Schematic DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1998, Model line: RAM 1500, Model: DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.GPages: 2627
Page 3 of 2627
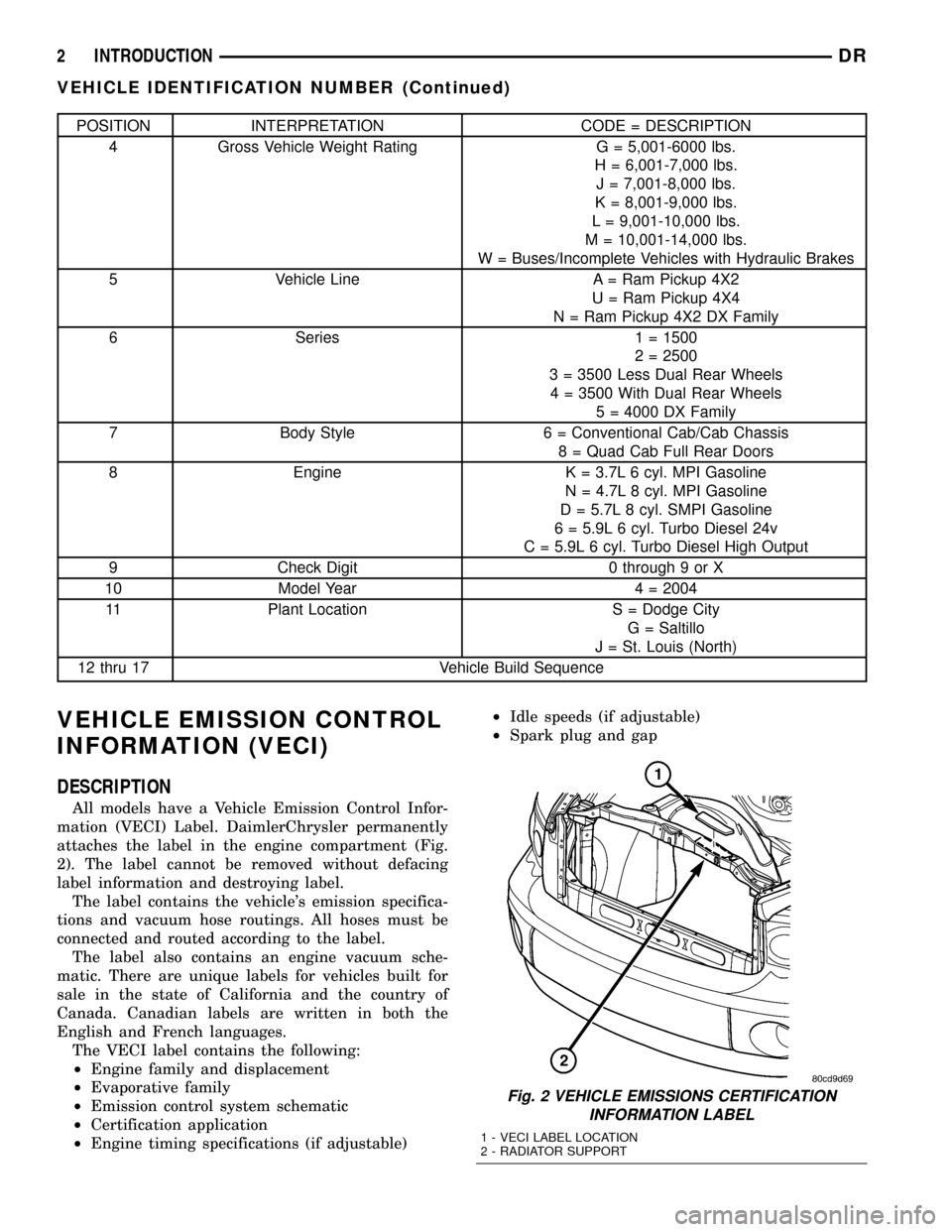
POSITION INTERPRETATION CODE = DESCRIPTION
4 Gross Vehicle Weight Rating G = 5,001-6000 lbs.
H = 6,001-7,000 lbs.
J = 7,001-8,000 lbs.
K = 8,001-9,000 lbs.
L = 9,001-10,000 lbs.
M = 10,001-14,000 lbs.
W = Buses/Incomplete Vehicles with Hydraulic Brakes
5 Vehicle Line A = Ram Pickup 4X2
U = Ram Pickup 4X4
N = Ram Pickup 4X2 DX Family
6 Series 1 = 1500
2 = 2500
3 = 3500 Less Dual Rear Wheels
4 = 3500 With Dual Rear Wheels
5 = 4000 DX Family
7 Body Style 6 = Conventional Cab/Cab Chassis
8 = Quad Cab Full Rear Doors
8 Engine K = 3.7L 6 cyl. MPI Gasoline
N = 4.7L 8 cyl. MPI Gasoline
D = 5.7L 8 cyl. SMPI Gasoline
6 = 5.9L 6 cyl. Turbo Diesel 24v
C = 5.9L 6 cyl. Turbo Diesel High Output
9 Check Digit 0 through 9 or X
10 Model Year 4 = 2004
11 Plant Location S = Dodge City
G = Saltillo
J = St. Louis (North)
12 thru 17 Vehicle Build Sequence
VEHICLE EMISSION CONTROL
INFORMATION (VECI)
DESCRIPTION
All models have a Vehicle Emission Control Infor-
mation (VECI) Label. DaimlerChrysler permanently
attaches the label in the engine compartment (Fig.
2). The label cannot be removed without defacing
label information and destroying label.
The label contains the vehicle's emission specifica-
tions and vacuum hose routings. All hoses must be
connected and routed according to the label.
The label also contains an engine vacuum sche-
matic. There are unique labels for vehicles built for
sale in the state of California and the country of
Canada. Canadian labels are written in both the
English and French languages.
The VECI label contains the following:
²Engine family and displacement
²Evaporative family
²Emission control system schematic
²Certification application
²Engine timing specifications (if adjustable)²Idle speeds (if adjustable)
²Spark plug and gap
Fig. 2 VEHICLE EMISSIONS CERTIFICATION
INFORMATION LABEL
1 - VECI LABEL LOCATION
2 - RADIATOR SUPPORT
2 INTRODUCTIONDR
VEHICLE IDENTIFICATION NUMBER (Continued)
Page 326 of 2627
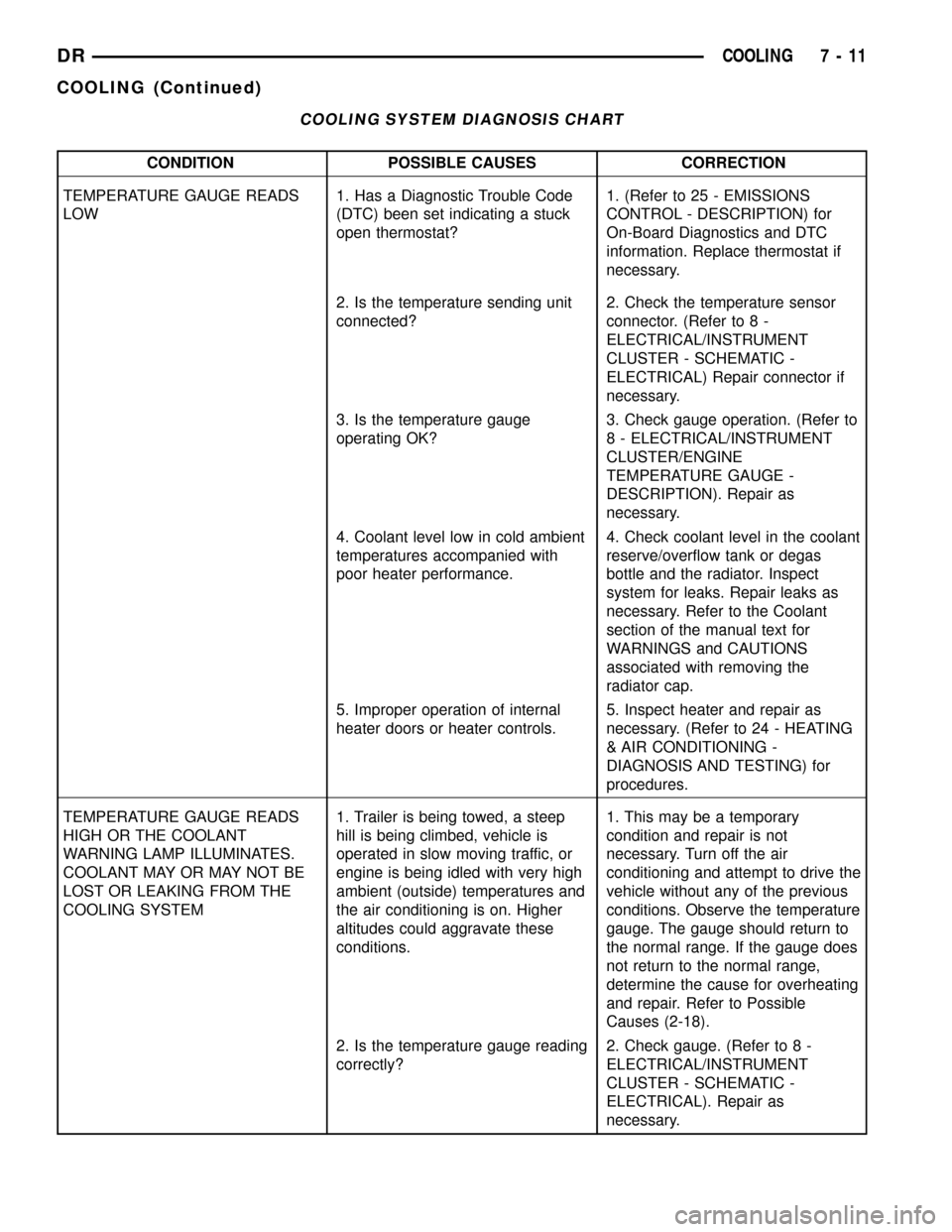
COOLING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS CHART
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
TEMPERATURE GAUGE READS
LOW1. Has a Diagnostic Trouble Code
(DTC) been set indicating a stuck
open thermostat?1. (Refer to 25 - EMISSIONS
CONTROL - DESCRIPTION) for
On-Board Diagnostics and DTC
information. Replace thermostat if
necessary.
2. Is the temperature sending unit
connected?2. Check the temperature sensor
connector. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/INSTRUMENT
CLUSTER - SCHEMATIC -
ELECTRICAL) Repair connector if
necessary.
3. Is the temperature gauge
operating OK?3. Check gauge operation. (Refer to
8 - ELECTRICAL/INSTRUMENT
CLUSTER/ENGINE
TEMPERATURE GAUGE -
DESCRIPTION). Repair as
necessary.
4. Coolant level low in cold ambient
temperatures accompanied with
poor heater performance.4. Check coolant level in the coolant
reserve/overflow tank or degas
bottle and the radiator. Inspect
system for leaks. Repair leaks as
necessary. Refer to the Coolant
section of the manual text for
WARNINGS and CAUTIONS
associated with removing the
radiator cap.
5. Improper operation of internal
heater doors or heater controls.5. Inspect heater and repair as
necessary. (Refer to 24 - HEATING
& AIR CONDITIONING -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING) for
procedures.
TEMPERATURE GAUGE READS
HIGH OR THE COOLANT
WARNING LAMP ILLUMINATES.
COOLANT MAY OR MAY NOT BE
LOST OR LEAKING FROM THE
COOLING SYSTEM1. Trailer is being towed, a steep
hill is being climbed, vehicle is
operated in slow moving traffic, or
engine is being idled with very high
ambient (outside) temperatures and
the air conditioning is on. Higher
altitudes could aggravate these
conditions.1. This may be a temporary
condition and repair is not
necessary. Turn off the air
conditioning and attempt to drive the
vehicle without any of the previous
conditions. Observe the temperature
gauge. The gauge should return to
the normal range. If the gauge does
not return to the normal range,
determine the cause for overheating
and repair. Refer to Possible
Causes (2-18).
2. Is the temperature gauge reading
correctly?2. Check gauge. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/INSTRUMENT
CLUSTER - SCHEMATIC -
ELECTRICAL). Repair as
necessary.
DRCOOLING 7 - 11
COOLING (Continued)
Page 327 of 2627

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
3. Is the temperature warning
illuminating unnecessarily?3. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER -
SCHEMATIC - ELECTRICAL).
4. Coolant low in coolant reserve/
overflow tank and radiator?4. Check for coolant leaks and
repair as necessary. (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
5. Pressure cap not installed tightly.
If cap is loose, boiling point of
coolant will be lowered. Also refer
to the following Step 6.5. Tighten cap
6. Poor seals at the radiator cap. 6. (a) Check condition of cap and
cap seals. Refer to Radiator Cap.
Replace cap if necessary.
(b) Check condition of radiator filler
neck. If neck is bent or damaged,
replace radiator (5.9L) or degas
bottle (3.7L, 4.7L).
7. Coolant level low in radiator but
not in coolant reserve/overflow
tank. This means the radiator is not
drawing coolant from the coolant
reserve/overflow tank as the engine
cools (5.9L).7. (a) Check condition of radiator
cap and cap seals. Refer to
Radiator Cap in this Group. Replace
cap if necessary.
(b) Check condition of radiator filler
neck. If neck is bent or damaged,
replace radiator.
(c) Check condition of the hose from
the radiator to the coolant tank. It
should fit tight at both ends without
any kinks or tears. Replace hose if
necessary.
(d) Check coolant reserve/overflow
tank and tanks hoses for blockage.
Repair as necessary.
8. Incorrect coolant concentration 8. Check coolant. (Refer to
LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE/
FLUID TYPES - DESCRIPTION).
9. Coolant not flowing through
system9. Check for coolant flow at radiator
filler neck with some coolant
removed, engine warm and
thermostat open. Coolant should be
observed flowing through radiator. If
flow is not observed, determine area
of obstruction and repair as
necessary.
10. Radiator or A/C condenser fins
are dirty or clogged.10. Remove insects and debris.
(Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
7 - 12 COOLINGDR
COOLING (Continued)
Page 344 of 2627

REMOVAL
CAUTION: Do not attempt to check belt tension with
a belt tension gauge on vehicles equipped with an
automatic belt tensioner. Refer to Automatic Belt
Tensioner in this group.
NOTE: The belt routing schematics are published
from the latest information available at the time of
publication. If anything differs between these sche-
matics and the Belt Routing Label, use the sche-
matics on Belt Routing Label.This label is located in
the engine compartment.
Drive belts on diesel engines are equipped with a
spring loaded automatic belt tensioner.
This belt tensioner will be used on all belt config-
urations, such as with or without air conditioning.
For more information, (Refer to 7 - COOLING/AC-
CESSORY DRIVE/BELT TENSIONERS - DESCRIP-
TION).
(1) A 1/2 inch square hole is provided in the auto-
matic belt tensioner. Attach a 1/2 inch drive-long
handle ratchet to this hole.(2) Rotate ratchet and tensioner assembly clock-
wise (as viewed from front) until tension has been
relieved from belt.
(3) Remove belt from water pump pulley first.
(4) Remove belt from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: When installing the accessory drive belt,
the belt must be routed correctly. If not, engine may
overheat due to water pump rotating in wrong
direction. Refer to (Fig. 10) or (Fig. 11)for correct
engine belt routing. The correct belt with correct
length must be used.
(1) Position drive belt over all pulleysexcept
water pump pulley.
(2) Attach a 1/2 inch ratchet to tensioner.
(3) Rotate ratchet and belt tensioner clockwise.
Place belt over water pump pulley. Let tensioner
rotate back into place. Remove ratchet. Be sure belt
is properly seated on all pulleys.
Fig. 10 Belt Routing ± 5.9L Diesel Engine With A/C
1 - GENERATOR PULLEY
2 - WATER PUMP PULLEY
3 - IDLER PULLEY
4 - POWER STEERING PUMP PULLEY
5 - RADIATOR FAN PULLEY
6 - CRANKSHAFT PULLEY
7 - AUTOMATIC TENSIONER
8 - A/C COMPRESSOR PUMP PULLEY
Fig. 11 Belt Routing - 5.9L Diesel Engine Without
A/C
1 - GENERATOR PULLEY
2 - WATER PUMP PULLEY
3 - IDLER PULLEY
4 - POWER STEERING PUMP PULLEY
5 - RADIATOR FAN PULLEY
6 - CRANKSHAFT PULLEY
7 - AUTOMATIC TENSIONER
DRACCESSORY DRIVE 7 - 29
DRIVE BELT - 5.9L DIESEL (Continued)
Page 455 of 2627

INSTALLATION
3.7L / 4.7L
(1) Position generator to engine and install 2 hor-
izontal bolts and 1 vertical bolt.
(2) Tighten all 3 bolts. Refer to Torque Specifica-
tions.
(3) Snap field wire connector into rear of genera-
tor.
(4) Install B+ terminal eyelet to generator output
stud. Tighten mounting nut. Refer to Torque Specifi-
cations.
CAUTION: Never force a belt over a pulley rim
using a screwdriver. The synthetic fiber of the belt
can be damaged.
CAUTION: When installing a serpentine accessory
drive belt, the belt MUST be routed correctly. The
water pump may be rotating in the wrong direction
if the belt is installed incorrectly, causing the
engine to overheat. Refer to belt routing label in
engine compartment, or refer to Belt Schematics in
7, Cooling System.
(5) Install generator drive belt. Refer to 7, Cooling
System for procedure.
(6) Install negative battery cable to battery.5.7L
(1) Position generator to engine and install 2
mounting bolts.
(2) Tighten bolts. Refer to Torque Specifications.
(3) Position support bracket to front of generator
and install bolt and nuts. Tighten bolt / nuts. Refer
to Torque Specifications.
(4) Snap field wire connector into rear of genera-
tor.
(5) Install B+ terminal eyelet to generator output
stud. Tighten mounting nut. Refer to Torque Specifi-
cations.
CAUTION: Never force a belt over a pulley rim
using a screwdriver. The synthetic fiber of the belt
can be damaged.
CAUTION: When installing a serpentine accessory
drive belt, the belt MUST be routed correctly. The
water pump may be rotating in the wrong direction
if the belt is installed incorrectly, causing the
engine to overheat. Refer to belt routing label in
engine compartment, or refer to Belt Schematics in
7, Cooling System.
(6) Install generator drive belt. Refer to 7, Cooling
System for procedure.
(7) Install negative battery cable to battery.
5.9L Diesel
(1) Position generator to upper and lower mount-
ing brackets and install upper bolt and lower bolt /
nut.
(2) Tighten all bolts / nut. Refer to Torque Specifi-
cations.
(3) Snap field wire connector into rear of genera-
tor.
(4) Install B+ terminal eyelet to generator output
stud. Tighten mounting nut. Refer to Torque Specifi-
cations.
CAUTION: Never force a belt over a pulley rim
using a screwdriver. The synthetic fiber of the belt
can be damaged.
CAUTION: When installing a serpentine accessory
drive belt, the belt MUST be routed correctly. The
water pump may be rotating in the wrong direction
if the belt is installed incorrectly, causing the
engine to overheat. Refer to belt routing label in
engine compartment, or refer to Belt Schematics in
7, Cooling System.
(5) Install generator drive belt. Refer to 7, Cooling
System for procedure.
Fig. 7 5.9L DIESEL GENER. CONNECTORS
1 - B+ CONNECTOR
2 - GENERATOR
3 - FIELD WIRE CONNECTOR
8F - 24 CHARGINGDR
GENERATOR (Continued)
Page 587 of 2627

The compass unit also will compensate for magne-
tism the body of the vehicle may acquire during nor-
mal use. However, avoid placing anything magnetic
directly on the roof of the vehicle. Magnetic mounts
for an antenna, a repair order hat, or a funeral pro-
cession flag can exceed the compensating ability of
the compass unit if placed on the roof panel. Mag-
netic bit drivers used on the fasteners that hold the
overhead console assembly to the roof header can
also affect compass operation. If the vehicle roof
should become magnetized, the demagnetizing and
calibration procedures found in this section may be
required to restore proper compass operation.
TEMPERATURE DISPLAY
All the available overhead consoles on this model
include Temperature information. The temperature
displays the outside ambient temperature in whole
degrees. The temperature display can be toggled
from Fahrenheit to Celsius by selecting the desired
U.S./Metric option from the customer programmable
features. The displayed temperature is not an instant
reading of conditions, but an average temperature. It
may take the temperature display several minutes to
respond to a major temperature change, such as driv-
ing out of a heated garage into winter temperatures.
When the ignition switch is turned to the Off posi-
tion, the last displayed temperature reading stays in
the electronic control modules, (CMTC, EVIC) mem-
ory. When the ignition switch is turned to the On
position again, the electronic module will display the
memory temperature for one minute; then update the
display to the current average temperature reading
within five minutes.The temperature function is supported by an ambi-
ent temperature sensor. This sensor is mounted out-
side the passenger compartment near the front and
center of the vehicle, and is hard wired to the Front
Control Module (FCM). The FCM sends temperature
status messages to the module over the J1850 PCI
data bus circuit. For more information on the ambi-
ent temperature sensor, refer to Ambient Tempera-
ture Sensor later in this section.
Following are general descriptions of the major
components used in the overhead console. Refer to
Wiring Diagrams for complete circuit schematics.
OPERATION
Refer to the vehicle Owner's Manual for specific
operation of each overhead console and its systems.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - OVERHEAD
CONSOLE
If the problem with the overhead console is an
inaccurate or scrambled display, refer toSELF-DI-
AGNOSTIC TESTlater in this text. If the problem
with the overhead console is incorrect Vacuum Fluo-
rescent Display (VFD) dimming levels, use a DRB
IIItscan tool and the proper Diagnostic Procedures
manual to test for the correct dimming message
inputs being received from the Body Control Module
(BCM) or Front Control Module (FCM) over the
J1850 Programmable Communications Interface
(PCI) data bus circuit. If the problem is a no-display
condition, use the following procedure. For complete
circuit diagrams, refer toOverhead Consolein the
Wiring Diagrams section of the service manual.
(1) Remove the overhead console from the head-
liner (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/OVERHEAD CON-
SOLE - REMOVAL).
(2) Check for battery voltage at the overhead con-
sole electrical connector. Refer to Wiring for connec-
tor information. If OK, go to Step 3. If not OK, Check
for battery voltage at the appropriate B(+) fuse in the
integrated power module, repair the open fused B(+)
circuit as required.
(3) Turn the ignition switch to the On position.
Check the fused ignition switch output circuit(s) at
the overhead console electrical connector. If OK, go to
Step 4. If not OK, repair the open or shorted circuit
as required.
(4) Turn the ignition switch to the Off position.
Disconnect and isolate the battery negative cable.
Check for continuity between the ground circuit cav-
ity of the overhead console electrical connector and a
good ground. There should be continuity. If OK, refer
toSELF-DIAGNOSTIC TESTbelow for further
diagnosis of the electronics module and the J1850
PCI data bus circuit. If not OK, repair the open
ground circuit as required.
Fig. 1 DR OVERHEAD CONSOLE ± EVIC
8M - 2 MESSAGE SYSTEMSDR
OVERHEAD CONSOLE (Continued)
Page 1218 of 2627

INTEGRATED POWER MODULE
DESCRIPTION
The Integrated Power Module (IPM) (Fig. 1) is a
combination of the Power Distribution Center (PDC)
and the Front Control Module (FCM). The IPM is
located in the engine compartment, next to the bat-
tery on this model. The power distribution center
mates directly with the Front Control Module (FCM)
to form the Integrated Power Module Fuse and Relay
Center. The power distribution center (PDC) is a
printed circuit board based module that contains
fuses and relays, while the front control module con-
tains the electronics controlling the integrated power
module and other functions. This integrated power
module connects directly to the battery positive via a
stud located on top of the unit. The ground connec-
tion is via electrical connectors. The integrated power
module provides the primary means of voltage distri-
bution and protection for the entire vehicle.
The molded plastic integrated power module hous-
ing includes a base and cover. The integrated power
module cover is easily opened or removed for service
access by unscrewing the cover retaining nut and has
a fuse and relay layout map integral to the inside
surface of the cover. This integrated power module
housing base and cover are secured in place via bolts
to the left front fender support assembly.
Replaceable components of the integrated power
module assembly are broken down into the followingcomponents: the Power Distribution Center (PDC),
the integrated power module cover, the Front Control
Module (FCM) and the Integrated Power Module
Assembly which includes the power distribution cen-
ter, the cover and FCM.Refer to the Front Con-
trol Module in the Electronic Control Module
sectionof this service manual for information on the
front control module.
OPERATION
All of the current from the battery and the gener-
ator output enters the integrated power module via a
stud on the top of the module. The integrated power
module cover is removed to access the fuses or relays.
Internal connections of all of the power distribution
center circuits is accomplished by a combination of
bus bars and a printed circuit board. Refer to the
Wiring section of the service manual for complete
integrated power module circuit schematics.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the negative and positive battery
cables.
(2) Unsnap cover and remove the B+ terminal nut
from the integrated power module B+ terminal.
Remove the B+ cable from the integrated power mod-
ule.
(3) Disconnect the gray connector from the inte-
grated power module.
Fig. 1 DR INTEGRATED POWER MODULE
1 - POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER HOUSING
2 - FRONT CONTROL MODULE ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
Fig. 2 DR INTEGRATED POWER MODULE
1 - COVER RETAINING BOLT
2 - INTEGRATED POWER MODULE RETAINING BOLT
3 - RETAINING SCREW
4 - INTEGRATED POWER MODULE COVER
DR8W-97 POWER DISTRIBUTION 8W - 97 - 3
Page 1666 of 2627

(8) For columns without tilt remove the bracket to
gain access to the ignition switch mounting screws.
(Fig. 10)
(9) Disconnect the electrical connector at rear of
ignition switch (Fig. 11).
(10) Remove ignition switch mounting screw.
(11) Using a small screwdriver, push on locking
tab and remove switch from steering column.
INSTALLATION
The ignition key must be in the key cylinder for
cylinder removal. The key cylinder must be removed
first before installing ignition switch.
(1) Before installing ignition switch, rotate the slot
in the switch to the ON position.(2) Connect the electrical connector to rear of the
ignition switch. Make sure that locking tabs are fully
seated into wiring connector.
(3) Position switch to column and install the
mounting screw. Tighten screw to 3 N´m (26 in. lbs.).
(4) Install the tilt lever bracket mounting screws.
Tighten screws to 4.5 N´m (40 in. lbs.).
(5) If the column is non-tilt install the bracket.
Tighten screws to 4.5 N´m (40 in. lbs.) (Fig. 10)
(6) Position the wire retainer into the tilt lever
bracket.
(7) Reconnect the lower clockspring connectors.
(8) Install the key cylinder.
(9) Install steering column upper and lower
shrouds.
(10) Enable the airbag system. (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/RESTRAINTS/DRIVER AIRBAG - INSTAL-
LATION).
KEY-IN IGNITION SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
The key-in ignition switch is integral to the igni-
tion switch, which is mounted on the left side of the
steering column. It closes a path to ground for the
Central Timer Module (CTM) when the ignition key
is inserted in the ignition key cylinder and the driver
door ajar switch is closed (driver door is open). The
key-in ignition switch opens the ground path when
the key is removed from the ignition key cylinder.
The ground path is also opened when the driver door
ajar switch is open (driver door is closed).
The key-in ignition switch cannot be repaired and,
if faulty or damaged, the entire ignition switch must
be replaced, (Refer to 19 - STEERING/COLUMN/IG-
NITION SWITCH - REMOVAL).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - IGNITION SWITCH
AND KEY LOCK CYLINDER
ELECTRICAL DIAGNOSIS
For ignition switch electrical schematics, refer to
Ignition Switch in the appropriate section of Electri-
cal Wiring Diagrams.
MECHANICAL DIAGNOSIS (KEY DIFFICULT TO
ROTATE)
(Refer to 19 - STEERING/COLUMN/IGNITION
SWITCH - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
Fig. 10 IGNITION SWITCH WITHOUT TILT
1 - Ignition Switch Mounting Screws
2 - Non-Tilt Mounitng Bracket Screws
Fig. 11 IGNITION SWITCH
1 - Ignition Switch
2 - Ignition Switch Mounting Screws
DRCOLUMN 19 - 11
IGNITION SWITCH (Continued)
Page 1833 of 2627

AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE
DESCRIPTION........................132
OPERATION..........................134
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION.....................140
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PRELIMINARY . 140
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ROAD
TESTING...........................140
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC
PRESSURE TEST....................141
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AIR TESTING
TRANSMISSION CLUTCH AND BAND
OPERATION........................144
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CONVERTER
HOUSING FLUID LEAK................144
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - DIAGNOSIS
CHARTS...........................145
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ALUMINUM
THREAD REPAIR.....................158
REMOVAL............................158
DISASSEMBLY........................160
CLEANING...........................166
INSPECTION.........................166
ASSEMBLY...........................166
INSTALLATION........................174
SCHEMATICS AND DIAGRAMS
HYDRAULIC SCHEMATICS.............176
SPECIFICATIONS
TRANSMISSION.....................189
SPECIAL TOOLS
RE TRANSMISSION..................191
ACCUMULATOR
DESCRIPTION........................193
OPERATION..........................193
INSPECTION.........................194
BANDS
DESCRIPTION........................194
OPERATION..........................194
ADJUSTMENTS
ADJUSTMENT - BANDS...............195
BRAKE TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK
SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION........................196
OPERATION..........................196
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BRAKE
TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK......196
ADJUSTMENTS - BRAKE TRANSMISSION
SHIFT INTERLOCK...................196ELECTRONIC GOVERNOR
DESCRIPTION........................197
OPERATION..........................198
REMOVAL............................199
INSTALLATION........................200
EXTENSION HOUSING SEAL
REMOVAL............................201
INSTALLATION........................201
FLUID AND FILTER
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - EFFECTS OF
INCORRECT FLUID LEVEL.............201
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CAUSES OF
BURNT FLUID.......................201
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FLUID
CONTAMINATION....................202
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID LEVEL
CHECK............................202
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID AND
FILTER REPLACEMENT...............203
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TRANSMISSION
FILL...............................204
FRONT CLUTCH
DESCRIPTION........................205
OPERATION..........................205
DISASSEMBLY........................205
INSPECTION.........................206
ASSEMBLY...........................207
FRONT SERVO
DESCRIPTION........................208
OPERATION..........................208
DISASSEMBLY........................209
CLEANING...........................209
INSPECTION.........................209
ASSEMBLY...........................209
GEARSHIFT CABLE
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - GEARSHIFT
CABLE.............................210
REMOVAL............................210
INSTALLATION........................211
ADJUSTMENTS
GEARSHIFT CABLE..................212
OIL PUMP
DESCRIPTION........................213
OPERATION..........................213
DISASSEMBLY........................214
CLEANING...........................214
INSPECTION.........................214
ASSEMBLY...........................214
21 - 130 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
Page 1848 of 2627

TORQUE CONVERTER LEAK POINTS
Possible sources of converter leaks are:
²Leaks at the weld joint around the outside diam-
eter weld.
²Leaks at the converter hub weld.
CONVERTER HOUSING AREA LEAK CORRECTION
(1) Remove converter.
(2) Tighten front band adjusting screw until band
is tight around front clutch retainer. This prevents
front/rear clutches from coming out when oil pump is
removed.
(3) Remove oil pump and remove pump seal.
Inspect pump housing drainback and vent holes for
obstructions. Clear holes with solvent and wire.(4) Inspect pump bushing and converter hub. If
bushing is scored, replace it. If converter hub is
scored, either polish it with crocus cloth or replace
converter.
(5) Install new pump seal, O-ring, and gasket.
Replace oil pump if cracked, porous or damaged in
any way. Be sure to loosen the front band before
installing the oil pump, damage to the oil pump seal
may occur if the band is still tightened to the front
clutch retainer.
(6) Loosen kickdown lever pin access plug three
turns. Apply LoctiteŸ 592, or PermatextNo.2to
plug threads and tighten plug to 17 N´m (150 in. lbs.)
torque.
(7) Adjust front band.
(8) Lubricate pump seal and converter hub with
transmission fluid or petroleum jelly and install con-
verter.
(9) Install transmission and converter housing
dust shield.
(10) Lower vehicle.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - DIAGNOSIS
CHARTS
The diagnosis charts provide additional reference
when diagnosing a transmission fault. The charts
provide general information on a variety of transmis-
sion, overdrive unit and converter clutch fault condi-
tions.
The hydraulic flow charts in the Schematics and
Diagrams section of this group, outline fluid flow and
hydraulic circuitry. Circuit operation is provided for
PARK, NEUTRAL, FIRST, SECOND, THIRD,
FOURTH, MANUAL FIRST, MANUAL SECOND,
and REVERSE gear ranges. Normal working pres-
sures are also supplied for each of the gear ranges.
Fig. 11 Converter Housing Leak Paths
1 - PUMP SEAL
2 - PUMP VENT
3 - PUMP BOLT
4 - PUMP GASKET
5 - CONVERTER HOUSING
6 - CONVERTER
7 - REAR MAIN SEAL LEAK
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 145
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE (Continued)