wheel DODGE RAM 2003 Service Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2003, Model line: RAM, Model: DODGE RAM 2003Pages: 2895, PDF Size: 83.15 MB
Page 91 of 2895

FRONT AXLE - C205F
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
FRONT AXLE - C205F
DESCRIPTION.........................18
OPERATION...........................18
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING................18
REMOVAL.............................21
INSTALLATION.........................21
ADJUSTMENTS........................21
SPECIFICATIONS.......................29
SPECIAL TOOLS.......................30
AXLE SHAFTS
REMOVAL.............................33
INSTALLATION.........................33
AXLE SHAFT SEALS
REMOVAL.............................33
INSTALLATION.........................33
AXLE BEARINGS
REMOVAL.............................33INSTALLATION.........................34
PINION SEAL
REMOVAL.............................34
INSTALLATION.........................35
DIFFERENTIAL
DESCRIPTION.........................36
OPERATION...........................36
REMOVAL.............................36
DISASSEMBLY.........................37
ASSEMBLY............................38
INSTALLATION.........................38
DIFFERENTIAL CASE BEARINGS
REMOVAL.............................39
INSTALLATION.........................39
PINION GEAR/RING GEAR
REMOVAL.............................40
INSTALLATION.........................42
FRONT AXLE - C205F
DESCRIPTION
The axle consists of an alumunum center section
with an axle tube extending from one side. The tube
is pressed into the differential housing. The power is
transferred from the axle through two constant veloc-
ity (C/V) drive shafts to the wheel hubs. The drive
shafts are identical and interchangeable.
OPERATION
The axle receives power from the propeller shaft.
The propeller shaft is connected to the pinion gear
which rotates the differential through the gear mesh
with the ring gear bolted to the differential case. The
engine power is transmitted to the axle shafts
through the pinion mate and side gears. The side
gears are splined to the axle shafts.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
GEAR NOISE
Axle gear noise can be caused by insufficient lubri-
cant, incorrect backlash, tooth contact, worn/damaged
gears or the carrier housing not having the proper
offset and squareness.
Gear noise usually happens at a specific speed
range. The noise can also occur during a specific type
of driving condition. These conditions are accelera-
tion, deceleration, coast, or constant load.When road testing, first warm-up the axle fluid by
driving the vehicle at least 5 miles and then acceler-
ate the vehicle to the speed range where the noise is
the greatest. Shift out-of-gear and coast through the
peak-noise range. If the noise stops or changes
greatly:
²Check for insufficient lubricant.
²Incorrect ring gear backlash.
²Gear damage.
Differential side gears and pinions can be checked
by turning the vehicle. They usually do not cause
noise during straight-ahead driving when the gears
are unloaded. The side gears are loaded during vehi-
cle turns. A worn pinion mate shaft can also cause a
snapping or a knocking noise.
BEARING NOISE
The axle shaft, differential and pinion bearings can
all produce noise when worn or damaged. Bearing
noise can be either a whining, or a growling sound.
Pinion bearings have a constant-pitch noise. This
noise changes only with vehicle speed. Pinion bearing
noise will be higher pitched because it rotates at a
faster rate. Drive the vehicle and load the differen-
tial. If bearing noise occurs, the rear pinion bearing
is the source of the noise. If the bearing noise is
heard during a coast, the front pinion bearing is the
source.
Worn or damaged differential bearings usually pro-
duce a low pitch noise. Differential bearing noise is
similar to pinion bearing noise. The pitch of differen-
3 - 18 FRONT AXLE - C205FDR
Page 92 of 2895

tial bearing noise is also constant and varies only
with vehicle speed.
Axle shaft bearings produce noise and vibration
when worn or damaged. The noise generally changes
when the bearings are loaded. Road test the vehicle.
Turn the vehicle sharply to the left and to the right.
This will load the bearings and change the noise
level. Where axle bearing damage is slight, the noise
is usually not noticeable at speeds above 30 mph.
LOW SPEED KNOCK
Low speed knock is generally caused by a worn
U-joint or by worn side-gear thrust washers. A worn
pinion shaft bore will also cause low speed knock.
VIBRATION
Vibration at the rear of the vehicle is usually
caused by:
²Damaged drive shaft.
²Missing drive shaft balance weight(s).
²Worn or out of balance wheels.
²Loose wheel lug nuts.
²Worn U-joint(s).
²Loose/broken springs.
²Damaged axle shaft bearing(s).
²Loose pinion gear nut.
²Excessive pinion yoke run out.
²Bent axle shaft(s).Check for loose or damaged front end components
or engine/transmission mounts. These components
can contribute to what appears to be a rear end
vibration. Do not overlook engine accessories, brack-
ets and drive belts.
All driveline components should be examined
before starting any repair.
(Refer to 22 - TIRES/WHEELS - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING)
DRIVELINE SNAP
A snap or clunk noise when the vehicle is shifted
into gear (or the clutch engaged) can be caused by:
²High engine idle speed.
²Transmission shift operation.
²Loose engine/transmission/transfer case mounts.
²Worn U-joints.
²Loose spring mounts.
²Loose pinion gear nut and yoke.
²Excessive ring gear backlash.
²Excessive side gear to case clearance.
The source of a snap or a clunk noise can be deter-
mined with the assistance of a helper. Raise the vehi-
cle on a hoist with the wheels free to rotate. Instruct
the helper to shift the transmission into gear. Listen
for the noise, a mechanics stethoscope is helpful in
isolating the source of a noise.
DIAGNOSTIC CHART
Condition Possible Causes Correction
Wheel Noise 1. Wheel loose. 1. Tighten loose nuts.
2. Faulty, brinelled wheel bearing. 2. Replace bearing.
Axle Shaft Noise 1. Misaligned axle tube. 1. Inspect axle tube alignment.
Correct as necessary.
2. Bent or sprung axle shaft. 2. Inspect and correct as necessary.
3. End-play in pinion bearings. 3. Refer to pinion pre-load
information and correct as
necessary.
4. Excessive gear backlash
between the ring gear and pinion.4. Check adjustment of the ring
gear and pinion backlash. Correct
as necessary.
5. Improper adjustment of pinion
gear bearings.5. Adjust the pinion bearings
pre-load.
6. Loose pinion yoke nut. 6. Tighten the pinion yoke nut.
7. Scuffed gear tooth contact
surfaces.7. Inspect and replace as
necessary.
DRFRONT AXLE - C205F 3 - 19
FRONT AXLE - C205F (Continued)
Page 93 of 2895
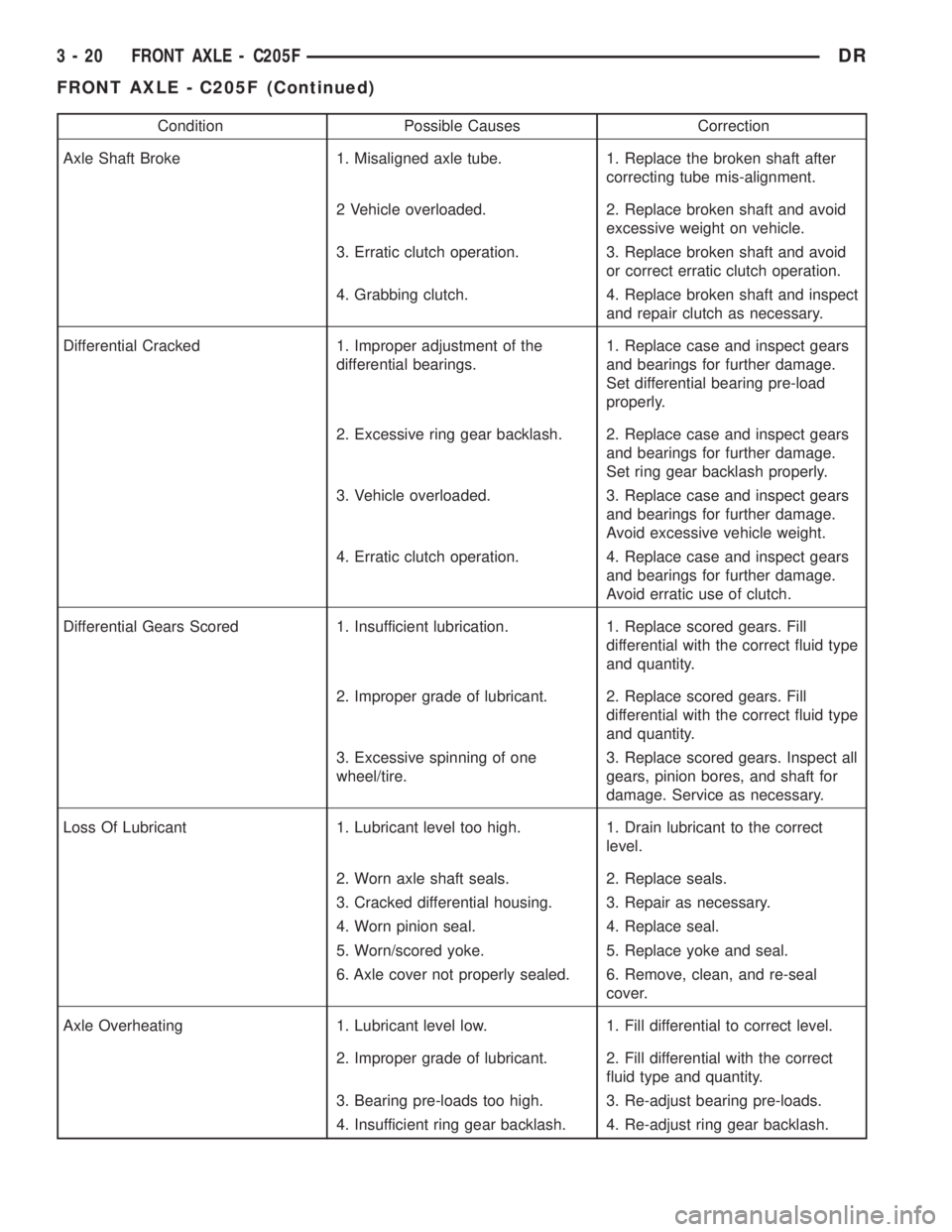
Condition Possible Causes Correction
Axle Shaft Broke 1. Misaligned axle tube. 1. Replace the broken shaft after
correcting tube mis-alignment.
2 Vehicle overloaded. 2. Replace broken shaft and avoid
excessive weight on vehicle.
3. Erratic clutch operation. 3. Replace broken shaft and avoid
or correct erratic clutch operation.
4. Grabbing clutch. 4. Replace broken shaft and inspect
and repair clutch as necessary.
Differential Cracked 1. Improper adjustment of the
differential bearings.1. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Set differential bearing pre-load
properly.
2. Excessive ring gear backlash. 2. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Set ring gear backlash properly.
3. Vehicle overloaded. 3. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Avoid excessive vehicle weight.
4. Erratic clutch operation. 4. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Avoid erratic use of clutch.
Differential Gears Scored 1. Insufficient lubrication. 1. Replace scored gears. Fill
differential with the correct fluid type
and quantity.
2. Improper grade of lubricant. 2. Replace scored gears. Fill
differential with the correct fluid type
and quantity.
3. Excessive spinning of one
wheel/tire.3. Replace scored gears. Inspect all
gears, pinion bores, and shaft for
damage. Service as necessary.
Loss Of Lubricant 1. Lubricant level too high. 1. Drain lubricant to the correct
level.
2. Worn axle shaft seals. 2. Replace seals.
3. Cracked differential housing. 3. Repair as necessary.
4. Worn pinion seal. 4. Replace seal.
5. Worn/scored yoke. 5. Replace yoke and seal.
6. Axle cover not properly sealed. 6. Remove, clean, and re-seal
cover.
Axle Overheating 1. Lubricant level low. 1. Fill differential to correct level.
2. Improper grade of lubricant. 2. Fill differential with the correct
fluid type and quantity.
3. Bearing pre-loads too high. 3. Re-adjust bearing pre-loads.
4. Insufficient ring gear backlash. 4. Re-adjust ring gear backlash.
3 - 20 FRONT AXLE - C205FDR
FRONT AXLE - C205F (Continued)
Page 94 of 2895
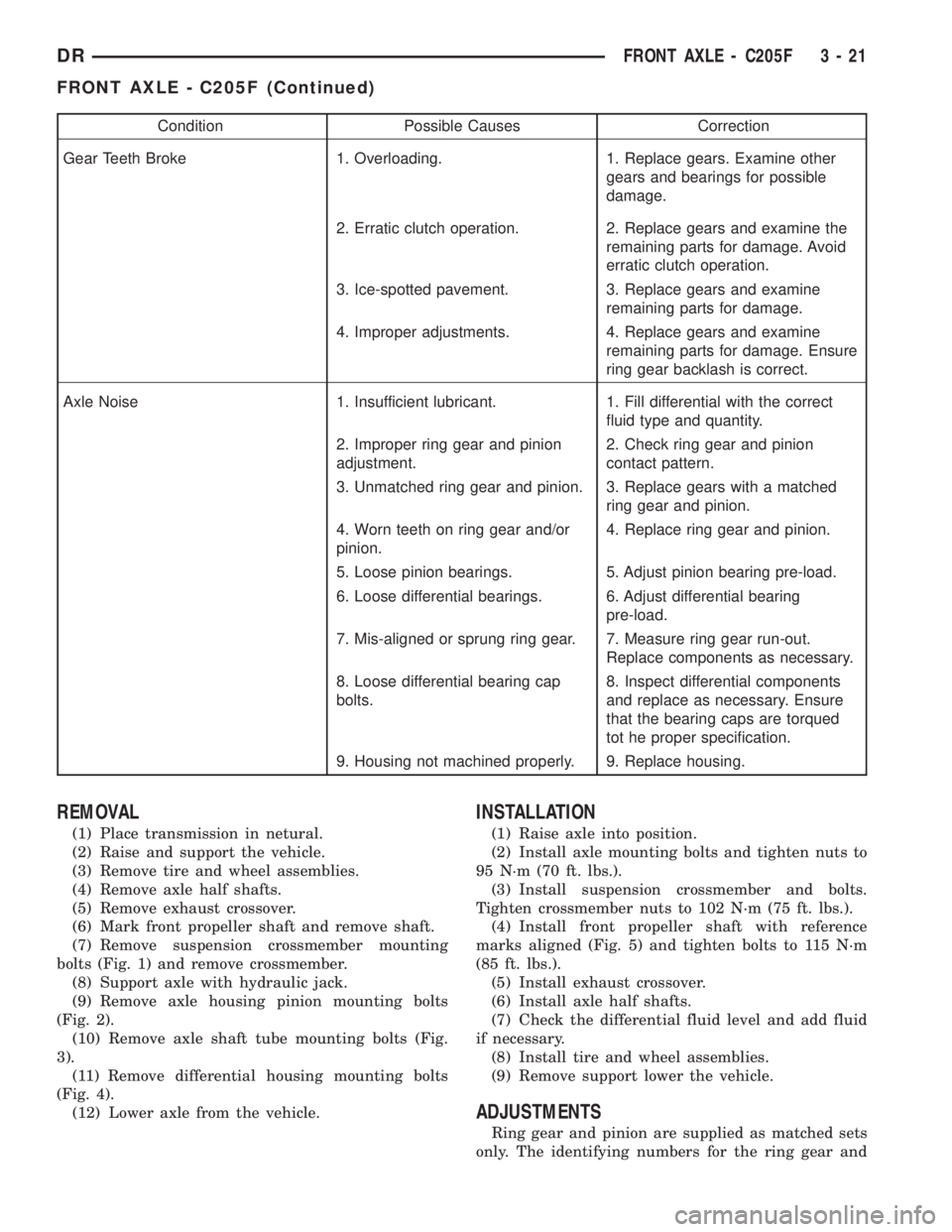
Condition Possible Causes Correction
Gear Teeth Broke 1. Overloading. 1. Replace gears. Examine other
gears and bearings for possible
damage.
2. Erratic clutch operation. 2. Replace gears and examine the
remaining parts for damage. Avoid
erratic clutch operation.
3. Ice-spotted pavement. 3. Replace gears and examine
remaining parts for damage.
4. Improper adjustments. 4. Replace gears and examine
remaining parts for damage. Ensure
ring gear backlash is correct.
Axle Noise 1. Insufficient lubricant. 1. Fill differential with the correct
fluid type and quantity.
2. Improper ring gear and pinion
adjustment.2. Check ring gear and pinion
contact pattern.
3. Unmatched ring gear and pinion. 3. Replace gears with a matched
ring gear and pinion.
4. Worn teeth on ring gear and/or
pinion.4. Replace ring gear and pinion.
5. Loose pinion bearings. 5. Adjust pinion bearing pre-load.
6. Loose differential bearings. 6. Adjust differential bearing
pre-load.
7. Mis-aligned or sprung ring gear. 7. Measure ring gear run-out.
Replace components as necessary.
8. Loose differential bearing cap
bolts.8. Inspect differential components
and replace as necessary. Ensure
that the bearing caps are torqued
tot he proper specification.
9. Housing not machined properly. 9. Replace housing.
REMOVAL
(1) Place transmission in netural.
(2) Raise and support the vehicle.
(3) Remove tire and wheel assemblies.
(4) Remove axle half shafts.
(5) Remove exhaust crossover.
(6) Mark front propeller shaft and remove shaft.
(7) Remove suspension crossmember mounting
bolts (Fig. 1) and remove crossmember.
(8) Support axle with hydraulic jack.
(9) Remove axle housing pinion mounting bolts
(Fig. 2).
(10) Remove axle shaft tube mounting bolts (Fig.
3).
(11) Remove differential housing mounting bolts
(Fig. 4).
(12) Lower axle from the vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Raise axle into position.
(2) Install axle mounting bolts and tighten nuts to
95 N´m (70 ft. lbs.).
(3) Install suspension crossmember and bolts.
Tighten crossmember nuts to 102 N´m (75 ft. lbs.).
(4) Install front propeller shaft with reference
marks aligned (Fig. 5) and tighten bolts to 115 N´m
(85 ft. lbs.).
(5) Install exhaust crossover.
(6) Install axle half shafts.
(7) Check the differential fluid level and add fluid
if necessary.
(8) Install tire and wheel assemblies.
(9) Remove support lower the vehicle.
ADJUSTMENTS
Ring gear and pinion are supplied as matched sets
only. The identifying numbers for the ring gear and
DRFRONT AXLE - C205F 3 - 21
FRONT AXLE - C205F (Continued)
Page 109 of 2895

CAUTION: Never loosen pinion nut to decrease pin-
ion bearing rotating torque and never exceed spec-
ified preload torque. If preload torque or rotating
torque is exceeded a new collapsible spacer must
be installed.
(6) Record pinion rotating torque using an inch
pound torque wrench. The rotating torque should be
equal to the reading recorded during removal plus an
additional 0.56 N´m (5 in. lbs.) (Fig. 36).
(7) If rotating torque is low, tighten the pinion nut
in 6.8 N´m (5 ft. lbs.) increments until the proper
rotating torque is achieved.
CAUTION: If maximum tightening torque 475 N´m
(350 ft. lbs.) is reached prior to reaching the
required rotating torque, the collapsible spacer may
have been damaged. Replace the collapsible
spacer.
(8) Install propeller shaft with reference marks
aligned.
(9) Add gear lubricant to differential housing if
necessary.
(10) Install half shafts and skid plate if equipped.DIFFERENTIAL
DESCRIPTION
The differential case is a one-piece design. The dif-
ferential pinion shaft is retained with a snap ring.
Differential bearing preload and ring gear backlash
is adjusted by the use of adjusters. The adjuster are
between the differential bearings and the differential
housing. Pinion bearing preload is set and main-
tained by the use of a collapsible spacer. The
stamped steel cover provides a means for inspection
and servicing the differential.
OPERATION
During straight-ahead driving, the differential pin-
ion gears do not rotate on the pinion mate shaft. This
occurs because input torque applied to the gears is
divided and distributed equally between the two side
gears. As a result, the pinion gears revolve with the
pinion mate shaft but do not rotate around it (Fig.
37).
When turning corners, the outside wheel must
travel a greater distance than the inside wheel to
complete a turn. To accomplish this, the differential
allows the axle shafts to turn at unequal speeds (Fig.
38). In this instance, the input torque applied to the
pinion gears is not divided equally. The pinion gears
now rotate around the pinion mate shaft in opposite
directions. This allows the side gear and axle shaft
attached to the outside wheel to rotate at a faster
speed.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove differential housing cover and drain
fluid.
Fig. 36 PINION ROTATION TORQUE
1 - COMPANION FLANGE
2 - INCH POUND TORQUE WRENCH
Fig. 37 DIFFERENTIAL-STRAIGHT AHEAD DRIVING
1 - IN STRAIGHT AHEAD DRIVING EACH WHEEL ROTATES AT
100% OF CASE SPEED
2 - PINION GEAR
3 - SIDE GEAR
4 - PINION GEARS ROTATE WITH CASE
3 - 36 FRONT AXLE - C205FDR
PINION SEAL (Continued)
Page 119 of 2895

heard during a coast, the front pinion bearing is the
source.
Worn or damaged differential bearings usually pro-
duce a low pitch noise. Differential bearing noise is
similar to pinion bearing noise. The pitch of differen-
tial bearing noise is also constant and varies only
with vehicle speed.
Axle shaft bearings produce noise and vibration
when worn or damaged. The noise generally changes
when the bearings are loaded. Road test the vehicle.
Turn the vehicle sharply to the left and to the right.
This will load the bearings and change the noise
level. Where axle bearing damage is slight, the noise
is usually not noticeable at speeds above 30 mph.
LOW SPEED KNOCK
Low speed knock is generally caused by a worn
U-joint or by worn side-gear thrust washers. A worn
pinion shaft bore will also cause low speed knock.
VIBRATION
Vibration at the front/rear of the vehicle is usually
caused by:
²Damaged drive shaft.
²Missing drive shaft balance weight(s).
²Worn or out of balance wheels.
²Loose wheel lug nuts.
²Worn U-joint(s).²Loose/broken springs.
²Damaged axle shaft bearing(s).
²Loose pinion gear nut.
²Excessive pinion yoke run out.
²Bent axle shaft(s).
Check for loose or damaged front end components
or engine/transmission mounts. These components
can contribute to what appears to be a vibration. Do
not overlook engine accessories, brackets and drive
belts.
DRIVELINE SNAP
A snap or clunk noise when the vehicle is shifted
into gear (or the clutch engaged) can be caused by:
²High engine idle speed.
²Transmission shift operation.
²Loose engine/transmission/transfer case mounts.
²Worn U-joints.
²Loose spring mounts.
²Loose pinion gear nut and yoke.
²Excessive ring gear backlash.
²Excessive side gear to case clearance.
The source of a snap or a clunk noise can be deter-
mined with the assistance of a helper. Raise the vehi-
cle on a hoist with the wheels free to rotate. Instruct
the helper to shift the transmission into gear. Listen
for the noise, a mechanics stethoscope is helpful in
isolating the source of a noise.
DIAGNOSTIC CHART
Condition Possible Causes Correction
Wheel Noise 1. Wheel loose. 1. Tighten loose nuts.
2. Faulty, brinelled wheel bearing. 2. Replace bearing.
Axle Shaft Noise 1. Misaligned axle tube. 1. Inspect axle tube alignment.
Correct as necessary.
2. Bent or sprung axle shaft. 2. Inspect and correct as necessary.
3. End-play in pinion bearings. 3. Refer to pinion pre-load
information and correct as
necessary.
4. Excessive gear backlash
between the ring gear and pinion.4. Check adjustment of the ring
gear and pinion backlash. Correct
as necessary.
5. Improper adjustment of pinion
gear bearings.5. Adjust the pinion bearings
pre-load.
6. Loose pinion yoke nut. 6. Tighten the pinion yoke nut.
7. Scuffed gear tooth contact
surfaces.7. Inspect and replace as
necessary.
3 - 46 FRONT AXLE - 9 1/4 AADR
FRONT AXLE - 9 1/4 AA (Continued)
Page 120 of 2895
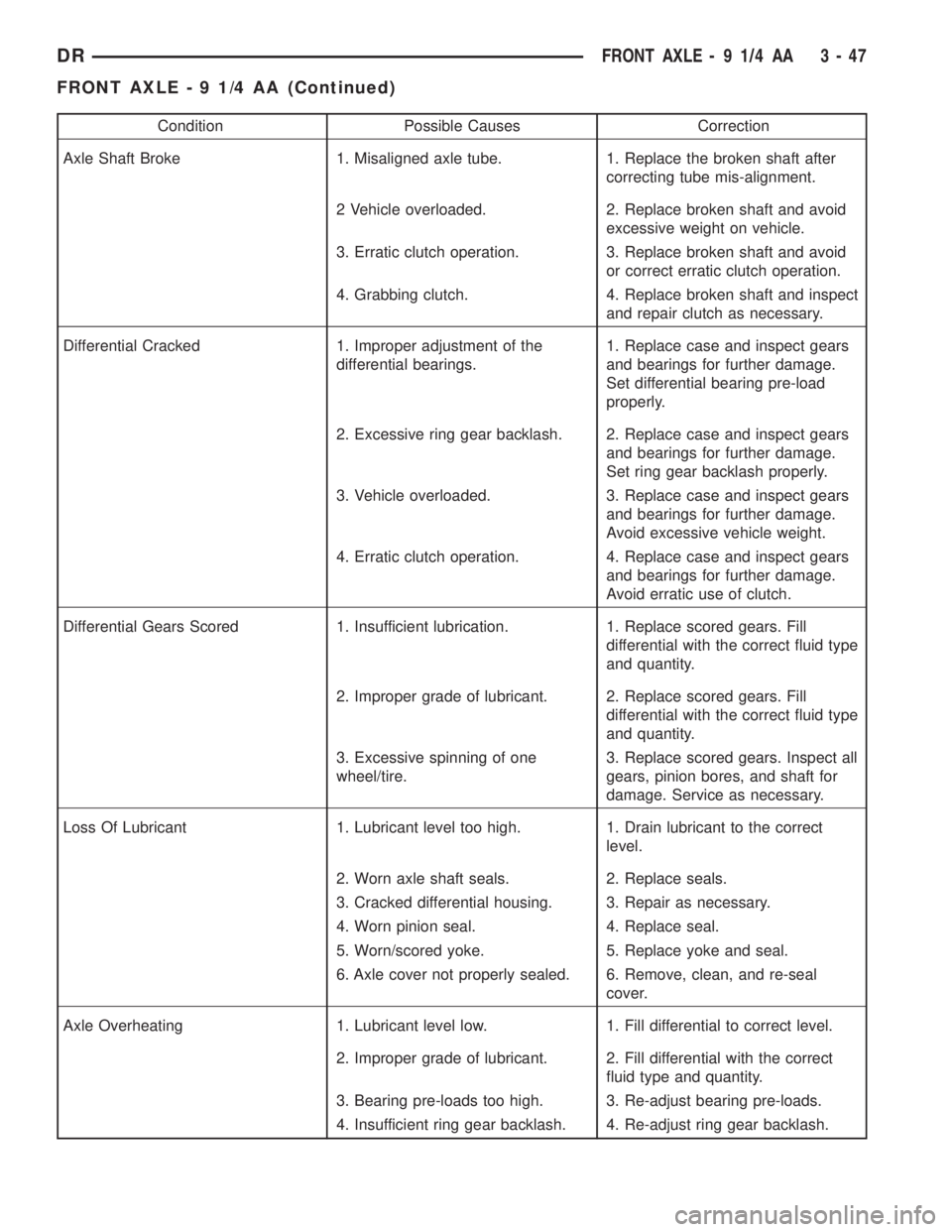
Condition Possible Causes Correction
Axle Shaft Broke 1. Misaligned axle tube. 1. Replace the broken shaft after
correcting tube mis-alignment.
2 Vehicle overloaded. 2. Replace broken shaft and avoid
excessive weight on vehicle.
3. Erratic clutch operation. 3. Replace broken shaft and avoid
or correct erratic clutch operation.
4. Grabbing clutch. 4. Replace broken shaft and inspect
and repair clutch as necessary.
Differential Cracked 1. Improper adjustment of the
differential bearings.1. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Set differential bearing pre-load
properly.
2. Excessive ring gear backlash. 2. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Set ring gear backlash properly.
3. Vehicle overloaded. 3. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Avoid excessive vehicle weight.
4. Erratic clutch operation. 4. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Avoid erratic use of clutch.
Differential Gears Scored 1. Insufficient lubrication. 1. Replace scored gears. Fill
differential with the correct fluid type
and quantity.
2. Improper grade of lubricant. 2. Replace scored gears. Fill
differential with the correct fluid type
and quantity.
3. Excessive spinning of one
wheel/tire.3. Replace scored gears. Inspect all
gears, pinion bores, and shaft for
damage. Service as necessary.
Loss Of Lubricant 1. Lubricant level too high. 1. Drain lubricant to the correct
level.
2. Worn axle shaft seals. 2. Replace seals.
3. Cracked differential housing. 3. Repair as necessary.
4. Worn pinion seal. 4. Replace seal.
5. Worn/scored yoke. 5. Replace yoke and seal.
6. Axle cover not properly sealed. 6. Remove, clean, and re-seal
cover.
Axle Overheating 1. Lubricant level low. 1. Fill differential to correct level.
2. Improper grade of lubricant. 2. Fill differential with the correct
fluid type and quantity.
3. Bearing pre-loads too high. 3. Re-adjust bearing pre-loads.
4. Insufficient ring gear backlash. 4. Re-adjust ring gear backlash.
DRFRONT AXLE - 9 1/4 AA 3 - 47
FRONT AXLE - 9 1/4 AA (Continued)
Page 121 of 2895

Condition Possible Causes Correction
Gear Teeth Broke 1. Overloading. 1. Replace gears. Examine other
gears and bearings for possible
damage.
2. Erratic clutch operation. 2. Replace gears and examine the
remaining parts for damage. Avoid
erratic clutch operation.
3. Ice-spotted pavement. 3. Replace gears and examine
remaining parts for damage.
4. Improper adjustments. 4. Replace gears and examine
remaining parts for damage. Ensure
ring gear backlash is correct.
Axle Noise 1. Insufficient lubricant. 1. Fill differential with the correct
fluid type and quantity.
2. Improper ring gear and pinion
adjustment.2. Check ring gear and pinion
contact pattern.
3. Unmatched ring gear and pinion. 3. Replace gears with a matched
ring gear and pinion.
4. Worn teeth on ring gear and/or
pinion.4. Replace ring gear and pinion.
5. Loose pinion bearings. 5. Adjust pinion bearing pre-load.
6. Loose differential bearings. 6. Adjust differential bearing
pre-load.
7. Mis-aligned or sprung ring gear. 7. Measure ring gear run-out.
Replace components as necessary.
8. Loose differential bearing cap
bolts.8. Inspect differential components
and replace as necessary. Ensure
that the bearing caps are torqued
tot he proper specification.
9. Housing not machined properly. 9. Replace housing.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove wheels and tires.
(2) Remove brake calipers and rotors.
(3) Disconnect ABS wheel speed sensors.
(4) Disconnect axle vent hose.
(5) Remove front propeller shaft.
(6) Disconnect stabilizer bar links at the axle
brackets.
(7) Disconnect shock absorbers from axle brackets.
(8) Disconnect track bar from the axle bracket.
(9) Disconnect tie rod and drag link from the steer-
ing knuckles.
(10) Position suitable lifting device under the axle
assembly.
(11) Secure axle to lifting device.
(12) Mark suspension alignment cams for installa-
tion reference.
(13) Disconnect upper and lower suspension arms
from the axle bracket.(14) Lower the axle. The coil springs will drop
with the axle.
(15) Remove the coil springs from the axle bracket.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Suspension components with rubber
bushings should be tightened with the weight of the
vehicle on the suspension, at normal height. If
springs are not at their normal ride position, vehicle
ride comfort could be affected and premature bush-
ing wear may occur. Rubber bushings must never
be lubricated.
(1) Support the axle on a suitable lifting device.
(2) Secure axle to lifting device.
(3) Position the axle under the vehicle.
(4) Install springs, retainer clip and bolts.
(5) Raise axle and align it with the spring pads.
3 - 48 FRONT AXLE - 9 1/4 AADR
FRONT AXLE - 9 1/4 AA (Continued)
Page 122 of 2895

(6) Position upper and lower suspension arms in
the axle brackets. Install bolts, nuts and align the
suspension alignment cams to the reference marks.
Do not tighten at this time.
(7) Connect track bar to the axle bracket and
install the bolt. Do not tighten at this time.
(8) Install shock absorber and tighten bolts to 121
N´m (89 ft. lbs.).
(9) Install stabilizer bar link to the axle bracket.
Tighten the nut to 68 N´m (50 ft. lbs.).
(10) Install drag link and tie rod to the steering
knuckles and tighten the nuts to 108 N´m (80 ft.
lbs.).
(11) Install ABS wheel speed sensors.
(12) Install rotors and brake calipers.
(13) Connect the axle vent hose.
(14) Install front propeller shaft.
(15) Check and add differential lubricant, if neces-
sary.
(16) Install wheel and tire assemblies.
(17) Remove lower the vehicle.
(18) Tighten upper suspension arm nuts at axle to
149 N´m (110 ft. lbs.). Tighten upper suspension arm
nuts at frame to 149 N´m (110 ft. lbs.).
(19) Tighten lower suspension arm nuts at axle to
190 N´m (140 ft. lbs.). Tighten the lower suspension
arm nuts at frame to 190 N´m (140 ft. lbs.).
(20) Tighten track bar bolt at the axle bracket to
176 N´m (130 ft. lbs.).
(21) Check front wheel alignment.
ADJUSTMENTS
Ring and pinion gears are supplied as matched
sets only. Compensation for pinion depth variance is
achieved with a select shim. The shim is located
between the rear pinion bearing and the pinion gear
head.
PINION DEPTH MEASUREMENT AND ADJUSTMENT
Measurements are taken with pinion bearing cups
and pinion bearings installed in the housing. Take
measurements with Pinion Gauge Set and Dial Indi-
cator C-3339 (Fig. 1).
(1) Assemble Pinion Height Block 6739, Pinion
Block 8878 and rear pinion bearing onto Screw 6741
(Fig. 1).
(2) Insert assembled height gauge components,
rear bearing and screw into the housing through pin-
ion bearing cups (Fig. 2).
(3) Install front pinion bearing and install the
Cone-nut 6740 hand tight. Then check tool rotating
torque with an inch pound torque wrench. The rotat-
ing torque should be 1.7-2.26 N´m (15-20 in. lbs.)
(4) Place Arbor Disc 8289 on Arbor D-115-3 in posi-
tion in the housing side bearing cradles (Fig. 3).(5) Install differential bearing caps on arbor discs
and snug the bearing cap bolts. Then cross tighten
cap bolts to 85 N´m (63 ft. lbs.).
Fig. 1 PINION GEAR DEPTH GAUGE TOOLS
1 - DIAL INDICATOR
2 - ARBOR
3 - PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
4 - CONE
5 - SCREW
6 - PINION BLOCK
7 - SCOOTER BLOCK
8 - ARBOR DISC
Fig. 2 PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
1. PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
2. PINION BLOCK
DRFRONT AXLE - 9 1/4 AA 3 - 49
FRONT AXLE - 9 1/4 AA (Continued)
Page 129 of 2895

AXLE SHAFTS
REMOVAL
(1) Remove wheel and tire assembly.
(2) Remove brake caliper, rotor and ABS wheel
speed sensor if equipped.
(3) Remove axle shaft cotter pin, hub nut and
washer (Fig. 14).
(4) Remove the four hub bearing bolts (Fig. 15)
from the back of the steering knuckle.
(5) Remove hub bearing from the steering knuckle.
(6) Remove axle shaft (Fig. 16) from steering
knuckle and axle housing.
DISASSEMBLY
Single cardan U-joint components are not service-
able. If defective they must be replaced as a unit.
CAUTION: Clamp only the narrow forged portion of
the yoke in the vise. To avoid distorting the yoke,
do not over tighten the vise jaws.
(1) Remove the bearing cap retaining snap rings
(Fig. 17).
NOTE: Saturate the bearing caps with penetrating
oil prior to removal.
(2) Locate a socket with an inside diameter that is
larger than the bearing cap. Place the socket (receiv-
er) against the yoke and around the perimeter of the
bearing cap to be removed.
ADAPTERS 8879
ADJUSTER WRENCH 8883
FLANGE WRENCH 8979
FLANGE PULLER 8992
Fig. 14 AXLE NUT
1 - AXLE NUT
2 - AXLE
3 - COTTER PIN
3 - 56 FRONT AXLE - 9 1/4 AADR
FRONT AXLE - 9 1/4 AA (Continued)