system DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.G Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1998, Model line: RAM 1500, Model: DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.GPages: 2627
Page 298 of 2627

TONE WHEEL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REAR WHEEL
SPEED SENSOR
Diagnosis of base brake conditions which are
mechanical in nature should be performed first. This
includes brake noise, lack of power assist, parking
brake, or vehicle vibration during normal braking.
The Antilock brake system performs several self-
tests every time the ignition switch is turned on and
the vehicle is driven. The CAB monitors the system
inputs and outputs circuits to verify the system is
operating properly. If the CAB senses a malfunction
in the system it will set a DTC into memory and trig-
ger the warning lamp.
NOTE: The MDS or DRB III scan tool is used to
diagnose the Antilock Brake system. For test proce-
dures refer to the Chassis Diagnostic Manual.
HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL
DESCRIPTION - ELECTRONIC VARIABLE
BRAKE PROPORTIONING
Vehicles equipped with ABS use electronic variable
brake proportioning (EVBP) to balance front-to-rear
braking. The EVBP is used in place of a rear propor-
tioning valve. The EVBP system uses the ABS sys-
tem to control the slip of the rear wheels in partial
braking range. The braking force of the rear wheels
is controlled electronically by using the inlet and out-
let valves located in the integrated control unit
(ICU).
OPERATION - ELECTRONIC VARIABLE BRAKE
PROPORTIONING
EVBP is able to decrease, hold and increase rear
brake pressure without activating full ABS control.
Upon entry into EVBP the inlet valve for the rear
brake circuit is switched on so that the fluid supply
from the master cylinder is shut off. In order to
decrease the rear brake pressure, the outlet valve for
the rear brake circuit is pulsed. This allows fluid to
enter the low pressure accumulator (LPA) in the
hydraulic control unit (HCU) resulting in a drop in
fluid pressure to the rear brakes. In order to increase
the rear brake pressure, the outlet valve is switched
off and the inlet valve is pulsed. This increases the
pressure to the rear brakes.
The EVBP will remain functional during many
ABS fault modes. If both the red BRAKE and amber
ABS warning indicators are illuminated, the EVBP
may not be functioning.
HCU (HYDRAULIC CONTROL
UNIT)
DESCRIPTION
The HCU consists of a valve body, pump motor, low
pressure accumulators, inlet valves, outlet valves and
noise attenuators.
OPERATION
Accumulators in the valve body store extra fluid
released to the system for ABS mode operation. The
pump provides the fluid volume needed and is oper-
ated by a DC type motor. The motor is controlled by
the CAB.
The valves modulate brake pressure during
antilock braking and are controlled by the CAB.
The HCU provides three channel pressure control
to the front and rear brakes. One channel controls
the rear wheel brakes in tandem. The two remaining
channels control the front wheel brakes individually.
During antilock braking, the solenoid valves are
opened and closed as needed.
During normal braking, the HCU solenoid valves
and pump are not activated. The master cylinder and
power booster operate the same as a vehicle without
an ABS brake system.
NOTE: The three modes mentioned below do occur
but not necessarily in the order listed everytime.
During antilock braking, solenoid valve pressure
modulation occurs in three stages, pressure increase,
pressure hold, and pressure decrease. The valves are
all contained in the valve body portion of the HCU.
PRESSURE DECREASE
The outlet valve is opened and the inlet valve is
closed during the pressure decrease cycle.
A pressure decrease cycle is initiated when speed
sensor signals indicate high wheel slip at one or
more wheels. At this point, the CAB closes the inlet
then opens the outlet valve, which also opens the
return circuit to the accumulators. Fluid pressure is
allowed to bleed off (decrease) as needed to prevent
wheel lock.
Once the period of high wheel slip has ended, the
CAB closes the outlet valve and begins a pressure
increase or hold cycle as needed.
PRESSURE HOLD
Both solenoid valves are closed in the pressure
hold cycle but only the inlet valve is energized. Fluid
apply pressure in the control channel is maintained
at a constant rate. The CAB maintains the hold cycle
until sensor inputs indicate a pressure change is nec-
essary.
DRBRAKES - ABS 5 - 49
Page 299 of 2627

PRESSURE INCREASE
The inlet valve is open and the outlet valve is
closed during the pressure increase cycle. The pres-
sure increase cycle is used to reapply thew brakes.
This cycle controls re-application of fluid apply pres-
sure.
REMOVAL
(1) Install a prop rod on the brake pedal to keep
pressure on the brake system.
(2) Disconnect the battery cables from the battery.
(3) Remove the battery.
(4) Disconnect the two electrical harness connec-
tors (Fig. 5).
(5) Remove the five brake lines from the HCU
(Fig. 5).
(6) Remove HCU/CAB mounting bolts and remove
the HCU/CAB (Fig. 5).
INSTALLATION
NOTE: If the CAB is being replaced with a new CAB
is must be reprogrammed with the use of a DRB III.
(1) Install HCU/CAB on the mounts and Tighten
the bolts to 15N´m (11 ft. lbs.) (Fig. 5).
(2) Install the five brake lines to the HCU and
tighten to 19 N´m (170 in. lbs.) (Fig. 5).
(3) Install the two electrical harness connectors to
the HCU/CAB and push down on the release to
secure the connectors.
(4) Install the battery.
(5) Install the battery cables to the battery.
(6) Remove the prop rod on the brake pedal.
(7) Bleed ABS brake system (Refer to 5 - BRAKES
- STANDARD PROCEDURE).
RWAL VALVE
DESCRIPTION
Rear Wheel Antilock (RWAL) brake system is stan-
dard equipment on 1500 series vehicles. The RWAL
brake system is designed to prevent rear wheel
lock-up on virtually all types of road surfaces. RWAL
braking is desirable because a vehicle which is
stopped without locking the rear wheels will retain
directional stability. This allows the driver to retain
greater control of the vehicle during braking.
The valve is located on the drivers side inner
fender under the hood. The valve modulates hydrau-
lic pressure to the rear brakes.
The RWAL components include:
²RWAL Valve
²Controller Antilock brake (CAB)
²Rear Wheel Speed Sensor (WSS)
OPERATION
When the brakes are applied, hydraulic fluid is
routed from the master cylinder's secondary circuit to
the RWAL valve. From there hydraulic fluid is routed
to the rear brakes. The Controller Antilock Brake
(CAB) contains an Electronic Variable Brake Propor-
tioning (EVBP) control algorithm, which proportions
the applied braking force to the rear wheels during
braking. The EVBP function of the RWAL system
takes the place of a conventional hydraulic propor-
tioning valve. The CAB monitors the rear wheel
speed through the rear wheel speed sensor and cal-
culates an estimated vehicle deceleration. When an
established deceleration threshold is exceeded, an
isolation valve is closed to hold the applied brake
pressure to the rear brakes constant. Upon further
increases in the estimated vehicle deceleration, the
isolation valve is selectively opened to increase rear
brake pressure in proportion to the front brake pres-
sure. If impending rear wheel lock-up is sensed, the
CAB signals the RWAL valve to modulate hydraulic
brake pressure to the rear wheels to prevent lock-up.
NORMAL BRAKING Since the RWAL valve also
performs the EVBP or proportioning function, vehicle
deceleration under normal braking may be sufficient
to trigger the EVBP function of the RWAL system
without full RWAL activity as would normally occur
during an impending rear wheel lock-up. As previ-
ously mentioned, the isolation valve is selectively
closed and opened to increase rear brake pressure in
proportion to the front brake pressure under EVBP
control. Slight brake pedal pulsations may be noticed
as the isolation valve is opened.
Fig. 5 HYDRAULIC CONTROL UNIT
1 - HYDRAULIC CONTROL UNIT
2 - MOUNTING BOLTS
5 - 50 BRAKES - ABSDR
HCU (HYDRAULIC CONTROL UNIT) (Continued)
Page 300 of 2627

REMOVAL
(1) Install a prop rod on the brake pedal to keep
pressure on the brake system.
(2) Disconnect the battery cables from the battery.
(3) Remove the battery.
(4) Disconnect the electrical harness connector
(Fig. 6).
(5) Remove the brake lines from the rwal valve
(Fig. 6).
(6) Remove rwal valve mounting nuts and remove
the rwal valve (Fig. 6).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install rwal valve and Tighten the nuts to 15
N´m (11 ft. lbs.) (Fig. 6).
(2) Install the brake lines to the rwal valve and
tighten to 19 N´m (170 in. lbs.) (Fig. 6).
(3) Install the electrical harness connector to the
rwal valve and secure the connector.
(4) Install the battery.
(5) Install the battery cables to the battery.
(6) Remove the prop rod on the brake pedal.
(7) Bleed ABS brake system (Refer to 5 - BRAKES
- STANDARD PROCEDURE).
Fig. 6 RWAL VALVE
1 - RWAL VALVE
2 - MOUNTING NUTS
DRBRAKES - ABS 5 - 51
RWAL VALVE (Continued)
Page 314 of 2627

(2) Apply a light coating of grease to the inside
diameter of the master cylinder push rod eye.
(3) Install clutch master cylinder on dash panel
and tighten clutch master cylinder nuts to 28 N´m
(21 ft. lbs.).
(4) Install clutch master cylinder push rod pin.
(5) Connect clutch pedal position interlock switch
wires.
(6) Install plastic clip securing hydraulic line to
the dash panel into the lower dash panel flange.
(7) Install plastic clip securing hydraulic line to
the dash panel onto the upper dash panel stud.
(8) Raise vehicle.
(9) Install slave cylinder and verify cylinder rod is
properly seated in release lever.
(10) Install and tighten slave cylinder nuts to 23
N´m (17 ft. lbs.).
(11) Ifnewclutch linkage is being installed, con-
nect the clutch hydraulic line to the clutch slave cyl-
inder.
CAUTION: Once the clutch hydraulic line is con-
nected to the slave cylinder, it should never be dis-
connected.
(12) Lower vehicle.
(13) Operate linkage several times to verify proper
operation.
CLUTCH PEDAL POSITION
SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
A clutch pedal position switch (CPPS) is mounted
on the clutch master cylinder push rod (Fig. 20). The
wiring harness connector is inside of the vehicle
under the left side of the instrument panel.
NOTE: Switch is serviced with clutch master cylin-
der.
OPERATION
The clutch pedal position switch is used to prevent
starter motor engagement unless the clutch pedal is
depressed. An input from this switch is also used to
either shut down/prevent operation of the speed con-
trol system when pedal is depressed. The position
switch is an integral part of the clutch master cylin-
der push rod.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
(1) Disconnect switch 2-wire connector attached to
pedal support bracket, under instrument panel to left
of clutch pedal (Fig. 21).(2) Check switch continuity with an ohmmeter
while operating clutch pedal.
²Pedal Depressed - Continuity
²Pedal Released - No Continuity
(3) If continuity is not present or always present,
replace clutch master cylinder. Switch is not serviced
separately.
Fig. 20 LOCATION, CLUTCH PEDAL
POSITION SWITCH
1 - CLUTCH MASTER CYLINDER
2 - CLUTCH PEDAL POSITION SWITCH
Fig. 21 CLUTCH SWITCH TEST POINT
1 - PEDAL SUPPORT BRACKET
2 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
DRCLUTCH 6 - 13
LINKAGE (Continued)
Page 316 of 2627

COOLING
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
COOLING
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - COOLING SYSTEM FLOW
3.7L/4.7L/5.7L ENGINE..................1
DESCRIPTION - COOLING SYSTEM FLOW -
5.9L DIESEL..........................3
DESCRIPTION - HOSE CLAMPS...........3
OPERATION
OPERATION - COOLING SYSTEM.........5
OPERATION - HOSE CLAMPS............5
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐON-BOARD
DIAGNOSTICS (OBD)...................5
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COOLING
SYSTEM - TESTING FOR LEAKS..........5
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COOLING
SYSTEM DIESEL ENGINE................7
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PRELIMINARY
CHECKS............................10
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - COOLANT
LEVEL CHECK........................17STANDARD PROCEDURE - COOLING
SYSTEM CLEANING/REVERSE FLUSHING . . 17
STANDARD PROCEDURE - DRAINING
COOLING SYSTEM - ALL GAS ENGINES . . . 17
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFILLING
COOLING SYSTEM - ALL GAS ENGINES . . . 18
STANDARD PROCEDURE - DRAINING
COOLING SYSTEM 5.9L DIESEL ENGINE . . . 18
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFILLING
COOLING SYSTEM 5.9L DIESEL ENGINE . . . 19
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ADDING
ADDITIONAL COOLANT.................19
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE............................19
SPECIFICATIONS -....................20
SPECIAL TOOLS
COOLING...........................20
ACCESSORY DRIVE......................21
ENGINE...............................30
TRANSMISSION.........................67
COOLING
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - COOLING SYSTEM FLOW
3.7L/4.7L/5.7L ENGINE
The cooling system regulates engine operating tem-
perature. It allows the engine to reach normal oper-
ating temperature as quickly as possible. It also
maintains normal operating temperature and pre-
vents overheating.The cooling system provides a means of heating
the passenger compartment and cooling the auto-
matic transmission fluid (if equipped). The cooling
system is pressurized and uses a centrifugal water
pump to circulate coolant through the system. The
coolant recovery/reserve system utilizes an ambient
overflow bottle (Fig. 2).
An optional factory installed maximum duty cool-
ing package is available on most models. This pack-
age will provide additional cooling capacity for
vehicles used under extreme conditions such as
trailer towing in high ambient temperatures (Fig. 1).
DRCOOLING 7 - 1
Page 317 of 2627

Fig. 1 Engine Cooling System Flow - 3.7L/4.7L
1 - LH CYL. HEAD
2 - BLEED
3 - THERMOSTAT LOCATION
4 - RH CYL. HEAD
5 - RH BANK CYL. BLOCK6 - LH BANK CYL. BLOCK
7 - COOLANT TEMP. SENSOR
8 - FROM HEATER CORE
9 - TO HEATER CORE
7 - 2 COOLINGDR
COOLING (Continued)
Page 318 of 2627

DESCRIPTION - COOLING SYSTEM FLOW -
5.9L DIESEL
The diesel engine cooling system consists of :
²Cross-flow radiator
²Belt driven water pump
²Cooling fan (attached to the electronic viscous
fan drive)
²Belt driven Electronic viscous fan drive
²Two piece fan shroud
²Radiator pressure cap
²Vertically mounted thermostat
²Coolant reserve/recovery system
²Transmission oil cooler
²Coolant
Coolant flow circuits for the 5.9L diesel engine are
shown in (Fig. 3).
DESCRIPTION - HOSE CLAMPS
The cooling system utilizes spring type hose
clamps. If a spring type clamp replacement is neces-
sary, replace with the original Mopartequipment
spring type clamp.
CAUTION: A number or letter is stamped into the
tongue of constant tension clamps. If replacement
is necessary, use only a original equipment clamp
with matching number or letter and ensure the
clamp has the same size width (Fig. 4).
Fig. 2 5.7L Engine Coolant System Flow
1 - LH CYLINDER HEAD
2 - TO RADIATOR3 - FROM RADIATOR
4 - TO RH CYLINDER HEAD
DRCOOLING 7 - 3
COOLING (Continued)
Page 319 of 2627
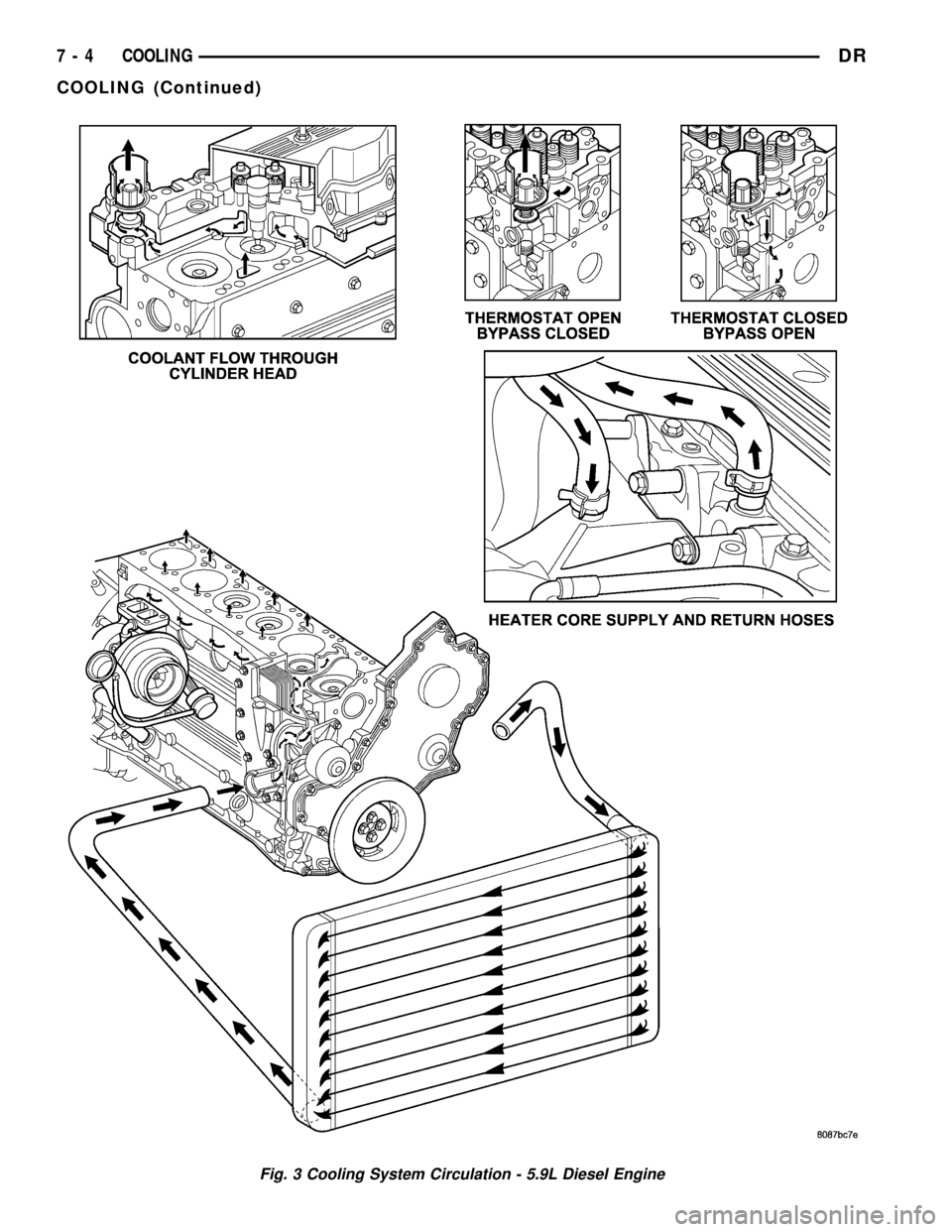
Fig. 3 Cooling System Circulation - 5.9L Diesel Engine
7 - 4 COOLINGDR
COOLING (Continued)
Page 320 of 2627

OPERATION
OPERATION - COOLING SYSTEM
The cooling system regulates engine operating tem-
perature. It allows the engine to reach normal oper-
ating temperature as quickly as possible. It also
maintains normal operating temperature and pre-
vents overheating.
The cooling system also provides a means of heat-
ing the passenger compartment and cooling the auto-
matic transmission fluid (if equipped). The cooling
system is pressurized and uses a centrifugal water
pump to circulate coolant throughout the system.
All engines utilize an ambient overflow bottle for
coolant recovery/reserve.
An optional factory installed maximum duty cool-
ing package is available on most models. This pack-
age will provide additional cooling capacity for
vehicles used under extreme conditions such as
trailer towing in high ambient temperatures.
OPERATION - HOSE CLAMPS
The spring type hose clamp applies constant ten-
sion on a hose connection. To remove a spring type
hose clamp, only use constant tension clamp pliers
designed to compress the hose clamp.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐON-BOARD
DIAGNOSTICS (OBD)
COOLING SYSTEM RELATED DIAGNOSTICS
The Engine Control Module (ECM) has been pro-
grammed to monitor certain cooling system compo-
nents:
²If the engine has remained cool for too long a
period, such as with a stuck open thermostat, a Diag-
nostic Trouble Code (DTC) can be set.
²If an open or shorted condition has developed in
the electronically controlled viscous fan clutch circuit,
a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) can be set.
²If fan speed is not detected a DTC will be set.
²Coolant temperature sensor circuit problems can
set a DTC.
If the problem is sensed in a monitored circuit
often enough to indicated an actual problem, a DTC
is stored. The DTC will be stored in the ECM mem-
ory for eventual display to the service technician.
(Refer to 25 - EMISSIONS CONTROL - DESCRIP-
TION).
ACCESSING DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
To read DTC's and to obtain cooling system data,
(Refer to 25 - EMISSIONS CONTROL - DESCRIP-
TION).
ERASING TROUBLE CODES
After the problem has been repaired, use the
DRBIIItscan tool to erase a DTC. Refer to the
appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures ser-
vice information for operation of the DRBIIItscan
tool.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COOLING SYSTEM
- TESTING FOR LEAKS
ULTRAVIOLET LIGHT METHOD
A leak detection additive is available through the
parts department that can be added to cooling sys-
tem. The additive is highly visible under ultraviolet
light (black light). Pour one ounce of additive into
cooling system. Place heater control unit in HEAT
position. Start and operate the engine until the radi-
ator upper hose is warm to the touch. Aim the com-
mercially available black light tool at the components
to be checked. If leaks are present, the black light
will cause the additive to glow a bright green color.
The black light can be used in conjunction with a
pressure tester to determine if any external leaks
exist (Fig. 5).
Fig. 4 Spring Clamp Size Location
1 - SPRING CLAMP SIZE LOCATION
DRCOOLING 7 - 5
COOLING (Continued)
Page 321 of 2627

PRESSURE TESTER METHOD
The engine should be at normal operating temper-
ature. Recheck the system cold if the cause of coolant
loss is not located during the warm engine examina-
tion.
WARNING: HOT, PRESSURIZED COOLANT CAN
CAUSE INJURY BY SCALDING.
Carefully remove the radiator pressure cap from
the filler neck and check the coolant level. Push
down on the cap to disengage it from the stop tabs.
Wipe the inside of the filler neck and examine the
lower inside sealing seat for nicks, cracks, paint, dirt
and solder residue. Inspect the radiator-to- reserve/
overflow tank hose for internal obstructions. Insert a
wire through the hose to be sure it is not obstructed.
Inspect the cams on the outside of the filler neck.
If the cams are damaged, seating of the pressure cap
valve and tester seal will be affected.
Attach pressure tester (7700 or an equivalent) to
radiator filler neck.
Operate the tester pump to apply 103.4 kPa (15
psi) pressure to the system. If the hoses enlarge
excessively or bulges while testing, replace as neces-
sary. Observe the gauge pointer and determine the
condition of the cooling system according to following
criteria:
Holds Steady:If the pointer remains steady for
two minutes, serious coolant leaks are not present in
system. However, there could be an internal leakthat does not appear with normal system test pres-
sure. If it is certain that coolant is being lost and
leaks cannot be detected, inspect for interior leakage
or perform Internal Leakage Test. Refer to INTER-
NAL LEAKAGE INSPECTION.
Drops Slowly:Indicates a small leak or seepage
is occurring. Examine all of the connections for seep-
age or slight leakage with a flashlight. Inspect the
radiator, hoses, gasket edges and heater. Seal the
small leak holes with a Sealer Lubricant (or equiva-
lent). Repair the leak holes and inspect the system
again with pressure applied.
Drops Quickly:Indicates that serious leakage is
occurring. Examine the system for external leakage.
If leaks are not visible, inspect for internal leakage.
Large radiator leak holes should be repaired by a
reputable radiator repair shop.
INTERNAL LEAKAGE INSPECTION
Remove the engine oil pan drain plug and drain a
small amount of engine oil. If coolant is present in
the pan, it will drain first because it is heavier than
oil. An alternative method is to operate engine for a
short period to churn the oil. After this is done,
remove the engine dipstick and inspect for water
globules. Also inspect the transmission dipstick for
water globules and transmission fluid cooler for leak-
age.
WARNING: WITH RADIATOR PRESSURE TESTER
TOOL INSTALLED ON RADIATOR, DO NOT ALLOW
PRESSURE TO EXCEED 145 kPa (21 PSI). PRES-
SURE WILL BUILD UP QUICKLY IF A COMBUSTION
LEAK IS PRESENT. TO RELEASE PRESSURE,
ROCK TESTER FROM SIDE TO SIDE. WHEN
REMOVING TESTER, DO NOT TURN TESTER MORE
THAN 1/2 TURN IF SYSTEM IS UNDER PRESSURE.
Operate the engine without the pressure cap on
the radiator until the thermostat opens. Attach a
Pressure Tester to the filler neck. If pressure builds
up quickly it indicates a combustion leak exists. This
is usually the result of a cylinder head gasket leak or
crack in engine. Repair as necessary.
If there is not an immediate pressure increase,
pump the Pressure Tester. Do this until indicated
pressure is within system range of 110 kPa (16 psi).
Fluctuation of the gauge pointer indicates compres-
sion or combustion leakage into cooling system.
Because the vehicle is equipped with a catalytic
converter,do notshort out cylinders to isolate com-
pression leak.
If the needle on dial of the pressure tester does not
fluctuate, race engine a few times to check for an
abnormal amount of coolant or steam. This would be
emitting from exhaust pipe. Coolant or steam from
Fig. 5 Leak Detection Using Black Light - Typical
1 - TYPICAL BLACK LIGHT TOOL
7 - 6 COOLINGDR
COOLING (Continued)