ESP FIAT ULYSSE 2007 2.G User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FIAT, Model Year: 2007, Model line: ULYSSE, Model: FIAT ULYSSE 2007 2.GPages: 254, PDF Size: 3.42 MB
Page 71 of 254

GETTING TO KNOW YOUR CAR
70
In addition, still with the climate con-
trol system working in automatic
mode, when the external temperature
is lower than 18°C, supplementary
fans can be used to direct some warm
air to the second and third row.
If cold air is required, treated air di-
rected to the feet is distributed to all
three rows.
MAX-DEF function
Air is completely directed to the
windscreen and front side windows.
This function is used for the wind-
screen/side window rapid defrost-
ing/demisting and rear heated window
activation with only one operation.
Such function is activated manually
and enables the following functions:
– ventilation with maximum air ca-
pacity;
– air mixing completely hot;– air recirculation off (outside air);
– compressor on;
– air distribution to the windscreen;
– rear heated window on.
When the MAX-DEF function is on
it is possible to alter the air capacity
(the minimum corresponds to 1 fan
notch) and to deactivate the rear heat-
ed window.
The rear heated window works for
a limited time and turns off automati-
cally.
MIXING
Temperature can be adjusted rang-
ing from a minimum of 14°C to a max-
imum of 28°C, i.e. “completely cold”
and “completely hot”. AIR QUALITY
The system is fitted with a pollen fil-
ter which prevents dust particles and
pollen coming from the outside from
getting into the system.
Have the pollen filter checked at a
Fiat Dealership at least once a year,
possibly at the beginning of spring/
summer.
If the car is often used in dusty or
highly polluted areas, you should check
or change the pollen filter more fre-
quently.
Failure to replace the fil-
ter can reduce the cli-
mate control system’s ef-
ficiency considerably.
Page 89 of 254
GETTING TO KNOW YOUR CAR
88
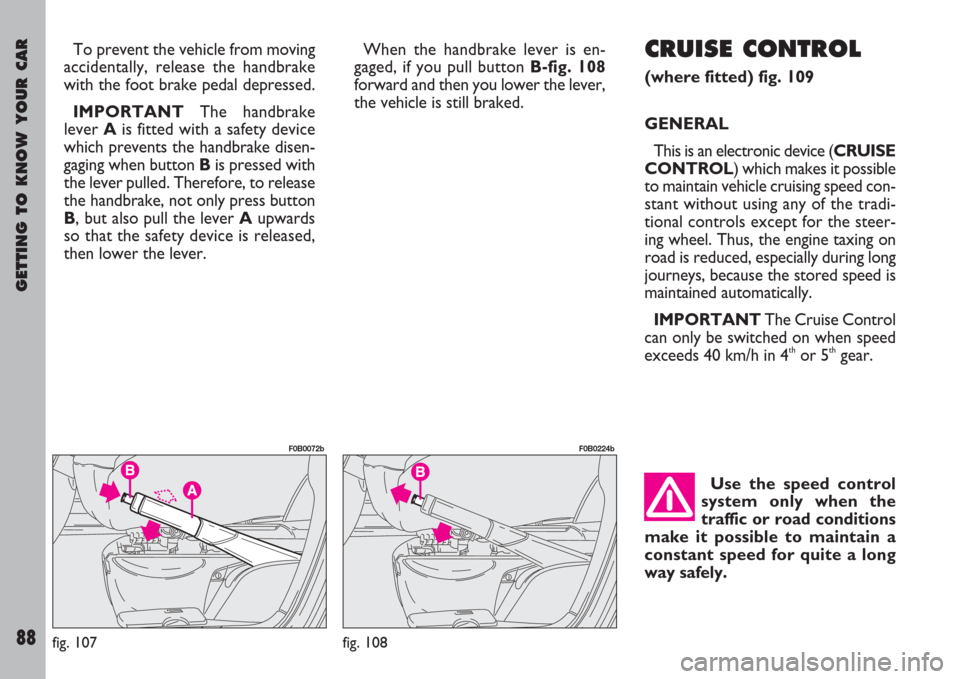
To prevent the vehicle from moving
accidentally, release the handbrake
with the foot brake pedal depressed.
IMPORTANTThe handbrake
lever A is fitted with a safety device
which prevents the handbrake disen-
gaging when button Bis pressed with
the lever pulled. Therefore, to release
the handbrake, not only press button
B, but also pull the lever Aupwards
so that the safety device is released,
then lower the lever.When the handbrake lever is en-
gaged, if you pull button B-fig. 108
forward and then you lower the lever,
the vehicle is still braked.CRUISE CONTROL
(where fitted) fig. 109
GENERAL
This is an electronic device (CRUISE
CONTROL) which makes it possible
to maintain vehicle cruising speed con-
stant without using any of the tradi-
tional controls except for the steer-
ing wheel. Thus, the engine taxing on
road is reduced, especially during long
journeys, because the stored speed is
maintained automatically.
IMPORTANTThe Cruise Control
can only be switched on when speed
exceeds 40 km/h in 4
thor 5thgear.
fig. 107
F0B0072b
fig. 108
F0B0224b
Use the speed control
system only when the
traffic or road conditions
make it possible to maintain a
constant speed for quite a long
way safely.
Page 93 of 254

GETTING TO KNOW YOUR CAR
92
Neutral (N)
It corresponds to the neutral posi-
tion of a traditional mechanic gear.Reverse (R)
To engage the reverse
the vehicle must be sta-
tionary, the engine idling
and the accelerator pedal re-
leased. Then follow the instruc-
tions given in “Engine starting”
paragraph in this chapter.
When the engine is at Rit is not pos-
sible to start the engine.Parking (P)
Pposition locks drive wheels.
Engage this gear only when the ve-
hicle is stationary and apply also the
handbrake. Then follow the instruc-
tions given in “Engine starting” para-
graph in this chapter.
IMPORTANTIf the lever is not
positioned correctly, the last stable en-
gaged gear flashes on the display. To move the lever from
N, release the accelerator
pedal, let the engine idling
and follow the instructions given
in “Engine starting” paragraph in
this chapter.
When the lever is at N it is possible
to start the engine.
Page 115 of 254

GETTING TO KNOW YOUR CAR
114
HEADLAMPS
XENON LAMPS (where fitted)
Xenon lamps work with a voltaic arc
in a pressure Xenon saturated envi-
ronment, in place of the traditional fil-
ament.
The produced light is far greater than
that of traditional lamps, both for its
quality (lighter) and its lighting range.
The advantages in using such lamps
are the following: less eyes fatigue, im-
proved driver’s orientation and driving
safety, especially with the bad weath-
er, with fog and/or inadequate road
signs, illumination of side bands usu-
ally in the shadow.Illumination of side bands consider-
ably improves driving safety because
the driver is able to identify other road
users on the road margins (pedestri-
ans, bikers and motor-bikers).
When the lights come on, the volta-
ic arc tension is very high, but then it
falls.
The maximum light is obtained after
0.5 seconds after turning the head-
lamps on.
The great light produced by this type
of headlamps requires an automatic
system for maintaining the headlight
beam constant and preventing dazzling
other vehicles in the event of sudden
braking, acceleration or while carrying
heavy loads. Never load the rack with
more than the weight al-
lowed (see the “Technical
specifications” section).
Be careful not to knock
the tailgate into objects
on the roof rack.
After travelling a few
miles, check that the an-
chorage bolts of the at-
tachments are still fully tight.
Page 118 of 254

GETTING TO KNOW YOUR CAR
117
In the event of a failure, the braking
capacity of the car will not be pe-
nalised in any way although the an-
tilocking effect cannot be relied upon.
If this is the first time you are dri-
ving a car with ABS, we recommend
you learn how to use it by testing the
brakes on slippery ground - obvious-
ly in conditions of safety and respect-
ing the highway code enforced in the
country you are driving in - and read
the following notes carefully.
The advantage of ABS with respect
to the traditional braking system is the
fact that maximum drivability is en-
sured even when braking to the grip
limit and wheel locking is prevented.
You should, however, not always ex-
pect the braking distance to decrease.
For example, on soft surfaces - i.e.
gravel or fresh snow on a slippery
road - the braking distance could, in
fact, increase.To make the most of the possibilities
offered by the anti-locking system
when it is required, attain to the fol-
lowing advice.If there is a fault, the in-
strument panel warning
light >will come on. At
this point, reduce speed and go to
a Fiat Dealership to have your car
checked and full system opera-
tion restored.
When the ABS inter-
venes and you feel the
brake pedal pushing, do
not release the pressure on the
pedal but hold it down without
hesitation. This will ensure the
car stops in the shortest time
compatibly to the road surface
conditions.In any case, always pay the utmost
care when braking and cornering even
with ABS.
The most important piece of advice
is, however, the following: The ABS makes the
most of the available grip
but cannot increase it.
Consequently, drive very care-
fully on slippery roads without
taking unnecessary risks.
When the ABS inter-
venes, you have reached
the grip limit between
tyres and road surface: slow
down to suit speed to the avail-
able grip.
Page 119 of 254

GETTING TO KNOW YOUR CAR
118
MBA AND HBA
SYSTEMS
(where fitted)
The MBA (Mechanic Brake Assis-
tance) and HBA (Hydraulic Brake As-
sistance) systems increase braking
pressure in emergency braking. When
the driver is forced by the critical dri-
ving conditions to press violently the
brake pedal, the system increases the
braking pressure to assure the quick-
est vehicle stop.
These two systems behave in the
same way, the only difference is that
one increases braking pressure
through the ESP control unit and the
other with a mechanic action. By following these indications you
will be able to brake in the best con-
ditions in all events.
IMPORTANTVehicles fitted with
ABS may only be fitted with wheel
rims, tyres and brake pads of the make
and model approved by the vehicle
manufacturer.
The system is completed with an
Electronic Brake Distributor EBD
which increases the brake system per-
formance and employs the ABS con-
trol unit and sensors.
If the xbrake fluid low
warning light comes on,
stop the vehicle immedi-
ately and contact the nearest Fi-
at Dealership. Fluid leaks from
the hydraulic system, in fact, can
compromise brake system oper-
ation, both traditional systems
and systems with ABS. The car is fitted with an
electronic braking device
(EBD). The xand >
warning lights will come on at the
same time when the engine is
running to indicate that there is
an EBD system failure. In this
case violent braking may be ac-
companied by early rear wheel
locking with the possibility of
skidding. Drive the car extreme-
ly carefully to the nearest Fiat
Dealership to have the system
checked.Warning light >alone,
with the engine running,
normally indicates a fault
in the ABS system. In this case,
the braking system is still effi-
cient, though without the an-
tilocking device. Under these
conditions, performance of the
EBD system may be reduced. Al-
so in this case, you are advised to
go immediately to the nearest Fi-
at Dealership, driving in such a
way to avoid sharp braking to
have the system checked.
Page 120 of 254

GETTING TO KNOW YOUR CAR
119
ESP SYSTEM
(where fitted)
The ESP (Electronic Stability Pro-
gram) system controls the vehicle sta-
bility. It brakes drive wheels in a dif-
ferent way from the other wheels and
if grip is lost, it helps the car recover
stability and the correct travelling di-
rection.
While travelling the vehicle is subject
to side and longitudinal forces which
can be controlled by the driver as long
as the tyre grip is good. When the tyre
grip falls below the minimum level, the
vehicle starts deviating from the dri-
ver’s wished direction.
Especially when travelling on uneven
roads (paving, water, ice or earth) or
irregular roads (bends or other ob-
stacles) the tyre grip may be greatly
reduced.When the sensors detect such con-
ditions, the ESP system intervenes on
the engine and the brakes and makes
the vehicle recover stability.
The system perfor-
mance, in terms of active
safety, should not make
the driver run useless risks. Dri-
ving must suit road conditions, vis-
ibility and traffic. Nevertheless it
is always the behaviour of the dri-
ver that determines road safety.
The ESP system helps the driver keep
the vehicle control in the event of tyre
grip loss. Anyway, the ESP operation
depends on the grip between tyre and
roadbed.
ESP SYSTEM OPERATION
The ESP system is activated when-
ever the engine is started; it can be
turned on/off manually by pressing
button A-fig. 165on the dashboard.
fig. 165
F0B0112b
Page 121 of 254

Cars with ESP may only
be fitted with tyres of the
same make, model and
size and be in good conditions.
GETTING TO KNOW YOUR CAR
120
ESP SYSTEM ACTION
The ESP system action is signalled by
warning light
ñflashing to inform the
driver that the vehicle stability and grip
are critical.
ESP failure indication
In the event of an ESP system failure,
it turns off automatically and warning
light
ñcomes on together with the
relative message on the multifunction
display.
In the event of an ESP system failure,
the vehicle behaves as the version
without this type of system. We rec-
ommend you to contact a Fiat Deal-
ership as soon as possible. The ESP main components are:
– an electronic control unit which
processes the sensor signals and ap-
plies the best strategy;
– an angle sensor which detects the
steering position;
– four sensors which detect each
wheel rotation speed;
– a braking system pressure sensor;
– a yawing sensor which detects the
vehicle spinning around a vertical axis;
– a sensor which detects side accel-
eration (centrifugal force).
The ESP heart is the control unit
which processes the centrifugal forces
deriving from cornering on the basis
of the data coming from the sensors
installed on the vehicle. The yawing
sensor detects the vehicle spinning
around its vertical axis. Centrifugal
forces resulting from cornering are de-
tected by a highly sensible side accel-
eration sensor.
The ESP stabilising action is based on
the control unit processing of data
coming from the steering wheel rota-
tion sensors, side acceleration sensors
and wheel rotation speed sensors.These signals make the control unit
recognise the driver’s manoeuvre
when he/she turns the steering wheel.
The control unit processes such in-
formation and is able to detect the ve-
hicle position at any time and compare
it with the driver’s wished direction. If
they do not match, the control unit is
able to adjust the vehicle’s position in-
stantly, by choosing the best strategy:
it can brake one or more wheels with
different force and reduce the engine
power, if needed.
Adjustments are made for continu-
ously adapting to the driver’s wished
travelling direction.
The ESP system action improves the
vehicle safety in many critical situations
and is useful especially when the
roadbed grip changes.
Page 122 of 254

GETTING TO KNOW YOUR CAR
121
TC and ASR FUNCTIONS
The TC (Traction Control) and ASR
(Anti Slip Regulation), integrated in the
ESP system, prevent drive wheel slip
in poor grip conditions.
Two different control systems inter-
vene:
– if both drive wheels slip because of
excessive power, the ASR system re-
duces the engine power;
– if only one drive wheel slips, the TC
function brakes the slipping wheel as
a self-locking differential would do.
The TC and ASR functions are par-
ticularly useful in the following condi-
tions:
– inside wheel slipping due to load
variations and excessive acceleration;too much power to the wheels de-
pending also on the road conditions;
– acceleration on snowy or icy roads;
– wet road grip loss.
The TC and ASR system
performance, in terms of
active safety, should not
make the driver run useless risks.
Driving must suit road condi-
tions, visibility and traffic. Never-
theless it is always the behaviour
of the driver that determines
road safety.
Cars with TC and ASR
functions may only be fit-
ted with tyres of the same
make, model and size and be in
good conditions.IMPORTANTWhen travelling on
snowy roads with the snow chains ap-
plied, we suggest turning the ESP sys-
tem off and switching on the TC and
ASR functions, so that the drive action
is increased in the event the drive
wheels slip.
MSR FUNCTION
The MSR (Motor Schleppmoment
Regelung) function controls automat-
ically the engine braking torque while
shifting the gears. In the event of sud-
den gear shifting, this function prevents
the drive wheel dragging, especially in
poor grip conditions, and restores the
vehicle stability.
Page 128 of 254

GETTING TO KNOW YOUR CAR
127
SIDE AIR BAGS
(SIDE BAG - WINDOW BAG)
Purpose of the side airbags is to in-
crease passenger protection in the
event of a side impact of medium to
high severity.
They consist of two instantly inflat-
able bag types:
– side bags are housed in the back
rest of the front seats; this solution
makes it possible to always have the
cushion in the optimum position with
respect to the passenger, regardless of
the seat position;
– window bags, being a “curtain” sys-
tem, are housed in the side roof lin-
ing and are covered by a special trim
that enables bag deflation downwards.
This solution, designed to protect the
head, offers the occupants the highest
degree of protection in the case of aside crash due to the wide deflation
surface of the bags.
In the event of a side collision the
electronic control unit processes the
signals coming from a deceleration
sensor and, if required, triggers the in-
flation of the bags.
The bags inflate immediately, setting
as a protective barrier between the
passengers and the car door. The bags
deflate immediately afterwards.
In minor side crashes (for which the
restraining action of the seat belts is
sufficient), the air bags are not de-
ployed.Therefore the side air bags are not
a replacement of but complementary
to the belts, which you are recom-
mended to always wear, as specified
by law in Europe and most non-Euro-
pean countries.
Operation of the side air bags is not
disabled by the passenger’s front air
bag deactivation switch, as described
in the previous paragraph.
IMPORTANTThe front and/or
side air bags may be deployed if the car
is subject to heavy knocks or accidents
involving the underbody area, such as
for example violent shocks against
steps, kerbs or low obstacles, falling of
the car in big holes or sags in the road.