ECU DODGE RAM 2001 Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2001, Model line: RAM, Model: DODGE RAM 2001Pages: 2889, PDF Size: 68.07 MB
Page 125 of 2889
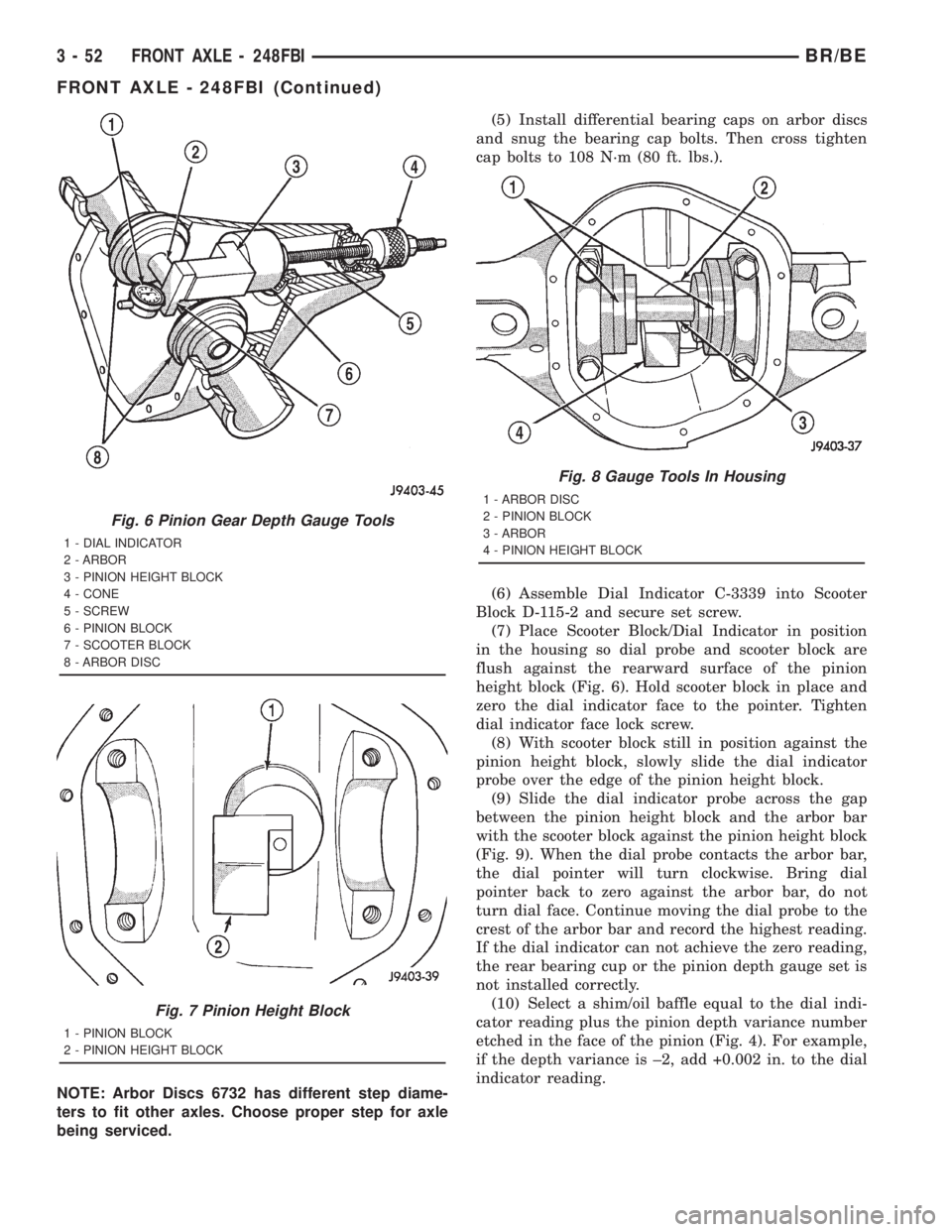
NOTE: Arbor Discs 6732 has different step diame-
ters to fit other axles. Choose proper step for axle
being serviced.(5) Install differential bearing caps on arbor discs
and snug the bearing cap bolts. Then cross tighten
cap bolts to 108 N´m (80 ft. lbs.).
(6) Assemble Dial Indicator C-3339 into Scooter
Block D-115-2 and secure set screw.
(7) Place Scooter Block/Dial Indicator in position
in the housing so dial probe and scooter block are
flush against the rearward surface of the pinion
height block (Fig. 6). Hold scooter block in place and
zero the dial indicator face to the pointer. Tighten
dial indicator face lock screw.
(8) With scooter block still in position against the
pinion height block, slowly slide the dial indicator
probe over the edge of the pinion height block.
(9) Slide the dial indicator probe across the gap
between the pinion height block and the arbor bar
with the scooter block against the pinion height block
(Fig. 9). When the dial probe contacts the arbor bar,
the dial pointer will turn clockwise. Bring dial
pointer back to zero against the arbor bar, do not
turn dial face. Continue moving the dial probe to the
crest of the arbor bar and record the highest reading.
If the dial indicator can not achieve the zero reading,
the rear bearing cup or the pinion depth gauge set is
not installed correctly.
(10) Select a shim/oil baffle equal to the dial indi-
cator reading plus the pinion depth variance number
etched in the face of the pinion (Fig. 4). For example,
if the depth variance is ±2, add +0.002 in. to the dial
indicator reading.
Fig. 6 Pinion Gear Depth Gauge Tools
1 - DIAL INDICATOR
2 - ARBOR
3 - PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
4 - CONE
5 - SCREW
6 - PINION BLOCK
7 - SCOOTER BLOCK
8 - ARBOR DISC
Fig. 7 Pinion Height Block
1 - PINION BLOCK
2 - PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
Fig. 8 Gauge Tools In Housing
1 - ARBOR DISC
2 - PINION BLOCK
3 - ARBOR
4 - PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
3 - 52 FRONT AXLE - 248FBIBR/BE
FRONT AXLE - 248FBI (Continued)
Page 156 of 2889

Condition Possible Causes Correction
Axle Overheating 1. Lubricant level low. 1. Fill differential to correct level.
2. Improper grade of lubricant. 2. Fill differential with the correct fluid
type and quantity.
3. Bearing pre-loads too high. 3. Re-adjust bearing pre-loads.
4. Insufficient ring gear backlash. 4. Re-adjust ring gear backlash.
Gear Teeth Broke 1. Overloading. 1. Replace gears. Examine other gears
and bearings for possible damage.
2. Erratic clutch operation. 2. Replace gears and examine the
remaining parts for damage. Avoid
erratic clutch operation.
3. Ice-spotted pavement. 3. Replace gears and examine
remaining parts for damage.
4. Improper adjustments. 4. Replace gears and examine
remaining parts for damage. Ensure ring
gear backlash is correct.
Axle Noise 1. Insufficient lubricant. 1. Fill differential with the correct fluid
type and quantity.
2. Improper ring gear and pinion
adjustment.2. Check ring gear and pinion contact
pattern. Adjust backlash or pinion depth.
3. Unmatched ring gear and pinion. 3. Replace gears with a matched ring
gear and pinion.
4. Worn teeth on ring gear and/or
pinion.4. Replace ring gear and pinion.
5. Loose pinion bearings. 5. Adjust pinion bearing pre-load.
6. Loose differential bearings. 6. Adjust differential bearing pre-load.
7. Mis-aligned or sprung ring gear. 7. Measure ring gear run-out. Replace
components as necessary.
8. Loose differential bearing cap bolts. 8. Inspect differential components and
replace as necessary. Ensure that the
bearing caps are torqued tot he proper
specification.
9. Housing not machined properly. 9. Replace housing.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Position a suitable lifting device under the
axle.
(3) Secure axle to device.
(4) Remove the wheels and tires.
(5) Secure brake drums to the axle shaft.
(6) Remove the RWAL sensor from the differential
housing, if necessary. Refer to 5 Brakes for proce-
dures.
(7) Disconnect the brake hose at the axle junction
block. Do not disconnect the brake hydraulic lines at
the wheel cylinders. Refer to 5 Brakes for procedures.(8) Disconnect the parking brake cables and cable
brackets.
(9) Disconnect the vent hose from the axle shaft
tube.
(10) Mark the propeller shaft and companion
flange for installation alignment reference.
(11) Remove propeller shaft.
(12) Disconnect shock absorbers from axle.
(13) Remove the spring clamps and spring brack-
ets. Refer to 2 Suspension for procedures.
(14) Separate the axle from the vehicle.
BR/BEREAR AXLE - 9 1/4 3 - 83
REAR AXLE - 9 1/4 (Continued)
Page 159 of 2889

(5) Assemble Dial Indicator C-3339 into Scooter
Block D-115-2 and secure set screw.
(6) Place Scooter Block/Dial Indicator in position
in axle housing so dial probe and scooter block are
flush against the rearward surface of the pinion
height block (Fig. 8). Hold scooter block in place and
zero the dial indicator. Tighten dial indicator face
lock screw.
(7) Slowly slide the dial indicator probe over the
edge of the pinion height block.
(8) Slide the dial indicator probe across the gap
between the pinion height block and the arbor bar
with the scooter block against the pinion height block
(Fig. 11). When the dial probe contacts the arbor bar,
the dial pointer will turn clockwise. Continue moving
the dial probe to the crest of the arbor bar and record
the highest reading. If the dial indicator can not
achieve the zero reading, the rear bearing cup or the
pinion depth gauge set is not installed correctly.
(9) Select a shim equal to the dial indicator read-
ing plus the drive pinion gear depth variance number
marked on the shaft of the pinion. For example, if
the depth variance is ±2, add +0.002 in. to the dial
indicator reading.
DIFFERENTIAL BEARING PRELOAD AND GEAR
BACKLASH
The following must be considered when adjusting
bearing preload and gear backlash:
²The maximum ring gear backlash variation is
0.003 inch (0.076 mm).
²Mark the gears so the same teeth are meshed
during all backlash measurements.²Maintain the torque while adjusting the bearing
preload and ring gear backlash.
²Excessive adjuster torque will introduce a high
bearing load and cause premature bearing failure.
Insufficient adjuster torque can result in excessive
differential case free-play and ring gear noise.
²Insufficient adjuster torque will not support the
ring gear correctly and can cause excessive differen-
tial case free-play and ring gear noise.
NOTE: The differential bearing cups will not always
immediately follow the threaded adjusters as they
are moved during adjustment. To ensure accurate
bearing cup responses to the adjustments:
²Maintain the gear teeth engaged (meshed) as
marked.
²The bearings must be seated by rapidly rotating
the drive pinion gear a half turn back and forth.
²Do this five to ten times each time the threaded
adjusters are adjusted.
(1) Use Wrench C-4164 to adjust each threaded
adjuster inward until the differential bearing free-
play is eliminated (Fig. 12). Allow some ring gear
backlash (approximately 0.25 mm / 0.01 inch)
between the ring and pinion gear. Seat the bearing
cups with the procedure described above.
(2) Install dial indicator and position the plunger
against the drive side of a ring gear tooth (Fig. 13).
Measure the backlash at 4 positions (90 degrees
apart) around the ring gear. Locate and mark the
area of minimum backlash.
(3) Rotate the ring gear to the position of the least
backlash. Mark the gear so that all future backlash
Fig. 10 Pinion Depth Tools
1 - ARBOR DISC
2 - PINION BLOCK
3 - ARBOR
4 - PINION HEIGHT BLOCKFig. 11 Pinion Gear Depth Measurement
1 - ARBOR
2 - SCOOTER BLOCK
3 - DIAL INDICATOR
3 - 86 REAR AXLE-91/4BR/BE
REAR AXLE - 9 1/4 (Continued)
Page 168 of 2889

INSTALLATION
(1) Wipe the axle tube bore clean. Remove any old
sealer or burrs from the tube.
(2) Install the axle shaft bearing with Installer
C-4198 and Handle C-4171 . Ensure that the bearing
part number is against the installer. Verify that the
bearing in installed straight and the tool fully con-
tacts the axle tube when seating the bearing.
(3) Install anewaxle seal with Installer C-4076-B
and Handle C-4735-1. When the tool contacts the
axle tube, the seal is installed to the correct depth.
(4) Coat the lip of the seal with axle lubricant for
protection prior to installing the axle shaft.
(5) Install the axle shaft.
PINION SEAL
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Mark the universal joint, companion flange and
pinion shaft for installation reference.
(3) Remove the propeller shaft from the companion
flange. Secure the propeller shaft in an upright posi-
tion to prevent damage to the rear universal joint.
(4) Remove the wheel and tire assemblies.
(5) Remove the brake drums to prevent any drag.
The drag may cause a false bearing preload torque
measurement.
(6) Rotate the companion flange three or four
times.
(7) Measure the amount of torque necessary to
rotate the pinion with an inch pound torque wrench.
Record the torque reading for installation reference.
(8) Install socket head bolts into two of the
threaded holes in the companion flange, 180É apart.
(9) Position Holder 6719A against the companion
flange and install a hex head bolt and washer into
one of the remaining threaded holes. Tighten the
bolts so the holder is held to the flange.
(10) Hold the flange with holder and remove the
pinion nut and washer.
(11) Remove the companion flange with Remover
C-452 (Fig. 22).
(12) Remove pinion seal with a pry tool or slide-
hammer mounted screw.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: The outer perimeter of the seal is pre-coated
with a special sealant. An additional application of
sealant is not required.
(1) Apply a light coating of gear lubricant on the
lip of pinion seal.
(2) Installnewpinion seal with Installer C-3860-A
and Handle C-4171.NOTE: The seal is correctly installed when the seal
flange contacts the face of the differential housing.
(3) Position the companion flange on the end of the
shaft with the reference marks aligned.
(4) Install socket head bolts into two of the
threaded holes in the companion flange, 180É apart.
(5) Position Holder 6719A against the companion
flange and install a hex head bolt and washer into
one of the remaining threaded holes. Tighten the
bolts so the holder is held to the flange.
(6) Seat companion flange on pinion shaft with
Installer C-3718 and Holder 6719.
(7) Remove the installer and install the pinion
washer and anewpinion nut. The convex side of the
washer must face outward.
CAUTION: Do not exceed the minimum tightening
torque when installing the companion flange retain-
ing nut at this point. Damage to collapsible spacer
or bearings may result.
(8) Hold companion flange with Holder 6719 and
tighten the pinion nut to 285 N´m (210 ft. lbs.) (Fig.
23). Rotate pinion several revolutions to ensure the
bearing rollers are seated.
(9) Rotate the pinion using an (in. lbs.) torque
wrench. Rotating torque should be equal to the read-
ing recorded during removal, plus an additional 0.56
N´m (5 in. lbs.) (Fig. 24).
Fig. 22 Companion Flange Remover
1 - COMPANION FLANGE
2 - PULLER TOOL
BR/BEREAR AXLE - 9 1/4 3 - 95
AXLE BEARINGS (Continued)
Page 174 of 2889

ASSEMBLY
Clean all components in cleaning solvent. Dry com-
ponents with compressed air. Inspect clutch pack
plates for wear, scoring or damage. Replace both
clutch packs if any one component in either pack is
damaged. Inspect side gears and pinions. Replace
any gear that is worn, cracked, chipped or damaged.
Inspect differential case and pinion shaft. Replace if
worn or damaged.Lubricate each component with gear lubricant
before assembly.
(1) Assemble the clutch discs into packs and
secure disc packs with retaining clips (Fig. 40).
NOTE: New Plates and discs with fiber coating (no
grooves or lines) must be presoaked in Friction
Modifier before assembly. Soak plates and discs for
a minimum of 20 minutes.
(2) Position assembled clutch disc packs on the
side gear hubs.
(3) Install clutch pack and side gear in the ring
gear side of the differential case (Fig. 41).Be sure
clutch pack retaining clips remain in position
and are seated in the case pockets.
(4) Position the differential case on the Holding
Fixture 6965.
(5) Install lubricated Step Plate C-6960-3 in lower
side gear (Fig. 42).
(6) Install the upper side gear and clutch disc pack
(Fig. 42).
(7) Hold assembly in position. Insert Threaded
Adapter C-6960-1 into top side gear.
(8) Install Forcing Screw C-6960-4 and tighten
screw to slightly compress clutch disc.
(9) Place differential pinion gears in position in
side gears and verify that the pinion shaft hole is
aligned.
Fig. 37 Pinion Gear Thrust Washer
1 - THRUST WASHER
2 - FEELER GAUGE
Fig. 38 Pinion Gear
1 - PINION GEARS
2 - TOOL
Fig. 39 Side Gear & Clutch Pack
1 - DIFFERENTIAL CASE
2 - RETAINER
3 - SIDE GEAR AND CLUTCH DISC PACK
BR/BEREAR AXLE - 9 1/4 3 - 101
DIFFERENTIAL - TRAC-LOK (Continued)
Page 186 of 2889

Condition Possible Causes Correction
Axle Overheating 1. Lubricant level low. 1. Fill differential to correct level.
2. Improper grade of lubricant. 2. Fill differential with the correct fluid
type and quantity.
3. Bearing pre-loads too high. 3. Re-adjust bearing pre-loads.
4. Insufficient ring gear backlash. 4. Re-adjust ring gear backlash.
Gear Teeth Broke 1. Overloading. 1. Replace gears. Examine other gears
and bearings for possible damage.
2. Erratic clutch operation. 2. Replace gears and examine the
remaining parts for damage. Avoid
erratic clutch operation.
3. Ice-spotted pavement. 3. Replace gears and examine
remaining parts for damage.
4. Improper adjustments. 4. Replace gears and examine
remaining parts for damage. Ensure ring
gear backlash is correct.
Axle Noise 1. Insufficient lubricant. 1. Fill differential with the correct fluid
type and quantity.
2. Improper ring gear and pinion
adjustment.2. Check ring gear and pinion contact
pattern. Adjust backlash or pinion depth.
3. Unmatched ring gear and pinion. 3. Replace gears with a matched ring
gear and pinion.
4. Worn teeth on ring gear and/or
pinion.4. Replace ring gear and pinion.
5. Loose pinion bearings. 5. Adjust pinion bearing pre-load.
6. Loose differential bearings. 6. Adjust differential bearing pre-load.
7. Mis-aligned or sprung ring gear. 7. Measure ring gear run-out. Replace
components as necessary.
8. Loose differential bearing cap bolts. 8. Inspect differential components and
replace as necessary. Ensure that the
bearing caps are torqued tot he proper
specification.
9. Housing not machined properly. 9. Replace housing.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Position a suitable lifting device under the
axle.
(3) Secure axle to device.
(4) Remove the wheels and tires.
(5) Secure brake drums to the axle shaft.
(6) Remove RWAL sensor from the differential
housing, if necessary. Refer to 5 Brakes for proce-
dures.
(7) Disconnect the brake hose at the axle junction
block. Do not disconnect the brake hydraulic lines at
the wheel cylinders. Refer to 5 Brakes for procedures.(8) Disconnect the parking brake cables and cable
brackets.
(9) Disconnect the vent hose from the axle shaft
tube.
(10) Mark propeller shaft and yoke for installation
alignment reference.
(11) Remove propeller shaft.
(12) Disconnect shock absorbers from axle.
(13) Remove spring clamps and spring brackets.
Refer to 2 Suspension for procedures.
(14) Separate axle from the vehicle.
BR/BEREAR AXLE - 248RBI 3 - 113
REAR AXLE - 248RBI (Continued)
Page 189 of 2889
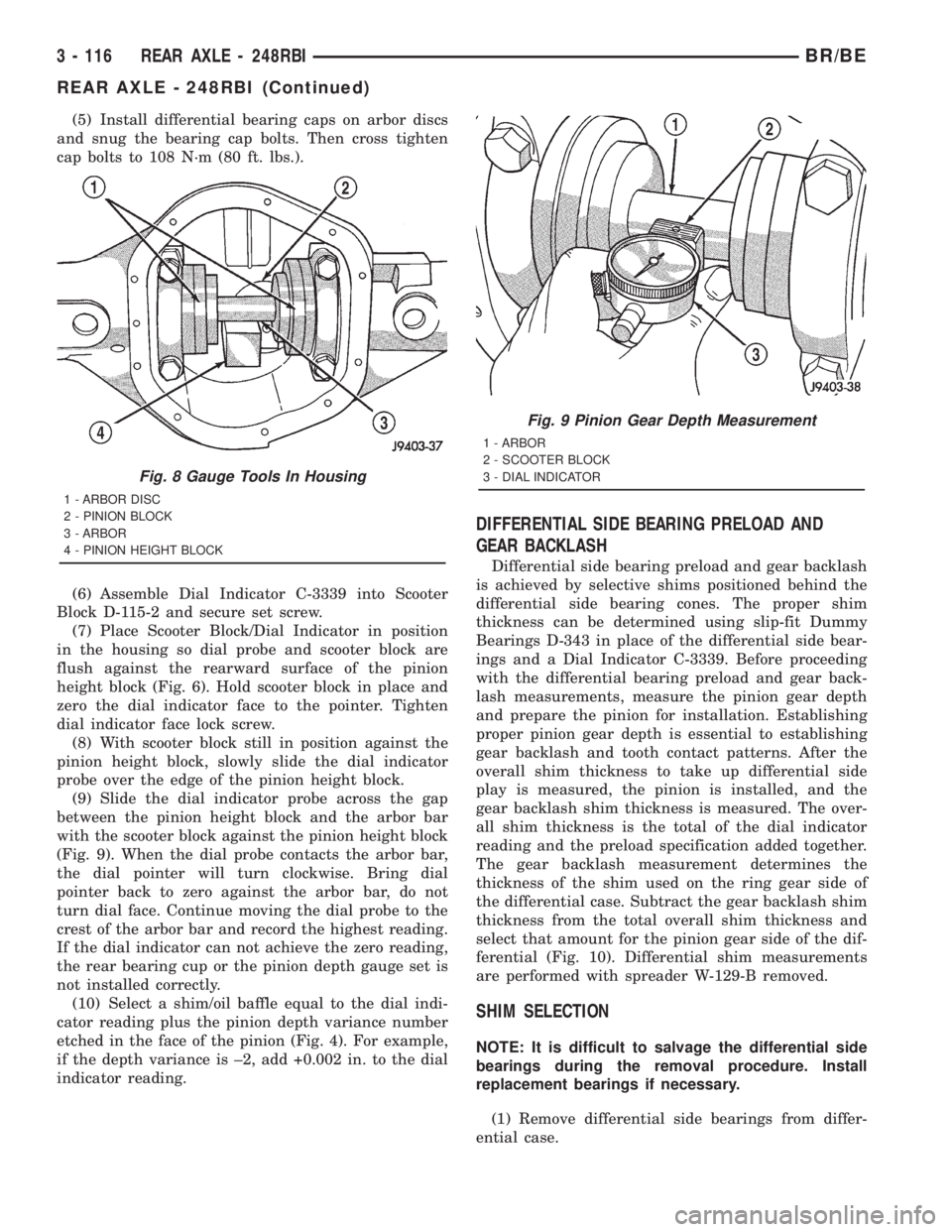
(5) Install differential bearing caps on arbor discs
and snug the bearing cap bolts. Then cross tighten
cap bolts to 108 N´m (80 ft. lbs.).
(6) Assemble Dial Indicator C-3339 into Scooter
Block D-115-2 and secure set screw.
(7) Place Scooter Block/Dial Indicator in position
in the housing so dial probe and scooter block are
flush against the rearward surface of the pinion
height block (Fig. 6). Hold scooter block in place and
zero the dial indicator face to the pointer. Tighten
dial indicator face lock screw.
(8) With scooter block still in position against the
pinion height block, slowly slide the dial indicator
probe over the edge of the pinion height block.
(9) Slide the dial indicator probe across the gap
between the pinion height block and the arbor bar
with the scooter block against the pinion height block
(Fig. 9). When the dial probe contacts the arbor bar,
the dial pointer will turn clockwise. Bring dial
pointer back to zero against the arbor bar, do not
turn dial face. Continue moving the dial probe to the
crest of the arbor bar and record the highest reading.
If the dial indicator can not achieve the zero reading,
the rear bearing cup or the pinion depth gauge set is
not installed correctly.
(10) Select a shim/oil baffle equal to the dial indi-
cator reading plus the pinion depth variance number
etched in the face of the pinion (Fig. 4). For example,
if the depth variance is ±2, add +0.002 in. to the dial
indicator reading.
DIFFERENTIAL SIDE BEARING PRELOAD AND
GEAR BACKLASH
Differential side bearing preload and gear backlash
is achieved by selective shims positioned behind the
differential side bearing cones. The proper shim
thickness can be determined using slip-fit Dummy
Bearings D-343 in place of the differential side bear-
ings and a Dial Indicator C-3339. Before proceeding
with the differential bearing preload and gear back-
lash measurements, measure the pinion gear depth
and prepare the pinion for installation. Establishing
proper pinion gear depth is essential to establishing
gear backlash and tooth contact patterns. After the
overall shim thickness to take up differential side
play is measured, the pinion is installed, and the
gear backlash shim thickness is measured. The over-
all shim thickness is the total of the dial indicator
reading and the preload specification added together.
The gear backlash measurement determines the
thickness of the shim used on the ring gear side of
the differential case. Subtract the gear backlash shim
thickness from the total overall shim thickness and
select that amount for the pinion gear side of the dif-
ferential (Fig. 10). Differential shim measurements
are performed with spreader W-129-B removed.
SHIM SELECTION
NOTE: It is difficult to salvage the differential side
bearings during the removal procedure. Install
replacement bearings if necessary.
(1) Remove differential side bearings from differ-
ential case.
Fig. 8 Gauge Tools In Housing
1 - ARBOR DISC
2 - PINION BLOCK
3 - ARBOR
4 - PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
Fig. 9 Pinion Gear Depth Measurement
1 - ARBOR
2 - SCOOTER BLOCK
3 - DIAL INDICATOR
3 - 116 REAR AXLE - 248RBIBR/BE
REAR AXLE - 248RBI (Continued)
Page 198 of 2889

AXLE SHAFTS
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the axle shaft flange bolts.
(2) Slide the axle shaft out from the axle tube.
INSTALLATION
(1) Clean the gasket contact surface area on the
flange with an appropriate solvent. Install a new
flange gasket and slide the axle shaft into the tube.
(2) Install the bolts and tighten to 129 N´m (95 ft.
lbs.).
AXLE BEARINGS
REMOVAL
(1) Remove wheel and tire assembly.
(2) Remove brake drum.
(3) Remove the axle shaft.
(4) Remove the lock wedge and adjustment nut.
Use Socket DD-1241±JD to remove the adjustment
nut.
(5) Remove the hub assembly. The outer axle bear-
ing will slide out as the hub is being removed.
(6) Remove inner grease seal and discard. Use
Installer 5064 and Handle C-4171 to drive grease
seal and inner axle bearing from the hub.
(7) Remove the bearing cups from the hub bore.
Use a brass drift, or an appropriate removal tool, to
tap out the cups.
INSTALLATION
(1) Thoroughly clean both axle bearings and inte-
rior of the hub with an appropriate cleaning solvent.
(2) Install bearing cups with Installer 8151 and
Handle C-4171.
(3)Pack inner and outer bearings with
Mopar wheel bearing grease or equivalent.
(4) Apply grease to inner and outer bearing cup
surfaces.
(5) Install inner axle bearing in the hub.
(6) Installnewgrease seal in hub with Installer
8149 and Handle C-4171.(7) Inspect bearing and seal contact surfaces on
the axle tube for burrs/roughness. Remove all the
rough contact surfaces from the axle tube.
(8) Carefully slide the hub onto the axle.
CAUTION: Do not let grease seal contact axle tube
threads during installtion.
(9) Install outer axle bearing.
(10) Install hub bearing adjustment nut with
Socket DD-1241±JD.
(11) Tighten adjustment nut to 163-190 N´m (120-
140 ft. lbs.) while rotating the wheel. Then loosen
adjustment nut 1/8 to 1/3 of-a-turn to provide 0.025-
0.250mm (0.001-0.009 in.) wheel bearing end play.
(12) Tap locking wedge into the spindle keyway
and adjustment nut.
NOTE: Located locking wedge in a new position in
the adjustment nut.
(13) Install axle shaft and brake drum.
(14) Install the wheel and tire assembly.
PINION SEAL
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Scribe a mark on the universal joint, pinion
yoke, and pinion shaft for reference.
(3) Disconnect the propeller shaft from the pinion
yoke. Secure the propeller shaft in an upright posi-
tion to prevent damage to the rear universal joint.
(4) Remove the wheel and tire assemblies.
(5) Remove the brake drums to prevent any drag.
The drag may cause a false bearing preload torque
measurement.
(6) Rotate the pinion yoke three or four times.
(7) Measure the amount of torque necessary to
rotate the pinion gear with a (in. lbs.) dial-type
torque wrench. Record the torque reading for instal-
lation reference.
(8) Hold the yoke with Wrench 6719. Remove the
pinion shaft nut and washer.
(9) Remove the yoke with Remover C-452 (Fig. 22).
(10) Remove the pinion shaft seal with suitable
pry tool or slide-hammer mounted screw.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: The outer perimeter of the seal is pre-coated
with a special sealant. An additional application of
sealant is not required.
(1) Apply a light coating of gear lubricant on the
lip of pinion seal.
Arbor Discs 6732
BR/BEREAR AXLE - 248RBI 3 - 125
REAR AXLE - 248RBI (Continued)
Page 205 of 2889
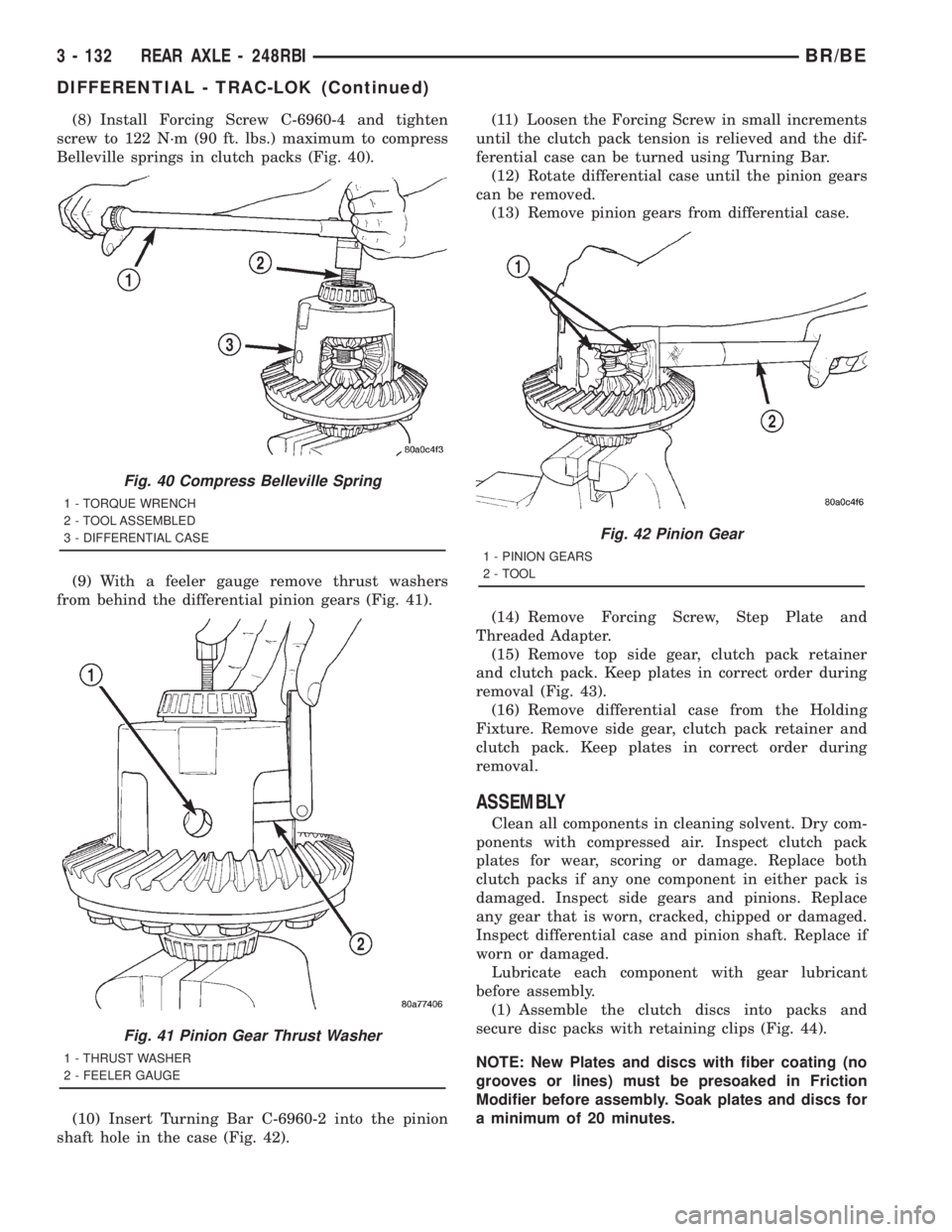
(8) Install Forcing Screw C-6960-4 and tighten
screw to 122 N´m (90 ft. lbs.) maximum to compress
Belleville springs in clutch packs (Fig. 40).
(9) With a feeler gauge remove thrust washers
from behind the differential pinion gears (Fig. 41).
(10) Insert Turning Bar C-6960-2 into the pinion
shaft hole in the case (Fig. 42).(11) Loosen the Forcing Screw in small increments
until the clutch pack tension is relieved and the dif-
ferential case can be turned using Turning Bar.
(12) Rotate differential case until the pinion gears
can be removed.
(13) Remove pinion gears from differential case.
(14) Remove Forcing Screw, Step Plate and
Threaded Adapter.
(15) Remove top side gear, clutch pack retainer
and clutch pack. Keep plates in correct order during
removal (Fig. 43).
(16) Remove differential case from the Holding
Fixture. Remove side gear, clutch pack retainer and
clutch pack. Keep plates in correct order during
removal.
ASSEMBLY
Clean all components in cleaning solvent. Dry com-
ponents with compressed air. Inspect clutch pack
plates for wear, scoring or damage. Replace both
clutch packs if any one component in either pack is
damaged. Inspect side gears and pinions. Replace
any gear that is worn, cracked, chipped or damaged.
Inspect differential case and pinion shaft. Replace if
worn or damaged.
Lubricate each component with gear lubricant
before assembly.
(1) Assemble the clutch discs into packs and
secure disc packs with retaining clips (Fig. 44).
NOTE: New Plates and discs with fiber coating (no
grooves or lines) must be presoaked in Friction
Modifier before assembly. Soak plates and discs for
a minimum of 20 minutes.
Fig. 40 Compress Belleville Spring
1 - TORQUE WRENCH
2 - TOOL ASSEMBLED
3 - DIFFERENTIAL CASE
Fig. 41 Pinion Gear Thrust Washer
1 - THRUST WASHER
2 - FEELER GAUGE
Fig. 42 Pinion Gear
1 - PINION GEARS
2 - TOOL
3 - 132 REAR AXLE - 248RBIBR/BE
DIFFERENTIAL - TRAC-LOK (Continued)
Page 217 of 2889

Condition Possible Causes Correction
Axle Overheating 1. Lubricant level low. 1. Fill differential to correct level.
2. Improper grade of lubricant. 2. Fill differential with the correct fluid
type and quantity.
3. Bearing pre-loads too high. 3. Re-adjust bearing pre-loads.
4. Insufficient ring gear backlash. 4. Re-adjust ring gear backlash.
Gear Teeth Broke 1. Overloading. 1. Replace gears. Examine other gears
and bearings for possible damage.
2. Erratic clutch operation. 2. Replace gears and examine the
remaining parts for damage. Avoid
erratic clutch operation.
3. Ice-spotted pavement. 3. Replace gears and examine
remaining parts for damage.
4. Improper adjustments. 4. Replace gears and examine
remaining parts for damage. Ensure ring
gear backlash is correct.
Axle Noise 1. Insufficient lubricant. 1. Fill differential with the correct fluid
type and quantity.
2. Improper ring gear and pinion
adjustment.2. Check ring gear and pinion contact
pattern. Adjust backlash or pinion depth.
3. Unmatched ring gear and pinion. 3. Replace gears with a matched ring
gear and pinion.
4. Worn teeth on ring gear and/or
pinion.4. Replace ring gear and pinion.
5. Loose pinion bearings. 5. Adjust pinion bearing pre-load.
6. Loose differential bearings. 6. Adjust differential bearing pre-load.
7. Mis-aligned or sprung ring gear. 7. Measure ring gear run-out. Replace
components as necessary.
8. Loose differential bearing cap bolts. 8. Inspect differential components and
replace as necessary. Ensure that the
bearing caps are torqued tot he proper
specification.
9. Housing not machined properly. 9. Replace housing.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Position a suitable lifting device under the
axle.
(3) Secure axle to device.
(4) Remove the wheels and tires.
(5) Secure brake drums to the axle shaft.
(6) Remove RWAL sensor from the differential
housing, if necessary. Refer to 5 Brakes for proce-
dures.
(7) Disconnect the brake hose at the axle junction
block. Do not disconnect the brake hydraulic lines at
the wheel cylinders. Refer to 5 Brakes for procedures.(8) Disconnect the parking brake cables and cable
brackets.
(9) Disconnect the vent hose from the axle shaft
tube.
(10) Mark propeller shaft and yoke for installation
alignment reference.
(11) Remove propeller shaft.
(12) Disconnect shock absorbers from axle.
(13) Remove spring clamps and spring brackets.
Refer to 2 Suspension for procedures.
(14) Separate axle from the vehicle.
3 - 144 REAR AXLE - 267RBIBR/BE
REAR AXLE - 267RBI (Continued)