4B 1 FIAT PUNTO 1998 176 / 1.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FIAT, Model Year: 1998, Model line: PUNTO, Model: FIAT PUNTO 1998 176 / 1.GPages: 225, PDF Size: 18.54 MB
Page 181 of 225

Braking system 9®5
2 Rotate the brake disc by hand and examine the whole of the surface area swept by the brake pads, on both sides ot the disc. Note: /( will bo necessary to remove the front brake pads to allow an adequate inspection of the disc's rear surface; refer to Section 2 tor details. 3 Typically, the disc surface will have a polished appearance and should be free from heavy scoring. Smooth rippling is produced by normal operation and does not indicate excessive wear. Deep scoring and cracks, however, are indications of more serious damage in need of correction. 4 If deep scoring Is discovered, it may be possible to have the disc reground to restore the surface, depending on the extent of the damage. To determine whether this is a feasible course of action, it will be necessary to measure the thickness of the disc, as described later. 5 Check the whole surface of the disc for cracks, particularly around the roadwheel bolt holes. A cracked disc mutt be renewed. 6 A ridge of rust and brake dust at the inner and outer edges of the disc, beyond the pad contact area is normal - this can be scraped tway quite easily. 7 Raised ridges caused by the brake pads eroding the disc material, however, are an indication of excessive wear. If close examination reveals such ridges, the oiicknoss of the disc must be measured, to usess whether it is still fit for use. 8 To measure the thickness of the disc, take readings at several points on the surface using a micrometer. In the area swept by the brake pads (see Illustration). Include any points where the disc has been scored: align me Jaws of the micrometer with the deepest ares of scoring, to get a true indication of the extent of the wear. Compare these ineasurements with the limits listed in the Specifications. If the disc has worn below its minimum thickness, at any point, it must be renewed. 9 If the discs are suspected of causing brake luddor, check the disc runout, using one of
me
following methods: Runout measurement -
DTI
gauge method 10 Refit the four roadwheel bolts, together
w.1h
one M14 plain washer per stud • this will ensure adequate disc to hub contact. Tighten te studs to 5 Nm (4 Ibf ft). 11 Clamp the DTI gauge to a stand and attach the stand, preferably via a magnetic oase. to the strut mounting bracket. Align the jauge so that its pointer rests upon the area of the dtsc swept by the brake pads, on an arc i mm from the outer edge of tho disc (soe illustration). 12 Zero the gauge and slowly rotate the disc trough one revolution, observing tho pointer rcovement. Note the maximum deflection recorded and compare the figure with that >«ted In Specifications.
4.8 Measuring brake disc thickness with a micrometer
Runout measurement -feeler blade method 13 Use the feeler blades to measure the clearance between the disc and a convenient fixed point, such as the disc backplate. Rotate the disc and measure the variation in clearance at several points around the disc, Compare the maximum figure with that listed in Specifications. 14 If the disc runout Is outside of its specified tolerance, first check that the hub Is not worn (see Steering and suspension check in Chapter 1A or 1B). If the hub is In good condition, remove the disc (as described later in this Section), rotate it through 180° and refit it. This may improve the seating and eradicate Ihe excessive runout. 15 If the runout is still unacceptable, then It may be possible to restore the disc by regrinding; consult your Fiat dealer or a machine shop for a professional opinion - it may prove more economical to purchase a new disc. If the disc cannot be reground, then it must be renewed.
Removal 16 Mark the relationship between the disc and the hub with chalk or a marker pen, to allow correct refitting. 17 To allow the disc to be removed, undo the two bolts securing (he brake caliper mounting bracket to the hub carrier (see illustration 3.7). Withdraw the brake caliper and mounting bracket assembly, complete with brake pads, from the hub carrier, and hang it from a rigid point on the suspension, using v/lre or a
4.18a Slacken and remove the disc locating studs ...
4.11 Brake disc runout measurement - DTI gauge method
cable-tie. Oo not allow it to dangle freely as this will strain the brake hose. 18 Slacken and remove the disc locating stud(s). Support the disc as you do this and lift it off as it becomes free (see illustrations). 19 Remove the polished glaze from the surface of the disc with sand/emery paper. Use small, circular motions to avoid producing a directional finish on the surface.
Refitting 20 If a new disc Is being fitted, remove the protective coating from the surface U9ing an appropriate solvent. 21 Locate Ihe disc on ihe hub so that the roadwheel bolt and locating stud holes are all correctly lined up; use the alignment marks made during removal. If the disc is being removed in an attempt to improve seating and hence runout, turn the disc through 180° and then refit it. 22 Refit the locating stud and retaining screw, tightening them securely. 23 Re-check the disc runout, using one of the methods described earlier in this Section. 24 Refil the brake caliper and mounting bracket assembly to the hub carrier. Coat the threads of the mounting bolts with locking compound, then tighten them to the specified torque. 25 Depress the brake pedal several times to bnng the brake pads into contact with the disc. 26 Refit the roadwheel and lower the vehicle to the ground. Tighten the roadwheel bolts to the specified torque. 27 Check the hydraulic fluid level as described in Weekly checks.
4,18b ... and lift off the disc as It becomes free
Page 182 of 225
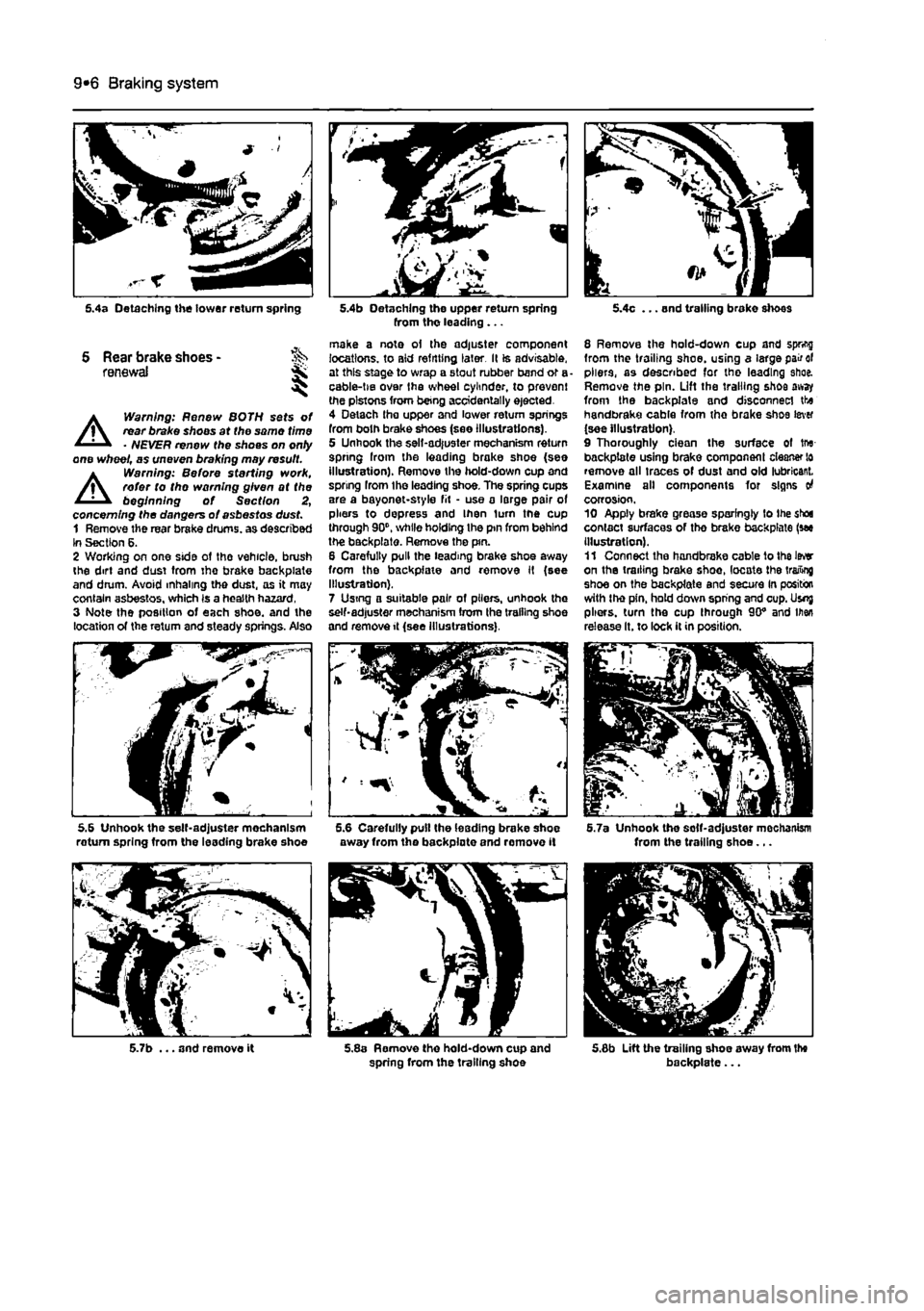
9*6 Braking system
5.4a Detaching the tower return spring
S Rear brake shoes -renewal ji,
A
Warning: Renew BOTH sets of rear brake shoos at the same time • NEVER renew the shoes on onty one wheel, as uneven braking may result.
A
Warning: Before sterling work, refer to tho warning given at the beginning of Section 2, concerning the dangers of asbestos dust. 1 Remove the rear brake drums, as described In Section 6. 2 Working on one side ot the vehicle, brush the dirt and dust tram tho brake backpiate and drum. Avoid inhaling the dust, as it may contain asbestos, which Is a health hazard, 3 Note the position of each shoe, and the location of the return and steady springs. Also
5.6 Unhook the self-adjuster mechanism roturn spring from the leading brake shoe
5.7b ... and remove it
5.4b Detaching the upper return spring from tho leading ...
make a note oi the adjuster component locations, to aid refitting later. Il is advisable, at this stage to wrap a stout rubber band or a cable-tie over Ihe wheel cylinder, to prevent the pistons from being accidentally ejected. 4 Detach tha upper and lower return springs from both brake shoes (see illustrations). 5 Unhook the sell-adjuster mechanism return spring Iroin the leading brake shoe (see illustration). Remove the hold-down cup and spring from the leading shoe. The spring cups are a bayonet-style fit • use a large pair of pliers to depress and Ihen turn the cup through 90", while holding Ihe pin from behind the backpiate. Remove the pin. 6 Carefully pull the leading brake shoe away from the backpfaie and remove It (see Illustration). 7 Using a suitable pair of pliers, unhook the self-adjuster mechanism from the trailing shoe and remove it (see Illustrations).
away from the backpiate and remove it
5.8a Remove the hold-down cup and spring from the trailing shoe
5.4c ... and trailing brake shoes
8 Remove the hold-down cup and spring from the trailing shoe, using a large pair of pliers, as described for the leading shoe. Remove the pin. Lift the trailing shoe away from the backpiate and disconnect the handbrake cable from the brake shoe lever (see illustration). 9 Thoroughly ciean the surface of tru-backpiate using brake component cleaner lo remove all traces of dust and old lubricant. Examine all components for signs o4 corrosion. 10 Apply brake grease sparingly to the shoe contact surfaces of tho brake backpiate (see Illustration). 11 Connect tha handbrake cable to the Iwr on the trailing brake shoe, locate the trailing shoe on the backpiate and secure In position with the pin, hold down spring and cup. Usnj pliers, turn the cup through 90" and men release It. to lock it in position.
5.7a Unhook the solf-adjuster mochanism from the trailing shoe...
5.6b Lift the trailing shoe away from the backpiate...
Page 183 of 225

Braking system 9®7
5JJc ... and disconnect the handbrake cable from the brake shoe lever
5.14a Lower return spring fitted in place
12 Fit the self-adjuster mechanism Into the recess in the trailing brake shoe and anchor the retaining spring in the slot provided in the shoe (see Illustration). 13 Fit the leading shoe In position on the backpiste and secure it with the hold down pin. spring and cup as described for the trailing shoe. Engage the end of'the self-adjuster mechanism with the recess In the leading brake shoe. Hook the retaining spring into the slot provided. 14 Fit the upper and lower shoe return spnngs. engaging them with the slots In the shoes as shown (see illustrations). Remove
me
elastic band from the wheel cylinder. 15 Turn Ihe serrated wheel at the end of the self-adjuster mechanism, to retract the brake shoes - this will give additional clearance to ilow Ihe drum to pass over the shoes during refitting. 16 Repeat the procedure on the remaining tide of the vehicle. 17 Refit the brake drums as described in Section 6. Check and if necessary adjust the operation of the handbrake, as described in Section 9. IB Apply the brake pedal and handbrake 'ever several times to settle the self-adjusting mechanism. With both rear roadwheels rsfitted and Ihe rear of the vehicle still raised, turn Ihe wheels by hand to check that the take shoes are not binding. 19 Lower the vehicle to the ground and thoroughly check the operation of the braking system.
5.10 Apply brake grease sparingly to the shoe contact surfaces (arrowed) of the brake backplate
5.14b Correct location of upper return spring In leading shoe...
6 Rear brake drums -removal, inspection and refitting ^
A
Warning: Before starting work, refer to the warning at the beginning of Section 2 concerning the dangers of asbestos dust Removal 1 Chock the front wheels, then jack up the roar of the vehicle and support it on axle stands (see Jacking and vehicle support). Remove the appropriate rear roadwheel. Fully release the handbrake. 2 If the original drum is to be refitted, mark the relationship between the drum and the hub. Slacken and remove the two locating studs and pull the drum from the hub (see illustration).
6.2 Slacken and remove the two drum locating studs
5.12 Fit the self-adjuster mechanism into the recess (arrowed) in the trailing brake shoe
5.14c ... and trailing shoe
3 If the drum is binding on Ihe brake shoes, it can be drawn off as follows. Hold the drum still and turn the hub so that the drum and hub flange bolt holes no longer line up. Screw two bofts into the locating stud threaded holes In tho drum, and progressively lighten them against the hub llange to push the drum from the hub (see illustration).
Inspection Note: If either drum requires renewal, BOTH should be renewed at the same time, to ensure even and consistent braking. New brake shoes should also be fitted. 4 Working carefully, remove all traces of brake dust from the drum, but avoid Inhaling the dust, as it is a health hazard. 5 Clean the outside of the drum, and check it for obvious signs of wear or damage, such as cracks around the roadwheel stud holes; renew the drum if necessary.
6.3 Using two bolts to draw the drum off the brake shoes
Page 184 of 225

9*8 Braking system
6 Carefully examine the Inside of tho drum. Light scoring of the friction surface is normal, but if heavy scoring Is found, the drum must be renewed. 7 It is usual to find a lip on the dmm's inboard edge which consists of a mixture of rust and brake dust: this should be carefully scraped away, to leave a smooth surface which can be polished with fine (120 to 150-grade) emery paper. If, however, the tip is due to the friction surface being recessed by excessive wear, then the drum must be renewed. 6 If the drum Is thought to be excessively worn, or oval, its internal diameter must be measured at several points using an internal micrometer. Take measurements In pairs, the second at right-angles to the first, and compare the two, to check for signs of ovality. Provided that it does not enlarge the dium to beyond the specified maximum diameter, it may be possible to have the drum refinished by skimming or grinding; if this is not possible, Ihe drums on both sides must be renewed. Note that if the drum is to be skimmed, BOTH drums must be refinished. to maintain a consistent Internal diameter on both sides.
Refitting 9 II a new brake drum is to be Installed, use a suitable solvent to remove any preservative coating thai may have been applied to its internal fnction surfaces. Note that it may also be necessary to shorten the adjuster strut length, by rotating the sedated strut wheel, lo allow Ihe drum lo poss over the brake shoes • see Section S for details. 10 II tho original dfum is being refitted, align the marks made on the drum and hub before removal, then lit the drum over the hub. Refit the locating studs and tighten them to the specified torque. 11 Depress the footbrake repeatedly to expand the brake shoes against the drum, and ensure that normal pedal pressure Is restored. 12 Check and if necessary adjust the handbrake cable as described In Section 9. 13 Refit tho roadwheels, and lower the vehicle to the ground.
7 Rear wheel cylinder -removal, overhaul and refitting jS
A
Warning: Before starting work, refer to the warnings at tho beginning of Sections 2 and 11 concerning the dangers ot handling asbestos dust and hydraulic fluid.
Removal 1 Remove the brake drum fsee Section 6). 2 Remove the brake shoes (see Section 5). 3 To minimise fluid loss during the following operations, remove the master cylinder reservoir cap. then tighten it down onto a piece of polythene, lo obtain an airtight seal.
the hydraulic pipe from the rear of the wheel cylinder 4 Clean the brake backplate around Ihe wheel cylinder mounting boits and the hydraulic pipe union, then unscrew the union nut and disconnect Ihe hydraulic pipe (see illustration). Cover the open ends of the pipe and the master cylinder to prevent dirt ingress, 5 Remove the securing bolts, then withdraw the wheel cylinder from the backplate (soe Illustration).
Overhaul Note: Before commencing woric, ensure that the appropriate wheel cylinder overhaul kit is obtained. 6 Clean tho assembly thoroughly, using only methylated spirit or clean brake fluid, 7 Peel off both rubber dust covers, then use paint or similar to mark one ot the pistons so that the pistons are not interchanged on reassembly. 8 Withdraw both pistons and tho spring. 9 Discard the rubber piston cups and the dust covers. These components should be renewed as a matter of course, and are available 3s part of an overhaul kit, which also Includes the bleed nipple dust cap. 10 Check the condition of the cylinder bore and the pistons - the surfaces must be perfect and free from scratches, scoring and corrosion, It is advisable to renew the complete wheel cylinder if there is any doubt as to the condition ot the cylinder bore or pistons. 11 Ensure thai all components are clean and dry. The pistons, spring and cups should be
8.4 Location of brake tight switch-LHD model shown
withdraw the wheel cylinder from the backplate fitted wet, using hydraulic fluid as a lubricant • soak them in clean fluid before installation. 12 Fit the cups to the pistons, ensuring that they are the correct way round. Use only your fingers (no tools) to manipulate the cups into position. 13 Fit the first piston to the cylinder, taking care not to distort the cup. If the original pistons are being re-used, ihe marks
made on
dismantling should be used to ensure that the pistons are refitted to their original bores, 14 Refit the spring and the second pfston. 15 Apply a smear of rubber grease to Ihe exposed end of each piston and to the dust cover sealing lips, then fit Ihe dust covers to each end of the wheel cylinder.
Refitting 16 Refitting is a reversal of removal, bearirg in mind the following points: a) Tighten the mounting bolts to the specified torque. b) Refit the brake shoes as desenbod
In
Section 5. and refit the brake drum
as
described in Section 6. c) Before refitting the roadwheel
and
lowering the vehicle to the ground, remove the polythene from the fluid reservoir, and bleed the hydraulic
system
as described in Section f
1.
Note that if
nc
other part of the system has been disturbed, it should only bo necessary
to
bleed the relevant rear circuit.
8 Stop-light switch • & adjustment, removal J? and refitting
Adjustment 1 The switch plunger operates on a ratchet 2 If adjustment Is required, pull the plunge fully out - (he 9witch then sell-adjusts as the brake pedal Is applied and released.
Removal 3 Ensure that the ignition Is switched to OfF. 4 For Improved access, remove the driver's side lower facia panel, as described in Chapter 11 (see Illustration). 5 Disconnect the wiring plug from the switch.
Page 185 of 225

Braking system 9®9
6.8 Brake light switch assembly f Hexagonal' 3 Spacer section 4 Mounting bracket 2 Bush S Locating lug 6 Twist the switch anti-clockwise through about half a turn, and withdraw the switch from the pedal bracket. Note the position of the spacer and fitting bush.
10.3a Prise the bung (arrowed) from the access hatch in the rear of the relevant brake backplate
10.3b Unhook the cable end from the brake shoe lever (arrowed)
Refitting 7 Depress the brake pedal and hold it in this position. 8 Fit the bush and spacer over the end of the switch, then Insert the switch Into its mounting bracket. Rotate the switch body clockwise through 60° until the locating lug is felt to engage in its recess (seo illustration). 9 Release the brake pedal and allow It to rest against the switch spacer tab - this adjusts the position of the switch body Inside Ihe bush. 10 Now depress the brake pedal again - this has the effect of breaking off the spacer tab and fixes the position of the switch Inside the bush. 11 Restore Ihe wiring at the connector, then refit the facia lower trim panel. 12 Switch on the ignition and test the operation of the brake lights.
9 Handbrake - ^ checking and adjustment
Checking 1 Apply the handbrake by pulling it through three to four clicks of the ratchet mechanism and check that this locks the rear wheels, holding the vehicle stationary on an incline. In this position, there should be sufficient reserve travel in the handbrake lever to allow for brako shoe wear and cable stretching. If not. Ihe handbrake mechanism Is need of adjustment.
Adjustment 2 Remove the securing screws and lift off the handbrake lever trim cover - refer to Chapter 11. Section 19. for details. 3 Pull the handbrake lever through three clicks of the ratchet mechanism and leave it in this position. 4 The adjustment mechanism is underneath the handbrake lever. Hold the locknut with a ring spanner, then rotate the adjustment screw through one turn anticlockwise, so that the adjustment mechanism tensions the handbrake cable draw bar (see illustration). 5 Release the handbrake lever, then re-apply
10.5a Unscrew the bolts (arrowed) securing the handbrake cable bracket to the suspension lower arm
the handbrake it and check the operation of the handbrake as described in paragraph 1. Repeat the adjustment procedure as necessary. 6 Chock the front wheels then |ack up the rear of the car and support it on axle stands (see Jacking and Vehicle Support). Release the handbrake lever and check that the rear wheels are free to rotate v/ithout binding. Re-adjust the cable if the brakes appear to be binding. 7 On completion, tighten the cable locknut and refit the handbrake lever trim cover. Lower the car to the ground.
10 Handbrake cables -removal and refitting
Removal 1 There are two rear handbrake cables, one on each side of the vehicle. To renew either rear cable, proceed as follows. 2 Chock the front wheels, then jack up the rear of tho vehicle and support securely on axle stands (see Jacking and vehicle support). Release the handbrake fully, 3 Working under the rear of the car, prise the bung from the access hatch in the rear of the relevant brake backplato, Using pointed-nose pliers, compress the cable spring and release the cable end from the brake shoe lever (see Illustrations). 4 Extract the handbrake outer cable from the brake backplate. then withdraw the end of the cable from the brake assembly. 5 Unscrew the nuts and bolts securing the handbrake cable bracket to the suspension lower arm. Release the cable from the clips on the floorpan heatshield (see Illustrations).
10.5b Release the cable from the clips (arrowed) on the floorpsn heatshield
Page 186 of 225

9*10 Braking system
10.6 Disconnect the relevant handbrake inner cable (arrowed) from the draw bar 6 Working inside ihe vehicle, remove Ihe screws and lift off the handbrake lever trim panel (refer to Section 9 for more detail). At the base of the handbrake lever, full/ slacken off the handbrake adjusting screw and locknut, to remove oil tension from the cable draw bar, then disconnect the relevant handbrake inner cable from the cable draw bar (see illustration) 7 Release the cable grommet from tho floor-pan, then withdraw the cable from the vehicle.
Refitting 8 Refitting Is a reversal of removal, bearing in mind the following points: a) Ensure that the cables are securely fastened In the clips on the floorpan beetshield and lower suspension a/m. b) On completion, check the handbrake adiustment, as described in Section 9.
11 Hydraulic system -bleeding
A
Warning: Hydraulic fluid is poisonous; wash off immediately and thoroughly In the case ot skin contact, and seek immediate medical advice if any fluid is swallowed, or gets into the eyes. Certain types of hydraulic fluid are Inflammable, and may ignite when allowed into contact with hot components. When servicing any hydraulic system, it Is safest to assume that the fluid IS inflammable, and to take precautions
11.17 Bleeding a rear brake line
against the risk of fire as though it is petrol that Is being handled. Hydraulic fluid is also an effective paint stripper, and will attack plastics; If any is spilt, It should be washed off immediately, using copious quantities of fresh water. Finally, it Is hygroscopic (it absorbs moisture from the air) • old fluid may be contaminated and unfit tor further use. Whan topping-up or renewing the fluid, always use the recommended type, and ensure that It comes from a freshly-opened sealed container.
General 1 The correct operation of any hydraulic system is only possible after removing all air from the components and circuit; and this Is achieved by bleeding the syslem. 2 During the bleeding procedure, add only clean, unused hydraulic fluid of the recommended type; never re-use fluid that has already been bled from the system. Ensure that sufficient fluid is available before starting work. 3 If there is any possibility of incorrect fluid being already in the system, the brake com-ponents and circuit must be Flushed completely with uncontamlnated, correct fluid, and new seals should be fitted throughout the system. 4 If hydraulic fluid has been lost from the system, or air has ontered because of a leak, ensure that the fault is cured before proceeding further. 5 Park Ihe vehicle on level ground, switch off the engine and select first or reverse gear (or P), then chock the wheels and release the handbrake. 6 Cheek that all pipes and hoses are secure, unions tight and bleed screws closed. Remove Ihe dust caps (whore applicable), and clean any dirt from around the bleed screws. 7 Unscrew the master cylinder reservoir cap, and top Ihe master cylinder reservoir up to the MAX level line; refit the cap loosely. Rememoer to maintain the fluid level at least above the MIN level line throughout the procedure, otherwise there is a risk of further air entering the syslem. 8 There are a number of one-man. do-It-yourself brake bleeding kits currently available from motor accessory shops. It is recommended that one of these kits is used whenever possible, as they greatly simplify the bleeding operation, and also reduce the risk of expelled air and fluid being drawn back into the system. If such a kit is not available, the basic (two-man) method must be used, which is described in detail below. 9 If a kit Is to be used, prepare the vehicle as described previously, and follow the kit manufacturer's instructions, as Ihe procedure may vary slightly according to the type being used; generally, they are as outlined below in the relevant sub-section. 10 Whichever method is used, the same sequence must be followed (paragraphs 11 and 12) to ensure Ihe removal of all air from the system.
Bleeding sequence 11 If Ihe system has been only
partial!?
disconnected, and suitable precautions wwe taken to minimise fluid loss, it should be necessary to bteod only that part of the system (le the primary or secondary circuit). 12 If the complete system Is to be bled, then It should be done working in the following sequence: a) Left-hand rear wheel b) Right-hand front wheel. c) Right-hand rear wheel. d) Left-hand front wheel. Note: When bleeding the rear brakes
on a
vehicle ritled with load proportioning valves: i the rear of the vehicle has been jacked
up to
allow access to ihe brake wheel cylinder,
tha
rear suspension must be compressed
(eg
raising the beam axle with a trolley
jack) so
that the load proportioning valves
remain open
throughout the bleeding process.
Bleeding -basic (two~man) method 13 Collect a clean glass jar, a suitable length of plastic or rubber tubing which Is a light fit over the bleed screw, end a ring spanner lo
Rt
the screw. The help of an assistant will also tie required. 14 Remove the dust cap from the first screw In the sequence if not already done. Fit a suitable spanner and tube to the screw, place the other end of Ihe tube In the jar. and
pour in
sufficient fluid to cover the end of the tube. 15 Ensure that the master cylinder reservoir fluid level is maintained at least above the
MIN
level line throughout the procedure. 16 Have the assistant fully depress the brefce pedal several times to build up pressure, then maintain it on the final downstroke. 17 While pedal pressure is maintained, unscrew ihe bleed screw (approximately one turn) and allow the compressed fluid and orto flow into the
Jar,
The assistant should maintah pedal pressure, following the pedal down to the floor if necessary, and should not rrtaase Ihe pedal until instructed to do so. When ihe flow stops, tighten the bleed screw again, have the assistant retease the pedal sfowty, and recheck the reservoir fluid level (see Illustration). 18 Repeat Ihe steps given in paragraphs 16 end 17 until the fluid emerging from the bled screw is free from air bubbles. If Ihe master cylinder has been drained and refilled,
and
at Is being bled from the first screw In the sequence, allow approximately five seconds between cycles for the master cylinder passages to refill. 19 When no more air bubbles appear, tighter, the bleed screw securely, remove Ihe tube arc spanner, and refit the dust cap (where applicable). Do not overtighten the bleed sew. 20 Repeat the procedure on tho remaining screws In the sequence, until ail air is removed from the system, and the brake pedal feels firm again.
Page 187 of 225
Braking system 9®11
Bleeding • using a one-way valve kit 21 As their name implies, these kits consist ol a length of tubing with a one-way valve Fitted, to prevent expelled air and fluid being drawn back into the system; some kits include a translucent container, which can be positioned so that the air bubbles can be more easily seen flowing from the end of the tube. 22 The kit is connected to the bleed screw, which is then opened. The user returns to the driver's seat, depresses the brake pedal with a smooth, steady stroke, and stowty releases it; this is repeated until the expelled fluid is clear of air bubbles. 23 Note that these kits simplify work so much that It is easy lo forget the master cylinder reservoir fluid level; ensure that this Is maintained at least above the MIN level line at all times.
Bleeding -using a pressure-bleeding kit 24 These kits are usually operated by the reservoir of pressurised air contained in the spare tyre. However, note that it will probably be necessary to reduce the pressure lo a lower level than normal; refer to the instructions supplied with the kit. 2$ By connecting a pressurised, fluid-filled container to the master cylinder reservoir, bleeding can be carried out simply by opening each screw In turn (in the specified sequence), and allowing the fluid to flow out until no more air bubbles can be seen in the expelled fluid. 28 This method has the advantage that the large reservoir of fluid provides an additional safeguard against air being drawn into the system during bleeding. 27 Pressure-bleeding is particularly effective when bleeding 'difficult' systems, or when bleeding the complete system at the time of routine fluid renewal.
All methods 28 When bleeding is complete, and firm pedal feel is restored, wash off any split fluid, lighten the bleed screws securely, and refit their dust caps (where applicable). 29 Check the hydraulic fluid level in the master cylinder reservoir, and top-up if necessary. 30 Discard any hydraulic fluid thai has been Wed from the system; it will not be fit for re-use. 91 Check the feel of the brake pedal. If it feels at all spongy, air must still be present in Vie system, and further bleeding is required. Failure to bleed satisfactorily after a reasonable repetition of the bleeding procedure may be due to worn master cylinder seals.
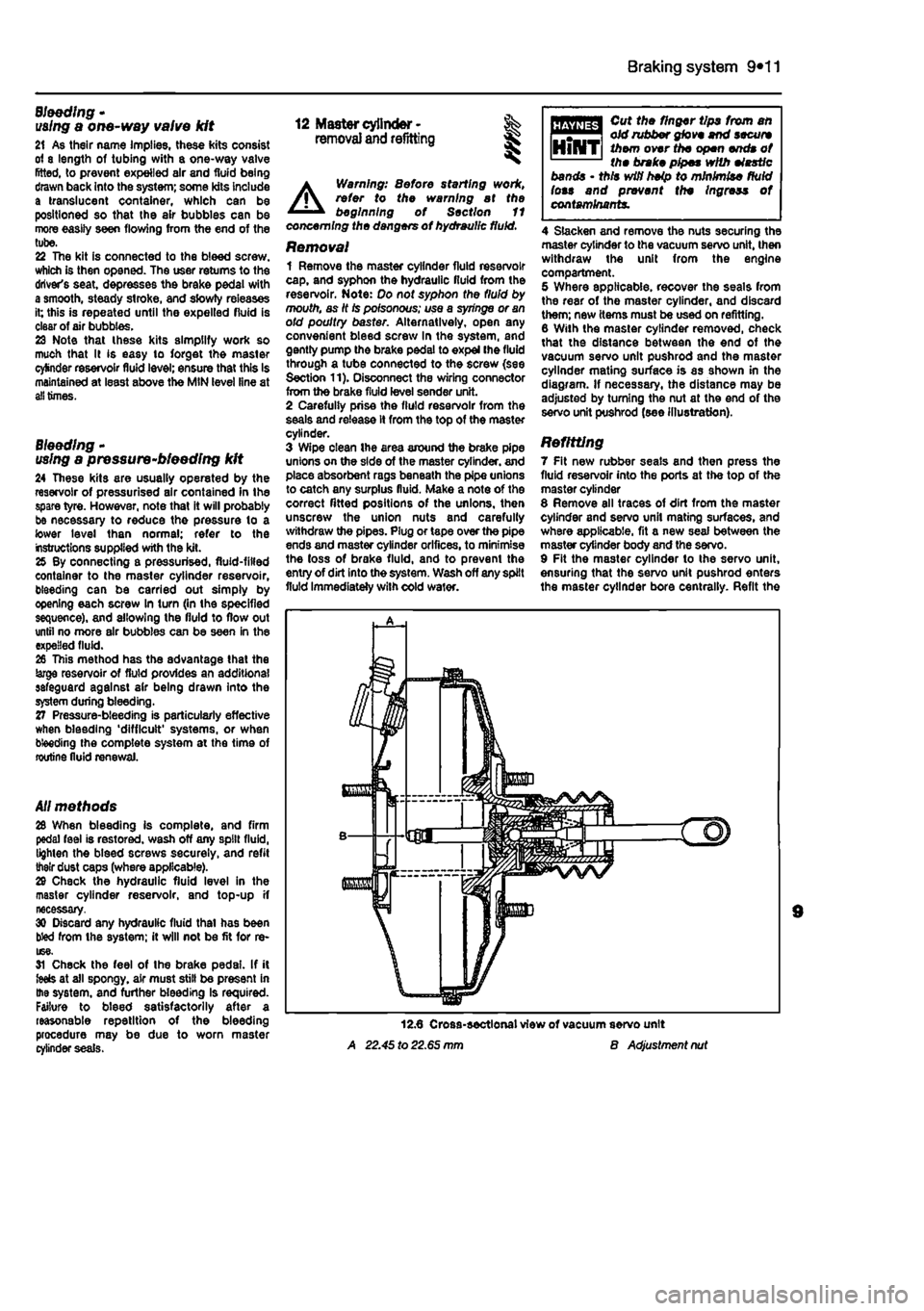
12 Master cylinder- % removal
and
refitting SK
A
Warning: 8efore starting work, refer to the warning at the beginning of Section 11 concerning the dangers of hydraulic fluid.
Removal 1 Remove the master cylinder fluid reservoir cap, and syphon the hydraulic fluid from the reservoir. Note: Do not syphon the fluid by mouth, as It Is poisonous; use a syringe or an old poultry baster. Alternatively, open any convenient bleed screw In the system, and gently pump the brake pedal to expel (he fluid through a tube connected to the screw (see Section 11). Disconnect the wiring connector from the brake fiuld level sender unit. 2 Carefully prise the fiuld reservoir from the seals and release it from the top of the master cylinder. 3 Wipe clean Ihe area around the brake pipe unions on the side of the master cylinder, and place absorbent rags beneath the pipe unions to catch any surplus fluid. Make a note of the correct fitted positions of the unions, then unscrew the union nuts and carefully withdraw the pipes. Plug or tape over the pipe ends and master cylinder orifices, to minimise the loss of brake fluid, and to prevent the entry of dirt into the system. Wash off any spilt fluid immediately with cold wafer.
A 22.45 to 22.65 mm
Cut the finger tips from an old rubber glove end secure them over the open ends of the brake pipes with elastic bands • this wifi heip to minimise fluid lots and prevent the Ingress of contaminants.
4 Slacken and remove the nuts securing the master cylinder to the vacuum servo unit, then withdraw the unit from the engine compartment. 5 Where applicable, recover the seals from the rear of the master cylinder, and discard them; new items must be used on refitting. 8 With the master cylinder removed, check that the distance between the end of the vacuum servo unit pushrod and the master cylinder mating surface is as shown in the diagram. If necessary, the distance may be adjusted by turning the nut at the end of the servo unit pushrod (see illustration).
Refitting 7 Fit new rubber seals and then press the fluid reservoir into the ports at the top of the master cylinder 8 Remove all traces of dirt from the master cylinder and servo unit mating surfaces, and where applicable, fit a new seal between the master cylinder body and the servo. 9 Fit the master cylinder to the servo unit, ensuring that the servo unit pushrod enters the master cylinder bore centrally. Refit the
B Adjustment nut
Page 188 of 225

9*12 Braking system
master cylinder mounting nuts, and tighten them securely. 10 Wipe clean the brake pipe unions, then refit them to the correct master cylinder ports, as noted before removal, and lighten the union nuts securely. 11 Refill tha master cylinder reservoir with new fluid, and bleed the complete hydraulic system as described In Section 11. 12 Check the operation of the braking system thoroughly.
13 Hydraulic pipes and hoses - % renewal S§
A
Warning: Before starting work, refer to the warning at the beginning of Section 11 concerning the dangers of hydraulic fluid, 1 If any pipe or hose is to be renewed, minimise fluid loss by first removing the master cylinder reservoir cap. then tighten the cap down onto a piece of polythene to obtain
an airtight seal. Alternatively, flexible hoses can be sealed, If required, using a proprietary brake hose clamp; metal brake pipe unions can be plugged (if care Is taken not to allow dirt into the system) or capped immediately they are disconnected. Place a wad of rag under any union that is to be disconnected, to catch any spilt fluid-2 If a flexible hose Is to be disconnected, unscrew the brake pipe union nut before removing the spring clip which seeurea the hose to its mounting bracket. 3 To unscrew the union nuts, ll is preferable lo obtain a brake pipe spanner of the correct size; these are available from most large molor accessory shops. Failing this, a close-fitting open-ended spanner will be required, though if the nuts are tight or corroded, their flats may be rounded-off if the spanner slips. In such a case, a self-locking wrench is often the only way to unscrew a stubborn union, but It follows that Ihe pipe and the damaged nuts must be renewed on reassembly. Always clean a union and surrounding area before disconnecting it If disconnecting a compo-
nent with more than one union, make a carefJ note of the connections before disturbing
any
of them. 4 If a brake pipe Is to be renewed, it can b« obtained, cut to length and with the union nuts and end flares in place, from Fiat dealers. All that is then necessary is to bend It to shape, following the line of the original, baton fitting It to the vehicle. Alternatively, most motor accessory shops can make up bra Ha pipes from kits, bul this requires very carefii measurement of the original, to ensure (hat the replacement is of the correct length. Tha safest answer is usually to take the original lo the shop as a pattern. 5 On refitting, do not overtighten the union nuts. It is not necessary to exercise brute force to obtain a sound joint. 6 Ensure that the pipes and hoses an correctly routed, with no kinks, and that they are secured in the clips or brackets provided. After fitting, remove the polythene from lbs reservoir, and bleed the hydraulic system
88
described In Section 11. Wash off any split fluid, and check carefully for fluid leaks.
Page 189 of 225

10*1
Chapter 10
Suspension and steering
Contents
Front hub bearings - renewal 2 Front suspension anti-roll bar • removal and refitting 6 Front suspension lower arm - removal and refitting 4 Front suspension lower arm balljolnt - renewal 5 From suspension strut - removal, overhaul and refitting 3 General information 1 Ignition switch/steering column lock - removal and refitting 10 Manual steering gear assembly - removal, overhaul and refitting ... 12 Power steering fluid level check See Weekly checks Power steering gear assembly - removal and refitting 13 Power steering hydraulic system - bleeding 15
Degrees of difficulty
Power steering pump • removal and refitting 16 Rear hub bearings - renewal 7 Rear suspension components- removal, overhaul and refitting 8 Steering and suspension check See Chapter 1A or 1B Steering column - removal, overhaul and refitting 11 Steering gear rubber gaiters - renewal 14 Steering wheel - removal and refitting 9 Track-rod end - removal and refitting 17 Wheel alignment and steering angles • general information 18 Wheel and tyre maintenance and tyre pressure checks See Weekly checks
Easy, suitable for nowoe with little
Jg experience ^
Fakty easy,
suitable for beginner
with
J£>
some experience
^
FaMy difficult,
% suitable for competent ^
DIY mechanic
^
Difficult,
suitable for & experienced DIY « mechsmc ^
Very difficult,
^ suitable for expert
DIY
fij or professional ^
Specifications
Front suspension Type
Rear suspension Type
Steering Type Turns lock-to-lock: Manual Power assisted Toe setting (front)
Roadwheeis and tyres See Weekly checks
Torque wrench settings Front suspension Anti-roll bar bush bracket bolts Driveshaft nut:' All models except turbo diesel (M22 plain) Turbo diesel (M24 with staking and captive washer) Lower arm balljoint to hub carrier Lower arm front bush securing bolt Lower arm rear bush securing bolt Suspension strut damper nut Suspension strut to hub carrier Suspension strut to inner wing
Independent, incorporating transverse lower wishbones and coil spring-over-teiescopic damper strut units. Anti-roll bar fitted to all models.
Independent, incorporating trailing arms with telescopic dampers and coil springs.
Rack-and-pinlon, manual or power assisted, depending on model
4.4 approx. 2.9 approx. 0° (parallel) ± 1a
Nm ibfft
30 22
240 177 280 207 30 22 95 70 70 52 60 44 70 52 50 37
Page 190 of 225

Suspension and steering 10*2
Torque wrench settings (continued) Nm ibt ft Rasr suspension Damper lower securing bolt 95 70 Damper upper securing bolt 60 44 Handbrake cable support bracket-to-trailing arm screws 15 11 Hub nut 280 207 Trailing arm securing bolt 150 111 Steering Ignition switch/steering column lock securing bolts 4 3 Steering column mounting bolts 55 41 Steering gear mounting bolts 70 52 Steering wheel nut' 50 37 Subframe-to-body bolts 110 81 Track-rod end to hub carrier 40 30 Unlversaijointclampbolts 20 15 Roadwheels Roadwheel bolts 85 63 * Use a new nut
1 General information
Front suspension The front suspension is independent, comprising transverse lower wishbones, coil spring-over-damper strut units and an anti-roll bar. The hub carriors are bolted to the base of the stmt units and are linked to the lower arms by means ot balliotnts. The entire front suspension assembly is mounted on a subframe, which is In turn botted to the vehicle body.
Rear suspension The rear suspension incorporates a torsion beam axle, trailing arms, coil springs and separate telescopic dampers. In addition, a rear anil-roll bar is fitted to certain models. The components form a discrete sub-assembly which can be unboiled from the underside of the vehicle separately or as a complete unit.
Steering The two-piece steering shaft runs in a tubular column assembly, which is bolted to a bracket mounted on the vehicles bulkhead. The shaft Is articulated at its lower end by means of a universal Joint, which is clamped to the steering shaft and the steering gear pinion by moans of clamp bolts. The steering gear is mounted on the engine compartment bulkhead, and is connected to the steering arms projecting rearwards from Ihe hub carriers. The track-rods are fitted with balljoints at their inner and outer ends, to allow for suspension movement, and are threaded to facilitate ad|ustment. Hydrauiically-assisted power steering ts fittod to some models. The hydraulic system is powered by a belt-driven servo pump, which is driven from the crankshaft pulley.
Certain models are fitted with an airbag system. Sensors built into the vehicle body are triggered in the event of a front end collision and prompt an Electronic Control Unll (ECU) to activate the airbag, mounted In the centre of the steering wheel and the facia. This reduces the risk of the front seat occupants striking the steering wheel, windscreen or facia during an accident.
A
Warning: For safety reasons, owners are strongty advised to entrust to an authorised Flat dealer any work which involves disturbing the airbag system components. The airbag inflation devices contain explosive material and legislation exists to control their handling and storage, in addition, specialised test equipment Is needed to check that the airbag system Is fully operational following reassembly.
2 Front hub bearings -renewal *
Note: A balljoint separator tool, and a press or suitable alternative tools (see text) will be required for this operation. The bearing will be destroyed during the removal procedure.
Removal 1 Chock the rear wheels, apply the handbrake, then jack up the front of the vehicle and support on axle stands (see Jacking and vehicle support). Remove the appropriate roadwheel. 2 Remove the brake disc and caliper, with reference to Chapter 9. Note that the caliper body can remain bolted to its bracket: there is no need lo disconnect the brake fluid hose from the caliper. 3 With reference to Chapter 8. slacken and remove the driveshaft hub nut. 4 On models with ABS, unbolt the ABS wheel sensor, and remove the screw securing the
ABS sensor wiring to the hub carrier. Suspend the sensor away from the working ares, to avoid the possibility of damage. 5 With reference to Section 17, separate
th»
track-rod end from the hub carrier, using
a
suitable balljoint splitter. 6 Remove the two nuts from tho botts securing Ihe hub carrier to the base of th» suspension strut (refer to Section
3).
Withdrew the bolts and separate the top of hub earrtt from the strut. 7 Disconnect the outboard end of Ito driveshaft from the hub, as described durirg the driveshaft removal and refitting procedm in Chapter 8. Note: There is no naod fo disconnect the Inboard end of the
drivestett
from the transmission. Caution: Do not allow the end of tin driveshaft to hang down under its
own
weight, as this places strain on the
CV
joints; support the end of the shaft uskg wire or string. 8 Slacken and remove the nut and clamp bolt, then push the lower arm down anc separate the balljoint from the base of the tab carrier (see illustrations). 9 At this stage, it is recommended that
the bub
carrier be taken to a engineering workshop,
as
the hub and bearing should ideally be removed from the hub carrier using a hydraulic press
2.8a ... Slacken and remove the nut...