open gas tank DODGE RAM 2002 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2002, Model line: RAM, Model: DODGE RAM 2002Pages: 2255, PDF Size: 62.07 MB
Page 256 of 2255
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COOLING SYSTEM GAS ENGINE
COOLING SYSTEM DIAGNOSISÐGASOLINE ENGINE
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
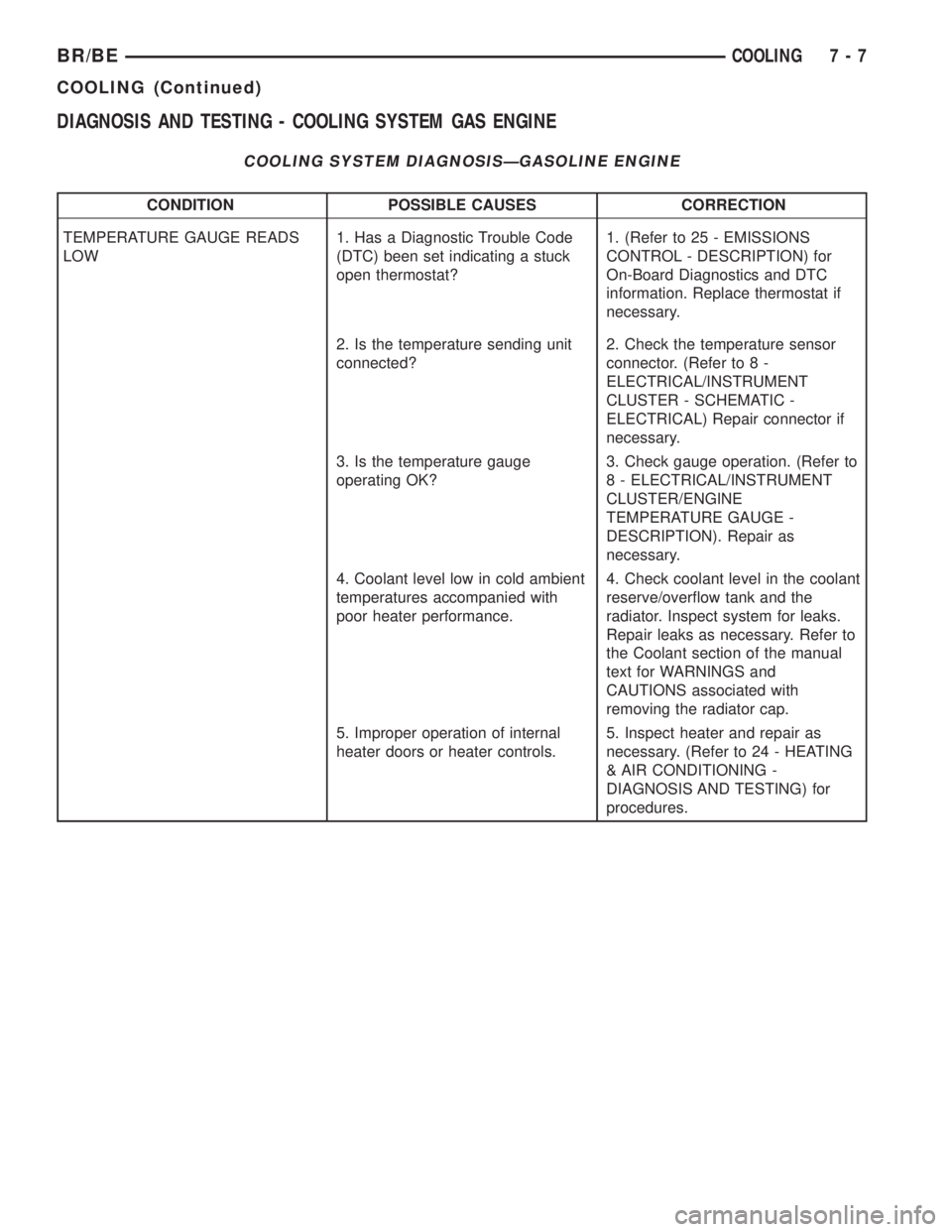
TEMPERATURE GAUGE READS
LOW1. Has a Diagnostic Trouble Code
(DTC) been set indicating a stuck
open thermostat?1. (Refer to 25 - EMISSIONS
CONTROL - DESCRIPTION) for
On-Board Diagnostics and DTC
information. Replace thermostat if
necessary.
2. Is the temperature sending unit
connected?2. Check the temperature sensor
connector. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/INSTRUMENT
CLUSTER - SCHEMATIC -
ELECTRICAL) Repair connector if
necessary.
3. Is the temperature gauge
operating OK?3. Check gauge operation. (Refer to
8 - ELECTRICAL/INSTRUMENT
CLUSTER/ENGINE
TEMPERATURE GAUGE -
DESCRIPTION). Repair as
necessary.
4. Coolant level low in cold ambient
temperatures accompanied with
poor heater performance.4. Check coolant level in the coolant
reserve/overflow tank and the
radiator. Inspect system for leaks.
Repair leaks as necessary. Refer to
the Coolant section of the manual
text for WARNINGS and
CAUTIONS associated with
removing the radiator cap.
5. Improper operation of internal
heater doors or heater controls.5. Inspect heater and repair as
necessary. (Refer to 24 - HEATING
& AIR CONDITIONING -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING) for
procedures.
BR/BECOOLING 7 - 7
COOLING (Continued)
Page 259 of 2255
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
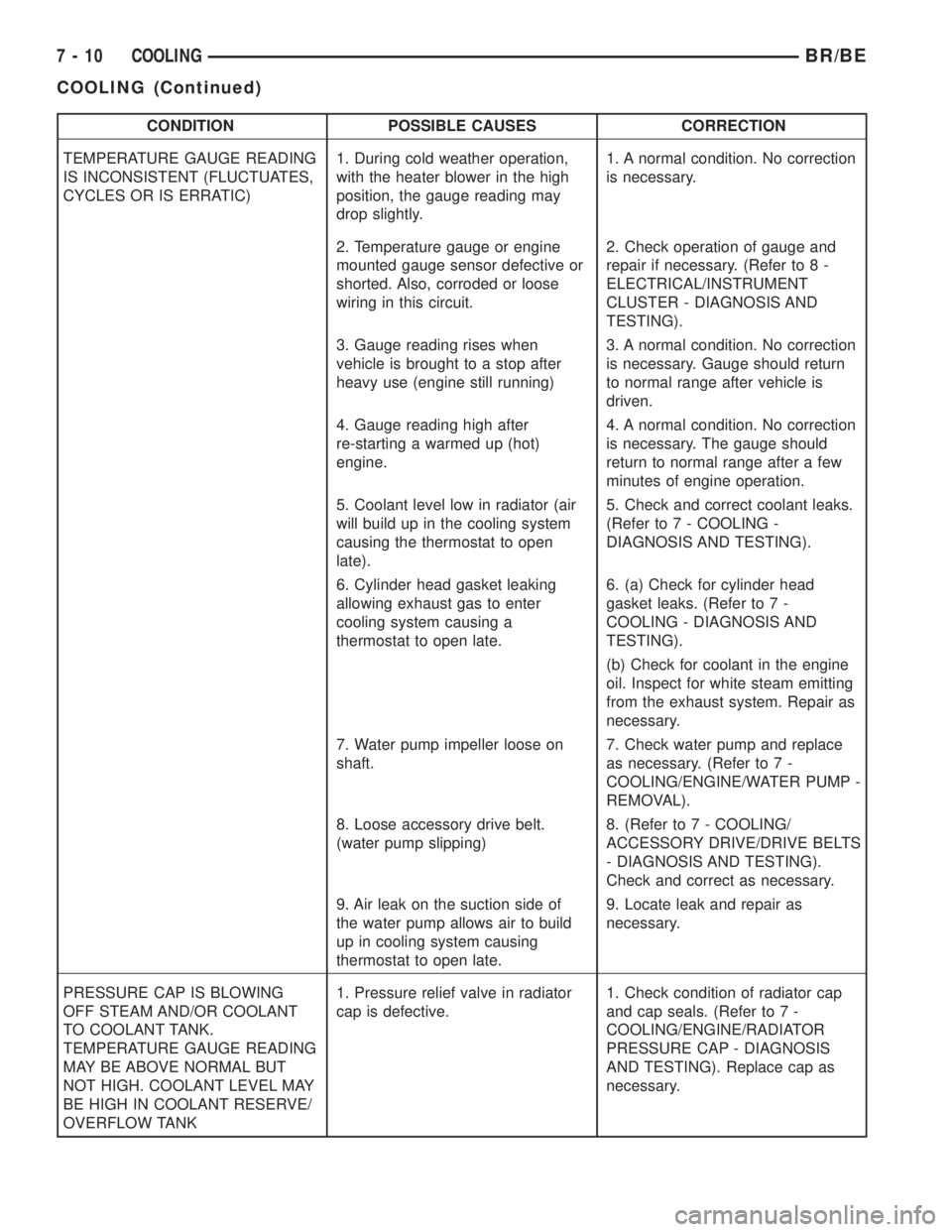
TEMPERATURE GAUGE READING
IS INCONSISTENT (FLUCTUATES,
CYCLES OR IS ERRATIC)1. During cold weather operation,
with the heater blower in the high
position, the gauge reading may
drop slightly.1. A normal condition. No correction
is necessary.
2. Temperature gauge or engine
mounted gauge sensor defective or
shorted. Also, corroded or loose
wiring in this circuit.2. Check operation of gauge and
repair if necessary. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/INSTRUMENT
CLUSTER - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
3. Gauge reading rises when
vehicle is brought to a stop after
heavy use (engine still running)3. A normal condition. No correction
is necessary. Gauge should return
to normal range after vehicle is
driven.
4. Gauge reading high after
re-starting a warmed up (hot)
engine.4. A normal condition. No correction
is necessary. The gauge should
return to normal range after a few
minutes of engine operation.
5. Coolant level low in radiator (air
will build up in the cooling system
causing the thermostat to open
late).5. Check and correct coolant leaks.
(Refer to 7 - COOLING -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
6. Cylinder head gasket leaking
allowing exhaust gas to enter
cooling system causing a
thermostat to open late.6. (a) Check for cylinder head
gasket leaks. (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
(b) Check for coolant in the engine
oil. Inspect for white steam emitting
from the exhaust system. Repair as
necessary.
7. Water pump impeller loose on
shaft.7. Check water pump and replace
as necessary. (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ENGINE/WATER PUMP -
REMOVAL).
8. Loose accessory drive belt.
(water pump slipping)8. (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS
- DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
Check and correct as necessary.
9. Air leak on the suction side of
the water pump allows air to build
up in cooling system causing
thermostat to open late.9. Locate leak and repair as
necessary.
PRESSURE CAP IS BLOWING
OFF STEAM AND/OR COOLANT
TO COOLANT TANK.
TEMPERATURE GAUGE READING
MAY BE ABOVE NORMAL BUT
NOT HIGH. COOLANT LEVEL MAY
BE HIGH IN COOLANT RESERVE/
OVERFLOW TANK1. Pressure relief valve in radiator
cap is defective.1. Check condition of radiator cap
and cap seals. (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ENGINE/RADIATOR
PRESSURE CAP - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING). Replace cap as
necessary.
7 - 10 COOLINGBR/BE
COOLING (Continued)
Page 307 of 2255

CAUTION: Some engines equipped with serpentine
drive belts have reverse rotating fans and viscous
fan drives. They are marked with the word
REVERSE to designate their usage. Installation of
the wrong fan or viscous fan drive can result in
engine overheating.
CAUTION: If the viscous fan drive is replaced
because of mechanical damage, the cooling fan
blades should also be inspected. Inspect for fatigue
cracks, loose blades, or loose rivets that could
have resulted from excessive vibration. Replace fan
blade assembly if any of these conditions are
found. Also inspect water pump bearing and shaft
assembly for any related damage due to a viscous
fan drive malfunction.
RADIATOR - 5.9L
DESCRIPTION
The radiator is a aluminum cross-flow design with
horizontal tubes through the radiator core and verti-
cal plastic side tanks (Fig. 32).
This radiator contains an internal transmission oil
cooler only on the V-10 gas engine and the 5.9L die-
sel engine combinations.
OPERATION
The radiator supplies sufficient heat transfer using
the cooling fins interlaced between the horizontal
tubes in the radiator core to cool the engine.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐRADIATOR
COOLANT FLOW
Use the following procedure to determine if coolant
is flowing through the cooling system.
(1) Idle engine until operating temperature is
reached. If the upper radiator hose is warm to the
touch, the thermostat is opening and coolant is flow-
ing to the radiator.
WARNING: HOT, PRESSURIZED COOLANT CAN
CAUSE INJURY BY SCALDING. USING A RAG TO
COVER THE RADIATOR PRESSURE CAP, OPEN
RADIATOR CAP SLOWLY TO THE FIRST STOP. THIS
WILL ALLOW ANY BUILT-UP PRESSURE TO VENT
TO THE RESERVE/OVERFLOW TANK. AFTER PRES-
SURE BUILD-UP HAS BEEN RELEASED, REMOVE
CAP FROM FILLER NECK.
(2) Drain a small amount of coolant from the radi-
ator until the ends of the radiator tubes are visible
through the filler neck. Idle the engine at normal
operating temperature. If coolant is flowing past the
exposed tubes, the coolant is circulating.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery negative cables.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE CYLINDER
BLOCK DRAIN PLUGS OR LOOSEN THE RADIATOR
DRAINCOCK WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER
PRESSURE. SERIOUS BURNS FROM COOLANT
CAN OCCUR.
(2) Drain the cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
WARNING: CONSTANT TENSION HOSE CLAMPS
ARE USED ON MOST COOLING SYSTEM HOSES.
WHEN REMOVING OR INSTALLING, USE ONLY
TOOLS DESIGNED FOR SERVICING THIS TYPE OF
CLAMP, SUCH AS SPECIAL CLAMP TOOL (NUMBER
6094). SNAP-ON CLAMP TOOL (NUMBER HPC-20)
MAY BE USED FOR LARGER CLAMPS. ALWAYS
WEAR SAFETY GLASSES WHEN SERVICING CON-
STANT TENSION CLAMPS.
CAUTION: A number or letter is stamped into the
tongue of constant tension clamps. If replacement
is necessary, use only an original equipment clamp
with a matching number or letter.
Fig. 32 Cross Flow RadiatorÐTypical
1 - COOLING TUBES
2 - TANKS
7 - 58 ENGINEBR/BE
FAN DRIVE VISCOUS CLUTCH - 5.9L DIESEL (Continued)
Page 309 of 2255

INSPECTION
Inspect the radiator side tanks for cracks, broken
or missing fittings also inspect the joint where the
tanks seam up to the radiator core for signs of leak-
age and/or deteriorating seals.
Inspect radiator core for corroded, bent or missing
cooling fins. Inspect the core for bent or damaged
cooling tubes.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position fan shroud over the fan blades rear-
ward towards engine.
(2) Install rubber insulators to alignment dowels
at lower part of radiator.
(3) Lower the radiator into position while guiding
the two alignment dowels into lower radiator sup-
port. Different alignment holes are provided in the
lower radiator support for each engine application.
(4) Install two upper radiator mounting bolts.
Tighten bolts to 11 N´m (95 in. lbs.) torque.
(5) Position the rubber shields to the sides of radi-
ator. Install the plastic clips retaining the rubber
shields to the sides of radiator.
(6) Connect both radiator hoses and install hose
clamps.
(7) Install windshield washer reservoir tank.
(8) Position fan shroud to flanges on sides of radi-
ator. Install fan shroud mounting bolts (Fig. 34).
Tighten bolts to 6 N´m (50 in. lbs.) torque.
(9) Install coolant reserve/overflow tank hose to
radiator filler neck nipple.
(10) Install coolant reserve/overflow tank to fan
shroud (fits into T-slots on shroud).
(11) Install battery negative cables.
(12) Position heater controls tofull heatposition.
(13) Fill cooling system with coolant (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(14) Operate engine until it reaches normal tem-
perature. Check cooling system fluid levels.
RADIATOR - 8.0L
DESCRIPTION
The radiator is a aluminum cross-flow design with
horizontal tubes through the radiator core and verti-
cal plastic side tanks (Fig. 36).
This radiator contains an internal transmission oil
cooler only on the V-10 gas engine and the 5.9L die-
sel engine combinations.
OPERATION
The radiator supplies sufficient heat transfer using
the cooling fins interlaced between the horizontal
tubes in the radiator core to cool the engine.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐRADIATOR
COOLANT FLOW
Use the following procedure to determine if coolant
is flowing through the cooling system.
(1) Idle engine until operating temperature is
reached. If the upper radiator hose is warm to the
touch, the thermostat is opening and coolant is flow-
ing to the radiator.
WARNING: HOT, PRESSURIZED COOLANT CAN
CAUSE INJURY BY SCALDING. USING A RAG TO
COVER THE RADIATOR PRESSURE CAP, OPEN
RADIATOR CAP SLOWLY TO THE FIRST STOP. THIS
WILL ALLOW ANY BUILT-UP PRESSURE TO VENT
TO THE RESERVE/OVERFLOW TANK. AFTER PRES-
SURE BUILD-UP HAS BEEN RELEASED, REMOVE
CAP FROM FILLER NECK.
(2) Drain a small amount of coolant from the radi-
ator until the ends of the radiator tubes are visible
through the filler neck. Idle the engine at normal
operating temperature. If coolant is flowing past the
exposed tubes, the coolant is circulating.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery negative cables.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE CYLINDER
BLOCK DRAIN PLUGS OR LOOSEN THE RADIATOR
DRAINCOCK WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER
PRESSURE. SERIOUS BURNS FROM COOLANT
CAN OCCUR.
Fig. 36 Cross Flow RadiatorÐTypical
1 - COOLING TUBES
2 - TANKS
7 - 60 ENGINEBR/BE
RADIATOR - 5.9L (Continued)
Page 311 of 2255

(2) Install rubber insulators to alignment dowels
at lower part of radiator.
(3) Lower the radiator into position while guiding
the two alignment dowels into lower radiator sup-
port. Different alignment holes are provided in the
lower radiator support for each engine application.
(4) Install two upper radiator mounting bolts.
Tighten bolts to 11 N´m (95 in. lbs.) torque.
(5) Connect both radiator hoses and install hose
clamps.
(6) Install windshield washer reservoir tank.
(7) Position fan shroud to flanges on sides of radi-
ator. Install fan shroud mounting bolts (Fig. 37).
Tighten bolts to 6 N´m (50 in. lbs.) torque.
(8) Install coolant reserve/overflow tank hose to
radiator filler neck nipple.
(9) Connect the overflow hose to the radiator.
(10) Install battery negative cables.
(11) Position heater controls tofull heatposition.
(12) Fill cooling system with coolant (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(13) Operate engine until it reaches normal tem-
perature. Check cooling system fluid levels.
RADIATOR - 5.9L DIESEL
DESCRIPTION
The radiator is a aluminum cross-flow design with
horizontal tubes through the radiator core and verti-
cal plastic side tanks (Fig. 39).
This radiator contains an internal transmission oil
cooler only on the V-10 gas engine and the 5.9L die-
sel engine combinations.
OPERATION
The radiator supplies sufficient heat transfer using
the cooling fins interlaced between the horizontal
tubes in the radiator core to cool the engine.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐRADIATOR
COOLANT FLOW
Use the following procedure to determine if coolant
is flowing through the cooling system.
(1) Idle engine until operating temperature is
reached. If the upper radiator hose is warm to the
touch, the thermostat is opening and coolant is flow-
ing to the radiator.
WARNING: HOT, PRESSURIZED COOLANT CAN
CAUSE INJURY BY SCALDING. USING A RAG TO
COVER THE RADIATOR PRESSURE CAP, OPEN
RADIATOR CAP SLOWLY TO THE FIRST STOP. THIS
WILL ALLOW ANY BUILT-UP PRESSURE TO VENT
TO THE RESERVE/OVERFLOW TANK. AFTER PRES-SURE BUILD-UP HAS BEEN RELEASED, REMOVE
CAP FROM FILLER NECK.
(2) Drain a small amount of coolant from the radi-
ator until the ends of the radiator tubes are visible
through the filler neck. Idle the engine at normal
operating temperature. If coolant is flowing past the
exposed tubes, the coolant is circulating.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect both battery negative cables.
Remove the nuts retaining the positive cable to the
top of radiator. Position positive battery cable to rear
of vehicle.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE CYLINDER
BLOCK DRAIN PLUGS OR LOOSEN THE RADIATOR
DRAINCOCK WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER
PRESSURE. SERIOUS BURNS FROM COOLANT
CAN OCCUR.
(2) Drain the cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
WARNING: CONSTANT TENSION HOSE CLAMPS
ARE USED ON MOST COOLING SYSTEM HOSES.
WHEN REMOVING OR INSTALLING, USE ONLY
TOOLS DESIGNED FOR SERVICING THIS TYPE OF
CLAMP, SUCH AS SPECIAL CLAMP TOOL (NUMBER
6094). SNAP-ON CLAMP TOOL (NUMBER HPC-20)
MAY BE USED FOR LARGER CLAMPS. ALWAYS
WEAR SAFETY GLASSES WHEN SERVICING CON-
STANT TENSION CLAMPS.
Fig. 39 Cross Flow RadiatorÐTypical
1 - COOLING TUBES
2 - TANKS
7 - 62 ENGINEBR/BE
RADIATOR - 8.0L (Continued)
Page 313 of 2255

CLEANING
Clean radiator fins are necessary for good heat
transfer. The radiator and air conditioning fins
should be cleaned when an accumulation of debris
has occurred. With the engine cold, apply cold water
and compressed air to the back (engine side) of the
radiator to flush the radiator and/or A/C condenser of
debris.
INSPECTION
Inspect the radiator side tanks for cracks, broken
or missing fittings also inspect the joint where the
tanks seam up to the radiator core for signs of leak-
age and/or deteriorating seals.
Inspect radiator core for corroded, bent or missing
cooling fins. Inspect the core for bent or damaged
cooling tubes.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position fan shroud over the fan blades rear-
ward towards engine.
(2) Install rubber insulators to alignment dowels
at lower part of radiator.
(3) Lower the radiator into position while guiding
the two alignment dowels into lower radiator sup-
port. Different alignment holes are provided in the
lower radiator support for each engine application.
(4) Install two upper radiator mounting bolts.
Tighten bolts to 11 N´m (95 in. lbs.) torque.
(5) Connect both radiator hoses and install hose
clamps.
(6) Connect transmission cooler lines to radiator
tank. Inspect quick connect fittings for debris and
install until an audible ªclickº is heard. Pull apart to
verify connection.
(7) Install windshield washer reservoir tank.
(8) Position fan shroud to flanges on sides of radi-
ator. Install fan shroud mounting bolts (Fig. 41).
Tighten bolts to 6 N´m (50 in. lbs.) torque.
(9) Install metal clips to top of fan shroud.
(10) Install coolant reserve/overflow tank hose to
radiator filler neck nipple.
(11) Install coolant reserve/overflow tank to fan
shroud (fits into T-slots on shroud).
(12) Install battery negative cables.
(13) Install positive battery cable to top of radia-
tor. Tighten radiator-to-battery cable mounting nuts.
(14) Position heater controls tofull heatposition.
(15) Fill cooling system with coolant (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(16) Operate engine until it reaches normal tem-
perature. Check cooling system and automatic trans-
mission (if equipped) fluid levels.
RADIATOR PRESSURE CAP
DESCRIPTION
Radiators are equipped with a pressure cap, which
releases pressure at some point within a range of
97-124 kPa (14-18 psi). The pressure relief point (in
pounds) is engraved on top of cap.
The cooling system will operate at pressures
slightly above atmospheric pressure. This results in a
higher coolant boiling point allowing increased radi-
ator cooling capacity.
A rubber gasket seals radiator filler neck to pre-
vent leakage. This is done to keep system under
pressure. It also maintains vacuum during coolant
cool-down allowing coolant to return from reserve/
overflow tank.
OPERATION
The cap (Fig. 43) contains a spring-loaded pressure
relief valve that opens when system pressure reaches
release range of 97-124 kPa (14-18 psi).
A vent valve in the center of cap allows a small
coolant flow through cap when coolant is below boil-
ing temperature. The valve is completely closed when
boiling point is reached. As the coolant cools, it con-
tracts and creates a vacuum in the cooling system.
This causes the vacuum valve to open and coolant in
the reserve/overflow tank to be drawn through its
connecting hose into radiator. If the vacuum valve is
stuck shut, the radiator hoses will collapse on cool-
down. Clean the vent valve (Fig. 43).
Fig. 43 Radiator Pressure Cap and Filler NeckÐ
Typical
1 - STAINLESS-STEEL SWIVEL TOP
2 - RUBBER SEALS
3 - VENT VALVE
4 - RADIATOR TANK
5 - FILLER NECK
6 - OVERFLOW NIPPLE
7 - MAIN SPRING
8 - GASKET RETAINER
7 - 64 ENGINEBR/BE
RADIATOR - 5.9L DIESEL (Continued)
Page 314 of 2255

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐRADIATOR
CAP-TO-FILLER NECK SEAL
The pressure cap upper gasket (seal) pressure
relief can be tested by removing overflow hose from
radiator filler neck nipple. Attach hose of pressure
tester tool 7700 (or equivalent) to nipple. It will be
necessary to disconnect hose from its adapter for
filler neck. Pump air into radiator. The pressure cap
upper gasket should relieve at 69-124 kPa (10-18 psi)
and hold pressure at a minimum of 55 kPa (8 psi).
WARNING: THE WARNING WORDS ÐDO NOT
OPEN HOTÐ ON RADIATOR PRESSURE CAP, ARE
A SAFETY PRECAUTION. WHEN HOT, PRESSURE
BUILDS UP IN COOLING SYSTEM. TO PREVENT
SCALDING OR INJURY, RADIATOR CAP SHOULD
NOT BE REMOVED WHILE SYSTEM IS HOT AND/OR
UNDER PRESSURE.
Do not remove radiator cap at any timeexceptfor
the following purposes:
²Check and adjust antifreeze freeze point
²Refill system with new antifreeze
²Conducting service procedures
²Checking for vacuum leaks
WARNING: IF VEHICLE HAS BEEN RUN RECENTLY,
WAIT AT LEAST 15 MINUTES BEFORE REMOVING
RADIATOR CAP. WITH A RAG, SQUEEZE RADIATOR
UPPER HOSE TO CHECK IF SYSTEM IS UNDER
PRESSURE. PLACE A RAG OVER CAP AND WITH-
OUT PUSHING CAP DOWN, ROTATE IT COUNTER-
CLOCKWISE TO FIRST STOP. ALLOW FLUID TO
ESCAPE THROUGH THE COOLANT RESERVE/
OVERFLOW HOSE INTO RESERVE/OVERFLOW
TANK. SQUEEZE RADIATOR UPPER HOSE TO
DETERMINE WHEN PRESSURE HAS BEEN
RELEASED. WHEN COOLANT AND STEAM STOP
BEING PUSHED INTO TANK AND SYSTEM PRES-
SURE DROPS, REMOVE RADIATOR CAP COM-
PLETELY.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐRADIATOR CAP
Remove cap from radiator. Be sure that sealing
surfaces are clean. Moisten rubber gasket with water
and install cap on pressure tester 7700 or an equiv-
alent (Fig. 44).NOTE: Radiator pressure testing tools are very sen-
sitive to small air leaks, which will not cause cool-
ing system problems. A pressure cap that does not
have a history of coolant loss should not be
replaced just because it leaks slowly when tested
with this tool. Add water to tool. Turn tool upside
down and recheck pressure cap to confirm that cap
needs replacement.
Operate tester pump to bring pressure to 104 kPa
(15 psi) on gauge. If pressure cap fails to hold pres-
sure of at least 97 kPa (14 psi) replace cap.
The pressure cap may test properly while posi-
tioned on tool 7700 (or equivalent). It may not hold
pressure or vacuum when installed on radiator. If so,
inspect radiator filler neck and cap's top gasket for
damage. Also inspect for dirt or distortion that may
prevent cap from sealing properly.CLEANING
Clean radiator pressure cap using a mild soap and
water mixture. DO NOT use any chemicals stronger
than mild soap, damage to the seal can occur.
Fig. 44 Pressure Testing Radiator CapÐTypical
Tester
1 - PRESSURE CAP
2 - TYPICAL COOLING SYSTEM PRESSURE TESTER
BR/BEENGINE 7 - 65
RADIATOR PRESSURE CAP (Continued)
Page 315 of 2255

INSPECTION
Hold cap at eye level, right side up. The vent valve
(Fig. 45) at bottom of cap should open. If rubber gas-
ket has swollen and prevents vent valve from open-
ing, replace cap.
Hold cap at eye level, upside down. If any light can
be seen between vent valve and rubber gasket,
replace cap.Do not use a replacement cap that
has a spring to hold vent shut.A replacement cap
must be the type designed for a coolant reserve/over-
flow system with a completely sealed diaphragm
spring and a rubber gasket. This gasket is used to
seal to radiator filler neck top surface. Use of proper
cap will allow coolant return to radiator.
WATER PUMP - 5.9L
DESCRIPTION
The water pump is located on the engine front
cover, and has an integral pulley attached (Fig. 46).
The water pump impeller is pressed onto the rear
of a shaft that rotates in a bearing pressed into the
water pump body. The body has a small hole for ven-
tilation. The water pump seals are lubricated by
antifreeze in the coolant mixture. Additional lubrica-
tion is not necessary.
OPERATION
A centrifugal water pump circulates coolant
through the water jackets, passages, intake manifold,
radiator core, cooling system hoses and heater core,this coolant absorbs the heat generated when the
engine is running. The pump is driven by the engine
crankshaft via a drive belt.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐWATER PUMP
A quick test to determine if pump is working is to
check if heater warms properly. A defective water
pump will not be able to circulate heated coolant
through the long heater hose to the heater core.
REMOVAL
The water pump on all models can be removed
without discharging the air conditioning system (if
equipped).
The water pump on all gas powered engines is
bolted directly to the engine timing chain case/cover.
On the 5.9L gas powered engine, a gasket is used
as a seal between the water pump and timing chain
case/cover.
If water pump is replaced because of bearing/shaft
damage or leaking shaft seal, the mechanical cooling
fan assembly should also be inspected. Inspect for
fatigue cracks, loose blades or loose rivets that could
have resulted from excessive vibration. Replace fan if
any of these conditions are found. Also check condi-
tion of the thermal viscous fan drive (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ENGINE/FAN DRIVE VISCOUS
CLUTCH - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Drain cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
Do not waste reusable coolant. If solution is clean,
drain coolant into a clean container for reuse.
Fig. 45 Radiator Pressure Cap
1 - STAINLESS-STEEL SWIVEL TOP
2 - RUBBER SEALS
3 - VENT VALVE
4 - RADIATOR TANK
5 - FILLER NECK
6 - OVERFLOW NIPPLE
7 - MAIN SPRING
8 - GASKET RETAINER
Fig. 46 Water Pump LocationÐTypical
1 - WATER PUMP BYPASS HOSE
2 - FAN BLADE ASSEMBLY
3 - VISCOUS FAN DRIVE
4 - WATER PUMP AND PULLEY
7 - 66 ENGINEBR/BE
RADIATOR PRESSURE CAP (Continued)
Page 1304 of 2255

FUEL FILTER/PRESSURE
REGULATOR
DESCRIPTION
A combination fuel filter and fuel pressure regula-
tor (Fig. 2) is used on all engines. It is located on the
top of the fuel pump module. A separate frame
mounted fuel filter is not used with any engine.
Both fuel filters (at bottom of fuel pump module
and within fuel pressure regulator) are designed for
extended service. They do not require normal sched-
uled maintenance. Filters should only be replaced if
a diagnostic procedure indicates to do so.
OPERATION
Fuel Pressure Regulator Operation:The pres-
sure regulator is a mechanical device that is not con-
trolled by engine vacuum or the powertrain control
module (PCM).
The regulator is calibrated to maintain fuel system
operating pressure of approximately 339 kPa 34
kPa (49.2 psi 5 psi) at the fuel injectors. It contains
a diaphragm, calibrated springs and a fuel return
valve. The internal fuel filter (Fig. 2) is also part of
the assembly.
Fuel is supplied to the filter/regulator by the elec-
tric fuel pump through an opening tube at the bot-
tom of filter/regulator (Fig. 2) .
The regulator acts as a check valve to maintain
some fuel pressure when the engine is not operating.
This will help to start the engine. A second checkvalve is located at the outlet end of the electric fuel
pump.Refer to Fuel PumpÐDescription and
Operation for more information. Also refer to
the Fuel Pressure Leak Down Test and the Fuel
Pump Pressure Tests.
If fuel pressure at the pressure regulator exceeds
approximately 49.2 psi, an internal diaphragm opens
and excess fuel pressure is routed back into the tank
through the bottom of pressure regulator.
Both fuel filters (at bottom of fuel pump module
and within fuel pressure regulator) are designed for
extended service. They do not require normal sched-
uled maintenance. Filters should only be replaced if
a diagnostic procedure indicates to do so.
REMOVAL
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER A CON-
STANT PRESSURE, EVEN WITH ENGINE OFF.
BEFORE SERVICING FUEL FILTER/FUEL PRES-
SURE REGULATOR, FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE
MUST BE RELEASED.
Refer to Fuel System Pressure Release in Fuel
Delivery System section of this group.
The fuel filter/fuel pressure regulator (Fig. 3) is
located at top of fuel pump module (Fig. 4) or (Fig.
5).
Fuel pump module removal is not necessary.
(1) Drain fuel tank and remove tank. Refer to Fuel
Tank Removal/Installation.
Fig. 2 Side ViewÐFilter/Regulator
1 - INTERNAL FUEL FILTER
2 - FUEL FLOW TO FUEL INJECTORS
3 - FUEL FILTER/FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
4 - EXCESS FUEL BACK TO TANK
5 - FUEL INLET
6 - RUBBER GROMMET
7 - TOP OF PUMP MODULE
Fig. 3 Fuel Filter/Fuel Pressure Regulator
1 - INTERNAL FUEL FILTER
2 - FUEL FLOW TO FUEL INJECTORS
3 - FUEL FILTER/FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
4 - EXCESS FUEL BACK TO TANK
5 - FUEL INLET
6 - RUBBER GROMMET
7 - TOP OF PUMP MODULE
BR/BEFUEL DELIVERY - GASOLINE 14 - 5
Page 1308 of 2255

FUEL PUMP
DESCRIPTION
The electric fuel pump is located inside of the fuel
pump module. A 12 volt, permanent magnet, electric
motor powers the fuel pump. The electric fuel pump
is not a separate, serviceable component.
OPERATION
Voltage to operate the electric pump is supplied
through the fuel pump relay.
Fuel is drawn in through a filter at the bottom of
the module and pushed through the electric motor
gearset to the pump outlet.
Check Valve Operation:The pump outlet con-
tains a one-way check valve to prevent fuel flow back
into the tank and to maintain fuel supply line pres-
sure (engine warm) when pump is not operational. It
is also used to keep the fuel supply line full of gaso-
line when pump is not operational. After the vehicle
has cooled down, fuel pressure may drop to 0 psi
(cold fluid contracts), but liquid gasoline will remain
in fuel supply line between the check valve and fuel
injectors.Fuel pressure that has dropped to 0
psi on a cooled down vehicle (engine off) is a
normal condition.Refer to the Fuel Pressure Leak
Down Test for more information.
The electric fuel pump is not a separate, service-
able component.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL PUMP
CAPACITY TEST
Before performing this test, verify fuel pump
pressure. Refer to Fuel Pump Pressure Test.
Use this test in conjunction with the Fuel Pres-
sure Leak Down Test.
(1) Release fuel system pressure. Refer to Fuel
Pressure Release Procedure.
(2) Disconnect fuel supply line at fuel rail. Refer to
Quick-Connect Fittings. Some engines may require
air cleaner housing removal before line disconnection.
(3) Obtain correct Fuel Line Pressure Test Adapter
Tool Hose. Tool number 6539 is used for 5/16º fuel
lines and tool number 6631 is used for 3/8º fuel lines.
(4) Connect correct Fuel Line Pressure Test
Adapter Tool Hose into disconnected fuel supply line.
Insert other end of Adaptor Tool Hose into a gradu-
ated container.
(5) Remove fuel fill cap.
(6) To activate fuel pump and pressurize system,
obtain DRBtscan tool and actuate ASD Fuel System
Test.(7) A good fuel pump will deliver at least 1/4 liter
of fuel in 7 seconds. Do not operate fuel pump for
longer than 7 seconds with fuel line disconnected as
fuel pump module reservoir may run empty.
(a) If capacity is lower than specification, but
fuel pump can be heard operating through fuel fill
cap opening, check for a kinked/damaged fuel sup-
ply line somewhere between fuel rail and fuel
pump module.
(b) If line is not kinked/damaged, and fuel pres-
sure is OK, but capacity is low, replace fuel filter/
fuel pressure regulator. The filter/regulator may be
serviced separately on certain applications. Refer
to Fuel Filter/Fuel Pressure Regulator Removal/In-
stallation for additional information.
(c) If both fuel pressure and capacity are low,
replace fuel pump module assembly. Refer to Fuel
Pump Module Removal/Installation.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL PUMP
PRESSURE TEST
Use this test in conjunction with the Fuel Pump
Capacity Test, Fuel Pressure Leak Down Test and
Fuel Pump Amperage Test found elsewhere in this
group.
Check Valve Operation:The electric fuel pump
outlet contains a one-way check valve to prevent fuel
flow back into the tank and to maintain fuel supply
line pressure (engine warm) when pump is not oper-
ational. It is also used to keep the fuel supply line
full of gasoline when pump is not operational. After
the vehicle has cooled down, fuel pressure may drop
to 0 psi (cold fluid contracts), but liquid gasoline will
remain in fuel supply line between the check valve
and fuel injectors.Fuel pressure that has
dropped to 0 psi on a cooled down vehicle
(engine off) is a normal condition.When the elec-
tric fuel pump is activated, fuel pressure should
immediately(1±2 seconds) rise to specification.
All fuel systems are equipped with a fuel tank
module mounted, combination fuel filter/fuel pressure
regulator. The fuel pressure regulator is not con-
trolled by engine vacuum.
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER CON-
STANT FUEL PRESSURE EVEN WITH THE ENGINE
OFF. BEFORE DISCONNECTING FUEL LINE AT
FUEL RAIL, THIS PRESSURE MUST BE RELEASED.
REFER TO THE FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE
RELEASE PROCEDURE.
(1) Remove protective cap at fuel rail test port.
Connect the 0±414 kPa (0-60 psi) fuel pressure gauge
(from gauge set 5069) to test port pressure fitting on
fuel rail (Fig. 11).The DRBtIII Scan Tool along
with the PEP module, the 500 psi pressure
BR/BEFUEL DELIVERY - GASOLINE 14 - 9