compression ratio FORD E SERIES 2002 4.G Natural Gas Vehicle Supplement Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 2002, Model line: E SERIES, Model: FORD E SERIES 2002 4.GPages: 16, PDF Size: 0.13 MB
Page 6 of 16
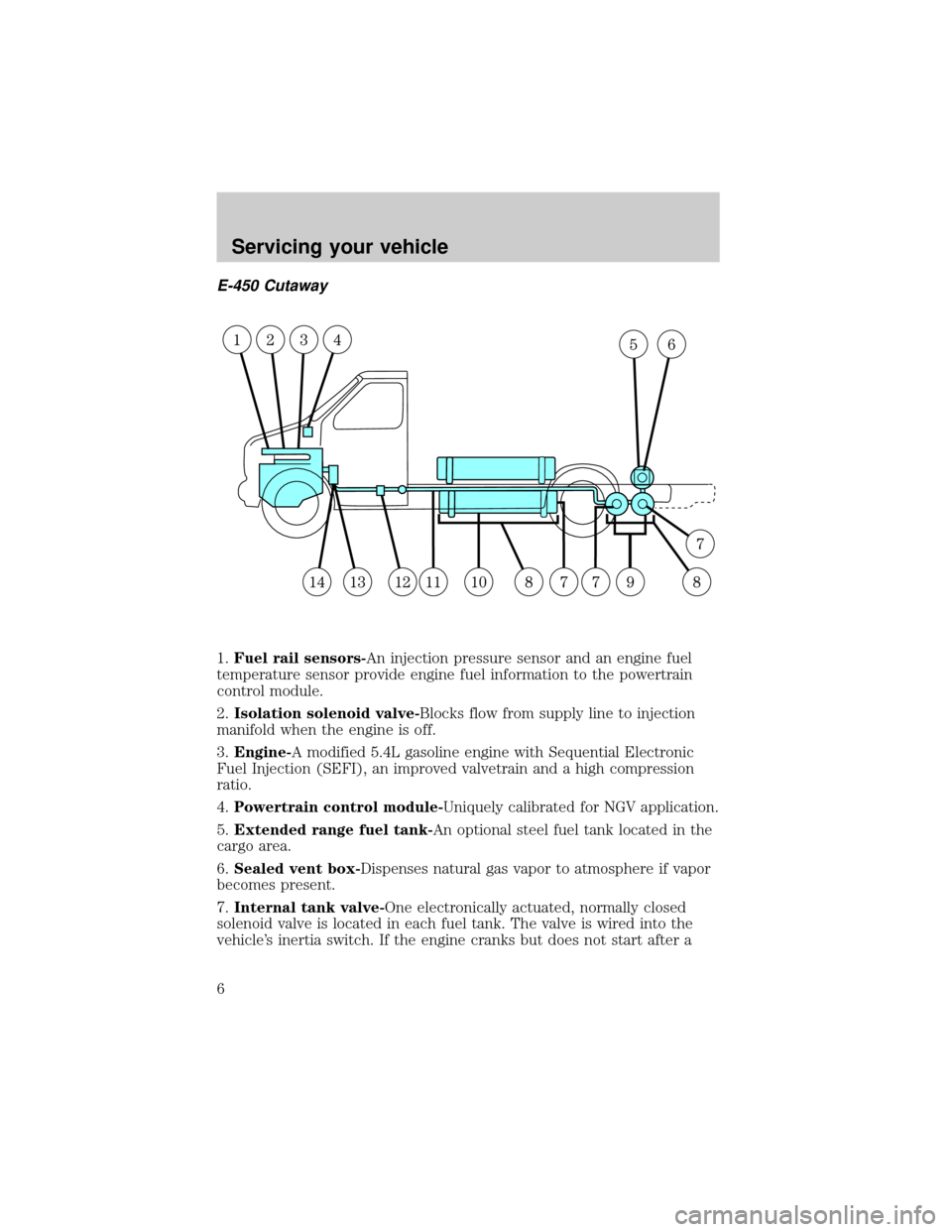
E-450 Cutaway
1.Fuel rail sensors-An injection pressure sensor and an engine fuel
temperature sensor provide engine fuel information to the powertrain
control module.
2.Isolation solenoid valve-Blocks flow from supply line to injection
manifold when the engine is off.
3.Engine-A modified 5.4L gasoline engine with Sequential Electronic
Fuel Injection (SEFI), an improved valvetrain and a high compression
ratio.
4.Powertrain control module-Uniquely calibrated for NGV application.
5.Extended range fuel tank-An optional steel fuel tank located in the
cargo area.
6.Sealed vent box-Dispenses natural gas vapor to atmosphere if vapor
becomes present.
7.Internal tank valve-One electronically actuated, normally closed
solenoid valve is located in each fuel tank. The valve is wired into the
vehicle's inertia switch. If the engine cranks but does not start after a
Servicing your vehicle
6
Page 8 of 16

2.Isolation solenoid valve-Blocks flow from supply line to injection
manifold when the engine is off.
3.Engine-A modified 5.4L gasoline engine with Sequential Electronic
Fuel Injection (SEFI), an improved valvetrain and a high compression
ratio.
4.Powertrain control module-Uniquely calibrated for NGV application.
5.Internal tank valve-One electronically actuated, normally closed
solenoid valve is located in each fuel tank. The valve is wired into the
vehicle's inertia switch. If the engine cranks but does not start after a
collision, the fuel solenoid valve inertia switch may have been activated.
The inertia switch is a device intended to close the fuel solenoid valve
when your vehicle has been involved in a substantial jolt.
6.Standard fuel tanks-Two steel fuel tanks located in the bed of the
truck.
6b.In-bed tank cover-Cover to prevent damage to the fuel tanks.
Protective shield to prevent damage to the fuel tank caused by road
debris or other road hazards.Do not sit, stand or place heavy loads
on the fuel tank cover.
7.Stone shield-Protective shield to prevent damage to the fuel tank
caused by road debris or other road hazards.
8.Optional fuel tank-A steel fuel tank located underbody.
9.High pressure fuel lines-Delivers high pressure fuel to the fuel
tanks and fuel pressure regulator.
10.Fuel pressure regulator/Coalescent fuel filter-Reduces fuel
pressure to 95 psi and removes impurities from the gas.
11.Low pressure fuel line-Supplies 95 psi of natural gas to the
injectors.
12.NGV module-Contains the unique powertrain electronics that are
required for an NGV.
Servicing your vehicle
8
Page 9 of 16

Crown Victoria
1.NGV module-Provides power for the fuel injectors. Also, drives the
fuel gauge using fuel tank pressure and temperature sensors.
2.Isolation solenoid valve-Blocks flow from the injection manifold
when the engine is off.
3.Engine-Is a modified 4.6L engine with Sequential Electronic Fuel
Injection (SEFI) and increased compression ratio.
4.Engine coolant lines-Provide required heat to high pressure
regulator.
5.Powertrain control module-Required for NGV application.
6.Sealed vent box-Vented to underbody. Dispenses natural gas vapor
to atmosphere if vapor becomes present.
7.Tank pressure sensor-Fuel tank pressure sensor located in this
tank's solenoid valve is used for fuel indication.
8.Solenoid tank valves-One solenoid per tank. Internal valves with
shut-off solenoids wired into inertia circuit for crash protection.
9.Two fuel tanks-Located in the trunk. On taxi or police vehicles, an
extended range fuel system is available which includes two additional NG
fuel tanks mounted in the trunk (total of four).
10.Fueling point-Fueling receptacle is conveniently located with the
fuel door. Same location as gasoline fueled vehicles.
11.Tank temperature sensors-One each in set of tanks (solenoid
valves) used for fuel indication.
13
2456879
10
11
12
131415171816
Servicing your vehicle
9
Page 11 of 16

NATURAL GAS DISPENSING
Most dispensers have a digital indicator displaying the cost and amount
of fuel delivered to your vehicle. Fuel delivery to the vehicle is stopped
when the pressure of fuel stored on the vehicle equalizes with the
temperature compensated pressure of fuel stored at the station. As the
pressure between the station and vehicle equalizes, the cost and quantity
meters slow to a near stop. When this occurs, refueling is complete.
Certain noises can be expected during the refueling process and may
vary depending on the type of fuel station and your proximity to the fuel
compression and storage equipment. At the beginning of refueling you
might hear the rushing noise of gas entering the vehicle through the
station hose and tubing. At the end of refueling, the fuel receptacle on
the vehicle may make a high pitch noise or chatter. This is another
indication that refueling is nearly complete. Also, the station compression
equipment may turn on at any time during the refueling process.
FUEL QUALITY
Use only a CNG fuel that meets the specification of NFPA-52 and SAE
J1616 in your NGV. Specifications NFPA-52 and SAE J1616 place limits
on particulate contamination and moisture content to ensure a quality
CNG fuel.
The use of a CNG fuel that does not meet specifications NFPA-52 and
SAE J1616 isnot recommendedand may cause engine damage.
Use of poor quality CNG fuel may result in:
²component failure.
²leakage from the fueling point.
²poor vehicle operation.
Use of poor quality fuel may also result in your warranty being
invalidated.
SERVICING YOUR NATURAL GAS VEHICLE
Service to the CNG fuel system should be conducted at a
qualified dealership by a trained NGV technician only. Failure to
do so may cause damage to components or cause bodily harm.
Servicing your vehicle
11