transmission DODGE RAM 2003 Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2003, Model line: RAM, Model: DODGE RAM 2003Pages: 2895, PDF Size: 83.15 MB
Page 29 of 2895

A towed vehicle should be raised until lifted wheels
are a minimum 100 mm (4 in) from the ground. Be
sure there is adequate ground clearance at the oppo-
site end of the vehicle, especially when towing over
rough terrain or steep rises in the road. If necessary,
remove the wheels from the lifted end of the vehicle
and lower the vehicle closer to the ground, to
increase the ground clearance at the opposite end of
the vehicle. Install lug nuts on wheel attaching studs
to retain brake drums or rotors.
RAMP ANGLE
If a vehicle with flat-bed towing equipment is used,
the approach ramp angle should not exceed 15
degrees.
TOWING WHEN KEYS ARE NOT AVAILABLE
When the vehicle is locked and keys are not avail-
able, use a flat bed hauler. A Wheel-lift or Sling-type
device can be used on 4WD vehicles providedall the
wheels are lifted off the ground using tow dol-
lies.
FOUR-WHEEL-DRIVE VEHICLE TOWING
Chrysler Corporation recommends that a vehicle be
transported on a flat-bed device. A Wheel-lift or
Sling-type device can be used providedall the
wheels are lifted off the ground using tow dol-
lies.
WARNING: WHEN TOWING A DISABLED VEHICLE
AND THE DRIVE WHEELS ARE SECURED IN A
WHEEL LIFT OR TOW DOLLIES, ENSURE THE
TRANSMISSION IS IN THE PARK POSITION (AUTO-
MATIC TRANSMISSION) OR A FORWARD DRIVE
GEAR (MANUAL TRANSMISSION).
CAUTION: Many vehicles are equipped with air
dams, spoilers, and/or ground effect panels. To
avoid component damage, a wheel-lift towing vehi-
cle or a flat-bed hauling vehicle is recommended.
0 - 16 LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCEDR
TOWING (Continued)
Page 63 of 2895

KNUCKLE
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the hub bearing (Refer to 2 - SUSPEN-
SION/FRONT/HUB / BEARING - REMOVAL).
(2) Remove tie-rod or drag link end from the steer-
ing knuckle arm.
(3) Remove the ABS sensor wire and bracket from
knuckle. Refer to Brakes, for proper procedures.
(4) Remove the cotter pin from the upper ball stud
nut. Remove the upper and lower ball stud nuts.
(5) Strike the steering knuckle with a brass ham-
mer to loosen.
(6) Remove knuckle from axle tube yokes.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the steering knuckle on the ball studs.
(2) Install and tighten lower ball stud nut to 47
N´m (35 ft. lbs.) torque. Do not install cotter pin at
this time.
(3) Install and tighten upper ball stud nut to 94
N´m (70 ft. lbs.) torque. Advance nut to next slot to
line up hole and install new cotter pin.
(4) Retorque lower ball stud nut to 190±217 N´m
(140±160 ft. lbs.) torque. Advance nut to next slot to
line up hole and install new cotter pin.
(5) Install the hub bearing (Refer to 2 - SUSPEN-
SION/FRONT/HUB / BEARING - INSTALLATION).
(6) Install tie-rod or drag link end onto the steer-
ing knuckle arm.
(7) Install the ABS sensor wire and bracket to the
knuckle. Refer to Brakes, for proper procedure.
UPPER SUSPENSION ARM
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - LEFT
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove the upper suspension arm nut and bolt
at the axle bracket (Fig. 16).
(3) Remove the nut and bolt at the frame rail and
remove the upper suspension arm.
REMOVAL - RIGHT
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Disconnect the exhaust system at the mani-
folds.
(3) Disconnect the rubber exhaust mounts at the
muffler.
(4) Support the transmission.
(5) Remove the transmission cross member.
(6) Lower the exhaust system down in order to
gain access to the removal of the upper bolt.(7) Remove the nut and bolt at the frame rail and
remove the upper suspension arm.
(8) Remove the upper suspension arm nut and bolt
at the axle bracket.
(9) Remove the suspension arm from the vehicle.
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - LEFT
(1) Position the upper suspension arm at the axle
and frame rail.
(2) Install the bolts and finger tighten the nuts.
(3) Remove the supports and lower the vehicle.
(4) Tighten nut at the axle bracket to 163 N´m
(120 ft. lbs.). Tighten nut at frame bracket to 163
N´m (120 ft. lbs.).
INSTALLATION - RIGHT
(1) Position the upper suspension arm at the axle
and frame rail.
(2) Install the bolts, then finger tighten the nuts.
(3) Reconnect the rubber exhaust mounts at the
muffler.
(4) Reconnect the exhaust at the manifolds.
(5) Install the transmission crossmember.
(6) Remove the supports and lower the vehicle.
(7) Tighten nut at the axle bracket to 163 N´m
(120 ft. lbs.). Tighten nut at frame bracket to 163
N´m (120 ft. lbs.).
Fig. 16 Link/Coil Suspension
1 - STABILIZER BAR
2 - SHOCK ABSORBER
3 - COIL SPRING
4 - UPPER SUSPENSION ARM
5 - LOWER SUSPENSION ARM
6 - TRACK BAR
2 - 34 FRONT - LINK/COILDR
Page 76 of 2895

(15) If the vibration remains unacceptable, apply
the same steps to the front end of the propeller shaft.
(16) Install the wheel and tires. Lower the vehicle.
PROPELLER SHAFT RUNOUT
(1) Remove dirt, rust, paint and undercoating from
the propeller shaft surface where the dial indicator
will contact the shaft.
(2) The dial indicator must be installed perpendic-
ular to the shaft surface.
(3) Measure runout at the center and ends of the
shaft sufficiently far away from weld areas to ensure
that the effects of the weld process will not enter into
the measurements.
(4) Refer to Runout Specifications chart.
(5) If the propeller shaft runout is out of specifica-
tion, remove the propeller shaft, index the shaft 180É,
and re-install the propeller shaft. Measure shaft
runout again.
(6) If the propeller shaft runout is now within
specifications, mark the shaft and yokes for proper
orientation.
(7) If the propeller shaft runout is not within spec-
ifications, verify that the runout of the transmission/
transfer case and axle are within specifications.
Correct as necessary and re-measure propeller shaft
runout.
(8) Replace the propeller shaft if the runout still
exceeds the limits.
RUNOUT SPECIFICATIONS
Front of Shaft 0.020 in. (0.50 mm)
Center of Shaft 0.025 in. (0.63 mm)
Rear of Shaft 0.020 in. (0.50 mm)
note:
Measure front/rear runout approximately 3 inches (76
mm) from the weld seam at each end of the shaft
tube for tube lengths over 30 inches. For tube lengths
under 30 inches, the maximum allowed runout is
0.020 in. (0.50 mm) for the full length of the tube.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
PROPELLER SHAFT ANGLE
This procedure applies to both the front/rear pro-
peller shafts. To obtain the front output angle (A) on
the front propeller shaft, place the inclinometer the
machined surface of the C/V joint.
(1) To check driveline alignment, raise and support
the vehicle at the axles as level as possible. Allow the
wheels and propeller shaft to turn.
(2) Remove any external bearing snap rings, if
equipped from universal joint so protractor base sits
flat.
Fig. 1 CLAMP SCREW AT POSITION 1
1 - CLAMP
2 - SCREWDRIVER
Fig. 2 TWO CLAMP SCREWS
Fig. 3 CLAMP SCREWS SEPARATED
1-1¤2INCH
DRPROPELLER SHAFT 3 - 3
PROPELLER SHAFT (Continued)
Page 77 of 2895

(3) Rotate the shaft until transmission/transfer
case output yoke bearing is facing downward.
NOTE: Always make measurements from front to
rear and from the same side of the vehicle.
(4) Place Inclinometer 7663 on yoke bearing (A)
parallel to the shaft (Fig. 4). Center bubble in sight
glass and record measurement.
This measurement will give you the transmis-
sion yoke Output Angle (A).
(5) Rotate propeller shaft 90 degrees and place
Inclinometer on yoke bearing parallel to the shaft
(Fig. 5). Center bubble in sight glass and record mea-
surement. This measurement can also be taken at
the rear end of the shaft.
This measurement will give you the Propeller
Shaft Angle (C).
(6) Rotate propeller shaft 90 degrees and place
Inclinometer on companion flange yoke bearing par-
allel to the shaft (Fig. 6). Center bubble in sight glass
and record measurement.
This measurement will give you the pinion
Companion Flange Input Angle (B).
(7) Subtract smaller figure from larger (C minus
A) to obtain Transmission/Transfer CaseOutput
Operating Angle.
(8) Subtract smaller figure from larger (C minus
B) to obtain axleInput Operating Angle.Refer to rules given below and the example in (Fig.
7) for additional information.
²Good cancellation of U-joint operating angles
should be within 1É.
²Operating angles should be less than 3É.
²At least 1/2 of one degree continuous operating
(propeller shaft) angle.
Fig. 4 OUTPUT ANGLE (A)
Fig. 5 PROPELLER SHAFT ANGLE (C)
Fig. 6 INPUT ANGLE (B)
3 - 4 PROPELLER SHAFTDR
PROPELLER SHAFT (Continued)
Page 79 of 2895

SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Center Bearing Bolts 54 40 -
Front Pinion Flange Bolts 115 85 -
Rear Pinion Flange Bolts 115 85 -
SPECIAL TOOLSFRONT PROPELLER SHAFT
REMOVAL
(1) Position transmission and transfer case into
neutral.
(2) Raise and support vehicle.
(3) Remove exhaust crossover pipe.
(4) Mark a line across the axle companion flange
and propeller shaft flange yoke (Fig. 9) for installa-
tion reference.
(5) Remove companion flange bolts.
(6) Remove dust boot clamp (Fig. 10) from the C/V
jonit end of the shaft.
(7) Remove propeller shaft.
INCLINOMETER 7663
Bearing Splitter 1130
INSTALLER 6052
Fig. 9 COMPANION FLANGE
1 - COMPANION FLANGE
2 - PROPELLER SHAFT
3 - FLANGE YOKE
4 - REFERENCE MARK
3 - 6 PROPELLER SHAFTDR
PROPELLER SHAFT (Continued)
Page 80 of 2895

INSTALLATION
(1) Install propeller shaft with with all reference
marks aligned.
(2) Install transfer case companion flange bolts
and tighten to 30.5 N´m (22.5 ft. lbs.).
(3) Install axle companion flange bolts and tighten
to 108 N´m (80 ft. lbs.).
(4) Install skid plate, if equipped.
(5) Lower vehicle and road test to verify repair.
REAR PROPELLER SHAFT
REMOVAL
(1) Shift transmission into Neutral.
(2) Raise and support vehicle.
(3) Mark a line across the pinion companion flange
and propeller shaft flange yoke (Fig. 11) for installa-
tion reference.
(4) Mark the outline of the center bearing (Fig. 12)
on the crossmember for installation reference, if
equipped.
(5) Remove center bearing mounting nuts, if
equipped.
(6) Remove pinion yoke companion flange bolts.
(7) Slide slip yoke off of the transmission or trans-
fer case output shaft and remove propeller shaft.
Fig. 10 DUST BOOT
1 - C/V JOINT
2 - TRANSFER CASE
3 - BOOT CLAMP
4 - PROPELLER SHAFT
Fig. 11 COMPANION FLANGE
1 - PROPELLER SHAFT
2 - COMPANION FLANGE
3 - REFERENCE MARK
4 - SHAFT FLANGE YOKE
Fig. 12 CENTER BEARING
1 - CENTER BEARING
2 - DUST BOOT
3 - MOUNTING NUTS
DRPROPELLER SHAFT 3 - 7
FRONT PROPELLER SHAFT (Continued)
Page 81 of 2895

INSTALLATION
(1) Slide the slip yoke onto the transmission/trans-
fer case output shaft.
(2) Align and install center bearing on crossmem-
ber, if necessary and tighten nutts to 54 N´m (40 ft.
lbs.).
(3) Align reference marks on the propeller shaft
yoke and pinion companion flange (Fig. 13).
(4) Tighten pinion companion flange bolts to 115
N´m (85 ft. lbs.).
(5) Lower the vehicle.
CENTER BEARING
REMOVAL
(1) Remove rear propeller shaft.
(2) Mark the two shafts (Fig. 14) for installation
reference.
(3) Remove slip joint boot clamp and separate the
two shafts.
(4) Use hammer and punch to tap slinger away
from shaft to provide room for bearing splitter.
(5) Position Bearing Splitter Tool 1130 between
slinger and shaft.
CAUTION: Do not damage shaft spline during
removal of center bearing.
(6) Set shaft in press and press bearing off the
shaft.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: Two types of center bearings are used and
are not interchangeable. Install the same type as
the vehicle was built with.
(1) Install new slinger on shaft and drive into posi-
tion with appropriate installer tool.
(2) Install new center bearing on shaft with Bear-
ing Installer Tool 6052. Drive on shaft with hammer
until bearing is seated.
(3) Clean shaft splines and apply a coat of multi-
purpose grease.
(4) Align master splines and slide front and rear
half-shafts together. Reposition slip yoke boot and
install new clamp.
(5) Install propeller shaft in vehicle.
ADJUSTMENTS
CENTER BEARING
Launch shudder is a vibration that occurs at first
acceleration from a stop. Shudder vibration usually
peaks at the engines highest torque output. Shudder
is a symptom associated with vehicles using a two-
piece propeller shaft. To decrease shudder, lower the
center bearing in 1/8 inch increments. Use shim
stock or fabricated plates. Plate stock must be used
to maintain compression of the rubber insulator
around the bearing. Do not use washers. Replace the
original bolts with the appropriate increased length
bolts.
Fig. 13 REAR PROPELLER SHAFT
1 - COMPANION FLANGE
2 - PROPELLER SHAFT
Fig. 14 REFERENCE MARKS
1 - REFERENCE MARK
2 - CENTER BEARING
3 - BOOT CLAMP
4 - DUST BOOT
3 - 8 PROPELLER SHAFTDR
REAR PROPELLER SHAFT (Continued)
Page 84 of 2895

HALF SHAFT
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
HALF SHAFT
CAUTION.............................11
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING................11
REMOVAL.............................11
INSTALLATION.........................12
SPECIFICATIONS.......................12
SPECIAL TOOLS.......................12CV JOINT-OUTER
REMOVAL.............................13
INSTALLATION.........................13
CV JOINT-INNER
REMOVAL.............................16
INSTALLATION.........................16
HALF SHAFT
CAUTION
CAUTION:: Never grasp half shaft assembly by the
boots. This may cause the boot to pucker or crease
and reduce the service life of the boot.
Avoid over angulating or stroking the C/V joints
when handling the half shaft.
Half shafts exposed to battery acid, transmission
fluid, brake fluid, differential fluid or gasoline may
cause the boots to deteriorate.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
Check for grease at the inboard and outboard C/V
joint. This is a sign of boot or boot clamp damage.
NOISE/VIBRATION IN TURNS
A clicking noise or a vibration in turns could be
caused by a damaged outer C/V or inner tripod joint
seal boot or seal boot clamps. This will result in the
loss/contamination of the joint grease, resulting in
inadequate lubrication of the joint. Noise could also
be caused by another component of the vehicle com-
ing in contact with the half shafts.
CLUNKING NOISE DURING ACCELERATION
This noise may be a result of a damaged or worn
C/V joint. A torn boot or loose/missing clamp on the
inner/outer joint which has allowed the grease to be
lost will damage the C/V joint.
SHUDDER/VIBRATION DURING ACCELERATION
This problem could be a result of a worn/damaged
inner tripod joint or a sticking tripod joint. Improper
wheel alignment may also cause a shudder or vibra-
tion.
VIBRATION AT HIGHWAY SPEEDS
This problem could be a result of out of balance
front tires or tire/wheel runout. Foreign material
(mud, etc.) packed on the backside of the wheel(s)
will also cause a vibration.
REMOVAL
(1) Loosen lug nuts and hub nut while the with
the vehicle brakes applied.
(2) Raise and support the vehicle.
(3) Remove wheel and tire assembly
(4) Remove half shaft hub nut.
(5) Remove brake caliper and rotor.
(6) Position hydraulic jack under lower suspension
arm and raise jack to unload rebound bumper.
(7) Remove lower shock absorber bolt.
(8) Remove upper ball joint nut and seperate ball
with Remover 8677 (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1 UPPER BALL JOINT SEPARATION
1 - UPPER CONTROL ARM
2 - REMOVER
3 - STEERING KNUCKLE
DRHALF SHAFT 3 - 11
Page 92 of 2895

tial bearing noise is also constant and varies only
with vehicle speed.
Axle shaft bearings produce noise and vibration
when worn or damaged. The noise generally changes
when the bearings are loaded. Road test the vehicle.
Turn the vehicle sharply to the left and to the right.
This will load the bearings and change the noise
level. Where axle bearing damage is slight, the noise
is usually not noticeable at speeds above 30 mph.
LOW SPEED KNOCK
Low speed knock is generally caused by a worn
U-joint or by worn side-gear thrust washers. A worn
pinion shaft bore will also cause low speed knock.
VIBRATION
Vibration at the rear of the vehicle is usually
caused by:
²Damaged drive shaft.
²Missing drive shaft balance weight(s).
²Worn or out of balance wheels.
²Loose wheel lug nuts.
²Worn U-joint(s).
²Loose/broken springs.
²Damaged axle shaft bearing(s).
²Loose pinion gear nut.
²Excessive pinion yoke run out.
²Bent axle shaft(s).Check for loose or damaged front end components
or engine/transmission mounts. These components
can contribute to what appears to be a rear end
vibration. Do not overlook engine accessories, brack-
ets and drive belts.
All driveline components should be examined
before starting any repair.
(Refer to 22 - TIRES/WHEELS - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING)
DRIVELINE SNAP
A snap or clunk noise when the vehicle is shifted
into gear (or the clutch engaged) can be caused by:
²High engine idle speed.
²Transmission shift operation.
²Loose engine/transmission/transfer case mounts.
²Worn U-joints.
²Loose spring mounts.
²Loose pinion gear nut and yoke.
²Excessive ring gear backlash.
²Excessive side gear to case clearance.
The source of a snap or a clunk noise can be deter-
mined with the assistance of a helper. Raise the vehi-
cle on a hoist with the wheels free to rotate. Instruct
the helper to shift the transmission into gear. Listen
for the noise, a mechanics stethoscope is helpful in
isolating the source of a noise.
DIAGNOSTIC CHART
Condition Possible Causes Correction
Wheel Noise 1. Wheel loose. 1. Tighten loose nuts.
2. Faulty, brinelled wheel bearing. 2. Replace bearing.
Axle Shaft Noise 1. Misaligned axle tube. 1. Inspect axle tube alignment.
Correct as necessary.
2. Bent or sprung axle shaft. 2. Inspect and correct as necessary.
3. End-play in pinion bearings. 3. Refer to pinion pre-load
information and correct as
necessary.
4. Excessive gear backlash
between the ring gear and pinion.4. Check adjustment of the ring
gear and pinion backlash. Correct
as necessary.
5. Improper adjustment of pinion
gear bearings.5. Adjust the pinion bearings
pre-load.
6. Loose pinion yoke nut. 6. Tighten the pinion yoke nut.
7. Scuffed gear tooth contact
surfaces.7. Inspect and replace as
necessary.
DRFRONT AXLE - C205F 3 - 19
FRONT AXLE - C205F (Continued)
Page 94 of 2895
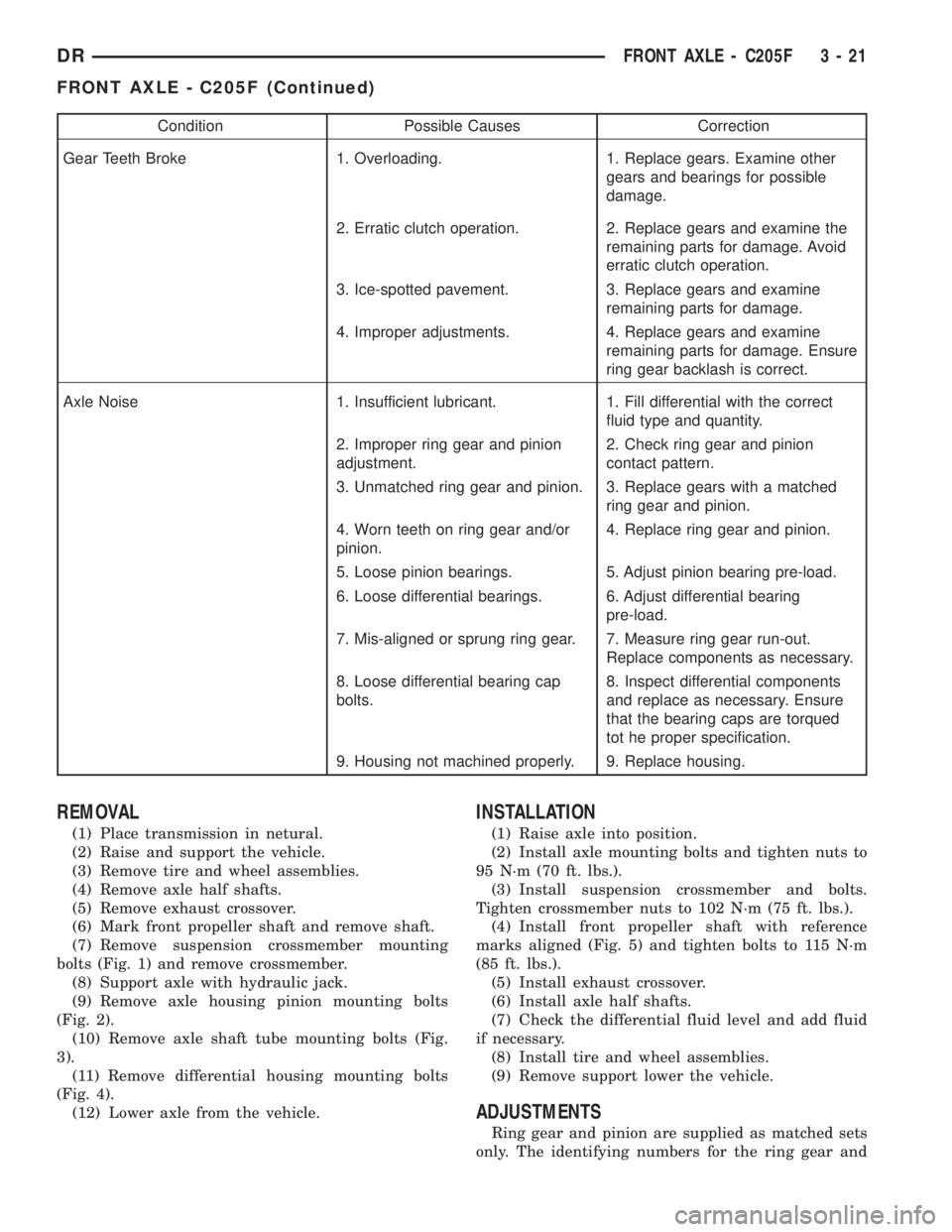
Condition Possible Causes Correction
Gear Teeth Broke 1. Overloading. 1. Replace gears. Examine other
gears and bearings for possible
damage.
2. Erratic clutch operation. 2. Replace gears and examine the
remaining parts for damage. Avoid
erratic clutch operation.
3. Ice-spotted pavement. 3. Replace gears and examine
remaining parts for damage.
4. Improper adjustments. 4. Replace gears and examine
remaining parts for damage. Ensure
ring gear backlash is correct.
Axle Noise 1. Insufficient lubricant. 1. Fill differential with the correct
fluid type and quantity.
2. Improper ring gear and pinion
adjustment.2. Check ring gear and pinion
contact pattern.
3. Unmatched ring gear and pinion. 3. Replace gears with a matched
ring gear and pinion.
4. Worn teeth on ring gear and/or
pinion.4. Replace ring gear and pinion.
5. Loose pinion bearings. 5. Adjust pinion bearing pre-load.
6. Loose differential bearings. 6. Adjust differential bearing
pre-load.
7. Mis-aligned or sprung ring gear. 7. Measure ring gear run-out.
Replace components as necessary.
8. Loose differential bearing cap
bolts.8. Inspect differential components
and replace as necessary. Ensure
that the bearing caps are torqued
tot he proper specification.
9. Housing not machined properly. 9. Replace housing.
REMOVAL
(1) Place transmission in netural.
(2) Raise and support the vehicle.
(3) Remove tire and wheel assemblies.
(4) Remove axle half shafts.
(5) Remove exhaust crossover.
(6) Mark front propeller shaft and remove shaft.
(7) Remove suspension crossmember mounting
bolts (Fig. 1) and remove crossmember.
(8) Support axle with hydraulic jack.
(9) Remove axle housing pinion mounting bolts
(Fig. 2).
(10) Remove axle shaft tube mounting bolts (Fig.
3).
(11) Remove differential housing mounting bolts
(Fig. 4).
(12) Lower axle from the vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Raise axle into position.
(2) Install axle mounting bolts and tighten nuts to
95 N´m (70 ft. lbs.).
(3) Install suspension crossmember and bolts.
Tighten crossmember nuts to 102 N´m (75 ft. lbs.).
(4) Install front propeller shaft with reference
marks aligned (Fig. 5) and tighten bolts to 115 N´m
(85 ft. lbs.).
(5) Install exhaust crossover.
(6) Install axle half shafts.
(7) Check the differential fluid level and add fluid
if necessary.
(8) Install tire and wheel assemblies.
(9) Remove support lower the vehicle.
ADJUSTMENTS
Ring gear and pinion are supplied as matched sets
only. The identifying numbers for the ring gear and
DRFRONT AXLE - C205F 3 - 21
FRONT AXLE - C205F (Continued)