power systems DODGE RAM 2002 Service Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2002, Model line: RAM, Model: DODGE RAM 2002Pages: 2255, PDF Size: 62.07 MB
Page 669 of 2255

DESCRIPTION - SECTION IDENTIFICATION AND
INFORMATION
The wiring diagrams are grouped into individual
sections. If a component is most likely found in a par-
ticular group, it will be shown complete (all wires,
connectors, and pins) within that group. For exam-
ple, the Auto Shutdown Relay is most likely to be
found in Group 30, so it is shown there complete. It
can, however, be shown partially in another group if
it contains some associated wiring.
Splice diagrams in Section 8W-70 show the entire
splice and provide references to other sections the
splices serves. Section 8W-70 only contains splice dia-
grams that are not shown in their entirety some-
where else in the wiring diagrams.
Section 8W-80 shows each connector and the cir-
cuits involved with that connector. The connectors
are identified using the name/number on the dia-
gram pages.
WIRING SECTION CHART
GROUP TOPIC
8W-01 thru
8W-09General information and Diagram
Overview
8W-10 thru
8W-19Main Sources of Power and
Vehicle Grounding
8W-20 thru
8W-29Starting and Charging
8W-30 thru
8W-39Powertrain/Drivetrain Systems
GROUP TOPIC
8W-40 thru
8W-49Body Electrical items and A/C
8W-50 thru
8W-59Exterior Lighting, Wipers and
Trailer Tow
8W-60 thru
8W-69Power Accessories
8W-70 Splice Information
8W-80 Connector Pin Outs
8W-91 Connector, Ground and Splice
Locations
DESCRIPTION - CONNECTOR, GROUND AND
SPLICE INFORMATION
CAUTION: Not all connectors are serviced. Some
connectors are serviced only with a harness. A typ-
ical example might be the Supplemental Restraint
System connectors. Always check parts availability
before attempting a repair.
IDENTIFICATION
In-line connectors are identified by a number, as
follows:
²In-line connectors located in the engine compart-
ment are C100 series numbers
²In-line connectors located in the Instrument
Panel area are C200 series numbers.
²In-line connectors located in the body are C300
series numbers.
²Jumper harness connectors are C400 series
numbers.
²Grounds and ground connectors are identified
with a ªGº and follow the same series numbering as
the in-line connectors.
²Splices are identified with an ªSº and follow the
same series numbering as the in-line connectors.
²Component connectors are identified by the com-
ponent name instead of a number. Multiple connec-
tors on a component use a C1, C2, etc. identifier.
LOCATIONS
Section 8W-91 contains connector/ground/splice
location illustrations. The illustrations contain the
connector name (or number)/ground number/splice
number and component identification. Connector/
ground/splice location charts in section 8W-91 refer-
ence the figure numbers of the illustrations.
The abbreviation T/O is used in the component
location section to indicate a point in which the wir-
ing harness branches out to a component. The abbre-
viation N/S means Not Shown in the illustrations
Fig. 4 WIRE CODE IDENTIFICATION
1 - COLOR OF WIRE (LIGHT BLUE WITH YELLOW TRACER
2 - GAGE OF WIRE (18 GAGE)
3 - PART OF MAIN CIRCUIT (VARIES DEPENDING ON
EQUIPMENT)
4 - MAIN CIRCUIT IDENTIFICATION
8W - 01 - 6 8W-01 WIRING DIAGRAM INFORMATIONBR/BE
WIRING DIAGRAM INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 1060 of 2255

8W-97 POWER DISTRIBUTION
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
POWER DISTRIBUTION
DESCRIPTION..........................1
OPERATION............................1
SPECIAL TOOLS
POWER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS.........2
CIGAR LIGHTER OUTLET
DESCRIPTION..........................2
OPERATION............................2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CIGAR LIGHTER
OUTLET.............................2
REMOVAL.............................3
INSTALLATION..........................4
CIRCUIT BREAKER
DESCRIPTION..........................4
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CIRCUIT
BREAKER............................4
GENERATOR CARTRIDGE FUSE
DESCRIPTION..........................4
OPERATION............................4
REMOVAL.............................4
INSTALLATION..........................4
IOD FUSE
DESCRIPTION..........................5
OPERATION............................5
REMOVAL.............................6
INSTALLATION..........................6
JUNCTION BLOCK
DESCRIPTION..........................6
OPERATION............................7
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - JUNCTION
BLOCK..............................7
REMOVAL.............................7
INSTALLATION..........................8POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER
DESCRIPTION..........................8
OPERATION............................8
REMOVAL.............................8
INSTALLATION.........................10
POWER OUTLET
DESCRIPTION.........................10
OPERATION...........................10
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER OUTLET . 10
REMOVAL.............................11
INSTALLATION.........................11
HORN RELAY
DESCRIPTION.........................12
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HORN RELAY . . . 12
REMOVAL.............................12
INSTALLATION.........................12
HEADLAMP RELAY
DESCRIPTION.........................13
REMOVAL.............................13
INSTALLATION.........................13
MICRO-RELAY
DESCRIPTION.........................13
OPERATION...........................14
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - MICRO-RELAY . . 14
REMOVAL.............................14
INSTALLATION.........................14
RELAY
DESCRIPTION.........................14
OPERATION...........................14
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - RELAY.........15
REMOVAL.............................15
INSTALLATION.........................15
POWER DISTRIBUTION
DESCRIPTION
This group covers the various standard and
optional power distribution components used on this
model. The power distribution system for this vehicle
consists of the following components:
²Power Distribution Center (PDC)
²Junction Block (JB).
The power distribution system also incorporates
various types of circuit control and protection fea-
tures, including:
²Automatic resetting circuit breakers
²Blade-type fuses²Cartridge fuses
²Circuit splice blocks
²Flashers
²Relays.
Following are general descriptions of the major
components in the power distribution system. See the
owner's manual in the vehicle glove box for more
information on the features and use of all of the
power distribution system components. Refer toWir-
ing Diagramsfor complete circuit diagrams for the
various power distribution system components.
OPERATION
The power distribution system for this vehicle is
designed to provide safe, reliable, and centralized dis-
BR/BE8W-97 POWER DISTRIBUTION 8W - 97 - 1
Page 1061 of 2255

tribution points for the electrical current required to
operate all of the many standard and optional facto-
ry-installed electrical and electronic powertrain,
chassis, safety, security, comfort and convenience sys-
tems. At the same time, the power distribution sys-
tem was designed to provide ready access to these
electrical distribution points for the vehicle techni-
cian to use when conducting diagnosis and repair of
faulty circuits. The power distribution system can
also prove useful for the sourcing of additional elec-
trical circuits that may be required to provide the
electrical current needed to operate many accessories
that the vehicle owner may choose to have installed
in the aftermarket.
SPECIAL TOOLS
POWER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS
CIGAR LIGHTER OUTLET
DESCRIPTION
A cigar lighter is standard equipment on this
model. The cigar lighter is installed in the instru-
ment panel next to the ash receiver, which is located
near the center of the instrument panel, below the
radio. The cigar lighter base is secured by a snap fit
within the instrument panel.
The cigar lighter knob and heating element unit,
and the cigar lighter receptacle unit are available for
service. These components cannot be repaired and, if
faulty or damaged, they must be replaced.
OPERATION
The cigar lighter consists of two major components:
a knob and heating element unit, and the cigar
lighter base or receptacle shell. The receptacle shell
is connected to ground, and an insulated contact in
the bottom of the shell is connected to battery cur-
rent. The cigar lighter receives battery voltage from afuse in the junction block only when the ignition
switch is in the Accessory or On positions.
The knob and heating element are encased within
a spring-loaded housing, which also features a sliding
protective heat shield. When the knob and heating
element are inserted in the receptacle shell, the heat-
ing element resistor coil is grounded through its
housing to the receptacle shell. If the cigar lighter
knob is pushed inward, the heat shield slides up
toward the knob exposing the heating element, and
the heating element extends from the housing toward
the insulated contact in the bottom of the receptacle
shell.
Two small spring-clip retainers are located on
either side of the insulated contact inside the bottom
of the receptacle shell. These clips engage and hold
the heating element against the insulated contact
long enough for the resistor coil to heat up. When the
heating element is engaged with the contact, battery
current can flow through the resistor coil to ground,
causing the resistor coil to heat.
When the resistor coil becomes sufficiently heated,
excess heat radiates from the heating element caus-
ing the spring-clips to expand. Once the spring-clips
expand far enough to release the heating element,
the spring-loaded housing forces the knob and heat-
ing element to pop back outward to their relaxed
position. When the cigar lighter knob and element
are pulled out of the receptacle shell, the protective
heat shield slides downward on the housing so that
the heating element is recessed and shielded around
its circumference for safety.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CIGAR LIGHTER
OUTLET
For complete circuit diagrams, refer toCigar
Lighterin Wiring Diagrams.
WARNING: REFER TO THE PASSIVE RESTRAINT
SECTION OF THE SERVICE MANUAL BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. FAILURE TO TAKE THE
PROPER PRECAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCI-
DENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE
PERSONAL INJURY.
(1) Check the fused ignition switch output (run/ac-
cessory) fuse in the junction block. If OK, go to Step
2. If not OK, repair the shorted circuit or component
as required and replace the faulty fuse.
(2) Turn the ignition switch to the On position.
Check for battery voltage at the fused ignition switch
output (run/accessory) fuse in the junction block. If
OK, go to Step 3. If not OK, repair the open fused
Terminal Pick Kit 6680
8W - 97 - 2 8W-97 POWER DISTRIBUTIONBR/BE
POWER DISTRIBUTION (Continued)
Page 1065 of 2255

If a vehicle will be stored for more than about thirty
days, the battery negative cable should be discon-
nected to eliminate normal IOD; and, the battery
should be tested and recharged at regular intervals
during the vehicle storage period to prevent the bat-
tery from becoming discharged or damaged. Refer to
theBatterysection of the service manual for the
location of additional service information covering
the battery.
REMOVAL
The Ignition-Off Draw (IOD) fuse is disconnected
from Junction Block (JB) fuse cavity 12 when the
vehicle is shipped from the assembly plant. Dealer
personnel must reconnect the IOD fuse when the
vehicle is being prepared for delivery in order to
restore full electrical system operation.
(1) Turn the ignition switch to the Off position.
(2) Remove the fuse access panel by unsnapping it
from the left outboard end of the instrument panel.
(3) Grasp the upper and lower tabs of the IOD
fuse holder unit in fuse cavity 12 (Fig. 4) of the JB
between the thumb and forefinger and pull the unit
firmly outward.
(4) Install the fuse access panel by snapping it
onto the left outboard end of the instrument panel.
INSTALLATION
The Ignition-Off Draw (IOD) fuse is disconnected
from Junction Block (JB) fuse cavity 12 when the
vehicle is shipped from the assembly plant. Dealer
personnel must reconnect the IOD fuse when the
vehicle is being prepared for delivery in order to
restore full electrical system operation.
(1) Turn the ignition switch to the Off position.
(2) To install the IOD fuse, use a thumb to press
the IOD fuse holder unit in fuse cavity 12 firmly into
the JB.
(3) Install the fuse access panel by snapping it
onto the left outboard end of the instrument panel.
JUNCTION BLOCK
DESCRIPTION
An electrical Junction Block (JB) is concealed
behind the left outboard end of the instrument panel
cover (Fig. 5). The JB combines the functions previ-
ously provided by a separate fuseblock module and
relay center, serves to simplify and centralize numer-
ous electrical components, and to distribute electrical
current to many of the accessory systems in the vehi-
cle. It also eliminates the need for numerous splice
connections and serves in place of a bulkhead connec-
Fig. 4 Ignition-Off Draw Fuse
1 - JUNCTION BLOCK
2 - IGNITION-OFF DRAW FUSE AND HOLDER
3 - LEFT INSTRUMENT PANEL END BRACKETFig. 5 Junction Block Location
1 - JUNCTION BLOCK
2 - FUSE ACCESS PANEL
8W - 97 - 6 8W-97 POWER DISTRIBUTIONBR/BE
IOD FUSE (Continued)
Page 1281 of 2255

(4) Connect the DRBIIItto the pressure trans-
ducer following the instructions supplied with the
DRB IIIt.
(5) Enter DRBIIItinto pressure reading mode and
test drive vehicle.
(6) The turbocharger boost pressure must be
between 110 - 138 kpa (16 - 20 psi.). If pressure read-
ings are lower than 110 kpa (16 psi.) inspect for the
following:
²Restricted air inlet system
²Leak in the charge air cooler system (Refer to 11
- EXHAUST SYSTEM/TURBOCHARGER SYSTEM/
CHARGE AIR COOLER AND PLUMBING - DIAG-
NOSIS AND TESTING)
²Turbocharger wastegate broken or misadjusted
²Turbocharger damaged (Refer to 11 - EXHAUST
SYSTEM/TURBOCHARGER SYSTEM/TURBO-
CHARGER - INSPECTION)
TURBOCHARGER
DESCRIPTION
The turbocharger is an exhaust-driven super-
charger which increases the pressure and density of
the air entering the engine. With the increase of air
entering the engine, more fuel can be injected into
the cylinders, which creates more power during com-
bustion.
The turbocharger assembly consists of four (4)
major component systems (Fig. 19) (Fig. 20) :
²Turbine section
²Compressor section
²Bearing housing
²Wastegate
OPERATION
Exhaust gas pressure and energy drive the tur-
bine, which in turn drives a centrifugal compressor
that compresses the inlet air, and forces the air into
the engine through the charge air cooler and plumb-
ing. Since heat is a by-product of this compression,
the air must pass through a charge air cooler to cool
the incoming air and maintain power and efficiency.
Increasing air flow to the engine provides:
²Improved engine performance
²Lower exhaust smoke density
²Improved operating economy
²Altitude compensation
²Noise reduction.
The turbocharger also uses a wastegate (Fig. 21) ,
which regulates intake manifold air pressure and
prevents over boosting at high engine speeds. When
the wastegate valve is closed, all of the exhaust gases
flow through the turbine wheel. As the intake mani-
fold pressure increases, the wastegate actuator opensthe valve, diverting some of the exhaust gases away
from the turbine wheel. This limits turbine shaft
speed and air output from the impeller.
Fig. 19 Turbocharger Operation
1 - TURBINE SECTION
2 - EXHAUST GAS
3 - BEARING HOUSING
4 - COMPRESSOR SECTION
5 - INLET AIR
6 - COMPRESSED AIR TO ENGINE
7 - EXHAUST GAS
8 - EXHAUST GAS TO EXHAUST PIPE
Fig. 20 Turbocharger Wastegate Actuator
1 - TURBOCHARGER
2 - DIAPHRAGM
3 - WASTE GATE ACTUATOR
11 - 14 EXHAUST SYSTEMBR/BE
TURBOCHARGER SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 1301 of 2255

FUEL DELIVERY - GASOLINE
DESCRIPTION - FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM
The fuel delivery system consists of:
²the fuel pump module containing the electric
fuel pump, fuel filter/fuel pressure regulator, rollover
valve (certain modules), fuel gauge sending unit (fuel
level sensor) and a separate fuel filter located at bot-
tom of pump module
²fuel tubes/lines/hoses
²quick-connect fittings
²fuel injector rail
²fuel injectors
²fuel tank
²fuel tank filler/vent tube assembly
²fuel tank filler tube cap
²accelerator pedal
²throttle cable
OPERATION - FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM
Fuel is returned through the fuel pump module
and back into the fuel tank through the fuel filter/
fuel pressure regulator. A separate fuel return line
from the engine to the tank is not used with any gas-
oline powered engine.
The fuel tank assembly consists of: the fuel tank,
fuel pump module assembly, fuel pump module lock-
nut/gasket and fuel tank check valve(s) (refer to 25,
Emission Control System for Fuel Tank Check Valve
information).
A fuel filler/vent tube assembly using a pressure/
vacuum, 1/4 turn fuel filler cap is used. The fuel
filler tube contains a flap door located below the fuel
fill cap.
Also to be considered part of the fuel system is the
evaporation control system. This is designed to
reduce the emission of fuel vapors into the atmo-
sphere. The description and function of the Evapora-
tive Control System is found in 25, Emission Control
Systems.
Both fuel filters (at bottom of fuel pump module
and within fuel pressure regulator) are designed for
extended service. They do not require normal sched-
uled maintenance. Filters should only be replaced if
a diagnostic procedure indicates to do so.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL PRESSURE
LEAK DOWN TEST
Use this test in conjunction with the Fuel Pump
Pressure Test and Fuel Pump Capacity Test.
Check Valve Operation:The electric fuel pump
outlet contains a one-way check valve to prevent fuel
flow back into the tank and to maintain fuel supply
line pressure (engine warm) when pump is not oper-
ational. It is also used to keep the fuel supply linefull of gasoline when pump is not operational. After
the vehicle has cooled down, fuel pressure may drop
to 0 psi (cold fluid contracts), but liquid gasoline will
remain in fuel supply line between the check valve
and fuel injectors.Fuel pressure that has
dropped to 0 psi on a cooled down vehicle
(engine off) is a normal condition.When the elec-
tric fuel pump is activated, fuel pressure should
immediately(1±2 seconds) rise to specification.
Abnormally long periods of cranking to restart a
hotengine that has been shut down for a short
period of time may be caused by:
²Fuel pressure bleeding past a fuel injector(s).
²Fuel pressure bleeding past the check valve in
the fuel pump module.
(1) Disconnect the fuel inlet line at fuel rail. Refer
to Fuel Tubes/Lines/Hoses and Clamps for proce-
dures. On some engines, air cleaner housing removal
may be necessary before fuel line disconnection.
(2) Obtain correct Fuel Line Pressure Test Adapter
Tool Hose. Tool number 6539 is used for 5/16º fuel
lines and tool number 6631 is used for 3/8º fuel lines.
(3) Connect correct Fuel Line Pressure Test
Adapter Tool Hose between disconnected fuel line
and fuel rail (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1 CONNECTING ADAPTER TOOLÐTYPICAL
1 - VEHICLE FUEL LINE
2 - TEST PORT ªTº
3 - SPECIAL TOOL 6923, 6631, 6541 OR 6539
4 - FUEL PRESSURE TEST GAUGE
5 - FUEL LINE CONNECTION AT RAIL
6 - FUEL RAIL
14 - 2 FUEL DELIVERY - GASOLINEBR/BE
Page 1308 of 2255

FUEL PUMP
DESCRIPTION
The electric fuel pump is located inside of the fuel
pump module. A 12 volt, permanent magnet, electric
motor powers the fuel pump. The electric fuel pump
is not a separate, serviceable component.
OPERATION
Voltage to operate the electric pump is supplied
through the fuel pump relay.
Fuel is drawn in through a filter at the bottom of
the module and pushed through the electric motor
gearset to the pump outlet.
Check Valve Operation:The pump outlet con-
tains a one-way check valve to prevent fuel flow back
into the tank and to maintain fuel supply line pres-
sure (engine warm) when pump is not operational. It
is also used to keep the fuel supply line full of gaso-
line when pump is not operational. After the vehicle
has cooled down, fuel pressure may drop to 0 psi
(cold fluid contracts), but liquid gasoline will remain
in fuel supply line between the check valve and fuel
injectors.Fuel pressure that has dropped to 0
psi on a cooled down vehicle (engine off) is a
normal condition.Refer to the Fuel Pressure Leak
Down Test for more information.
The electric fuel pump is not a separate, service-
able component.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL PUMP
CAPACITY TEST
Before performing this test, verify fuel pump
pressure. Refer to Fuel Pump Pressure Test.
Use this test in conjunction with the Fuel Pres-
sure Leak Down Test.
(1) Release fuel system pressure. Refer to Fuel
Pressure Release Procedure.
(2) Disconnect fuel supply line at fuel rail. Refer to
Quick-Connect Fittings. Some engines may require
air cleaner housing removal before line disconnection.
(3) Obtain correct Fuel Line Pressure Test Adapter
Tool Hose. Tool number 6539 is used for 5/16º fuel
lines and tool number 6631 is used for 3/8º fuel lines.
(4) Connect correct Fuel Line Pressure Test
Adapter Tool Hose into disconnected fuel supply line.
Insert other end of Adaptor Tool Hose into a gradu-
ated container.
(5) Remove fuel fill cap.
(6) To activate fuel pump and pressurize system,
obtain DRBtscan tool and actuate ASD Fuel System
Test.(7) A good fuel pump will deliver at least 1/4 liter
of fuel in 7 seconds. Do not operate fuel pump for
longer than 7 seconds with fuel line disconnected as
fuel pump module reservoir may run empty.
(a) If capacity is lower than specification, but
fuel pump can be heard operating through fuel fill
cap opening, check for a kinked/damaged fuel sup-
ply line somewhere between fuel rail and fuel
pump module.
(b) If line is not kinked/damaged, and fuel pres-
sure is OK, but capacity is low, replace fuel filter/
fuel pressure regulator. The filter/regulator may be
serviced separately on certain applications. Refer
to Fuel Filter/Fuel Pressure Regulator Removal/In-
stallation for additional information.
(c) If both fuel pressure and capacity are low,
replace fuel pump module assembly. Refer to Fuel
Pump Module Removal/Installation.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL PUMP
PRESSURE TEST
Use this test in conjunction with the Fuel Pump
Capacity Test, Fuel Pressure Leak Down Test and
Fuel Pump Amperage Test found elsewhere in this
group.
Check Valve Operation:The electric fuel pump
outlet contains a one-way check valve to prevent fuel
flow back into the tank and to maintain fuel supply
line pressure (engine warm) when pump is not oper-
ational. It is also used to keep the fuel supply line
full of gasoline when pump is not operational. After
the vehicle has cooled down, fuel pressure may drop
to 0 psi (cold fluid contracts), but liquid gasoline will
remain in fuel supply line between the check valve
and fuel injectors.Fuel pressure that has
dropped to 0 psi on a cooled down vehicle
(engine off) is a normal condition.When the elec-
tric fuel pump is activated, fuel pressure should
immediately(1±2 seconds) rise to specification.
All fuel systems are equipped with a fuel tank
module mounted, combination fuel filter/fuel pressure
regulator. The fuel pressure regulator is not con-
trolled by engine vacuum.
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER CON-
STANT FUEL PRESSURE EVEN WITH THE ENGINE
OFF. BEFORE DISCONNECTING FUEL LINE AT
FUEL RAIL, THIS PRESSURE MUST BE RELEASED.
REFER TO THE FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE
RELEASE PROCEDURE.
(1) Remove protective cap at fuel rail test port.
Connect the 0±414 kPa (0-60 psi) fuel pressure gauge
(from gauge set 5069) to test port pressure fitting on
fuel rail (Fig. 11).The DRBtIII Scan Tool along
with the PEP module, the 500 psi pressure
BR/BEFUEL DELIVERY - GASOLINE 14 - 9
Page 1345 of 2255

around 70ÉF, the resistance of the heating element is
approximately 4.5 ohms. As the sensor's temperature
increases, resistance in the heater element increases.
This allows the heater to maintain the optimum
operating temperature of approximately 930É-1100ÉF
(500É-600É C). Although the sensors operate the
same, there are physical differences, due to the envi-
ronment that they operate in, that keep them from
being interchangeable.
Maintaining correct sensor temperature at all
times allows the system to enter into closed loop
operation sooner. Also, it allows the system to remain
in closed loop operation during periods of extended
idle.
In Closed Loop operation, the PCM monitors cer-
tain O2 sensor input(s) along with other inputs, and
adjusts the injector pulse width accordingly. During
Open Loop operation, the PCM ignores the O2 sensor
input. The PCM adjusts injector pulse width based
on preprogrammed (fixed) values and inputs from
other sensors.
Upstream Sensors:Two upstream sensors are
used (1/1 and 2/1). The 1/1 sensor is the first sensor
to receive exhaust gases from the #1 cylinder. They
provide an input voltage to the PCM. The input tells
the PCM the oxygen content of the exhaust gas. The
PCM uses this information to fine tune fuel delivery
to maintain the correct oxygen content at the down-
stream oxygen sensors. The PCM will change the air/
fuel ratio until the upstream sensors input a voltage
that the PCM has determined will make the down-
stream sensors output (oxygen content) correct.
The upstream oxygen sensors also provide an input
to determine mini-catalyst efficiency. Main catalytic
convertor efficiency is not calculated with this pack-
age.
Downstream Sensors:Two downstream sensors
are used (1/2 and 2/2). The downstream sensors are
used to determine the correct air-fuel ratio. As the
oxygen content changes at the downstream sensor,
the PCM calculates how much air-fuel ratio change is
required. The PCM then looks at the upstream oxy-
gen sensor voltage, and changes fuel delivery until
the upstream sensor voltage changes enough to cor-
rect the downstream sensor voltage (oxygen content).
The downstream oxygen sensors also provide an
input to determine mini-catalyst efficiency. Main cat-
alytic convertor efficiency is not calculated with this
package.
Medium and Heavy Duty 8.0L V-10 Engine:
Four oxygen sensors are used (2 upstream, 1 pre-cat-
alyst and 1 post-catalyst). The upstream sensors (1/1
and 2/1) will fine-tune the air-fuel ratio through the
Powertrain Control Module (PCM). The pre-catalyst
(1/2) and post-catalyst (1/3) sensors will determine
catalytic convertor efficiency (efficiency of the maincatalytic convertor). This is also done through the
PCM.
Heavy Duty 5.9L Engine:Downstream sensors
are not used with this emissions package, meaning
catalytic convertor efficiency is not calculated with
this package. Two upstream sensors are used. The
left upstream sensor (1/1) will monitor cylinders 1, 3,
5 and 7. The right upstream sensor (2/1) will monitor
cylinders 2, 4, 6 and 8. The PCM monitors the oxy-
gen content of the sensors, and will fine-tune the air-
fuel ratio.
Engines equipped with either a downstream sen-
sor(s), or a post-catalytic sensor, will monitor cata-
lytic convertor efficiency. If efficiency is below
emission standards, the Malfunction Indicator Lamp
(MIL) will be illuminated and a Diagnostic Trouble
Code (DTC) will be set. Refer to Monitored Systems
in Emission Control Systems for additional informa-
tion.
REMOVAL
Never apply any type of grease to the oxygen
sensor electrical connector, or attempt any sol-
dering of the sensor wiring harness.
The O2S (oxygen sensors) are numbered 1/1, 1/2,
1/3, 2/1 and 2/2.
On HDC engines, the pre-catalyst/post catalyst
O2S sensors are located at the inlet and outlet ends
of the catalytic converter (Fig. 38).
The 1/1 and 2/1 sensors are located before the
mini-cats (Fig. 39). The 1/2 and 2/2 sensors are
located after the mini-cats (Fig. 39).
WARNING: THE EXHAUST MANIFOLD, EXHAUST
PIPES AND CATALYTIC CONVERTER BECOME
VERY HOT DURING ENGINE OPERATION. ALLOW
ENGINE TO COOL BEFORE REMOVING OXYGEN
SENSOR.
Fig. 38 Pre-catalyst/Post catalyst Oxygen SensorsÐ
HDC Engines
1 - POST CATALYST OXYGEN SENSOR (1/3)
2 - PRE-CATALYST OXYGEN SENSOR (1/2)
14 - 46 FUEL INJECTION - GASOLINEBR/BE
O2 SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1390 of 2255

FUEL INJECTION - DIESEL
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
FUEL INJECTION - DIESEL
DESCRIPTION - DIESEL FUEL INJECTION
SYSTEM............................91
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BOOST
PRESSURE..........................93
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE - DIESEL ENGINE.............94
ACCELERATOR PEDAL POSITION SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................95
OPERATION...........................95
REMOVAL.............................95
INSTALLATION.........................97
FUEL INJECTOR
DESCRIPTION.........................97
OPERATION...........................98
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐFUEL INJECTOR
TEST...............................99
REMOVAL............................101
INSTALLATION........................102
FUEL INJECTION PUMP RELAY
DESCRIPTION........................103
OPERATION..........................103
FUEL TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION........................104
OPERATION..........................104
INTAKE AIR HEATER
DESCRIPTION........................104OPERATION..........................104
REMOVAL............................104
INSTALLATION........................105
INTAKE AIR HEATER RELAY
DESCRIPTION........................105
OPERATION..........................105
REMOVAL............................106
INSTALLATION........................106
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION - DIESEL.................106
OPERATION - DIESEL..................106
REMOVAL - DIESEL....................107
INSTALLATION - DIESEL................107
MAP SENSOR
DESCRIPTION - DIESEL.................108
OPERATION - DIESEL..................108
REMOVAL - DIESEL....................108
INSTALLATION........................108
PTO SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
OPERATION........................108
THROTTLE CONTROL CABLE
REMOVAL............................109
INSTALLATION........................110
FUEL INJECTION - DIESEL
DESCRIPTION - DIESEL FUEL INJECTION
SYSTEM
The Engine Control Module (ECM) and Fuel Injec-
tion Pump Control Module (FPCM) are used prima-
rily for fuel system control. The ECM is a separate
replaceable component, while the FPCM is internal
to the fuel injection pump and is a non-serviceable
part. The ECM and FPCM are interconnected (wired
together) for fuel injection control.The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) is used to
regulate or control the A/C, charging and speed con-
trol systems. It is also used to partially control cer-
tain electronic automatic transmission components.
The PCM also has control over certain instrument
panel components.
Refer to either Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
or Engine Control Module (ECM) for additional infor-
mation. Refer to (Fig. 1) for a partial list of fuel sys-
tem components.
BR/BEFUEL INJECTION - DIESEL 14 - 91
Page 1411 of 2255
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER STEERING SYSTEM
STEERING NOISE
There is some noise in all power steering systems. One of the most common is a hissing sound evident at a
standstill parking. Or when the steering wheel is at the end of it's travel. Hiss is a high frequency noise similar
to that of a water tap being closed slowly. The noise is present in all valves that have a high velocity fluid passing
through an orifice. There is no relationship between this noise and steering performance.
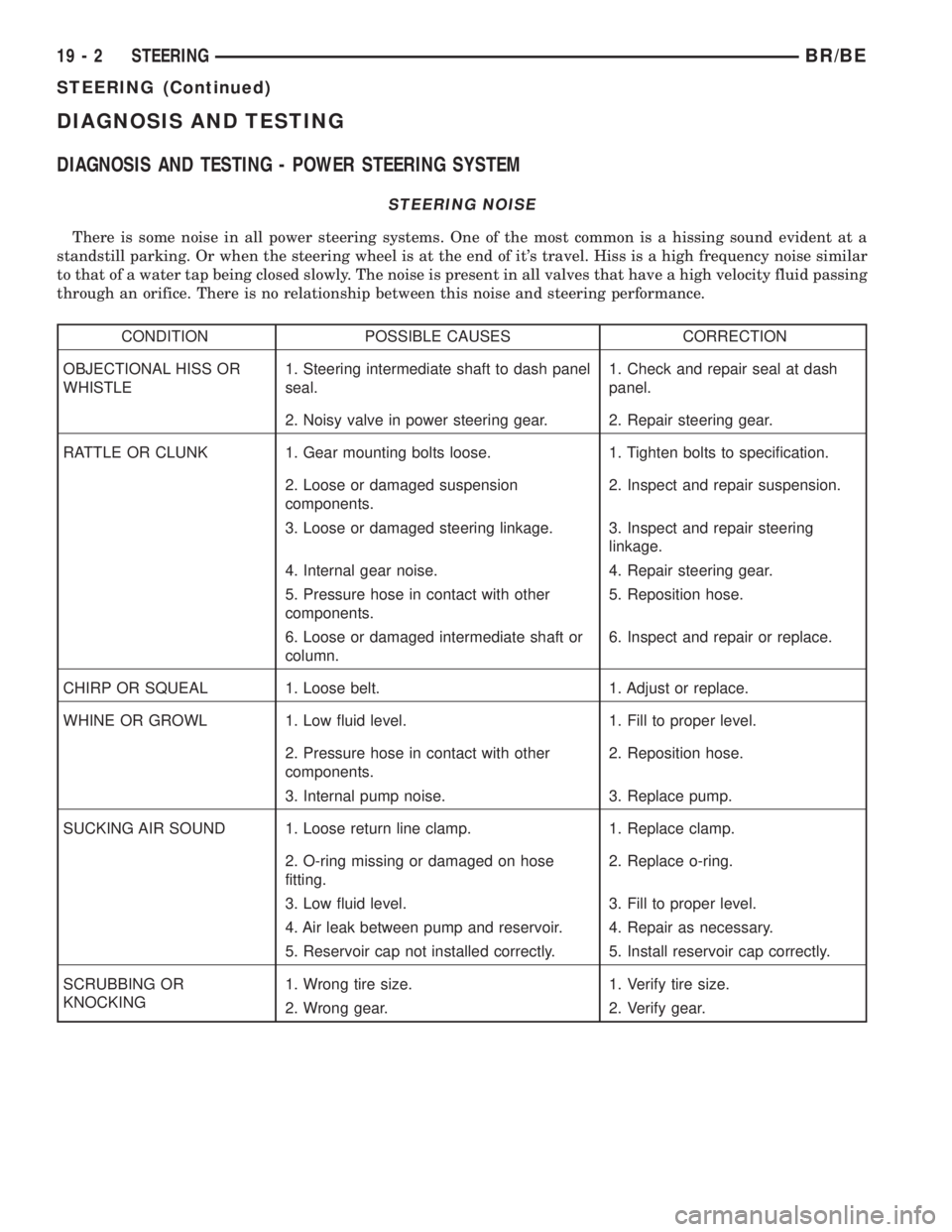
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
OBJECTIONAL HISS OR
WHISTLE1. Steering intermediate shaft to dash panel
seal.1. Check and repair seal at dash
panel.
2. Noisy valve in power steering gear. 2. Repair steering gear.
RATTLE OR CLUNK 1. Gear mounting bolts loose. 1. Tighten bolts to specification.
2. Loose or damaged suspension
components.2. Inspect and repair suspension.
3. Loose or damaged steering linkage. 3. Inspect and repair steering
linkage.
4. Internal gear noise. 4. Repair steering gear.
5. Pressure hose in contact with other
components.5. Reposition hose.
6. Loose or damaged intermediate shaft or
column.6. Inspect and repair or replace.
CHIRP OR SQUEAL 1. Loose belt. 1. Adjust or replace.
WHINE OR GROWL 1. Low fluid level. 1. Fill to proper level.
2. Pressure hose in contact with other
components.2. Reposition hose.
3. Internal pump noise. 3. Replace pump.
SUCKING AIR SOUND 1. Loose return line clamp. 1. Replace clamp.
2. O-ring missing or damaged on hose
fitting.2. Replace o-ring.
3. Low fluid level. 3. Fill to proper level.
4. Air leak between pump and reservoir. 4. Repair as necessary.
5. Reservoir cap not installed correctly. 5. Install reservoir cap correctly.
SCRUBBING OR
KNOCKING1. Wrong tire size. 1. Verify tire size.
2. Wrong gear. 2. Verify gear.
19 - 2 STEERINGBR/BE
STEERING (Continued)