Oss DODGE RAM 2003 Service Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2003, Model line: RAM, Model: DODGE RAM 2003Pages: 2895, PDF Size: 83.15 MB
Page 149 of 2895

(7) Slide the dial indicator probe across the gap
between the pinion height block and the arbor bar
with the scooter block against the pinion height block
(Fig. 7). Continue moving the dial probe to the crest
of the arbor bar and record the highest reading.
(8) Select a shim equal to the dial indicator read-
ing plus the drive pinion gear depth variance number
marked on the shaft of the pinion. For example, if
the depth variance is ±2, add +0.002 in. to the dial
indicator reading.
DIFFERENTIAL BEARING PRELOAD AND GEAR
BACKLASH
The following must be considered when adjusting
bearing preload and gear backlash:²The maximum ring gear backlash variation is
0.076 mm (0.003 in.).
²Mark the gears so the same teeth are meshed
during all backlash measurements.
²Maintain the torque while adjusting the bearing
preload and ring gear backlash.
²Excessive adjuster torque will introduce a high
bearing load and cause premature bearing failure.
Insufficient adjuster torque can result in excessive
differential case free-play and ring gear noise.
²Insufficient adjuster torque will not support the
ring gear correctly and can cause excessive differen-
tial case free-play and ring gear noise.
NOTE: The differential bearing cups will not always
immediately follow the threaded adjusters as they
are moved during adjustment. To ensure accurate
bearing cup responses to the adjustments:
²Maintain the gear teeth engaged (meshed) as
marked.
²The bearings must be seated by rapidly rotat-
ing the pinion gear a half turn back and forth.
²Do this five to ten times each time the threaded
adjusters are adjusted.
(1) Throught the axle tube use Wrench C-4164 to
adjust each threaded adjuster inward until the differ-
ential bearing free-play is eliminated. Allow some
ring gear backlash approximately 0.25 mm (0.01 in.)
between the ring and pinion gear. Seat the bearing
cups with the procedure described above.
(2) Install dial indicator and position the plunger
against the drive side of a ring gear tooth (Fig. 8).
Measure the backlash at 4 positions, 90 degrees
apart around the ring gear. Locate and mark the
area of minimum backlash.
Fig. 5 PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
1 - PINION BLOCK
2 - PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
Fig. 6 PINION DEPTH TOOLS
1 - ARBOR DISC
2 - PINION BLOCK
3 - ARBOR
4 - PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
Fig. 7 PINION GEAR DEPTH MEASUREMENT
1 - ARBOR
2 - SCOOTER BLOCK
3 - DIAL INDICATOR
3 - 76 REAR AXLE-91/4DR
REAR AXLE - 9 1/4 (Continued)
Page 162 of 2895

CAUTION: If cover is not installed within 3 to 5 min-
utes, the cover must be cleaned and new RTV
applied or adhesion quality will be compromised.
(8) Install the cover and any identification tag and
tighten cover bolts to 41 N´m (30 ft. lbs.).
(9) Fill differential with lubricant to bottom of the
fill plug hole. Refer to the Lubricant Specifications
for the correct quantity and type.
NOTE: Trac-lokŸ differential equipped vehicles
should be road tested by making 10 to 12 slow fig-
ure-eight turns. This maneuver will pump the lubri-
cant through the clutch discs to eliminate a
possible chatter noise complaint.
DIFFERENTIAL-TRAC-LOK
DESCRIPTION
The optional Trac-Loktdifferential case has a one-
piece design and the similar internal components as
a standard differential, plus two clutch disc pack-
s.The differential pinion mate shaft is retained with
a threaded pin. Differential bearing preload and ring
gear backlash are set and maintained by threaded
adjusters at the outside of the differential housing.
Pinion bearing preload is set and maintained by the
use of a collapsible spacer. The removable differential
cover provides a means for inspection and service.
OPERATION
This differential clutches are engaged by two con-
current forces. The first being the preload force
exerted through Belleville spring washers within the
clutch packs. The second is the separating forces gen-erated by the side gears as torque is applied through
the ring gear (Fig. 36).
This design provides the differential action needed
for turning corners and for driving straight ahead
during periods of unequal traction. When one wheel
looses traction, the clutch packs transfer additional
torque to the wheel having the most traction. This
differential resist wheel spin on bumpy roads and
provide more pulling power when one wheel looses
traction. Pulling power is provided continuously until
both wheels loose traction. If both wheels slip due to
unequal traction, Trac-loktoperation is normal. In
extreme cases of differences of traction, the wheel
with the least traction may spin.DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
The most common problem is a chatter noise when
turning corners. Before removing the unit for repair,
drain, flush and refill the axle with the specified
lubricant. A container of Mopar Trac-loktLubricant
Fig. 35 COVER SEALANT
1 - SEALANT
2 - DIFFERENTIAL COVER
Fig. 36 TRAC-LOK LIMITED SLIP DIFFERENTIAL
1 - CASE
2 - RING GEAR
3 - DRIVE PINION
4 - PINION GEAR
5 - MATE SHAFT
6 - CLUTCH PACK
7 - SIDE GEAR
8 - CLUTCH PACK
DRREAR AXLE - 9 1/4 3 - 89
DIFFERENTIAL (Continued)
Page 174 of 2895

BEARING NOISE
The axle shaft, differential and pinion bearings can
all produce noise when worn or damaged. Bearing
noise can be either a whining, or a growling sound.
Pinion bearings have a constant-pitch noise. This
noise changes only with vehicle speed. Pinion bearing
noise will be higher pitched because it rotates at a
faster rate. Drive the vehicle and load the differen-
tial. If bearing noise occurs, the rear pinion bearing
is the source of the noise. If the bearing noise is
heard during a coast, the front pinion bearing is the
source.
Worn or damaged differential bearings usually pro-
duce a low pitch noise. Differential bearing noise is
similar to pinion bearing noise. The pitch of differen-
tial bearing noise is also constant and varies only
with vehicle speed.
Axle shaft bearings produce noise and vibration
when worn or damaged. The noise generally changes
when the bearings are loaded. Road test the vehicle.
Turn the vehicle sharply to the left and to the right.
This will load the bearings and change the noise
level. Where axle bearing damage is slight, the noise
is usually not noticeable at speeds above 30 mph.
LOW SPEED KNOCK
Low speed knock is generally caused by a worn
U-joint or by worn side-gear thrust washers. A worn
pinion shaft bore will also cause low speed knock.
VIBRATION
Vibration at the rear of the vehicle is usually
caused by a:
²Damaged drive shaft.
²Missing drive shaft balance weight(s).²Worn or out-of-balance wheels.
²Loose wheel lug nuts.
²Worn U-joint(s).
²Loose/broken springs.
²Damaged axle shaft bearing(s).
²Loose pinion gear nut.
²Excessive pinion yoke run out.
²Bent axle shaft(s).
Check for loose or damaged front-end components
or engine/transmission mounts. These components
can contribute to what appears to be a rearend vibra-
tion. Do not overlook engine accessories, brackets
and drive belts.
NOTE: All driveline components should be exam-
ined before starting any repair.
DRIVELINE SNAP
A snap or clunk noise when the vehicle is shifted
into gear (or the clutch engaged), can be caused by:
²High engine idle speed.
²Transmission shift operation.
²Loose engine/transmission/transfer case mounts.
²Worn U-joints.
²Loose spring mounts.
²Loose pinion gear nut and yoke.
²Excessive ring gear backlash.
²Excessive side gear to case clearance.
The source of a snap or a clunk noise can be deter-
mined with the assistance of a helper. Raise the vehi-
cle on a hoist with the wheels free to rotate. Instruct
the helper to shift the transmission into gear. Listen
for the noise, a mechanics stethoscope is helpful in
isolating the source of a noise.
DIAGNOSTIC CHART
Condition Possible Causes Correction
Wheel Noise 1. Wheel loose. 1. Tighten loose nuts.
2. Faulty, brinelled wheel bearing. 2. Replace bearing.
Axle Shaft Noise 1. Misaligned axle tube. 1. Inspect axle tube alignment.
Correct as necessary.
2. Bent or sprung axle shaft. 2. Inspect and correct as necessary.
DRREAR AXLE - 10 1/2 AA 3 - 101
REAR AXLE - 10 1/2 AA (Continued)
Page 175 of 2895
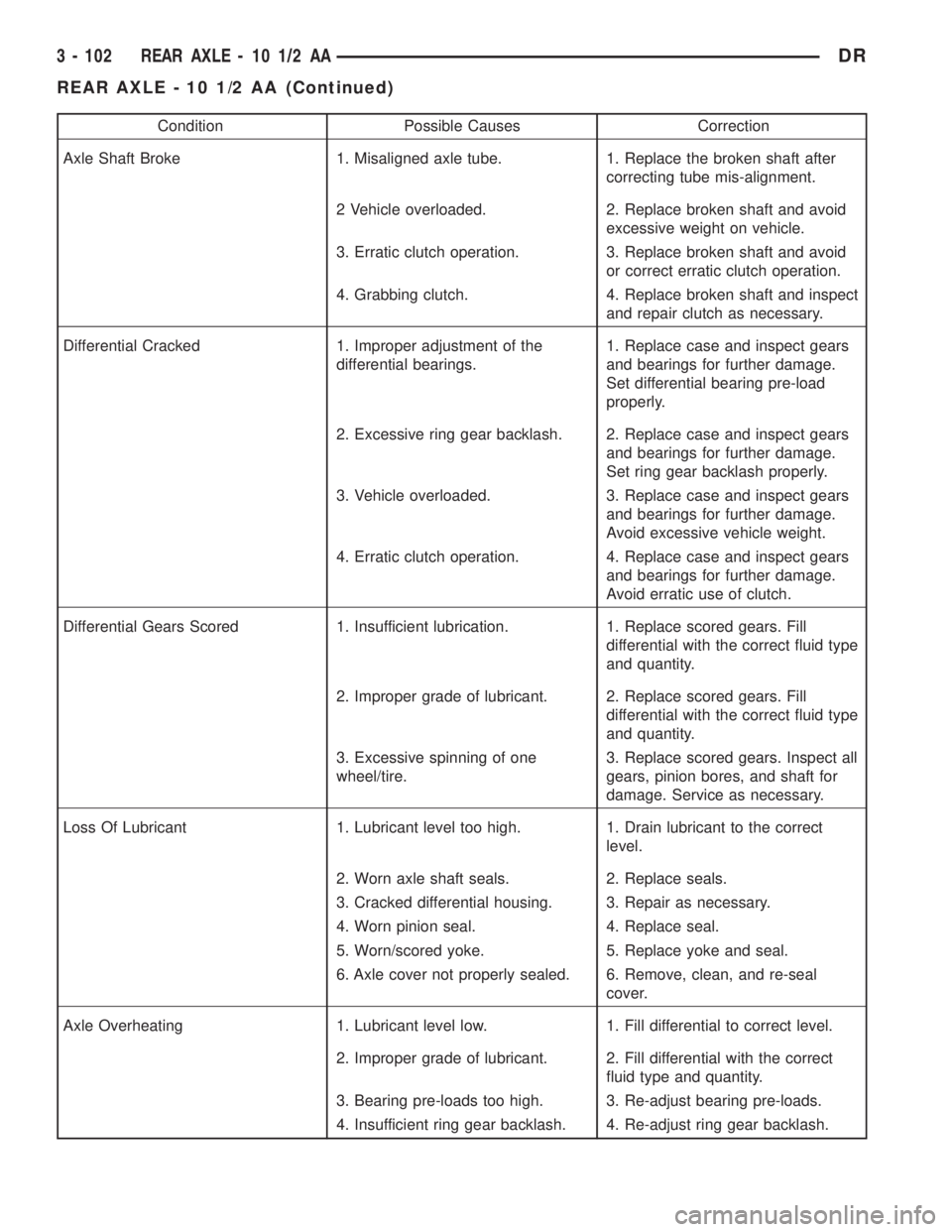
Condition Possible Causes Correction
Axle Shaft Broke 1. Misaligned axle tube. 1. Replace the broken shaft after
correcting tube mis-alignment.
2 Vehicle overloaded. 2. Replace broken shaft and avoid
excessive weight on vehicle.
3. Erratic clutch operation. 3. Replace broken shaft and avoid
or correct erratic clutch operation.
4. Grabbing clutch. 4. Replace broken shaft and inspect
and repair clutch as necessary.
Differential Cracked 1. Improper adjustment of the
differential bearings.1. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Set differential bearing pre-load
properly.
2. Excessive ring gear backlash. 2. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Set ring gear backlash properly.
3. Vehicle overloaded. 3. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Avoid excessive vehicle weight.
4. Erratic clutch operation. 4. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Avoid erratic use of clutch.
Differential Gears Scored 1. Insufficient lubrication. 1. Replace scored gears. Fill
differential with the correct fluid type
and quantity.
2. Improper grade of lubricant. 2. Replace scored gears. Fill
differential with the correct fluid type
and quantity.
3. Excessive spinning of one
wheel/tire.3. Replace scored gears. Inspect all
gears, pinion bores, and shaft for
damage. Service as necessary.
Loss Of Lubricant 1. Lubricant level too high. 1. Drain lubricant to the correct
level.
2. Worn axle shaft seals. 2. Replace seals.
3. Cracked differential housing. 3. Repair as necessary.
4. Worn pinion seal. 4. Replace seal.
5. Worn/scored yoke. 5. Replace yoke and seal.
6. Axle cover not properly sealed. 6. Remove, clean, and re-seal
cover.
Axle Overheating 1. Lubricant level low. 1. Fill differential to correct level.
2. Improper grade of lubricant. 2. Fill differential with the correct
fluid type and quantity.
3. Bearing pre-loads too high. 3. Re-adjust bearing pre-loads.
4. Insufficient ring gear backlash. 4. Re-adjust ring gear backlash.
3 - 102 REAR AXLE - 10 1/2 AADR
REAR AXLE - 10 1/2 AA (Continued)
Page 176 of 2895

Condition Possible Causes Correction
Gear Teeth Broke 1. Overloading. 1. Replace gears. Examine other
gears and bearings for possible
damage.
2. Erratic clutch operation. 2. Replace gears and examine the
remaining parts for damage. Avoid
erratic clutch operation.
3. Ice-spotted pavement. 3. Replace gears and examine
remaining parts for damage.
4. Improper adjustments. 4. Replace gears and examine
remaining parts for damage. Ensure
ring gear backlash is correct.
Axle Noise 1. Insufficient lubricant. 1. Fill differential with the correct
fluid type and quantity.
2. Improper ring gear and pinion
adjustment.2. Check ring gear and pinion
contact pattern. Adjust backlash or
pinion depth.
3. Unmatched ring gear and pinion. 3. Replace gears with a matched
ring gear and pinion.
4. Worn teeth on ring gear and/or
pinion.4. Replace ring gear and pinion.
5. Loose pinion bearings. 5. Adjust pinion bearing pre-load.
6. Loose differential bearings. 6. Adjust differential bearing
pre-load.
7. Mis-aligned or sprung ring gear. 7. Measure ring gear run-out.
Replace components as necessary.
8. Loose differential bearing cap
bolts.8. Inspect differential components
and replace as necessary. Ensure
that the bearing caps are torqued
tot he proper specification.
9. Housing not machined properly. 9. Replace housing.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Position a lifting device under the axle.
(3) Secure axle to device.
(4) Remove wheels and tires assemblies.
(5) Remove RWAL sensor from the differential
housing.
(6) Remove brake hose at the axle junction block
and axle vent hose.
(7) Disconnect parking brake cables and cable
brackets.
(8) Remove brake calipers and rotors.
(9) Mark propeller shaft and companion flange for
installation alignment reference.
(10) Remove propeller shaft.
(11) Remove shock absorbers from axle.
(12) Remove U-bolts from axle.
(13) Separate the axle from the vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Raise axle with lifting device and align to the
leaf spring centering bolts.
(2) Install axle U-bolts and tighten to 149 N´m
(110 ft. lbs.).
(3) Install shock absorbers to axle and tighten to
specification.
(4) Install the RWAL sensor to the differential
housing.
(5) Connect the parking brake cables and cable
brackets.
(6) Install brake calipers.
(7) Connect brake hose to the axle junction block
and axle vent hose.
(8) Align propeller shaft and pinion companion
flange reference marks and tighten companion flange
bolts to 115 N´m (85 ft. lbs.).
(9) Install the wheels and tires.
DRREAR AXLE - 10 1/2 AA 3 - 103
REAR AXLE - 10 1/2 AA (Continued)
Page 177 of 2895

(10) Fill differential to specifications.
(11) Remove lifting device from axle and lower the
vehicle.
ADJUSTMENTS
Ring and pinion gears are supplied as matched
sets only. Compensation for pinion depth variance is
achieved with a select shim. The shim is located
between the rear pinion bearing and the pinion gear
head.
PINION DEPTH MEASUREMENT AND ADJUSTMENT
Measurements are taken with pinion bearing cups
and pinion bearings installed in the housing. Take
measurements with Pinion Gauge Set and Dial Indi-
cator C-3339 (Fig. 1).
(1) Assemble Pinion Height Block 6739, Pinion
Block 8899 and rear pinion bearing onto Screw 6741
(Fig. 1).
(2) Insert assembled height gauge components,
rear bearing and screw into the housing through pin-
ion bearing cups (Fig. 2).
(3) Install front pinion bearing and install the
Cone-nut 6740 hand tight. Then check tool rotating
torque with an inch pound torque wrench. The rotat-ing torque should be 1.7-2.26 N´m (15-20 in. lbs.)
(Fig. 1).
(4) Place Arbor Disc 6732 on Arbor D-115-3 in posi-
tion in the housing side bearing cradles (Fig. 3).
(5) Install differential bearing caps on arbor discs
and snug the bearing cap bolts. Then cross tighten
cap bolts to 165 N´m (122 ft. lbs.).
NOTE: Arbor should rotate freely in the arbor discs.
(6) Assemble Dial Indicator C-3339 into Scooter
Block D-115-2 and secure set screw.
(7) Position Scooter Block/Dial Indicator flush on
the pinion height block. Hold scooter block and zero
the dial indicator.
Fig. 1 PINION GEAR DEPTH GAUGE TOOLS
1 - DIAL INDICATOR
2 - ARBOR
3 - PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
4 - CONE
5 - SCREW
6 - PINION BLOCK
7 - SCOOTER BLOCK
8 - ARBOR DISC
Fig. 2 PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
1 - PINION BLOCK
2 - PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
Fig. 3 GAUGE TOOLS IN HOUSING
1 - ARBOR DISC
2 - PINION BLOCK
3 - ARBOR
4 - PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
3 - 104 REAR AXLE - 10 1/2 AADR
REAR AXLE - 10 1/2 AA (Continued)
Page 178 of 2895

(8) Slowly slide the scooter block across the pinion
height block over to the arbor (Fig. 4). Move the
scooter block till dial indicator crests the arbor, then
record the highest reading.
(9) Select a shim equal to the dial indicator read-
ing.
(10) Install the select shim between the rear pin-
ion bearing and the pinion gear head.
DIFFERENTIAL CASE BEARING PRELOAD AND
GEAR BACKLASH
Backlash is adjusted by moving the adjusters in
and out or both. By moving the adjusters the case/
ring gear will move closer or further away from the
pinion. In most cases this adjustment can be used to
achieve the correct gear tooth pattern and set the
case bearing preload.
(1) Remove adjuster lock bolts and adjuster locks
(Fig. 5).
(2) Loosen the differential bearing caps.
(3) Slide differential case toward the pinion gear
until the gears make contact/zero backlash. If zero
backlash cannot be obtained, turn the pinion side
adjuster until zero backlash is obtained.
(4) Holding the differential case toward the pinion
gear, turn bearing adjusters with Spanner Wrench
8883 (Fig. 6) until they make contact with the differ-
ential bearings/cups.
(5) Back off the ring gear side adjuster 4 holes, to
obtain initial ring gear backlash.
(6) Install ring gear side adjuster lock and bolt. Do
not tighten adjuster lock bolt at this time.
(7) Tighten pinion gear side adjuster firmly
against the differential case bearing cup.
(8) Rotate the pinion several times to seat the def-
erential bearings.(9) Loosen pinion gear side adjuster until it is no
longer in contact with the bearing cup, then tighten
it until it makes contact.
(10) Tighten pinion gear side adjuster an addi-
tional:
²New Bearings:6 Adjuster Holes
²Original Bearings:4 Adjuster Holes
(11) Install pinion gear side adjuster lock and bolt.
Do not tighten adjuster lock bolt at this time.
Fig. 4 PINION GEAR DEPTH MEASUREMENT
1 - ARBOR
2 - SCOOTER BLOCK
3 - DIAL INDICATOR
Fig. 5 ADJUSTER LOCK BOLT
1 - DIFFERENTIAL CASE
2 - ADJUSTER LOCK
3 - ADJUSTER LOCK BOLT
4 - BEARING CAP BOLT
Fig. 6 ADJUSTER SPANNER WRENCH
1 - WRENCH
2 - DIFFERENTIAL
DRREAR AXLE - 10 1/2 AA 3 - 105
REAR AXLE - 10 1/2 AA (Continued)
Page 201 of 2895

BEARING NOISE
The axle shaft, differential and pinion bearings can
all produce noise when worn or damaged. Bearing
noise can be either a whining, or a growling sound.
Pinion bearings have a constant-pitch noise. This
noise changes only with vehicle speed. Pinion bearing
noise will be higher pitched because it rotates at a
faster rate. Drive the vehicle and load the differen-
tial. If bearing noise occurs, the rear pinion bearing
is the source of the noise. If the bearing noise is
heard during a coast, the front pinion bearing is the
source.
Worn or damaged differential bearings usually pro-
duce a low pitch noise. Differential bearing noise is
similar to pinion bearing noise. The pitch of differen-
tial bearing noise is also constant and varies only
with vehicle speed.
Axle shaft bearings produce noise and vibration
when worn or damaged. The noise generally changes
when the bearings are loaded. Road test the vehicle.
Turn the vehicle sharply to the left and to the right.
This will load the bearings and change the noise
level. Where axle bearing damage is slight, the noise
is usually not noticeable at speeds above 30 mph.
LOW SPEED KNOCK
Low speed knock is generally caused by a worn
U-joint or by worn side±gear thrust washers. A worn
pinion shaft bore will also cause low speed knock.
VIBRATION
Vibration at the rear of the vehicle is usually
caused by a:
²Damaged drive shaft.
²Missing drive shaft balance weight(s).²Worn or out-of-balance wheels.
²Loose wheel lug nuts.
²Worn U-joint(s).
²Loose/broken springs.
²Damaged axle shaft bearing(s).
²Loose pinion gear nut.
²Excessive pinion yoke run out.
²Bent axle shaft(s).
Check for loose or damaged front-end components
or engine/transmission mounts. These components
can contribute to what appears to be a rearend vibra-
tion. Do not overlook engine accessories, brackets
and drive belts.
NOTE: All driveline components should be exam-
ined before starting any repair.
DRIVELINE SNAP
A snap or clunk noise when the vehicle is shifted
into gear (or the clutch engaged), can be caused by:
²High engine idle speed.
²Transmission shift operation.
²Loose engine/transmission/transfer case mounts.
²Worn U-joints.
²Loose spring mounts.
²Loose pinion gear nut and yoke.
²Excessive ring gear backlash.
²Excessive side gear to case clearance.
The source of a snap or a clunk noise can be deter-
mined with the assistance of a helper. Raise the vehi-
cle on a hoist with the wheels free to rotate. Instruct
the helper to shift the transmission into gear. Listen
for the noise, a mechanics stethoscope is helpful in
isolating the source of a noise.
DIAGNOSTIC CHART
Condition Possible Causes Correction
Wheel Noise 1. Wheel loose. 1. Tighten loose nuts.
2. Faulty, brinelled wheel bearing. 2. Replace bearing.
Axle Shaft Noise 1. Misaligned axle tube. 1. Inspect axle tube alignment.
Correct as necessary.
2. Bent or sprung axle shaft. 2. Inspect and correct as necessary.
3 - 128 REAR AXLE - 11 1/2 AADR
REAR AXLE - 11 1/2 AA (Continued)
Page 202 of 2895
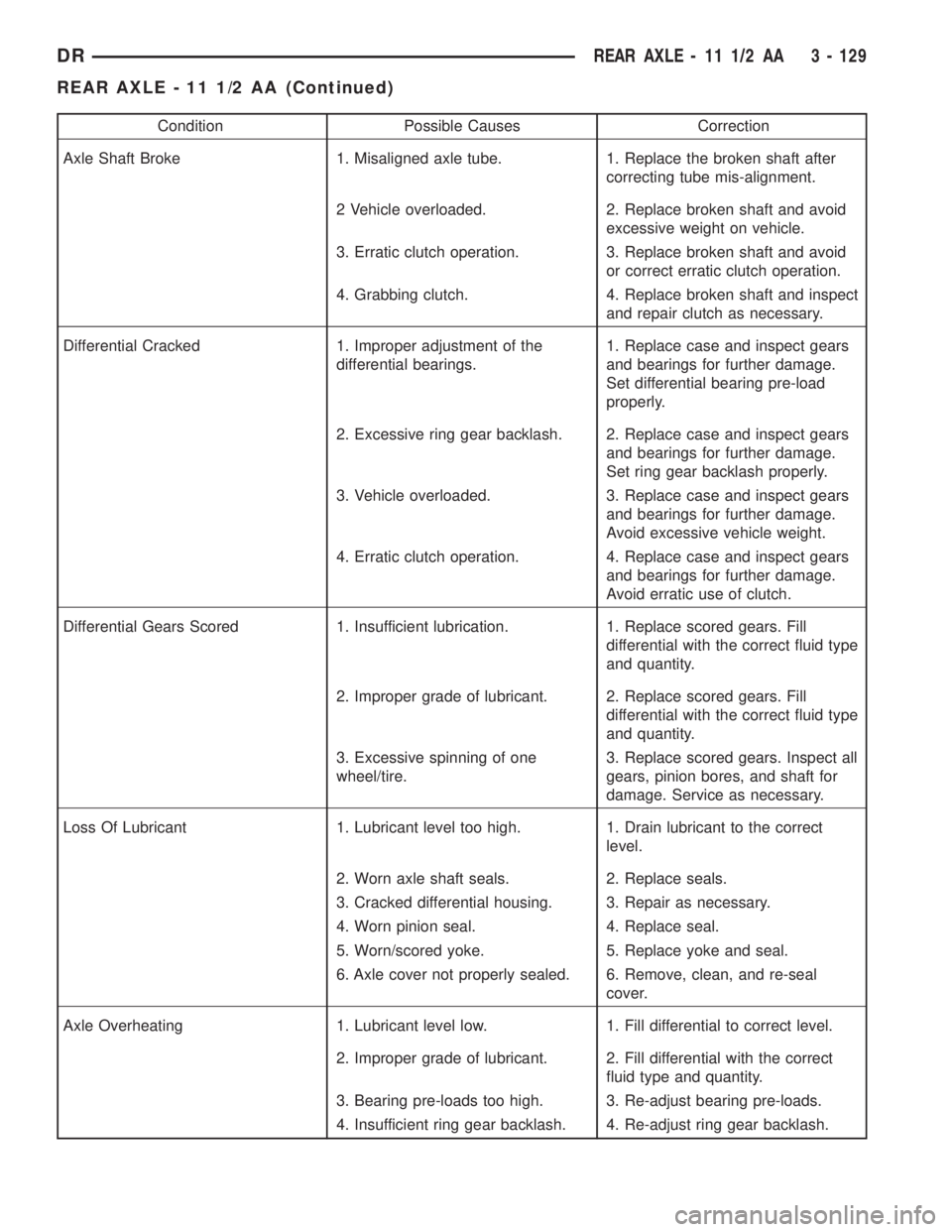
Condition Possible Causes Correction
Axle Shaft Broke 1. Misaligned axle tube. 1. Replace the broken shaft after
correcting tube mis-alignment.
2 Vehicle overloaded. 2. Replace broken shaft and avoid
excessive weight on vehicle.
3. Erratic clutch operation. 3. Replace broken shaft and avoid
or correct erratic clutch operation.
4. Grabbing clutch. 4. Replace broken shaft and inspect
and repair clutch as necessary.
Differential Cracked 1. Improper adjustment of the
differential bearings.1. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Set differential bearing pre-load
properly.
2. Excessive ring gear backlash. 2. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Set ring gear backlash properly.
3. Vehicle overloaded. 3. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Avoid excessive vehicle weight.
4. Erratic clutch operation. 4. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Avoid erratic use of clutch.
Differential Gears Scored 1. Insufficient lubrication. 1. Replace scored gears. Fill
differential with the correct fluid type
and quantity.
2. Improper grade of lubricant. 2. Replace scored gears. Fill
differential with the correct fluid type
and quantity.
3. Excessive spinning of one
wheel/tire.3. Replace scored gears. Inspect all
gears, pinion bores, and shaft for
damage. Service as necessary.
Loss Of Lubricant 1. Lubricant level too high. 1. Drain lubricant to the correct
level.
2. Worn axle shaft seals. 2. Replace seals.
3. Cracked differential housing. 3. Repair as necessary.
4. Worn pinion seal. 4. Replace seal.
5. Worn/scored yoke. 5. Replace yoke and seal.
6. Axle cover not properly sealed. 6. Remove, clean, and re-seal
cover.
Axle Overheating 1. Lubricant level low. 1. Fill differential to correct level.
2. Improper grade of lubricant. 2. Fill differential with the correct
fluid type and quantity.
3. Bearing pre-loads too high. 3. Re-adjust bearing pre-loads.
4. Insufficient ring gear backlash. 4. Re-adjust ring gear backlash.
DRREAR AXLE - 11 1/2 AA 3 - 129
REAR AXLE - 11 1/2 AA (Continued)
Page 203 of 2895

Condition Possible Causes Correction
Gear Teeth Broke 1. Overloading. 1. Replace gears. Examine other
gears and bearings for possible
damage.
2. Erratic clutch operation. 2. Replace gears and examine the
remaining parts for damage. Avoid
erratic clutch operation.
3. Ice-spotted pavement. 3. Replace gears and examine
remaining parts for damage.
4. Improper adjustments. 4. Replace gears and examine
remaining parts for damage. Ensure
ring gear backlash is correct.
Axle Noise 1. Insufficient lubricant. 1. Fill differential with the correct
fluid type and quantity.
2. Improper ring gear and pinion
adjustment.2. Check ring gear and pinion
contact pattern. Adjust backlash or
pinion depth.
3. Unmatched ring gear and pinion. 3. Replace gears with a matched
ring gear and pinion.
4. Worn teeth on ring gear and/or
pinion.4. Replace ring gear and pinion.
5. Loose pinion bearings. 5. Adjust pinion bearing pre-load.
6. Loose differential bearings. 6. Adjust differential bearing
pre-load.
7. Mis-aligned or sprung ring gear. 7. Measure ring gear run-out.
Replace components as necessary.
8. Loose differential bearing cap
bolts.8. Inspect differential components
and replace as necessary. Ensure
that the bearing caps are torqued
tot he proper specification.
9. Housing not machined properly. 9. Replace housing.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Position a lifting device under the axle.
(3) Secure axle to device.
(4) Remove wheels and tires assemblies.
(5) Remove RWAL sensor from the differential
housing.
(6) Remove brake hose at the axle junction block
and axle vent hose.
(7) Disconnect parking brake cables and cable
brackets.
(8) Remove brake calipers.
(9) Mark propeller shaft and companion flange for
installation alignment reference.
(10) Remove propeller shaft.
(11) Remove shock absorbers from axle.
(12) Remove U-bolets from axle.
(13) Separate the axle from the vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Raise axle with lifting device and align to the
leaf spring centering bolts.
(2) Install axle U-bolts and tighten to 149 N´m
(110 ft. lbs.).
(3) Install shock absorbers to axle and tighten to
specification.
(4) Install the RWAL sensor to the differential
housing.
(5) Connect the parking brake cables and cable
brackets.
(6) Connect brake hose to the axle junction block
and axle vent hose.
(7) Align propeller shaft and pinion companion
flange reference marks and tighten companion flange
bolts to 115 N´m (85 ft. lbs.).
(8) Install the wheels and tires.
(9) Fill differential to specifications.
3 - 130 REAR AXLE - 11 1/2 AADR
REAR AXLE - 11 1/2 AA (Continued)