width DODGE RAM 2003 Service Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2003, Model line: RAM, Model: DODGE RAM 2003Pages: 2895, PDF Size: 83.15 MB
Page 1297 of 2895

STANDARD PROCEDURE
CONNECTING ROD BEARING FITTING
Inspect the connecting rod bearings for scoring.
Check the bearings for normal wear patterns, scor-
ing, grooving, fatigue and pitting (Fig. 45). Replace
any bearing that shows abnormal wear.
Inspect the connecting rod journals for signs of
scoring, nicks and burrs (Fig. 46).
Misaligned or bent connecting rods can cause
abnormal wear on pistons, piston rings, cylinder
walls, connecting rod bearings and crankshaft con-
necting rod journals. If wear patterns or damage to
any of these components indicate the probability of a
misaligned connecting rod, inspect it for correct rod
alignment. Replace misaligned, bent or twisted con-
necting rods.
(1) Wipe the oil from the connecting rod journal.
(2) Lubricate the upper bearing insert and position
in connecting rod. Center bearing insert in connect-
ing rod (Fig. 47)
(3) Use piston ring compressor and Guide Pins
Special Tool 8507 (Fig. 48) to install the rod and pis-
ton assemblies. The oil slinger slots in the rods must
face front of the engine. The ªFº's near the piston
wrist pin bore should point to the front of the engine.
(4) Install the lower bearing insert in the bearing
cap. Center bearing insert in connecting rod (Fig. 47).The lower insert must be dry. Place strip of Plasti-
gage across full width of the lower insert at the cen-
ter of bearing cap. Plastigage must not crumble in
use. If brittle, obtain fresh stock.
Fig. 45 Connecting Rod Bearing Inspection
1 - UPPER BEARING HALF
2 - MATING EDGES
3 - GROOVES CAUSED BY ROD BOLTS SCRATCHING JOURNAL
DURING INSTALLATION
4 - WEAR PATTERN - ALWAYS GREATER ON UPPER BEARING
Fig. 46 Scoring Caused by Insufficient Lubrication
or Damaged Crankshaft Journal
Fig. 47 Bearing Insert Location
1 - Connecting Rod
2 - Bearing Insert
- A, B less then .50 mm (.0196 in.)
9 - 48 ENGINE - 3.7LDR
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD (Continued)
Page 1298 of 2895

(5) Install bearing cap and connecting rod on the
journal and tighten bolts to 27 N´m (20 ft. lbs.) plus a
90É turn. DO NOT rotate crankshaft. Plastigage will
smear, resulting in inaccurate indication.
(6) Remove the bearing cap and determine amount
of bearing-to-journal clearance by measuring the
width of compressed Plastigage (Fig. 49). Refer to
Engine Specifications for the proper clearance.Plas-
tigage should indicate the same clearance
across the entire width of the insert. If the
clearance varies, it may be caused by either a
tapered journal, bent connecting rod or foreign
material trapped between the insert and cap or
rod.
(7) If the correct clearance is indicated, replace-
ment of the bearing inserts is not necessary. Remove
the Plastigage from crankshaft journal and bearing
insert. Proceed with installation.
(8) If bearing-to-journal clearance exceeds the
specification, determin which services bearing set to
use the bearing sizes are as follows:
Bearing
MarkSIZE USED WITH
JOURNAL SIZE
.025 US.025 mm 57.883-57.867 mm
(.001 in.) (2.2788-2.2783 in.)
Std.STANDARD 57.908-57.892 mm
(2.2798-2.2792 in.)
.250 US.250 mm 57.658-57.646 mm
(.010 in.) (2.2700-2.2695 in.)
CAUTION: Connecting Rod Bolts are Torque to
Yield Bolts and Must Not Be Reused. Always
replace the Rod Bolts whenever they are loosened
or removed.
(9) Repeat the Plastigage measurement to verify
your bearing selection prior to final assembly.
(10) Once you have selected the proper insert,
install the insert and cap. Tighten the connecting rod
bolts to 27 N´m (20 ft. lbs.) plus a 90É turn.Fig. 48 Piston and Connecting Rod -Installation -
Typical
1 - ªFº TOWARD FRONT OF ENGINE
2 - OIL SLINGER SLOT
3 - RING COMPRESSOR
4 - SPECIAL TOOL 8507
Fig. 49 Measuring Bearing Clearance with
Plastigage
1 - PLASTIGAGE SCALE
2 - COMPRESSED PLASTIGAGE
DRENGINE - 3.7L 9 - 49
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD (Continued)
Page 1306 of 2895

FRONT MOUNT
REMOVAL
2WD
(1) Disconnect the negative cable from the battery.
CAUTION: Remove the viscous fan before raising
engine. Failure to do so may cause damage to the
fan blade, fan clutch and fan shroud.
(2) Remove the viscous fan (Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING/ENGINE/FAN DRIVE VISCOUS CLUTCH -
REMOVAL).
(3) Raise the vehicle.
(4) Remove the engine oil filter.
(5) Remove the oil drain trough.
(6) Support the engine with a suitable jack and a
block of wood across the full width of the engine oil
pan.
(7) Support the front axle with a suitable jack.
(8) Remove the (4) bolts that attach the engine
mounts to the front axle.
(9) Remove the (3) bolts that attach the front axle
to the left engine bracket.
(10) Lower the front axle.
(11) Remove the through bolts(12) Raise the engine far enough to be able to
remove the left and right engine mounts.
(13) Remove the (8) mount to engine attaching
bolts
(14) Remove the engine mounts.4WD
(1) Disconnect the negative cable from the battery.
CAUTION: Remove the viscous fan before raising
engine. Failure to do so may cause damage to the
fan blade, fan clutch and fan shroud.
(2) Remove the viscous fan (Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING/ENGINE/FAN DRIVE VISCOUS CLUTCH -
REMOVAL).
(3) Raise the vehicle.
(4) Remove the skid plate.
(5) Remove the front crossmember.
(6) Remove the engine oil filter.
(7) Remove the oil drain trough.
(8) Support the engine with a suitable jack and a
block of wood across the full width of the engine oil
pan.
(9) Support the front axle with a suitable jack.
(10) Remove the (4) bolts that attach the engine
mounts to the front axle (Fig. 66).
Fig. 66 ENGINE INSULATOR MOUNTS 4X4
1 - RH INSULATOR TO AXLE BOLT
2 - NUT
3 - PINION SUPPORT MOUNT
4 - LH INSULATOR MOUNT5 - LH INSULATOR TO AXLE BOLT
6 - FRONT AXLE
7 - NUT
8 - RH INSULATOR MOUNT
DRENGINE - 3.7L 9 - 57
Page 1342 of 2895

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE
DIAGNOSIS - INTRODUCTION
Engine diagnosis is helpful in determining the
causes of malfunctions not detected and remedied by
routine maintenance.
These malfunctions may be classified as either per-
formance (e.g., engine idles rough and stalls) or
mechanical (e.g., a strange noise).
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TEST-
ING)ÐPERFORMANCE and (Refer to 9 - ENGINE -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING)ÐMECHANICAL for
possible causes and corrections of malfunctions.
(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING) and (Refer to 14 -
FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING) for the fuel system diagnosis.
Additional tests and diagnostic procedures may be
necessary for specific engine malfunctions that can
not be isolated with the Service Diagnosis charts.
Information concerning additional tests and diagno-
sis is provided within the following diagnosis:
²Cylinder Compression Pressure Test (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
²Cylinder Combustion Pressure Leakage Test
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TEST-
ING).
²Engine Cylinder Head Gasket Failure Diagnosis
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - DIAGNO-
SIS AND TESTING).
²Intake Manifold Leakage Diagnosis (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REPAIR DAMAGED
OR WORN THREADS
CAUTION: Be sure that the tapped holes maintain
the original center line.
Damaged or worn threads can be repaired. Essen-
tially, this repair consists of:
²Drilling out worn or damaged threads.
²Tapping the hole with a special Heli-Coil Tap, or
equivalent.
²Installing an insert into the tapped hole to bring
the hole back to its original thread size.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FORM-IN-PLACE
GASKETS AND SEALERS
There are numerous places where form-in-place
gaskets are used on the engine. Care must be taken
when applying form-in-place gaskets to assure
obtaining the desired results.Do not use form-in-place gasket material unless specified.Bead size,
continuity, and location are of great importance. Too
thin a bead can result in leakage while too much can
result in spill-over which can break off and obstruct
fluid feed lines. A continuous bead of the proper
width is essential to obtain a leak-free gasket.
There are numerous types of form-in-place gasket
materials that are used in the engine area. Mopart
Engine RTV GEN II, MopartATF-RTV, and Mopart
Gasket Maker gasket materials, each have different
properties and can not be used in place of the other.
MOPARtENGINE RTV GEN II
MopartEngine RTV GEN II is used to seal com-
ponents exposed to engine oil. This material is a spe-
cially designed black silicone rubber RTV that
retains adhesion and sealing properties when
exposed to engine oil. Moisture in the air causes the
material to cure. This material is available in three
ounce tubes and has a shelf life of one year. After one
year this material will not properly cure. Always
inspect the package for the expiration date before
use.
MOPARtATF RTV
MopartATF RTV is a specifically designed black
silicone rubber RTV that retains adhesion and seal-
ing properties to seal components exposed to auto-
matic transmission fluid, engine coolants, and
moisture. This material is available in three ounce
tubes and has a shelf life of one year. After one year
this material will not properly cure. Always inspect
the package for the expiration date before use.
MOPARtGASKET MAKER
MopartGasket Maker is an anaerobic type gasket
material. The material cures in the absence of air
when squeezed between two metallic surfaces. It will
not cure if left in the uncovered tube. The anaerobic
material is for use between two machined surfaces.
Do not use on flexible metal flanges.
MOPARtGASKET SEALANT
MopartGasket Sealant is a slow drying, perma-
nently soft sealer. This material is recommended for
sealing threaded fittings and gaskets against leakage
of oil and coolant. Can be used on threaded and
machined parts under all temperatures. This mate-
rial is used on engines with multi-layer steel (MLS)
cylinder head gaskets. This material also will pre-
vent corrosion. MopartGasket Sealant is available in
a 13 oz. aerosol can or 4oz./16 oz. can w/applicator.
FORM-IN-PLACE GASKET AND SEALER
APPLICATION
Assembling parts using a form-in-place gasket
requires care but it's easier than using precut gas-
kets.
MopartGasket Maker material should be applied
sparingly 1 mm (0.040 in.) diameter or less of sealant
DRENGINE - 4.7L 9 - 93
ENGINE - 4.7L (Continued)
Page 1347 of 2895

SPECIFICATIONS
4.7L ENGINE
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
Engine Type 90É SOHC V-8 16-Valve
Displacement 4.7 Liters / 4701cc
(287 Cubic Inches)
Bore 93.0 mm (3.66 in.)
Stroke 86.5 mm (3.40 in.)
Compression Ratio 9.0:1
Horsepower 235 BHP @ 4800 RPM
Torque 295 LB-FT @ 3200 RPM
Lead Cylinder #1 Left Bank
Firing Order 1-8-4-3-6-5-7-2
CYLINDER BLOCK
Cylinder Block Cast Iron
Bore Diameter 93.010 .0075 mm
(3.6619 0.0003 in.)
Out of Round (MAX) 0.076 mm (0.003 in.)
Taper (MAX) 0.051 mm (0.002 in.)
PISTONS
Material Aluminum Alloy
Diameter 92.975 mm (3.6605 in.)
Weight 367.5 grams (12.96 oz)
Ring Groove Diameter
No. 1 83.73 - 83.97 mm
(3.296 - 3.269 in.)
No. 2 82.833 - 83.033 mm
(3.261 - 3.310 in.)
No. 3 83.88 - 84.08 mm
(3.302 - 3.310 in.)
PISTON PINS
Type Pressed Fit
Clearance In Piston 0.010 - 0.019 mm
(0.0004 - 0.0008 in.)
Diameter 24.013 - 24.016 mm
(0.9454 - 0.9455 in.)
PISTON RINGS
Ring Gap
Top Compression Ring 0.37 - 0.63 mm
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
(0.0146 - 0.0249 in.)
Second Compression
Ring0.37 - 0.63 mm
(0.0146 - 0.0249 in.)
Oil Control (Steel Rails) 0.25 - 0.76 mm
(0.0099 - 0.30 in.)
Side Clearance
Top Compression Ring .051 - .094 mm
(0.0020 - 0.0037 in.)
Second Compression
Ring0.040 - 0.080 mm
(0.0016 - 0.0031 in.)
Oil Ring (Steel Ring) .019 - .229 mm
(.0007 - .0091 in.)
Ring Width
Top Compression Ring 1.472 - 1.490 mm
(0.057 - 0.058 in.)
Second Compression
Ring1.472 - 1.490 mm
(0.057 - 0.058 in.)
Oil Ring (Steel Rails) 0.445 - 0.470 mm
(0.017 - 0.018 in.)
CONNECTING RODS
Bearing Clearance 0.015 - 0.055 mm
(0.0006 - 0.0022 in.)
Side Clearance 0.10 - 0.35 mm
(0.004 - 0.0138 in.)
Piston Pin Bore Diameter .025 - .048 mm
(Interference Fit) (0.001 - 0.0019 in.)
Bearing Bore Out of
Round0.004 mm
(MAX) (0.0002 in.)
Total Weight (Less
Bearing)555 grams (19.5771
ounces)
CRANKSHAFT
Main BearingJournal
Diameter 63.488 - 63.512 mm
(2.4996 - 2.5005 in.)
Bearing Clearance 0.018 - 0.052 mm
(0.0008 - 0.0021 in.)
Out of Round (MAX) 0.005 mm (0.0002 in.)
9 - 98 ENGINE - 4.7LDR
ENGINE - 4.7L (Continued)
Page 1349 of 2895
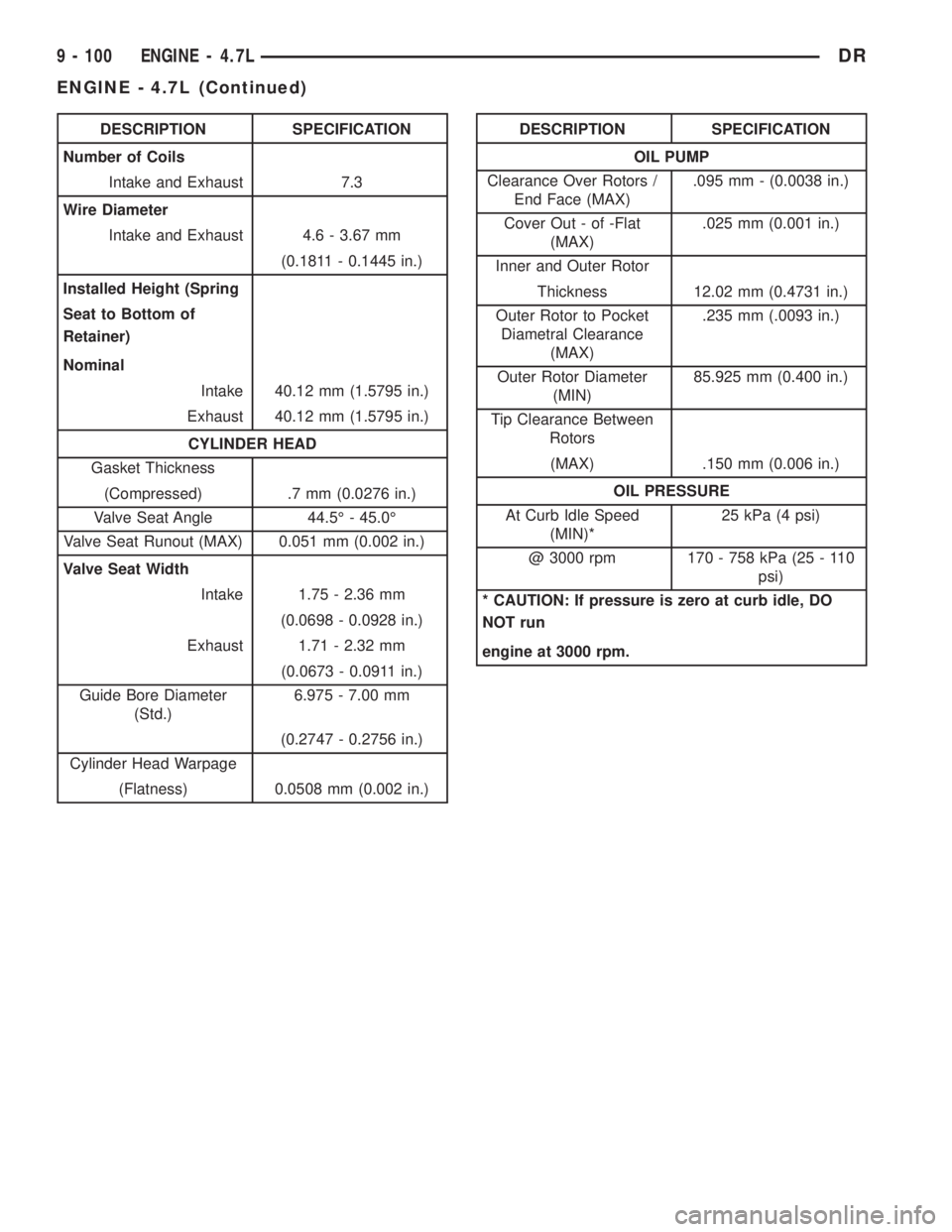
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Number of Coils
Intake and Exhaust 7.3
Wire Diameter
Intake and Exhaust 4.6 - 3.67 mm
(0.1811 - 0.1445 in.)
Installed Height (Spring
Seat to Bottom of
Retainer)
Nominal
Intake 40.12 mm (1.5795 in.)
Exhaust 40.12 mm (1.5795 in.)
CYLINDER HEAD
Gasket Thickness
(Compressed) .7 mm (0.0276 in.)
Valve Seat Angle 44.5É - 45.0É
Valve Seat Runout (MAX) 0.051 mm (0.002 in.)
Valve Seat Width
Intake 1.75 - 2.36 mm
(0.0698 - 0.0928 in.)
Exhaust 1.71 - 2.32 mm
(0.0673 - 0.0911 in.)
Guide Bore Diameter
(Std.)6.975 - 7.00 mm
(0.2747 - 0.2756 in.)
Cylinder Head Warpage
(Flatness) 0.0508 mm (0.002 in.)DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
OIL PUMP
Clearance Over Rotors /
End Face (MAX).095 mm - (0.0038 in.)
Cover Out - of -Flat
(MAX).025 mm (0.001 in.)
Inner and Outer Rotor
Thickness 12.02 mm (0.4731 in.)
Outer Rotor to Pocket
Diametral Clearance
(MAX).235 mm (.0093 in.)
Outer Rotor Diameter
(MIN)85.925 mm (0.400 in.)
Tip Clearance Between
Rotors
(MAX) .150 mm (0.006 in.)
OIL PRESSURE
At Curb Idle Speed
(MIN)*25 kPa (4 psi)
@ 3000 rpm 170 - 758 kPa (25 - 110
psi)
* CAUTION: If pressure is zero at curb idle, DO
NOT run
engine at 3000 rpm.
9 - 100 ENGINE - 4.7LDR
ENGINE - 4.7L (Continued)
Page 1377 of 2895

CONNECTING ROD BEARINGS
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CONNECTING ROD
BEARING FITTING
Inspect the connecting rod bearings for scoring and
bent alignment tabs (Fig. 50). Check the bearings for
normal wear patterns, scoring, grooving, fatigue and
pitting (Fig. 51). Replace any bearing that shows
abnormal wear.
Inspect the connecting rod journals for signs of
scoring, nicks and burrs.
Misaligned or bent connecting rods can cause
abnormal wear on pistons, piston rings, cylinder
walls, connecting rod bearings and crankshaft con-
necting rod journals. If wear patterns or damage to
any of these components indicate the probability of a
misaligned connecting rod, inspect it for correct rod
alignment. Replace misaligned, bent or twisted con-
necting rods.
(1) Wipe the oil from the connecting rod journal.
(2) Lubricate the upper bearing insert and install
in connecting rod.(3) Use piston ring compressor and Guide Pins
Special Tool 8507 (Fig. 52) to install the rod and pis-
ton assemblies. The oil slinger slots in the rods must
face front of the engine. The ªFº's near the piston
wrist pin bore should point to the front of the engine.
(4) Install the lower bearing insert in the bearing
cap. The lower insert must be dry. Place strip of Plas-
tigage across full width of the lower insert at the cen-
ter of bearing cap. Plastigage must not crumble in
use. If brittle, obtain fresh stock.
(5) Install bearing cap and connecting rod on the
journal and tighten bolts to 27 N´m (20 ft. lbs.) plus a
90É turn. DO NOT rotate crankshaft. Plastigage will
smear, resulting in inaccurate indication.
(6) Remove the bearing cap and determine amount
of bearing-to-journal clearance by measuring the
width of compressed Plastigage (Fig. 53). Refer to
Engine Specifications for the proper clearance.Plas-
tigage should indicate the same clearance
across the entire width of the insert. If the
clearance varies, it may be caused by either a
Fig. 50 Locking Tab Inspection
1 - ABNORMAL CONTACT AREA CAUSED BY LOCKING TABS
NOT FULLY SEATED OR BEING BENT
Fig. 51 Scoring Caused by Insufficient Lubrication
or Damaged Crankshaft Journal
Fig. 52 Piston and Connecting Rod - Installation
1 - ªFº TOWARD FRONT OF ENGINE
2 - OIL SLINGER SLOT
3 - RING COMPRESSOR
4 - SPECIAL TOOL 8507
9 - 128 ENGINE - 4.7LDR
Page 1393 of 2895

(3) Install the four cover-to-transmission bolts. Do
NOT tighten at this time.
CAUTION: The structural cover must be held tightly
against both the engine and the transmission bell
housing during tightening sequence. Failure to do
so may cause damage to the cover.
(4) Starting with the two rear cover-to-engine
bolts, tighten bolts (1) (Fig. 86) to 54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.),
then tighten bolts (2) (Fig. 86) and (3) to 54 N´m ( 40
ft. lbs.) in the sequence shown.
(5) Install the exhaust pipe on left hand exhaust
manifold.
(6) Tighten exhaust manifold-to-exhaust pipe
retaining bolts to 20±26 N´m (15±20 ft. lbs.).
FRONT MOUNT
REMOVAL
2WD
(1) Disconnect the negative cable from the battery.
CAUTION: Remove the viscous fan before raising
engine. Failure to do so may cause damage to the
fan blade, fan clutch and fan shroud.
(2) Remove the viscous fan (Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING/ENGINE/FAN DRIVE VISCOUS CLUTCH -
REMOVAL).
(3) Raise the vehicle.
(4) Remove the engine oil filter.
(5) Remove the oil drain trough.(6) Support the engine with a suitable jack and a
block of wood across the full width of the engine oil
pan.
(7) Support the front axle with a suitable jack.
(8) Remove the (4) bolts that attach the engine
mounts to the front axle.
(9) Remove the (3) bolts that attach the front axle
to the left engine bracket.
(10) Lower the front axle.
(11) Remove the through bolts
(12) Raise the engine far enough to be able to
remove the left and right engine mounts.
(13) Remove the (8) mount to engine attaching
bolts
(14) Remove the engine mounts.
4WD
(1) Disconnect the negative cable from the battery.
(2) Remove the viscous fan.
(3) Raise the vehicle.
(4) Remove the skid plate.
(5) Remove the front crossmember.
(6) Remove the engine oil filter.
(7) Remove the oil drain trough.
(8) Support the engine with a suitable jack and a
block of wood across the full width of the engine oil
pan.
(9) Support the front axle with a suitable jack.
(10) Remove the (4) bolts that attach the engine
mounts to the front axle (Fig. 87).
(11) Remove the (3) bolts that attach the front axle
to the left engine bracket.
(12) Lower the front axle.
(13) Remove the (6) through bolts
(14) Raise the engine far enough to be able to
remove the left (Fig. 89) and right (Fig. 88) engine
mounts.
(15) Remove the engine mounts.
INSTALLATION
2WD
NOTE: For mount to engine block and left engine
bracket to front axle bolts, apply MoparTLock and
Seal Adhesive, Medium Strength Threadlocker.
(1) Install the right and left side engine mounts to
the engine block with (8) bolts. Torque bolts to 54
N´m (40 ft. lbs.).
(2) Insert the (2) through bolts into the right and
left side engine mounts and loose assemble the two
nuts onto the through bolts.
(3) Lower the engine until the through bolts rest
onto the slots in the frame brackets.
(4) Tighten the through bolt nuts to 94 N´m (70 ft.
lbs.).
Fig. 86 Structural Cover
1 - BOLT
2 - BOLT
3 - BOLT
9 - 144 ENGINE - 4.7LDR
STRUCTURAL COVER (Continued)
Page 1438 of 2895
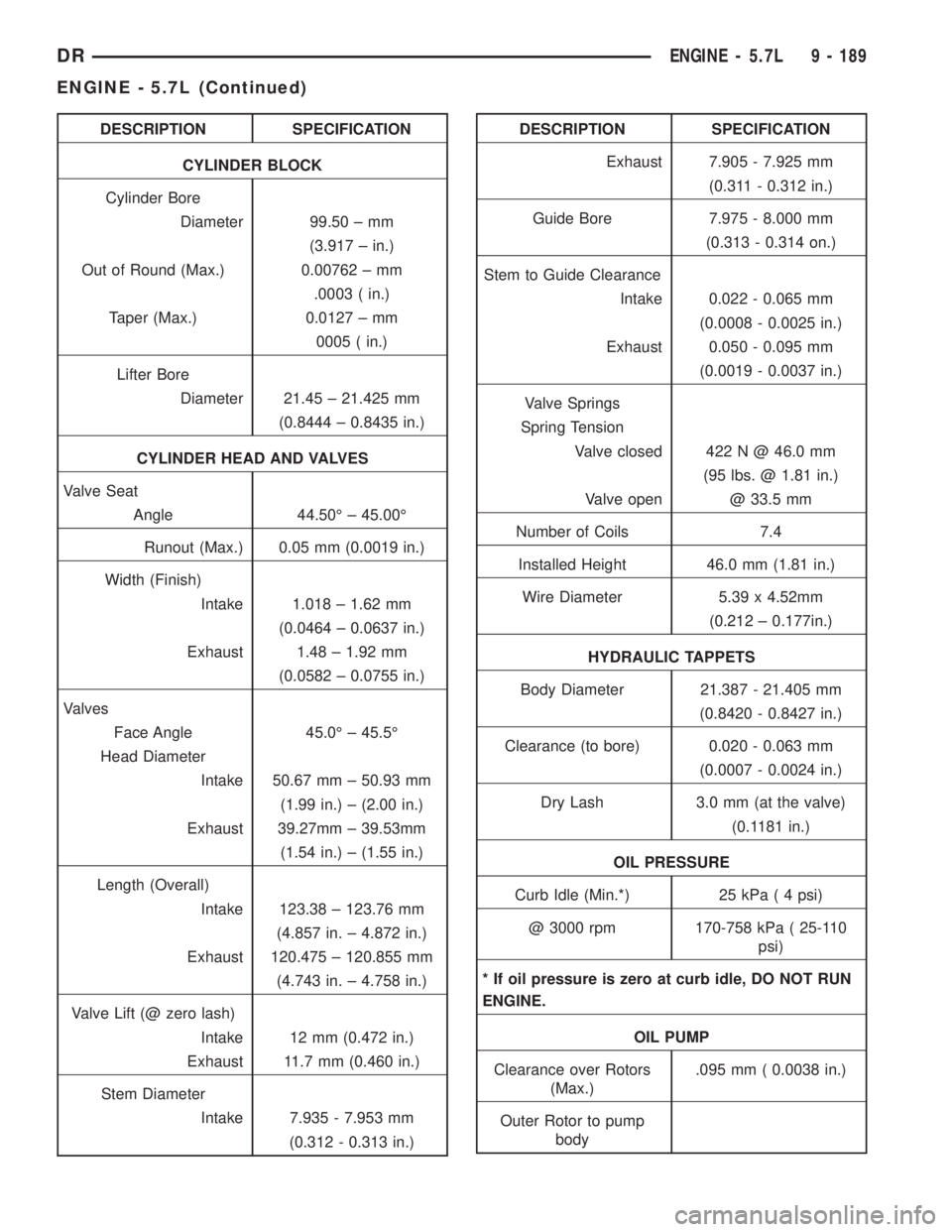
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
CYLINDER BLOCK
Cylinder Bore
Diameter 99.50 ± mm
(3.917 ± in.)
Out of Round (Max.) 0.00762 ± mm
.0003 ( in.)
Taper (Max.) 0.0127 ± mm
0005 ( in.)
Lifter Bore
Diameter 21.45 ± 21.425 mm
(0.8444 ± 0.8435 in.)
CYLINDER HEAD AND VALVES
Valve Seat
Angle 44.50É ± 45.00É
Runout (Max.) 0.05 mm (0.0019 in.)
Width (Finish)
Intake 1.018 ± 1.62 mm
(0.0464 ± 0.0637 in.)
Exhaust 1.48 ± 1.92 mm
(0.0582 ± 0.0755 in.)
Valves
Face Angle 45.0É ± 45.5É
Head Diameter
Intake 50.67 mm ± 50.93 mm
(1.99 in.) ± (2.00 in.)
Exhaust 39.27mm ± 39.53mm
(1.54 in.) ± (1.55 in.)
Length (Overall)
Intake 123.38 ± 123.76 mm
(4.857 in. ± 4.872 in.)
Exhaust 120.475 ± 120.855 mm
(4.743 in. ± 4.758 in.)
Valve Lift (@ zero lash)
Intake 12 mm (0.472 in.)
Exhaust 11.7 mm (0.460 in.)
Stem Diameter
Intake 7.935 - 7.953 mm
(0.312 - 0.313 in.)DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Exhaust 7.905 - 7.925 mm
(0.311 - 0.312 in.)
Guide Bore 7.975 - 8.000 mm
(0.313 - 0.314 on.)
Stem to Guide Clearance
Intake 0.022 - 0.065 mm
(0.0008 - 0.0025 in.)
Exhaust 0.050 - 0.095 mm
(0.0019 - 0.0037 in.)
Valve Springs
Spring Tension
Valve closed 422 N @ 46.0 mm
(95 lbs. @ 1.81 in.)
Valve open @ 33.5 mm
Number of Coils 7.4
Installed Height 46.0 mm (1.81 in.)
Wire Diameter 5.39 x 4.52mm
(0.212 ± 0.177in.)
HYDRAULIC TAPPETS
Body Diameter 21.387 - 21.405 mm
(0.8420 - 0.8427 in.)
Clearance (to bore) 0.020 - 0.063 mm
(0.0007 - 0.0024 in.)
Dry Lash 3.0 mm (at the valve)
(0.1181 in.)
OIL PRESSURE
Curb Idle (Min.*) 25 kPa ( 4 psi)
@ 3000 rpm 170-758 kPa ( 25-110
psi)
* If oil pressure is zero at curb idle, DO NOT RUN
ENGINE.
OIL PUMP
Clearance over Rotors
(Max.).095 mm ( 0.0038 in.)
Outer Rotor to pump
body
DRENGINE - 5.7L 9 - 189
ENGINE - 5.7L (Continued)
Page 1439 of 2895
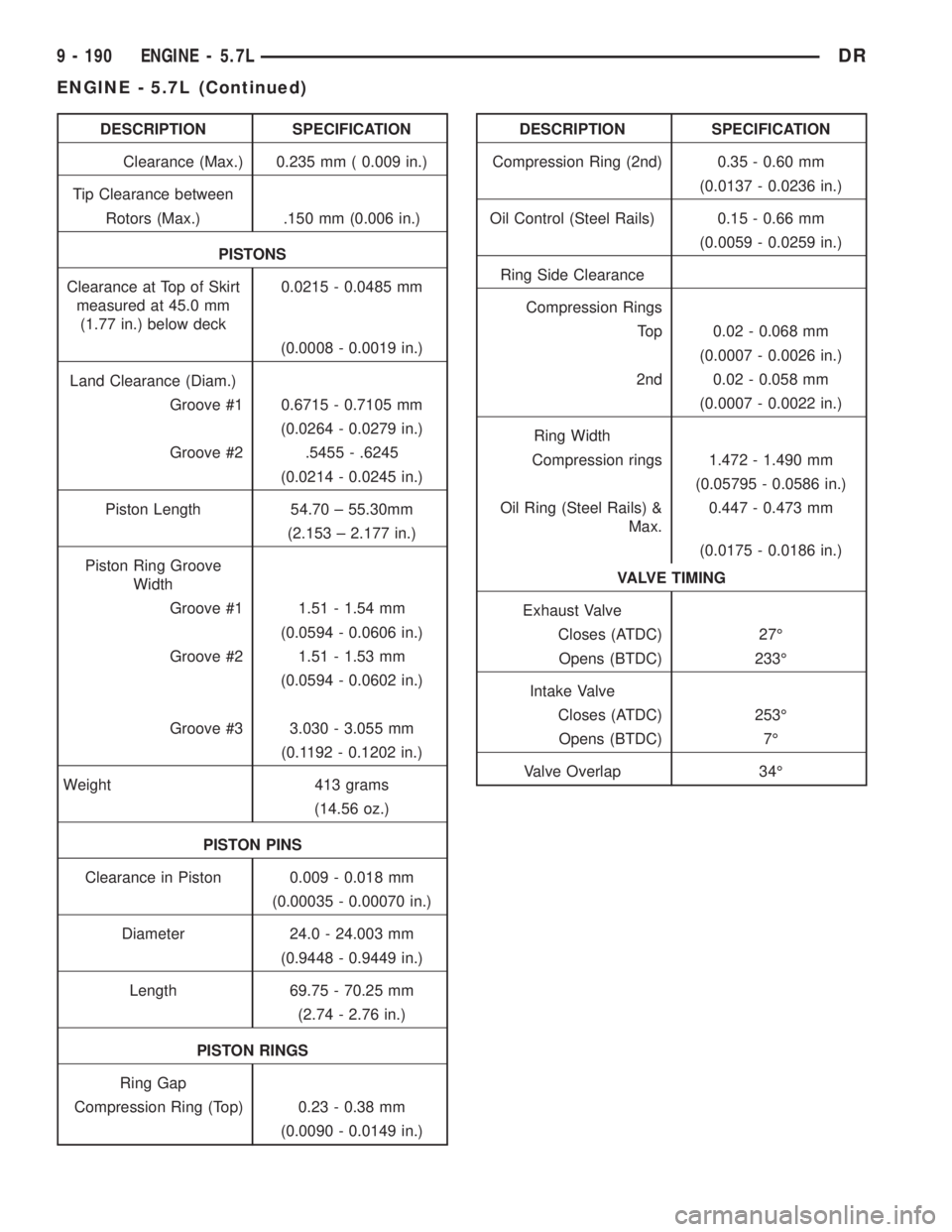
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Clearance (Max.) 0.235 mm ( 0.009 in.)
Tip Clearance between
Rotors (Max.) .150 mm (0.006 in.)
PISTONS
Clearance at Top of Skirt
measured at 45.0 mm
(1.77 in.) below deck0.0215 - 0.0485 mm
(0.0008 - 0.0019 in.)
Land Clearance (Diam.)
Groove #1 0.6715 - 0.7105 mm
(0.0264 - 0.0279 in.)
Groove #2 .5455 - .6245
(0.0214 - 0.0245 in.)
Piston Length 54.70 ± 55.30mm
(2.153 ± 2.177 in.)
Piston Ring Groove
Width
Groove #1 1.51 - 1.54 mm
(0.0594 - 0.0606 in.)
Groove #2 1.51 - 1.53 mm
(0.0594 - 0.0602 in.)
Groove #3 3.030 - 3.055 mm
(0.1192 - 0.1202 in.)
Weight 413 grams
(14.56 oz.)
PISTON PINS
Clearance in Piston 0.009 - 0.018 mm
(0.00035 - 0.00070 in.)
Diameter 24.0 - 24.003 mm
(0.9448 - 0.9449 in.)
Length 69.75 - 70.25 mm
(2.74 - 2.76 in.)
PISTON RINGS
Ring Gap
Compression Ring (Top) 0.23 - 0.38 mm
(0.0090 - 0.0149 in.)DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Compression Ring (2nd) 0.35 - 0.60 mm
(0.0137 - 0.0236 in.)
Oil Control (Steel Rails) 0.15 - 0.66 mm
(0.0059 - 0.0259 in.)
Ring Side Clearance
Compression Rings
Top 0.02 - 0.068 mm
(0.0007 - 0.0026 in.)
2nd 0.02 - 0.058 mm
(0.0007 - 0.0022 in.)
Ring Width
Compression rings 1.472 - 1.490 mm
(0.05795 - 0.0586 in.)
Oil Ring (Steel Rails) &
Max.0.447 - 0.473 mm
(0.0175 - 0.0186 in.)
VALVE TIMING
Exhaust Valve
Closes (ATDC) 27É
Opens (BTDC) 233É
Intake Valve
Closes (ATDC) 253É
Opens (BTDC) 7É
Valve Overlap 34É
9 - 190 ENGINE - 5.7LDR
ENGINE - 5.7L (Continued)