oil dipstick DODGE RAM 2002 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2002, Model line: RAM, Model: DODGE RAM 2002Pages: 2255, PDF Size: 62.07 MB
Page 255 of 2255

hoses, gasket edges and heater. Seal small leak holes
with a Sealer Lubricant (or equivalent). Repair leak
holes and inspect system again with pressure
applied.
Drops Quickly:Indicates that serious leakage is
occurring. Examine system for external leakage. If
leaks are not visible, inspect for internal leakage.
Large radiator leak holes should be repaired by a
reputable radiator repair shop.
INTERNAL LEAKAGE INSPECTION
Remove engine oil pan drain plug and drain a
small amount of engine oil. If coolant is present in
the pan, it will drain first because it is heavier than
oil. An alternative method is to operate engine for a
short period to churn the oil. After this is done,
remove engine dipstick and inspect for water glob-
ules. Also inspect transmission dipstick for water
globules and transmission fluid cooler for leakage.
WARNING: WITH RADIATOR PRESSURE TESTER
TOOL INSTALLED ON RADIATOR, DO NOT ALLOW
PRESSURE TO EXCEED 110 KPA (20 PSI). PRES-
SURE WILL BUILD UP QUICKLY IF A COMBUSTION
LEAK IS PRESENT. TO RELEASE PRESSURE,
ROCK TESTER FROM SIDE TO SIDE. WHEN
REMOVING TESTER, DO NOT TURN TESTER MORE
THAN 1/2 TURN IF SYSTEM IS UNDER PRESSURE.
Operate engine without pressure cap on radiator
until thermostat opens. Attach a Pressure Tester to
filler neck. If pressure builds up quickly it indicates acombustion leak exists. This is usually the result of a
cylinder head gasket leak or crack in engine. Repair
as necessary.
If there is not an immediate pressure increase,
pump the Pressure Tester. Do this until indicated
pressure is within system range of 110 kPa (16 psi).
Fluctuation of gauge pointer indicates compression or
combustion leakage into cooling system.
Because the vehicle is equipped with a catalytic
converter,do notremove spark plug cables or short
out cylinders to isolate compression leak.
If the needle on dial of pressure tester does not
fluctuate, race engine a few times to check for an
abnormal amount of coolant or steam. This would be
emitting from exhaust pipe. Coolant or steam from
exhaust pipe may indicate a faulty cylinder head gas-
ket, cracked engine cylinder block or cylinder head.
A convenient check for exhaust gas leakage into
cooling system is provided by a commercially avail-
able Block Leak Check tool. Follow manufacturers
instructions when using this product.
COMBUSTION LEAKAGE TEST - WITHOUT
PRESSURE TESTER
DO NOT WASTE reusable coolant. If solution is
clean, drain coolant into a clean container for reuse.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE CYLINDER BLOCK
DRAIN PLUGS OR LOOSEN RADIATOR DRAIN-
COCK WITH SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER PRESSURE.
SERIOUS BURNS FROM COOLANT CAN OCCUR.
Drain sufficient coolant to allow thermostat
removal. (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/ENGINE
COOLANT THERMOSTAT - REMOVAL). Remove
accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ACCES-
SORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS - REMOVAL).
Add coolant to radiator to bring level to within 6.3
mm (1/4 in) of top of thermostat housing.
CAUTION: Avoid overheating. Do not operate
engine for an excessive period of time. Open drain-
cock immediately after test to eliminate boil over.
Start engine and accelerate rapidly three times, to
approximately 3000 rpm while observing coolant. If
internal engine combustion gases are leaking into
cooling system, bubbles will appear in coolant. If bub-
bles do not appear, internal combustion gas leakage
is not present.
Fig. 6 Pressure Testing Cooling SystemÐTypical
1 - TYPICAL COOLING SYSTEM PRESSURE TESTER
7 - 6 COOLINGBR/BE
COOLING (Continued)
Page 323 of 2255

(1) Disconnect negative battery cable from battery.
(2) Partially drain cooling system (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).Do not
waste reusable coolant. If the solution is clean, drain
the coolant into a clean container for reuse.
(3) Remove upper radiator hose clamp at radiator.
A special clamp tool must be used to remove the con-
stant tension clamps. Remove hose at radiator.
(4) Disconnect throttle cable from clip at radiator
fan shroud.
(5) Unplug wiring harness from A/C compressor.
(6) Remove the air cleaner assembly.
(7) Remove accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
(8)5.9L V-8 LDC-Gas:The drive belt idler pulley
must be removed to gain access to one of the A/C
compressor/generator bracket mounting bolts.
Remove the idler pulley bolt and remove idler pulley
(Fig. 64).(9)5.9L HDC-Gas:The automatic belt tensioner/
pulley assembly must be removed to gain access to
one of the A/C compressor/generator bracket mount-
ing bolts. Remove the tensioner mounting bolt (Fig.
65) and remove tensioner.
(10) Remove the engine oil dipstick tube mounting
bolt at the side of the A/C-generator mounting
bracket.
(11) Disconnect throttle body control cables.
(12) Remove heater hose coolant return tube
mounting bolt (Fig. 66) (Fig. 67) and remove tube
from engine. Discard the old tube O-ring.
(13) Remove bracket-to-intake manifold bolts
(number 1 and 2 (Fig. 63).
(14) Remove remaining bracket-to-engine bolts
(Fig. 68) (Fig. 69).
Fig. 64 Idler Pulley - 5.9L V-8 LDC-Gas Engine
Fig. 65 Belt Tensioner - 5.9L HDC-Gas Engine
1 - PULLEY BOLT
2 - IDLER PULLEY
3 - TENSIONER PULLEY
4 - TENSIONER
5 - TENSIONER MOUNTING BOLT
7 - 74 ENGINEBR/BE
WATER PUMP INLET TUBE - 5.9L (Continued)
Page 325 of 2255

(15) Lift and position generator and A/C compres-
sor (along with their common mounting bracket) to
gain access to bypass hose. A block of wood may be
used to hold assembly in position.
(16) Loosen and position both hose clamps to the
center of bypass hose. A special clamp tool must be
used to remove the constant tension clamps. Remove
hose from vehicle.
REMOVAL - WATER PUMP BYPASS HOSE
WITHOUT AIR CONDITIONING
A water pump bypass hose (Fig. 70) is used
between the intake manifold and water pump on all
gas powered engines. To test for leaks, (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
(1) Partially drain cooling system (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE). Do not
waste reusable coolant. If the solution is clean, drain
the coolant into a clean container for reuse.WARNING: CONSTANT TENSION HOSE CLAMPS
ARE USED ON MOST COOLING SYSTEM HOSES.
WHEN REMOVING OR INSTALLING, USE ONLY
TOOLS DESIGNED FOR SERVICING THIS TYPE OF
CLAMP, SUCH AS SPECIAL CLAMP TOOL (NUMBER
6094). SNAP-ON CLAMP TOOL (NUMBER HPC-20)
MAY BE USED FOR LARGER CLAMPS. ALWAYS
WEAR SAFETY GLASSES WHEN SERVICING CON-
STANT TENSION CLAMPS.
CAUTION: A number or letter is stamped into the
tongue of constant tension clamps. If replacement
is necessary, use only an original equipment clamp
with a matching number or letter.
(2) Loosen both bypass hose clamps and position to
the center of hose.
(3) Remove hose from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - WATER PUMP BYPASS HOSE
WITH AIR CONDITIONING
(1) Position bypass hose clamps to the center of
hose.
(2) Install bypass hose to engine.
(3) Secure both hose clamps.
(4) Install generator-A/C mounting bracket assem-
bly to engine. Tighten bolt number 1 (Fig. 63) to 41
N´m (30 ft. lbs.) torque. Tighten bolt number 2 (Fig.
63) to 28 N´m (20 ft. lbs.) torque. Tighten bracket
mounting bolts (Fig. 68) (Fig. 69) to 40 N´m (30 ft.
lbs.) torque.
(5) Install a new O-ring to the heater hose coolant
return tube (Fig. 66) (Fig. 67). Coat the new O-ring
with antifreeze before installation.
(6) Install coolant return tube and its mounting
bolt to engine (Fig. 66) (Fig. 67).
(7) Connect throttle body control cables.
(8) Install oil dipstick mounting bolt.
(9)/5.9L V-8 LDC-Gas Engine:Install idler pul-
ley. Tighten bolt to 41 N´m (30 ft. lbs.) torque.
Fig. 70 Water Pump Bypass Hose - Typical
1 - WATER PUMP BYPASS HOSE
2 - FAN BLADE ASSEMBLY
3 - VISCOUS FAN DRIVE
4 - WATER PUMP AND PULLEY
7 - 76 ENGINEBR/BE
WATER PUMP INLET TUBE - 5.9L (Continued)
Page 1111 of 2255

CAUTION: This procedure MUST be followed when
installing a new bushing or seizure to shaft may
occur.
(4) Install the intake manifold (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD -
INSTALLATION).
(5) Install the distributor (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/IGNITION CONTROL/DISTRIBUTOR -
INSTALLATION).
HYDRAULIC LIFTERS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐHYDRAULIC
TAPPETS
Before disassembling any part of the engine to cor-
rect tappet noise, check the oil pressure. If vehicle
has no oil pressure gauge, install a reliable gauge at
the pressure sending-unit. The pressure should be
between 207-552 kPa (30-80 psi) at 3,000 RPM.
Check the oil level after the engine reaches normal
operating temperature. Allow 5 minutes to stabilize
oil level, check dipstick. The oil level in the pan
should never be above the FULL mark or below the
ADD OIL mark on dipstick. Either of these two con-
ditions could be responsible for noisy tappets.
OIL LEVEL
HIGH
If oil level is above the FULL mark, it is possible
for the connecting rods to dip into the oil. With the
engine running, this condition could create foam in
the oil pan. Foam in oil pan would be fed to the
hydraulic tappets by the oil pump causing them to
lose length and allow valves to seat noisily.
LOW
Low oil level may allow oil pump to take in air.
When air is fed to the tappets, they lose length,
which allows valves to seat noisily. Any leaks on
intake side of oil pump through which air can be
drawn will create the same tappet action. Check the
lubrication system from the intake strainer to the
pump cover, including the relief valve retainer cap.
When tappet noise is due to aeration, it may be
intermittent or constant, and usually more than one
tappet will be noisy. When oil level and leaks have
been corrected, operate the engine at fast idle. Run
engine for a sufficient time to allow all of the air
inside the tappets to be bled out.
TAPPET NOISE DIAGNOSIS
(1) To determine source of tappet noise, operate
engine at idle with cylinder head covers removed.
(2) Feel each valve spring or rocker arm to detect
noisy tappet. The noisy tappet will cause the affected
spring and/or rocker arm to vibrate or feel rough in
operation.
NOTE: Worn valve guides or cocked springs are
sometimes mistaken for noisy tappets. If such is
the case, noise may be dampened by applying side
thrust on the valve spring. If noise is not apprecia-
bly reduced, it can be assumed the noise is in the
tappet. Inspect the rocker arm push rod sockets
and push rod ends for wear.
(3)
Valve tappet noise ranges from light noise to a
heavy click. A light noise is usually caused by exces-
sive leak-down around the unit plunger, or by the
plunger partially sticking in the tappet body cylinder.
The tappet should be replaced. A heavy click is caused
by a tappet check valve not seating, or by foreign par-
ticles wedged between the plunger and the tappet
body. This will cause the plunger to stick in the down
position. This heavy click will be accompanied by
excessive clearance between the valve stem and rocker
arm as valve closes. In either case, tappet assembly
should be removed for inspection and cleaning.
(4) The valve train generates a noise very much
like a light tappet noise during normal operation.
Care must be taken to ensure that tappets are mak-
Fig. 34 Distributor Driveshaft Bushing Installation
1 - SPECIAL TOOL C-3053
2 - BUSHING
Fig. 35 Burnishing Distributor Driveshaft Bushing
1 - SPECIAL TOOL C-3053
2 - BUSHING
9 - 36 ENGINE 5.9LBR/BE
DISTRIBUTOR BUSHING (Continued)
Page 1118 of 2255
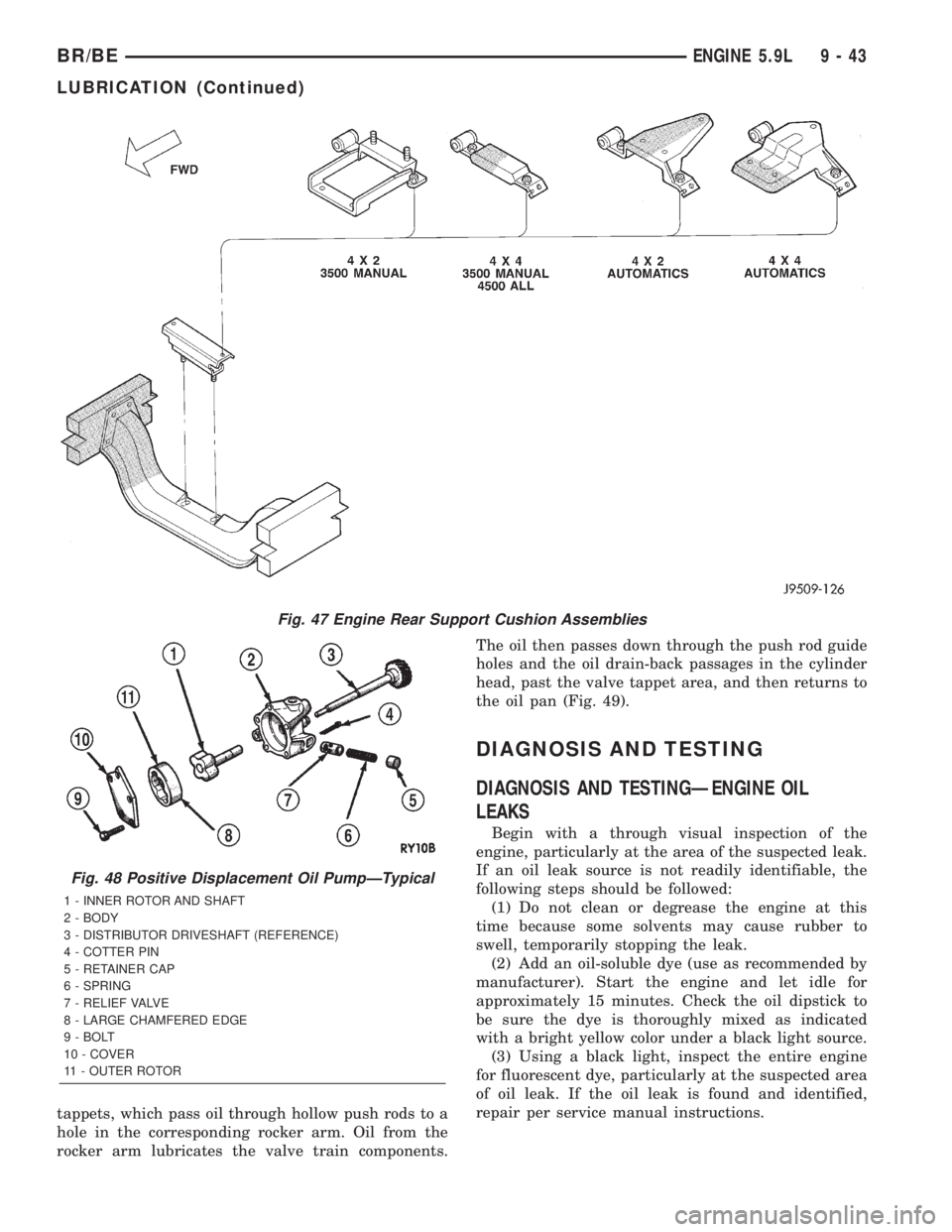
tappets, which pass oil through hollow push rods to a
hole in the corresponding rocker arm. Oil from the
rocker arm lubricates the valve train components.The oil then passes down through the push rod guide
holes and the oil drain-back passages in the cylinder
head, past the valve tappet area, and then returns to
the oil pan (Fig. 49).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐENGINE OIL
LEAKS
Begin with a through visual inspection of the
engine, particularly at the area of the suspected leak.
If an oil leak source is not readily identifiable, the
following steps should be followed:
(1) Do not clean or degrease the engine at this
time because some solvents may cause rubber to
swell, temporarily stopping the leak.
(2) Add an oil-soluble dye (use as recommended by
manufacturer). Start the engine and let idle for
approximately 15 minutes. Check the oil dipstick to
be sure the dye is thoroughly mixed as indicated
with a bright yellow color under a black light source.
(3) Using a black light, inspect the entire engine
for fluorescent dye, particularly at the suspected area
of oil leak. If the oil leak is found and identified,
repair per service manual instructions.
Fig. 47 Engine Rear Support Cushion Assemblies
Fig. 48 Positive Displacement Oil PumpÐTypical
1 - INNER ROTOR AND SHAFT
2 - BODY
3 - DISTRIBUTOR DRIVESHAFT (REFERENCE)
4 - COTTER PIN
5 - RETAINER CAP
6 - SPRING
7 - RELIEF VALVE
8 - LARGE CHAMFERED EDGE
9 - BOLT
10 - COVER
11 - OUTER ROTOR
BR/BEENGINE 5.9L 9 - 43
LUBRICATION (Continued)
Page 1120 of 2255

(4) If dye is not observed, drive the vehicle at var-
ious speeds for approximately 24km (15 miles), and
repeat previous step.
(5) If the oil leak source is not positively identified
at this time, proceed with the air leak detection test
method as follows:
(6) Disconnect the breather cap to air cleaner hose
at the breather cap end. Cap or plug breather cap
nipple.
(7) Remove the PCV valve from the cylinder head
cover. Cap or plug the PCV valve grommet.
(8) Attach an air hose with pressure gauge and
regulator to the dipstick tube.
CAUTION: Do not subject the engine assembly to
more than 20.6 kpa (3 PSI) of test pressure.
(9) Gradually apply air pressure from 1 psi to 2.5
psi maximum while applying soapy water at the sus-
pected source. Adjust the regulator to the suitable
test pressure that provide the best bubbles which
will pinpoint the leak source. If the oil leak is
detected and identified, repair per service manual
procedures.
(10) If the leakage occurs at the rear oil seal area,
refer to the section, Inspection for Rear Seal Area
Leak.
(11) If no leaks are detected, turn off the air sup-
ply and remove the air hose and all plugs and caps.
Install the PCV valve and breather cap hose. Proceed
to next step.
(12) Clean the oil off the suspect oil leak area
using a suitable solvent. Drive the vehicle at various
speeds approximately 24 km (15 miles). Inspect the
engine for signs of an oil leak by using a black light.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐENGINE OIL
PRESSURE
(1) Remove oil pressure sending unit.
(2) Install Oil Pressure Line and Gauge Tool
C-3292. Start engine and record pressure. (Refer to 9
- ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS).
OIL
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE OIL
OIL LEVEL INDICATOR (DIPSTICK)
The engine oil level indicator is located at the right
front of the engine, left of the generator (Fig. 50).
CRANKCASE OIL LEVEL INSPECTION
CAUTION: Do not overfill crankcase with engine oil,
oil foaming and oil pressure loss can result.To ensure proper lubrication of an engine, the
engine oil must be maintained at an acceptable level.
The acceptable levels are indicated between the ADD
and SAFE marks on the engine oil dipstick.
(1) Position vehicle on level surface.
(2) With engine OFF, allow approximately ten min-
utes for oil to settle to bottom of crankcase, remove
engine oil dipstick.
(3) Wipe dipstick clean.
(4) Install dipstick and verify it is seated in the
tube.
(5) Remove dipstick, with handle held above the
tip, take oil level reading.
(6) Add oil only if level is below the ADD mark on
dipstick.
ENGINE OIL CHANGE
Change engine oil at mileage and time intervals
described in the Maintenance Schedule. This infor-
mation can be found in the owner's manual.
TO CHANGE ENGINE OIL
Run engine until achieving normal operating tem-
perature.
(1) Position the vehicle on a level surface and turn
engine off.
(2) Hoist vehicle.
(3) Remove oil fill cap.
(4) Place a suitable drain pan under crankcase
drain.
(5) Remove drain plug from crankcase and allow
oil to drain into pan. Inspect drain plug threads for
Fig. 50 Oil Level Indicator Location
1 - CYLINDER HEAD COVER
2 - ENGINE OIL FILL CAP
3 - DIPSTICK
4 - ENGINE OIL FILTER
5 - FILTER BOSS
BR/BEENGINE 5.9L 9 - 45
LUBRICATION (Continued)
Page 1121 of 2255
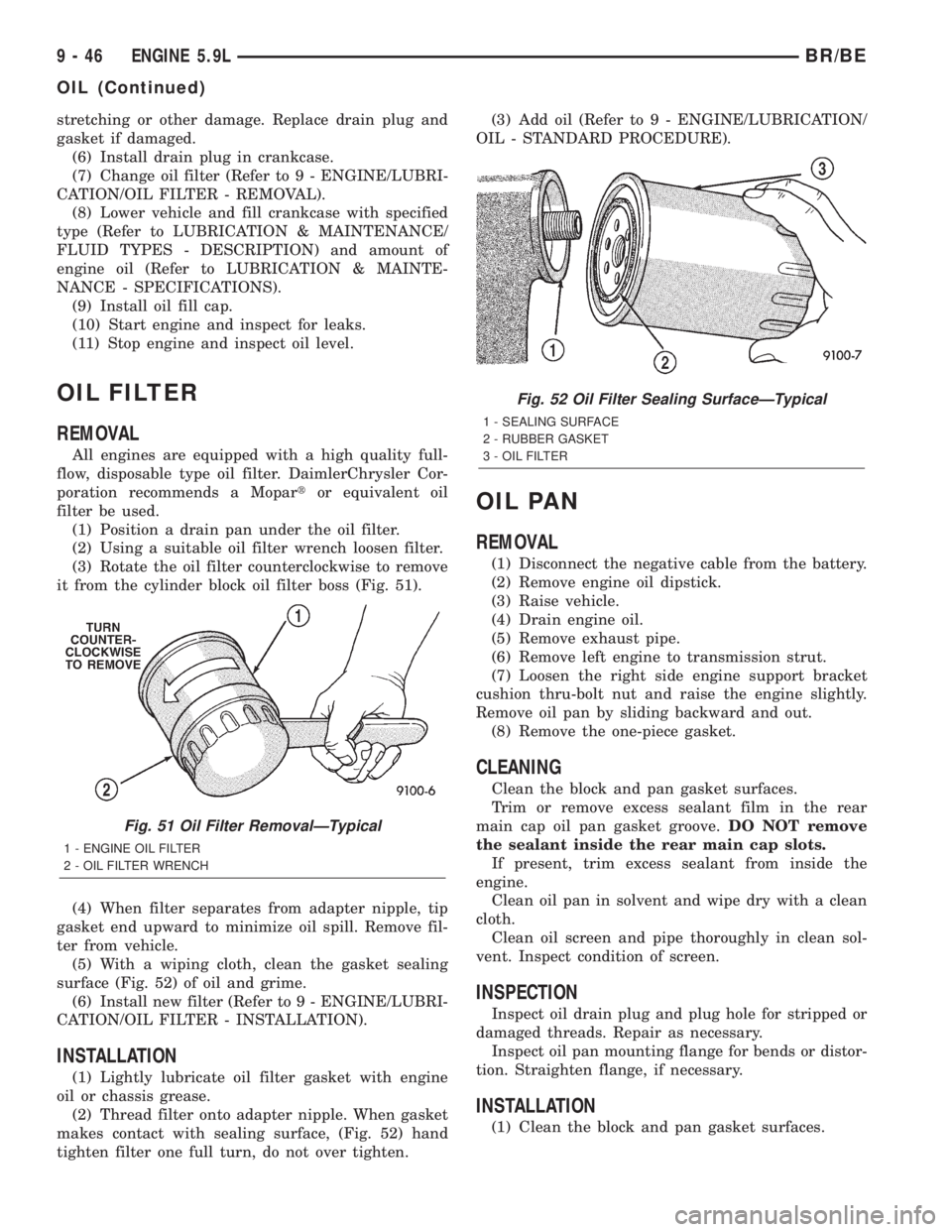
stretching or other damage. Replace drain plug and
gasket if damaged.
(6) Install drain plug in crankcase.
(7) Change oil filter (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRI-
CATION/OIL FILTER - REMOVAL).
(8) Lower vehicle and fill crankcase with specified
type (Refer to LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE/
FLUID TYPES - DESCRIPTION) and amount of
engine oil (Refer to LUBRICATION & MAINTE-
NANCE - SPECIFICATIONS).
(9) Install oil fill cap.
(10) Start engine and inspect for leaks.
(11) Stop engine and inspect oil level.
OIL FILTER
REMOVAL
All engines are equipped with a high quality full-
flow, disposable type oil filter. DaimlerChrysler Cor-
poration recommends a Mopartor equivalent oil
filter be used.
(1) Position a drain pan under the oil filter.
(2) Using a suitable oil filter wrench loosen filter.
(3) Rotate the oil filter counterclockwise to remove
it from the cylinder block oil filter boss (Fig. 51).
(4) When filter separates from adapter nipple, tip
gasket end upward to minimize oil spill. Remove fil-
ter from vehicle.
(5) With a wiping cloth, clean the gasket sealing
surface (Fig. 52) of oil and grime.
(6) Install new filter (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRI-
CATION/OIL FILTER - INSTALLATION).
INSTALLATION
(1) Lightly lubricate oil filter gasket with engine
oil or chassis grease.
(2) Thread filter onto adapter nipple. When gasket
makes contact with sealing surface, (Fig. 52) hand
tighten filter one full turn, do not over tighten.(3) Add oil (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRICATION/
OIL - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
OIL PAN
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the negative cable from the battery.
(2) Remove engine oil dipstick.
(3) Raise vehicle.
(4) Drain engine oil.
(5) Remove exhaust pipe.
(6) Remove left engine to transmission strut.
(7) Loosen the right side engine support bracket
cushion thru-bolt nut and raise the engine slightly.
Remove oil pan by sliding backward and out.
(8) Remove the one-piece gasket.
CLEANING
Clean the block and pan gasket surfaces.
Trim or remove excess sealant film in the rear
main cap oil pan gasket groove.DO NOT remove
the sealant inside the rear main cap slots.
If present, trim excess sealant from inside the
engine.
Clean oil pan in solvent and wipe dry with a clean
cloth.
Clean oil screen and pipe thoroughly in clean sol-
vent. Inspect condition of screen.
INSPECTION
Inspect oil drain plug and plug hole for stripped or
damaged threads. Repair as necessary.
Inspect oil pan mounting flange for bends or distor-
tion. Straighten flange, if necessary.
INSTALLATION
(1) Clean the block and pan gasket surfaces.
Fig. 51 Oil Filter RemovalÐTypical
1 - ENGINE OIL FILTER
2 - OIL FILTER WRENCH
Fig. 52 Oil Filter Sealing SurfaceÐTypical
1 - SEALING SURFACE
2 - RUBBER GASKET
3 - OIL FILTER
9 - 46 ENGINE 5.9LBR/BE
OIL (Continued)
Page 1122 of 2255

(2) Trim or remove excess sealant film in the rear
main cap oil pan gasket groove.DO NOT remove
the sealant inside the rear main cap slots.
(3) If present, trim excess sealant from inside the
engine.
(4) Fabricate 4 alignment dowels from 5/16x11/2
inch bolts. Cut the head off the bolts and cut a slot
into the top of the dowel. This will allow easier
installation and removal with a screwdriver (Fig. 53).
(5) Install the dowels in the cylinder block (Fig.
54) .
(6) Apply small amount of MopartSilicone Rubber
Adhesive Sealant, or equivalent in the corner of the
cap and the cylinder block.
(7) Slide the one-piece gasket over the dowels and
onto the block.
(8) Position the oil pan over the dowels and onto
the gasket.
(9) Install the oil pan bolts. Tighten the bolts to 24
N´m (215 in. lbs.) torque.
(10) Remove the dowels. Install the remaining oil
pan bolts. Tighten these bolts to 24 N´m (215 in. lbs.)
torque.
(11) Lower the engine into the support cushion
brackets and tighten the thru bolt nut to the proper
torque.
(12) Install the drain plug. Tighten drain plug to
34 N´m (25 ft. lbs.) torque.
(13) Install the engine to transmission strut.
(14) Install exhaust pipe.
(15) Lower vehicle.
(16) Install dipstick.
(17) Connect the negative cable to the battery.
(18) Fill crankcase with oil to proper level.
OIL PUMP
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the oil pan (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LU-
BRICATION/OIL PAN - REMOVAL).
(2) Remove the oil pump from rear main bearing
cap.
DISASSEMBLY
(1) Remove the relief valve as follows:
(a) Remove cotter pin. Drill a 3.175 mm (1/8
inch) hole into the relief valve retainer cap and
insert a self-threading sheet metal screw.
(b) Clamp screw into a vise and while support-
ing oil pump, remove cap by tapping pump body
using a soft hammer. Discard retainer cap and
remove spring and relief valve (Fig. 55).
(2) Remove oil pump cover (Fig. 56).
(3) Remove pump outer rotor and inner rotor with
shaft (Fig. 56).
(4) Wash all parts in a suitable solvent and inspect
carefully for damage or wear.
INSPECTION
Mating surface of the oil pump cover should be
smooth. Replace pump assembly if cover is scratched
or grooved.
Fig. 53 Fabrication of Alignment Dowels
1 - 5/16º X 1óº BOLT
2 - DOWEL
3 - SLOT
Fig. 54 Position of Dowels in Cylinder Block
1 - DOWEL
2 - DOWEL
3 - DOWEL
4 - DOWEL
BR/BEENGINE 5.9L 9 - 47
OIL PAN (Continued)
Page 1166 of 2255

(2) Use extream care and clean all gasket resdue
from the retainer.
(3) Apply a small amount of MopartSilicone Rub-
ber Adhesive Sealant to the retainer gasket. Position
the gasket onto the retainer.
(4) Position Special Tool 6687 Seal Guide onto the
crankshaft.
(5) Position the retainer and seal over the guide
and onto the engine block.
(6) Install the retainer mounting bolts. Tighten the
bolts to 22 N´m (16 ft. lbs.).
(7) Install the oil pan (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LU-
BRICATION/OIL PAN - INSTALLATION).
(8) Install the drive plate / flywheel.
(9) Install the transmission.
(10) Check and verify engine oil level.
(11) Start engine and check for leaks.
HYDRAULIC LIFTERS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐHYDRAULIC
TAPPETS
Before disassembling any part of the engine to cor-
rect tappet noise, check the oil pressure. If vehicle
has no oil pressure gauge, install a reliable gauge at
the pressure sending-unit. The pressure should be
between 207-552 kPa (30-80 psi) at 3,000 RPM.
Check the oil level after the engine reaches normal
operating temperature. Allow 5 minutes to stabilize
oil level, check dipstick. The oil level in the pan
should never be above the FULL mark or below the
ADD OIL mark on dipstick. Either of these two con-
ditions could be responsible for noisy tappets.
OIL LEVEL
HIGH
If oil level is above the FULL mark, it is possible
for the connecting rods to dip into the oil. With the
engine running, this condition could create foam in
the oil pan. Foam in oil pan would be fed to the
hydraulic tappets by the oil pump causing them to
lose length and allow valves to seat noisily.
LOW
Low oil level may allow oil pump to take in air.
When air is fed to the tappets, they lose length,
which allows valves to seat noisily. Any leaks on
intake side of oil pump through which air can be
drawn will create the same tappet action. Check the
lubrication system from the intake strainer to the
pump cover, including the relief valve retainer cap.
When tappet noise is due to aeration, it may be
intermittent or constant, and usually more than one
tappet will be noisy. When oil level and leaks havebeen corrected, operate the engine at fast idle. Run
engine for a sufficient time to allow all of the air
inside the tappets to be bled out.
TAPPET NOISE DIAGNOSIS
(1) To determine source of tappet noise, operate
engine at idle with cylinder head covers removed.
(2) Feel each valve spring or rocker arm to detect
noisy tappet. The noisy tappet will cause the affected
spring and/or rocker arm to vibrate or feel rough in
operation.
NOTE: Worn valve guides or cocked springs are
sometimes mistaken for noisy tappets. If such is
the case, noise may be dampened by applying side
thrust on the valve spring. If noise is not apprecia-
bly reduced, it can be assumed the noise is in the
tappet. Inspect the rocker arm push rod sockets
and push rod ends for wear.
(3) Valve tappet noise ranges from light noise to a
heavy click. A light noise is usually caused by exces-
sive leak-down around the unit plunger, or by the
plunger partially sticking in the tappet body cylinder.
The tappet should be replaced. A heavy click is
caused by a tappet check valve not seating, or by for-
eign particles wedged between the plunger and the
tappet body. This will cause the plunger to stick in
the down position. This heavy click will be accompa-
nied by excessive clearance between the valve stem
and rocker arm as valve closes. In either case, tappet
assembly should be removed for inspection and clean-
ing.
(4) The valve train generates a noise very much
like a light tappet noise during normal operation.
Care must be taken to ensure that tappets are mak-
ing the noise. If more than one tappet seems to be
noisy, it's probably not the tappets.
LEAK-DOWN TEST
After cleaning and inspection, test each tappet for
specified leak-down rate tolerance to ensure zero-lash
operation (Fig. 36).
Swing the weighted arm of the hydraulic valve tap-
pet tester away from the ram of the Universal Leak-
Down Tester.
(1) Place a 7.925-7.950 mm (0.312-0.313 inch)
diameter ball bearing on the plunger cap of the tap-
pet.
(2) Lift the ram and position the tappet (with the
ball bearing) inside the tester cup.
(3) Lower the ram, then adjust the nose of the ram
until it contacts the ball bearing. DO NOT tighten
the hex nut on the ram.
(4) Fill the tester cup with hydraulic valve tappet
test oil until the tappet is completely submerged.
BR/BEENGINE 8.0L 9 - 91
CRANKSHAFT REAR OIL SEAL RETAINER (Continued)
Page 1174 of 2255
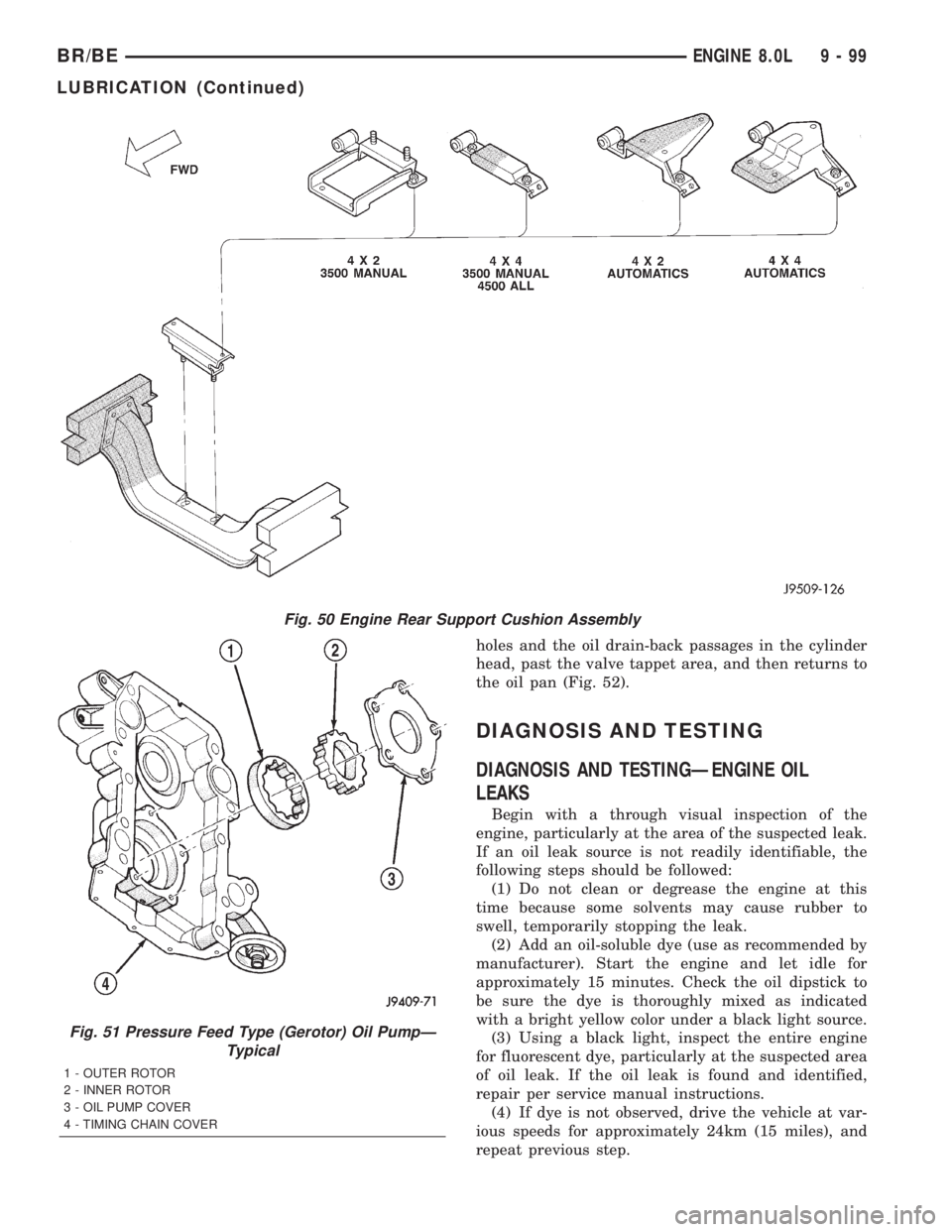
holes and the oil drain-back passages in the cylinder
head, past the valve tappet area, and then returns to
the oil pan (Fig. 52).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐENGINE OIL
LEAKS
Begin with a through visual inspection of the
engine, particularly at the area of the suspected leak.
If an oil leak source is not readily identifiable, the
following steps should be followed:
(1) Do not clean or degrease the engine at this
time because some solvents may cause rubber to
swell, temporarily stopping the leak.
(2) Add an oil-soluble dye (use as recommended by
manufacturer). Start the engine and let idle for
approximately 15 minutes. Check the oil dipstick to
be sure the dye is thoroughly mixed as indicated
with a bright yellow color under a black light source.
(3) Using a black light, inspect the entire engine
for fluorescent dye, particularly at the suspected area
of oil leak. If the oil leak is found and identified,
repair per service manual instructions.
(4) If dye is not observed, drive the vehicle at var-
ious speeds for approximately 24km (15 miles), and
repeat previous step.
Fig. 50 Engine Rear Support Cushion Assembly
Fig. 51 Pressure Feed Type (Gerotor) Oil PumpÐ
Typical
1 - OUTER ROTOR
2 - INNER ROTOR
3 - OIL PUMP COVER
4 - TIMING CHAIN COVER
BR/BEENGINE 8.0L 9 - 99
LUBRICATION (Continued)