Idle FIAT PUNTO 1998 176 / 1.G Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FIAT, Model Year: 1998, Model line: PUNTO, Model: FIAT PUNTO 1998 176 / 1.GPages: 225, PDF Size: 18.54 MB
Page 153 of 225

5B*1
Chapters PartB:
Ignition system - petrol models
Contents
General information 1 Ignition system - testing 2 Ignriton HT coil - removal, testing and refitting 3 Ignition timing - checking and adjustment 4 Igrrtion system - check See Chapter 1A Spark plugs - renewal See Chapter 1A
Degrees of difficulty
Easy,
suitable for Falrty easy, sulabte Fafety difficult, suitable for competent Difficult, suitable for Very difficult, ^ novice with littie
1
for beginner with Fafety difficult, suitable for competent experienced DIY suitable for expert DIY or professional ^ expenence 1 some experience DIY mechanic mechanic *
suitable for expert DIY or professional ^
Specifications
General System type
firing order Ignition timing at Idle speed (non-adjustable, for reference onlyy. 6-valve engines: Single-point injection engine with manual transmission .... Single-point injection engine with automatic transmission.. Multi-point injection engine 16-valve engines
Ignition
coil winding resistance (at 20°C): Primary Secondary
Weber-Marelli static (distributorless), wasted spark Ignition system controlled by engine management ECU
1
-3-4-2 (No 1 cylinder at timing belt end of engine)
10® ± 3° BTDC 6° ± 3° STDC 13° ±3° BTDC 8° x 3° BTDC
0.495 to 0.605 ohms 6660 to 8140 Ohms
Page 155 of 225

Ignition system - petrol models 5B®3
Chapter 1A tor further information. Also check tnat tha accelerator cable is correctly adjusted
as
described in the relevant part of Chapter 4. If the engine is running very roughly, check the compression pressures and the valve clearances as descnbed In the relevant parts of Chapters 1 and 2. 2
H
these checks fall to reveal the cause of the problem, the vehicle should be taken to a suitably equipped Fiat dealer for testing. A wiring block connector Is Incorporated in the engine management circuit Into which a special electronic diagnostic tester can be plugged. The tester will locate the fault quickly and simply alleviating the need to test all the system components Individually which is a time consuming operation that carries a high risk of damaging the ECU. 3 The only Ignition system checks which can
oe
earned out by the home mechanic are those cescribed in Chapter 1A, relating to the spark plugs, and the ignition coll test descnbed In this Chapter. If necessary, the system wiring and wiring connectors can oe checked as descnbed in Chapter 12, Section 2, ensuring that the ECU wiring connector(s) have first
been
disconnected.
3 Ignition HT coil - ^ removal, testing and refitting
Removal 1 On 6-valve engines, unscrew the boll and remove the plastic cover from the left-hand
end
of the cylinder head (see Illustration). On 15-valve engines, remove the air cleaner, resonator and Inlet air duct as described in Chapter 4B. 2 Identify the two HT leads for position then disconnect them from the coil HT terminals jsee illustration). 3 Disconnect the LT wiring plug.
4 Unscrew the mounting bolts and remove the relevant ignition coil from the end of the cylinder head,
Testing 5 Testing of the coil consists of using a multimeter set to its resistance function, to check the primary and secondary windings for continuity and resistance. Compare the results obtained to those given In the Specifications at the start of this Chapter. Note the resistance of the coil windings varies slightly according to the coil temperature; the results In the Specifications are approximate values for the coil at 20°C. 6 Check that there is no continuity between the HT lead terminals and the coil body/ mourning bracket. 7 Note that with the ignition switched on and the engine stationary, voltage will only be supplied to the ignition cotls for approx-imately 2 seconds. However, when tho engine is being cranked or running, voltage will be continually supplied. 8 If faulty, the coil should be renewed.
Refitting 9 Refitting ts a reversal of the removal procedure ensuring that the winng and HT leads are correctly reconnected (see illustration).
4 ignition timing • checking and adjustment
1 The Ignition timing is constantly being monitored and adjusted by the engine management ECU, and although it is possible to check the base ignition liming using a standard timing light It is not possible to adjust it. 2 For those wishing to check the ignition timing a stroboscope timing light will be required, and it will need to be the type which
3.1 Removing the ignition coll cover
can determine the amount of advance from the TDC markings on the crankshaft pulley or flywheel. It Is recommended that the timing mark is highlighted as follows. 3 Remove the plug from the top of the transmission then turn tho engine slowly (raise the front right-hand wheel and engage 4th gear) until the timing mark scribed on the edge of the flywheel appears in the aperture. Highlight the line with quick-drying white paint - typist's correction fluid is ideal. 4 Start the engine and run It to normal operating temperature, then stop it. 5 Connect the timing light to No 1 cylinder spark plug lead (No 1 cylinder Is at the timing belt end of the engine) as described in the timing light manufacturer's Instructions. 6 Start the engine, allowing it to idle at the specified speed (Chapter 1A), and point the timing light at the transmission housing aperture. Adjust the timing light until the TDC marks are aligned with each other and read off the amount of advance. 7 If the ignition timing is incorrect, the car should be taken to a Fiat dealer who will be able to check the system quickly using special diagnostic equipment. 8 After making the check stop the engine, disconnect the timing light and refit the plug to the transmission.
3.2 HT terminals (1) and LT wiring plugs (2) on the two ignition colls 3.9 Ignition colt connections
Page 167 of 225
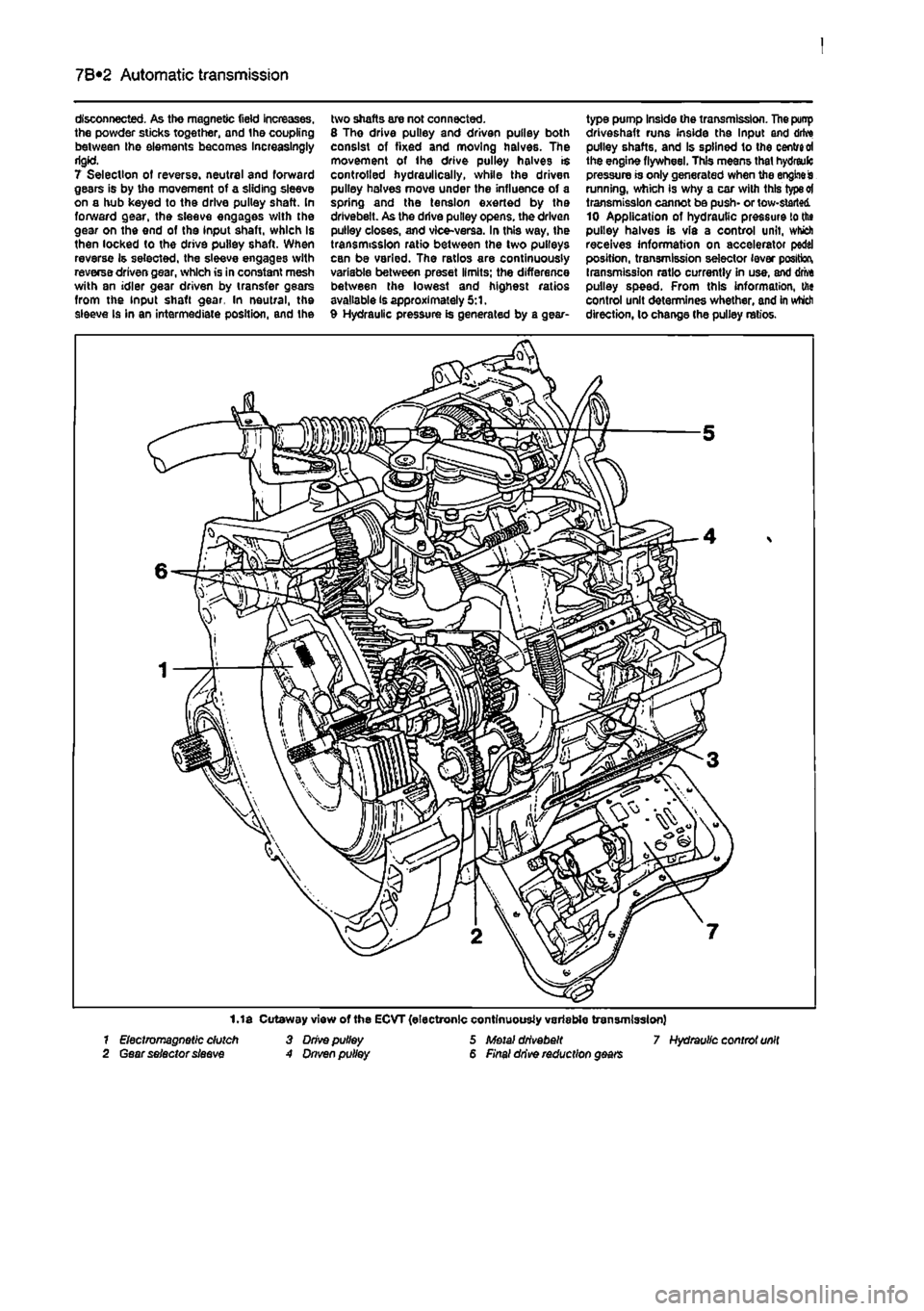
7B*2 Automatic transmission
disconnected. As the magnetic field increases, the powder sticks together, and the coupling between Ihe elements becomes Increasingly rigid. 7 Selection of reverse, neutral and forward gears is by the movement of a sliding sleeve on a hub keyed to the drive pulley shaft. In forward gear, the sleeve engages with the gear on the end of the input shaft, which is then locked to the drive pulley shaft. When reverse is selected, the sleeve engages with reverse driven gear, which is in constant mesh with an idler gear driven by transfer gears from the input shaft gear. In neutral, the sleeve Is in an intermediate position, and the
two shafts are not connected. 8 Tho drive pulley and driven pulley both consist of fixed and moving halves. The movement of ihe drive pulley halves is controlled hydraulically, while the driven pulley halves move under the influence of a spring and the tension exerted by the drivebeit. As the drive pulley opens, the driven pulley closes, and vice-versa. In this way, the transmission ratio between the two pulleys can be varied. The ratios are continuously variable between preset limits; the difference between the lowest and highest ratios available is approximately 5:1. 9 Hydraulic pressure is generated by a gear-
type pump Inside the transmission. The punp driveshaft runs inside the Input and drive pulley shafts, and Is splined to the centred the engine flywheel. This means that hydreulc pressure is only generated when the engine is running, which is why a car with this type ot transmission cannot be push- or tow-started 10 Application of hydrautic pressure to the pulley halves is via a control unit, which receives information on accelerator pedal position, transmission selector lever position, transmission ratio currently in use, and drive pulley speed. From this information, the control unit determines whether, and in which direction, lo change the pulley ratios.
1.1 a Cutaway view of the ECVT (electronic continuously variable transmission) 7 Electromagnetic dutch 3 Drive pulley 5 Metal drivebeit 7 Hydraulic controt unit 2 Gear selector sleeve A Dnven pulley 6 Final drive reduction gears