ABS FIAT UNO 1983 Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FIAT, Model Year: 1983, Model line: UNO, Model: FIAT UNO 1983Pages: 303, PDF Size: 10.36 MB
Page 112 of 303
10 Trailing arm rubber bush-
renewal
3
1A worn trailing arm rubber bush may be
renewed in the following way.
2Raise the rear of the car and support
securely on axle stands placed under the
body side-members or sill jacking points.
3Remove the roadwheels.
4Unscrew and remove both pivot bolts
which hold the forward ends of the trailing
arms to the body brackets.5Pull the trailing arms downward out of the
body brackets.
6A two-legged puller may be used to press
the old bush out and to force the new one in.
Smear the bush with soapy water or brake
fluid to facilitate fitting.
7Reconnect the trailing arms to the body
brackets. Use jacks if necessary to push the
arms upwards into the brackets.
8Tighten the pivot bolts to the specified
torque, but only when the car has been
located with four occupants or the equivalent
plus 40 kg (88 lb) of luggage.11 Rear suspension-
removal and refitting
3
1Raise the rear of the car, support it securely
and remove the rear road wheels.
2Unhook the brake pressure regulating valve
arm tension spring from its bracket.
3Disconnect the handbrake cables from the
brake backplate levers.
4Disconnect the flexible brake hose at its
junction with the rigid pipeline adjacent to the
pressure regulating valve. Cap the open ends
of hose and pipe.
5Support the trailing arms and then
disconnect the shock absorber upper
mountings.
6Unbolt the trailing arm forward end support
brackets from the body, lower the complete
rear suspension and withdraw it from under
the car.
7Refitting is a reversal of removal, but tighten
the trailing arm pivot bolts to the specified
torque only when the car is loaded with four
occupants and 40 kg (88 lb) of luggage
(photo).
8Bleed the brakes as described in Chap-
ter 8.
Suspension 11•5
Fig. 11.9 Removing trailing arm pivot bolt
(Sec 10)
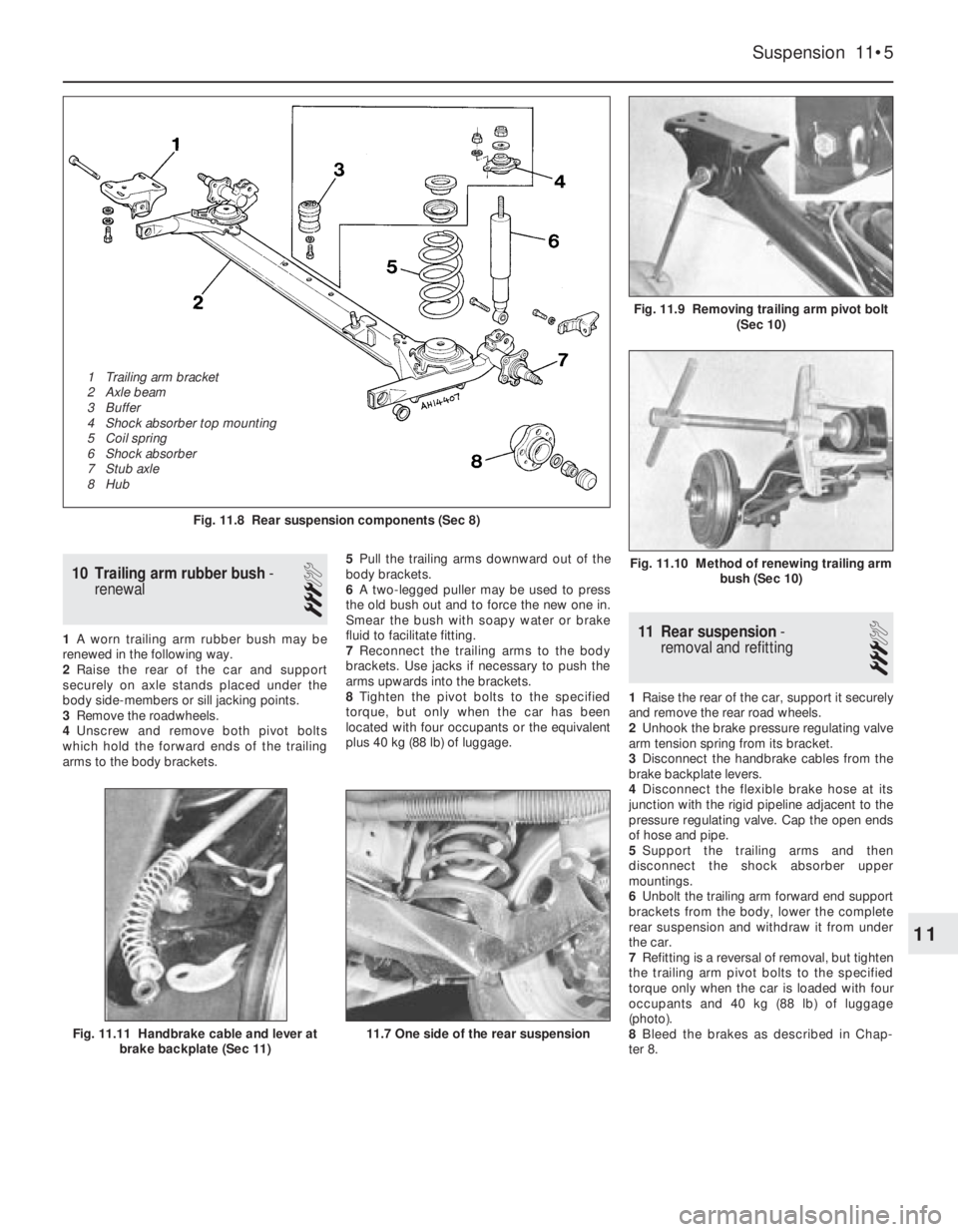
Fig. 11.8 Rear suspension components (Sec 8)
11.7 One side of the rear suspensionFig. 11.11 Handbrake cable and lever at
brake backplate (Sec 11)
Fig. 11.10 Method of renewing trailing arm
bush (Sec 10)
11
1 Trailing arm bracket
2 Axle beam
3 Buffer
4 Shock absorber top mounting
5 Coil spring
6 Shock absorber
7 Stub axle
8 Hub
Page 113 of 303

Car pulls to one side
m mWorn or weak shock absorbers or struts on one side
Excessive roll on corners
m
mWeak shock absorbers or struts
m mCoil spring weak or cracked
Car wanders or skips on rough surfaces
m
mDefective shock absorbers or struts
Vibration and wheel wobble
m
mLoose or defective shock absorbers or struts
Excessive or uneven tyre wear
m
mWorn suspension components
Fault finding - suspension
Note: Before diagnosing suspension defects, be sure that trouble is not due to incorrect or uneven tyre pressures, in inappropriate combinations.
11•6 Suspension
Page 115 of 303

can be drained out (photos). Brightwork
should be treated in the same way as
paintwork. Windscreens and windows can be
kept clear of the smeary film which often
appears, by the use of proprietary glass
cleaner. Never use any form of wax or other
body or chromium polish on glass.
3 Maintenance-
upholstery and carpets
1
Mats and carpets should be brushed or
vacuum-cleaned regularly, to keep them free
of grit. If they are badly stained, remove them
from the vehicle for scrubbing or sponging,
and make quite sure they are dry before
refitting. Seats and interior trim panels can be
kept clean by wiping with a damp cloth. If they
do become stained (which can be more
apparent on light-coloured upholstery), use a
little liquid detergent and a soft nail brush to
scour the grime out of the grain of the
material. Do not forget to keep the headlining
clean in the same way as the upholstery.
When using liquid cleaners inside the vehicle,
do not over-wet the surfaces being cleaned.
Excessive damp could get into the seams and
padded interior, causing stains, offensive
odours or even rot.
4 Minor body damage-
repair
3
Note:For more detailed information about
bodywork repair, Haynes Publishing produce
a book by Lindsay Porter called “The Car
Bodywork Repair Manual”. This incorporates
information on such aspects as rust treatment,
painting and glass-fibre repairs, as well asdetails on more ambitious repairs involving
welding and panel beating.
Repairs of minor scratches in
bodywork
If the scratch is very superficial, and does
not penetrate to the metal of the bodywork,
repair is very simple. Lightly rub the area of
the scratch with a paintwork renovator, or a
very fine cutting paste, to remove loose paint
from the scratch, and to clear the surrounding
bodywork of wax polish. Rinse the area with
clean water.
Apply touch-up paint to the scratch using a
fine paint brush; continue to apply fine layers
of paint until the surface of the paint in the
scratch is level with the surrounding
paintwork. Allow the new paint at least two
weeks to harden, then blend it into the
surrounding paintwork by rubbing the scratch
area with a paintwork renovator or a very fine
cutting paste. Finally, apply wax polish.
Where the scratch has penetrated right
through to the metal of the bodywork, causing
the metal to rust, a different repair technique
is required. Remove any loose rust from the
bottom of the scratch with a penknife, then
apply rust-inhibiting paint to prevent the
formation of rust in the future. Using a rubber
or nylon applicator, fill the scratch with
bodystopper paste. If required, this paste can
be mixed with cellulose thinners to provide a
very thin paste which is ideal for filling narrow
scratches. Before the stopper-paste in the
scratch hardens, wrap a piece of smooth
cotton rag around the top of a finger. Dip the
finger in cellulose thinners, and quickly sweep
it across the surface of the stopper-paste in
the scratch; this will ensure that the surface of
the stopper-paste is slightly hollowed. The
scratch can now be painted over as described
earlier in this Section.
Repairs of dents in bodywork
When deep denting of the vehicle’s
bodywork has taken place, the first task is to
pull the dent out, until the affected bodywork
almost attains its original shape. There is little
point in trying to restore the original shape
completely, as the metal in the damaged area
will have stretched on impact, and cannot be
reshaped fully to its original contour. It isbetter to bring the level of the dent up to a
point which is about 3 mm below the level of
the surrounding bodywork. In cases where the
dent is very shallow anyway, it is not worth
trying to pull it out at all. If the underside of the
dent is accessible, it can be hammered out
gently from behind, using a mallet with a
wooden or plastic head. Whilst doing this,
hold a suitable block of wood firmly against
the outside of the panel, to absorb the impact
from the hammer blows and thus prevent a
large area of the bodywork from being
“belled-out”.
Should the dent be in a section of the
bodywork which has a double skin, or some
other factor making it inaccessible from
behind, a different technique is called for. Drill
several small holes through the metal inside
the area - particularly in the deeper section.
Then screw long self-tapping screws into the
holes, just sufficiently for them to gain a good
purchase in the metal. Now the dent can be
pulled out by pulling on the protruding heads
of the screws with a pair of pliers.
The next stage of the repair is the removal
of the paint from the damaged area, and from
an inch or so of the surrounding “sound”
bodywork. This is accomplished most easily
by using a wire brush or abrasive pad on a
power drill, although it can be done just as
effectively by hand, using sheets of abrasive
paper. To complete the preparation for filling,
score the surface of the bare metal with a
screwdriver or the tang of a file, or
alternatively, drill small holes in the affected
area. This will provide a really good “key” for
the filler paste.
To complete the repair, see the Section on
filling and respraying.
Repairs of rust holes or gashes
in bodywork
Remove all paint from the affected area,
and from an inch or so of the surrounding
“sound” bodywork, using an abrasive pad or a
wire brush on a power drill. If these are not
available, a few sheets of abrasive paper will
do the job most effectively. With the paint
removed, you will be able to judge the severity
of the corrosion, and therefore decide
whether to renew the whole panel (if this is
possible) or to repair the affected area. New
body panels are not as expensive as most
people think, and it is often quicker and more
satisfactory to fit a new panel than to attempt
to repair large areas of corrosion.
Remove all fittings from the affected area,
except those which will act as a guide to the
original shape of the damaged bodywork (eg
headlight shells etc). Then, using tin snips or a
hacksaw blade, remove all loose metal and
any other metal badly affected by corrosion.
Hammer the edges of the hole inwards, in
order to create a slight depression for the filler
paste.
Wire-brush the affected area to remove the
powdery rust from the
surface of the remaining metal. Paint the
12•2 Bodywork
2.4B Sill drain with non-return valve2.4A Door drain hole
If the inside of the vehicle
gets wet accidentally, it is
worthwhile taking some
trouble to dry it out properly,
particularly where carpets are involved.
Do not leave oil or electric heaters
inside the vehicle for this purpose.
Page 119 of 303

rag between the handle and the door trim
panel at its lower gap (photo).
5Insert the fingers or a broad blade between
the trim panel and the door and release the
panel.
6Remove the trim panel and the waterproof
sheet (photo).
7Refitting is a reversal of removal, but when
refitting the window regulator handle locate its
retaining spring clip fully and then simply
locate the handle on its splined shaft and
strike it sharply with the hand. Make sure that
with the window fully closed, the angle of the
regulator handle matches the one on the
opposite door (photo).
12 Door- dismantling
3
1Remove the trim panel as described in the
preceding Section.
Lock remote control handle
2Slide the handle rearwards to disengage
the tabs from the cut-outs.
3Rotate the lock handle and disconnect it
from the link rod.
Door glass
4Extract the screws from the glass
mounting.
5With the glass fully lowered, remove the
weatherseal strips from the glass slot in the
door.
Fig. 12.9 Door window regulator fixing
screws (Sec 12)Fig. 12.8 Removing door glass (Sec 12)
Fig. 12.7 Removing door weatherseal
(Sec 12)Fig. 12.6 Door glass mounting screw
(Sec 12)
12•6 Bodywork
11.7 Window regulator handle ready for
fitting11.6 Removing door trim panel11.4 Window regulator handle removed
11.3B Remote control handle withdrawn11.3A Removing remote control handle
escutcheon11.2 Door tidy bin screw
Page 178 of 303
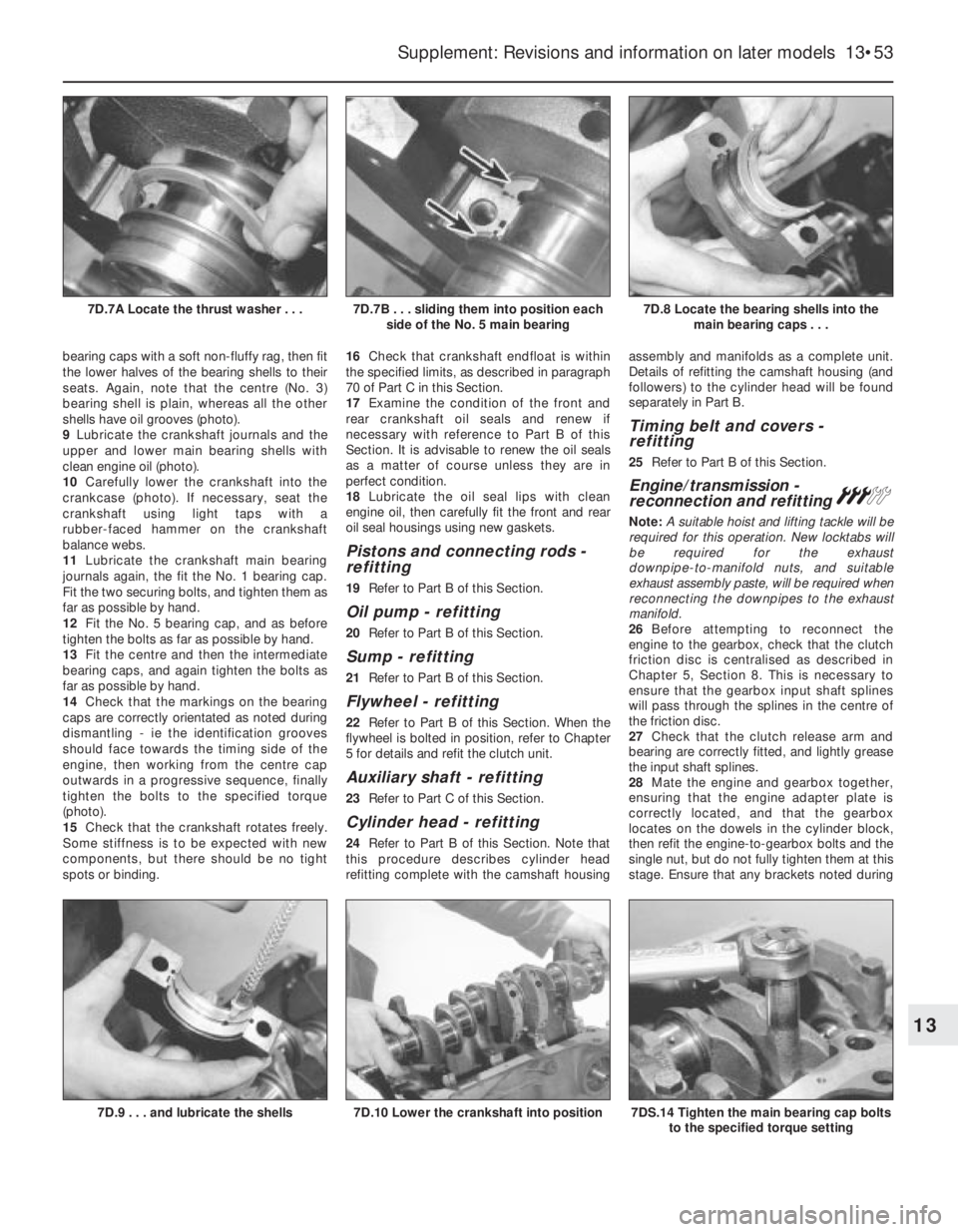
bearing caps with a soft non-fluffy rag, then fit
the lower halves of the bearing shells to their
seats. Again, note that the centre (No. 3)
bearing shell is plain, whereas all the other
shells have oil grooves (photo).
9Lubricate the crankshaft journals and the
upper and lower main bearing shells with
clean engine oil (photo).
10Carefully lower the crankshaft into the
crankcase (photo). If necessary, seat the
crankshaft using light taps with a
rubber-faced hammer on the crankshaft
balance webs.
11Lubricate the crankshaft main bearing
journals again, the fit the No. 1 bearing cap.
Fit the two securing bolts, and tighten them as
far as possible by hand.
12Fit the No. 5 bearing cap, and as before
tighten the bolts as far as possible by hand.
13Fit the centre and then the intermediate
bearing caps, and again tighten the bolts as
far as possible by hand.
14Check that the markings on the bearing
caps are correctly orientated as noted during
dismantling - ie the identification grooves
should face towards the timing side of the
engine, then working from the centre cap
outwards in a progressive sequence, finally
tighten the bolts to the specified torque
(photo).
15Check that the crankshaft rotates freely.
Some stiffness is to be expected with new
components, but there should be no tight
spots or binding.16Check that crankshaft endfloat is within
the specified limits, as described in paragraph
70 of Part C in this Section.
17Examine the condition of the front and
rear crankshaft oil seals and renew if
necessary with reference to Part B of this
Section. It is advisable to renew the oil seals
as a matter of course unless they are in
perfect condition.
18Lubricate the oil seal lips with clean
engine oil, then carefully fit the front and rear
oil seal housings using new gaskets.
Pistons and connecting rods -
refitting
19Refer to Part B of this Section.
Oil pump - refitting
20Refer to Part B of this Section.
Sump - refitting
21Refer to Part B of this Section.
Flywheel - refitting
22Refer to Part B of this Section. When the
flywheel is bolted in position, refer to Chapter
5 for details and refit the clutch unit.
Auxiliary shaft - refitting
23Refer to Part C of this Section.
Cylinder head - refitting
24Refer to Part B of this Section. Note that
this procedure describes cylinder head
refitting complete with the camshaft housingassembly and manifolds as a complete unit.
Details of refitting the camshaft housing (and
followers) to the cylinder head will be found
separately in Part B.
Timing belt and covers -
refitting
25Refer to Part B of this Section.
Engine/transmission -
reconnection and refitting#
Note: A suitable hoist and lifting tackle will be
required for this operation. New locktabs will
be required for the exhaust
downpipe-to-manifold nuts, and suitable
exhaust assembly paste, will be required when
reconnecting the downpipes to the exhaust
manifold.
26Before attempting to reconnect the
engine to the gearbox, check that the clutch
friction disc is centralised as described in
Chapter 5, Section 8. This is necessary to
ensure that the gearbox input shaft splines
will pass through the splines in the centre of
the friction disc.
27Check that the clutch release arm and
bearing are correctly fitted, and lightly grease
the input shaft splines.
28Mate the engine and gearbox together,
ensuring that the engine adapter plate is
correctly located, and that the gearbox
locates on the dowels in the cylinder block,
then refit the engine-to-gearbox bolts and the
single nut, but do not fully tighten them at this
stage. Ensure that any brackets noted during
Supplement: Revisions and information on later models 13•53
7D.8 Locate the bearing shells into the
main bearing caps . . .7D.7B . . . sliding them into position each
side of the No. 5 main bearing
7DS.14 Tighten the main bearing cap bolts
to the specified torque setting7D.10 Lower the crankshaft into position7D.9 . . . and lubricate the shells
13
7D.7A Locate the thrust washer . . .
Page 194 of 303

39Now use the ohmmeter to check the
resistance of the following components.
Supplementary air valve
40Resistance between the terminals should
be between 40 and 60 ohms at 20ºC (68ºF).
Airflow meter
41Resistance between terminals 5 and 8 of
the potentiometer should be between 330 and
360 ohms at 20ºC (68ºF).
42Resistance between terminals 8 and 9 of
the internal circuit should be between 190 and
210 ohms at 20ºC (68ºF) and between 170
and 190 ohms at 60ºC (140ºF).
Coolant temperature sensor
43At 20ºC (68ºF) the resistance should be
between 2 and 4 k ohms. At 50ºC (122ºF) the
resistance should be between 600 and
900 ohms. At 90ºC (194ºF) the resistance
should be between 100 and 300 ohms.
Fuel injectors
44The winding resistance should be
between 15 and 17 ohms at 20ºC (68ºF).
Throttle position switch
45With the throttle butterfly valve closed,
there should be continuity between ter-
minals 18 and 2, and with the valve fully open,
there should be no continuity between
terminals 18 and 3.
46The throttle position switch should not be
disturbed unless absolutely necessary. If it
has to be removed, then refit it so that themicroswitch is heard to click immediately the
throttle butterfly is opened.
Fuel injection system -
mechanical tests ª
Fuel pump
47To test the pressure of the fuel pump, a
pressure gauge will be required, connected
into the fuel delivery hose.
48Remove the multipin plug from the system
control relay and bridge terminals 87b and 30.
49Turn the ignition switch on. The pump
should operate and indicate a pressure of
between 2.8 and 3.0 bars (40 and 44 lbf/in
2).
50To check the operation of the peak
pressure regulator, pinch the fuel return hose.
If the fuel pressure increases, the regulator
must be faulty, and should be renewed.
51Check that the fuel pressure increases
when, with the engine idling, the accelerator is
depressed sharply.
Supplementary air valve
52With the engine at normal operating
temperature and idling, pinch the
supplementary air valve hose using a pair of
pliers. The engine speed should not drop by
more than 50 rpm. If it does, renew the valve.
Fuel injection system
components -
removal and refitting
ª
53Disconnect the battery before carrying out
any of the following operations.
Air cleaner
54Remove the cover and filter element as
previously described.
55Disconnect the duct from the air cleaner
casing, and then unbolt and remove the
casing. Note that the lower bracket bolt need
not be completely removed, only unscrewed,
due to the design of the bracket. The air
cleaner metal duct is routed over the top of
the radiator (photos).
Airflow meter
56Release the securing clip and disconnect
the air intake duct (photo).
57Release the securing clip and disconnect
the air outlet duct (photo).
58Disconnect the wiring plug.
59Unscrew the fixing screws and remove
the airflow meter from its mounting bracket.
Supplement: Revisions and information on later models 13•69
9C.55B Removing the air cleaner casing
upper bracket9C.55A Disconnecting the duct from the air
cleanerFig. 13.43 System control relay connector
plug terminals 1301 cc Turbo ie engine
(Sec 9C)
9C.57 Air outlet duct securing clip removal
from airflow meter
9C.55C Air cleaner casing lower bracket
and bolt (arrowed)
9C.56 Air intake duct at airflow meter
(securing clip arrowed)9C.55D Air cleaner metal duct over
radiator
13
Page 202 of 303

air temperature sensor. Undo the retaining
screw and remove the sensor from the
injector unit (photo).
50Refit in the reverse order of removal.
Fuel injector -
removal and refittingÁ
51Depressurise the fuel system as
described previously, then disconnect the
battery negative lead.
52Remove the air cleaner unit.
53Release the injector feed wiring mutliplug
and detach it from the injector.
54Bend over the locking tabs retaining the
injector screws, then undo and remove the
screws. Withdraw the injector retaining collar,
then carefully withdraw the injector (noting its
orientation) followed by its seal.
55Refit in the reverse order of removal.
Always use new seals in the unit and the
retaining collar and lightly lubricate them with
clean engine oil prior to assembly. Take care
not to damage the seals when fitting and also
when the injector is fitted; check that it
engages correctly.
Fuel injection electronic
control unit (ECU) -
removal and refitting
Á
56The control unit is located under the facia
on the driver’s side of the vehicle. Commence
by disconnecting the battery negative lead.
57To gain access to the control unit, detach
and remove the trim panel from the underside
of the facia on the driver’s side of the car.
58Disconnect the wiring multiplug from the
control unit, then undo the retaining screw
and remove the unit from the car (photos).
59Refit in the reverse order of removal.
Inlet manifold -
removal and refittingÁ
60Remove the fuel injector unit as described
previously.
61Drain the cooling system as described in
Section 8 of this Chapter.
62Detach the coolant hose and coolant
temperature sensor from the inlet manifold.
63Unbolt and remove the accelerator
cable/throttle linkage support bracket from
the top of the inlet manifold. The cable can be
left attached to the bracket.64Detach the brake servo vacuum hose
from the connector on the manifold.
65Unscrew and remove the inlet manifold
securing bolts and nuts and remove the
manifold from the cylinder head. As they are
removed, note the location of the fastenings
and their spacers.
66Remove the gasket and clean the mating
faces of the manifold and the cylinder head.
The gasket must be renewed when refitting
the manifold.
67Refitting is a reversal of the removal
procedure. Ensure that the spacers are
correctly located (where applicable) and
tighten the retaining bolts and nuts to the
specified torque settings.
Exhaust manifold -
removal and refittingÁ
68Remove the inlet manifold as described
previously (1372 cc models only).
69Disconnect the Lambda sensor lead
(photo).
70Raise and support the car at the front end
on axle stands to allow sufficient clearance to
work underneath the car and disconnect the
exhaust downpipe from the manifold.
71Straighten the tab washers, then unscrew
and remove the exhaust downpipe-
to-manifold retaining nuts (photo). Detach the
downpipe from the manifold. Support the
downpipe so that the Lambda sensor will not
get knocked and/or damaged.72Undo the manifold-to-cylinder head
securing bolts/nuts and withdraw and remove
the manifold and heat shield.
73Remove the gasket and clean the mating
faces of the manifold, cylinder head and
downpipe flange. The gasket must be
renewed when refitting the manifold.
74Refitting is a reversal of the removal
procedure. Tighten the retaining bolts/nuts to
the specified torque setting.
Catalytic converter -
general information
75The catalytic converter is a reliable and
simple device which needs no maintenance in
itself, but there are some facts of which an
owner should be aware if the converter is to
function properly for its full service life.
a) DO NOT use leaded petrol in a car
equipped with a catalytic converter - the
lead will coat the precious metals,
reducing their converting efficiency and
will eventually destroy the converter.
b) Always keep the ignition and fuel systems
well-maintained in accordance with the
maintenance schedule - particularly, en-
sure that the air cleaner filter element the
fuel filter and the spark plugs are renewed
at the correct interval - if the intake air/fuel
mixture is allowed to become too rich due
to neglect, the unburned surplus will enter
and burn in the catalytic converter,
overheating the element and eventually
destroying the converter.
Supplement: Revisions and information on later models 13•77
9D.58B . . . for access to the ECU retaining
screw (arrowed)9D.58A Detach the multiplug (arrowed) . . .9D.49 Fuel injector unit sensor retaining
screw (1). Also shown is the intake air
temperature sensor (2)
9D.71 Exhaust downpipe to manifold
flange connection showing retaining nuts
and locktabs9D.69 Lambda sensor in exhaust
downpipe
13
Page 203 of 303

c) If the engine develops a misfire, do not
drive the car at all (or at least as little as
possible) until the fault is cured - the
misfire will allow unburned fuel to enter
the converter, which will result in its
overheating, as noted above.
d) DO NOT push- or tow-start the car - this
will soak the catalytic converter in
unburned fuel, causing it to overheat
when the engine does start - see b)
above.
e) DO NOT switch off the ignition at high
engine speeds - if the ignition is switched
off at anything above idle speed,
unburned fuel will enter the (very hot)
catalytic converter, with the possible risk
of its igniting on the element and
damaging the converter.
f) DO NOT use fuel or engine oil additives -
these may contain substances harmful to
the catalytic converter.
g) DO NOT continue to use the car if the
engine burns oil to the extent of leaving a
visible trail of blue smoke - the unburned
carbon deposits will clog the converter
passages and reduce its efficiency; in
severe cases the element will overheat.
h) Remember that the catalytic converter
operates at very high temperatures and
the casing will become hot enough to
ignite combustible materials which brush
against it. DO NOT, therefore, park the car
in dry undergrowth, over long grass or
piles of dead leaves.
i) Remember that the catalytic converter is
FRAGILE - do not strike it with tools
during servicing work, take great care
when working on the exhaust system,
ensure that the converter is well clear of
any jacks or other lifting gear used to raise
the car and do not drive the car over
rough ground road humps, etc., in such a
way as to ground the exhaust system.
j) In some cases, particularly when the car is
new and/or is used for stop/start driving, a
sulphurous smell (like that of rotten eggs)
may be noticed from the exhaust. This is
common to many catalytic
converter-equipped cars and seems to be
due to the small amount of sulphur found
in some petrols reacting with hydrogen in
the exhaust to produce hydrogen sulphide
(H
2S) gas; while this gas is toxic, it is not
produced in sufficient amounts to be a
problem. Once the car has covered a few
thousand miles the problem should
disappear - in the meanwhile a change of
driving style or of the brand of petrol used
may effect a solution.
k) The catalytic converter, used on a
well-maintained and well driven car,
should last for at least 50 000 miles
(80 000 km) or five years - from this point
on, careful checks should be made at all
specified service intervals on the CO level
to ensure that the converter is still
operating efficiently - if the converter is no
longer effective it must be renewed.
Fuel evaporation control system
- general
76As mentioned earlier, fuel evaporation is
contained within the system. In high outdoor
temperatures, when the vehicle is parked for a
period of time, the fuel in the tank evaporates,
building up pressure. When the pressure builds
up to a predetermined level a vent valve opens
to allow the vapours to pass on to and absorbed
by a carbon filter. However, if extreme pressure
or vacuum should build up, a two way safety
valve opens to allow external venting.
77If the safety valve needs replacing, note
that it must be fitted correctly. The black end
should be connected to the fuel tank and the
blue to the carbon filter.
78The vapours in the carbon filter are
flushed by warm air passing through the filter
on to a ECU controlled vapour cut-off
solenoid.
79The cut-off solenoid is closed when
starting the engine and opens to allow
vapours to be drawn into the inlet manifold,
through a second solenoid. If the cut-off
solenoid needs replacing ensure that the
black arrow on the casing is pointing towards
the inlet manifold.
80The second solenoid, known as an Elbi
solenoid, is closed when the engine is turned
off, thus preventing engine run-on. The side
facing connection is for the inlet manifold
pipe.
PART E:
BOSCH L3.1/2 JETRONIC
FUEL INJECTION SYSTEMS
Warning: Refer to the beginning
of this Section before starting
any work.
Description
1A Bosch L3.1 (or L3.2, as fitted from 1992)
Jetronic fuel injection system is fitted to the
1372 cc Turbo ie engine. The system circuit
and main component locations are shown in
Figs. 13.48 and 13.49.
2The L3.1/2 Jetronic system is a multi-point
fuel injection (MPi) system. It operates in a
similar manner to that of the LE2-Jetronic
system fitted to the 1301 cc Turbo ie engine
described in Part C of this Section. The L3.1/2
system is more sophisticated and has the
ability to provide reasonably efficient engine
operation when system sensors malfunction.
As with the LE2 system, the fuel and air
supply mixture circuits are regulated in
accordance with the electronic control unit
(ECU), but on the L3.1/2 system the control
unit is attached to the upper part of the
airflow meter.
3The ECU analyses the information passed
to it from the system sensors. These signals
are then processed and the air/fuel mixture is
constantly adjusted as required to provide the
13•78 Supplement: Revisions and information on later models
Fig. 13.48 Bosch L3.1 Jetronic fuel injection system - 1372 cc Turbo ie engine (Sec 9E)
1 ECU
1A Diagnostic socket
2 Injection system relay and
fuel pump relay
3 Ignition switch
4 Battery
5 Fuel tank
6 Fuel pump
6A Primary fuel filter7 Coolant temperature
sensor
8 Intake air cooling radiator
(intercooler)
9 Air cleaner
10 Supplementary air valve
11 Throttle position switch
11A Throttle housing
12 Airflow meter12A Intake air temperature
sensor
13 Fuel pressure regulator
14 Fuel rail (to injectors)
15 Secondary fuel filter
16 Injectors
17 Injector cooling fan
18 Thermostatic switch (to
engage injector cooling fan)
Page 205 of 303

operation twice. Also prior to making
adjustments ensure that the supplementary
air valve pipe is in good condition, with no
leaks. Compress the air valve pipe using a
pair of grips to prevent incorrect adjustment
caused by a defective supplementary air
valve.
15The air cleaner must be connected when
checking and/or adjusting the engine idle
speed. To adjust, turn the adjuster screw in
the required direction to set the engine idle
speed to that specified.
16It is unlikely that the mixture will require
adjustment and unless this is proven by
measuring the exhaust gases using a CO
content analyser, its setting should not be
altered. As with idle speed adjustment, the
engine must be at its normal operating
temperature when making this check and
adjustment. It is also necessary to ensure that
the ignition idle advance is as specified.
Checking and adjustment must not be made
with the engine cooling fan, air conditioning
(where fitted) or other related items switched
on.
17If adjustment to the mixture is required,
prise free the tamperproof plug from the front
of the mixture adjustment screw in the control
unit, then turn the screw as required. Turn the
screw inwards (clockwise) to increase the CO
content or outwards (anti-clockwise) to
weaken it.
Throttle position switch adjustment
18This switch will not normally require
adjustment having been set during
production. The switch should not be
loosened off or reset unless absolutely
necessary.
19If a new switch is fitted it can be set by
loosely fitting the securing bolts, turning the
switch fully anti-clockwise, then clockwise
until one of the internal contacts is felt to click
into engagement. Hold the switch in this
position and tighten the retaining screws.
Reconnect the wiring multiplug to the switch.
Accelerator cable adjustment
20If the accelerator cable is removed or
detached from the support bracket at the
throttle control housing at any time, care must
be taken to adjust it correctly. When the inner
cable is connected to the throttle quadrant,
set the outer cable in the bracket so that the
inner cable has a minimal amount of free play,
yet does not prevent the throttle valve from
fully closing.
21When the engine is restarted, check that
the engine idle speed is as specified and that
the action of the accelerator is satisfactory.
Fuel pump and supply system checks
22Although the following basic checks can
be made to the fuel pump and fuel supply
system, specialised equipment is required to
undertake full and accurate tests of the fuel
supply system. Such checks must therefore
be entrusted to a FIAT dealer or a fuel
injection specialist.
23If the fuel pump is suspected of
malfunction, a basic check can be made by
turning the ignition on and listening around
the area of the pump unit to hear if it is
operating. The pump is located on the
underside of the car, just forward of the fuel
tank. If the pump fails to operate, check thatthe pump fuse is sound and that its
connection (and also that the relay) are clean
and secure.
24The pump can be further checked as
described previously for the LE2 fuel injection
system fuel pump in Part C of this Section.
Supplementary air valve check
25With the engine at its normal operating
temperature, allow it to idle, then pinch the
supplementary air valve hose using suitable
pliers as shown in Fig. 13.52 and check to see
if the engine speed drops by more than 50
rpm. If it does, the supplementary air valve is
defective and in need of renewal.
Injection system
components -
removal and refitting
Á
Warning: Refer to the beginning
of this Section before starting
any work.
26With the exception of the items mentioned
below, the various components of the fuel
injection system are removed in the same
manner as that described for the equivalent
items in Part C of this Chapter.
27Disconnect the battery negative lead
before carrying out any of the removal and
refitting operations. Where fuel lines are to be
disconnected it will first be necessary to
depressurise the injection system.
Airflow meter
28Release the retaining clips and detach the
air intake and outlet ducts from the airflow
meter.
29Ensure that the ignition is switched off,
then disconnect the multiplug from the ECU.
Unscrew the retaining bolts and remove the
airflow meter complete with the ECU.
30If required, the ECU can be separated
from the airflow meter by undoing the
securing bolts.
Throttle valve housing/inlet manifold
31Loosen off the retaining clip and detach
the air intake duct from the throttle housing,
the air cooling hoses for the injectors and the
supplementary air valve.
32Detach the accelerator cable from the
throttle linkage.
13•80 Supplement: Revisions and information on later models
Fig. 13.56 Disconnecting the injector air
cooling hoses and the supplementary air
valve hose on the 1372 cc Turbo ie engine
(Sec 9E)Fig. 13.55 Disconnecting the air intake
duct and accelerator cable from the
throttle housing on the 1372 cc Turbo ie
engine (Sec 9E)
Fig. 13.54 Accelerator cable adjustment
on the 1372 cc Turbo ie engine (Sec 9E)
1 Adjuster 3 Quadrant support
2 Inner cableFig. 13.53 Mixture adjustment screw
location on the 1372 cc Turbo ie engine
(Sec 9E)
Page 222 of 303

27The engine must now be supported at its
left-hand end. If the engine/transmission lift
bracket is unbolted it can be attached at
another suitable position on the engine and
the lift sling/tool attached to it, but take care
not to attach it to a weak fixing point.
28The engine will need to be supported
using an engine lift beam/support bar of the
type shown in Fig. 13.93. A strong wood or
metal beam resting on blocks in the front wing
drain channels will suffice, or alternatively use
an engine lift hoist and sling.
29Refer to Section 13 in this Chapter and
Section 2 in Chapter 7 for details and remove
the front driveshaft each side.
30Prise back the tabs of the retaining
washers, then undo the retaining nuts and
detach the exhaust downpipe from the
manifold. Detach the exhaust mounting
bracket (where applicable) and lower the
exhaust to allow access to the gearchange
linkages.
31Disconnect the gearchange control and
selector link rod balljoints (photo). Do not alter
their lengths or the adjustment setting will be
affected.
32Using a small diameter pin punch, drive the
retaining pins from the retaining clips which
secure the left-hand side underwing shield.
Prise free the clips and detach the shield.
33Undo the retaining bolts and remove the
lower cover plate from the flywheel housing
(photo).
34Position a trolley jack under the
transmission with an interposed block ofwood to protect the casing and spread the
load. Raise the jack to support the weight of
the transmission.
35Check that the weight of the engine is
securely supported, then unbolt and detach
the front engine mounting unit, then the rear
engine mounting unit.
36Unscrew and remove the remaining bolts
securing the transmission to the engine. As
they are removed, note the position of any
brackets or additional fixings secured by
these bolts (photo).
37Check around the transmission to ensure
that all fixings are detached from it and out of
the way, then carefully pull the transmission
free from the engine dowel pins. If possible
engage the aid of an assistant to help in
guiding or lowering the unit as it is removed.
As the unit is withdrawn from the engine, take
care not to place any strain on the input shaft.
Once the input shaft is clear of the clutch, the
transmission can be lowered and manoeuvred
from underneath the car. If available, lower the
unit onto a suitable crawler board to ease its
withdrawal from under the front end of the car.
38Dismantling and overhaul of this
transmission is not recommended. If the
transmission has covered a high mileage it is
likely that several internal components are in
need of renewal. The cumulative cost of
renewing all worn and defective components
will almost certainly make overhaul
uneconomical when compared with the cost
of a new or service exchange transmission
from a FIAT dealer or transmission specialist.39Refitting is a reversal of the removal
procedure, but note the following special
points.
a) Ensure that the engine and transmission
mating surfaces and the dowel pins are
clean and that all clutch components are
in good condition.
b) Apply a thin smear of molybdenum
disulphide grease to the splines of the
input shaft. Do not over-lubricate though
or the grease may work its way onto the
clutch friction surfaces and cause clutch
slip.
c) Raise the transmission so that it is in-line
with the engine, engage the end of the
input shaft into the clutch driven plate hub
and align the splines of each to enable the
transmission to be pushed home. It may
well be necessary to turn the flywheel a
fraction so that the splines align for
re-engagement
d) Do not fully tighten the engine and
transmission retaining bolts until all are
attached.
e) Tighten all retaining bolts and nuts of the
specified torque wrench settings (where
given).
f) Refer to Section 13 in this Chapter for
details on refitting the driveshafts.
g) Refill the transmission with the specified
quantity and grade of oil before lowering
the car to the ground (see paragraph 11).
Supplement: Revisions and information on later models 13•97
Fig. 13.93 FIAT lift beam/support bar in
place to support the weight of the engine.
Inset shows lift hook engagement point -
1372 cc models (Sec 12)
12B.24B . . . and retaining bolts (arrowed)
on the 1372 cc ie engine12B.24A Starter motor electrical
connection . . .
12B.36 Transmission upper retaining bolts.
Note bracket under the left-hand bolt12B.33 Lower cover plate and retaining
bolts (arrowed)12B.31 Gear control and selector link rod
joints
13