)