sensor DODGE RAM 2001 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2001, Model line: RAM, Model: DODGE RAM 2001Pages: 2889, PDF Size: 68.07 MB
Page 2346 of 2889

temperature is at, or above, 10ÉC (50ÉF) during nor-
mal city or highway driving. A third curve is used
during wide-open throttle operation. The fourth curve
is used when driving with the transfer case in low
range.
OPERATION
Compensation is required for performance varia-
tions of two of the input devices. Though the slope of
the transfer functions is tightly controlled, offset may
vary due to various environmental factors or manu-
facturing tolerances.
The pressure transducer is affected by barometric
pressure as well as temperature. Calibration of the
zero pressure offset is required to compensate for
shifting output due to these factors.
Normal calibration will be performed when sump
temperature is above 50 degrees F, or in the absence
of sump temperature data, after the first 10 minutes
of vehicle operation. Calibration of the pressure
transducer offset occurs each time the output shaft
speed falls below 200 RPM. Calibration shall be
repeated each 3 seconds the output shaft speed is
below 200 RPM. A 0.5 second pulse of 95% duty cycle
is applied to the governor pressure solenoid valve
and the transducer output is read during this pulse.
Averaging of the transducer signal is necessary to
reject electrical noise.
Under cold conditions (below 50 degrees F sump),
the governor pressure solenoid valve response may
be too slow to guarantee 0 psi during the 0.5 second
calibration pulse. Calibration pulses are continued
during this period, however the transducer output
valves are discarded. Transducer offset must be read
at key-on, under conditions which promote a stable
reading. This value is retained and becomes the off-
set during the9cold9period of operation.
GOVERNOR PRESSURE SOLENOID VALVE
The inlet side of the solenoid valve is exposed to
normal transmission line pressure. The outlet side of
the valve leads to the valve body governor circuit.
The solenoid valve regulates line pressure to produce
governor pressure. The average current supplied to the
solenoid controls governor pressure. One amp current
produces zero kPa/psi governor pressure. Zero amps sets
the maximum governor pressure.
The powertrain control module (PCM) turns on the
trans control relay which supplies electrical power to
the solenoid valve. Operating voltage is 12 volts (DC).
The PCM controls the ground side of the solenoid using
the governor pressure solenoid control circuit.
GOVERNOR PRESSURE SENSOR
The sensor output signal provides the necessary
feedback to the PCM. This feedback is needed to ade-
quately control governor pressure.
GOVERNOR BODY AND TRANSFER PLATE
The transfer plate channels line pressure to the
solenoid valve through the governor body. It also
channels governor pressure from the solenoid valve
to the governor circuit. It is the solenoid valve that
develops the necessary governor pressure.
GOVERNOR PRESSURE CURVES
LOW TRANSMISSION FLUID TEMPERATURE
When the transmission fluid is cold the conventional
governor can delay shifts, resulting in higher than nor-
mal shift speeds and harsh shifts. The electronically
controlled low temperature governor pressure curve is
higher than normal to make the transmission shift at
normal speeds and sooner. The PCM uses a temperature
sensor in the transmission oil sump to determine when
low temperature governor pressure is needed.
NORMAL OPERATION
Normal operation is refined through the increased
computing power of the PCM and through access to
data on engine operating conditions provided by the
PCM that were not available with the previous stand-
alone electronic module. This facilitated the develop-
ment of a load adaptive shift strategy - the ability to
alter the shift schedule in response to vehicle load con-
dition. One manifestation of this capability is grade
9hunting9prevention - the ability of the transmission
logic to delay an upshift on a grade if the engine does
not have sufficient power to maintain speed in the
higher gear. The 3-2 downshift and the potential for
hunting between gears occurs with a heavily loaded
vehicle or on steep grades. When hunting occurs, it is
very objectionable because shifts are frequent and
accompanied by large changes in noise and acceleration.
Fig. 70 Governor Pressure Sensor
1 - GOVERNOR BODY
2 - GOVERNOR PRESSURE SENSOR/TRANSMISSION FLUID
TEMPERATURE THERMISTOR
BR/BEAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 47RE 21 - 711
ELECTRONIC GOVERNOR (Continued)
Page 2347 of 2889

WIDE OPEN THROTTLE OPERATION
In wide-open throttle (WOT) mode, adaptive memory
in the PCM assures that up-shifts occur at the prepro-
grammed optimum speed. WOT operation is determined
from the throttle position sensor, which is also a part of
the emission control system. The initial setting for the
WOT upshift is below the optimum engine speed. As
WOT shifts are repeated, the PCM learns the time
required to complete the shifts by comparing the engine
speed when the shifts occur to the optimum speed. After
each shift, the PCM adjusts the shift point until the
optimum speed is reached. The PCM also considers
vehicle loading, grade and engine performance changes
due to high altitude in determining when to make WOT
shifts. It does this by measuring vehicle and engine
acceleration and then factoring in the shift time.
TRANSFER CASE LOW RANGE OPERATION
On four-wheel drive vehicles operating in low
range, the engine can accelerate to its peak more
rapidly than in Normal range, resulting in delayed
shifts and undesirable engine9flare.9The low range
governor pressure curve is also higher than normal
to initiate upshifts sooner. The PCM compares elec-
tronic vehicle speed signal used by the speedometer
to the transmission output shaft speed signal to
determine when the transfer case is in low range.
REMOVAL
(1) Hoist and support vehicle on safety stands.
(2) Remove transmission fluid pan and filter.
(3) Disengage wire connectors from pressure sen-
sor and solenoid (Fig. 71).
(4) Remove screws holding pressure solenoid
retainer to governor body.(5) Separate solenoid retainer from governor (Fig.
72).
(6) Pull solenoid from governor body (Fig. 73).
(7) Pull pressure sensor from governor body.
(8) Remove bolts holding governor body to valve
body.
Fig. 71 Governor Solenoid And Pressure Sensor
1 - PRESSURE SENSOR
2 - PRESSURE SOLENOID
3 - GOVERNOR
Fig. 72 Pressure Solenoid Retainer
1 - PRESSURE SOLENOID RETAINER
2 - GOVERNOR
Fig. 73 Pressure Solenoid and O-ring
1 - PRESSURE SOLENOID
2 - O-RING
3 - GOVERNOR
21 - 712 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 47REBR/BE
ELECTRONIC GOVERNOR (Continued)
Page 2348 of 2889

(9) Separate governor body from valve body (Fig.
74).
(10) Remove governor body gasket.
INSTALLATION
Before installing the pressure sensor and solenoid
in the governor body, replace o-ring seals, clean the
gasket surfaces and replace gasket.
(1) Place gasket in position on back of governor
body (Fig. 75).
(2) Place governor body in position on valve body.
(3) Install bolts to hold governor body to valve
body.
(4) Lubricate o-ring on pressure sensor with trans-
mission fluid.
(5) Align pressure sensor to bore in governor body.(6) Push pressure sensor into governor body.
(7) Lubricate o-ring, on pressure solenoid, with
transmission fluid.
(8) Align pressure solenoid to bore in governor
body (Fig. 76).
(9) Push solenoid into governor body.
(10) Place solenoid retainer in position on governor
(Fig. 77).
(11) Install screws to hold pressure solenoid
retainer to governor body.
Fig. 74 Governor Body and Gasket
1 - GOVERNOR BODY
2 - GASKET
Fig. 75 Governor Body and Gasket
1 - GOVERNOR BODY
2 - GASKET
Fig. 76 Pressure Solenoid and O-ring
1 - PRESSURE SOLENOID
2 - O-RING
3 - GOVERNOR
Fig. 77 Pressure Solenoid Retainer
1 - PRESSURE SOLENOID RETAINER
2 - GOVERNOR
BR/BEAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 47RE 21 - 713
ELECTRONIC GOVERNOR (Continued)
Page 2349 of 2889
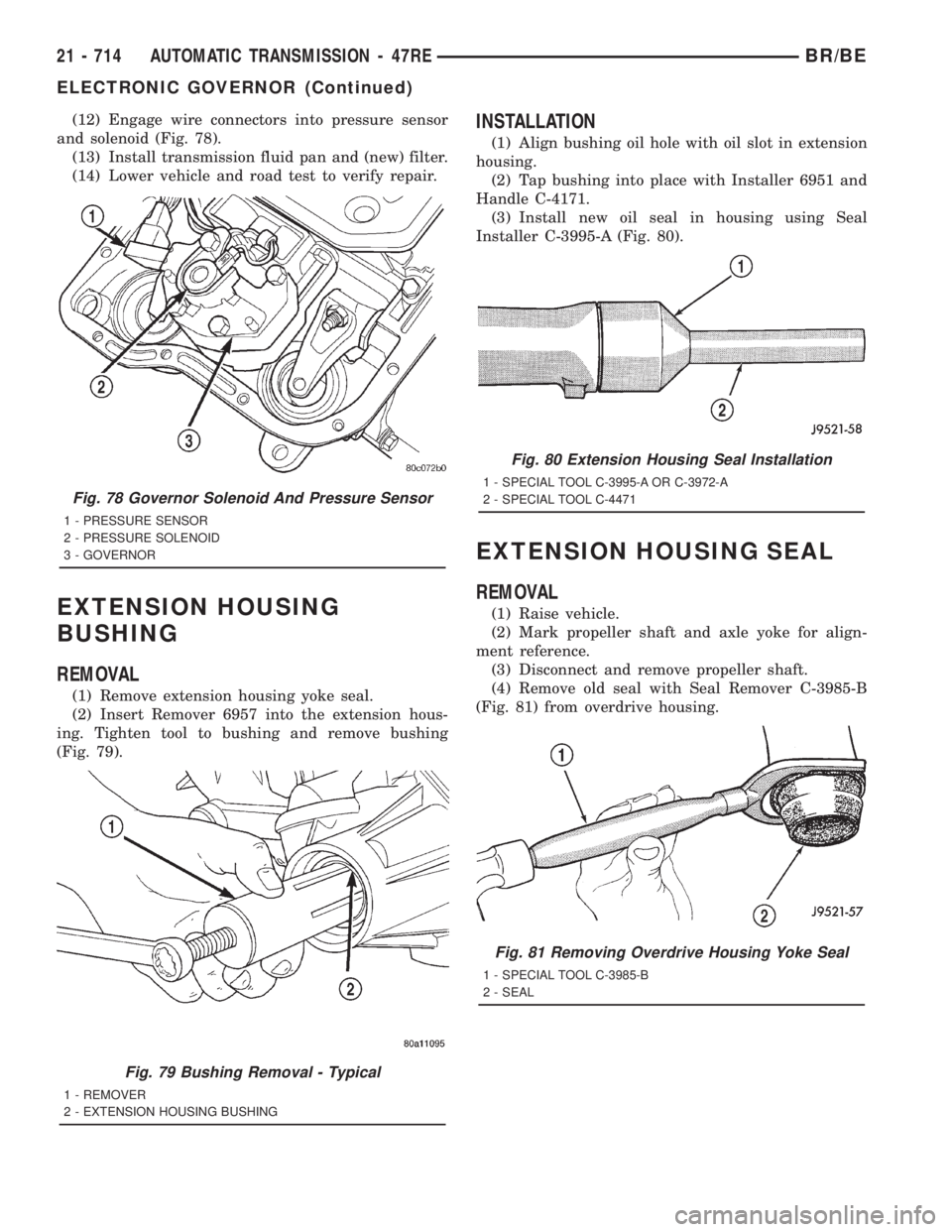
(12) Engage wire connectors into pressure sensor
and solenoid (Fig. 78).
(13) Install transmission fluid pan and (new) filter.
(14) Lower vehicle and road test to verify repair.
EXTENSION HOUSING
BUSHING
REMOVAL
(1) Remove extension housing yoke seal.
(2) Insert Remover 6957 into the extension hous-
ing. Tighten tool to bushing and remove bushing
(Fig. 79).
INSTALLATION
(1) Align bushing oil hole with oil slot in extension
housing.
(2) Tap bushing into place with Installer 6951 and
Handle C-4171.
(3) Install new oil seal in housing using Seal
Installer C-3995-A (Fig. 80).
EXTENSION HOUSING SEAL
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle.
(2) Mark propeller shaft and axle yoke for align-
ment reference.
(3) Disconnect and remove propeller shaft.
(4) Remove old seal with Seal Remover C-3985-B
(Fig. 81) from overdrive housing.
Fig. 78 Governor Solenoid And Pressure Sensor
1 - PRESSURE SENSOR
2 - PRESSURE SOLENOID
3 - GOVERNOR
Fig. 79 Bushing Removal - Typical
1 - REMOVER
2 - EXTENSION HOUSING BUSHING
Fig. 80 Extension Housing Seal Installation
1 - SPECIAL TOOL C-3995-A OR C-3972-A
2 - SPECIAL TOOL C-4471
Fig. 81 Removing Overdrive Housing Yoke Seal
1 - SPECIAL TOOL C-3985-B
2 - SEAL
21 - 714 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 47REBR/BE
ELECTRONIC GOVERNOR (Continued)
Page 2351 of 2889

Improper filling can also raise the fluid level too
high. When the transmssion has too much fluid, the
geartrain churns up foam and cause the same condi-
tions which occur with a low fluid level.
In either case, air bubbles can cause overheating
and/or fluid oxidation, and varnishing. This can
interfere with normal valve, clutch, and accumulator
operation. Foaming can also result in fluid escaping
from the transmission vent where it may be mis-
taken for a leak.
Along with fluid level, it is important to check the
condition of the fluid. When the fluid smells burned,
and is contaminated with metal or friction material
particles, a complete transmission recondition is
needed. Be sure to examine the fluid on the dipstick
closely. If there is any doubt about its condition,
drain out a sample for a double check.
After the fluid has been checked, seat the dipstick
fully to seal out water and dirt.
The transmission has a dipstick to check oil level.
It is located on the right side of the engine. Be sure
to wipe all dirt from dipstick handle before removing.
Fluid level is checked with the engine running at
curb idle speed, the transmission in NEUTRAL and
the transmission fluid at normal operating tempera-
ture.The engine should be running at idle
speed for at least one minute, with the vehicle
on level ground.
The transmission fluid level can be checked two
ways.
PROCEDURE ONE
(1) Transmission fluid must be at normal operat-
ing temperature for accurate fluid level check. Drive
vehicle if necessary to bring fluid temperature up to
normal hot operating temperature of 82ÉC (180ÉF).
(2) Position vehicle on level surface.
(3) Start and run engine at curb idle speed.
(4) Apply parking brakes.
(5) Shift transmission momentarily into all gear
ranges. Then shift transmission back to NEUTRAL.
(6) Clean top of filler tube and dipstick to keep
dirt from entering tube.(7) Remove dipstick (Fig. 83) and check fluid level
as follows:
(a) Correct acceptable level is in crosshatch area.
(b) Correct maximum level is to MAX arrow
mark.
(c) Incorrect level is at or below MIN line.
(d) If fluid is low, add only enough MopartAT F
+4, type 9602, to restore correct level. Do not over-
fill.
PROCEDURE TWO
(1) Start engine and apply parking brake.
(2) Shift the transmission into DRIVE for approxi-
mately 2 seconds.
(3) Shift the transmission into REVERSE for
approximately 2 seconds.
(4) Shift the transmission into PARK.
(5) Hook up DRBtscan tool and select engine.
(6) Select sensors.
(7) Read the transmission temperature value.
(8) Compare the fluid temperature value with the
chart.
(9) Adjust transmission fluid level shown on the
dipstick according to the chart (Fig. 84).
NOTE: After adding any fluid to the transmission,
wait a minimum of 2 minutes for the oil to fully
drain from the fill tube into the transmission before
rechecking the fluid level.
(10) Check transmission for leaks.
Fig. 83 Dipstick Fluid Level MarksÐTypical
1 - DIPSTICK
2 - MAXIMUM CORRECT FLUID LEVEL
3 - ACCEPTABLE FLUID LEVEL
21 - 716 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 47REBR/BE
FLUID AND FILTER (Continued)
Page 2369 of 2889

(9) Remove bolts attaching overdrive unit to trans-
mission (Fig. 117).
CAUTION: Support the overdrive unit with a jack
before moving it rearward. This is necessary to pre-
vent damaging the intermediate shaft. Do not allow
the shaft to support the entire weight of the over-
drive unit.
(10) Carefully work overdrive unit off intermediate
shaft. Do not tilt unit during removal. Keep it as
level as possible.
(11) If overdrive unit does not require service,
immediately insert Alignment Tool 6227-2 in splines
of planetary gear and overrunning clutch to prevent
splines from rotating out of alignment. If misalign-
ment occurs, overdrive unit will have to be disassem-
bled in order to realign splines.
(12) Remove and retain overdrive piston thrust
bearing. Bearing may remain on piston or in clutch
hub during removal.
(13) Position drain pan on workbench.
(14) Place overdrive unit over drain pan. Tilt unit
to drain residual fluid from case.
(15) Examine fluid for clutch material or metal
fragments. If fluid contains these items, overhaul will
be necessary.
(16) If overdrive unit does not require any service,
leave alignment tool in position. Tool will prevent
accidental misalignment of planetary gear and over-
running clutch splines.DISASSEMBLY
(1) Remove transmission speed sensor and o-ring
seal from overdrive case (Fig. 118).
(2) Remove overdrive piston thrust bearing (Fig.
119).
Fig. 117 Overdrive Unit Bolts
1 - OVERDRIVE UNIT
2 - ATTACHING BOLTS (7)
Fig. 118 Transmission Speed Sensor
1 - SOCKET AND WRENCH
2 - SPEED SENSOR
3 - O-RING
Fig. 119 Overdrive Piston Thrust Bearing Removal/
Installation
1 - THRUST BEARING
2 - OVERDRIVE PISTON
3 - THRUST PLATE
21 - 734 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 47REBR/BE
OVERDRIVE UNIT (Continued)
Page 2385 of 2889
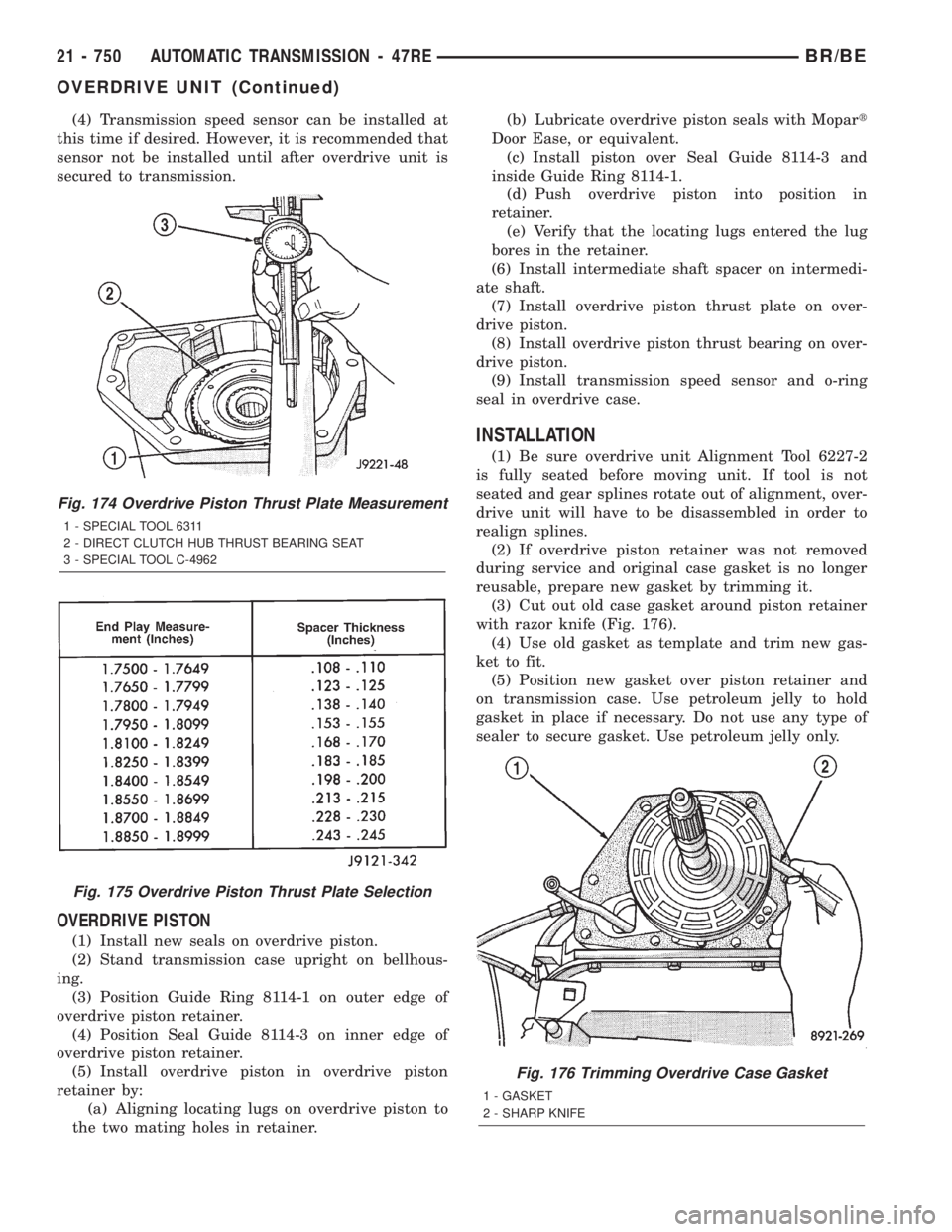
(4) Transmission speed sensor can be installed at
this time if desired. However, it is recommended that
sensor not be installed until after overdrive unit is
secured to transmission.
OVERDRIVE PISTON
(1) Install new seals on overdrive piston.
(2) Stand transmission case upright on bellhous-
ing.
(3) Position Guide Ring 8114-1 on outer edge of
overdrive piston retainer.
(4) Position Seal Guide 8114-3 on inner edge of
overdrive piston retainer.
(5) Install overdrive piston in overdrive piston
retainer by:
(a) Aligning locating lugs on overdrive piston to
the two mating holes in retainer.(b) Lubricate overdrive piston seals with Mopart
Door Ease, or equivalent.
(c) Install piston over Seal Guide 8114-3 and
inside Guide Ring 8114-1.
(d) Push overdrive piston into position in
retainer.
(e) Verify that the locating lugs entered the lug
bores in the retainer.
(6) Install intermediate shaft spacer on intermedi-
ate shaft.
(7) Install overdrive piston thrust plate on over-
drive piston.
(8) Install overdrive piston thrust bearing on over-
drive piston.
(9) Install transmission speed sensor and o-ring
seal in overdrive case.
INSTALLATION
(1) Be sure overdrive unit Alignment Tool 6227-2
is fully seated before moving unit. If tool is not
seated and gear splines rotate out of alignment, over-
drive unit will have to be disassembled in order to
realign splines.
(2) If overdrive piston retainer was not removed
during service and original case gasket is no longer
reusable, prepare new gasket by trimming it.
(3) Cut out old case gasket around piston retainer
with razor knife (Fig. 176).
(4) Use old gasket as template and trim new gas-
ket to fit.
(5) Position new gasket over piston retainer and
on transmission case. Use petroleum jelly to hold
gasket in place if necessary. Do not use any type of
sealer to secure gasket. Use petroleum jelly only.
Fig. 174 Overdrive Piston Thrust Plate Measurement
1 - SPECIAL TOOL 6311
2 - DIRECT CLUTCH HUB THRUST BEARING SEAT
3 - SPECIAL TOOL C-4962
Fig. 175 Overdrive Piston Thrust Plate Selection
Fig. 176 Trimming Overdrive Case Gasket
1 - GASKET
2 - SHARP KNIFE
21 - 750 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 47REBR/BE
OVERDRIVE UNIT (Continued)
Page 2386 of 2889

(6) Install selective spacer on intermediate shaft, if
removed. Spacer goes in groove just rearward of
shaft rear splines (Fig. 177).
(7) Install thrust bearing in overdrive unit sliding
hub. Use petroleum jelly to hold bearing in position.
CAUTION: Be sure the shoulder on the inside diam-
eter of the bearing is facing forward.
(8) Verify that splines in overdrive planetary gear
and overrunning clutch hub are aligned with Align-
ment Tool 6227-2. Overdrive unit cannot be installed
if splines are not aligned. If splines have rotated out
of alignment, unit will have to be disassembled to
realign splines.
(9) Carefully slide Alignment Tool 6227-2 out of
overdrive planetary gear and overrunning clutch
splines.
(10) Raise overdrive unit and carefully slide it
straight onto intermediate shaft. Insert park rod into
park lock reaction plug at same time. Avoid tilting
overdrive during installation as this could cause
planetary gear and overrunning clutch splines to
rotate out of alignment. If this occurs, it will be nec-
essary to remove and disassemble overdrive unit to
realign splines.
(11) Work overdrive unit forward on intermediate
shaft until seated against transmission case.
(12) Install bolts attaching overdrive unit to trans-
mission unit. Tighten bolts in diagonal pattern to 34
N´m (25 ft-lbs).
(13) Connect the transmission speed sensor and
overdrive wiring connectors.
(14) Install the transfer case, if equipped.
(15) Align and install rear propeller shaft, if nec-
essary. (Refer to 3 - DIFFERENTIAL & DRIVELINE/
PROPELLER SHAFT/PROPELLER SHAFT -
INSTALLATION)OVERRUNNING CLUTCH
CAM/OVERDRIVE PISTON
RETAINER
DESCRIPTION
The overrunning clutch (Fig. 178) consists of an
inner race, an outer race (or cam), rollers and
springs, and the spring retainer. The number of roll-
ers and springs depends on what transmission and
which overrunning clutch is being dealt with.
OPERATION
As the inner race is rotated in a clockwise direction
(as viewed from the front of the transmission), the
race causes the rollers to roll toward the springs,
causing them to compress against their retainer. The
compression of the springs increases the clearance
between the rollers and cam. This increased clear-
ance between the rollers and cam results in a free-
wheeling condition. When the inner race attempts to
rotate counterclockwise, the action causes the rollers
to roll in the same direction as the race, aided by the
pushing of the springs. As the rollers try to move in
the same direction as the inner race, they are
wedged between the inner and outer races due to the
design of the cam. In this condition, the clutch is
locked and acts as one unit.
DISASSEMBLY
(1) Remove the overdrive piston (Fig. 179).
(2) Remove the overdrive piston retainer bolts.
(3) Remove overdrive piston retainer.
Fig. 177 Intermediate Shaft Selective Spacer
Location
1 - SELECTIVE SPACER
2 - SPACER GROOVE
3 - INTERMEDIATE SHAFT
Fig. 178 Overrunning Clutch
1 - OUTER RACE (CAM)
2 - ROLLER
3 - SPRING
4 - SPRING RETAINER
5 - INNER RACE (HUB)
BR/BEAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 47RE 21 - 751
OVERDRIVE UNIT (Continued)
Page 2405 of 2889

plunger also contribute to the response speed possi-
ble by a particular solenoid design.
A solenoid can also be described by the method by
which it is controlled. Some of the possibilities
include variable force, pulse-width modulated, con-
stant ON, or duty cycle. The variable force and pulse-
width modulated versions utilize similar methods to
control the current flow through the solenoid to posi-
tion the solenoid plunger at a desired position some-
where between full ON and full OFF. The constant
ON and duty cycled versions control the voltage
across the solenoid to allow either full flow or no flow
through the solenoid's valve.
OPERATION
When an electrical current is applied to the sole-
noid coil, a magnetic field is created which produces
an attraction to the plunger, causing the plunger to
move and work against the spring pressure and the
load applied by the fluid the valve is controlling. The
plunger is normally directly attached to the valve
which it is to operate. When the current is removed
from the coil, the attraction is removed and the
plunger will return to its original position due to
spring pressure.
The plunger is made of a conductive material and
accomplishes this movement by providing a path for
the magnetic field to flow. By keeping the air gap
between the plunger and the coil to the minimum
necessary to allow free movement of the plunger, the
magnetic field is maximized.
SPEED SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The speed sensor (Fig. 223) is located in the over-
drive gear case. The sensor is positioned over the
park gear and monitors transmission output shaft
rotating speed.
OPERATION
Speed sensor signals are triggered by the park
gear lugs as they rotate past the sensor pickup face.
Input signals from the sensor are sent to the trans-
mission control module for processing. Signals from
this sensor are shared with the powertrain control
module.
THROTTLE VALVE CABLE
DESCRIPTION
Transmission throttle valve cable (Fig. 224) adjust-
ment is extremely important to proper operation.
This adjustment positions the throttle valve, which
controls shift speed, quality, and part-throttle down-
shift sensitivity.
If cable setting is too loose, early shifts and slip-
page between shifts may occur. If the setting is too
tight, shifts may be delayed and part throttle down-
shifts may be very sensitive.
Fig. 223 Transmission Output Speed Sensor
1 - TRANSMISSION OUTPUT SHAFT SPEED SENSOR
2 - SEAL
Fig. 224 Throttle Valve Cable Attachment - At
Engine
1 - THROTTLE VALVE CABLE
2 - CABLE BRACKET
3 - THROTTLE BODY LEVER
4 - ACCELERATOR CABLE
5 - SPEED CONTROL CABLE
21 - 770 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 47REBR/BE
SOLENOID (Continued)
Page 2414 of 2889

vehicle is parked for lengthy periods. The valve check
ball is spring loaded and has an opening pressure of
approximately 2 psi.
The valve is serviced as an assembly; it is not
repairable. Do not clean the valve if restricted, or
contaminated by sludge, or debris. If the valve fails,
or if a transmission malfunction occurs that gener-
ates significant amounts of sludge and/or clutch par-
ticles and metal shavings, the valve must be
replaced.
The valve must be removed whenever the cooler
and lines are reverse flushed. The valve can be flow
tested when necessary. The procedure is exactly the
same as for flow testing a cooler.
If the valve is restricted, installed backwards, or in
the wrong line, it will cause an overheating condition
and possible transmission failure.
CAUTION: The drainback valve is a one-way flow
device. It must be properly oriented in terms of flow
direction for the cooler to function properly. The
valve must be installed in the pressure line. Other-
wise flow will be blocked and would cause an over-
heating condition and eventual transmission failure.
TRANSMISSION
TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
Transmission fluid temperature readings are sup-
plied to the transmission control module by the ther-
mistor (Fig. 238). The temperature readings are used
to control engagement of the fourth gear overdrive
clutch, the converter clutch, and governor pressure.
Normal resistance value for the thermistor at room
temperature is approximately 1000 ohms.
The thermistor is part of the governor pressure
sensor assembly and is immersed in transmission
fluid at all times.
OPERATION
The PCM prevents engagement of the converter
clutch and overdrive clutch, when fluid temperature
is below approximately 10ÉC (50ÉF).
If fluid temperature exceeds 126ÉC (260ÉF), the
PCM causes a 4-3 downshift and engage the con-
verter clutch. Engagement is according to the third
gear converter clutch engagement schedule.
The overdrive OFF lamp in the instrument panel
illuminates when the shift back to third occurs. The
transmission will not allow fourth gear operation
until fluid temperature decreases to approximately
110ÉC (230ÉF).
Fig. 237 Typical Method Of Checking Converter
Seating
1 - SCALE
2 - STRAIGHTEDGE
Fig. 238 Governor Pressure Sensor
1 - GOVERNOR BODY
2 - GOVERNOR PRESSURE SENSOR/TRANSMISSION FLUID
TEMPERATURE THERMISTOR
BR/BEAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 47RE 21 - 779
TORQUE CONVERTER DRAINBACK VALVE (Continued)