height adjustment DODGE RAM 2002 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2002, Model line: RAM, Model: DODGE RAM 2002Pages: 2255, PDF Size: 62.07 MB
Page 28 of 2255

STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURES - ALIGNMENT I.F.S.
Before each alignment reading the vehicle should
be jounced (rear first, then front). Grasp each
bumper at the center and jounce the vehicle up and
down several times. Always release the bumper in
the down position.Set the front end alignment to
specifications while the vehicle is in its NOR-
MALLY LOADED CONDITION.
Camber and caster angle adjustments involve
changing the position of the upper suspension arm
pivot bar (Fig. 3). Refer to the Alignment Specifica-
tion Chart for the correct setting.
CASTER:Move the rear position of the pivot bar
in or out. This will change the caster angle signifi-
cantly and camber angle only slightly. To retain cam-
ber move the forward pivot very slightly in the
opposite direction.
NOTE: For example, to increase a positive caster
angle, move the rear position of the pivot barinward (toward the engine). Move the front of pivot
bar outward (away from the engine) slightly until
the original camber angle is obtained.
CAMBER:Move the forward position of the pivot
bar in or out. This will change the camber angle sig-
nificantly and caster angle only slightly. The camber
angle should be adjusted as close as possible to the
preferred service specification. After adjustment
is made tighten pivot bar nuts to specifications.
TOE POSITION:The wheel toe position adjust-
ment should be the final adjustment.
(1) Start the engine and turn wheels both ways
before straightening the wheels. Center and secure
the steering wheel and turn off engine.
(2) Loosen the tie rod adjustment sleeve clamp
bolts/nuts.
NOTE: Each front wheel should be adjusted for
one-half of the total toe position specification. This
will ensure the steering wheel will be centered
when the wheels are positioned straight-ahead.
(3) Adjust the wheel toe position by turning the tie
rod adjustment sleeves as necessary.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CASTER
CORRECTION MEASUREMENT
NOTE: To determine the correct caster alignment
angle for Cab-Chassis vehicles the following proce-
dure must be performed.
NOTE: 4x2 11000 GVW has a solid front axle and
uses a 4x4 frame.
(1) Take a height measurement to the center of the
front gauge hole in the frame. Take another measure-
ment to the center of the rear spring hanger bolt
(Fig. 4). Take these measurements on both sides of
the vehicle.
(2) Subtract the front measurement from the rear
measurement and use the average between the right
and left side. Use this number (caster correlation
valve) with the Corrected Caster Chart to obtain the
preferred caster angle.
Fig. 3 Caster Camber Adjustment Location
1 - PIVOT BAR
2 - UPPER SUSPENSION ARM
3 - SUSPENSION ARM FRAME MOUNT
4 - ADJUSTMENT SLOTS
BR/BEWHEEL ALIGNMENT 2 - 3
WHEEL ALIGNMENT (Continued)
Page 40 of 2255
CAUTION: Components attached with a nut and cot-
ter pin must be torqued to specification. Then if the
slot in the nut does not line up with the cotter pin
hole, tighten nut until it is aligned. Never loosen the
nut to align the cotter pin hole.
CAUTION: Suspension components with rubber
bushings (except stabilizer bar) should be tightened
with the vehicle at normal height. It is important to
have the springs supporting the weight of the vehi-
cle when the fasteners are torqued. If springs arenot at their normal ride position, vehicle ride com-
fort could be affected and premature bushing wear
may occur.
DESCRIPTION
The upper and lower suspension arms use bush-
ings to isolate road noise. The suspension arms are
bolted to the frame and axle through the rubber
bushings. The lower suspension arm uses cam bolts
at the axle to allow for caster and pinion angle
adjustment.
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE CHART
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Shock Absorber
Upper Nut47 35 Ð
Shock Absorber
Lower Bolt135 100 Ð
Shock Absorber
Bracket75 55 Ð
Suspension Arm Lower
Axle Nut190 140 Ð
Suspension Arm Lower
Frame Nut190 140 Ð
Suspension Arm Upper
Axle Nut163 120 Ð
Suspension Arm Upper
Frame Nut163 120 Ð
Stabilizer Bar
Clamp Bolt54 40 Ð
Stabilizer Bar
Link Upper Nut37 27 Ð
Stabilizer Bar
Link Lower Nut47 35 Ð
Track Bar
Ball Stud Nut95 70 Ð
Track Bar
Axle Bracket Bolt176 130 Ð
Hub/Bearing
Nut245 180 Ð
Hub/Bearing
Bolts166 122 Ð
BR/BEFRONT - 4WD 2 - 15
FRONT - 4WD (Continued)
Page 73 of 2255
Condition Possible Causes Correction
Gear Teeth Broke 1. Overloading. 1. Replace gears. Examine other
gears and bearings for possible
damage.
2. Erratic clutch operation. 2. Replace gears and examine the
remaining parts for damage. Avoid
erratic clutch operation.
3. Ice-spotted pavement. 3. Replace gears and examine
remaining parts for damage.
4. Improper adjustments. 4. Replace gears and examine
remaining parts for damage. Ensure
ring gear backlash is correct.
Axle Noise 1. Insufficient lubricant. 1. Fill differential with the correct
fluid type and quantity.
2. Improper ring gear and pinion
adjustment.2. Check ring gear and pinion
contact pattern.
3. Unmatched ring gear and pinion. 3. Replace gears with a matched
ring gear and pinion.
4. Worn teeth on ring gear and/or
pinion.4. Replace ring gear and pinion.
5. Loose pinion bearings. 5. Adjust pinion bearing pre-load.
6. Loose differential bearings. 6. Adjust differential bearing
pre-load.
7. Mis-aligned or sprung ring gear. 7. Measure ring gear run-out.
Replace components as necessary.
8. Loose differential bearing cap
bolts.8. Inspect differential components
and replace as necessary. Ensure
that the bearing caps are torqued
tot he proper specification.
9. Housing not machined properly. 9. Replace housing.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove wheels and tires.
(3) Remove brake calipers and rotors. Refer to 5
Brakes for procedures.
(4) Remove ABS wheel speed sensors, if equipped.
Refer to 5 Brakes for procedures.
(5) Disconnect axle vent hose.
(6) Disconnect vacuum hose and electrical connec-
tor at disconnect housing.
(7) Remove front propeller shaft.
(8) Disconnect stabilizer bar links at the axle
brackets.
(9) Disconnect shock absorbers from axle brackets.
(10) Disconnect track bar from the axle bracket.
(11) Disconnect tie rod and drag link from the
steering knuckles.
(12) Position suitable lifting device under the axle
assembly.(13) Secure axle to lifting device.
(14) Mark suspension alignment cams for installa-
tion reference.
(15) Disconnect upper and lower suspension arms
from the axle bracket.
(16) Lower the axle. The coil springs will drop
with the axle.
(17) Remove the coil springs from the axle bracket.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Suspension components with rubber
bushings should be tightened with the weight of the
vehicle on the suspension, at normal height. If
springs are not at their normal ride position, vehicle
ride comfort could be affected and premature bush-
ing wear may occur. Rubber bushings must never
be lubricated.
(1) Support the axle on a suitable lifting device.
3 - 18 FRONT AXLE - 248FBIBR/BE
FRONT AXLE - 248FBI (Continued)
Page 76 of 2255

PINION DEPTH MEASUREMENT AND ADJUSTMENT
Measurements are taken with pinion bearing cups
and pinion bearings installed in the housing. Take
measurements with Pinion Gauge Set and Dial Indi-
cator C-3339 (Fig. 5).
(1) Assemble Pinion Height Block 6739, Pinion
Block 6736 and rear pinion bearing onto Screw 6741
(Fig. 5).
(2) Insert assembled height gauge components,
rear bearing and screw into the housing through pin-
ion bearing cups (Fig. 6).
(3) Install front pinion bearing and Cone-nut 6740
hand tight (Fig. 5).
(4) Place Arbor Disc 6732 on Arbor D-115-3 in posi-
tion in the housing side bearing cradles (Fig. 7).
NOTE: Arbor Discs 6732 has different step diame-
ters to fit other axles. Choose proper step for axle
being serviced.
(5) Install differential bearing caps on arbor discs
and snug the bearing cap bolts. Then cross tighten
cap bolts to 108 N´m (80 ft. lbs.).
(6) Assemble Dial Indicator C-3339 into Scooter
Block D-115-2 and secure set screw.(7) Position Scooter Block/Dial Indicator flush on
the pinion height block. Hold scooter block and zero
the dial indicator.
(8) Slowly slide the scooter block across the pinion
height block over to the arbor (Fig. 8). Move the
scooter block till dial indicator crests the arbor, then
record the highest reading.
(9) Select a shim/slinger equal to the dial indicator
reading plus the pinion depth variance number
etched in the face of the pinion (Fig. 3). For example,
if the depth variance is ±2, add +0.002 in. to the dial
indicator reading.
Fig. 5 PINION GEAR DEPTH GAUGE TOOLS
1 - DIAL INDICATOR
2 - ARBOR
3 - PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
4 - CONE
5 - SCREW
6 - PINION BLOCK
7 - SCOOTER BLOCK
8 - ARBOR DISC
Fig. 6 PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
1 - PINION BLOCK
2 - PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
Fig. 7 GAUGE TOOLS IN HOUSING
1 - ARBOR DISC
2 - PINION BLOCK
3 - ARBOR
4 - PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
BR/BEFRONT AXLE - 248FBI 3 - 21
FRONT AXLE - 248FBI (Continued)
Page 107 of 2255

Note the etched number on the face of the pinion
gear head (±1, ±2, 0, +1, +2, etc.). The numbers rep-
resent thousands of an inch deviation from the stan-
dard. If the number is negative, add that value to therequired thickness of the depth shims. If the number
is positive, subtract that value from the thickness of
the depth shim. If the number is 0 no change is nec-
essary.
PINION GEAR DEPTH VARIANCE
Original Pinion
Gear Depth
VarianceReplacement Pinion Gear Depth Variance
24232221 0 +1 +2 +3 +4
+4+0.008 +0.007 +0.006 +0.005 +0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 0
+3+0.007 +0.006 +0.005 +0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 020.001
+2+0.006 +0.005 +0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 020.00120.002
+1+0.005 +0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 020.00120.00220.003
0+0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 020.00120.00220.00320.004
21+0.003 +0.002 +0.001 020.00120.00220.00320.00420.005
22+0.002 +0.001 020.00120.00220.00320.00420.00520.006
23+0.001 020.00120.00220.00320.00420.00520.00620.007
24020.00120.00220.00320.00420.00520.00620.00720.008
PINION DEPTH MEASUREMENT AND ADJUSTMENT
Measurements are taken with pinion bearing cups
and pinion bearings installed in the housing. Take
measurements with Pinion Gauge Set and Dial Indi-
cator C-3339 (Fig. 6).
(1) Assemble Pinion Height Block 6739, Pinion
Block 6736 and rear pinion bearing onto Screw 6741
(Fig. 6).
(2) Insert assembled height gauge components,
rear bearing and screw into the housing through pin-
ion bearing cups (Fig. 7).
(3) Install front pinion bearing and Cone-nut 6740
hand tight (Fig. 6).
(4) Place Arbor Disc 6732 on Arbor D-115-3 in posi-
tion in the housing side bearing cradles (Fig. 8).
NOTE: Arbor Discs 6732 has different step diame-
ters to fit other axles. Choose proper step for axle
being serviced.
(5) Install differential bearing caps on arbor discs
and snug the bearing cap bolts. Then cross tighten
cap bolts to 108 N´m (80 ft. lbs.).
(6) Assemble Dial Indicator C-3339 into Scooter
Block D-115-2 and secure set screw.
(7) Position Scooter Block/Dial Indicator flush on
the pinion height block. Hold scooter block and zero
the dial indicator.
(8) Slowly slide the scooter block across the pinion
height block over to the arbor (Fig. 9). Move the
Fig. 6 PINION DEPTH GAUGE TOOLS
1 - DIAL INDICATOR
2 - ARBOR
3 - PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
4 - CONE
5 - SCREW
6 - PINION BLOCK
7 - SCOOTER BLOCK
8 - ARBOR DISC
3 - 52 REAR AXLE - 248RBIBR/BE
REAR AXLE - 248RBI (Continued)
Page 139 of 2255

PINION GEAR DEPTH VARIANCE
Original Pinion
Gear Depth
VarianceReplacement Pinion Gear Depth Variance
24232221 0 +1 +2 +3 +4
+4+0.008 +0.007 +0.006 +0.005 +0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 0
+3+0.007 +0.006 +0.005 +0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 020.001
+2+0.006 +0.005 +0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 020.00120.002
+1+0.005 +0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 020.00120.00220.003
0+0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 020.00120.00220.00320.004
21+0.003 +0.002 +0.001 020.00120.00220.00320.00420.005
22+0.002 +0.001 020.00120.00220.00320.00420.00520.006
23+0.001 020.00120.00220.00320.00420.00520.00620.007
24020.00120.00220.00320.00420.00520.00620.00720.008
PINION DEPTH MEASUREMENT AND ADJUSTMENT
Measurements are taken with pinion bearing cups
and pinion bearings installed in the housing. Take
measurements with Pinion Gauge Set and Dial Indi-
cator C-3339 (Fig. 6).(1) Assemble Pinion Height Block 6739, Pinion
Block 6737 and rear pinion bearing onto Screw 6741
(Fig. 6).
(2) Insert assembled height gauge components,
rear bearing and screw into the housing through pin-
ion bearing cups (Fig. 7).
(3) Install front pinion bearing and Cone-nut 6740
hand tight (Fig. 6).
(4) Place Arbor Disc 6732 on Arbor D-115-3 in posi-
tion in the housing side bearing cradles (Fig. 8).
NOTE: Arbor Discs 6732 has different step diame-
ters to fit other axles. Choose proper step for axle
being serviced.
Fig. 6 PINION GEAR DEPTH GAUGE TOOLS
1 - DIAL INDICATOR
2 - ARBOR
3 - PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
4 - CONE
5 - SCREW
6 - PINION BLOCK
7 - SCOOTER BLOCK
8 - ARBOR DISC
Fig. 7 PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
1 - PINION BLOCK
2 - PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
3 - 84 REAR AXLE - 267RBIBR/BE
REAR AXLE - 267RBI (Continued)
Page 162 of 2255

REAR AXLE - 286RBI
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
REAR AXLE - 286RBI
DESCRIPTION........................107
OPERATION..........................108
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AXLE.........108
REMOVAL............................112
INSTALLATION........................112
ADJUSTMENTS.......................112
SPECIFICATIONS
REAR AXLE - 286RBI.................120
SPECIAL TOOLS
REAR AXLE - 286 RBI.................120
AXLE SHAFTS
REMOVAL............................123
INSTALLATION........................123
AXLE BEARINGS
REMOVAL............................123
INSTALLATION........................123
PINION SEAL
REMOVAL............................123INSTALLATION........................124
DIFFERENTIAL
REMOVAL............................125
DISASSEMBLY........................126
ASSEMBLY...........................126
INSTALLATION........................126
DIFFERENTIAL - TRAC-LOK
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TRAC-LOKT....128
DISASSEMBLY........................128
ASSEMBLY...........................129
DIFFERENTIAL CASE BEARINGS
REMOVAL............................129
INSTALLATION........................129
PINION GEAR/RING GEAR/TONE RING
REMOVAL............................131
INSTALLATION........................132
REAR AXLE - 286RBI
DESCRIPTION
The Rear Beam-design Iron (RBI) axle housings
consist of an iron center casting (differential housing)
with axle shaft tubes extending from either side. The
tubes are pressed into the differential housing and
welded. The axles are full-floating axle shafts, that
are supported by the axle housing tubes. The full-
float axle shafts are retained by bolts attached to the
hub.
The differential case for the standard differential is
a one-piece design. Differential bearing preload and
ring gear backlash are adjusted by the use of shims
located between the differential bearing cones andcase. Outboard protective spacers are located
between the differential bearing cup and housing.
Pinion bearing preload is set and maintained by the
use of shims. Pinion height is controlled by a shim
pack located under the inner pinion bearing cup. The
differential cover provides a means for inspection and
service.
Axles equipped with a Trac-Loktdifferential are
optional. The differential contains two clutch packs,
four pinion gears, and a one-piece pinion mate cross
shaft to provide increased torque to the non-slipping
wheel in addition to the standard differential compo-
nents. A Trac-loktdifferential for the has a two-piece
differential case.
BR/BEREAR AXLE - 286RBI 3 - 107
Page 168 of 2255

thousands of an inch deviation from the standard. If the
number is negative, add that value to the required
thickness of the depth shim(s). If the number is posi-tive, subtract that value from the thickness of the depth
shim(s). If the number is 0 no change is necessary. Refer
to the Pinion Gear Depth Variance Chart.
PINION GEAR DEPTH VARIANCE
Original
Pinion
Gear
Depth
VarianceReplacement Pinion Gear Depth Variance
24232221 0 +1 +2 +3 +4
+4+0.008 +0.007 +0.006 +0.005 +0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 0
+3+0.007 +0.006 +0.005 +0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 020.001
+2+0.006 +0.005 +0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 020.00120.002
+1+0.005 +0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 020.00120.00220.003
0+0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 020.00120.00220.00320.004
21+0.003 +0.002 +0.001 020.00120.00220.00320.00420.005
22+0.002 +0.001 020.00120.00220.00320.00420.00520.006
23+0.001 020.00120.00220.00320.00420.00520.00620.007
24020.00120.00220.00320.00420.00520.00620.00720.008
PINION DEPTH MEASUREMENT AND ADJUSTMENT
Measurements are taken with pinion cups and pin-
ion bearings installed in housing. Take measure-
ments with a Pinion Gauge Set 6730 and Dial
Indicator C-3339 (Fig. 6).
(1) Assemble Pinion Height Block 6739, Pinion
Block 6738 and rear pinion bearing onto Screw 6741
(Fig. 6).
(2) Insert assembled height gauge components,
rear bearing and screw into the housing through pin-
ion bearing cups (Fig. 7).
(3) Install front pinion bearing and Cone 6740
hand tight (Fig. 6).
(4) Place Arbor Disc 6732 on Arbor D-115-3 in posi-
tion in the housing side bearing cradles (Fig. 8).
Install differential bearing caps on Arbor Discs and
snug the bearing cap bolts. Then tighten cap bolts in
a criss-cross pattern to 108 N´m (80 ft. lbs.).
NOTE: Arbor Discs 6732 have different step diame-
ters to fit other axle sizes. Pick correct size step for
axle being serviced.
(5) Assemble Dial Indicator C-3339 into Scooter
Block D-115-2 and secure set screw.
(6) Position Scooter Block/Dial Indicator flush on
the pinion height block. Hold scooter block and zero
the dial indicator.
(7) Slowly slide the scooter block across the pinion
height block over to the arbor (Fig. 9). Move the
scooter block till dial indicator crests the arbor, then
record the highest reading.
Fig. 6 PINION GEAR DEPTH GAUGE
1 - DIAL INDICATOR
2 - ARBOR
3 - PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
4 - CONE
5 - SCREW
6 - PINION BLOCK
7 - SCOOTER BLOCK
8 - ARBOR DISC
BR/BEREAR AXLE - 286RBI 3 - 113
REAR AXLE - 286RBI (Continued)
Page 194 of 2255

CAUTION: Never use gasoline, kerosene, alcohol,
motor oil, transmission fluid, or any fluid containing
mineral oil to clean the system components. These
fluids damage rubber cups and seals. Use only
fresh brake fluid or Mopar brake cleaner to clean or
flush brake system components. These are the only
cleaning materials recommended. If system contam-
ination is suspected, check the fluid for dirt, discol-
oration, or separation into distinct layers. Also
check the reservoir cap seal for distortion. Drain
and flush the system with new brake fluid if con-
tamination is suspected.
CAUTION: Use Mopar brake fluid, or an equivalent
quality fluid meeting SAE/DOT standards J1703 and
DOT 3. Brake fluid must be clean and free of con-
taminants. Use fresh fluid from sealed containers
only to ensure proper antilock component opera-
tion.
CAUTION: Use Mopar multi-mileage or high temper-
ature grease to lubricate caliper slide surfaces,
drum brake pivot pins, and shoe contact points on
the backing plates. Use multi-mileage grease or GE
661 or Dow 111 silicone grease on caliper slide pins
to ensure proper operation.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BASE BRAKE
SYSTEM
Base brake components consist of the brake shoes,
calipers, wheel cylinders, brake drums, rotors, brake
lines, master cylinder, booster, and parking brake
components.
Brake diagnosis involves determining if the prob-
lem is related to a mechanical, hydraulic, or vacuum
operated component.
The first diagnosis step is the preliminary check.
PRELIMINARY BRAKE CHECK
(1) Check condition of tires and wheels. Damaged
wheels and worn, damaged, or underinflated tires
can cause pull, shudder, vibration, and a condition
similar to grab.
(2) If complaint was based on noise when braking,
check suspension components. Jounce front and rear
of vehicle and listen for noise that might be caused
by loose, worn or damaged suspension or steering
components.
(3) Inspect brake fluid level and condition. Note
that the brake reservoir fluid level will decrease in
proportion to normal lining wear.Also note that
brake fluid tends to darken over time. This is
normal and should not be mistaken for contam-
ination.(a) If fluid level is abnormally low, look for evi-
dence of leaks at calipers, wheel cylinders, brake
lines, and master cylinder.
(b) If fluid appears contaminated, drain out a
sample to examine. System will have to be flushed
if fluid is separated into layers, or contains a sub-
stance other than brake fluid. The system seals
and cups will also have to be replaced after flush-
ing. Use clean brake fluid to flush the system.
(4) Check parking brake operation. Verify free
movement and full release of cables and pedal. Also
note if vehicle was being operated with parking
brake partially applied.
(5) Check brake pedal operation. Verify that pedal
does not bind and has adequate free play. If pedal
lacks free play, check pedal and power booster for
being loose or for bind condition. Do not road test
until condition is corrected.
(6) Check booster vacuum check valve and hose.
(7) If components checked appear OK, road test
the vehicle.
ROAD TESTING
(1) If complaint involved low brake pedal, pump
pedal and note if it comes back up to normal height.
(2) Check brake pedal response with transmission
in Neutral and engine running. Pedal should remain
firm under constant foot pressure.
(3) During road test, make normal and firm brake
stops in 25-40 mph range. Note faulty brake opera-
tion such as low pedal, hard pedal, fade, pedal pulsa-
tion, pull, grab, drag, noise, etc.
(4) Attempt to stop the vehicle with the parking
brake only and note grab, drag, noise, etc.
PEDAL FALLS AWAY
A brake pedal that falls away under steady foot
pressure is generally the result of a system leak. The
leak point could be at a brake line, fitting, hose, or
caliper/wheel cylinder. If leakage is severe, fluid will
be evident at or around the leaking component.
Internal leakage (seal by-pass) in the master cylin-
der caused by worn or damaged piston cups, may
also be the problem cause.
An internal leak in the ABS or RWAL system may
also be the problem with no physical evidence.
LOW PEDAL
If a low pedal is experienced, pump the pedal sev-
eral times. If the pedal comes back up, worn linings,
rotors, drums, or rear brakes out of adjustment are
the most likely causes. The proper course of action is
to inspect and replace all worn component and make
the proper adjustments.
BR/BEBRAKES - BASE 5 - 5
HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL (Continued)
Page 528 of 2255
SPORT
(1) Position fog lamp in fascia.
(2) Install screws attaching fog lamp to fascia.
(3) Connect wire connector to fog lamp.
(4) Connect the battery negative cable.
(5) Check for proper operation and beam align-
ment.
ADJUSTMENTS
Prepare an alignment screen. (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR/HEAD-
LAMP UNIT - ADJUSTMENTS)
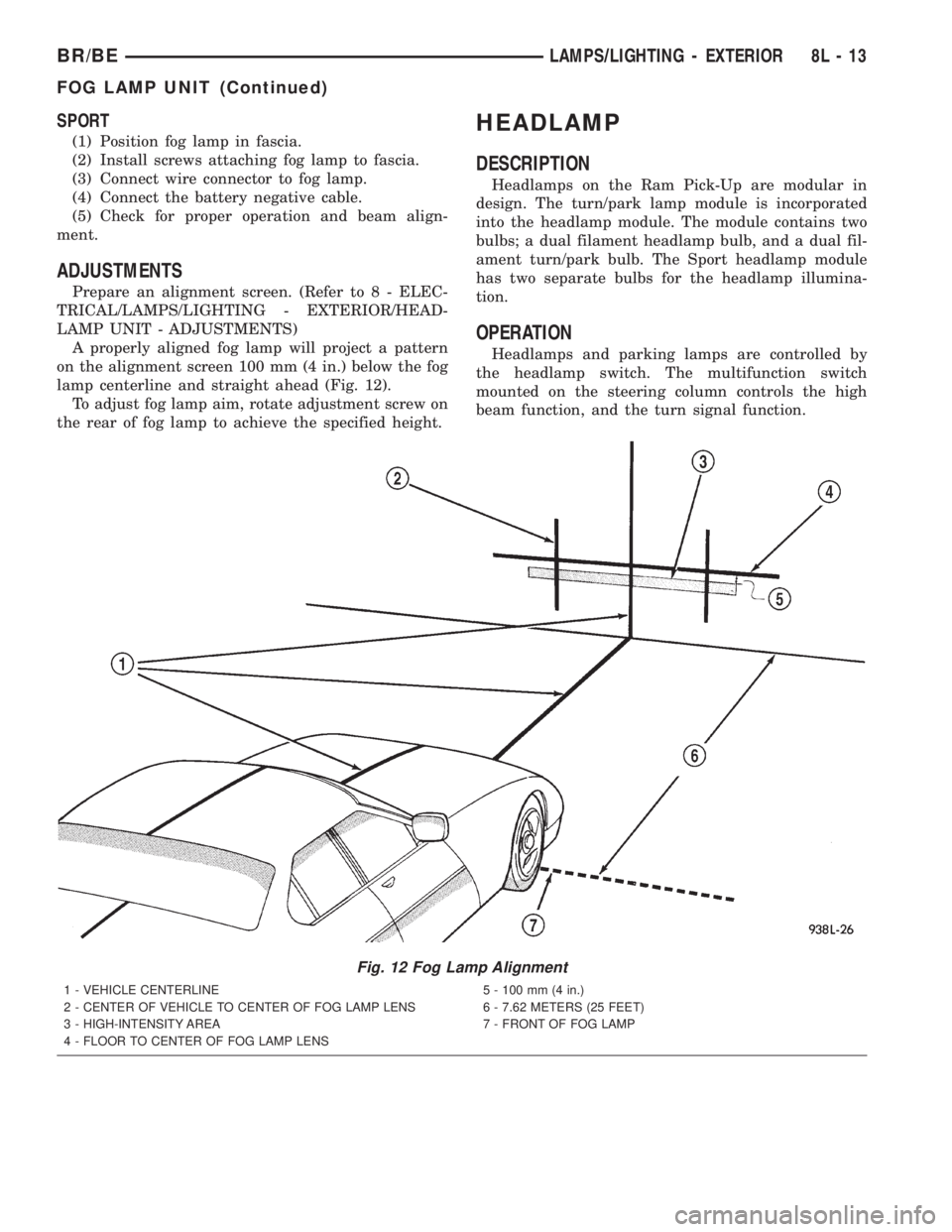
A properly aligned fog lamp will project a pattern
on the alignment screen 100 mm (4 in.) below the fog
lamp centerline and straight ahead (Fig. 12).
To adjust fog lamp aim, rotate adjustment screw on
the rear of fog lamp to achieve the specified height.
HEADLAMP
DESCRIPTION
Headlamps on the Ram Pick-Up are modular in
design. The turn/park lamp module is incorporated
into the headlamp module. The module contains two
bulbs; a dual filament headlamp bulb, and a dual fil-
ament turn/park bulb. The Sport headlamp module
has two separate bulbs for the headlamp illumina-
tion.
OPERATION
Headlamps and parking lamps are controlled by
the headlamp switch. The multifunction switch
mounted on the steering column controls the high
beam function, and the turn signal function.
Fig. 12 Fog Lamp Alignment
1 - VEHICLE CENTERLINE
2 - CENTER OF VEHICLE TO CENTER OF FOG LAMP LENS
3 - HIGH-INTENSITY AREA
4 - FLOOR TO CENTER OF FOG LAMP LENS5 - 100 mm (4 in.)
6 - 7.62 METERS (25 FEET)
7 - FRONT OF FOG LAMP
BR/BELAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR 8L - 13
FOG LAMP UNIT (Continued)