steering wheel FIAT PUNTO 1999 176 / 1.G Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FIAT, Model Year: 1999, Model line: PUNTO, Model: FIAT PUNTO 1999 176 / 1.GPages: 225, PDF Size: 18.54 MB
Page 172 of 225
6*172
Chapter 8
Driveshafts
Contents
Oriveshaft gaiter check See Chapter 1A or 1B General information 1 Oriveshaft overhaul and rubber gaiter renewal 3 intermediate driveshaft - removal and refitting 4 Driveshafts - removal and refitting 2
Degrees of difficulty
Easy,
suitable for ^ novtoewithittle experience ^
Fatly
easy,
suitable for beginner with
some experience
^
Fairty
difficult, suitable
tor
competent OtYmechanlc
Difficult,
suitable for experienced DIY mechanic ^
Veiydfficult, ^
suitable
for
expert DIY
or professional ^
Specifications
General Type
Lubrication lubricant type
Torque wrench settings Driveshaft nut* All models except turbo diesel (M22 plain) Turbo diesel (M24 with staking and captive washer) Roadwheel bolts Suspension strut-to-hub carrier bolts Track-rod balljolnt-to-hub carrier 'Use a new nut.
Unequal-length, solid steel shafts, splined to Inner and outer constant velocity joints. Intermediate shaft with support bearing on turbo diesel models with equal length driveshafts.
Fiat specification grease, supplied with gaiter repair kit
Nm Ibfft
240 177 280 207 85 63 70 52 40 30
1 General information
Power is transmitted from the differential to
Ihe
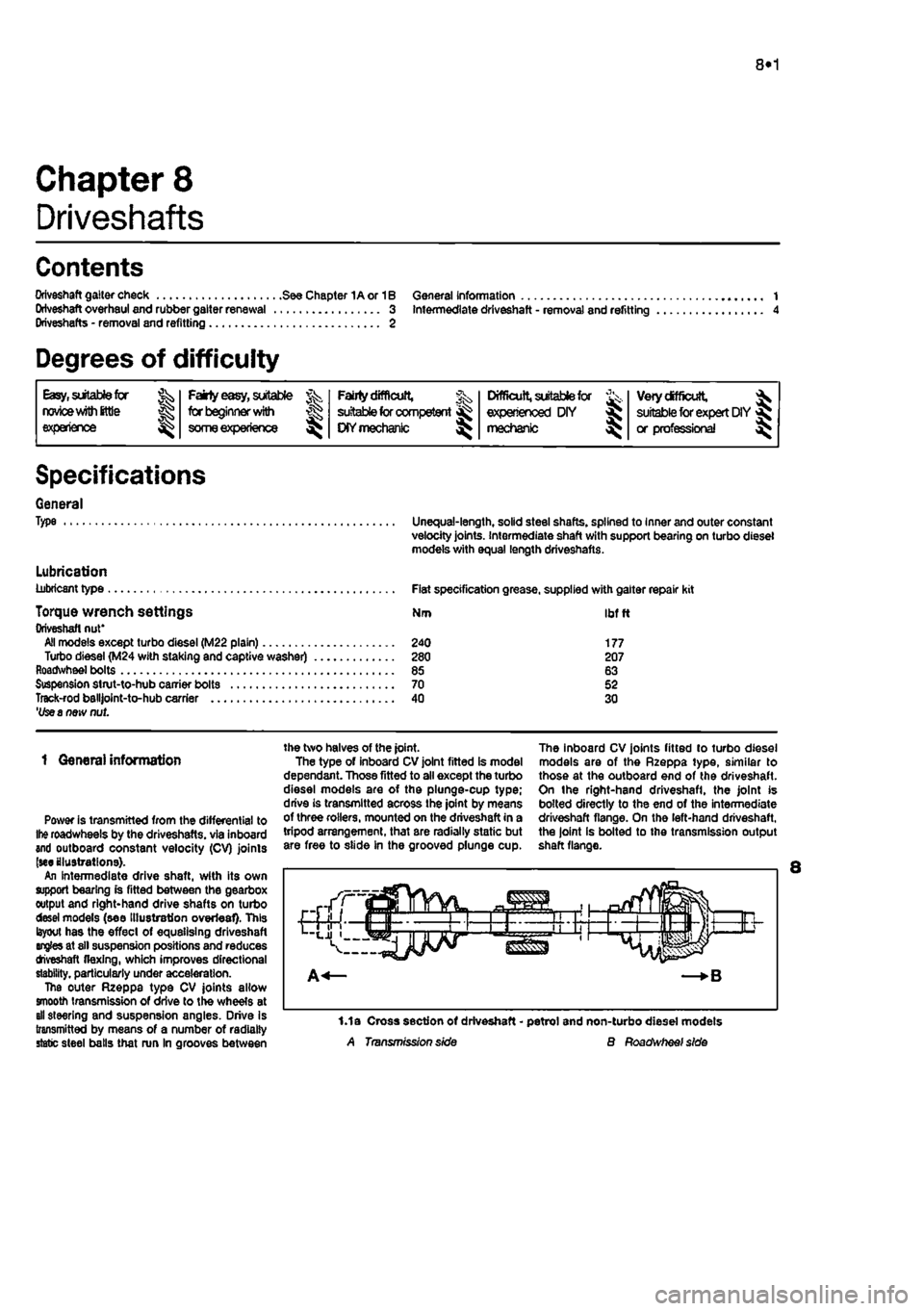
roadwheels by the driveshafts. via inboard and outboard constant velocity (CV) joints (we illustrations). An intermediate drive shaft, with its own support bearing is fitted between the gearbox output and right-hand drive shafts on turbo desei models (see Illustration overleaf). This layout has the effect of equalising driveshaft angles at sll suspension positions and reduces tfveshaft flexing, which improves directional stability, particularly under acceleration. The outer Rzeppa type CV joints allow smooth transmission of drive to the wheels at all steering and suspension angles. Drive Is transmitted by means of a number of radially static steel balls that run In grooves between
the two halves of the joint. The type of inboard CV joint fitted is model dependant. Those fitted to all except the turbo diesel models are of the plunge-cup type; drive is transmitted across the joint by means of three rollers, mounted on the driveshaft in a tripod arrangement, that are radially static but are free to slide in the grooved plunge cup.
The inboard CV joints fitted to turbo diesel models are of the Rzeppa type, similar to those at the outboard end of the driveshaft. On the right-hand driveshafl, the joint is bolted directly to the end of the intermediate driveshaft flange. On the left-hand driveshaft, the joint is bolted to the transmission output shaft flange.
1.1a Cross section of driveshaft - petrol and non-turbo diesel models A Transmission side B Roadwheef side
Page 178 of 225

9*2 Braking system
2.3a Release tho locking clip ...
1 General information
The braking system is of the vacuum servo-assisted. dual-circuit hydraulic type. The arrangement of Ihe hydraulic system is such that each circuit operates one front ond ono rear brake from a tandem master cylinder. Under normal circumstances, both circuits operate In unison However, in the event of hydraulic failure in one circuit, lull braking force will still be available at two diagonally-opposite wheels. All models covered in this manual are fitted with front disc brakes and rear drum brakes. The front disc brakes are aotuated by single-piston sliding lype calipers, which ensure lhat equal pressure is applied to each brake pad. The rear drum brakes incorporate leading and trailing shoes, which are actuated by twin-piston wheel cylinders. A self-adjust mechanism is incorporated, to automatically compensate for brako shoe wear. As the brake shoe linings wear, the footbrnke operation automatically operates the adjuster mechanism, which effectively lengthens the shoe strut and repositions the brake shoes, to remove the llning-to-drum clearance. The mechanical handbrake linkage operates the brake shoos via a lever attached to the trailing brake shoe.
2.3b ... and remove the pad wear indicator wiring and brake fluid line from the suspension strut Load sensitive proportioning valves operate on the rear brake hydraulic circuits, to prevent the possibility of the rear wheels locking before the front wheels under heavy braking. Note: When servicing any part of the system, work carefully and methodically; also observe scmpulous cleanliness when overhauling any part of the hydraulic sysiem. Always renew components (in axle sets, where applicable) if In doubt about their condition, and use only genuine Fiat replacement parts, or at least those of known good quality. Note the warnings given in Safety first and at relevant points in this Chapter concerning fhe dangers of asoestos dust and hydraulic fluid.
Models with anti-lock braking system (ABS) Available as an option on certain models, the anti-lock braking system prevents skidding which not only optimises stopping distances but allows full steering control to be maintained under maximum braking. By electronically monitoring the speed of each roadwheel in relation to the other wneete, Ihe system can detect when a wheel is about to lock-up, before control is actually lost. The brake fluid pressure applied to that wheel's brake caliper is then decreased and restored (or modulated) several times a second until control
£s
regained. The system components comprise an Electronic Control Unit (ECU), four wheel speed sensors, a hydraulic unit, brake lines and dashboard mounted warning lamps.
The hydraulic unit incorporates a tandem master cylinder, a valve block which modulates the pressure in the brake hydrauli: circuits during ABS operation, an accumulator which provides a supply of highly pressursed brake fluid, a hydraulic pump to charge Ihe accumulator and an integral electronic control unit (ECU). The four wheel sensors are mounted on the wheel hubs. The ECU uses the signals produced by the sensors to calculate Ihe rotational speed of each wheel, The ECU has a self-diagnostic capability and will inhibit the operation of the ABS il a fault is detected, lighting the dashboard mounted warning lamp. The braking system will then revert lo conventional. non-ABS operation. II the nature of the laull ie not immediately obvious upon inspection, the vehicle must be taken to a Fiat dealer, who will have the diagnostic equipment
required
lo interrogate the ABS ECU electronically and pin-point the problem
2 Front brake pads - & renewal S
A
Warning: Renew BOTH sets ol front brake pads at the same
time
- NEVER renew the pads on
only
one wheel, as uneven braking may result
A
Warning: Note that the dust created by wear of the pads
may
contain asbestos, which is a health hazard. Never blow It out with compressed air, and don't inhale any of
it.
An approved filtering mask should be worn when working on the brakes. DO NOT use petrol or petroleum-based solvents to clean brake parts; use proprietary braks cleaner or methylated spirit only. 1 Firmly apply the handbrake, then jack up the front of the car and support it securely
on
axle stands (see Jacking and vehicle supporti. Remove the front roadwheeis. 2 Wording on one side of the vehicle, puth the caliper piston into its bore by pulling the caliper outwards. If necessary, press the piston back into its bore using a large G-clamp or a piston retraction tool. Keep a careful eye on the level of brake llufd in Ihe I reservoir as you do this - ensure that the
level
I does not rise above the MAX marking. 3 Whore applicable, release the locking dp and remove the pad wear indicator
wiring end
brake fluid line from the bracket at Ihe
base of
the suspension strut (see illustrations).
Petrol models without ABS 4 Remove the locking clip and exlracl the lower guide pin from the caliper (see illustrations) 5 Pivot the caliper body upwards and support In position with a length of wire or a cabie-fc. Avoid straining the hydraulic hose.
2,4a Remove the locking clip ... 2.4b ... and extract the lower guide pin from the caliper (petrol models without ABS)
Page 179 of 225

Braking system 9®3
2.6a Unscrew the upper...
Petrol models with ABS and diesel models 6 Unscrew the upper and lower caliper guide cin bolts, using a slim open-ended spanner to counterhold the head of the guide pin (see illustrations). Discard the guide pin bolts -new items must be fitted on reassembly. 7 Lift the caliper from the hub/disc assembly (see illustration). Suspend it from a suitable point on the suspension using a length of wire or 8 cable-tie, to avoid straining the hydraulic hose.
All models Caution: Do not depress the brake pedal until the caliper is refitted, or the piston will
be
pushed out of Its bore. 8 Withdraw the brake pads from the caliper bracket (see illustrations). 9 Measure the thickness of each brake pad's foclion material. If either pad is worn at any point to the specified minimum thickness or less, all four pads must be renewed. Also, the pads should be renewed if any are fouled with oil or grease; there is no satisfactory way of degreasing friction material, once contaminated. If any of the brake pads are worn unevenly, or are fouled with oil or grease, trace and rectify the cause before reassembly.
A
Warning: Do not be tempted to swap brake pads over to compensate for uneven wear. 10 if the brake pads are still serviceable, carefully clean them using a clean, fine wire brush or similar and brake cleaning fluid. Pay particular attention to the sides and back of the metal backing. Where applicable, clean out the grooves in the friction material, and pick out any large embedded panicles of dirt
or
debris. 11 Clean the surfaces of the brake pad contact points In the caliper body and caliper mounting bracket. 12 Prior to fitting the pads, check that the giide pins can slide freely in the caliper body, and check that the rubber guide pin gaiters
are
undamaged. Brush the dust and din from
the
caliper and piston, but do not inhale it. as
4 may
contain asbestos. 13 Inspect the dust seal and the area around Ihe piston for signs of damage, corrosion or
models with ABS and diesel models)
brake fluid leaks. If evident, refer to Section 3 and overhaul the caliper assembly. 14 If new brake pads are to be fitted, the caliper piston must be pushed back into the cylinder, to allow for the extra depth of the friction material. Either use a G-clamp or similar tool, or use suitable pieces of wood as levers. Provided that the master cylinder reservoir has not oeen overfilled with hydraulic fluid, there should be no spillage, but keep a careful watch on the fluid level while retracting the piston. If the fluid level rises above the MAX level line at any time, the surplus should be siphoned off. A Warning: Do not syphon the fluid by mouth, as it is poisonous; use a syringe or an old poultry baster. 15 Apply a little high temperature brake grease to the contact surfaces of the pad backing plates: take great care not to allow any grease onto the pad friction linings. Similarly, apply brake grease to the pad contact points on the caliper bracket - again take care not to apply excess grease, which may contaminate the pads. 16 Place the brake pads in position on the caliper bracket, with the friction material facing the surfaces of the brake disc. Feed the wear indicator cable through the caliper body aperture.
Petrol models without ABS 17 Pivot the caliper body down over the brake pads, then refit the guide pin and clip.
2.7 Lift the caliper from the hub/disc assembly
Petrol models with ABS and diesel models 18 Fit the caliper body in position on the caliper bracket, then fit the new guide pin bolts and tighten them to the specified torque.
AH models 19 Check that the caliper body can slide freely on the guide pins. Ensure that the flexible hydraulic hose is not twisted or kinked In any way. Turn the steering from lock to lock and check that the hose does not chafe against the suspension or steering gear. 20 Where applicable, reconnect the pad wear indicator wiring and press it into the retaining clips on the suspension. 21 Repeat the above procedure on the remaining front caliper. 22 With both sets of front brake pads fitted, depress the brake pedal repeatedly until the pads are pressed into firm contact with the brake disc, and normal pedal pressure is restored. Any sponginess felt when depressing the pedal is most probably due to air trapped inside the hydraulic system - refer to Section 11 and bleed the braking system before progressing any further. 23 Refit the roadwheels. and lower the vehicle to the ground. 24 Check the hydraulic fluid level as described in Weekly checks. 25 Check the operation of the braking system thoroughly,
2.8a Withdraw the outboard... 2.8b ... and inboard brake pads from the caliper bracket
Page 181 of 225

Braking system 9®5
2 Rotate the brake disc by hand and examine the whole of the surface area swept by the brake pads, on both sides ot the disc. Note: /( will bo necessary to remove the front brake pads to allow an adequate inspection of the disc's rear surface; refer to Section 2 tor details. 3 Typically, the disc surface will have a polished appearance and should be free from heavy scoring. Smooth rippling is produced by normal operation and does not indicate excessive wear. Deep scoring and cracks, however, are indications of more serious damage in need of correction. 4 If deep scoring Is discovered, it may be possible to have the disc reground to restore the surface, depending on the extent of the damage. To determine whether this is a feasible course of action, it will be necessary to measure the thickness of the disc, as described later. 5 Check the whole surface of the disc for cracks, particularly around the roadwheel bolt holes. A cracked disc mutt be renewed. 6 A ridge of rust and brake dust at the inner and outer edges of the disc, beyond the pad contact area is normal - this can be scraped tway quite easily. 7 Raised ridges caused by the brake pads eroding the disc material, however, are an indication of excessive wear. If close examination reveals such ridges, the oiicknoss of the disc must be measured, to usess whether it is still fit for use. 8 To measure the thickness of the disc, take readings at several points on the surface using a micrometer. In the area swept by the brake pads (see Illustration). Include any points where the disc has been scored: align me Jaws of the micrometer with the deepest ares of scoring, to get a true indication of the extent of the wear. Compare these ineasurements with the limits listed in the Specifications. If the disc has worn below its minimum thickness, at any point, it must be renewed. 9 If the discs are suspected of causing brake luddor, check the disc runout, using one of
me
following methods: Runout measurement -
DTI
gauge method 10 Refit the four roadwheel bolts, together
w.1h
one M14 plain washer per stud • this will ensure adequate disc to hub contact. Tighten te studs to 5 Nm (4 Ibf ft). 11 Clamp the DTI gauge to a stand and attach the stand, preferably via a magnetic oase. to the strut mounting bracket. Align the jauge so that its pointer rests upon the area of the dtsc swept by the brake pads, on an arc i mm from the outer edge of tho disc (soe illustration). 12 Zero the gauge and slowly rotate the disc trough one revolution, observing tho pointer rcovement. Note the maximum deflection recorded and compare the figure with that >«ted In Specifications.
4.8 Measuring brake disc thickness with a micrometer
Runout measurement -feeler blade method 13 Use the feeler blades to measure the clearance between the disc and a convenient fixed point, such as the disc backplate. Rotate the disc and measure the variation in clearance at several points around the disc, Compare the maximum figure with that listed in Specifications. 14 If the disc runout Is outside of its specified tolerance, first check that the hub Is not worn (see Steering and suspension check in Chapter 1A or 1B). If the hub is In good condition, remove the disc (as described later in this Section), rotate it through 180° and refit it. This may improve the seating and eradicate Ihe excessive runout. 15 If the runout is still unacceptable, then It may be possible to restore the disc by regrinding; consult your Fiat dealer or a machine shop for a professional opinion - it may prove more economical to purchase a new disc. If the disc cannot be reground, then it must be renewed.
Removal 16 Mark the relationship between the disc and the hub with chalk or a marker pen, to allow correct refitting. 17 To allow the disc to be removed, undo the two bolts securing (he brake caliper mounting bracket to the hub carrier (see illustration 3.7). Withdraw the brake caliper and mounting bracket assembly, complete with brake pads, from the hub carrier, and hang it from a rigid point on the suspension, using v/lre or a
4.18a Slacken and remove the disc locating studs ...
4.11 Brake disc runout measurement - DTI gauge method
cable-tie. Oo not allow it to dangle freely as this will strain the brake hose. 18 Slacken and remove the disc locating stud(s). Support the disc as you do this and lift it off as it becomes free (see illustrations). 19 Remove the polished glaze from the surface of the disc with sand/emery paper. Use small, circular motions to avoid producing a directional finish on the surface.
Refitting 20 If a new disc Is being fitted, remove the protective coating from the surface U9ing an appropriate solvent. 21 Locate Ihe disc on ihe hub so that the roadwheel bolt and locating stud holes are all correctly lined up; use the alignment marks made during removal. If the disc is being removed in an attempt to improve seating and hence runout, turn the disc through 180° and then refit it. 22 Refit the locating stud and retaining screw, tightening them securely. 23 Re-check the disc runout, using one of the methods described earlier in this Section. 24 Refil the brake caliper and mounting bracket assembly to the hub carrier. Coat the threads of the mounting bolts with locking compound, then tighten them to the specified torque. 25 Depress the brake pedal several times to bnng the brake pads into contact with the disc. 26 Refit the roadwheel and lower the vehicle to the ground. Tighten the roadwheel bolts to the specified torque. 27 Check the hydraulic fluid level as described in Weekly checks.
4,18b ... and lift off the disc as It becomes free
Page 189 of 225

10*1
Chapter 10
Suspension and steering
Contents
Front hub bearings - renewal 2 Front suspension anti-roll bar • removal and refitting 6 Front suspension lower arm - removal and refitting 4 Front suspension lower arm balljolnt - renewal 5 From suspension strut - removal, overhaul and refitting 3 General information 1 Ignition switch/steering column lock - removal and refitting 10 Manual steering gear assembly - removal, overhaul and refitting ... 12 Power steering fluid level check See Weekly checks Power steering gear assembly - removal and refitting 13 Power steering hydraulic system - bleeding 15
Degrees of difficulty
Power steering pump • removal and refitting 16 Rear hub bearings - renewal 7 Rear suspension components- removal, overhaul and refitting 8 Steering and suspension check See Chapter 1A or 1B Steering column - removal, overhaul and refitting 11 Steering gear rubber gaiters - renewal 14 Steering wheel - removal and refitting 9 Track-rod end - removal and refitting 17 Wheel alignment and steering angles • general information 18 Wheel and tyre maintenance and tyre pressure checks See Weekly checks
Easy, suitable for nowoe with little
Jg experience ^
Fakty easy,
suitable for beginner
with
J£>
some experience
^
FaMy difficult,
% suitable for competent ^
DIY mechanic
^
Difficult,
suitable for & experienced DIY « mechsmc ^
Very difficult,
^ suitable for expert
DIY
fij or professional ^
Specifications
Front suspension Type
Rear suspension Type
Steering Type Turns lock-to-lock: Manual Power assisted Toe setting (front)
Roadwheeis and tyres See Weekly checks
Torque wrench settings Front suspension Anti-roll bar bush bracket bolts Driveshaft nut:' All models except turbo diesel (M22 plain) Turbo diesel (M24 with staking and captive washer) Lower arm balljoint to hub carrier Lower arm front bush securing bolt Lower arm rear bush securing bolt Suspension strut damper nut Suspension strut to hub carrier Suspension strut to inner wing
Independent, incorporating transverse lower wishbones and coil spring-over-teiescopic damper strut units. Anti-roll bar fitted to all models.
Independent, incorporating trailing arms with telescopic dampers and coil springs.
Rack-and-pinlon, manual or power assisted, depending on model
4.4 approx. 2.9 approx. 0° (parallel) ± 1a
Nm ibfft
30 22
240 177 280 207 30 22 95 70 70 52 60 44 70 52 50 37
Page 190 of 225

Suspension and steering 10*2
Torque wrench settings (continued) Nm ibt ft Rasr suspension Damper lower securing bolt 95 70 Damper upper securing bolt 60 44 Handbrake cable support bracket-to-trailing arm screws 15 11 Hub nut 280 207 Trailing arm securing bolt 150 111 Steering Ignition switch/steering column lock securing bolts 4 3 Steering column mounting bolts 55 41 Steering gear mounting bolts 70 52 Steering wheel nut' 50 37 Subframe-to-body bolts 110 81 Track-rod end to hub carrier 40 30 Unlversaijointclampbolts 20 15 Roadwheels Roadwheel bolts 85 63 * Use a new nut
1 General information
Front suspension The front suspension is independent, comprising transverse lower wishbones, coil spring-over-damper strut units and an anti-roll bar. The hub carriors are bolted to the base of the stmt units and are linked to the lower arms by means ot balliotnts. The entire front suspension assembly is mounted on a subframe, which is In turn botted to the vehicle body.
Rear suspension The rear suspension incorporates a torsion beam axle, trailing arms, coil springs and separate telescopic dampers. In addition, a rear anil-roll bar is fitted to certain models. The components form a discrete sub-assembly which can be unboiled from the underside of the vehicle separately or as a complete unit.
Steering The two-piece steering shaft runs in a tubular column assembly, which is bolted to a bracket mounted on the vehicles bulkhead. The shaft Is articulated at its lower end by means of a universal Joint, which is clamped to the steering shaft and the steering gear pinion by moans of clamp bolts. The steering gear is mounted on the engine compartment bulkhead, and is connected to the steering arms projecting rearwards from Ihe hub carriers. The track-rods are fitted with balljoints at their inner and outer ends, to allow for suspension movement, and are threaded to facilitate ad|ustment. Hydrauiically-assisted power steering ts fittod to some models. The hydraulic system is powered by a belt-driven servo pump, which is driven from the crankshaft pulley.
Certain models are fitted with an airbag system. Sensors built into the vehicle body are triggered in the event of a front end collision and prompt an Electronic Control Unll (ECU) to activate the airbag, mounted In the centre of the steering wheel and the facia. This reduces the risk of the front seat occupants striking the steering wheel, windscreen or facia during an accident.
A
Warning: For safety reasons, owners are strongty advised to entrust to an authorised Flat dealer any work which involves disturbing the airbag system components. The airbag inflation devices contain explosive material and legislation exists to control their handling and storage, in addition, specialised test equipment Is needed to check that the airbag system Is fully operational following reassembly.
2 Front hub bearings -renewal *
Note: A balljoint separator tool, and a press or suitable alternative tools (see text) will be required for this operation. The bearing will be destroyed during the removal procedure.
Removal 1 Chock the rear wheels, apply the handbrake, then jack up the front of the vehicle and support on axle stands (see Jacking and vehicle support). Remove the appropriate roadwheel. 2 Remove the brake disc and caliper, with reference to Chapter 9. Note that the caliper body can remain bolted to its bracket: there is no need lo disconnect the brake fluid hose from the caliper. 3 With reference to Chapter 8. slacken and remove the driveshaft hub nut. 4 On models with ABS, unbolt the ABS wheel sensor, and remove the screw securing the
ABS sensor wiring to the hub carrier. Suspend the sensor away from the working ares, to avoid the possibility of damage. 5 With reference to Section 17, separate
th»
track-rod end from the hub carrier, using
a
suitable balljoint splitter. 6 Remove the two nuts from tho botts securing Ihe hub carrier to the base of th» suspension strut (refer to Section
3).
Withdrew the bolts and separate the top of hub earrtt from the strut. 7 Disconnect the outboard end of Ito driveshaft from the hub, as described durirg the driveshaft removal and refitting procedm in Chapter 8. Note: There is no naod fo disconnect the Inboard end of the
drivestett
from the transmission. Caution: Do not allow the end of tin driveshaft to hang down under its
own
weight, as this places strain on the
CV
joints; support the end of the shaft uskg wire or string. 8 Slacken and remove the nut and clamp bolt, then push the lower arm down anc separate the balljoint from the base of the tab carrier (see illustrations). 9 At this stage, it is recommended that
the bub
carrier be taken to a engineering workshop,
as
the hub and bearing should ideally be removed from the hub carrier using a hydraulic press
2.8a ... Slacken and remove the nut...
Page 191 of 225
Suspension and steering 10*3
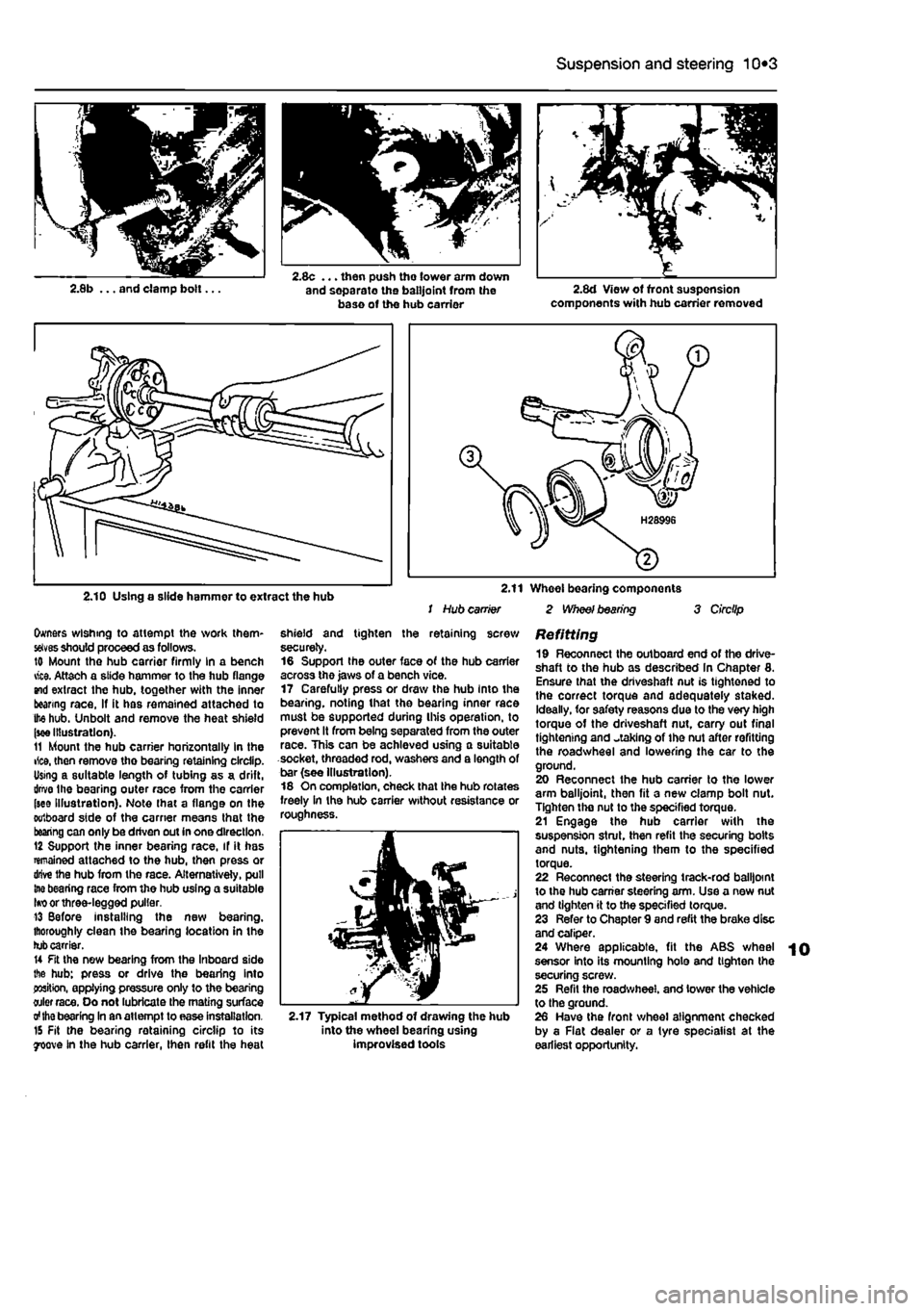
2.10 Using a slide hammer to extract the hub 2.11 Wheel bearing components / Hub carrier 2 Wheel bearing 3 Circlip
Owners wishing to attempt the work them-
selves
should proceed as follows. 10 Mount tho hub carrier firmly In a bench vice. Attach a slide hammer to the hub flange and extract the hub. together with the inner bearing race, If it has remained attached to the hub. Unbolt and remove the heat shield
(see
Illustration). 11 Mount the hub carrier horizontally in the rice, then remove tho bearing retaining circlip. Using a suitable length of tubing as a drift, drive Ihe bearing outer race from the carrier (see Illustration). Note that a flange on the outboard side of the carrier means that the bearing can only be driven out in one direction. 12 Support the inner bearing race, if it has remained attached to the hub, then press or drive the hub from the race. Alternatively, pull trie bearing race from the hub using a suitable Iw or three-legged puller. 13 Before Installing the new bearing, thoroughly clean the bearing location in the tub carrier. U Fit the new bearing from the Inboard side the hub: press or drive the bearing into position, applying pressure only to the bearing oiler race. Oo not lubricate the mating surface
ol the
bearing In an attempt to ease installation. 15 Fit the bearing retaining circlip to its 700ve in the hub carrier, then refit the heat
shield and tighten the retaining screw securely. 16 Support the outer face of the hub carrier across the jaws of a bench vice. 17 Carefully press or draw the hub into the bearing, noting that the bearing inner race must be supported during Ihis operation, to prevent It from being separated from the outer race. This can be achieved using a suitable socket, threaded rod, washers and a length of bar (see Illustration). 18 On completion, check that the hub rotates freely in the hub carrier without resistance or roughness.
2.17 Typical method of drawing the hub into the wheel bearing using improvised tools
Refitting 19 Reconnect the outboard end of the drive-shaft to the hub as described In Chapter 8. Ensure that the driveshaft nut is tightened to the correct torque and adequately staked. Ideally, for safety reasons due to the very high torque of the driveshaft nut, carry out final tightening and staking of the nut after refitting the roadwheel and lowering the car to the ground. 20 Reconnect the hub carrier to the lower arm balljoint, then fit a new clamp bolt nut. Tighten tho nut to the specified torque. 21 Engage the hub carrier with the suspension strut, then refit the securing bolts and nuts, tightening them to the specified torque. 22 Reconnect the steering track-rod balljoint to the hub carrier steering arm. Use a new nut and tighten it to the specified torque. 23 Refer to Chapter 9 and refit the brake disc and caliper. 24 Where applicable, fit the ABS wheel sensor into its mounting hole and tighten the securing screw. 25 Refit the roadwheel, and tower the vehicle to the ground. 26 Have the front wheel alignment checked by a Fiat dealer or a tyre specialist at the earliest opportunity.
Page 192 of 225

Suspension and steering 10*4
3.2 Release the brake fluid line (and where applicable, the pad wear/ABS sensor wiring) from the strut
3 Front suspension strut -removal, overhaul and refitting *
A
Warning: If renewing the Strut damper during overhaul both the left and right hand dampers should be renewed as a pair, to preserve the handling characteristics of the vehicle.
Removal 1 Chock the resr wheels, apply the handbrake, then jack up the fronl of the vehicle and support securely on axle stands (see Jacking and vehicle support). Remove the relevant roadwheel. 2 Release the brake fluid line (and wnere
3.3a Remove the two bolts (arrowed)...
applicable, the pad wear/ABS sensor wiring) from Ihe bracket on the base of the strut (see illustration). 3 Remove the two nuts from Ihe bolts securing the lower end of the strut to the hub carrier, noting that the nuls fit on the rear side of the strut (see illustrations). Withdraw the bolts, and support the hub carrier. Discard the bolts and nuts • new ones should be used on refitting. 4 Have an assistant support the strut from underneath the wheel arch then, working In the engine compartment, unscrew the two bolts and release the two stud clips that secure the strut upper mounting plate to the suspension turret. Do not unscrew the centre damper rod nut yet. Release the lower end ol the strut from the hub carrier, then withdraw the assembly from under the wheel arch.
3.7 Fully unsorew and remove tho damper rod top nut 3.3a Withdraw the washer.
3.3b ... and detach the lower end of the strut from the hub carrier
Overhaul Note: Suitable coil spring compressor fools will be required for this operation, and a
new
damper rod top nut must be used on reassembly. 5 Clamp Ihe lower end of Ihe strut in a vice fitted with jaw protectors - take care to avois deforming the mounting bracket at the lower end of the strut. Remove the protective plastic cap from the top of the strut. 6 Fit suitable spring compressors to the coil spring, and compress Ihe spring sutllciently to enable the upper spring seat to be turned by nand.
A
Warning: Ensure that the coil spring Is compressed sufficiently to remove all the tension from
tha
upper spring seat, before attempting to remove the damper rod nut. 7 Fully unscrew and remove the damper rod top nut. Countorhofd the domper rod. using
a
suitable Allen key or hex bit. as tho nut * unscrewed • do not allow the rod to rotate inside the damper (see Illustration). Discard the nut • a new one must be used on reassembly. 8 Withdraw tho washer, bush, upper mounting plate and upper spring seat • make a careful note of the order of assembly (see illustrations). 9 Withdraw the spring, complete with the compressors, thon v/ithdraw the dust cover, bump rubber and Ihe lower spring seat rubber (where fitted) (see illustrations).
Page 193 of 225

Suspension and steering 10*5
3,9s Withdraw the coll spring, complete with the compressors ... 3.9b ... then withdraw the dust cover and bump rubber 3.9c Fully dismantled strut
10 With the strut assembly now dismantled, examine all the components tor wear, damage or deformation. Check the rubber com-ponents for deterioration. Renew any of the components as necessary. 11 Examine tho damper for signs of fluid teakage. Check the damper rod for signs of pitting along its entire length, and check the stjul body for signs of damage. White holding fc
in an
upright position, test the operation of
Ihe
stmt by moving Ihe damper rod through a fut stroke, and then through short strokes of
SO
to 100 mm. In both cases, the resistance Id should be smooth and continuous. If the resistance is jerky, or uneven, or if there is any wsible sign of wear or damage to the strut, renewal is necessary. Note that the damper cannot be renewed independently, and if leakage, damage or corrosion Is evident, the complete strut/damper assembly must be renewed {in which case, the spring, upper mounting components, bushes, and associated components can be transferred to
Ihe
new strut). 12 If any doubt exists about the condition of
Ihe
coil spring, carefully remove the spring compressors, and check the spring for distortion and signs of cracking. Renew the spring if it is damaged or distorted, or if there isany doubt about its condition. a Warning: Coil springs are /j\ classified by their height when '
11
• undor load • this Is indicatod by a
coloured
paint marking on the side of the
coll windings (either green or yellow). All coll springs fitted to tho vehicle must be of the same classification to ensure the correct ride height. 13 Clamp the strut body in a vice, as dunng dismantling, then refit the lower spring seat rubber (where fitted), dust cover and bump rubber. 14 Ensure that the coil spring is compressed sufficiently to enable the upper mounting components to be fitted, then fit the spring over the damper rod. ensuring that the lower end of the spring is correctly located In the recess on the lower spring seat (soe illustration). 15 Refit the upper spring seat and upper mounting plate ensuring that the top end of
the spring is correctly located on the upper spring seat. Note that when the strut is reassembled, the orientation marking on the upper rubber mounting must be positioned in relation to the metal section of the upper mounting plate as shown, to maintain the correct front wheel castor setting (see illustration). 10 Fit the new damper rod top nut together with its washer and bush, then tighten the nut to the specified torque, counterholding the damper rod in a manner similar to that used during dismantling. Note that a suitable crows-foot adapter will be required to tighten the damper rod top nut to the specified torque. 17 Remove the spring compressors. Where applicable, refit the protective plastic cap over the damper rod top nut.
Refitting 18 Manoeuvre the strut assembly into position under the wheel arch, passing the locating stud clip through the holes in the body turret. Note that when the strut is refitted, the orientation marking on the upper mounting plate rubber mounting must be positioned in relation to the vehicle as shown, to maintain the correct front wheel castor setting • refer to illustration 3.15. Fit the upper mounting bolts, and tighten them to the specified torque (see illustration). 19 Engage Ihe lower end of the strut with the
3.14 Ensure that the lower end of the spring is correctly located in the recess (arrowed) on the lower spring seat
3.15 Correct positioning of the suspension strut upper mounting components A Left hand mounting for vehicles with manual steering B Left hand mounting tor vehicles with power-assisted steering C To front of vehicle O Orientation marking 3.18 Fit the strut upper mounting bolts, and tighten them to the specified torque
Page 194 of 225

Suspension and steering 10*6
hub earner, then fit the securing bolts and nuts, noting that the nuts fit on the rear side of the strut, and tighten to the specified torque (see illustrations). 20 Refit the brake fluid line to the bracket on Ihe base of the strut. 21 Where applicable, press the ABS wheel sensor winng into its retaining bracket. 22 Refit the roadwheel. and lower the vehicle to the ground.
4 Front suspension lower arm - removal and refitting 3.19a Fit the securing bolts, noting that the nuts fit on the rear side of the strut...
Removal 1 Chock the rear wheels, apply the handbrake, then jack up the front of the vehicle and support securely on axle stands (see Jacking and vehicle support). Remove the relevant roadwheel. 2 Unscrew the bolts securing the anti-roll bar mountings to the suspension lower arms on either side ot Ihe vehicle. Similarly, unscrew the bolts securing the anti-roll bar mountings to the suspension sub-frame (see illust-rations). Allow the ends of the anti-roll bar to pivot away from the suspension lower arms. 3 With reference to Section 2, unscrew Ihe nut. withdraw the clamp bolt and lever the end of the suspension lower arm down to release it from the base of the hub carrier.
4.2s Unscrew the bolts (arrowed) securing the anti-roll bar mountings to tho suspension lower arms...
4 Unscrow the two bolts and detach the suspension arm rear mounting bracket from the subframe (see Illustration). 5 Slacken and remove the nut from the through-bolt at the lower arm front mounting (seo illustration). Withdraw the bolt. 6 Withdraw Ihe suspension lower arm from under the vehicle. 7 With the lower arm removed, examine the lower arm Itself, and the mounting bushes, for wear, cracks or damage. S Check the balljoint for wear, excessive play, or stiffness. Also check Ihe balljoint dust boot for cracks or damage. 9 The mounting bushes and balljoint assembly are integral with the lower arm. and cannot be renewed independently. If either the bushes or the balljoint are worn or damaged, the complete lower arm assembly must be renewed.
Refitting Caution: Final tightening of all fixings must be carried out with the vehicle resting on Its wheels, or damage to the rubbor bushes will result 10 Offer the suspension arm up lo Its mountings. Fit the through-bolt to the front mounting bracket and engage it with the suspension arm bush. Fit Ihe securing nut. but do not fully tighten it at this stage.
. and tho suspension sub-frame (arrowed) 4.4 Unscrew the two bolts (arrowed) and detaoh the suspension arm rear mounting bracket from the subframe
3.19b ... and tighten them to the specified torque
11 Bolt Ihe rear mounting bracket to the subframe, but do not fully tighten the bolts a! this stage, 12 Engage the lower arm balljoint svith ifia hub carrier, then refii the balljoint clamp boll and nut. Do not fully tighten the nut at this stage. 13 Raise the anti-roll bar into position. Itan bolt the mounting brackets to the subfrarra The anti-roll bar must be pre-loaded before lis outer mounting brackets can be bolted to the suspension arms. Do this by raising tha erds of the anti-roll bar with a trolley jack and holding them in this position whilst the bracket mounting bolts are inserted and hand tightened. Do not fully tighten the bolls at trts stage, line up the holes at the ends of the anti-roll bar with those on the suspension lower arm. 14 Refit the roadwheel, and lower the vehrcfe to the ground. 15 Make sure that the vehicle is parked on level ground, then release the handbrake. Red the vehicle backwards and forwards, arc bounce the front of the vehicle to settle the suspension components. 16 Chock the wheels, then tighten all lit* anti-roll bar and suspension arm mounting nuts and bolts to the specified torque 17 On completion the front wheel alignment should be chocked by a Fiat dealer.
4.5 Slacken and romove tho nut (arrowed! from the through-bolt at the lower arm front mounting