oil viscosity DODGE TRUCK 1993 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1993, Model line: TRUCK, Model: DODGE TRUCK 1993Pages: 1502, PDF Size: 80.97 MB
Page 22 of 1502

•
LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE
0 - 3
CAUTION: UNLEADED FUEL ONLY must
be
used
in
vehicles equipped
with
a
catalyst emission
control
system.
All
vehicles have reminders
printed
on the
instrument
panel below
the
fuel
gauge
and on the
fuel
filler
door.
The
vehicles also have
fuel
filler
tubes
that
are
specially designed
to
accept only
the
small-diameter nozzles.
It is
illegal
to
bypass
the
design
of an
unleaded
fuel
filler
tube.
DIESEL ENGINES All
Ram
Truck
and Ram
Cab/Chassis Diesel
en
gines normally
can use
number
2D
Diesel fuel
for
most year-round operations.
A
fuel conforming
to
ASTM Specification D-975
is
recommended.
For ex
treme cold-weather, number
ID
Diesel fuel
is
recom mended.
CLASSIFICATION
OF
LUBRICANTS
Lubricating fluids
and
chassis lubricants
are
clas
sified according
to
standards recommended
by the:
• Society
of
Automotive Engineers
(SAE)
• American Petroleum Institute
(API)
• National Lubricating Grease Institute (NLGI)
ENGINE
OIL
SAE
VISCOSITY
GRADE
An
SAE
viscosity grade
is
used
to
specify
the
vis
cosity
of
engine
oil. SAE 30
specifies
a
single viscos
ity engine
oil.
Engine oils also have multiple viscosities. These
are specified with
a
dual
SAE
viscosity grade which
indicates
the
cold-to-hot temperature viscosity range (Fig.
3).
API
SERVICE
GRADE
The
API
Service Grade specifies
the
type
of
perfor
mance
the
engine
oil is
intended
to
provide.
The API
Service Grade specifications also apply
to
energy con
serving engine oils
(Fig. 3).
For maximum gasoline engine protection,
use API
Service Grade
SG,
SG/CD
or
SG/CE engine
oil.
For maximum Diesel engine protection,
use
API Service
CE or
SG/CE engine
oil.
GEAR LUBRICANTS A dual grade
is
also used
to
specify
the
viscosity
of
multi-purpose gear lubricants.
The
API
grade designation identifies gear lubri
cants
in
terms
of
recommended usage.
OIL
QUALITY
SAE
VISCOSITY
GRADE
FUEL
ECONOMY
NOTATION
J91004
Fig.
3 SAE Oil
Viscosity Grade
& API
Service
Grade
CHASSIS COMPONENT
AND
WHEEL BEARING
LUBRICANTS The chassis
and
wheel bearing lubricants
are
iden
tified
by the
NLGI Certification Symbol.
The
symbol
contains
a
coded designation. This identifies
the us
age
and
quality
of the
lubricant.
The letter
G
within
the
symbol designates wheel
bearing lubricant.
The
letter
L
designates chassis
lu
bricant. When
the
letters
are
combined,
the
lubricant can
be
used
for
dual applications.
Use
only lubricants
that display
the
NLGI Certification Symbol.
NATIONAL LUBRICATING
GREASE
INSTITUTE
NLGI
AUTOMOTIVE
WHEEL BEARING
&
CHASSIS LUBRICANT
GC-LB
-CERTIFICATION
SYMBOL
—
USAGE
AND
QUALITY
DESIGNATION
J920W7
Fig.
4
NLGI
Lubricant Container
Certification/
Identification
Symbol
LUBRICATION
AND
REPLACEMENT
PARTS
RECOMMENDATION
Ram Trucks
are
engineered
to
provide many years
of dependable operation. However, lubrication service
and maintenance
are
required
for
each vehicle. When
necessary, MOPAR®brand lubricants
and
genuine
re
placement parts
are
recommended.
Page 33 of 1502

0 - 14
LUBRICATION
AND
MAINTENANCE
•
ENGINE
MAINTENANCE
INDEX
page
Air
Injection
Systems/Air Pump
. 17
Air-Conditioner
Compressor
21
Battery
19
Cooling System
15
Crankcase
Ventilation
System
17
Diesel Engine
Air Filter
Canister
17
Drive Belts
20
Engine
Air
Cleaner
Filter
Element
16
Engine Break-In
14
Engine
Oil 14
Engine
Oil
Change
and Filter
Replacement
15
Exhaust Gas
Recirculation
(EGR) System
...... 19
page
Exhaust
Manifold
Heat
Control
Valve
. 17
Exhaust System
, 21
Fuel System
18
Hoses
and
Fittings
16
Ignition
Cables,
Distributor
Cap and
Rotor
...... 19
Ignition
Timing
. 19
Oxygen
(02)
Sensor
19
Rubber/Plastic Components
20
Spark Plugs
. 19
Throttle
Control
Linkage
18
Vacuum Operated, Emission
Control
Components
19
ENGINE BREAK-IN
After first starting a new engine, allow it to idle
for 15 seconds before shifting into a drive gear. Also:
• Drive the vehicle at varying speeds less than 88
km/h (55 mph) for the first 480 km (300 miles).
• Avoid fast acceleration and sudden stops.
• Do not drive at full-throttle for extended periods of
time
• Do not drive at constant speeds
• Do not idle the engine excessively A special break-in engine oil is not required. The
original engine oil installed is a high quality lubri
cant. New engines tend to consume more fuel and oil un
til after the break-in period has ended.
ENGINE
OIL SPECIFICATIONS
API SERWICE
GRADE
Use an engine oil that conforms to API Service
Grade S5 SG/CD or SG/CE. MOPAR®provides engine
oils that conform to all of these service grades.
SULFATED ASH—DIESEL ENGINES
Oils that contain an excessive amount of sulfated
ash can cause deposits to develop on Diesel engine
valves. These deposits can result in valve wear.
SAE
WISC0SITY
An SAE viscosity grade is used to specify the vis
cosity of engine oil. SAE 30 specifies a single viscos
ity engine oil.
Engine oils also have multiple viscosities. 10W-30
<
5W-30
1
1 1
F
-20 0 10 20 32 60 80 100
C
-29 -18 -12 -7 0 16 27 38
ANTICIPATED
TEMPERATURE RANGE BEFORE
NEXT
OIL
CHANGE
J9000-39
Fig.
1 Temperature/Engine Oil Viscosity—Gasoline
Engines
-12°C
-18°C 10°F
0°F- 15W-40
-23°c(^-10eF
I
10W-30
WITH
WITHOUT
BLOCK HEATER
BLOCK
SYNTHETIC
OIL
HEATER
10W-30 5W-30
J9100-29
Fig.
2 Temperature/Engine Oil Viscosity—Diesel
Engines
ENERGY
G0NSERWING
OIL
An Energy Conserving type oil is recommended for
gasoline engines. They are designated as either EN
ERGY CONSERVING or ENERGY CONSERVING
II.
OIL
LEVEL
INDICATOR (DIPSTICK)
GASOLINE ENGINES
The engine oil indicator is located at the right
front of the engine.
Page 37 of 1502

0-18
LUBRICATION
AND
MAINTENANCE
• MAINTENANCE SCHEDULE
A crankcase ventilation system must be clean to
provide good operation and durability. Periodic main
tenance is necessary. Replace the PCV valve. Re
move residual combustion deposits from the hoses and throttle body/intake manifold passages.
The PCV valve should be replaced and the system
should be serviced at the interval specified in main
tenance schedule. If a vehicle is routinely used for short trips, the crankcase ventilation system could
possibly require more maintenance.
CRANKCASE AIR INLET FILTER
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULE Replace or clean, the air inlet filter at the interval
specified in maintenance schedule.
More frequent PCV system maintenance could be
required for:
• Vehicles routinely used for short trips
• Vehicles routinely involved in stop and go traffic
operation
• Vehicles routinely involved in extended periods of
engine idle
MAINTENANCE Clean and lubricate the crankcase air inlet filter
according to the following procedure. (1) Disconnect the fresh air hose from the port on
the crankcase air inlet filter housing (Fig. 8).
(2) Remove the air filter housing from the cylinder
head cover (Fig. 8). Clean the filter in kerosene or a similar solvent.
(3) Lubricate the filter by inverting the housing
and filling it with SAE 30 viscosity engine oil.
(4) Insert the air filter housing nipple in the cylin
der head cover grommet. Connect the fresh air hose
to the upper port (Fig. 8).
J9000-52
Fig.
8
Crankcase
Air Inlet
Filter
THROTTLE CONTROL LINKAGE
Transmission linkage pivot pin areas (Fig. 9),
should be serviced. The areas lubricated every second
oil change with a multi-purpose lubricant (NLGI GC-
LB).
PIVOT
AREAS
Fig.
9
Transmission
Linkage
Pivot Areas
FUEL
SYSTEM
INSPECTION The fuel system filler cap, nozzle, tubes, hoses, and
connections should be inspected periodically.
FUEL FILTER The fuel filter requires service only when a fuel
contamination problem is suspected. For proper diag
nosis and service procedures refer to Group 14, Fuel
System.
GASOLINE ENGINE FUEL REQUIREMENTS All gasoline engines require fuel that has a mini
mum octane rating of 87 determined by the (R +
M)/2 calculation method.
The use of a brand of unleaded gasoline that con
tains additives is recommended. Gasoline with addi
tives will improve fuel economy and reduce emissions.
ALCOHOL/GASOLINE
BLENDS
Many brands of blended unleaded gasoline am now
available. Unleaded gasoline is blended with oxygenated-type
fuels to produce a clean air gasoline in many areas.
The use of this type of blended fuel is recommended.
ETH ANOL—Unleaded gasoline and ethanol
blended fuels are a mixture of 10 percent ethanol and 90 percent unleaded gasoline. This is an accept
able blend of fuel.
MTBE— MTBE blended fuels are a mixture of un
leaded gasoline and up to 15 percent MTBE (Methyl
Tertiary Butyl Ether). Unleaded gasoline blended
with MTBE is acceptable.
Page 388 of 1502
•
INSTRUMENT
PANEL
AND
GAUGES
8E - 7
STEERING PUMP
ENGINE
BLOCK
J9U9-74
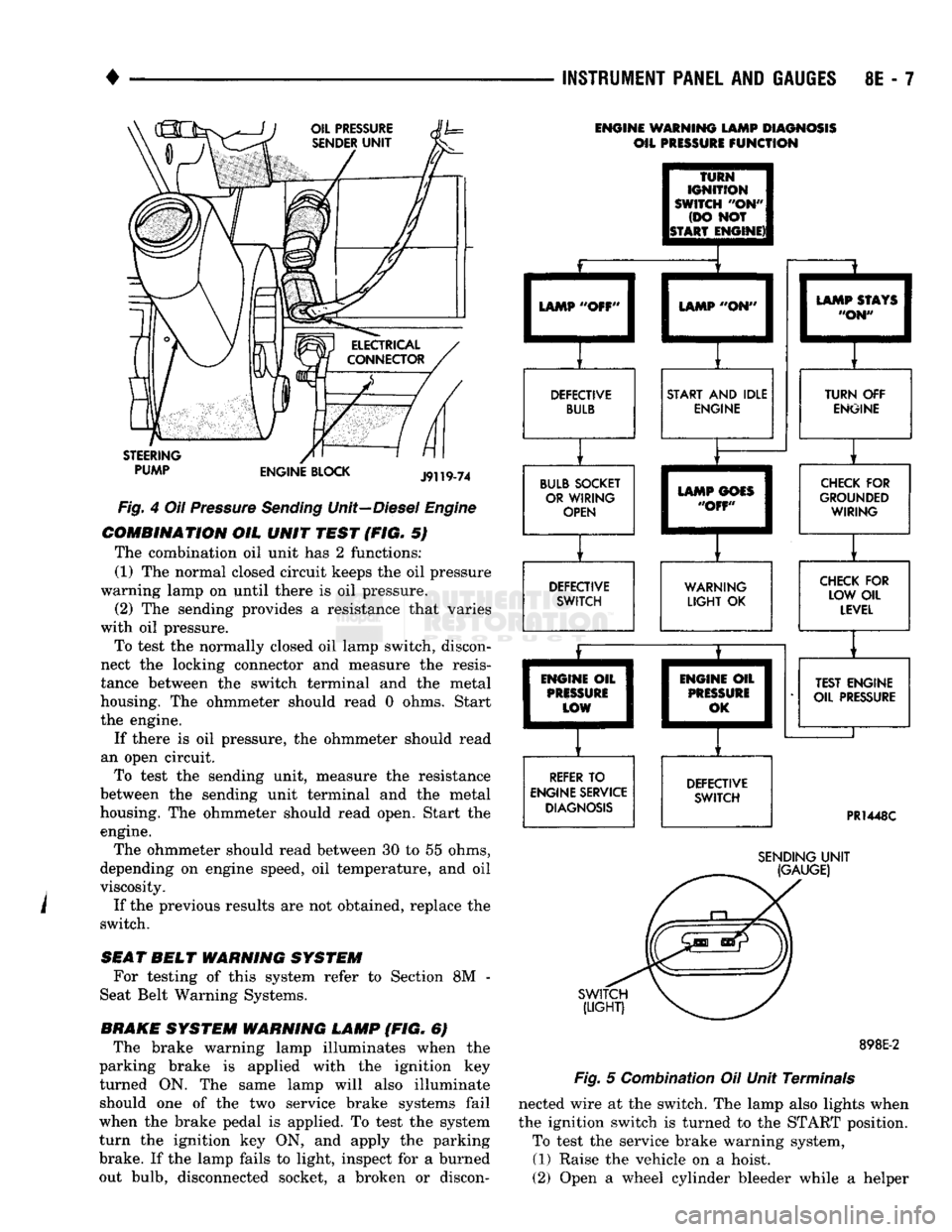
Fig.
4 Oil
Pressure
Sending
Unit—Diesel
Engine
COMBINATION
OIL
UNIT
TEST
(FIG. 5)
The combination oil unit has 2 functions:
(1) The normal closed circuit keeps the oil pressure
warning lamp on until there is oil pressure. (2) The sending provides a resistance that varies
with oil pressure.
To test the normally closed oil lamp switch, discon
nect the locking connector and measure the resis
tance between the switch terminal and the metal
housing. The ohmmeter should read 0 ohms. Start
the engine.
If there is oil pressure, the ohmmeter should read
an open circuit. To test the sending unit, measure the resistance
between the sending unit terminal and the metal
housing. The ohmmeter should read open, Start the engine.
The ohmmeter should read between 30 to 55 ohms,
depending on engine speed, oil temperature, and oil
viscosity.
If the previous results are not obtained, replace the
switch.
SEAT
BELT
WARNING
SYSTEM
For testing of this system refer to Section 8M -
Seat Belt Warning Systems.
BRAKE
SYSTEM
WARNING
LAMP
(FIG. 6) The brake warning lamp illuminates when the
parking brake is applied with the ignition key
turned ON. The same lamp will also illuminate should one of the two service brake systems fail
when the brake pedal is applied. To test the system
turn the ignition key ON, and apply the parking
brake. If the lamp fails to light, inspect for a burned
out bulb, disconnected socket, a broken or discon-
ENGINE WARNING LAMP DIAGNOSIS
OIL PRESSURE
FUNCTION
TURN
IGNITION
SWITCH
"OH"
(DO NOT
ISTART ENGINE)! LAMP "OFF'
LAMP "ON"
DEFECTIVE BULB START AND IDLE
ENGINE
BULB SOCKET OR WIRING OPEN LAMP STAYS
"ON" TURN OFF
ENGINE LAMP GOES
"OFF" DEFECTIVE
SWITCH CHECK FOR
GROUNDED WIRING
WARNING
LIGHT
OK CHECK FOR
LOW OIL LEVEL
ENGINE OIL
PRISSURi
LOW
REFER TO
ENGINE SERVICE DIAGNOSIS ENGIM
PRES
0
IE OIL
1
SURE
1
,K I
DEFECTIVE SWITCH TEST ENGINE
OIL PRESSURE
PR1448C
SWITCH
(LIGHT)
SENDING
UNIT
(GAUGE)
898E-2
Fig.
5 Combination Oil Unit Terminals
nected wire at the switch. The lamp also lights when
the ignition switch is turned to the START position. To test the service brake warning system,
(1) Raise the vehicle on a hoist.
(2) Open a wheel cylinder bleeder while a helper
Page 612 of 1502
•
ENGINES
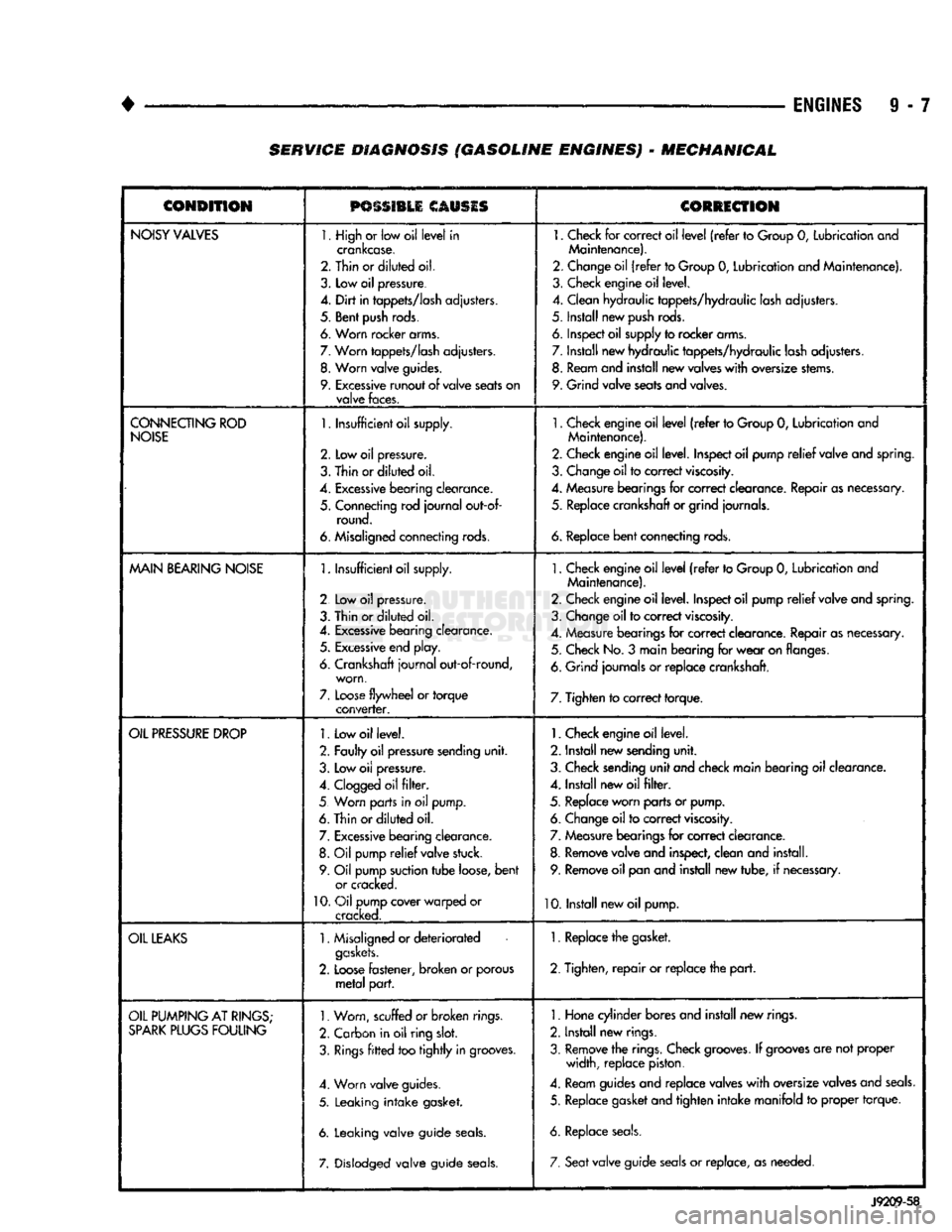
9 - 7 SERVICE DIAGNOSIS (GASOLINE ENGINES) - MECHANICAL
CONDITION
PSSSI1LI
CAUSIS
CORRECTION
NOISY
VALVES
1. High
or
low oil
level
in
crankcase.
2. Thin or
diluted
oil.
3.
Low
oil
pressure.
4.
Dirt
in
tappets/lash
adjusters.
5. Bent
push
rods.
6. Worn rocker arms.
7.
Worn
tappets/lash
adjusters.
8.
Worn
valve
guides.
9.
Excessive
runout
of
valve
seats
on
valve
faces.
1.
Check
for
correct oil
level
(refer
to
Group
0,
Lubrication and
Maintenance).
2. Change oil
(refer
to Group
0,
Lubrication and Maintenance).
3. Check engine oil level.
4. Clean hydraulic tappets/hydraulic lash adjusters.
5. Install new
push
rods.
6. Inspect oil supply to rocker arms.
7. Install new hydraulic tappets/hydraulic lash adjusters. 8. Ream and install new valves
with
oversize stems.
9. Grind valve seats and valves.
CONNECTING
ROD
NOISE
1.
Insufficient oil supply.
2.
Low oil
pressure.
3.
Thin
or
diluted
oil.
4.
Excessive
bearing
clearance.
5. Connecting rod
journal
out-of- round.
6. Misaligned connecting rods.
1.
Check engine oil
level
(refer
to Group
0,
Lubrication and
Maintenance).
2. Check engine oil level. Inspect oil pump
relief
valve and spring.
3. Change oil to correct
viscosity.
4. Measure bearings for correct clearance. Repair as necessary, 5. Replace crankshaft or grind journals.
6.
Replace
bent
connecting rods.
MAIN
BEARING
NOISE
1.
Insufficient oil supply.
2 Low
oil
pressure.
3. Thin or
diluted
oil.
4.
Excessive
bearing clearance. 5.
Excessive
end play.
6. Crankshaft
journal
out-of-round, worn,
7.
Loose
flywheel
or
torque
converter.
1.
Check engine oil
level
(refer
to Group
0,
Lubrication and
Maintenance).
2. Check engine oil level. Inspect oil pump
relief
valve and spring.
3. Change oil to correct
viscosity.
4. Measure bearings for correct clearance. Repair as necessary. 5. Check No.
3
main bearing for
wear
on flanges.
6. Grind journals
or
replace crankshaft.
7. Tighten to correct torque.
OIL
PRESSURE
DROP
1.
Low oil level.
2. Faulty oil pressure sending
unit.
3. Low
oil
pressure.
4.
Clogged
oil
filter.
5 Worn parts in
oil
pump.
6. Thin or
diluted
oil.
7.
Excessive
bearing clearance. 8.
Oil
pump
relief
valve stuck.
9. Oil pump suction
tube
loose,
bent
or cracked.
10.
Oil pump cover warped
or
cracked.
1.
Check engine oil level.
2. Install new sending
unit.
3. Check sending
unit
and check main bearing oil clearance.
4. Install new oil
filter.
5. Replace worn parts or pump. 6. Change oil to correct
viscosity.
7. Measure bearings for correct clearance.
8. Remove valve and inspect, clean and install. 9. Remove oil pan and install new tube,
if
necessary.
10. Install new oil pump.
OIL
LEAKS
1.
Misaligned or
deteriorated
gaskets.
2.
Loose
fastener, broken
or
porous
metal
part.
1. Replace the gasket.
2. Tighten,
repair
or replace the
part.
OIL
PUMPING
AT
RINGS;
SPARK
PLUGS
FOULING
1.
Worn, scuffed
or broken
rings.
2. Carbon in oil ring
slot.
3.
Rings
fitted
too
tightly
in grooves.
4. Worn valve guides.
5. Leaking
intake
gasket.
6. Leaking valve guide
seals.
7. Dislodged valve guide
seals.
1.
Hone cylinder bores and install new rings.
2. Install new rings.
3. Remove the rings. Check
grooves.
If
grooves
are not proper width, replace piston.
4. Ream guides and replace valves
with
oversize valves and
seals.
5. Replace gasket and tighten
intake
manifold
to
proper torque.
6. Replace
seals.
7. Seat
valve guide
seals
or
replace, as needed.
J9209-58
Page 619 of 1502
9
- 14
ENGINES
— — — •
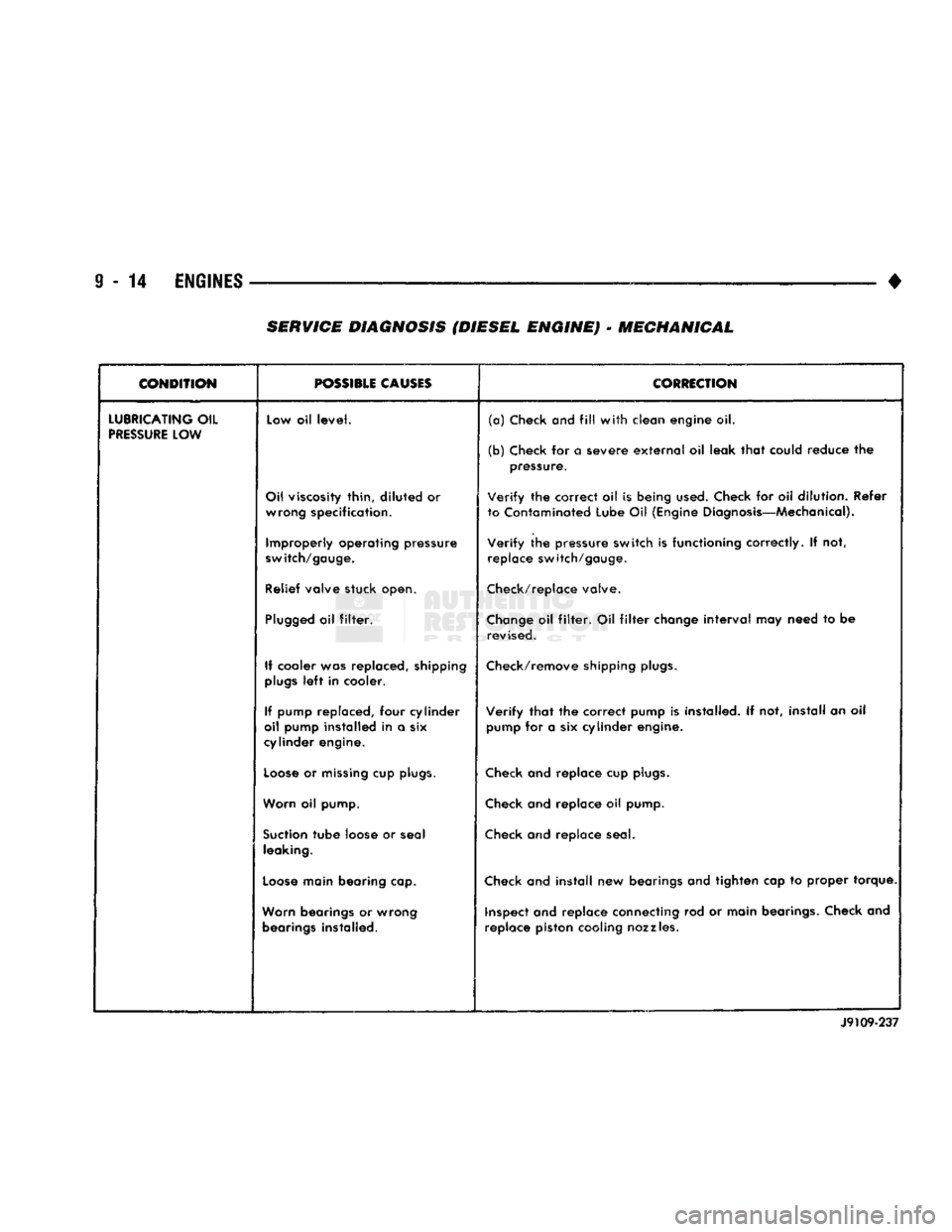
SERVICE
DIAGNOSIS (DIESEL ENGINE)
•
MECHANICAL
CONDITION
r— ———
POSSIBLE
CAUSES
CORRECTION
LUBRICATING
OIL
PRESSURE
LOW Low oil
level.
(a)
Check
and
fill
with
clean engine oil.
(b) Check for a severe
external
oil leak
that
could reduce the pressure.
Oil viscosity thin,
diluted
or wrong specification.
Verify
the correct oil is being
used.
Check for oil dilution. Refer
to Contaminated Lube Oil (Engine Diagnosis—Mechanical).
Improperly operating pressure
switch/gauge.
Verify
the pressure switch is functioning correctly. If not,
replace switch/gauge.
Relief valve stuck open. Check/replace valve.
Plugged
oil
filter.
Change
oil
filter.
Oil
filter
change
interval
may need to be
revised.
If cooler was replaced, shipping
plugs
left
in cooler. Check/remove shipping
plugs.
If pump replaced, four cylinder
oil pump installed in a six
cylinder engine.
Verify
that
the correct pump is installed. If not, install an oil
pump for a six cylinder engine.
Loose
or
missing
cup
plugs.
Check and replace cup
plugs.
Worn oil pump. Check and replace oil pump.
Suction
tube
loose or seal leaking. Check and replace seal.
Loose
main bearing cap. Check and
install
new bearings and tighten cap to proper torque.
Worn bearings or wrong bearings installed. inspect and replace connecting rod or main bearings. Check and
replace piston cooling nozzles.
J9109-237
Page 620 of 1502
•
• —
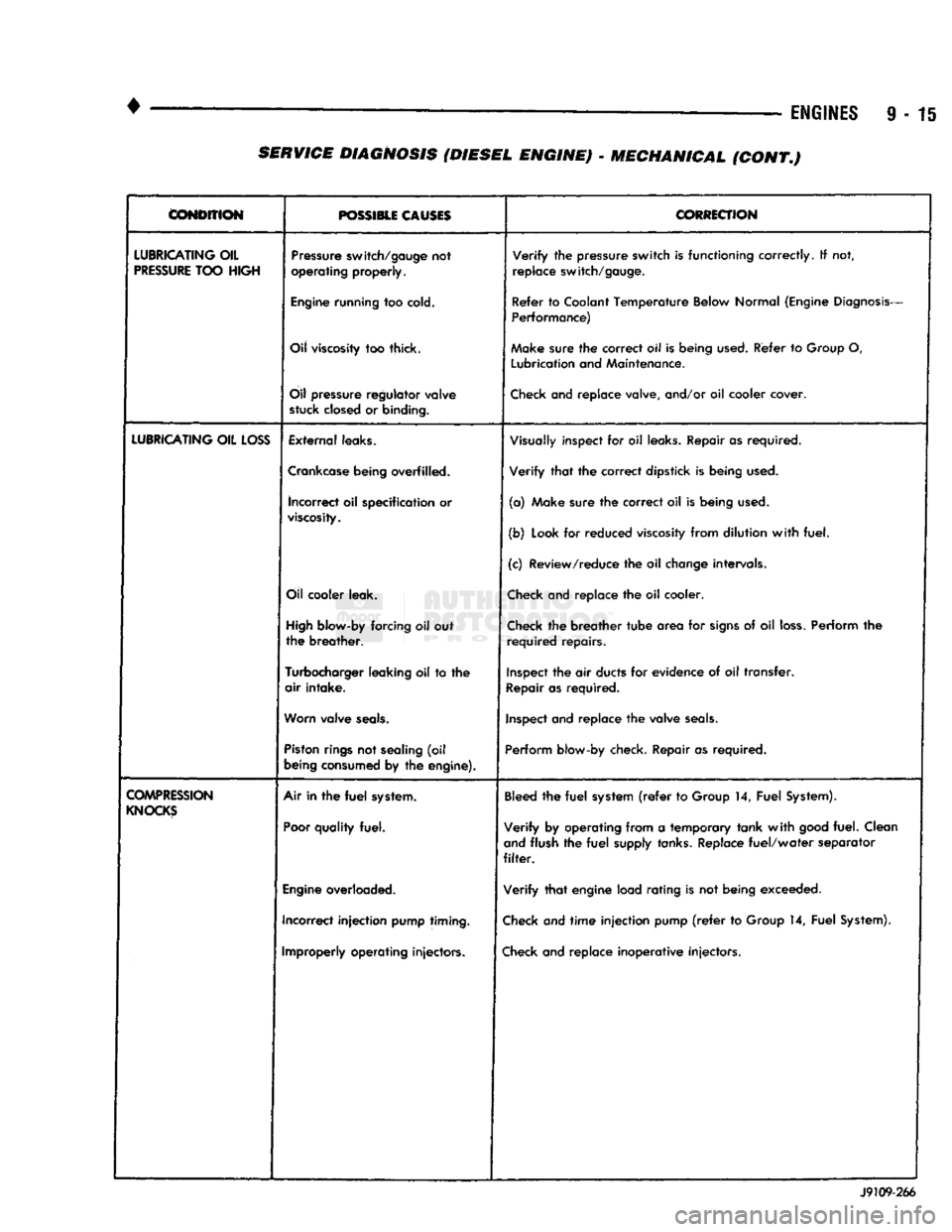
ENGINES
9 - 15
CONDITION
POSSIBLE CAUSES
CORRECTION
LUBRICATING
OIL
PRESSURE
TOO
HIGH
Pressure
switch/gauge
not
operating
properly.
Verify
the
pressure
switch
is
functioning
correctly.
If not,
replace
switch/gauge.
Engine
running
too
cold.
Refer
to
Coolant
Temperature
Below
Normal
(Engine
Diagnosis-
Performance)
Oil
viscosity
too thick. Make
sure
the
correct
oil Is
being
used.
Refer
to
Group
O,
Lubrication
and
Maintenance.
Oil
pressure
regulator
valve
stuck
closed
or
binding.
Check
and replace valve, and/or oil cooler cover.
LUBRICATING
OIL
LOSS
External
leaks.
Visually
inspect for oil
leaks.
Repair as required.
Crankcase
being
overfilled. Verify that the correct dipstick is being
used.
incorrect
oil specification or
viscosity.
(a) Make sure the correct oil is being
used.
(b)
Look
for reduced
viscosity
from dilution with fuel.
(c) Review/reduce the oil
change
intervals.
Oil
cooler
leak.
Check
and replace the oil cooler.
High
blow-by
forcing oil out
the breather.
Check
the breather tube area for
signs
of oil
loss.
Perform the
required repairs.
Turbocharger
leaking
oil to the
air intake.
Inspect
the air
ducts
for evidence of oil transfer.
Repair
as required.
Worn
valve
seals.
Inspect
and replace the valve
seals.
Piston
rings
not
sealing
(oil
being
consumed
by the
engine).
Perform
blow-by check. Repair as required.
COMPRESSION
KNOCKS
Air in the
fuel
system.
Poor
quality
fuel.
Bleed
the fuel
system
(refer
to
Group
14, Fuel
System).
Verify by operating from a temporary tank with
good
fuel. Clean
and
flush the fuel
supply
tanks.
Replace fuel/water separator
filter.
Engine
overloaded. Verify that engine load rating is not being exceeded.
Incorrect injection
pump
timing.
Check
and time injection pump
(refer
to
Group
14, Fuel
System).
Improperly
operating
injectors.
Check
and replace inoperative injectors. J9109-266 SERVICE DIAGNOSIS (DIESEL ENGINE) - MECHANICAL (CONT.)
Page 751 of 1502

9
- 148 5.9L
(DIESEL) ENGINE
• Make sure the idler gear pin is installed in the lo
cating bore in the cylinder block. (2) Install the pump. Tighten the oil pump mount
ing bolts in two steps and in the sequence shown (Fig. 2).
• Step
1—Tighten
to 5 N«m (44 in. lbs.) torque.
• Step 2-Tighten to 24 N*m (18 ft. lbs.) torque. (3) The back plate on the pump seats against the
bottom of the bore in the cylinder block. When the
pump is correctly installed, the flange on the pump will not touch the cylinder block.
(4) Measure the idler gear to pump drive gear
backlash and the idler gear to crankshaft gear back lash (Fig. 8). The backlash should be 0.080-0.330 mm (0.003-0.013 inch). If the backlash is out of limits, re
place the oil pump drive gear and the idler gear.
(5) If the adjoining gear moves when you measure
the backlash, the reading will be incorrect.
Fig.
8
idler
Gear to
Pump
Drive Gear and Crankshaft Gear
Backlash
OIL FILTER
When replacing the oil filter, Chrysler Corporation
recommends use of the replacement filter specified in
your Operator's Manual.
CAUTION:
The
internal filtering medium
of
some
fil
ters
has
been known
to
disintegrate. Debris from
failed filters
may
plug
the
piston
oil
cooling noz
zles,
resulting
in
scuffed pistons
and
eventual
en
gine
failure.
REMOVAL
WARNING:
HOT OIL CAN
CAUSE PERSONAL
IN
JURY.
(1) Operate the engine until the water tempera
ture reaches 60°C (140°F). Shut the engine off.
(2) Use a container that can hold at least 14 liters
(15 quarts) to hold the used oil. Remove the oil drain
plug and drain the used engine oil into the container.
(3) Always check the condition of the used oil. This
can give you an indication of some engine problems
that might exist. • Thin, black oil indicates fuel dilution.
• Milky discoloration indicates coolant dilution.
(4) Clean the area around the lubricating oil filter
head. Remove the filter using a 90-95 mm filter
wrench.
(5) Clean the gasket surface of the filter head. The
filter canister O-Ring seal can stick on the filter
head. Make sure it is removed.
INSTALLATION (1) Fill the oil filter element with clean oil before
installation. Use the same type oil that will be used
in the engine.
(2) Apply a light film of lubricating oil to the seal
ing surface before installing the filter.
CAUTION:
Mechanical over-tightening
may
distort
the threads
or
damage
the filter
element seal.
(3) Install the filter as specified by the filter man
ufacturer. (4) Clean the drain plug and the sealing surface of
the pan. Check the condition of the threads and seal ing surface on the oil pan and drain plug.
(5) Install the drain plug using a new sealing washer.
Tighten the plug to 80 N-m (60 ft. lbs.) torque.
(6) Use only High-Quality Multi-Viscosity lubricat
ing oil in the Cummins Turbo Diesel engine. Choose
the correct oil for the operating conditions outlined in Group 0, Lubrication and Maintenance.
(7) Fill the enginfe with the correct grade of new
oil.
The engine capacity is i0.4 liters (11 quarts) in
the crankcase and 0.95 liters (1 quart) in the lubri cating oil filter. (8) Start the engine and operate it at idle for several
minutes. Check for leaks at the filter and drain plug.
(9) Stop the engine. Wait approximately 5 minutes
to let the oil in the upper parts of the engine to drain
back to the oil pan. Check the oil level again. Add oil as necessary to bring the level to the "H" (High)
mark on the dipstick.
OIL FILTER
BYPASS
VALWE
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the oil cooler cover (Fig. 9). (2) Remove the valve from the cooler cover (Fig. 9).
INSTALLATION (1) Drive the new valve in until it bottoms against
the step in the bypass valve bore (Fig. 10).
(2) Install the oil cooler cover.
OIL PRESSURE REGULATOR VALVE
/
SPRING
When oil pressure from the oil pump exceeds 448
kPa (65 psi), the regulator valve opens to allow oil to
drain back into the pan.
Page 1458 of 1502
•
HEATING
AND AIR
CONDITIONING
24 - 21 (a) Loosen both test hoses at the manifold gauge
set. Tighten the hoses as soon as the air is purged. (b) Loosen charging hose connection at manifold
gauge set. This will purge air from the charging
hose.
Tighten connection as soon as air is purged.
(9) With vehicle windows open and hood up, oper
ate engine at 1,300 RPM. (10) Place air conditioner control on A/C and place
the fan switch on high. (11) If necessary, block the condenser to maintain
a discharge pressure of 1 550-1 725 kPag (225-250
psig).
System must be charged through the evapora
tor suction service ports as follows:
(a) Slowly open the suction service gauge valve.
Meter flow of refrigerant by adjusting the suction service gauge valve so the pressure registered at
the suction service gauge does not exceed 345 kPag
COMPRESSOR
J
(50
psig). Keep refrigerant container upright.
(b) Add refrigerant gas until there is no foam visi
ble at the sight glass. As soon as all foam clears, note the weight registered on the refrigerant scale.
(c) Watch the refrigerant weighing scale and add
437 g (14 oz.) of refrigerant (equivalent to 1 can).
(d) Close the suction gauge valve.
CAUTION:
TOO
much
refrigerant
in the
system
can
cause
abnormally high discharge pressures. Care
must
be
used
so the
exact recommended amount
of
refrigerant
is
added
after
foam clears
in the
sight
glass.
(e) Close dispensing manifold valve. Remove test
hoses and adapters from the service ports of com
pressor and install protective caps at service ports.
RVICE (SD-709)
INDEX
page
Compressor
21
Compressor
Shaft Seal
.................... 25
The A/C system uses a 7 piston design Sanden SD-
709 compressor. Designated the SD-709, the compres
sor is mounted on the front right side of the engine
and is driven by a serpentine belt.
System lubrication is provided by 135cc ±15cc (4.6
cu. in. ±0.5 cu. in.) of 500 viscosity refrigerant oil.
The clutch used on the compressor consists of 3 ba
sic components:
(1) The pulley.
(2) The front plate. (3) The field coil.
The pulley and field coil are attached to the front
head of the compressor with snap rings. The hub is keyed to the compressor shaft and is retained on the
shaft with a self-locking nut. Special service tools are
required to remove and install the clutch plate on
the compressor shaft.
COMPRESSOR
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the negative cable from the battery.
(2) Disconnect the clutch lead wire.
(3) Remove the discharge and inlet (suction) ser
vice valves from the compressor. Plug or tape all the
openings.
(4) Refer to Group 7, Cooling System and remove
the drive belt(s). (5) Remove the bolts and lift the compressor from
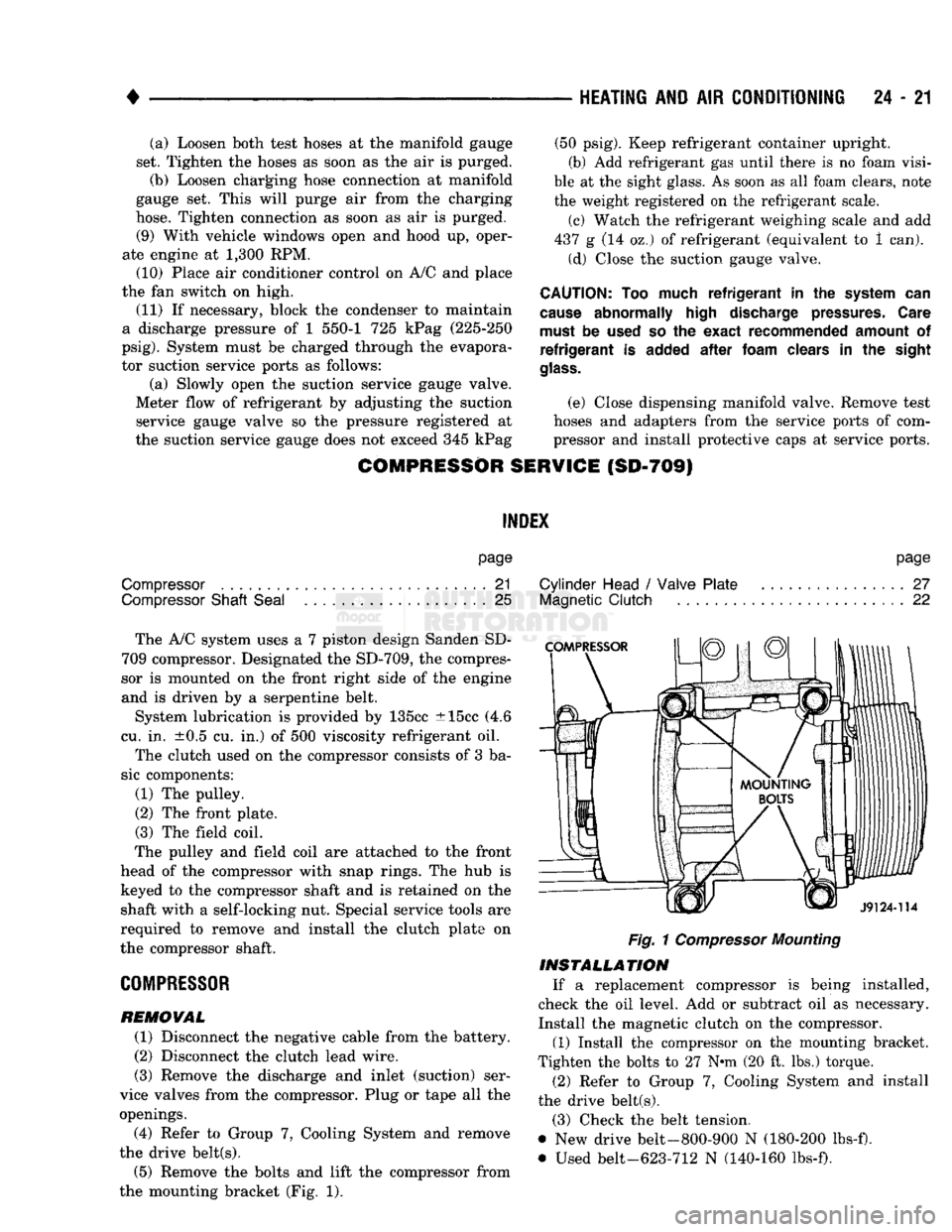
the mounting bracket (Fig. 1).
page
Cylinder Head
/
Valve Plate
27
Magnetic
Clutch
22
Fig.
1
Compressor
Mounting
INSTALLATION
If a replacement compressor is being installed,
check the oil level. Add or subtract oil as necessary.
Install the magnetic clutch on the compressor.
(1) Install the compressor on the mounting bracket.
Tighten the bolts to 27 N*m (20 ft. lbs.) torque.
(2) Refer to Group 7, Cooling System and install
the drive belt(s).
(3) Check the belt tension.
@ New drive belt-800-900 N (180-200 lbs-f).
• Used belt-623-712 N (140-160 lbs-f).