fuel DODGE RAM 2001 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2001, Model line: RAM, Model: DODGE RAM 2001Pages: 2889, PDF Size: 68.07 MB
Page 1449 of 2889
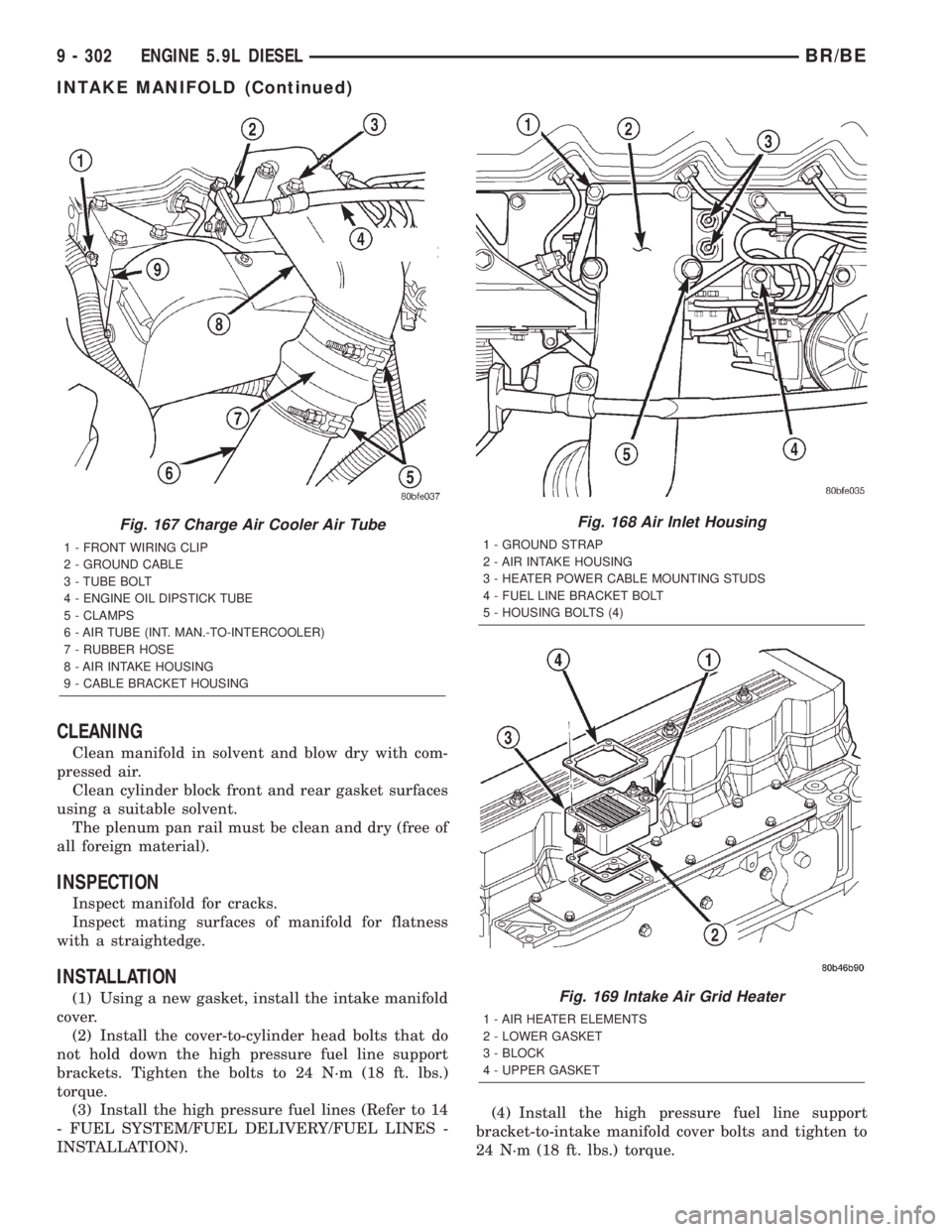
CLEANING
Clean manifold in solvent and blow dry with com-
pressed air.
Clean cylinder block front and rear gasket surfaces
using a suitable solvent.
The plenum pan rail must be clean and dry (free of
all foreign material).
INSPECTION
Inspect manifold for cracks.
Inspect mating surfaces of manifold for flatness
with a straightedge.
INSTALLATION
(1) Using a new gasket, install the intake manifold
cover.
(2) Install the cover-to-cylinder head bolts that do
not hold down the high pressure fuel line support
brackets. Tighten the bolts to 24 N´m (18 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(3) Install the high pressure fuel lines (Refer to 14
- FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY/FUEL LINES -
INSTALLATION).(4) Install the high pressure fuel line support
bracket-to-intake manifold cover bolts and tighten to
24 N´m (18 ft. lbs.) torque.
Fig. 167 Charge Air Cooler Air Tube
1 - FRONT WIRING CLIP
2 - GROUND CABLE
3 - TUBE BOLT
4 - ENGINE OIL DIPSTICK TUBE
5 - CLAMPS
6 - AIR TUBE (INT. MAN.-TO-INTERCOOLER)
7 - RUBBER HOSE
8 - AIR INTAKE HOUSING
9 - CABLE BRACKET HOUSING
Fig. 168 Air Inlet Housing
1 - GROUND STRAP
2 - AIR INTAKE HOUSING
3 - HEATER POWER CABLE MOUNTING STUDS
4 - FUEL LINE BRACKET BOLT
5 - HOUSING BOLTS (4)
Fig. 169 Intake Air Grid Heater
1 - AIR HEATER ELEMENTS
2 - LOWER GASKET
3 - BLOCK
4 - UPPER GASKET
9 - 302 ENGINE 5.9L DIESELBR/BE
INTAKE MANIFOLD (Continued)
Page 1450 of 2889
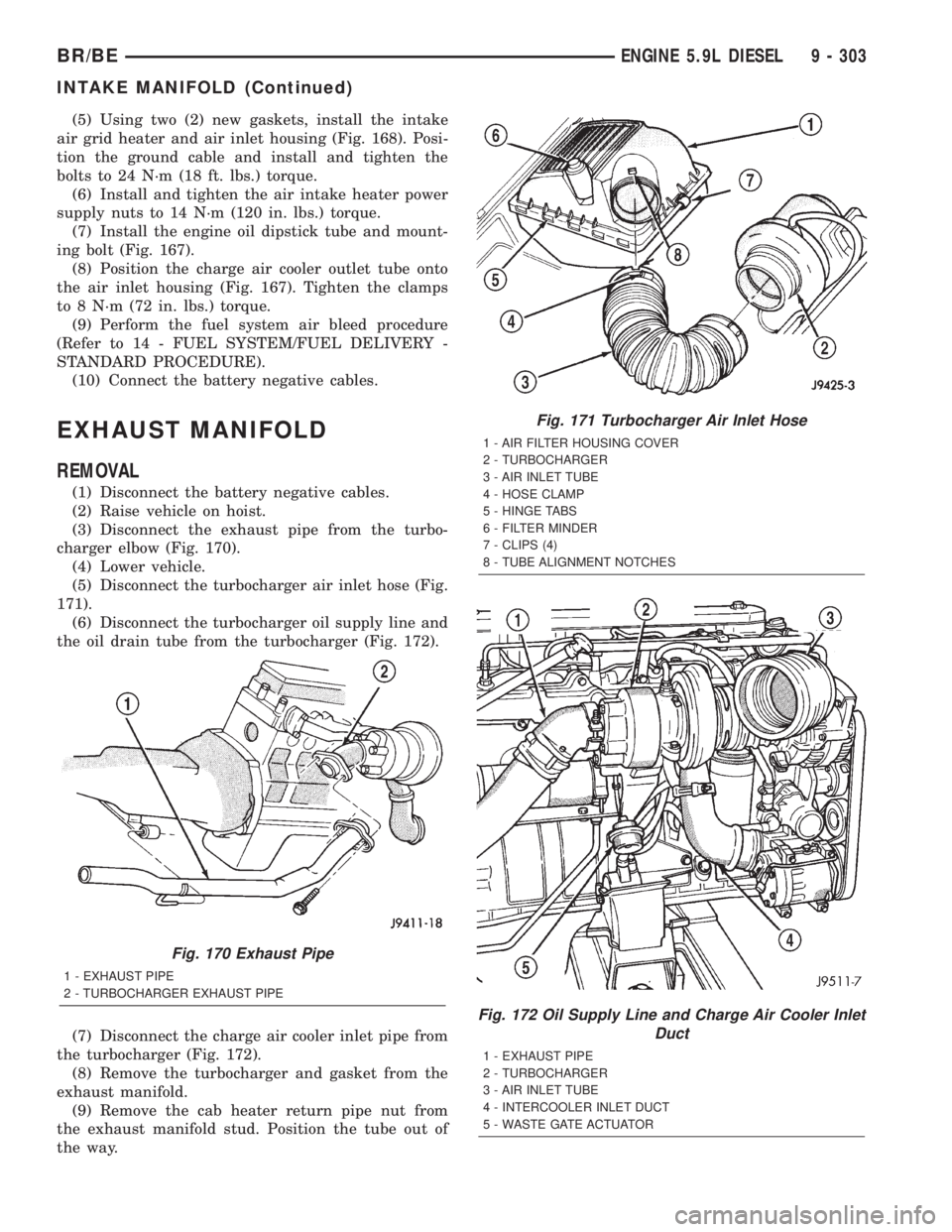
(5) Using two (2) new gaskets, install the intake
air grid heater and air inlet housing (Fig. 168). Posi-
tion the ground cable and install and tighten the
bolts to 24 N´m (18 ft. lbs.) torque.
(6) Install and tighten the air intake heater power
supply nuts to 14 N´m (120 in. lbs.) torque.
(7) Install the engine oil dipstick tube and mount-
ing bolt (Fig. 167).
(8) Position the charge air cooler outlet tube onto
the air inlet housing (Fig. 167). Tighten the clamps
to 8 N´m (72 in. lbs.) torque.
(9) Perform the fuel system air bleed procedure
(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(10) Connect the battery negative cables.
EXHAUST MANIFOLD
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the battery negative cables.
(2) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(3) Disconnect the exhaust pipe from the turbo-
charger elbow (Fig. 170).
(4) Lower vehicle.
(5) Disconnect the turbocharger air inlet hose (Fig.
171).
(6) Disconnect the turbocharger oil supply line and
the oil drain tube from the turbocharger (Fig. 172).
(7) Disconnect the charge air cooler inlet pipe from
the turbocharger (Fig. 172).
(8) Remove the turbocharger and gasket from the
exhaust manifold.
(9) Remove the cab heater return pipe nut from
the exhaust manifold stud. Position the tube out of
the way.
Fig. 170 Exhaust Pipe
1 - EXHAUST PIPE
2 - TURBOCHARGER EXHAUST PIPE
Fig. 171 Turbocharger Air Inlet Hose
1 - AIR FILTER HOUSING COVER
2 - TURBOCHARGER
3 - AIR INLET TUBE
4 - HOSE CLAMP
5 - HINGE TABS
6 - FILTER MINDER
7 - CLIPS (4)
8 - TUBE ALIGNMENT NOTCHES
Fig. 172 Oil Supply Line and Charge Air Cooler Inlet
Duct
1 - EXHAUST PIPE
2 - TURBOCHARGER
3 - AIR INLET TUBE
4 - INTERCOOLER INLET DUCT
5 - WASTE GATE ACTUATOR
BR/BEENGINE 5.9L DIESEL 9 - 303
INTAKE MANIFOLD (Continued)
Page 1452 of 2889
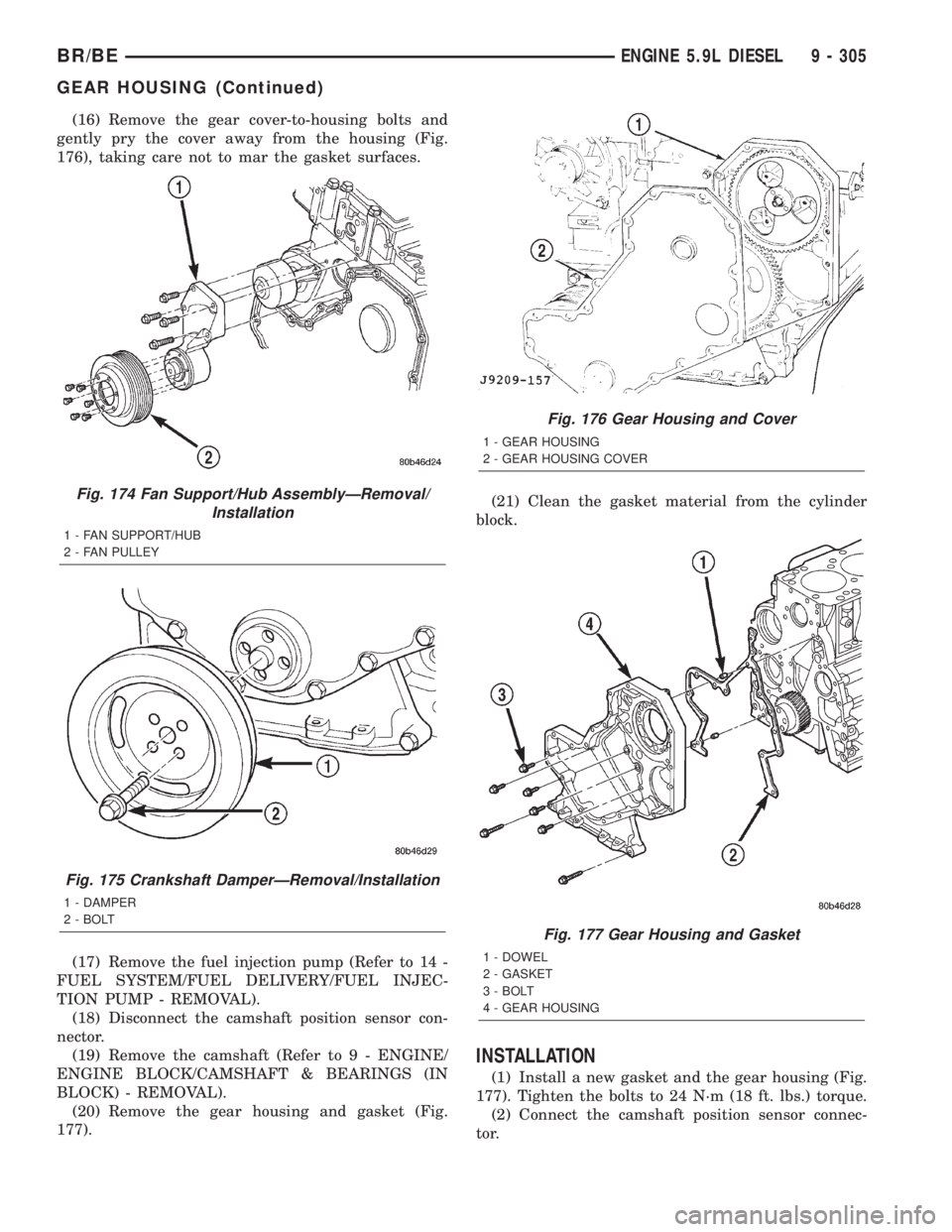
(16) Remove the gear cover-to-housing bolts and
gently pry the cover away from the housing (Fig.
176), taking care not to mar the gasket surfaces.
(17) Remove the fuel injection pump (Refer to 14 -
FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY/FUEL INJEC-
TION PUMP - REMOVAL).
(18) Disconnect the camshaft position sensor con-
nector.
(19) Remove the camshaft (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
ENGINE BLOCK/CAMSHAFT & BEARINGS (IN
BLOCK) - REMOVAL).
(20) Remove the gear housing and gasket (Fig.
177).(21) Clean the gasket material from the cylinder
block.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install a new gasket and the gear housing (Fig.
177). Tighten the bolts to 24 N´m (18 ft. lbs.) torque.
(2) Connect the camshaft position sensor connec-
tor.
Fig. 174 Fan Support/Hub AssemblyÐRemoval/
Installation
1 - FAN SUPPORT/HUB
2 - FAN PULLEY
Fig. 175 Crankshaft DamperÐRemoval/Installation
1 - DAMPER
2 - BOLT
Fig. 176 Gear Housing and Cover
1 - GEAR HOUSING
2 - GEAR HOUSING COVER
Fig. 177 Gear Housing and Gasket
1 - DOWEL
2 - GASKET
3 - BOLT
4 - GEAR HOUSING
BR/BEENGINE 5.9L DIESEL 9 - 305
GEAR HOUSING (Continued)
Page 1453 of 2889

(3) Install the injection pump (Refer to 14 - FUEL
SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY/FUEL INJECTION
PUMP - INSTALLATION).
(4) Install the camshaft (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/EN-
GINE BLOCK/CAMSHAFT & BEARINGS (IN
BLOCK) - INSTALLATION). Align the crankshaft,
camshaft, and injection pump gear marks as shown
in (Fig. 178).
(5) If a new housing is installed, the camshaft
position sensor must be transferred to the new hous-
ing.
(6) Obtain a seal pilot/installation tool from a
crankshaft front seal service kit and install the pilot
into the crankshaft front oil seal.
(7) Apply a bead of MopartSilicone Rubber Adhe-
sive Sealant or equivalent to the gear housing cover.
Be sure to surround all through holes.
(8) Using the seal pilot to align the cover (Fig.
179), install the cover to the housing and install the
bolts. Tighten the bolts to 24 N´m (18 ft. lbs.) torque.
(9) Remove the seal pilot.
(10) Raise the vehicle.
(11) Trim any excess gear housing gasket to make
it flush with the oil pan rail.
(12) Using a new gasket, install the oil pan and
suction tube (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRICATION/
OIL PAN - INSTALLATION).
(13) Install the crankshaft damper (Fig. 175)
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/VIBRATION
DAMPER - INSTALLATION).
(14) Lower vehicle.
(15) Install the fan support/hub assembly (Fig.
174) and tighten bolts to 24 N´m (18 ft. lbs.) torque.(16) Install the accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
INSTALLATION).
(17) Install the cooling fan and shroud together
(Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/RADIATOR FAN -
INSTALLATION).
(18) Install the windshield washer reservoir to the
fan shroud and connect the washer pump supply
hose and electrical connection.
(19) Install the coolant recovery bottle to the fan
shroud and connect the hose to the radiator filler
neck.
(20) Install the radiator upper hose and clamps.
(21) Add engine oil.
(22) Add coolant (Refer to 7 - COOLING - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE).
(23) Connect the battery cables.
(24) Start engine and inspect for leaks.
GEAR HOUSING COVER
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect both battery negative cables.
(2) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(3) Partially drain engine coolant into container
suitable for re-use (Refer to 7 - COOLING - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE).
(4) Lower vehicle.
(5) Remove radiator upper hose.
(6) Disconnect coolant recovery bottle hose from
radiator filler neck and lift bottle off of fan shroud.
(7) Disconnect windshield washer pump supply
hose and electrical connections and lift washer bottle
off of fan shroud.
(8) Remove viscous fan/drive assembly (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ENGINE/RADIATOR FAN - REMOVAL).
Fig. 178 Camshaft/Crankshaft Gear Alignment
Fig. 179 Installing Cover with Seal Pilot
1 - SEAL PILOT
9 - 306 ENGINE 5.9L DIESELBR/BE
GEAR HOUSING (Continued)
Page 1460 of 2889

SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. In.
Lbs. Lbs.
Adjusting StrapÐBolt 23 Ð 200
Air Heater Power SupplyÐ
Nuts14 Ð 124
Air Inlet HousingÐBolts 24 18 Ð
Cab Heater Supply/Return
LineÐNuts24 18 Ð
Exhaust ClampÐNuts 48 35 Ð
Exhaust Manifold to Cylinder
HeadÐBolts
(Diesel Engine) 43 32 Ð
Exhaust Manifold to Cylinder
HeadÐBolts
(3.9L/5.2L/5.9L) 31 23 Ð
Exhaust Manifold to Cylinder
HeadÐBolts
(8.0L) 22 Ð 195
Exhaust Pipe to ManifoldÐ
Bolts31 23 Ð
Generator MountingÐBolts 41 30 Ð
Charge Air Cooler
MountingÐBolts2Ð17
Charge Air Cooler DuctÐ
Nuts8Ð72
Heat ShieldÐNuts and Bolts 11 Ð 100
Turbocharger MountingÐ
Nuts32 24 Ð
Turbocharger Oil Drain
TubeÐBolts24 18 Ð
Turbocharger Oil Supply
LineÐFitting15 Ð 133
Turbocharger V-Band
ClampÐNut9Ð75
CATALYTIC CONVERTER -
3.9L/5.2L/5.9L
DESCRIPTION
The stainless steel catalytic converter is located
under the vehicle, integral to the exhaust pipe(s).
OPERATION
The catalytic converter captures and burns any
unburned fuel mixture exiting the combustion cham-
bers during the exhaust stroke of the engine. This
process aids in reducing emissions output.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support vehicle.
(2) Saturate the bolts and nuts with heat valve
lubricant. Allow 5 minutes for penetration.
(3) Remove clamps and nuts (Fig. 3) (Fig. 4).
(4) Remove the catalytic converter.
INSPECTION
Look at the stainless steel body of the converter,
inspect for bulging or other distortion that could be a
result of overheating. If the converter has a heat
shield attached make sure it is not bent or loose.
If you suspect internal damage to the catalyst, tap-
ping the bottom of the catalyst with a rubber mallet
may indicate a damaged core.
INSTALLATION
(1) Assemble converter and clamps loosely in
place.
Fig. 3 Catalytic Converter and Exhaust Pipe 3.9L,
5.2L and 5.9L Light Duty ( Federal )
1 - BOLT
2 - EXHAUST PIPE W/CONVERTER
3 - NUT
4 - RETAINER
BR/BEEXHAUST SYSTEM 11 - 5
Page 1461 of 2889

(2) Install the exhaust pipe onto exhaust mani-
folds, tighten 31 N´m (23 ft. lbs.).
(3) Tighten all clamp nuts to 48 N´m (35 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(4) Lower the vehicle.
(5) Start the engine and inspect for exhaust leaks
and exhaust system contact with the body panels. A
minimum of 25.4 mm (1.0 in.) is required between
exhaust system components and body/frame parts.
Adjust the alignment, if needed.
CATALYTIC CONVERTER - 5.9L
HEAVY DUTY/8.0L
DESCRIPTION
The stainless steel catalytic converter is located
under the vehicle, attached to the exhaust pipe(s).
OPERATION
The catalytic converter captures and burns any
unburned fuel mixture exiting the combustion cham-
bers during the exhaust stroke of the engine. This
process aids in reducing emissions output.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support vehicle.
(2) Saturate the bolts and nuts with heat valve
lubricant. Allow 5 minutes for penetration.
(3) Remove clamps and nuts (Fig. 5) (Fig. 6).
(4) Remove the catalytic converter.
Fig. 4 Catalytic Converter and Exhaust Pipe 3.9L,
5.2L and 5.9L Light Duty ( California )
1 - BOLT
2 - RETAINER
3 - EXHAUST MANIFOLD
4 - NUT
5 - MINI CATALYTIC CONVERTER
6 - CATALYTIC CONVERTER WITH PIPES
Fig. 5 Catalytic Converter 5.9L Heavy Duty
1 - DOWN PIPE RIGHT
2 - CLAMP
3 - CLAMP
4 - HANGER ASSY. DUAL CLAMP
5 - MUFFLER
6 - EXTENSION PIPE
7 - CATALYTIC CONVERTER
8 - DOWN PIPE LEFT
Fig. 6 Catalytic Converter 8.0L
1 - CLAMPS
2 - CATALYTIC CONVERTERS
3 - MUFFLER
4 - HANGER ASSY. DUAL CLAMP
5 - EXTENSION PIPES
6 - DOWN PIPE
11 - 6 EXHAUST SYSTEMBR/BE
CATALYTIC CONVERTER - 3.9L/5.2L/5.9L (Continued)
Page 1468 of 2889

(6) Start the engine and inspect for exhaust leaks
and exhaust system contact with the body panels.
Adjust the alignment, if needed.
RESONATOR
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the battery negative cables.
(2) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(3) Remove the exhaust clamps from the resonator
to extension pipes (Fig. 17).
(4) Separate the resonator from the front and rear
extension pipes (Fig. 17) and remove the resonator
from the vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Assemble the resonator to the front and rear
extension pipes (Fig. 17).
(2) Install new exhaust clamps, align the exhaust
system, and tighten the exhaust clamps to 48 N´m
(35 ft. lbs.) torque.
(3) Lower the vehicle.
(4) Connect the battery negative cables.
(5) Start the engine and inspect for exhaust leaks.
TURBOCHARGER
DESCRIPTION
The turbocharger is an exhaust-driven super-
charger which increases the pressure and density of
the air entering the engine. With the increase of air
entering the engine, more fuel can be injected into
the cylinders, which creates more power during com-
bustion.
The turbocharger assembly consists of four (4)
major component systems (Fig. 18) (Fig. 19):
²Turbine section
²Compressor section
²Bearing housing
²Wastegate
OPERATION
Exhaust gas pressure and energy drive the tur-
bine, which in turn drives a centrifugal compressor
that compresses the inlet air, and forces the air into
the engine through the charge air cooler and plumb-
ing. Since heat is a by-product of this compression,
the air must pass through a charge air cooler to cool
the incoming air and maintain power and efficiency.
Increasing air flow to the engine provides:
²Improved engine performance
²Lower exhaust smoke density
²Improved operating economy
²Altitude compensation
²Noise reduction.
Fig. 16 Tailpipe Removal/Installation
1 - HANGER BRACKETS
2 - ISOLATOR
3 - TAILPIPE
4 - MUFFLER
Fig. 17 Resonator Removal/Installation
1 - EXTENSION PIPE
2 - RESONATOR
3 - EXTENSION PIPE
4 - CLAMP
BR/BEEXHAUST SYSTEM 11 - 13
TAILPIPE - 5.9L DIESEL (Continued)
Page 1481 of 2889
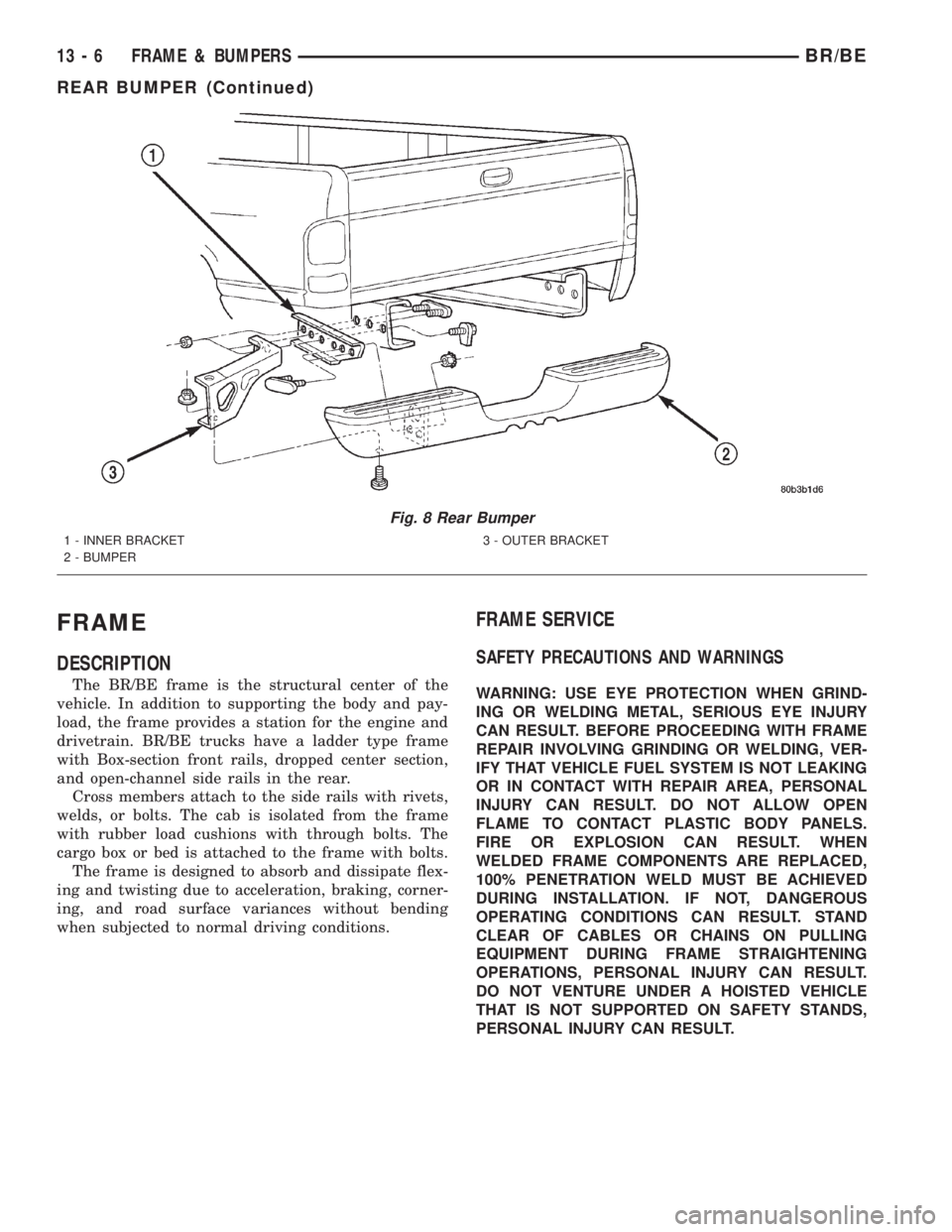
FRAME
DESCRIPTION
The BR/BE frame is the structural center of the
vehicle. In addition to supporting the body and pay-
load, the frame provides a station for the engine and
drivetrain. BR/BE trucks have a ladder type frame
with Box-section front rails, dropped center section,
and open-channel side rails in the rear.
Cross members attach to the side rails with rivets,
welds, or bolts. The cab is isolated from the frame
with rubber load cushions with through bolts. The
cargo box or bed is attached to the frame with bolts.
The frame is designed to absorb and dissipate flex-
ing and twisting due to acceleration, braking, corner-
ing, and road surface variances without bending
when subjected to normal driving conditions.
FRAME SERVICE
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS AND WARNINGS
WARNING: USE EYE PROTECTION WHEN GRIND-
ING OR WELDING METAL, SERIOUS EYE INJURY
CAN RESULT. BEFORE PROCEEDING WITH FRAME
REPAIR INVOLVING GRINDING OR WELDING, VER-
IFY THAT VEHICLE FUEL SYSTEM IS NOT LEAKING
OR IN CONTACT WITH REPAIR AREA, PERSONAL
INJURY CAN RESULT. DO NOT ALLOW OPEN
FLAME TO CONTACT PLASTIC BODY PANELS.
FIRE OR EXPLOSION CAN RESULT. WHEN
WELDED FRAME COMPONENTS ARE REPLACED,
100% PENETRATION WELD MUST BE ACHIEVED
DURING INSTALLATION. IF NOT, DANGEROUS
OPERATING CONDITIONS CAN RESULT. STAND
CLEAR OF CABLES OR CHAINS ON PULLING
EQUIPMENT DURING FRAME STRAIGHTENING
OPERATIONS, PERSONAL INJURY CAN RESULT.
DO NOT VENTURE UNDER A HOISTED VEHICLE
THAT IS NOT SUPPORTED ON SAFETY STANDS,
PERSONAL INJURY CAN RESULT.
Fig. 8 Rear Bumper
1 - INNER BRACKET
2 - BUMPER3 - OUTER BRACKET
13 - 6 FRAME & BUMPERSBR/BE
REAR BUMPER (Continued)
Page 1488 of 2889

FUEL SYSTEM
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
FUEL DELIVERY - GASOLINE................1
FUEL INJECTION - GASOLINE..............28FUEL DELIVERY - DIESEL.................54
FUEL INJECTION - DIESEL.................87
FUEL DELIVERY - GASOLINE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
FUEL DELIVERY - GASOLINE
DESCRIPTION............................2
OPERATION.............................2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING..................2
FUEL PRESSURE LEAK DOWN TEST........2
STANDARD PROCEDURE...................3
FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE RELEASE
PROCEDURE...........................3
SPECIFICATIONS.........................4
SPECIAL TOOLS..........................4
FUEL FILTER/PRESSURE REGULATOR
DESCRIPTION............................5
OPERATION.............................5
REMOVAL...............................5
INSTALLATION............................6
FUEL LEVEL SENDING UNIT / SENSOR
DESCRIPTION............................7
OPERATION.............................7
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING..................8
FUEL GAUGE SENDING UNIT..............8
REMOVAL...............................8
INSTALLATION............................9
FUEL LINES
DESCRIPTION............................9
FUEL PUMP
DESCRIPTION............................9
OPERATION.............................9
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING..................9
FUEL PUMP CAPACITY TEST..............9FUEL PUMP PRESSURE TEST............10
FUEL PUMP AMPERAGE TEST............10
FUEL PUMP MODULE
DESCRIPTION...........................12
OPERATION.............................13
REMOVAL..............................13
INSTALLATION...........................13
FUEL RAIL
DESCRIPTION...........................15
OPERATION.............................15
REMOVAL..............................16
INSTALLATION...........................18
FUEL TANK
DESCRIPTION...........................19
OPERATION.............................19
REMOVAL..............................19
INSTALLATION...........................20
INLET FILTER
REMOVAL..............................22
INSTALLATION...........................22
QUICK CONNECT FITTING
DESCRIPTION...........................22
STANDARD PROCEDURE..................22
QUICK-CONNECT FITTINGS..............22
ROLLOVER VALVE
DESCRIPTION...........................25
REMOVAL..............................26
INSTALLATION...........................27
BR/BEFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 1
Page 1489 of 2889

FUEL DELIVERY - GASOLINE
DESCRIPTION - FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM
The fuel delivery system consists of:
²the fuel pump module containing the electric
fuel pump, fuel filter/fuel pressure regulator, rollover
valve (certain modules), fuel gauge sending unit (fuel
level sensor) and a separate fuel filter located at bot-
tom of pump module
²fuel tubes/lines/hoses
²quick-connect fittings
²fuel injector rail
²fuel injectors
²fuel tank
²fuel tank filler/vent tube assembly
²fuel tank filler tube cap
²accelerator pedal
²throttle cable
OPERATION - FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM
Fuel is returned through the fuel pump module
and back into the fuel tank through the fuel filter/
fuel pressure regulator. A separate fuel return line
from the engine to the tank is not used with any gas-
oline powered engine.
The fuel tank assembly consists of: the fuel tank,
fuel pump module assembly, fuel pump module lock-
nut/gasket and rollover valve(s) (refer to 25, Emis-
sion Control System for rollover valve information).
A fuel filler/vent tube assembly using a pressure/
vacuum, 1/4 turn fuel filler cap is used. The fuel
filler tube contains a flap door located below the fuel
fill cap.
Also to be considered part of the fuel system is the
evaporation control system. This is designed to
reduce the emission of fuel vapors into the atmo-
sphere. The description and function of the Evapora-
tive Control System is found in 25, Emission Control
Systems.
Both fuel filters (at bottom of fuel pump module
and within fuel pressure regulator) are designed for
extended service. They do not require normal sched-
uled maintenance. Filters should only be replaced if
a diagnostic procedure indicates to do so.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL PRESSURE
LEAK DOWN TEST
Use this test in conjunction with the Fuel Pump
Pressure Test and Fuel Pump Capacity Test.
Check Valve Operation:The electric fuel pump
outlet contains a one-way check valve to prevent fuel
flow back into the tank and to maintain fuel supply
line pressure (engine warm) when pump is not oper-
ational. It is also used to keep the fuel supply line
full of gasoline when pump is not operational. Afterthe vehicle has cooled down, fuel pressure may drop
to 0 psi (cold fluid contracts), but liquid gasoline will
remain in fuel supply line between the check valve
and fuel injectors.Fuel pressure that has
dropped to 0 psi on a cooled down vehicle
(engine off) is a normal condition.When the elec-
tric fuel pump is activated, fuel pressure should
immediately(1±2 seconds) rise to specification.
Abnormally long periods of cranking to restart a
hotengine that has been shut down for a short
period of time may be caused by:
²Fuel pressure bleeding past a fuel injector(s).
²Fuel pressure bleeding past the check valve in
the fuel pump module.
(1) Disconnect the fuel inlet line at fuel rail. Refer
to Fuel Tubes/Lines/Hoses and Clamps for proce-
dures. On some engines, air cleaner housing removal
may be necessary before fuel line disconnection.
(2) Obtain correct Fuel Line Pressure Test Adapter
Tool Hose. Tool number 6539 is used for 5/16º fuel
lines and tool number 6631 is used for 3/8º fuel lines.
(3) Connect correct Fuel Line Pressure Test
Adapter Tool Hose between disconnected fuel line
and fuel rail (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1 Connecting Adapter ToolÐTypical
1 - VEHICLE FUEL LINE
2 - TEST PORT ªTº
3 - SPECIAL TOOL 6923, 6631, 6541 OR 6539
4 - FUEL PRESSURE TEST GAUGE
5 - FUEL LINE CONNECTION AT RAIL
6 - FUEL RAIL
14 - 2 FUEL DELIVERY - GASOLINEBR/BE