control arm DODGE RAM 2001 Service Manual PDF
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2001, Model line: RAM, Model: DODGE RAM 2001Pages: 2889, PDF Size: 68.07 MB
Page 1298 of 2889

nished to correct size (Fig. 35).DO NOT ream this
bushing.
CAUTION: This procedure MUST be followed when
installing a new bushing or seizure to shaft may
occur.(4) Install the intake manifold (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD -
INSTALLATION).
(5) Install the distributor (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/IGNITION CONTROL/DISTRIBUTOR -
INSTALLATION).
HYDRAULIC LIFTERS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐHYDRAULIC
TAPPETS
Before disassembling any part of the engine to cor-
rect tappet noise, check the oil pressure. If vehicle
has no oil pressure gauge, install a reliable gauge at
the pressure sending-unit. The pressure should be
between 207-552 kPa (30-80 psi) at 3,000 RPM.
Check the oil level after the engine reaches normal
operating temperature. Allow 5 minutes to stabilize
oil level, check dipstick. The oil level in the pan
should never be above the FULL mark or below the
ADD OIL mark on dipstick. Either of these two con-
ditions could be responsible for noisy tappets.
OIL LEVEL
HIGH
If oil level is above the FULL mark, it is possible
for the connecting rods to dip into the oil. With the
engine running, this condition could create foam in
the oil pan. Foam in oil pan would be fed to the
hydraulic tappets by the oil pump causing them to
lose length and allow valves to seat noisily.
LOW
Low oil level may allow oil pump to take in air. When
air is fed to the tappets, they lose length, which allows
valves to seat noisily. Any leaks on intake side of oil
pump through which air can be drawn will create the
same tappet action. Check the lubrication system from
the intake strainer to the pump cover, including the
relief valve retainer cap. When tappet noise is due to
aeration, it may be intermittent or constant, and usu-
ally more than one tappet will be noisy. When oil level
and leaks have been corrected, operate the engine at
fast idle. Run engine for a sufficient time to allow all of
the air inside the tappets to be bled out.
TAPPET NOISE DIAGNOSIS
(1) To determine source of tappet noise, operate
engine at idle with cylinder head covers removed.
(2) Feel each valve spring or rocker arm to detect
noisy tappet. The noisy tappet will cause the affected
spring and/or rocker arm to vibrate or feel rough in
operation.
Fig. 33 Distributor Driveshaft Bushing Removal
1 - SPECIAL TOOL C-3052
2 - BUSHING
Fig. 34 Distributor Driveshaft Bushing Installation
1 - SPECIAL TOOL C-3053
2 - BUSHING
Fig. 35 Burnishing Distributor Driveshaft Bushing
1 - SPECIAL TOOL C-3053
2 - BUSHING
BR/BEENGINE 5.9L 9 - 151
DISTRIBUTOR BUSHING (Continued)
Page 1300 of 2889

(2) Install tappets and push rods in their original
positions. Ensure that the oil feed hole in the side of
the tappet body faces up (away from the crankshaft).
(3) Install aligning yokes with ARROW toward
camshaft.
(4) Install yoke retainer. Tighten the bolts to 23
N´m (200 in. lbs.) torque. Install intake manifold
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANI-
FOLD - INSTALLATION).
(5) Install push rods in original positions.
(6) Install rocker arms.
(7) Install cylinder head cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
(8) Install air cleaner assembly and air in-let hose.
(9) Start and operate engine. Warm up to normal
operating temperature.
CAUTION: To prevent damage to valve mechanism,
engine must not be run above fast idle until all
hydraulic tappets have filled with oil and have
become quiet.
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD
DESCRIPTION
The pistons are made of aluminum and have three
ring grooves, the top two grooves are for the compres-
sion rings and the bottom groove is for the oil control
ring. The connecting rods are forged steel and are
coined prior to heat treat. The piston pins are press fit.
STANDARD PROCEDUREÐPISTON FITTING
Piston and cylinder wall must be clean and dry.
Specified clearance between the piston and the cylin-
der wall is 0.013-0.038 mm (0.0005-0.0015 inch) at
21ÉC (70ÉF).
Piston diameter should be measured at the top of
skirt, 90É to piston pin axis. Cylinder bores should be
measured halfway down the cylinder bore and trans-
verse to the engine crankshaft center line.
Pistons and cylinder bores should be measured at
normal room temperature, 21ÉC (70ÉF).
Check the pistons for taper and elliptical shape
before they are fitted into the cylinder bore (Fig. 37).
PISTON MEASUREMENT CHART
PISTON A DIA = PISTON BORE
SIZE DIAMETER DIAMETER
MIN. MAX. MIN. MAX.
mm
(in.)mm
(in.)mm
(in.)mm (in.)
AÐÐÐ Ð
B101.580 101.592 101.605 101.618
(3.9992) (3.9997) (4.0002) (4.0007)
C101.592 101.605 101.618 101.630
(3.9997) (4.0002) (4.0007) (4.0012)
D101.605 101.618 101.630 101.643
(4.0002) (4.0007) (4.0012) (4.0017)
EÐÐÐ Ð
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
PISTON PIN BORE 25.007 - 25.015 mm
(.9845 - .9848 in.)
RING GROOVE
HEIGHT
OIL RAIL 4.033 - 4.058 mm
(.1588 - .1598 in.)
COMPRESSION
RAIL1.529 - 1.554 mm
(.0602 - .0612 in.)
TOTAL FINISHED 470.8 2 grams
WEIGHT (16.607 .0706 ounces)
Fig. 37 Piston Measurements
1 - 49.53 mm (1.95 IN.)
BR/BEENGINE 5.9L 9 - 153
HYDRAULIC LIFTERS (Continued)
Page 1315 of 2889

(9) Install closed crankcase ventilation and evapo-
ration control systems.
(10) Connect the coil wires.
(11) Connect the heat indicator sending unit wire.
(12) Connect the heater hoses and bypass hose.
(13) Install distributor cap and wires.
(14) Hook up the return spring.
(15) Connect the accelerator linkage (Refer to 14 -
FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/THROTTLE
CONTROL CABLE - INSTALLATION) and if so
equipped, the speed control and transmission kick-
down cables.
(16) Install the fuel lines (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYS-
TEM/FUEL DELIVERY/QUICK CONNECT FIT-
TING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(17) Install the accessory drive bracket and A/C
compressor (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDI-
TIONING/PLUMBING/A/C COMPRESSOR -
INSTALLATION).
(18) Install the generator and drive belt (Refer to 7
- COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
INSTALLATION). Tighten generator mounting bolt
to 41 N´m (30 ft. lbs.) torque.
(19) Install the air cleaner.
(20) Fill cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(21) Connect the negative cable to the battery.
EXHAUST MANIFOLD
DESCRIPTION
The exhaust manifolds (Fig. 70) are constructed of
cast iron and are LOG type with balanced flow. One
exhaust manifold is attached to each cylinder head.
OPERATION
The exhaust manifolds collect the engine exhaust
exiting the combustion chambers, then channels the
exhaust gases to the exhaust pipes attached to the
manifolds.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the negative cable from the battery.
(2) Raise and support the vehicle.
(3) Remove the bolts and nuts attaching the
exhaust pipe to the engine exhaust manifold.
(4) Lower the vehicle.
(5) Remove the exhaust heat shields.
(6) Remove bolts, nuts and washers attaching
manifold to cylinder head.
(7) Remove manifold from the cylinder head.
CLEANING
Clean mating surfaces on cylinder head and mani-
fold. Wash with solvent and blow dry with com-
pressed air.
INSPECTION
Inspect manifold for cracks.
Inspect mating surfaces of manifold for flatness
with a straight edge. Gasket surfaces must be flat
within 0.2 mm per 300 mm (0.008 inch per foot).
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: If the studs came out with the nuts when
removing the engine exhaust manifold, install new
studs. Apply sealer on the coarse thread ends.
Water leaks may develop at the studs if this precau-
tion is not taken.
(1) Position the engine exhaust manifolds on the
two studs located on the cylinder head. Install coni-
cal washers and nuts on these studs (Fig. 71).
(2) Install two bolts and conical washers at the
inner ends of the engine exhaust manifold outboard
arms. Install two bolts WITHOUT washers on the
center arm of engine exhaust manifold (Fig. 71).
Starting at the center arm and working outward,
tighten the bolts and nuts to 34 N´m (25 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(3) Install the exhaust heat shields.
(4) Raise and support the vehicle.
(5) Assemble exhaust pipe to manifold and secure
with bolts, nuts and retainers. Tighten the bolts and
nuts to 34 N´m (25 ft. lbs.) torque.
Fig. 70 Exhaust ManifoldsÐV-8 Gas Engines Typical
1 - EXHAUST MANIFOLD (LEFT)
2 - BOLTS & WASHERS
3 - NUTS & WASHERS
4 - EXHAUST MANIFOLD (RIGHT)
5 - BOLTS & WASHERS
9 - 168 ENGINE 5.9LBR/BE
INTAKE MANIFOLD (Continued)
Page 1322 of 2889

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
7. Intake manifold vacuum leak 7. Inspect intake manifold gasket and
vacuum hoses (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE
MANIFOLD - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
ENGINE MISSES ON
ACCELERATION1. Worn or incorrectly gapped spark
plugs1. Replace spark plugs or clean and
set gap. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/SPARK PLUG -
CLEANING)
2. Spark plug cables defective or
crossed2. Replace or rewire secondary
ignition cables. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/IGNITION CONTROL/
SPARK PLUG CABLE - REMOVAL)
3. Dirt in fuel system 3. Clean fuel system
4. Burned, warped or pitted valves 4. Install new valves
5. Faulty coil 5. Test and replace as necessary
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/IGNITION
CONTROL/IGNITION COIL -
REMOVAL)
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐ MECHANICAL
ENGINE MECHANICAL DIAGNOSIS CHART
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
NOISY VALVES/LIFTERS 1. High or low oil level in crankcase 1. Check for correct oil level. Adjust
oil level by draining or adding as
needed
2. Thin or diluted oil 2. Change oil. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL -
STANDARD PROCEDURE)
3. Low oil pressure 3. Check engine oil level. If ok,
Perform oil pressure test. (Refer to
9 - ENGINE/LUBRICATION -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING) for
engine oil pressure test/
specifications
4. Dirt in tappets/lash adjusters 4. Clean/replace hydraulic
tappets/lash adjusters
5. Bent push rod(s) 5. Install new push rods
6. Worn rocker arms 6. Inspect oil supply to rocker arms
and replace worn arms as needed
7. Worn tappets/lash adjusters 7. Install new hydraulic tappets/lash
adjusters
8. Worn valve guides 8. Inspect all valve guides and
replace as necessary
9. Excessive runout of valve seats
or valve faces9. Grind valves and seats
BR/BEENGINE 8.0L 9 - 175
ENGINE 8.0L (Continued)
Page 1339 of 2889
COOLING SYSTEM TESTER METHOD
WARNING: WITH COOLING SYSTEM TESTER IN
PLACE, PRESSURE WILL BUILD UP FAST. EXCES-
SIVE PRESSURE BUILT UP, BY CONTINUOUS
ENGINE OPERATION, MUST BE RELEASED TO A
SAFE PRESSURE POINT. NEVER PERMIT PRES-
SURE TO EXCEED 138 kPa (20 psi).
Install Cooling System Tester 7700 or equivalent to
pressure cap neck. Start the engine and observe the
tester's pressure gauge. If gauge pulsates with every
power stroke of a cylinder a combustion pressure
leak is evident.
CHEMICAL TEST METHOD
Combustion leaks into the cooling system can also
be checked by using Bloc-Chek Kit C-3685-A or
equivalent. Perform test following the procedures
supplied with the tool kit.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the negative cable from the battery.
(2) Drain cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(3) Remove the heat shields (Fig. 8).
(4) Remove the intake manifold-to-generator
bracket support rod. Remove the generator (Refer to
8 - ELECTRICAL/CHARGING/GENERATOR -
REMOVAL).
(5) Remove closed crankcase ventilation system.
(6) Disconnect the evaporation control system.
(7) Remove the air cleaner.
(8) Perform the Fuel System Pressure release pro-
cedure (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIV-ERY - STANDARD PROCEDURE). Disconnect the
fuel line (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIV-
ERY/QUICK CONNECT FITTING - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
(9) Disconnect accelerator linkage and if so
equipped, the speed control and transmission kick-
down cables.
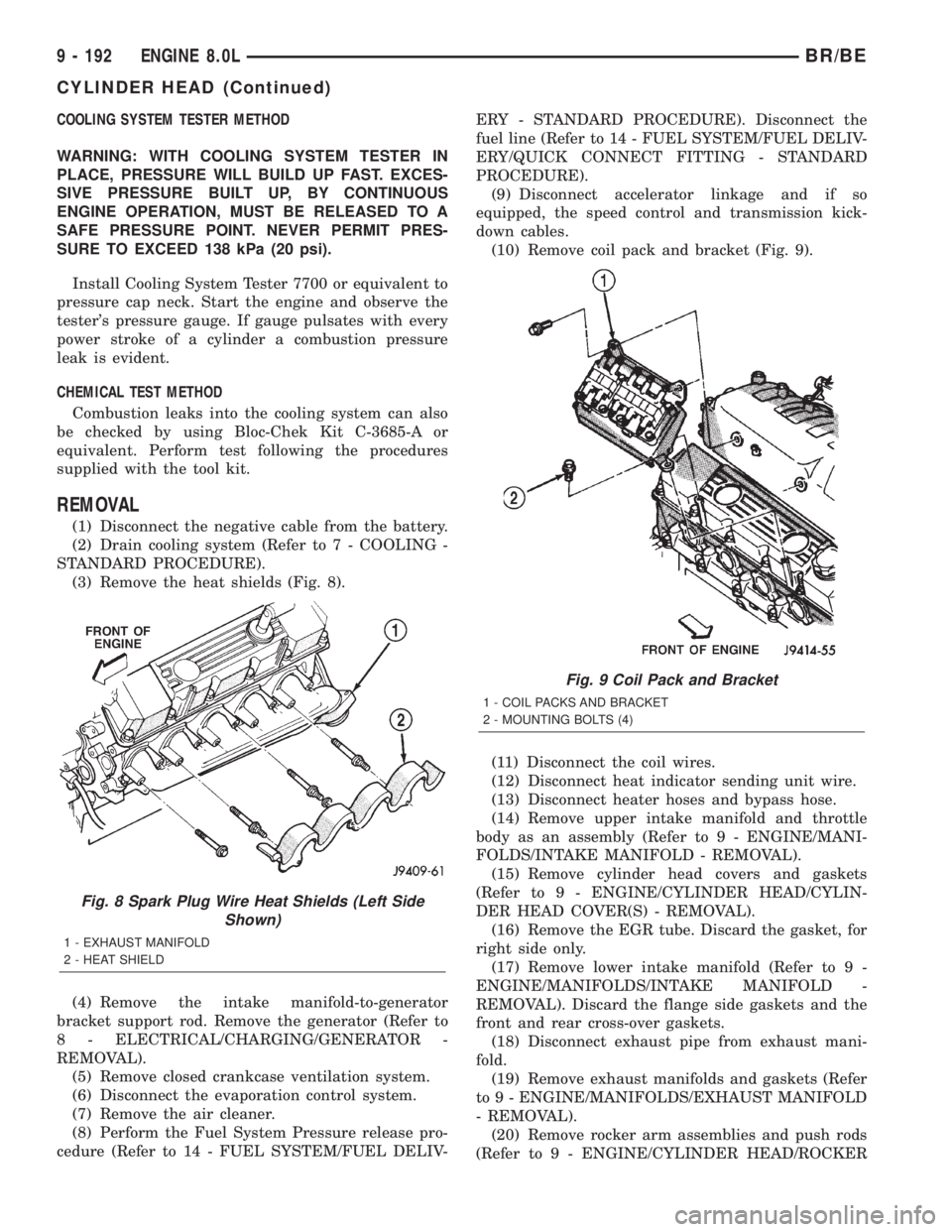
(10) Remove coil pack and bracket (Fig. 9).
(11) Disconnect the coil wires.
(12) Disconnect heat indicator sending unit wire.
(13) Disconnect heater hoses and bypass hose.
(14) Remove upper intake manifold and throttle
body as an assembly (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/MANI-
FOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD - REMOVAL).
(15) Remove cylinder head covers and gaskets
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLIN-
DER HEAD COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(16) Remove the EGR tube. Discard the gasket, for
right side only.
(17) Remove lower intake manifold (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD -
REMOVAL). Discard the flange side gaskets and the
front and rear cross-over gaskets.
(18) Disconnect exhaust pipe from exhaust mani-
fold.
(19) Remove exhaust manifolds and gaskets (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/EXHAUST MANIFOLD
- REMOVAL).
(20) Remove rocker arm assemblies and push rods
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/ROCKER
Fig. 8 Spark Plug Wire Heat Shields (Left Side
Shown)
1 - EXHAUST MANIFOLD
2 - HEAT SHIELD
Fig. 9 Coil Pack and Bracket
1 - COIL PACKS AND BRACKET
2 - MOUNTING BOLTS (4)
9 - 192 ENGINE 8.0LBR/BE
CYLINDER HEAD (Continued)
Page 1340 of 2889

ARM / ADJUSTER ASSY - REMOVAL). Identify to
ensure installation in original locations.
(21) Remove the head bolts from each cylinder
head and remove cylinder heads. Discard the cylin-
der head gasket.
(22) Remove spark plugs.
CLEANING
Clean all surfaces of cylinder block and cylinder
heads. Be sure material does not fall into the lifters
and surrounding valley.
Clean cylinder block front and rear gasket surfaces
using a suitable solvent.
Clean the exhaust manifold to cylinder head mat-
ing areas.
INSPECTION
Inspect all surfaces with a straightedge if there is
any reason to suspect leakage. The out-of-flatness
specifications are 0.0007 mm/mm (0.0004 inch/inch),
0.127 mm/152 mm (0.005 inch/6 inches) any direction
or 0.254 mm (0.010 inch) overall across head. If
exceeded, either replace head or lightly machine the
head surface.
The cylinder head surface finish should be
1.78-4.57 microns (15-80 microinches).
Inspect push rods. Replace worn or bent rods.
Inspect rocker arms. Replace if worn or scored.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the new cylinder head gaskets onto
the cylinder block.
(2) Position the cylinder heads onto head gaskets
and cylinder block.
(3) Tighten the cylinder head bolts in two steps
(Fig. 10):
²Step 1ÐTighten all cylinder head bolts, in
sequence, to 58 N´m (43 ft. lbs.) torque.
²Step 2ÐTighten all cylinder head bolts, in
sequence, to 143 N´m (105 ft. lbs.) torque.
²
CAUTION: When tightening the rocker arm bolts,
make sure the piston in that cylinder is NOT at
TDC. Contact between the valves and piston could
occur.
(4) Install push rods and rocker arm assemblies in
their original position (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLIN-
DER HEAD/ROCKER ARM / ADJUSTER ASSY -
INSTALLATION).
(5) Install lower intake manifold (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD -
INSTALLATION).(6) Install the upper intake manifold onto the
lower intake manifold (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/MANI-
FOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD - INSTALLATION).
(7) Install the exhaust manifolds and new gaskets
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/EXHAUST
MANIFOLD - INSTALLATION).
(8) Install exhaust pipe to the exhaust manifold.
Tighten the bolts to 34 n´m (25 ft. lbs.) torque.
(9) Using a new gasket, position the EGR tube to
the intake manifold and the exhaust manifold.
Tighten the EGR tube nut to 34 N´m (25 ft. lbs.)
torque. Tighten the bolts to 20 N´m (174 in. lbs.)
torque.
(10) Install the heat shields and the washers.
Make sure that heat shields tabs hook over the
exhaust gasket.Tighten the nuts to 15 N´m (132 in.
lbs.) torque.
(11) Adjust and Install the spark plugs (Refer to 8
- ELECTRICAL/IGNITION CONTROL/SPARK
PLUG - INSTALLATION).
(12) Install coil packs and bracket. Tighten the
bracket bolts to 21 N´m (190 in. lbs.) torque. Connect
the coil wires.
(13) Connect heat indicator sending unit wire.
(14) Connect the heater hoses and bypass hose.
(15) Connect the accelerator linkage and if so
equipped, the speed control and transmission kick-
down cables.
(16) Install the fuel line (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYS-
TEM/FUEL DELIVERY/QUICK CONNECT FIT-
TING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(17) Install the generator (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/CHARGING/GENERATOR - INSTALLATION)
and drive belt (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ACCESSORY
DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS - INSTALLATION).
(18) Install the intake manifold-to-generator
bracket support rod. Tighten the bolts to 41 N´m (30
ft. lbs.) torque.
(19) The cylinder head cover gasket can be used
again. Install the gasket onto the head rail.For the
left side the number tab is at the front of
engine with the number up. For the right side
the number tab is at the rear of engine with the
number up.
Fig. 10 Cylinder Head Bolt Tightening Sequence
BR/BEENGINE 8.0L 9 - 193
CYLINDER HEAD (Continued)
Page 1344 of 2889
(3) Inspect the valve seat with Prussian blue to
determine where the valve contacts the seat. To do
this, coat valve seat LIGHTLY with Prussian blue
then set valve in place. Rotate the valve with light
pressure. If the blue is transferred to the center of
valve face, contact is satisfactory. If the blue is trans-
ferred to the top edge of valve face, lower valve seat
with a 15É stone. If the blue is transferred to bottom
edge of valve face raise valve seat with a 60É stone.
(4) When seat is properly positioned the width of
valve seats should be 1.016-1.524 mm (0.040-0.060
inch).
VALVE SPRING INSPECTION
Whenever valves have been removed for inspection,
reconditioning or replacement, valve springs should
be tested. As an example the compression length of
the spring to be tested is 1-5/16 inch. Turn table of
Universal Valve Spring Tester Tool until surface is in
line with the 1-5/16 inch mark on the threaded stud.
Be sure the zero mark is to the front (Fig. 19). Place
spring over stud on the table and lift compressing
lever to set tone device. Pull on torque wrench until
ping is heard. Take reading on torque wrench at this
instant. Multiply this reading by 2. This will give the
spring load at test length. Fractional measurements
are indicated on the table for finer adjustments.
Refer to specifications to obtain specified height and
allowable tensions. Discard the springs that do not
meet specifications.
REMOVALÐVALVE STEM SEALS
NOTE: This procedure is done with the cylinder
head installed.
(1) Disconnect the negative cable from the battery.
(2) Set engine basic timing to Top Dead Center
(TDC) and remove air cleaner.
(3) Remove cylinder head covers (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - REMOVAL) and spark plugs (Refer to 8
- ELECTRICAL/IGNITION CONTROL/SPARK
PLUG - REMOVAL).
(4) Using suitable socket and flex handle at crank-
shaft retaining bolt, turn engine so that the piston of
the cylinder to be worked on, is at TDC on the com-
pression stroke.
(5) Remove rocker arms (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
CYLINDER HEAD/ROCKER ARM / ADJUSTER
ASSY - REMOVAL).
(6) With air hose attached to an adapter installed
in the spark plug hole, apply 620-689 kPa (90-100
psi) air pressure.
(7) Using Valve Spring Compressor Tool
MD-998772A with adapter 6716A (Fig. 20), compress
valve spring and remove retainer valve locks and
valve spring.
(8) Remove the valve stem seal.
REMOVALÐVALVES AND VALVE SPRINGS
(1) Remove the cylinder head (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - REMOVAL).
(2) Special studs must be used to adapt the Valve
Spring Compressor Tool to the V-10 cylinder head
(Fig. 21). Install the metric end into the Special Tool
MD998772A and the 5/16 end into the cylinder head.
Fig. 18 Intake and Exhaust Valves
1 - MARGIN
2 - VALVE SPRING RETAINER LOCK GROOVE
3 - STEM
4-FACE
Fig. 19 Testing Valve Spring for Compressed
1 - TORQUE WRENCH
2 - VALVE SPRING TESTER
BR/BEENGINE 8.0L 9 - 197
INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES & SEATS (Continued)
Page 1346 of 2889
(4) Compress valve spring and install retainer
valve locks.
(5) Remove air hose and adapter from spark plug
hole.
(6) Remove Valve Spring Compressor and Adapter
Studs.
(7) Install rocker arms (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYL-
INDER HEAD/ROCKER ARM / ADJUSTER ASSY -
INSTALLATION).
(8) The cylinder head cover gasket can be used
again. Install the gasket onto the head rail.For the
left side the number tab is at the front of
engine with the number up. For the right side
the number tab is at the rear of engine with the
number up.
CAUTION: The cylinder head cover fasteners have a
special plating. DO NOT use alternative fasteners.(9) Install cylinder head cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION) (Fig. 25).
(10) Install closed crankcase ventilation system.
(11) Connect the evaporation control system.
(12) Install air cleaner.
(13) Connect the negative cable to the battery.
(14) Road test vehicle and check for leaks.
INSTALLATIONÐVALVES AND VALVE SPRINGS
(1) Clean valves thoroughly. Discard burned,
warped and cracked valves.
(2) Remove carbon and varnish deposits from
inside of valve guides with a reliable guide cleaner.
(3) Measure valve stems for wear. If wear exceeds
0.051 mm (0.002 inch), replace the valve.
(4) Make sure there are no burrs on valve stems.
(5) Coat valve stems with lubrication oil. Insert
valves into valve guides in cylinder head.
(6) Install new seals on all valve guides(BLACK
on intake and BROWN on exhaust). Install valve
springs and valve retainers.
(7) Compress valve springs with Valve Spring
Compressor Tool MD-998772A and adapter 6716A,
Fig. 23 Positioning Valve with Tool C-3973
1 - VALVE
2 - SPACER TOOL
Fig. 24 Measuring Valve Guide Wear
1 - VALVE
2 - SPECIAL TOOL C-3339
Fig. 25 Cylinder Head Covers
1 - CYLINDER HEAD COVER
2 - CYLINDER HEAD COVER GASKET
BR/BEENGINE 8.0L 9 - 199
INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES & SEATS (Continued)
Page 1390 of 2889
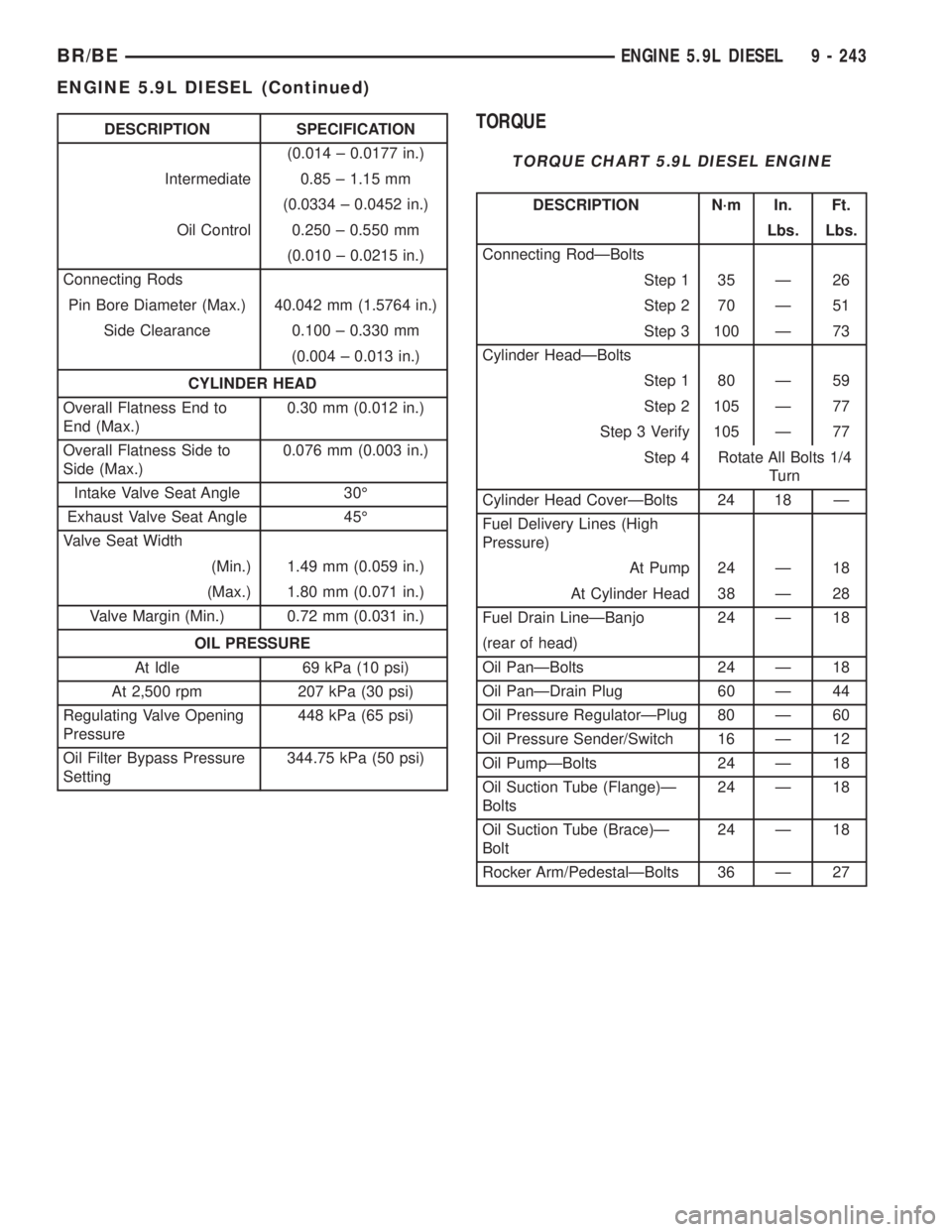
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
(0.014 ± 0.0177 in.)
Intermediate 0.85 ± 1.15 mm
(0.0334 ± 0.0452 in.)
Oil Control 0.250 ± 0.550 mm
(0.010 ± 0.0215 in.)
Connecting Rods
Pin Bore Diameter (Max.) 40.042 mm (1.5764 in.)
Side Clearance 0.100 ± 0.330 mm
(0.004 ± 0.013 in.)
CYLINDER HEAD
Overall Flatness End to
End (Max.)0.30 mm (0.012 in.)
Overall Flatness Side to
Side (Max.)0.076 mm (0.003 in.)
Intake Valve Seat Angle 30É
Exhaust Valve Seat Angle 45É
Valve Seat Width
(Min.) 1.49 mm (0.059 in.)
(Max.) 1.80 mm (0.071 in.)
Valve Margin (Min.) 0.72 mm (0.031 in.)
OIL PRESSURE
At Idle 69 kPa (10 psi)
At 2,500 rpm 207 kPa (30 psi)
Regulating Valve Opening
Pressure448 kPa (65 psi)
Oil Filter Bypass Pressure
Setting344.75 kPa (50 psi)TORQUE
TORQUE CHART 5.9L DIESEL ENGINE
DESCRIPTION N´m In. Ft.
Lbs. Lbs.
Connecting RodÐBolts
Step 1 35 Ð 26
Step 2 70 Ð 51
Step 3 100 Ð 73
Cylinder HeadÐBolts
Step 1 80 Ð 59
Step 2 105 Ð 77
Step 3 Verify 105 Ð 77
Step 4 Rotate All Bolts 1/4
Turn
Cylinder Head CoverÐBolts 24 18 Ð
Fuel Delivery Lines (High
Pressure)
At Pump 24 Ð 18
At Cylinder Head 38 Ð 28
Fuel Drain LineÐBanjo 24 Ð 18
(rear of head)
Oil PanÐBolts 24 Ð 18
Oil PanÐDrain Plug 60 Ð 44
Oil Pressure RegulatorÐPlug 80 Ð 60
Oil Pressure Sender/Switch 16 Ð 12
Oil PumpÐBolts 24 Ð 18
Oil Suction Tube (Flange)Ð
Bolts24 Ð 18
Oil Suction Tube (Brace)Ð
Bolt24 Ð 18
Rocker Arm/PedestalÐBolts 36 Ð 27
BR/BEENGINE 5.9L DIESEL 9 - 243
ENGINE 5.9L DIESEL (Continued)
Page 1489 of 2889

FUEL DELIVERY - GASOLINE
DESCRIPTION - FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM
The fuel delivery system consists of:
²the fuel pump module containing the electric
fuel pump, fuel filter/fuel pressure regulator, rollover
valve (certain modules), fuel gauge sending unit (fuel
level sensor) and a separate fuel filter located at bot-
tom of pump module
²fuel tubes/lines/hoses
²quick-connect fittings
²fuel injector rail
²fuel injectors
²fuel tank
²fuel tank filler/vent tube assembly
²fuel tank filler tube cap
²accelerator pedal
²throttle cable
OPERATION - FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM
Fuel is returned through the fuel pump module
and back into the fuel tank through the fuel filter/
fuel pressure regulator. A separate fuel return line
from the engine to the tank is not used with any gas-
oline powered engine.
The fuel tank assembly consists of: the fuel tank,
fuel pump module assembly, fuel pump module lock-
nut/gasket and rollover valve(s) (refer to 25, Emis-
sion Control System for rollover valve information).
A fuel filler/vent tube assembly using a pressure/
vacuum, 1/4 turn fuel filler cap is used. The fuel
filler tube contains a flap door located below the fuel
fill cap.
Also to be considered part of the fuel system is the
evaporation control system. This is designed to
reduce the emission of fuel vapors into the atmo-
sphere. The description and function of the Evapora-
tive Control System is found in 25, Emission Control
Systems.
Both fuel filters (at bottom of fuel pump module
and within fuel pressure regulator) are designed for
extended service. They do not require normal sched-
uled maintenance. Filters should only be replaced if
a diagnostic procedure indicates to do so.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL PRESSURE
LEAK DOWN TEST
Use this test in conjunction with the Fuel Pump
Pressure Test and Fuel Pump Capacity Test.
Check Valve Operation:The electric fuel pump
outlet contains a one-way check valve to prevent fuel
flow back into the tank and to maintain fuel supply
line pressure (engine warm) when pump is not oper-
ational. It is also used to keep the fuel supply line
full of gasoline when pump is not operational. Afterthe vehicle has cooled down, fuel pressure may drop
to 0 psi (cold fluid contracts), but liquid gasoline will
remain in fuel supply line between the check valve
and fuel injectors.Fuel pressure that has
dropped to 0 psi on a cooled down vehicle
(engine off) is a normal condition.When the elec-
tric fuel pump is activated, fuel pressure should
immediately(1±2 seconds) rise to specification.
Abnormally long periods of cranking to restart a
hotengine that has been shut down for a short
period of time may be caused by:
²Fuel pressure bleeding past a fuel injector(s).
²Fuel pressure bleeding past the check valve in
the fuel pump module.
(1) Disconnect the fuel inlet line at fuel rail. Refer
to Fuel Tubes/Lines/Hoses and Clamps for proce-
dures. On some engines, air cleaner housing removal
may be necessary before fuel line disconnection.
(2) Obtain correct Fuel Line Pressure Test Adapter
Tool Hose. Tool number 6539 is used for 5/16º fuel
lines and tool number 6631 is used for 3/8º fuel lines.
(3) Connect correct Fuel Line Pressure Test
Adapter Tool Hose between disconnected fuel line
and fuel rail (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1 Connecting Adapter ToolÐTypical
1 - VEHICLE FUEL LINE
2 - TEST PORT ªTº
3 - SPECIAL TOOL 6923, 6631, 6541 OR 6539
4 - FUEL PRESSURE TEST GAUGE
5 - FUEL LINE CONNECTION AT RAIL
6 - FUEL RAIL
14 - 2 FUEL DELIVERY - GASOLINEBR/BE