seats DODGE RAM SRT-10 2006 Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2006, Model line: RAM SRT-10, Model: DODGE RAM SRT-10 2006Pages: 5267, PDF Size: 68.7 MB
Page 1660 of 5267

INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - LEFT CYLINDER HEAD
NOTE: The cylinder head bolts are tightened using
a torque plus angle procedure. The bolts must be
examined BEFORE reuse. If the threads are
necked down (2) the bolts should be replaced.
Necking can be checked by holding a straight edge
against the threads. If all the threads do not contact
the scale, the bolt should be replaced.
CAUTION: When cleaning cylinder head and cylin-
der block surfaces, DO NOT use a metal scraper
because the surfaces could be cut or ground. Use
only a wooden or plastic scraper (1).
1. Clean the cylinder head and cylinder block mating
surfaces.
2. Position the new cylinder head gasket on the locat-
ing dowels.
CAUTION: When installing cylinder head, use care
not damage the tensioner arm or the guide arm.
3. Position the cylinder head onto the cylinder block.
Make sure the cylinder head seats fully over the
locating dowels.
NOTE: The four smaller cylinder head mounting
bolts require sealant to be added to them before
installing. Failure to do so may cause leaks.
Page 1663 of 5267

CAUTION: When cleaning cylinder head and cylin-
der block surfaces, DO NOT use a metal scraper
because the surfaces could be cut or ground. Use
only a wooden or plastic scraper (1).
1. Clean the cylinder head and cylinder block mating
surfaces.
2. Position the new cylinder head gasket on the locat-
ing dowels.
CAUTION: When installing cylinder head, use care
not damage the tensioner arm or the guide arm.
3. Position the cylinder head onto the cylinder block.
Make sure the cylinder head seats fully over the
locating dowels.
NOTE: The four smaller cylinder head mounting
bolts require sealant to be added to them before
installing. Failure to do so may cause leaks.
4. Lubricate the cylinder head bolt threads with clean
engine oil and install the ten M10 bolts.
5. Coat the four M8 cylinder head bolts withMopar
Lock and Seal Adhesivethen install the bolts.
NOTE: The cylinder head bolts are tightened using an angle torque procedure, however, the bolts are not a
torque-to-yield design.
6. Tighten the bolts in sequence using the following steps and torque values:
Step 1: Tighten bolts 1–10, 20 Nꞏm (15 ft. lbs.).
Step 2: Tighten bolts 1–10, 47 Nꞏm (35 ft. lbs.). Tighten bolts 11–14, 25 Nꞏm(18 ft. lbs.).
Step 3: Tighten bolts 1–10, 90 degrees. Tighten bolts 11–14, 30 Nꞏm (22 ft. lbs.).
Page 1680 of 5267

VALVES & SEATS - INTAKE/EXHAUST
DESCRIPTION
The valves are made of heat resistant steel and have chrome plated stems to prevent scuffing. Each valve is actu-
ated by a roller rocker arm which pivots on a stationary lash adjuster. All valves use three bead lock keepers to
retain the springs and promote valve rotation.
REMOVAL
NOTE: The cylinder heads must be removed in
order to perform this procedure.
1. Remove rocker arms and lash adjusters (Refer to 9
- ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/ROCKER ARM /
ADJUSTER ASSY - REMOVAL).
2. Remove the camshaft bearing caps and the cam-
shaft.
NOTE: All valve springs and valves are removed in
the same manner; this procedure only covers one
valve and valve spring.
3. Using Special Tool C-3422–B or C-3422–C Valve
Spring Compressor and Special tool 8519 Adapter,
compress the valve spring.
NOTE: It may be necessary to tap the top of the
valve spring to loosen the spring retainers locks
enough to be removed.
4. Remove the two spring retainer lock halves.
NOTE: the valve spring is under tension use care when releasing the valve spring compressor.
5. Remove the valve spring compressor.
6. Remove the spring retainer, and the spring.
NOTE: Check for sharp edges on the keeper grooves. Remove any burrs from thevalvestembeforeremov-
ing the valve from the cylinder head.
7. Remove the valve from the cylinder head.
NOTE: The valve stem seals are common between intake and exhaust.
8. Remove the valve stem seal. Mark the valve for proper installation.
Page 1703 of 5267

INSTALLATION
1. Lubricate the crankshaft flange with engine oil.
2. Position the magnetic seal guide Special Tool
8349-2 onto the crankshaft rear face. Then position
the crankshaft rear oil seal (1) onto the guide (2).
3. Using Special Tools 8349 Crankshaft Rear Oil Seal
Installer (2) and C-4171 Driver Handle (3), with a
hammer, tap the seal (1) into place. Continue to
tap on the driver handle until the seal installer
seats against the cylinder block crankshaft bore.
4. Install the flexplate.
5. Install the transmission.
Page 1756 of 5267

page page
ENGINE - 5.7L - SERVICE INFORMATION
DESCRIPTION ............................. 2449
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE
DIAGNOSIS - INTRODUCTION............. 2449
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE
DIAGNOSIS - PERFORMANCE............. 2449
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE
DIAGNOSIS - MECHANICAL............... 2451
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMPRESSION PRESSURE............... 2451
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE...... 2452
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE
DIAGNOSIS - LUBRICATION............... 2453
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE
DIAGNOSIS - MECHANICAL............... 2453
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REPAIR
DAMAGED OR WORN THREADS.......... 2456
STANDARD PROCEDURE—HYDROSTATIC
LOCK.................................... 2456
REMOVAL ................................. 2457
INSTALLATION ............................. 2462
SPECIFICATIONS
5.7L ENGINE ............................. 2467
TORQUE ................................. 2472
SPECIAL TOOLS
5.7L ENGINE ............................. 2475
ELEMENT - AIR CLEANER
REMOVAL ................................. 2478
INSTALLATION ............................. 2479
CYLINDER HEAD
OPERATION—CYLINDER HEAD ............. 2481
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING—CYLINDER HEAD
GASKET FAILURE........................ 2481
REMOVAL ................................. 2482
CLEANING ................................. 2484
INSPECTION ............................... 2484
INSTALLATION ............................. 2485
COVER - CYLINDER HEAD
REMOVAL ................................. 2490
INSTALLATION ............................. 2493
VALVES & SEATS - INTAKE/EXHAUST
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - VALVE GUIDES ........... 2496
DESCRIPTION ........................... 2496
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFACING ....... 2496
REMOVAL ................................. 2497
INSTALLATION ............................. 2497ROCKER ARM
REMOVAL ................................. 2498
INSTALLATION ............................. 2500
SEALS - VALVE GUIDE
DESCRIPTION ............................. 2503
SPRINGS - VALVE
REMOVAL ................................. 2504
INSTALLATION ............................. 2510
ENGINE BLOCK
CLEANING ................................. 2515
INSPECTION............................... 2515
CAMSHAFT
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - CAMSHAFT CORE HOLE PLUG . 2516
REMOVAL - CAMSHAFT ................... 2516
INSPECTION............................... 2520
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - CAMSHAFT CORE HOLE
PLUG.................................... 2520
INSTALLATION - CAMSHAFT .............. 2521
CRANKSHAFT
REMOVAL ................................. 2527
INSTALLATION ............................. 2531
BEARINGS - CRANKSHAFT MAIN
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CRANKSHAFT
MAIN BEARING - FITTING ................. 2536
INSPECTION............................... 2536
SEAL - CRANKSHAFT OIL - FRONT
REMOVAL ................................. 2537
INSTALLATION ............................. 2538
SEAL - CRANKSHAFT OIL - REAR
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REAR SEAL
AREA LEAKS . ............................ 2539
REMOVAL ................................. 2539
INSTALLATION ............................. 2540
RETAINER - CRANK REAR OIL - SEAL
REMOVAL ................................. 2541
INSTALLATION ............................. 2541
FLEX PLATE
REMOVAL ................................. 2542
INSTALLATION ............................. 2542
TAPPETS - HYDRAULIC ROLLER
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC
TAPPETS ................................ 2543
REMOVAL ................................. 2543
INSTALLATION ............................. 2544
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD
DESCRIPTION ............................. 2546
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PISTON FITTING . 2546
REMOVAL ................................. 2547
CLEANING ................................. 2548
Page 1760 of 5267
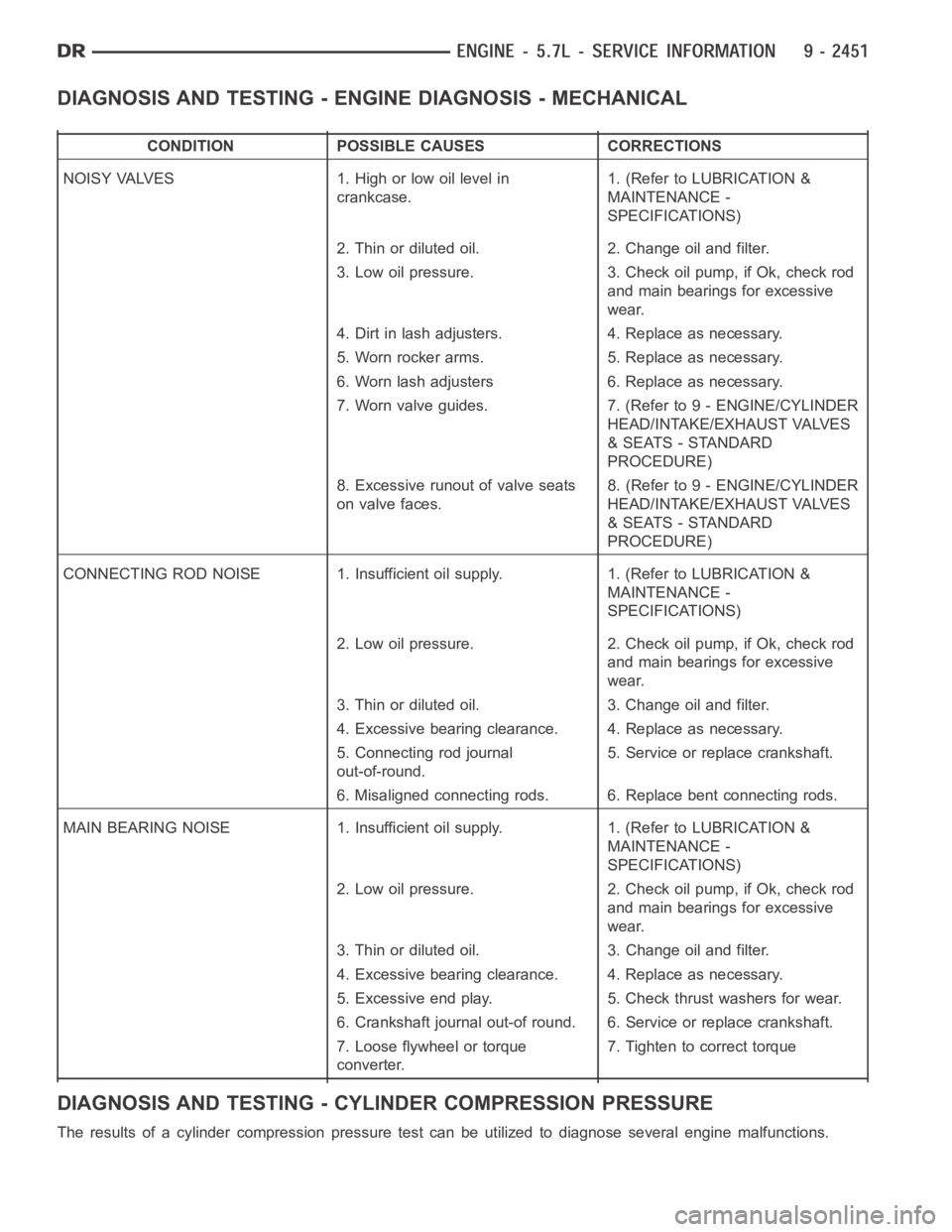
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE DIAGNOSIS - MECHANICAL
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTIONS
NOISY VALVES 1. High or low oil level in
crankcase.1. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE -
SPECIFICATIONS)
2. Thin or diluted oil. 2. Change oil and filter.
3. Low oil pressure. 3. Check oil pump, if Ok, check rod
and main bearings for excessive
wear.
4. Dirt in lash adjusters. 4. Replace as necessary.
5. Worn rocker arms. 5. Replace as necessary.
6. Worn lash adjusters 6. Replace as necessary.
7. Worn valve guides. 7. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER
HEAD/INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES
& SEATS - STANDARD
PROCEDURE)
8. Excessive runout of valve seats
on valve faces.8. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER
HEAD/INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES
& SEATS - STANDARD
PROCEDURE)
CONNECTING ROD NOISE 1. Insufficient oil supply. 1. (Refer to LUBRICATION&
MAINTENANCE -
SPECIFICATIONS)
2. Low oil pressure. 2. Check oil pump, if Ok, check rod
and main bearings for excessive
wear.
3. Thin or diluted oil. 3. Change oil and filter.
4. Excessive bearing clearance. 4. Replace as necessary.
5. Connecting rod journal
out-of-round.5. Service or replace crankshaft.
6. Misaligned connecting rods. 6. Replace bent connecting rods.
MAIN BEARING NOISE 1. Insufficient oil supply. 1. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE -
SPECIFICATIONS)
2. Low oil pressure. 2. Check oil pump, if Ok, check rod
and main bearings for excessive
wear.
3. Thin or diluted oil. 3. Change oil and filter.
4. Excessive bearing clearance. 4. Replace as necessary.
5. Excessive end play. 5. Check thrust washers for wear.
6. Crankshaft journal out-of round. 6. Service or replace crankshaft.
7. Loose flywheel or torque
converter.7. Tighten to correct torque
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER COMPRESSION PRESSURE
The results of a cylinder compressionpressure test can be utilized to diagnose several engine malfunctions.
Page 1763 of 5267
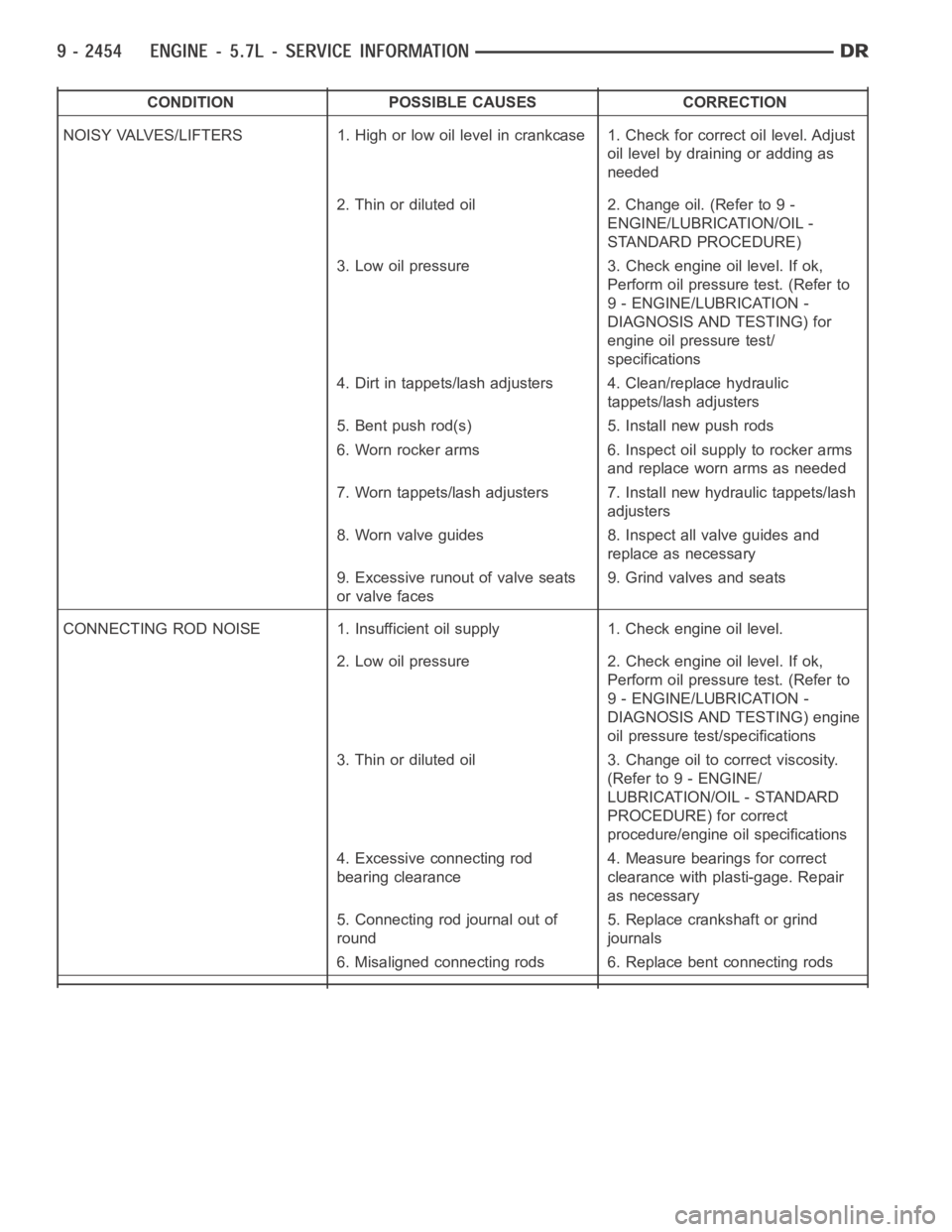
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
NOISY VALVES/LIFTERS 1. High or low oil level in crankcase 1. Check for correct oil level. Adjust
oil level by draining or adding as
needed
2. Thin or diluted oil 2. Change oil. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL -
STANDARD PROCEDURE)
3. Low oil pressure 3. Check engine oil level. If ok,
Perform oil pressure test. (Refer to
9 - ENGINE/LUBRICATION -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING) for
engine oil pressure test/
specifications
4. Dirt in tappets/lash adjusters 4. Clean/replace hydraulic
tappets/lash adjusters
5. Bent push rod(s) 5. Install new push rods
6. Worn rocker arms 6. Inspect oil supply to rocker arms
and replace worn arms as needed
7. Worn tappets/lash adjusters 7. Install new hydraulic tappets/lash
adjusters
8. Worn valve guides 8. Inspect all valve guides and
replace as necessary
9. Excessive runout of valve seats
or valve faces9. Grind valves and seats
CONNECTING ROD NOISE 1. Insufficient oil supply 1. Check engine oil level.
2. Low oil pressure 2. Check engine oil level. If ok,
Perform oil pressure test. (Refer to
9 - ENGINE/LUBRICATION -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING) engine
oil pressure test/specifications
3. Thin or diluted oil 3. Change oil to correct viscosity.
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
LUBRICATION/OIL - STANDARD
PROCEDURE) for correct
procedure/engine oil specifications
4. Excessive connecting rod
bearing clearance4. Measure bearings for correct
clearance with plasti-gage. Repair
as necessary
5. Connecting rod journal out of
round5. Replace crankshaft or grind
journals
6. Misaligned connecting rods 6. Replace bent connecting rods
Page 1793 of 5267

13. Remove the head bolts from each cylinder head,
using the sequence provided, and remove cylin-
der heads. Discard the cylinder head gasket.
CLEANING
Clean all surfaces of cylinder block and cylinder heads.
Clean cylinder block front and rear gasket surfaces using a suitable solvent.
INSPECTION
1. Inspect the cylinder head for out-of-flatness, using a straightedge and a feeler gauge. If tolerances exceed
0.0508 mm (0.002 in.) replace the cylinder head.
2. Inspect the valve seats for damage. Service the valve seats as necessary.
3. Inspect the valve guides for wear, cracks or looseness. If either condition exist, replace the cylinder head.
4. Inspect pushrods. Replace worn or bent pushrods.
Page 1805 of 5267

VALVES & SEATS - INTAKE/EXHAUST
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - VALVE GUIDES
The valve guides are made of powdered metal and are pressed into the cylinder head. The guides are not replace-
able or serviceable, and valve guide reaming is not recommended. If the guides are worn beyond acceptable limits,
replace the cylinder heads.
DESCRIPTION
Both the intake and exhaust valves are made of steel. The intake valve is 50.93 mm (2.00 inches) in diameter and
the exhaust valve is 39.53 mm (1.55 inches) in diameter. All valves use three bead lock keepers to retain the
springs and promote valve rotation.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFACING
NOTE: Valve seats that are worn or burned can be reworked, provided that correct angle and seat width are
maintained. Otherwise the cylinder head must be replaced.
NOTE: When refacing valves and valve seats, it is important that the correct size valve guide pilot be used
for reseating stones. A true and complete surface must be obtained.
1. Using a suitable dial indicator measure the center of the valve seat Total run out must not exceed 0.051 mm
(0.002 in).
2. Apply a small amount of Prussian blue to the valve seat, insert the valve into the cylinder head, while applying
light pressure on the valve rotate the valve. Remove the valve and examine the valve face. If the blue is trans-
ferred below the top edge of the valve face, lower the valve seat using a 15 degree stone. If the blue is trans-
ferred to the bottom edge of the valve face, raise the valve seat using a 65 degree stone.
3. When the seat is properly positioned the width of the intake seat must be 1.018 - 1.62 mm (0.0464 - 0.0637 in.)
and the exhaust seat must be 1.48 - 1.92 mm (0.058 - 0.075 in.).
4. Check the valve spring installed height after refacing the valve and seat.Theinstalledheightforbothintakeand
exhaust valve springs must not exceed 46.0 mm (1.81 in.).
VALVE FACE AND VALVE SEAT ANGLE CHART
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
SEAT WIDTH
INTAKE 1.018 - 1.62 mm
(0.0464 - 0.0637 in.)
EXHAUST 1.48 - 1.92 mm
(0.058 - 0.075 in.)
FA C E A N G L E
(INT. AND EXT.) 45° - 45
1⁄2°
SEAT ANGLE
(INT. AND EXT.) 44
1⁄2° - 45°
Page 1806 of 5267

5. The valve seat must maintain an angle of 44.5 –
45.0 degrees angle.
6. Thevalvefacemustmaintainafaceangleof45.0
– 45.5 degrees angle.
REMOVAL
1. Remove the cylinder head (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - REMOVAL).
2. Compress valve springs using Valve Spring Compressor Tool special tool# C-3422and adapter 8464.
3. Remove valve retaining locks, valve spring retainers, valve stem sealsand valve springs.
4. Before removing valves, remove any burrs from valve stem lock grooves toprevent damage to the valve guides.
Identify valves to ensure installation in original location.
INSTALLATION
1. Clean valves thoroughly. Discard burned, warped and cracked valves.
2. Remove carbon and varnish deposits from inside of valve guides with a reliable guide cleaner.
3. Measure valve stems for wear. If wear exceeds 0.051 mm (0.002 inch), replace the valve.
4. Coat valve stems with lubrication oil and insert them in cylinder head.
5. If valves or seats are reground, check valve stem height. If valve is too long, replace cylinder head.
6. Install new seals on all valve guides. Install valve springs and valve retainers.
7. Compress valve springs with Valve Spring Compressor Tool special tool #C- 3422and adapter 8464, install locks
and release tool. If valves and/or seats are ground, measure the installedheight of springs. Make sure the mea-
surement is taken from bottom of spring seat in cylinder head to the bottom surface of spring retainer.
8. Install cylinder head (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - INSTALLATION).