mileage DODGE RAM 2002 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2002, Model line: RAM, Model: DODGE RAM 2002Pages: 2255, PDF Size: 62.07 MB
Page 194 of 2255

CAUTION: Never use gasoline, kerosene, alcohol,
motor oil, transmission fluid, or any fluid containing
mineral oil to clean the system components. These
fluids damage rubber cups and seals. Use only
fresh brake fluid or Mopar brake cleaner to clean or
flush brake system components. These are the only
cleaning materials recommended. If system contam-
ination is suspected, check the fluid for dirt, discol-
oration, or separation into distinct layers. Also
check the reservoir cap seal for distortion. Drain
and flush the system with new brake fluid if con-
tamination is suspected.
CAUTION: Use Mopar brake fluid, or an equivalent
quality fluid meeting SAE/DOT standards J1703 and
DOT 3. Brake fluid must be clean and free of con-
taminants. Use fresh fluid from sealed containers
only to ensure proper antilock component opera-
tion.
CAUTION: Use Mopar multi-mileage or high temper-
ature grease to lubricate caliper slide surfaces,
drum brake pivot pins, and shoe contact points on
the backing plates. Use multi-mileage grease or GE
661 or Dow 111 silicone grease on caliper slide pins
to ensure proper operation.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BASE BRAKE
SYSTEM
Base brake components consist of the brake shoes,
calipers, wheel cylinders, brake drums, rotors, brake
lines, master cylinder, booster, and parking brake
components.
Brake diagnosis involves determining if the prob-
lem is related to a mechanical, hydraulic, or vacuum
operated component.
The first diagnosis step is the preliminary check.
PRELIMINARY BRAKE CHECK
(1) Check condition of tires and wheels. Damaged
wheels and worn, damaged, or underinflated tires
can cause pull, shudder, vibration, and a condition
similar to grab.
(2) If complaint was based on noise when braking,
check suspension components. Jounce front and rear
of vehicle and listen for noise that might be caused
by loose, worn or damaged suspension or steering
components.
(3) Inspect brake fluid level and condition. Note
that the brake reservoir fluid level will decrease in
proportion to normal lining wear.Also note that
brake fluid tends to darken over time. This is
normal and should not be mistaken for contam-
ination.(a) If fluid level is abnormally low, look for evi-
dence of leaks at calipers, wheel cylinders, brake
lines, and master cylinder.
(b) If fluid appears contaminated, drain out a
sample to examine. System will have to be flushed
if fluid is separated into layers, or contains a sub-
stance other than brake fluid. The system seals
and cups will also have to be replaced after flush-
ing. Use clean brake fluid to flush the system.
(4) Check parking brake operation. Verify free
movement and full release of cables and pedal. Also
note if vehicle was being operated with parking
brake partially applied.
(5) Check brake pedal operation. Verify that pedal
does not bind and has adequate free play. If pedal
lacks free play, check pedal and power booster for
being loose or for bind condition. Do not road test
until condition is corrected.
(6) Check booster vacuum check valve and hose.
(7) If components checked appear OK, road test
the vehicle.
ROAD TESTING
(1) If complaint involved low brake pedal, pump
pedal and note if it comes back up to normal height.
(2) Check brake pedal response with transmission
in Neutral and engine running. Pedal should remain
firm under constant foot pressure.
(3) During road test, make normal and firm brake
stops in 25-40 mph range. Note faulty brake opera-
tion such as low pedal, hard pedal, fade, pedal pulsa-
tion, pull, grab, drag, noise, etc.
(4) Attempt to stop the vehicle with the parking
brake only and note grab, drag, noise, etc.
PEDAL FALLS AWAY
A brake pedal that falls away under steady foot
pressure is generally the result of a system leak. The
leak point could be at a brake line, fitting, hose, or
caliper/wheel cylinder. If leakage is severe, fluid will
be evident at or around the leaking component.
Internal leakage (seal by-pass) in the master cylin-
der caused by worn or damaged piston cups, may
also be the problem cause.
An internal leak in the ABS or RWAL system may
also be the problem with no physical evidence.
LOW PEDAL
If a low pedal is experienced, pump the pedal sev-
eral times. If the pedal comes back up, worn linings,
rotors, drums, or rear brakes out of adjustment are
the most likely causes. The proper course of action is
to inspect and replace all worn component and make
the proper adjustments.
BR/BEBRAKES - BASE 5 - 5
HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL (Continued)
Page 206 of 2255
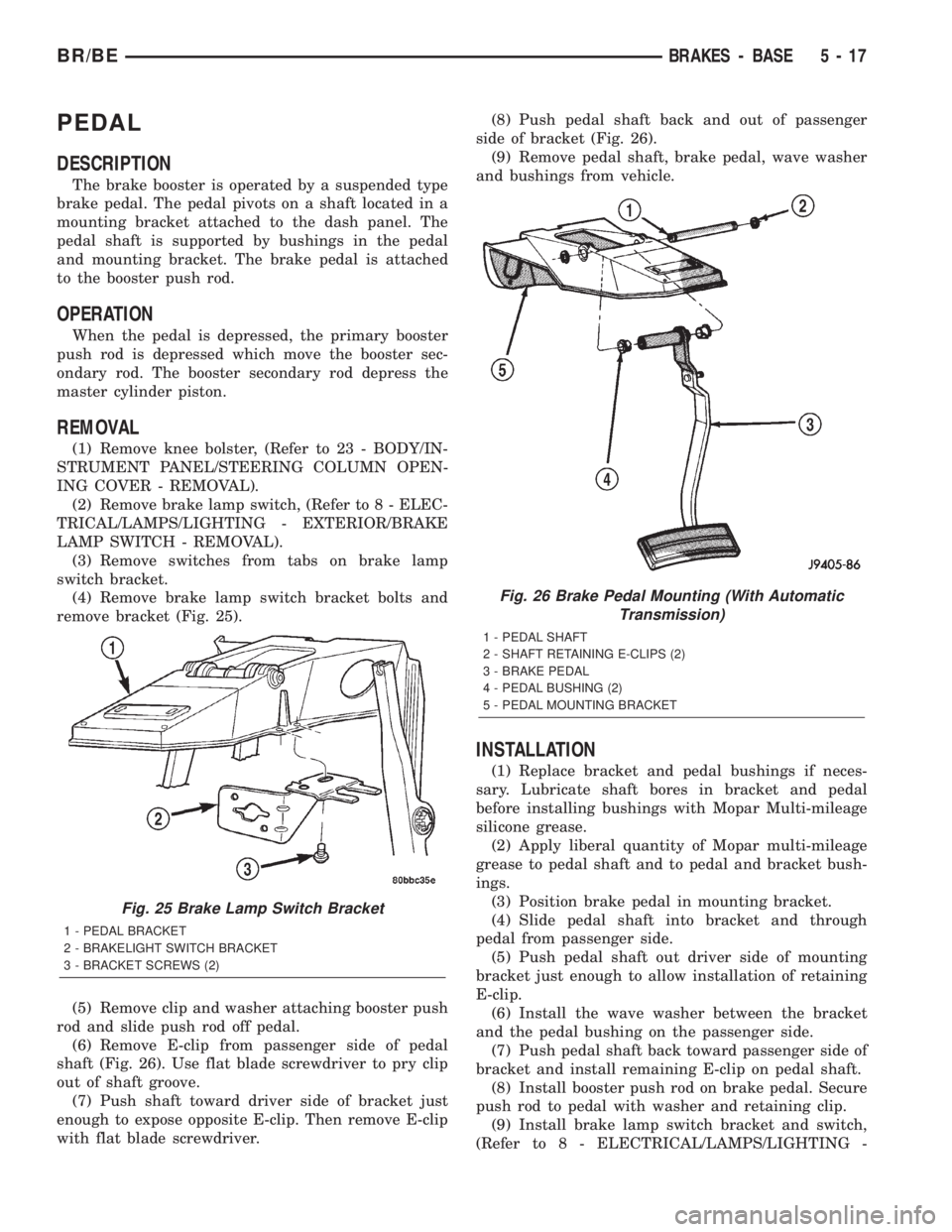
PEDAL
DESCRIPTION
The brake booster is operated by a suspended type
brake pedal. The pedal pivots on a shaft located in a
mounting bracket attached to the dash panel. The
pedal shaft is supported by bushings in the pedal
and mounting bracket. The brake pedal is attached
to the booster push rod.
OPERATION
When the pedal is depressed, the primary booster
push rod is depressed which move the booster sec-
ondary rod. The booster secondary rod depress the
master cylinder piston.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove knee bolster, (Refer to 23 - BODY/IN-
STRUMENT PANEL/STEERING COLUMN OPEN-
ING COVER - REMOVAL).
(2) Remove brake lamp switch, (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR/BRAKE
LAMP SWITCH - REMOVAL).
(3) Remove switches from tabs on brake lamp
switch bracket.
(4) Remove brake lamp switch bracket bolts and
remove bracket (Fig. 25).
(5) Remove clip and washer attaching booster push
rod and slide push rod off pedal.
(6) Remove E-clip from passenger side of pedal
shaft (Fig. 26). Use flat blade screwdriver to pry clip
out of shaft groove.
(7) Push shaft toward driver side of bracket just
enough to expose opposite E-clip. Then remove E-clip
with flat blade screwdriver.(8) Push pedal shaft back and out of passenger
side of bracket (Fig. 26).
(9) Remove pedal shaft, brake pedal, wave washer
and bushings from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Replace bracket and pedal bushings if neces-
sary. Lubricate shaft bores in bracket and pedal
before installing bushings with Mopar Multi-mileage
silicone grease.
(2) Apply liberal quantity of Mopar multi-mileage
grease to pedal shaft and to pedal and bracket bush-
ings.
(3) Position brake pedal in mounting bracket.
(4) Slide pedal shaft into bracket and through
pedal from passenger side.
(5) Push pedal shaft out driver side of mounting
bracket just enough to allow installation of retaining
E-clip.
(6) Install the wave washer between the bracket
and the pedal bushing on the passenger side.
(7) Push pedal shaft back toward passenger side of
bracket and install remaining E-clip on pedal shaft.
(8) Install booster push rod on brake pedal. Secure
push rod to pedal with washer and retaining clip.
(9) Install brake lamp switch bracket and switch,
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/LAMPS/LIGHTING -
Fig. 25 Brake Lamp Switch Bracket
1 - PEDAL BRACKET
2 - BRAKELIGHT SWITCH BRACKET
3 - BRACKET SCREWS (2)
Fig. 26 Brake Pedal Mounting (With Automatic
Transmission)
1 - PEDAL SHAFT
2 - SHAFT RETAINING E-CLIPS (2)
3 - BRAKE PEDAL
4 - PEDAL BUSHING (2)
5 - PEDAL MOUNTING BRACKET
BR/BEBRAKES - BASE 5 - 17
Page 246 of 2255
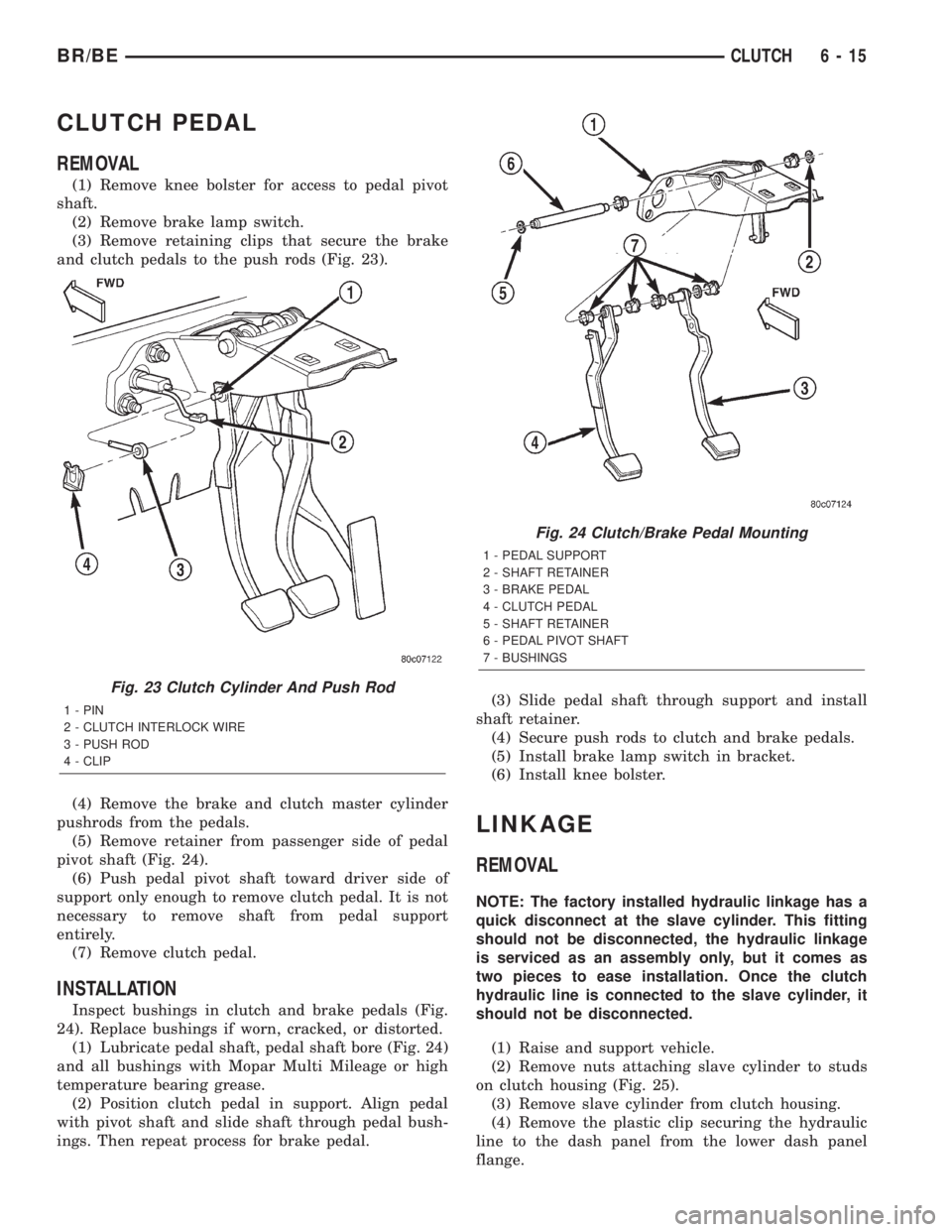
CLUTCH PEDAL
REMOVAL
(1) Remove knee bolster for access to pedal pivot
shaft.
(2) Remove brake lamp switch.
(3) Remove retaining clips that secure the brake
and clutch pedals to the push rods (Fig. 23).
(4) Remove the brake and clutch master cylinder
pushrods from the pedals.
(5) Remove retainer from passenger side of pedal
pivot shaft (Fig. 24).
(6) Push pedal pivot shaft toward driver side of
support only enough to remove clutch pedal. It is not
necessary to remove shaft from pedal support
entirely.
(7) Remove clutch pedal.
INSTALLATION
Inspect bushings in clutch and brake pedals (Fig.
24). Replace bushings if worn, cracked, or distorted.
(1) Lubricate pedal shaft, pedal shaft bore (Fig. 24)
and all bushings with Mopar Multi Mileage or high
temperature bearing grease.
(2) Position clutch pedal in support. Align pedal
with pivot shaft and slide shaft through pedal bush-
ings. Then repeat process for brake pedal.(3) Slide pedal shaft through support and install
shaft retainer.
(4) Secure push rods to clutch and brake pedals.
(5) Install brake lamp switch in bracket.
(6) Install knee bolster.
LINKAGE
REMOVAL
NOTE: The factory installed hydraulic linkage has a
quick disconnect at the slave cylinder. This fitting
should not be disconnected, the hydraulic linkage
is serviced as an assembly only, but it comes as
two pieces to ease installation. Once the clutch
hydraulic line is connected to the slave cylinder, it
should not be disconnected.
(1) Raise and support vehicle.
(2) Remove nuts attaching slave cylinder to studs
on clutch housing (Fig. 25).
(3) Remove slave cylinder from clutch housing.
(4) Remove the plastic clip securing the hydraulic
line to the dash panel from the lower dash panel
flange.
Fig. 23 Clutch Cylinder And Push Rod
1 - PIN
2 - CLUTCH INTERLOCK WIRE
3 - PUSH ROD
4 - CLIP
Fig. 24 Clutch/Brake Pedal Mounting
1 - PEDAL SUPPORT
2 - SHAFT RETAINER
3 - BRAKE PEDAL
4 - CLUTCH PEDAL
5 - SHAFT RETAINER
6 - PEDAL PIVOT SHAFT
7 - BUSHINGS
BR/BECLUTCH 6 - 15
Page 384 of 2255

The PCM can adapt its programming to meet
changing operating conditions.
The PCM receives input signals from various
switches and sensors. Based on these inputs, the
PCM regulates various engine and vehicle operations
through different system components. These compo-
nents are referred to asPCM Outputs.The sensors
and switches that provide inputs to the PCM are con-
sideredPCM Inputs.
NOTE: PCM Inputs:
²A/C request (if equipped with factory A/C)
²A/C select (if equipped with factory A/C)
²Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor (APPS) output
from ECM
²Auto shutdown (ASD) relay sense
²Battery temperature sensor
²Battery voltage
²Brake switch
²CCD bus (+) circuits
²CCD bus (-) circuits
²Crankshaft Position Sensor (CKP) output from
ECM
²Data link connection for DRB scan tool
²Fuel level sensor
²Generator (battery voltage) output
²Ignition sense
²Output shaft speed sensor
²Overdrive/override switch
²Park/neutral switch (auto. trans. only)
²Power ground
²Sensor return
²Signal ground
²Speed control resume switch
²Speed control set switch
²Speed control on/off switch
²Transmission governor pressure sensor
²Transmission temperature sensor
²Vehicle speed inputs from ABS or RWAL system
NOTE: PCM Outputs:
After inputs are received by the PCM, certain sen-
sors, switches and components are controlled or reg-
ulated by the PCM. These are consideredPCM
Outputs.These outputs are for:
²A/C clutch relay and A/C clutch
²Auto shutdown (ASD) relay
²CCD bus (+/-) circuits for: speedometer, voltme-
ter, fuel gauge, oil pressure gauge/lamp, engine temp.
gauge and speed control warn. lamp
²Data link connection for DRB scan tool
²Five volt sensor supply
²Generator field driver (-)
²Generator field driver (+)
²Generator lamp (if equipped)²Malfunction indicator lamp (Check engine lamp)
²Overdrive warning lamp (if equipped)
²Speed control vacuum solenoid
²Speed control vent solenoid
²Tachometer (if equipped)
²Transmission convertor clutch circuit
²Transmission 3±4 shift solenoid
²Transmission relay
²Transmission temperature lamp (if equipped)
²Transmission variable force solenoid (governor
sol.)
OPERATION - 5 VOLT SUPPLIES
Primary 5±volt supply:
²supplies the required 5 volt power source to the
Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor.
²supplies the required 5 volt power source to the
Camshaft Position (CMP) sensor.
²supplies a reference voltage for the Manifold
Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor.
²supplies a reference voltage for the Throttle
Position Sensor (TPS) sensor.
Secondary 5±volt supply:
²supplies the required 5 volt power source to the
oil pressure sensor.
²supplies the required 5 volt power source for the
Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS) (if equipped).
²supplies the 5 volt power source to the transmis-
sion pressure sensor (if equipped with an RE auto-
matic transmission).
OPERATION - IGNITION CIRCUIT SENSE
The ignition circuit sense input tells the PCM the
ignition switch has energized the ignition circuit.
Battery voltage is also supplied to the PCM
through the ignition switch when the ignition is in
the RUN or START position. This is referred to as
the9ignition sense9circuit and is used to9wake up9
the PCM. Voltage on the ignition input can be as low
as 6 volts and the PCM will still function. Voltage is
supplied to this circuit to power the PCM's 8-volt reg-
ulator and to allow the PCM to perform fuel, ignition
and emissions control functions.
REMOVAL
USE THE DRB SCAN TOOL TO REPROGRAM
THE NEW POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE
(PCM) WITH THE VEHICLES ORIGINAL IDEN-
TIFICATION NUMBER (VIN) AND THE VEHI-
CLES ORIGINAL MILEAGE. IF THIS STEP IS
NOT DONE, A DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE
(DTC) MAY BE SET.
The PCM is located in the engine compartment
(Fig. 18).
BR/BEELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES 8E - 19
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 385 of 2255
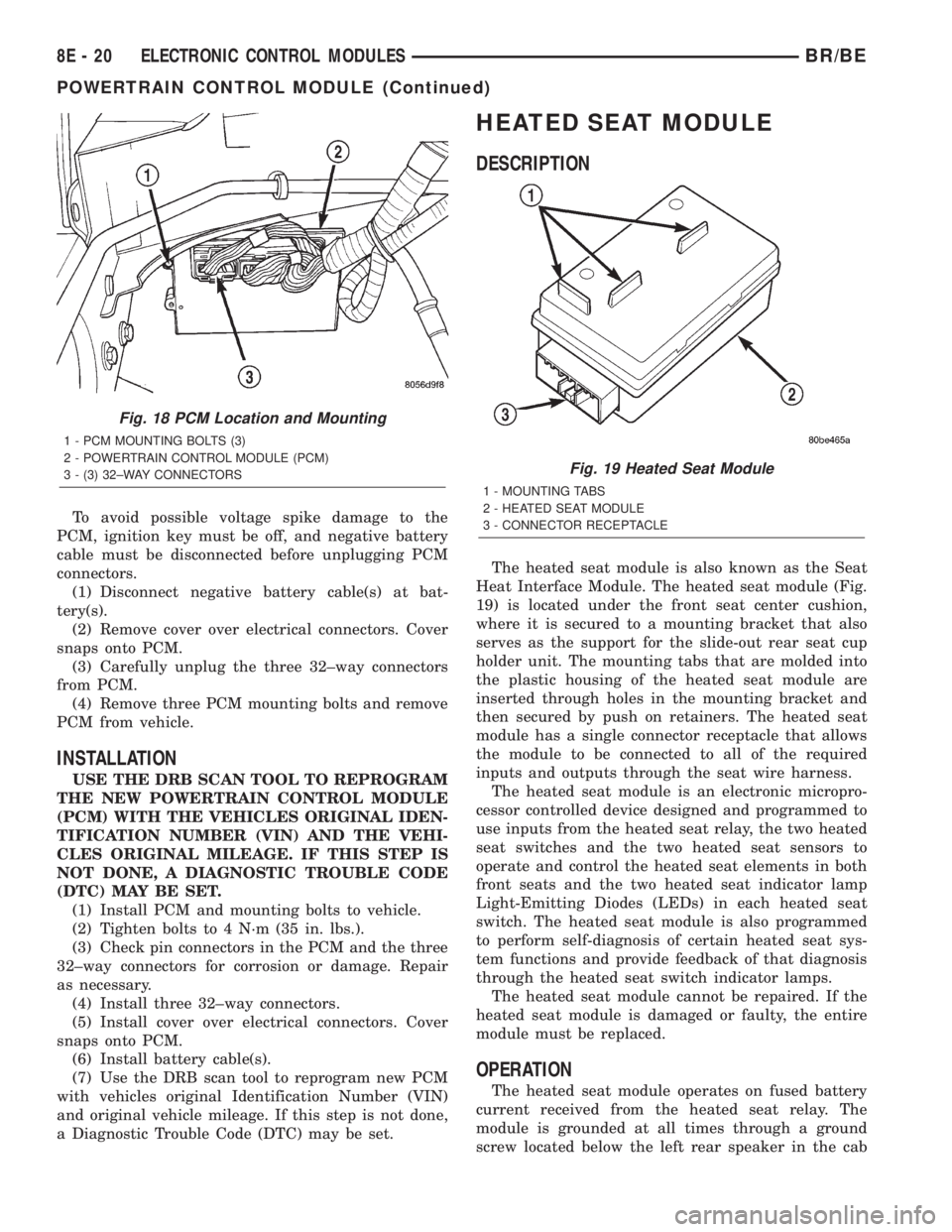
To avoid possible voltage spike damage to the
PCM, ignition key must be off, and negative battery
cable must be disconnected before unplugging PCM
connectors.
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable(s) at bat-
tery(s).
(2) Remove cover over electrical connectors. Cover
snaps onto PCM.
(3) Carefully unplug the three 32±way connectors
from PCM.
(4) Remove three PCM mounting bolts and remove
PCM from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
USE THE DRB SCAN TOOL TO REPROGRAM
THE NEW POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE
(PCM) WITH THE VEHICLES ORIGINAL IDEN-
TIFICATION NUMBER (VIN) AND THE VEHI-
CLES ORIGINAL MILEAGE. IF THIS STEP IS
NOT DONE, A DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE
(DTC) MAY BE SET.
(1) Install PCM and mounting bolts to vehicle.
(2) Tighten bolts to 4 N´m (35 in. lbs.).
(3) Check pin connectors in the PCM and the three
32±way connectors for corrosion or damage. Repair
as necessary.
(4) Install three 32±way connectors.
(5) Install cover over electrical connectors. Cover
snaps onto PCM.
(6) Install battery cable(s).
(7) Use the DRB scan tool to reprogram new PCM
with vehicles original Identification Number (VIN)
and original vehicle mileage. If this step is not done,
a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) may be set.
HEATED SEAT MODULE
DESCRIPTION
The heated seat module is also known as the Seat
Heat Interface Module. The heated seat module (Fig.
19) is located under the front seat center cushion,
where it is secured to a mounting bracket that also
serves as the support for the slide-out rear seat cup
holder unit. The mounting tabs that are molded into
the plastic housing of the heated seat module are
inserted through holes in the mounting bracket and
then secured by push on retainers. The heated seat
module has a single connector receptacle that allows
the module to be connected to all of the required
inputs and outputs through the seat wire harness.
The heated seat module is an electronic micropro-
cessor controlled device designed and programmed to
use inputs from the heated seat relay, the two heated
seat switches and the two heated seat sensors to
operate and control the heated seat elements in both
front seats and the two heated seat indicator lamp
Light-Emitting Diodes (LEDs) in each heated seat
switch. The heated seat module is also programmed
to perform self-diagnosis of certain heated seat sys-
tem functions and provide feedback of that diagnosis
through the heated seat switch indicator lamps.
The heated seat module cannot be repaired. If the
heated seat module is damaged or faulty, the entire
module must be replaced.
OPERATION
The heated seat module operates on fused battery
current received from the heated seat relay. The
module is grounded at all times through a ground
screw located below the left rear speaker in the cab
Fig. 18 PCM Location and Mounting
1 - PCM MOUNTING BOLTS (3)
2 - POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (PCM)
3 - (3) 32±WAY CONNECTORS
Fig. 19 Heated Seat Module
1 - MOUNTING TABS
2 - HEATED SEAT MODULE
3 - CONNECTOR RECEPTACLE
8E - 20 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESBR/BE
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 474 of 2255
in which they were removed from the engine. A sin-
gle plug displaying an abnormal condition indicates
that a problem exists in the corresponding cylinder.
Replace spark plugs at the intervals recommended in
Group O, Lubrication and Maintenance
Spark plugs that have low mileage may be cleaned
and reused if not otherwise defective, carbon or oil
fouled. Also refer to Spark Plug Conditions.
CAUTION: Never use a motorized wire wheel brush
to clean the spark plugs. Metallic deposits will
remain on the spark plug insulator and will cause
plug misfire.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SPARK PLUG
CONDITIONS
NORMAL OPERATING
The few deposits present on the spark plug will
probably be light tan or slightly gray in color. This is
evident with most grades of commercial gasoline
(Fig. 28). There will not be evidence of electrode
burning. Gap growth will not average more than
approximately 0.025 mm (.001 in) per 3200 km (2000
miles) of operation. Spark plugs that have normalwear can usually be cleaned, have the electrodes
filed, have the gap set and then be installed.
Some fuel refiners in several areas of the United
States have introduced a manganese additive (MMT)
for unleaded fuel. During combustion, fuel with MMT
causes the entire tip of the spark plug to be coated
with a rust colored deposit. This rust color can be
misdiagnosed as being caused by coolant in the com-
bustion chamber. Spark plug performance may be
affected by MMT deposits.
COLD FOULING/CARBON FOULING
Cold fouling is sometimes referred to as carbon
fouling. The deposits that cause cold fouling are basi-
cally carbon (Fig. 28). A dry, black deposit on one or
two plugs in a set may be caused by sticking valves
or defective spark plug cables. Cold (carbon) fouling
of the entire set of spark plugs may be caused by a
clogged air cleaner element or repeated short operat-
ing times (short trips).
WET FOULING OR GAS FOULING
A spark plug coated with excessive wet fuel or oil
is wet fouled. In older engines, worn piston rings,
leaking valve guide seals or excessive cylinder wear
can cause wet fouling. In new or recently overhauled
engines, wet fouling may occur before break-in (nor-
mal oil control) is achieved. This condition can usu-
ally be resolved by cleaning and reinstalling the
fouled plugs.
OIL OR ASH ENCRUSTED
If one or more spark plugs are oil or oil ash
encrusted (Fig. 29), evaluate engine condition for the
Fig. 27 Spark Plug Cable OrderÐ8.0L V-10 Engine
Fig. 28 Normal Operation and Cold (Carbon) Fouling
1 - NORMAL
2 - DRY BLACK DEPOSITS
3 - COLD (CARBON) FOULING
BR/BEIGNITION CONTROL 8I - 17
SPARK PLUG (Continued)
Page 1120 of 2255

(4) If dye is not observed, drive the vehicle at var-
ious speeds for approximately 24km (15 miles), and
repeat previous step.
(5) If the oil leak source is not positively identified
at this time, proceed with the air leak detection test
method as follows:
(6) Disconnect the breather cap to air cleaner hose
at the breather cap end. Cap or plug breather cap
nipple.
(7) Remove the PCV valve from the cylinder head
cover. Cap or plug the PCV valve grommet.
(8) Attach an air hose with pressure gauge and
regulator to the dipstick tube.
CAUTION: Do not subject the engine assembly to
more than 20.6 kpa (3 PSI) of test pressure.
(9) Gradually apply air pressure from 1 psi to 2.5
psi maximum while applying soapy water at the sus-
pected source. Adjust the regulator to the suitable
test pressure that provide the best bubbles which
will pinpoint the leak source. If the oil leak is
detected and identified, repair per service manual
procedures.
(10) If the leakage occurs at the rear oil seal area,
refer to the section, Inspection for Rear Seal Area
Leak.
(11) If no leaks are detected, turn off the air sup-
ply and remove the air hose and all plugs and caps.
Install the PCV valve and breather cap hose. Proceed
to next step.
(12) Clean the oil off the suspect oil leak area
using a suitable solvent. Drive the vehicle at various
speeds approximately 24 km (15 miles). Inspect the
engine for signs of an oil leak by using a black light.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐENGINE OIL
PRESSURE
(1) Remove oil pressure sending unit.
(2) Install Oil Pressure Line and Gauge Tool
C-3292. Start engine and record pressure. (Refer to 9
- ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS).
OIL
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE OIL
OIL LEVEL INDICATOR (DIPSTICK)
The engine oil level indicator is located at the right
front of the engine, left of the generator (Fig. 50).
CRANKCASE OIL LEVEL INSPECTION
CAUTION: Do not overfill crankcase with engine oil,
oil foaming and oil pressure loss can result.To ensure proper lubrication of an engine, the
engine oil must be maintained at an acceptable level.
The acceptable levels are indicated between the ADD
and SAFE marks on the engine oil dipstick.
(1) Position vehicle on level surface.
(2) With engine OFF, allow approximately ten min-
utes for oil to settle to bottom of crankcase, remove
engine oil dipstick.
(3) Wipe dipstick clean.
(4) Install dipstick and verify it is seated in the
tube.
(5) Remove dipstick, with handle held above the
tip, take oil level reading.
(6) Add oil only if level is below the ADD mark on
dipstick.
ENGINE OIL CHANGE
Change engine oil at mileage and time intervals
described in the Maintenance Schedule. This infor-
mation can be found in the owner's manual.
TO CHANGE ENGINE OIL
Run engine until achieving normal operating tem-
perature.
(1) Position the vehicle on a level surface and turn
engine off.
(2) Hoist vehicle.
(3) Remove oil fill cap.
(4) Place a suitable drain pan under crankcase
drain.
(5) Remove drain plug from crankcase and allow
oil to drain into pan. Inspect drain plug threads for
Fig. 50 Oil Level Indicator Location
1 - CYLINDER HEAD COVER
2 - ENGINE OIL FILL CAP
3 - DIPSTICK
4 - ENGINE OIL FILTER
5 - FILTER BOSS
BR/BEENGINE 5.9L 9 - 45
LUBRICATION (Continued)
Page 1150 of 2255
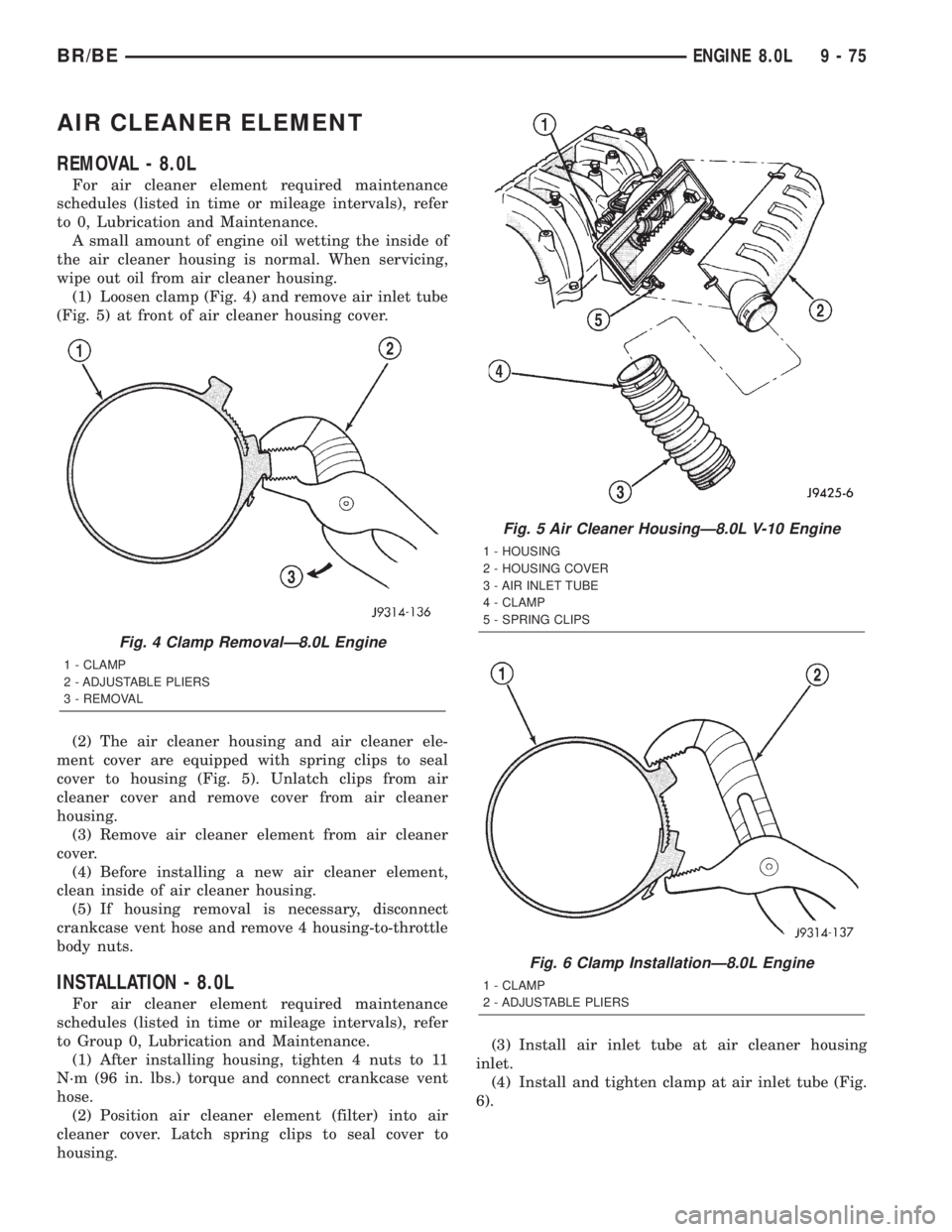
AIR CLEANER ELEMENT
REMOVAL - 8.0L
For air cleaner element required maintenance
schedules (listed in time or mileage intervals), refer
to 0, Lubrication and Maintenance.
A small amount of engine oil wetting the inside of
the air cleaner housing is normal. When servicing,
wipe out oil from air cleaner housing.
(1) Loosen clamp (Fig. 4) and remove air inlet tube
(Fig. 5) at front of air cleaner housing cover.
(2) The air cleaner housing and air cleaner ele-
ment cover are equipped with spring clips to seal
cover to housing (Fig. 5). Unlatch clips from air
cleaner cover and remove cover from air cleaner
housing.
(3) Remove air cleaner element from air cleaner
cover.
(4) Before installing a new air cleaner element,
clean inside of air cleaner housing.
(5) If housing removal is necessary, disconnect
crankcase vent hose and remove 4 housing-to-throttle
body nuts.
INSTALLATION - 8.0L
For air cleaner element required maintenance
schedules (listed in time or mileage intervals), refer
to Group 0, Lubrication and Maintenance.
(1) After installing housing, tighten 4 nuts to 11
N´m (96 in. lbs.) torque and connect crankcase vent
hose.
(2) Position air cleaner element (filter) into air
cleaner cover. Latch spring clips to seal cover to
housing.(3) Install air inlet tube at air cleaner housing
inlet.
(4) Install and tighten clamp at air inlet tube (Fig.
6).
Fig. 4 Clamp RemovalÐ8.0L Engine
1 - CLAMP
2 - ADJUSTABLE PLIERS
3 - REMOVAL
Fig. 5 Air Cleaner HousingÐ8.0L V-10 Engine
1 - HOUSING
2 - HOUSING COVER
3 - AIR INLET TUBE
4 - CLAMP
5 - SPRING CLIPS
Fig. 6 Clamp InstallationÐ8.0L Engine
1 - CLAMP
2 - ADJUSTABLE PLIERS
BR/BEENGINE 8.0L 9 - 75
Page 1177 of 2255

The acceptable levels are indicated between the ADD
and SAFE marks on the engine oil dipstick.
(1) Position vehicle on level surface.
(2) With engine OFF, allow approximately ten min-
utes for oil to settle to bottom of crankcase, remove
engine oil dipstick.
(3) Wipe dipstick clean.
(4) Install dipstick and verify it is seated in the
tube.
(5) Remove dipstick, with handle held above the
tip, take oil level reading.
(6) Add oil only if level is below the ADD mark on
dipstick.
ENGINE OIL CHANGE
Change engine oil at mileage and time intervals
described in the Maintenance Schedule. This infor-
mation can be found in the owner's manual.
TO CHANGE ENGINE OIL
Run engine until achieving normal operating tem-
perature.
(1) Position the vehicle on a level surface and turn
engine off.
(2) Hoist vehicle.
(3) Remove oil fill cap.
(4) Place a suitable drain pan under crankcase
drain.
(5) Remove drain plug from crankcase and allow
oil to drain into pan. Inspect drain plug threads for
stretching or other damage. Replace drain plug and
gasket if damaged.
(6) Install drain plug in crankcase.
(7) Change oil filter (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRI-
CATION/OIL FILTER - REMOVAL).
(8) Lower vehicle and fill crankcase with specified
type (Refer to LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE/
FLUID TYPES - DESCRIPTION) and amount of
engine oil (Refer to LUBRICATION & MAINTE-
NANCE - SPECIFICATIONS).
(9) Install oil fill cap.
(10) Start engine and inspect for leaks.
(11) Stop engine and inspect oil level.
OIL FILTER
REMOVAL
All engines are equipped with a high quality full-
flow, disposable type oil filter. DaimlerChrysler Cor-
poration recommends a Mopartor equivalent oil
filter be used.
(1) Position a drain pan under the oil filter.
(2) Using a suitable oil filter wrench loosen filter.
(3) Rotate the oil filter counterclockwise to remove
it from the cylinder block oil filter boss (Fig. 54).(4) When filter separates from adapter nipple, tip
gasket end upward to minimize oil spill. Remove fil-
ter from vehicle.
(5) With a wiping cloth, clean the gasket sealing
surface (Fig. 52) of oil and grime.
(6) Install new filter (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRI-
CATION/OIL FILTER - INSTALLATION).
INSTALLATION
(1) Lightly lubricate oil filter gasket with engine
oil or chassis grease.
(2) Thread filter onto adapter nipple. When gasket
makes contact with sealing surface, (Fig. 55) hand
tighten filter one full turn, do not over tighten.
(3) Add oil (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRICATION/
OIL - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
OIL PAN
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the negative cable from the battery.
(2) Raise vehicle.
Fig. 54 Oil Filter RemovalÐTypical
1 - ENGINE OIL FILTER
2 - OIL FILTER WRENCH
Fig. 55 Oil Filter Sealing SurfaceÐTypical
1 - SEALING SURFACE
2 - RUBBER GASKET
3 - OIL FILTER
9 - 102 ENGINE 8.0LBR/BE
OIL (Continued)
Page 1961 of 2255

TIRES
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - SPARE TIRE - TEMPORARY
The temporary spare tire is designed for emer-
gency use only. The original tire should be repaired
or replaced at the first opportunity, then reinstalled.
Do not exceed speeds of 50 M.P.H. when using the
temporary spare tire. Refer to Owner's Manual for
complete details.
DESCRIPTION - TIRES
Tires are designed and engineered for each specific
vehicle. They provide the best overall performance
for normal operation. The ride and handling charac-
teristics match the vehicle's requirements. With
proper care they will give excellent reliability, trac-
tion, skid resistance, and tread life.
Driving habits have more effect on tire life than
any other factor. Careful drivers will obtain in most
cases, much greater mileage than severe use or care-
less drivers. A few of the driving habits which will
shorten the life of any tire are:
²Rapid acceleration
²Severe brake applications
²High speed driving
²Excessive speeds on turns
²Striking curbs and other obstacles
Radial-ply tires are more prone to irregular tread
wear. It is important to follow the tire rotation inter-
val shown in the section on Tire Rotation, (Refer to
22 - TIRES/WHEELS - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
This will help to achieve a greater tread life.
TIRE IDENTIFICATION
Tire type, size, aspect ratio and speed rating are
encoded in the letters and numbers imprinted on the
side wall of the tire. Refer to the chart to decipher
the tire identification code (Fig. 11).
Performance tires have a speed rating letter after
the aspect ratio number. The speed rating is not
always printed on the tire sidewall. These ratings
are:
²Qup to 100 mph
²Rup to 106 mph
²Sup to 112 mph
²Tup to 118 mph
²Uup to 124 mph
²Hup to 130 mph
²Vup to 149 mph
²Zmore than 149 mph (consult the tire manu-
facturer for the specific speed rating)An All Season type tire will have eitherM+S,M
&SorM±S(indicating mud and snow traction)
imprinted on the side wall.
TIRE CHAINS
Tire snow chains may be used oncertainmodels.
Refer to the Owner's Manual for more information.
DESCRIPTION - RADIAL-PLY TIRES
Radial-ply tires improve handling, tread life and
ride quality, and decrease rolling resistance.
Radial-ply tires must always be used in sets of
four. Under no circumstances should they be used on
the front only. They may be mixed with temporary
spare tires when necessary. A maximum speed of 50
MPH is recommended while a temporary spare is in
use.
Radial-ply tires have the same load-carrying capac-
ity as other types of tires of the same size. They also
use the same recommended inflation pressures.
The use of oversized tires, either in the front or
rear of the vehicle, can cause vehicle drive train fail-
ure. This could also cause inaccurate wheel speed
signals when the vehicle is equipped with Anti-Lock
Brakes.
The use of tires from different manufactures on the
same vehicle is NOT recommended. The proper tire
pressure should be maintained on all four tires.
Fig. 11 Tire Identification
22 - 6 TIRES/WHEELSBR/BE