system DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1998, Model line: RAM 1500, Model: DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.GPages: 2627
Page 2016 of 2627

TRANSMISSION IDENTIFICATION
Transmission identification numbers are stamped
on the left side of the case just above the oil pan
sealing surface (Fig. 1). Refer to this information
when ordering replacement parts. A label is attached
to the transmission case above the stamped numbers.
The label gives additional information which may
also be necessary for identification purposes.
GEAR RATIOS
The 45RFE gear ratios are:
1st .................................3.00:1
2nd.................................1.67:1
2nd Prime...........................1.50:1
3rd.................................1.00:1
4th .................................0.75:1
Reverse.............................3.00:1
GEAR RATIOS
The 545RFE gear ratios are:
1st .................................3.00:1
2nd.................................1.67:1
2nd Prime...........................1.50:1
3rd.................................1.00:1
4th .................................0.75:1
5th .................................0.67:1
Reverse.............................3.00:1
OPERATION
The 45RFE/545RFE offers full electronic control of
all automatic up and downshifts, and features real-
time adaptive closed-loop shift and pressure control.
Electronic shift and torque converter clutch controls
help protect the transmission from damage due to
high temperatures, which can occur under severe
operating conditions. By altering shift schedules, line
pressure, and converter clutch control, these controls
reduce heat generation and increase transmission
cooling.
To help reduce efficiency-robbing parasitic losses,
the transmissions includes a dual-stage transmission
fluid pump with electronic output pressure control.
Under most driving conditions, pump output pres-
sure greatly exceeds that which is needed to keep the
clutches applied. The 45RFE/545RFE pump-pressure
control system monitors input torque and adjusts the
pump pressure accordingly. The primary stage of the
pump works continuously; the second stage is
bypassed when demand is low. The control system
also monitors input and output speed and, if incipi-
ent clutch slip is observed, the pressure control sole-
noid duty cycle is varied, increasing pressure in
proportion to demand.
A high-travel torque converter damper assembly
allows earlier torque converter clutch engagement to
reduce slippage. Needle-type thrust bearings reduce
internal friction. The 45RFE/545RFE is packaged in
a one-piece die-cast aluminum case. To reduce NVH,
the case has high lateral, vertical and torsional stiff-
ness. It is also designed to maximize the benefit of
the structural dust cover that connects the bottom of
the bell housing to the engine bedplate, enhancing
overall power train stiffness. Dual filters protect the
pump and other components. A pump return filter is
added to the customary main sump filter. Indepen-
dent lubrication and cooler circuits assure ample
pressure for normal transmission operation even if
the cooler is obstructed or the fluid cannot flow due
to extremely low temperatures.
The hydraulic control system design (without elec-
tronic assist) provides the transmission with PARK,
REVERSE, NEUTRAL, SECOND, and THIRD gears,
based solely on driver shift lever selection. This
design allows the vehicle to be driven (in ªlimp-inº
mode) in the event of a electronic control system fail-
ure, or a situation that the Transmission Control
Module (TCM) recognizes as potentially damaging to
the transmission.
The TCM also performs certain self-diagnostic
functions and provides comprehensive information
(sensor data, DTC's, etc.) which is helpful in proper
diagnosis and repair. This information can be viewed
with the DRBtscan tool.
Fig. 1 Transmission Part And Serial Number
Location
1 - IDENTIFICATION NUMBERS (STAMPED)
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE 21 - 313
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE (Continued)
Page 2067 of 2627

ADAPTER HOUSING SEAL
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the transfer case from the transmis-
sion.
(2) Using a screw mounted on a slide hammer,
remove the adapter housing seal.
INSTALLATION
(1) Clean the adapter seal bore in the adapter
housing of any residue or particles remaining from
the original seal.
(2) Install new oil seal in the adapter housing
using Seal Installer C-3860-A (Fig. 63). A properly
installed seal is flush to the face of the seal bore.
(3) Install the transfer case onto the transmission.
BRAKE TRANSMISSION SHIFT
INTERLOCK SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION
The Brake Transmission Shifter Interlock (BTSI)
(Fig. 64), is a solenoid operated system. It consists of
a solenoid permanently mounted on the gearshift
cable.
OPERATION
The system locks the shifter into the PARK position.
The interlock system is engaged whenever the ignition
switch is in the LOCK or ACCESSORY position. An
additional electrically activated feature will prevent
shifting out of the PARK position unless the brake pedalis depressed approximately one-half an inch. A magnetic
holding device in line with the park lock cable is ener-
gized when the ignition is in the RUN position. When
the key is in the RUN position and the brake pedal is
depressed, the shifter is unlocked and will move into
any position. The interlock system also prevents the
ignition switch from being turned to the LOCK or
ACCESSORY position, unless the shifter is fully locked
into the PARK position.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BRAKE
TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK
(1) Verify that the key can only be removed in the
PARK position
(2) When the shift lever is in PARK And the shift
handle pushbutton is in the ªOUTº position, the igni-
tion key cylinder should rotate freely from OFF to
LOCK. When the shifter is in any other gear or neu-
tral position, the ignition key cylinder should not
rotate to the LOCK position.
(3) Shifting out of PARK should not be possible
when the ignition key cylinder is in the OFF posi-
tion.
(4) Shifting out of PARK should not be possible
while applying normal pushbutton force and ignition
key cylinder is in the RUN or START positions
unless the foot brake pedal is depressed approxi-
mately 1/2 inch (12mm).
(5) Shifting out of PARK should not be possible
when the ignition key cylinder is in the ACCESSORY
or LOCK positions.
(6)
Shifting between any gears, NEUTRAL or into
PARK may be done without depressing foot brake pedal
with ignition switch in RUN or START positions.
Fig. 63 Adapter Housing Seal Installation
1 - TOOL C-3860-A
Fig. 64 Brake Transmission Interlock Mechanism
1 - STEERING COLUMN
2 - GEARSHIFT CABLE
3 - GEARSHIFT CABLE LOCK TAB
4 - BTSI SOLENOID LOCK TAB
5 - BTSI CONNECTOR
21 - 364 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR
Page 2068 of 2627

ADJUSTMENTS - BRAKE TRANSMISSION
SHIFT INTERLOCK
Correct cable adjustment is important to proper
interlock operation. The gearshift cable must be cor-
rectly adjusted in order to shift out of PARK.
ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURE
(1) Remove the steering column trim as necessary
for access to the brake transmission shift interlock.
(2) Shift the transmission into the PARK position.
(3) Pull upward on both the BTSI lock tab and the
gearshift cable lock tab (Fig. 65).
(4) Verify that the shift lever is in the PARK posi-
tion.
(5) Verify positive engagement of the transmission
park lock by attempting to rotate the propeller shaft.
The shaft will not rotate when the park lock is
engaged.
(6) Turn ignition switch to LOCK position.Be
sure ignition key cylinder is in the LOCK posi-
tion. Cable will not adjust correctly in any
other position.
(7) Ensure that the cable is free to self-adjust by
pushing cable rearward and releasing.
(8) Push the gearshift cable lock tab down until it
snaps in place.
(9) Locate the BTSI alignment hole in the bottom
of the BTSI mechanism between the BTSI lock tab
and the BTSI connector.(10) Move the BTSI assembly up or down on the
gearshift cable until an appropriate size drill bit can
be inserted into the alignment hole and through the
assembly.
(11) Push the BTSI lock tab down until it snaps
into place and remove the drill bit.
(12) Install any steering column trim previously
removed.
BTSI FUNCTION CHECK
(1) Verify removal of ignition key allowed in PARK
position only.
(2) When the shift lever is in PARK, the ignition
key cylinder should rotate freely from off to lock.
When the shifter is in any other position, the ignition
key should not rotate from off to lock.
(3) Shifting out of PARK should be possible when
the ignition key cylinder is in the off position.
(4) Shifting out of PARK should not be possible
while applying normal force, and ignition key cylin-
der is in the run or start positions, unless the foot
brake pedal is depressed approximately 1/2 inch
(12mm).
(5) Shifting out of PARK should not be possible
when the ignition key cylinder is in the accessory or
lock position.
(6) Shifting between any gear and NEUTRAL, or
PARK, may be done without depressing foot brake
with ignition switch in run or start positions.
(7) Engine starts must be possible with shifter
lever in PARK or NEUTRAL positions only. Engine
starts must not be possible in any position other than
PARK or NEUTRAL.
(8) With shifter lever in the:
²PARK position - Apply upward force on the shift
arm and remove pressure. Engine starts must be
possible.
²PARK position - Apply downward force on the
shift arm and remove pressure. Engine starts must
be possible.
²NEUTRAL position - Normal position. Engine
starts must be possible.
²NEUTRAL position - Engine running and brakes
applied, apply upward force on the shift arm. Trans-
mission shall not be able to shift from neutral to
reverse.
Fig. 65 Brake Transmission Interlock Mechanism
1 - STEERING COLUMN
2 - GEARSHIFT CABLE
3 - GEARSHIFT CABLE LOCK TAB
4 - BTSI SOLENOID LOCK TAB
5 - BTSI CONNECTOR
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE 21 - 365
BRAKE TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 2069 of 2627

FLUID AND FILTER
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - EFFECTS OF
INCORRECT FLUID LEVEL
A low fluid level allows the pump to take in air
along with the fluid. Air in the fluid will cause fluid
pressures to be low and develop slower than normal.
If the transmission is overfilled, the gears churn the
fluid into foam. This aerates the fluid and causing
the same conditions occurring with a low level. In
either case, air bubbles cause fluid overheating, oxi-
dation and varnish buildup which interferes with
valve and clutch operation. Foaming also causes fluid
expansion which can result in fluid overflow from the
transmission vent or fill tube. Fluid overflow can eas-
ily be mistaken for a leak if inspection is not careful.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CAUSES OF
BURNT FLUID
Burnt, discolored fluid is a result of overheating
which has three primary causes.
(1) Internal clutch slippage, usually caused by low
line pressure, inadequate clutch apply pressure, or
clutch seal failure.
(2) A result of restricted fluid flow through the
main and/or auxiliary cooler. This condition is usu-
ally the result of a faulty or improperly installed
drainback valve, a damaged main cooler, or severe
restrictions in the coolers and lines caused by debris
or kinked lines.
(3) Heavy duty operation with a vehicle not prop-
erly equipped for this type of operation. Trailer tow-
ing or similar high load operation will overheat the
transmission fluid if the vehicle is improperly
equipped. Such vehicles should have an auxiliary
transmission fluid cooler, a heavy duty cooling sys-
tem, and the engine/axle ratio combination needed to
handle heavy loads.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FLUID
CONTAMINATION
Transmission fluid contamination is generally a
result of:
²adding incorrect fluid
²failure to clean dipstick and fill tube when
checking level
²engine coolant entering the fluid
²internal failure that generates debris
²overheat that generates sludge (fluid break-
down)
²failure to replace contaminated converter after
repairThe use of non-recommended fluids can result in
transmission failure. The usual results are erratic
shifts, slippage, abnormal wear and eventual failure
due to fluid breakdown and sludge formation. Avoid
this condition by using recommended fluids only.
The dipstick cap and fill tube should be wiped
clean before checking fluid level. Dirt, grease and
other foreign material on the cap and tube could fall
into the tube if not removed beforehand. Take the
time to wipe the cap and tube clean before withdraw-
ing the dipstick.
Engine coolant in the transmission fluid is gener-
ally caused by a cooler malfunction. The only remedy
is to replace the radiator as the cooler in the radiator
is not a serviceable part. If coolant has circulated
through the transmission, an overhaul is necessary.
The torque converter should also be replaced when-
ever a failure generates sludge and debris. This is
necessary because normal converter flushing proce-
dures will not remove all contaminants.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID LEVEL
CHECK
Low fluid level can cause a variety of conditions
because it allows the pump to take in air along with
the fluid. As in any hydraulic system, air bubbles
make the fluid spongy, therefore, pressures will be
low and build up slowly.
Improper filling can also raise the fluid level too
high. When the transmssion has too much fluid, the
geartrain churns up foam and cause the same condi-
tions which occur with a low fluid level.
In either case, air bubbles can cause overheating
and/or fluid oxidation, and varnishing. This can
interfere with normal valve, clutch, and accumulator
operation. Foaming can also result in fluid escaping
from the transmission vent where it may be mis-
taken for a leak.
After the fluid has been checked, seat the dipstick
fully to seal out water and dirt.
The transmission has a dipstick to check oil level.
It is located on the right side of the engine. Be sure
to wipe all dirt from dipstick handle before removing.
The torque converter fills in both the P (PARK)
and N (NEUTRAL) positions. Place the selector lever
in P (PARK) to be sure that the fluid level check is
accurate.The engine should be running at idle
speed for at least one minute, with the vehicle
on level ground.At normal operating temperature
(approximately 82 C. or 180 F.), the fluid level is cor-
rect if it is in the HOT region (cross-hatched area) on
the oil level indicator. The fluid level will be approx-
21 - 366 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR
Page 2085 of 2627

(28) Install the number 2 bearing onto the under-
drive hub with outer race against the hub with petro-
leum jelly.
(29) Install the underdrive hub into the input
clutch retainer.
(30) Install the number 3 bearing into the over-
drive hub with the outer race against the hub with
petroleum jelly.
(31) Install the overdrive hub into the input clutch
retainer.
(32) Install the number 4 bearing into the reverse
hub with outer race against the hub with petroleum
jelly.
(33) Install the reverse hub into the input clutch
retainer.
(34) Install the complete reverse clutch pack.
(35) Install the reverse reaction plate and snap-
ring.
(36) Push up on reaction plate to allow reverse
clutch to move freely.
INPUT SPEED SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The Input and Output Speed Sensors are two-wire
magnetic pickup devices that generate AC signals as
rotation occurs. They are mounted in the left side of
the transmission case and are considered primary
inputs to the Transmission Control Module (TCM).
OPERATION
The Input Speed Sensor provides information on
how fast the input shaft is rotating. As the teeth of
the input clutch hub pass by the sensor coil, an AC
voltage is generated and sent to the TCM. The TCM
interprets this information as input shaft rpm.
The Output Speed Sensor generates an AC signal
in a similar fashion, though its coil is excited by rota-
tion of the rear planetary carrier lugs. The TCM
interprets this information as output shaft rpm.
The TCM compares the input and output speed
signals to determine the following:
²Transmission gear ratio
²Speed ratio error detection
²CVI calculation
The TCM also compares the input speed signal and
the engine speed signal to determine the following:
²Torque converter clutch slippage
²Torque converter element speed ratio
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle.
(2) Place a suitable fluid catch pan under the
transmission.(3) Remove the wiring connector from the input
speed sensor (Fig. 91).
(4) Remove the bolt holding the input speed sensor
to the transmission case.
(5) Remove the input speed sensor from the trans-
mission case.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the input speed sensor into the trans-
mission case.
(2) Install the bolt to hold the input speed sensor
into the transmission case. Tighten the bolt to 11.9
N´m (105 in.lbs.).
(3) Install the wiring connector onto the input
speed sensor
(4) Verify the transmission fluid level. Add fluid as
necessary.
(5) Lower vehicle.
LINE PRESSURE (LP) SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The TCM utilizes a closed-loop system to control
transmission line pressure. The system contains a
variable force style solenoid, the Pressure Control
Solenoid, mounted on the side of the solenoid and
pressure switch assembly. The solenoid is duty cycle
controlled by the TCM to vent the unnecessary line
pressure supplied by the oil pump back to the sump.
The system also contains a variable pressure style
sensor, the Line Pressure Sensor, which is a direct
input to the TCM. The line pressure solenoid moni-
tors the transmission line pressure and completes the
Fig. 91 Input Speed Sensor
1 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR
2 - LINE PRESSURE SENSOR
3 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR
21 - 382 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR
INPUT CLUTCH ASSEMBLY (Continued)
Page 2089 of 2627

(13) Measure the low/reverse clutch pack clearance
and adjust as necessary. The correct clutch clearance
is 1.00-1.74 mm (0.039-0.075 in.).
(14) Install the overrunning clutch into the low/re-
verse clutch retainer making sure that the index
splines are aligned with the retainer.
(15) Install the overrunning clutch inner snap-
ring.
OIL PUMP
DESCRIPTION
The oil pump (Fig. 96) is located at the front of the
transmission inside the bell housing and behind the
transmission front cover. The oil pump consists of
two independent pumps (Fig. 97), a number of valves
(Fig. 98), a front seal (Fig. 99), and a bolt on reaction
shaft. The converter clutch switch and regulator
valves, pressure regulator valve, and converter pres-
sure limit valve are all located in the oil pump valve
body.
OPERATION
As the torque converter rotates, the converter hub
rotates the oil pump drive gear. As the drive gear
rotates both driven gears, a vacuum is created when
the gear teeth come out of mesh. This suction draws
fluid through the pump inlet from the oil pan. As the
gear teeth come back into mesh, pressurized fluid is
forced into the pump outlet and to the oil pump
valves.
At low speeds, both sides of the pump supply fluid
to the transmission. As the speed of the torque con-verter increases, the flow from both sides increases
until the flow from the primary side alone is suffi-
cient to meet system demands. At this point, the
check valve located between the two pumps closes.
The secondary side is shut down and the primary
side supplies all the fluid to the transmission.
CONVERTER CLUTCH SWITCH VALVE
The converter clutch switch valve is used to control
the hydraulic pressure supplied to the front (OFF)
side of the torque converter clutch.
Fig. 96 Oil Pump
1 - OIL PUMP TO CASE BOLT (6)
2 - OIL PUMP
Fig. 97 Oil Pump Gears
1 - PUMP HOUSING
2 - DRIVE GEAR
3 - DRIVEN GEARS
Fig. 98 Oil Pump Valves
1 - TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH ACCUMULATOR VALVE
2 - TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH CONTROL VALVE
3 - TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH SWITCH VALVE
4 - PUMP VALVE BODY
5 - PRESSURE REGULATOR VALVE
6 - TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH LIMIT VALVE
21 - 386 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR
LOW/REVERSE CLUTCH (Continued)
Page 2096 of 2627
(2) Pull the switch outwards to release it from the
connector in the lever (Fig. 108)
INSTALLATION
NOTE: There is enough slack in the wire to pull out
the connector from the lever.
(1) Pull the connector out of the lever just enough
to grasp it.
CAUTION: Be careful not to bend the pins on the
tow/haul overdrive off switch. Use care when
installing the switch, as it is not indexed, and can
be accidentally installed incorrectly.
(2) Install the tow/haul overdrive off switch into
the connector (Fig. 109)
(3) Push the tow/haul overdrive off switch and wir-
ing into the shift lever.
(4) Install the tow/haul overdrive off switch
retainer onto the shift lever.
PISTONS
DESCRIPTION
There are several sizes and types of pistons used in
an automatic transmission. Some pistons are used to
apply clutches, while others are used to apply bands.
They all have in common the fact that they are
round or circular in shape, located within a smooth
walled cylinder, which is closed at one end and con-
verts fluid pressure into mechanical movement. The
fluid pressure exerted on the piston is contained
within the system through the use of piston rings or
seals.
OPERATION
The principal which makes this operation possible
is known as Pascal's Law. Pascal's Law can be stated
as: ªPressure on a confined fluid is transmitted
equally in all directions and acts with equal force on
equal areas.º
PRESSURE
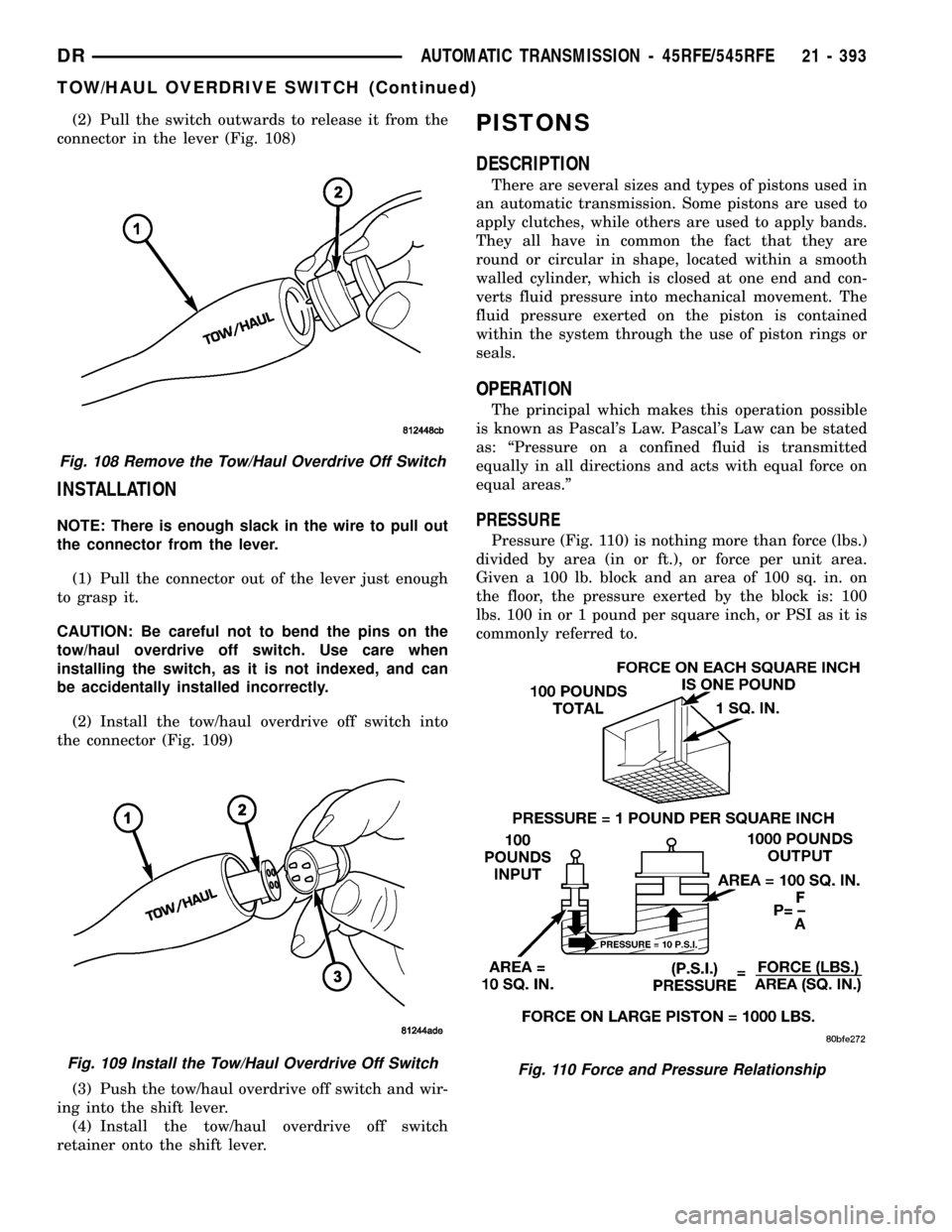
Pressure (Fig. 110) is nothing more than force (lbs.)
divided by area (in or ft.), or force per unit area.
Given a 100 lb. block and an area of 100 sq. in. on
the floor, the pressure exerted by the block is: 100
lbs. 100 in or 1 pound per square inch, or PSI as it is
commonly referred to.
Fig. 108 Remove the Tow/Haul Overdrive Off Switch
Fig. 109 Install the Tow/Haul Overdrive Off SwitchFig. 110 Force and Pressure Relationship
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE 21 - 393
TOW/HAUL OVERDRIVE SWITCH (Continued)
Page 2097 of 2627
PRESSURE ON A CONFINED FLUID
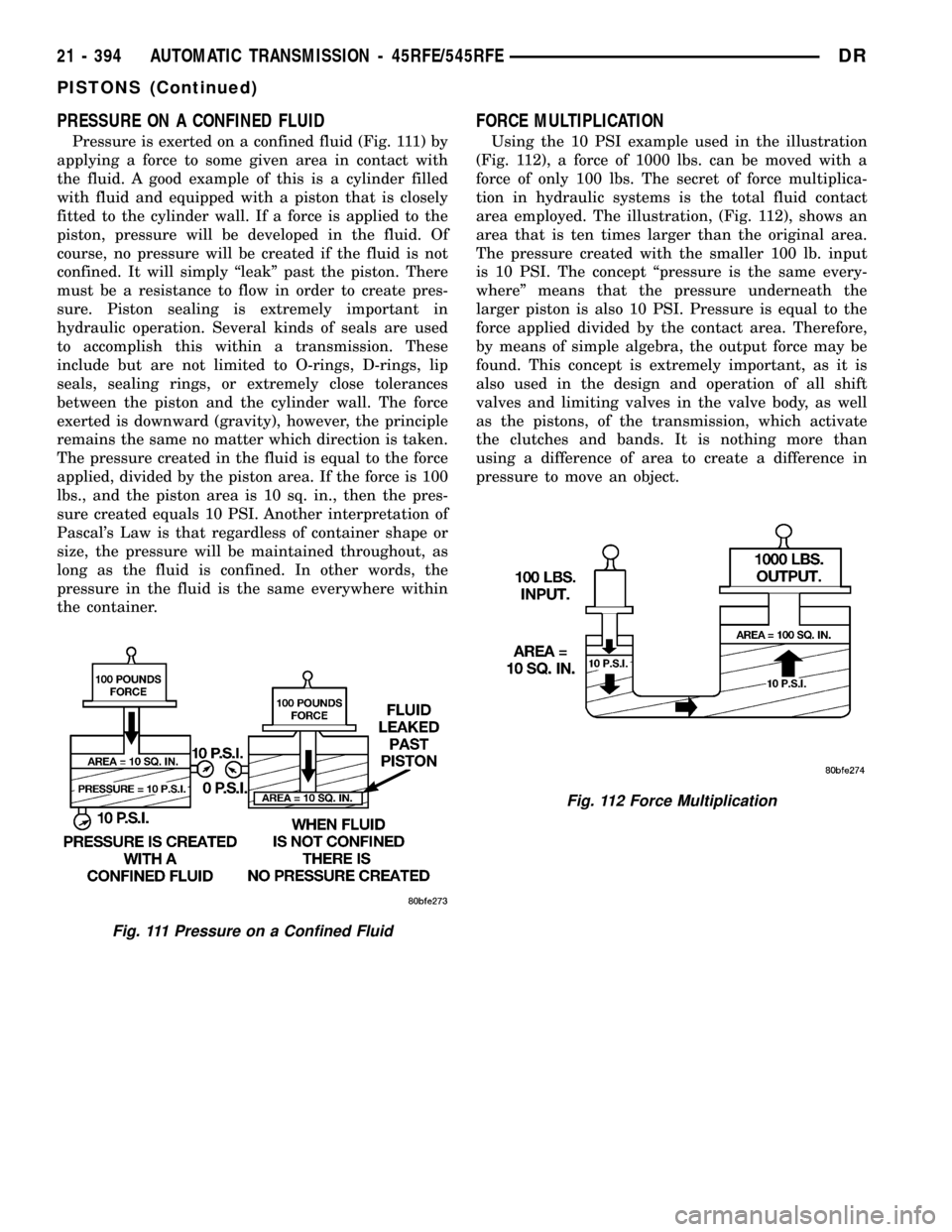
Pressure is exerted on a confined fluid (Fig. 111) by
applying a force to some given area in contact with
the fluid. A good example of this is a cylinder filled
with fluid and equipped with a piston that is closely
fitted to the cylinder wall. If a force is applied to the
piston, pressure will be developed in the fluid. Of
course, no pressure will be created if the fluid is not
confined. It will simply ªleakº past the piston. There
must be a resistance to flow in order to create pres-
sure. Piston sealing is extremely important in
hydraulic operation. Several kinds of seals are used
to accomplish this within a transmission. These
include but are not limited to O-rings, D-rings, lip
seals, sealing rings, or extremely close tolerances
between the piston and the cylinder wall. The force
exerted is downward (gravity), however, the principle
remains the same no matter which direction is taken.
The pressure created in the fluid is equal to the force
applied, divided by the piston area. If the force is 100
lbs., and the piston area is 10 sq. in., then the pres-
sure created equals 10 PSI. Another interpretation of
Pascal's Law is that regardless of container shape or
size, the pressure will be maintained throughout, as
long as the fluid is confined. In other words, the
pressure in the fluid is the same everywhere within
the container.
FORCE MULTIPLICATION
Using the 10 PSI example used in the illustration
(Fig. 112), a force of 1000 lbs. can be moved with a
force of only 100 lbs. The secret of force multiplica-
tion in hydraulic systems is the total fluid contact
area employed. The illustration, (Fig. 112), shows an
area that is ten times larger than the original area.
The pressure created with the smaller 100 lb. input
is 10 PSI. The concept ªpressure is the same every-
whereº means that the pressure underneath the
larger piston is also 10 PSI. Pressure is equal to the
force applied divided by the contact area. Therefore,
by means of simple algebra, the output force may be
found. This concept is extremely important, as it is
also used in the design and operation of all shift
valves and limiting valves in the valve body, as well
as the pistons, of the transmission, which activate
the clutches and bands. It is nothing more than
using a difference of area to create a difference in
pressure to move an object.
Fig. 111 Pressure on a Confined Fluid
Fig. 112 Force Multiplication
21 - 394 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR
PISTONS (Continued)
Page 2103 of 2627

IMPELLER
The impeller (Fig. 118) is an integral part of the
converter housing. The impeller consists of curved
blades placed radially along the inside of the housing
on the transmission side of the converter. As the con-
verter housing is rotated by the engine, so is the
impeller, because they are one and the same and are
the driving members of the system.
Fig. 118 Impeller
1 - ENGINE FLEXPLATE 4 - ENGINE ROTATION
2 - OIL FLOW FROM IMPELLER SECTION INTO TURBINE
SECTION5 - ENGINE ROTATION
3 - IMPELLER VANES AND COVER ARE INTEGRAL
21 - 400 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 2118 of 2627

TRANSFER CASE - NV241 GENII
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
TRANSFER CASE - NV241 GENII
DESCRIPTION........................415
OPERATION..........................415
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TRANSFER
CASE - NV241 GENII..................416
REMOVAL............................417
DISASSEMBLY........................417
CLEANING...........................426
INSPECTION.........................426
ASSEMBLY...........................428
INSTALLATION........................438
SPECIFICATIONS
TRANSFER CASE - NV241 GENII........438
SPECIAL TOOLS
TRANSFER CASE - NV241/NV243........439
EXTENSION HOUSING BUSHING AND SEAL
REMOVAL............................440INSTALLATION........................440
FLUID
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID DRAIN AND
REFILL............................441
FRONT OUTPUT SHAFT SEAL
REMOVAL............................441
INSTALLATION........................442
POSITION SENSOR
DESCRIPTION........................442
OPERATION..........................442
REMOVAL............................443
INSTALLATION........................443
SHIFT LEVER
REMOVAL............................444
INSTALLATION........................445
ADJUSTMENTS
ADJUSTMENT - SHIFT LEVER..........446
TRANSFER CASE - NV241
GENII
DESCRIPTION
The NV241 GENII transfer case is a part-time
transfer case with a low-range gear system. It pro-
vides three operating ranges plus a NEUTRAL posi-
tion. The low range position provides a gear
reduction ratio of 2.72:1 for increased low speed
torque capability.
The gear cases and extension are all of aluminum
(Fig. 1). Drive sprockets and an interconnecting drive
chain are used to transmit engine torque to the front/
rear propeller shafts. The mainshaft, input gear and
front output shaft are supported by ball and needle
bearings.
IDENTIFICATION
An identification tag (Fig. 2) is attached to the rear
case of every transfer case. The tag provides the
transfer case model number, assembly number, serial
number, and low range ratio.
The transfer case serial number also represents
the date of build.
OPERATION
OPERATING RANGE
Transfer case operating ranges are:
²2H (2-wheel drive)²4H (4-wheel drive)
²4LO (4-wheel drive low range)
The 2H range is for use on any road surface at any
time.
The 4H and 4LO ranges are for off road use only.
They are not for use on hard surface roads. The only
exception being when the road surface is covered by
ice and snow.
The low range reduction gear system is operative
in 4LO range only. This range is for extra pulling
Fig. 1 Transfer Case - Front View
1 - TRANSFER CASE
2 - MANUAL LEVER
3 - POSITION SENSOR
DRTRANSFER CASE - NV241 GENII 21 - 415