length DODGE RAM 2003 Service Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2003, Model line: RAM, Model: DODGE RAM 2003Pages: 2895, PDF Size: 83.15 MB
Page 1554 of 2895

INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES &
SEATS
DESCRIPTION
The valves are made of heat resistant steel, and
have chrome plated stems to prevent scuffing. The
intake and exhaust valves are both similar in head
diameter and overall length, but they have unique
face angles which makes them non-interchangeable.
The valves are distinguished by unique dimples on
the exhaust valve head (Fig. 21).
The exhaust valve springs are made from high
strength, chrome silicon steel. The exhaust valve
springs are also exhaust brake compatible.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - VALVES, GUIDES
AND SPRINGS
REMOVAL
(1) Remove cylinder head (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
CYLINDER HEAD - REMOVAL).
(2) Support cylinder head on stands, or install
head bolts upside down (through combustion surface
side) to protect injector tips from damage from work
bench.
(3) Install the valve spring compressor mounting
base as shown in (Fig. 22).
(4) Install the compressor top plate, washer, and
nut. Using a suitable wrench, tighten the nut (clock-
wise) to compress the valve springs (Fig. 23) and
remove the locks.
(5) Rotate the compressor nut counter-clockwise to
relieve tension on the springs. Remove the spring
compressor.(6) Remove the retainers, springs, valve seals (if
necessary), and valves (Fig. 24). Arrange or number
all components so they can be installed in their orig-
inal locations.
(7) Repeat the procedure on all cylinders to be ser-
viced.
CLEANING
Clean the valve stems with crocus cloth or a
Scotch-BriteŸ pad. Remove carbon with a soft wire
brush. Clean valves, springs, retainers, and valve
retaining locks in a suitable solvent. Rinse in hot
water and blow dry with compressed air.
Fig. 21 Valve Identification
1 - INTAKE VALVES
2 - EXHAUST VALVES
Fig. 22 Spring Compressor Mounting BaseÐPart of
Tool 8319±A
1 - COMPRESSOR MOUNTING BASE
Fig. 23 Compressing Valve Springs with Tool
8319±A
1 - SPECIAL TOOL 8319
DRENGINE 5.9L DIESEL 9 - 305
Page 1556 of 2895

Measure valve margin (rim thickness) (Fig. 28).
Measure the valve spring free length and maxi-
mum inclination (Fig. 29).
Test valve spring force with tool C-647 (Fig. 30).
Specification 72.0 Ð 80.7 lbs. when compressed to
35.33 mm (1.39 in.).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install new valve seals. The yellow seals are for
the intake valves and the green seals are for the
exhaust valves.
(2) Install the valves in their original postion. The
exhaust valves are identified by a dimple on the
valve head (Fig. 31).
(3) Install the valve springs and retainer.
(4) Install the valve spring compressor tool 8319±A
as shown in (Fig. 22) and (Fig. 23).(5) Compress the valve springs and install the
valve retaining locks (Fig. 24).
(6) Remove the compressor and repeat the proce-
dure on the remaining cylinders.
(7) Install new o-ring and sealing washer on injec-
tor.
(8) Lubricate o-ring and injector bore.
(9) Verify sealing washer (shim) was removed with
old injector.
(10) Install injector with fuel injector connector
port facing intake manifold.
(11) Install hold-down bolt. Torque to 10 Nm (89
in. lbs.).
(12) Install fuel injector connector and connector
nut. Torque nut to 50 Nm (36.8 ft. lbs.).
(13) Install the cylinder head (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - INSTALLATION).
Fig. 28 Measure Valve Margin (Rim Thickness)
VALVE MARGIN (RIM THICKNESS)
0.79 mm (0.031 in.) MIN.
Fig. 29 Measure Valve Spring Free Length and Max.
Inclination
APPROXIMATE VALVE SPRING FREE LENGTH
47.75 mm (1.88 in.)
MAX INCLINATION
1.5 mm (.059 in.)
Fig. 30 Testing Valve Spring with Tool C-647
1 - SPECIAL TOOL C-647
Fig. 31 Valve Identification
1 - INTAKE VALVES
2 - EXHAUST VALVES
DRENGINE 5.9L DIESEL 9 - 307
INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES & SEATS (Continued)
Page 1562 of 2895

(3) Consult the parts catalog for the proper head
gaskets which must be used with refaced blocks to
ensure proper piston-to-valve clearance.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CYLINDER BORE -
DE-GLAZE
(1) New piston rings may not seat in glazed cylin-
der bores.
(2) De-glazing gives the bore the correct surface
finish required to seat the rings. The size of the bore
is not changed by proper de-glazing.
(3) Cover the lube and tappet holes in the top of
the block with waterproof tape.
(4) It crankshaft is installed, wrap connecting rod
journals with clean cloth. Cover cloth with water-
proof tape.
(5) A correctly honed surface will have a cross-
hatch appearance with the lines at 15É to 25É angles
(Fig. 46). For the rough hone, use 80 grit honing
stones. To finish hone, use 280 grit honing stones.
(6) Use a drill, a fine grit Flex-hone and a mixture
of equal parts of mineral spirits and SAE 30W engine
oil to de-glaze the bores.
(7) The crosshatch angle is a function of drill
speed and how fast the hone is moved vertically (Fig.
47).
(8) Vertical strokes MUST be smooth continuous
passes along the full length of the bore (Fig. 47).(9) Inspect the bore after 10 strokes.
(10) Use a strong solution of hot water and laun-
dry detergent to clean the bores. Clean the cylinder
bores immediately after de-glazing.
(11) Rinse the bores until the detergent is removed
and blow the block dry with compressed air.
(12) Check the bore cleanliness by wiping with a
white, lint free, lightly oiled cloth. If grit residue is
still present, repeat the cleaning process until all res-
idue is removed. Wash the bores and the complete
block assembly with solvent and dry with compressed
air. Place a clean shop towel around the top main
bearing saddle to deflect water and residue from pis-
ton cooling nozzels. Remove directed piston cooling
nozzles if installed.
(13) Be sure to remove the tape covering the lube
holes, rod journals, and piston cooling nozzles after
the cleaning process is complete.
STANDARD PROCEDUREÐCYLINDER BORE
REPAIR
Cylinder bore(s) can be repaired by one of two
methods:
²Method 1:ÐOver boring and using oversize pis-
tons and rings.
²Method 2:ÐBoring and installing a repair sleeve
to return the bore to standard dimensions.
METHOD 1ÐOVERSIZE BORE
Cylinder bore(s) can be repaired by one of two
methods:
Oversize pistons and rings are available in two
sizes - 0.50 mm (0.0197 inch) and 1.00 mm (0.0393
inch).
Any combination of standard, 0.50 mm (0.0197
inch) or 1.00 mm (0.0393 inch) overbore may be used
in the same engine.
Fig. 45 Stamp Block after Reface
Fig. 46 Cylinder Bore Crosshatch Pattern
Fig. 47 De-Glazing Drill Speed and Vertical Speed
DRENGINE 5.9L DIESEL 9 - 313
ENGINE BLOCK (Continued)
Page 1576 of 2895

(11) Install the flywheel housing and bolts. Torque
bolts to 77 N´m (57 ft. lbs.).
(12) Install the flywheel or converter drive plate.
Tighten bolts to 137 N´m (101 ft. lbs.).
(13) Install the starter motor and torque to 43 N´m
(21 ft. lbs.)(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/STARTING/
STARTER MOTOR - INSTALLATION).
(14) Install the transmission and transfer case (if
equipped).
(15) Lower vehicle.
(16) Fill the crankcase with new engine oil.
(17) Connect the battery negative cables.
(18) Start engine and check for oil leaks.
SOLID LIFTERS/TAPPETS
REMOVAL
NOTE: This procedure requires use of Miller Tool
8502 Tappet Replacement Kit.
(1) Remove camshaft (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/EN-
GINE BLOCK/CAMSHAFT & BEARINGS (IN
BLOCK) - REMOVAL).
(2) Insert the trough (provided with tool kit) the
full length of the camshaft bore (Fig. 79). Make sure
the cap end goes in first and the open side faces up
(towards tappets).
(3)Remove only one tappet at a time.Remove
rubber band from one cylinder pair and attach tappet
dowel not being removed to the next cylinder pair
(Fig. 80).
Fig. 79 Inserting the Trough - Typical
1 - TROUGH
Fig. 80 Secure Dowel/Tappet to Adjacent Cylinder -
typical
Fig. 77 Installing Seal Using Alignment Tool and
Hammer
1 - SEAL PILOT TOOL
2 - INSTALLATION TOOL
3 - SEAL
4 - RETAINER
Fig. 78 Trimming Excess Gasket Material
1 - GASKET
DRENGINE 5.9L DIESEL 9 - 327
CRANKSHAFT REAR OIL SEAL RETAINER (Continued)
Page 1577 of 2895

(4) Raise dowel rod (disengage from tappet) and
allow tappet to fall into trough (Fig. 81).
(5) Carefully remove trough(do not rotate)and
tappet. If the tappet is not being replaced, mark it so
it can be installed in its original location.
(6) Re-install trough and repeat procedure on
remaining tappets.
CLEANING
Clean tappet with a suitable solvent. Rinse in hot
water and blow dry with a clean shop rag or com-
pressed air.
INSPECTION
(1) Visually inspect the tappet the tappet socket,
stem, and face for excessive wear, cracks, or obvious
damage (Fig. 82).
(2) Measure the tappet stem diameter. Replace the
tappet if it falls below the minimum size (Fig. 82).
INSTALLATION
(1) Insert the trough the full length of the cam-
shaft bore. Again, make sure the cap end goes in first
and the open side faces up (towards tappets).
(2) Lower the tappet installation tool through the
push rod hole (Fig. 83) and into the trough.
(3) Retrieve the tappet installation tool using the
hooked rod provided with the tool kit (Fig. 84).
Fig. 83 Insert Installation Tool through Push Rod
Hole - Typical
Fig. 84 Retrieve Tappet Installation Tool through
Cam Bore - Typical
Fig. 81 Lift Dowel Rod to Disengage from Tappet -
typical
Fig. 82 Tappet Inspection
TAPPET STEM DIAMETER
15.936 mm (0.627 in.) MIN.
15.977 mm (0.629 in.) MAX.
9 - 328 ENGINE 5.9L DIESELDR
SOLID LIFTERS/TAPPETS (Continued)
Page 1587 of 2895

the owners manual. The by-pass valve is calibrated
to open when it sees a pressure drop of more than
345 kPa (50 psi) across the oil filter.
The oil filter head then divides the oil between the
engine and the turbocharger. The turbocharger
receives filtered, cooled and pressurized oil through a
supply line from the filter head. The oil lubricates
the turbocharger and returns to the pan by way of a
drain tube connecting the bottom of the turbocharger
to a pressed in tube in the cylinder block.
Oil is then carried across the block to an angle
drilling which intersects the main oil rifle. The main
oil rifle runs the length of the block and delivers oil
to the crankshaft main journals and valve train. Oil
travels to the crankshaft through a series of transfer
drillings (one for each main bearing) and lubricates a
groove in the main bearing upper shell. From there
another drilling feeds the camshaft main journals.
The saddle jet piston cooling nozzles are also sup-
plied by the main bearing upper shell. J-jet piston
cooling nozzles are supplied by a separate oil rifle.
Plugs are used in place of saddle jets when J-jets are
used. J-jet hole locations are plugged when saddle jet
cooling nozzles are used. Crankshaft internal cross-
drillings supply oil to the connecting rod journals.
Another series of transfer drillings intersecting the
main oil rifle supply the valve train components. Oil
travels up the drilling, through a hole in the head
gasket, and through a drilling in the cylinder head
(one per cylinder), where it enters the rocker arm
pedestal and is divided between the intake and
exhaust rocker arm. Oil travels up and around therocker arm mounting bolt, and lubricates the rocker
shaft by cross drillings that intersect the mounting
bolt hole. Grooves at both ends of the rocker shaft
supply oil through the rocker arm where the oil trav-
els to the push rod and socket balls (Fig. 111) and
(Fig. 112).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐENGINE OIL
PRESSURE
(1) Remove the 1/8 npt plug from the top of the oil
filter housing.
(2) Install Oil Pressure Line and Gauge Tool
C-3292 with a suitable adapter.
(3) Start engine and warm to operating tempera-
ture.
(4) Record engine oil pressure and compare with
engine oil pressure chart.
CAUTION: If engine oil pressure is zero at idle, DO
NOT RUN THE ENGINE.
Engine Oil Pressure (MIN)
At Idle 68.9 kPa (10 psi)
At 2500 rpm 206.9 kPa (30 psi)
If minimum engine oil pressure is below these
ranges, (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
(5) Remove oil pressure gauge and install the 1/8
npt plug.
9 - 338 ENGINE 5.9L DIESELDR
LUBRICATION (Continued)
Page 1614 of 2895
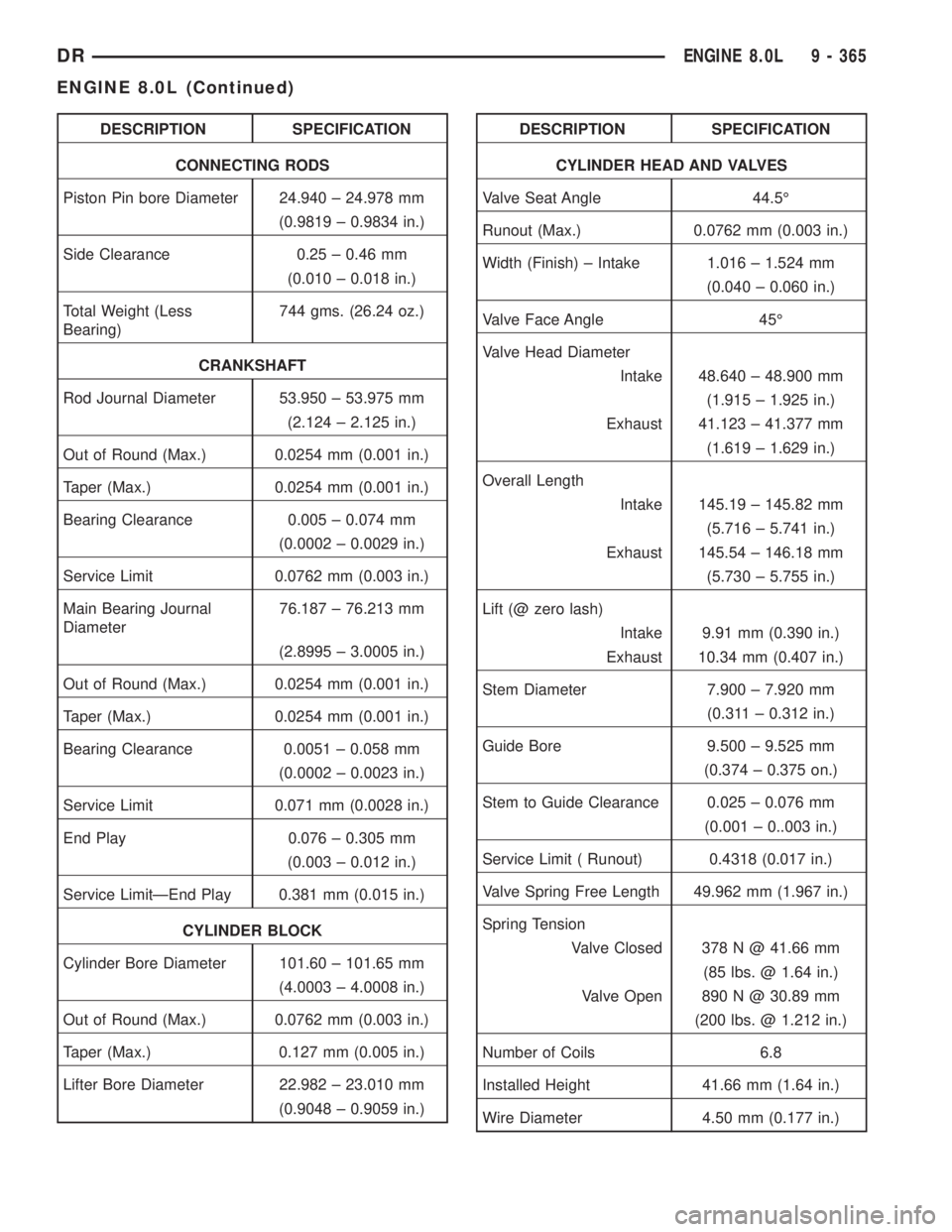
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
CONNECTING RODS
Piston Pin bore Diameter 24.940 ± 24.978 mm
(0.9819 ± 0.9834 in.)
Side Clearance 0.25 ± 0.46 mm
(0.010 ± 0.018 in.)
Total Weight (Less
Bearing)744 gms. (26.24 oz.)
CRANKSHAFT
Rod Journal Diameter 53.950 ± 53.975 mm
(2.124 ± 2.125 in.)
Out of Round (Max.) 0.0254 mm (0.001 in.)
Taper (Max.) 0.0254 mm (0.001 in.)
Bearing Clearance 0.005 ± 0.074 mm
(0.0002 ± 0.0029 in.)
Service Limit 0.0762 mm (0.003 in.)
Main Bearing Journal
Diameter76.187 ± 76.213 mm
(2.8995 ± 3.0005 in.)
Out of Round (Max.) 0.0254 mm (0.001 in.)
Taper (Max.) 0.0254 mm (0.001 in.)
Bearing Clearance 0.0051 ± 0.058 mm
(0.0002 ± 0.0023 in.)
Service Limit 0.071 mm (0.0028 in.)
End Play 0.076 ± 0.305 mm
(0.003 ± 0.012 in.)
Service LimitÐEnd Play 0.381 mm (0.015 in.)
CYLINDER BLOCK
Cylinder Bore Diameter 101.60 ± 101.65 mm
(4.0003 ± 4.0008 in.)
Out of Round (Max.) 0.0762 mm (0.003 in.)
Taper (Max.) 0.127 mm (0.005 in.)
Lifter Bore Diameter 22.982 ± 23.010 mm
(0.9048 ± 0.9059 in.)DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
CYLINDER HEAD AND VALVES
Valve Seat Angle 44.5É
Runout (Max.) 0.0762 mm (0.003 in.)
Width (Finish) ± Intake 1.016 ± 1.524 mm
(0.040 ± 0.060 in.)
Valve Face Angle 45É
Valve Head Diameter
Intake 48.640 ± 48.900 mm
(1.915 ± 1.925 in.)
Exhaust 41.123 ± 41.377 mm
(1.619 ± 1.629 in.)
Overall Length
Intake 145.19 ± 145.82 mm
(5.716 ± 5.741 in.)
Exhaust 145.54 ± 146.18 mm
(5.730 ± 5.755 in.)
Lift (@ zero lash)
Intake 9.91 mm (0.390 in.)
Exhaust 10.34 mm (0.407 in.)
Stem Diameter 7.900 ± 7.920 mm
(0.311 ± 0.312 in.)
Guide Bore 9.500 ± 9.525 mm
(0.374 ± 0.375 on.)
Stem to Guide Clearance 0.025 ± 0.076 mm
(0.001 ± 0..003 in.)
Service Limit ( Runout) 0.4318 (0.017 in.)
Valve Spring Free Length 49.962 mm (1.967 in.)
Spring Tension
Valve Closed 378 N @ 41.66 mm
(85 lbs. @ 1.64 in.)
Valve Open 890 N @ 30.89 mm
(200 lbs. @ 1.212 in.)
Number of Coils 6.8
Installed Height 41.66 mm (1.64 in.)
Wire Diameter 4.50 mm (0.177 in.)
DRENGINE 8.0L 9 - 365
ENGINE 8.0L (Continued)
Page 1615 of 2895

DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
HYDRAULIC TAPPETS
Body Diameter 22.949 ± 22.962 mm
(0.9035 ± 0.9040 in.)
Clearance (to bore) 0.0203 ± 0.0610 mm
(0.0008 ± 0.0024 in.)
Dry Lash 1.524 ± 5.334 mm
(0.060 ± 0.210 in.)
Push Rod Length 195.52 ± 196.02 mm
(7.698 ± 7.717 in.)
OIL PRESSURE
Curb Idle (Min.*) 83 kPa (12 psi)
@ 3000 rpm 345 ± 414 kPa (50 ± 60
psi)
* If oil pressure is zero at curb idle, DO NOT RUN
ENGINE.
OIL PUMP
Clearance over Rotors
(Max.)0.1906 mm (0.0075 in.)
Cover Out of Flat (Max.) 0.051 mm (0.002 in.)
Inner Rotor Thickness
(Min.)14.925 ± 14.950 mm
(0.5876 ± 0.5886 in.)
Outer Rotor
Clearance (Max.) 0.1626 mm (0.006 in.)
Diameter (Min.) 82.461 mm (3.246 in.)
Thickness (Min.) 14.925 mm (0.5876 in.)
Tip Clearance between
Rotors
(Max.) 0.584 mm (0.0230 in.)
PISTONS
Clearance at Top of Skirt 0.013 ± 0.038 mm
(0.0005 ± 0.0015 in.)
Piston Length 82.5 mm (3.25 in.)
Piston Ring Groove
Depth
#1&2 91.30 ± 91.55 mm
(3.594 ± 3.604 in.)
#3 92.90 ± 93.15 mmDESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
(3.657 ± 3.667 in.)
Weight 463 ± 473 grams (16.33
± 16.68 oz.)
Piston to Bore Clearance 0.013 ± 0.038 mm
(0.0005 ± 0.0015 in.)
Service Limit 0.0762 mm (0.003 in.)
PISTON PINS
Clearance in Piston 0.010 ± 0.020 mm
(0.0004 ± 0.0008 in.)
Diameter 24.996 ± 25.001 mm
(0.9841 ± 0.9843 in.)
End Play NONE
Length 67.8 ± 68.3 mm
(2.67 ± 2.69 in.)
PISTON RINGS
Ring Gap
Compression Rings 0.254 ± 0.508 mm
(0.010 ± 0.020 in.)
Oil Control (Steel Rails) 0.381 ± 1.397 mm
(0.015 ± 0.055 in.)
Ring Side Clearance
Compression Rings 0.074 ± 0.097 mm
(0.0029 ± 0.0038 in.)
Oil Ring (Steel Rails) 2.591 ± 2.743 mm
(0.102 ± 0.108 in.)
VALVE TIMING
Exhaust Valve
Closes (ATDC) 25É
Opens (BBDC) 60É
Duration 265É
Intake Valve
Closes (ATDC) 61É
Opens (BBDC) 6É
Duration 246É
Valve Overlap 31É
9 - 366 ENGINE 8.0LDR
ENGINE 8.0L (Continued)
Page 1625 of 2895

REFACING VALVES AND VALVE SEATS
The intake and exhaust valves have a 45É face
angle and a 45É to 44 1/2É seat angle (Fig. 16).
VALVE FACE AND SEAT ANGLES CHART
ITEM DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
ASEAT WIDTH 1.016 - 1.524
mm
INTAKE (0.040 - 0.060
in.)
SEAT WIDTH 1.016 - 1.524
mm
EXHAUST (0.040 - 0.060
in.)
BFACE ANGLE
(INT. and EXT.) 45É
CSEAT ANGLE
(INT. and EXT.) 44
1¤2É
DCONTACT
SURFACE Ð
VALVES
Inspect the remaining margin after the valves are
refaced (Fig. 17). Valves with less than 1.190 mm
(0.047 inch) margin should be discarded.
VALVE SEATS
(1) When refacing valve seats, it is important that
the correct size valve guide pilot be used for reseat-
ing stones. A true and complete surface must be
obtained.(2) Measure the concentricity of valve seat using a
dial indicator. Total runout should not exceed 0.038
mm (0.0015 inch) total indicator reading.
(3) Inspect the valve seat with Prussian blue to
determine where the valve contacts the seat. To do
this, coat valve seat LIGHTLY with Prussian blue
then set valve in place. Rotate the valve with light
pressure. If the blue is transferred to the center of
valve face, contact is satisfactory. If the blue is trans-
ferred to the top edge of valve face, lower valve seat
with a 15É stone. If the blue is transferred to bottom
edge of valve face raise valve seat with a 60É stone.
(4) When seat is properly positioned the width of
valve seats should be 1.016-1.524 mm (0.040-0.060
inch).
VALVE SPRING INSPECTION
Whenever valves have been removed for inspection,
reconditioning or replacement, valve springs should
be tested. As an example the compression length of
the spring to be tested is 1-5/16 inch. Turn table of
Universal Valve Spring Tester Tool until surface is in
line with the 1-5/16 inch mark on the threaded stud.
Be sure the zero mark is to the front (Fig. 18). Place
spring over stud on the table and lift compressing
lever to set tone device. Pull on torque wrench until
ping is heard. Take reading on torque wrench at this
instant. Multiply this reading by 2. This will give the
spring load at test length. Fractional measurements
are indicated on the table for finer adjustments.
Refer to specifications to obtain specified height and
allowable tensions. Discard the springs that do not
meet specifications.
Fig. 16 Valve Face and Seat Angles
1 - CONTACT POINT
Fig. 17 Intake and Exhaust Valves
1 - MARGIN
2 - VALVE SPRING RETAINER LOCK GROOVE
3 - STEM
4-FACE
9 - 376 ENGINE 8.0LDR
INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES & SEATS (Continued)
Page 1635 of 2895

CRANKSHAFT REAR OIL SEAL
RETAINER
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove the transmission.
(3) Remove the drive plate / flywheel.
(4) Remove the oil pan (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LU-
BRICATION/OIL PAN - REMOVAL).
(5) Remove the rear oil seal retainer mounting
bolts.
(6) Carefully remove the retainer from the engine
block.
INSTALLATION
(1) Throughly clean all gasket resdue from the
engine block.
(2) Use extream care and clean all gasket resdue
from the retainer.
(3) Apply a small amount of MopartSilicone Rub-
ber Adhesive Sealant to the retainer gasket. Position
the gasket onto the retainer.
(4) Position Special Tool 6687 Seal Guide onto the
crankshaft.
(5) Position the retainer and seal over the guide
and onto the engine block.
(6) Install the retainer mounting bolts. Tighten the
bolts to 22 N´m (16 ft. lbs.).
(7) Install the oil pan (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LU-
BRICATION/OIL PAN - INSTALLATION).
(8) Install the drive plate / flywheel.
(9) Install the transmission.
(10) Check and verify engine oil level.
(11) Start engine and check for leaks.
HYDRAULIC LIFTERS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐHYDRAULIC
TAPPETS
Before disassembling any part of the engine to cor-
rect tappet noise, check the oil pressure. If vehicle
has no oil pressure gauge, install a reliable gauge at
the pressure sending-unit. The pressure should be
between 207-552 kPa (30-80 psi) at 3,000 RPM.
Check the oil level after the engine reaches normal
operating temperature. Allow 5 minutes to stabilize
oil level, check dipstick. The oil level in the pan
should never be above the FULL mark or below the
ADD OIL mark on dipstick. Either of these two con-
ditions could be responsible for noisy tappets.
OIL LEVEL
HIGH
If oil level is above the FULL mark, it is possible
for the connecting rods to dip into the oil. With the
engine running, this condition could create foam in
the oil pan. Foam in oil pan would be fed to the
hydraulic tappets by the oil pump causing them to
lose length and allow valves to seat noisily.
LOW
Low oil level may allow oil pump to take in air.
When air is fed to the tappets, they lose length,
which allows valves to seat noisily. Any leaks on
intake side of oil pump through which air can be
drawn will create the same tappet action. Check the
lubrication system from the intake strainer to the
pump cover, including the relief valve retainer cap.
When tappet noise is due to aeration, it may be
intermittent or constant, and usually more than one
tappet will be noisy. When oil level and leaks have
been corrected, operate the engine at fast idle. Run
engine for a sufficient time to allow all of the air
inside the tappets to be bled out.
TAPPET NOISE DIAGNOSIS
(1) To determine source of tappet noise, operate
engine at idle with cylinder head covers removed.
(2) Feel each valve spring or rocker arm to detect
noisy tappet. The noisy tappet will cause the affected
spring and/or rocker arm to vibrate or feel rough in
operation.
NOTE: Worn valve guides or cocked springs are
sometimes mistaken for noisy tappets. If such is
the case, noise may be dampened by applying side
thrust on the valve spring. If noise is not apprecia-
bly reduced, it can be assumed the noise is in the
tappet. Inspect the rocker arm push rod sockets
and push rod ends for wear.
(3) Valve tappet noise ranges from light noise to a
heavy click. A light noise is usually caused by exces-
sive leak-down around the unit plunger, or by the
plunger partially sticking in the tappet body cylinder.
The tappet should be replaced. A heavy click is
caused by a tappet check valve not seating, or by for-
eign particles wedged between the plunger and the
tappet body. This will cause the plunger to stick in
the down position. This heavy click will be accompa-
nied by excessive clearance between the valve stem
and rocker arm as valve closes. In either case, tappet
assembly should be removed for inspection and clean-
ing.
9 - 386 ENGINE 8.0LDR