light FORD EXCURSION 2003 1.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 2003, Model line: EXCURSION, Model: FORD EXCURSION 2003 1.GPages: 240, PDF Size: 2.2 MB
Page 128 of 240

Important ventilating information
If the engine is idling while the vehicle is stopped for a long period of
time, open the windows at least 2.5 cm (one inch) or adjust the heating
or air conditioning to bring in fresh air.
BRAKES
Occasional brake noise is normal. If a metal-to-metal, continuous grinding
or continuous squeal sound is present, the brake linings may be worn-out
and should be inspected by a qualified service technician. If the vehicle
has continuous vibration or shudder in the steering wheel while braking,
the vehicle should be inspected by a qualified service technician.
Four-wheel anti-lock brake system (ABS)
Your vehicle is equipped with an Anti-lock Braking System (ABS). This
system helps you maintain steering control during emergency stops by
keeping the brakes from locking. Noise from the ABS pump motor and
brake pedal pulsation may be observed during ABS braking; any
pulsations or mechanical noise you may feel or hear is normal.
ABS warning lamp
ABS
TheABSlamp in the instrument cluster momentarily illuminates when
the ignition is turned to ON. If the light does not illuminate during start
up, remains on or flashes, the ABS may be disabled and the ABS may
need to be serviced.
Even when the ABS is disabled,
normal braking is still effective. (If
your BRAKE warning lamp
illuminates with the parking brake
released, have your brake system serviced immediately.)
Using ABS
When hard braking is required, apply continuous force on the brake
pedal; do not pump the brake pedal since this will reduce the
effectiveness of the ABS and will increase your vehicle’s stopping
distance. The ABS will be activated immediately, allowing you to retain
full steering control during hard braking and on slippery surfaces.
However, the ABS does not decrease stopping distance.
Driving
128
Page 134 of 240

an adaptive learning strategy. The adaptive learning strategy is
maintained by power from the battery. When the battery is disconnected
or a new battery is installed, the transmission must relearn its adaptive
strategy. Optimal shifting will resume within a few hundred kilometers
(miles) of operation.
If the shift quality does not improve within a few hundred
kilometers (miles) of operation, or if the downshifts and other
throttle conditions do not function normally, see your dealer or a
qualified service technician as soon as possible.
If your vehicle gets stuck in mud or snow
If your vehicle gets stuck in mud or snow, it may be rocked out by
shifting from forward and reverse gears, stopping between shifts in a
steady pattern. Press lightly on the accelerator in each gear.
Do not rock the vehicle if the engine is not at normal operating
temperature or damage to the transmission may occur.
Do not rock the vehicle for more than a minute or damage to the
transmission and tires may occur, or the engine may overheat.
REVERSE SENSING SYSTEM (IF EQUIPPED)
The RSS sounds a tone to warn the driver of obstacles near the rear
bumper when R (Reverse) is selected. The RSS will assist the driver in
detecting certain objects while:
•the vehicle is moving toward a stationary object at a speed of 5 km/h
(3 mph) or less.
•the vehicle is in R (Reverse) but not moving backward (the brake
pedal is depressed or the parking brake is applied), and a moving
object is approaching the rear of the vehicle at a speed of 5 km/h
(3 mph) or less.
•the vehicle is moving in reverse at a speed of less than 5 km/h
(3 mph) and a moving object is approaching the rear of the vehicle at
a speed of less than 5 km/h (3 mph).
The RSS is not effective at speeds greater than 5 km/h (3 mph) and may
not detect certain angular or moving objects.
To help avoid personal injury, please read and understand the
limitations of the reverse sensing system as contained in this
section. Reverse sensing is only an aid for some (generally large and
fixed) objects when moving in reverse on a flat surface at “parking
speeds”. Inclement weather may also affect the function of the RSS;
this may include reduced performance or a false activation.
Driving
134
Page 136 of 240

indicator light on the control will illuminate when the system is turned
off. If the indicator light illuminates when the RSS is not turned off, it
may indicate a failure in the RSS.
Keep the RSS sensors (located on the rear bumper/fascia) free
from snow, ice and large accumulations of dirt (do not clean the
sensors with sharp objects). If the sensors are covered, it will
affect the accuracy of the RSS.
If your vehicle sustains damage to the rear bumper/fascia, leaving
it misaligned or bent, the sensing zone may be altered causing
inaccurate measurement of obstacles or false alarms.
FOUR-WHEEL DRIVE (4WD) OPERATION (IF EQUIPPED)
For important information regarding safe operation of this type
of vehicle, seePreparing to drive your vehiclein this chapter.
Four–wheel drive (4WD) supplies power to all four wheels. 4WD should
not be operated on dry pavement; driveline damage may occur.
If equipped with the Electronic Shift 4WD System, and 4WD Low
is selected while the vehicle is moving, the 4WD system will not
engage. This is normal and should be no reason for concern.Refer
toShifting to/from 4WD Lowfor proper operation.
The 4WD system also uses hub locks that can be engaged and
disengaged based on the 4WD mode selected. Refer toFront wheel hub
locks (if equipped)for more information.
4WD system indicator lights
•4X4- illuminates when 4WD High
is selected.
•LOW RANGE- illuminates when
4WD Low is selected.
4x4
Driving
136
Page 138 of 240

4X4 HIGH (4WD High)- Used for extra traction such as in snow or icy
roads or in off-road situations. Not intended for use on dry pavement.
4X4 LOW (4WD Low)- Uses extra gearing to provide maximum power
to all four wheels. Intended only for off-road applications such as deep
sand, steep grades or pulling heavy objects. 4L (4WD Low) will not
engage while the vehicle is moving; this is normal and should be no
reason for concern. Refer toShifting to/from 4L (4WD Low)for proper
operation.
Shifting between 2WD (2WD High) and 4X4 HIGH (4WD High)
•Move the 4WD control between 2WD and 4X4 HIGH at any forward
speed.
Note:Do not perform this operation at speeds above 72 km/h (45 mph)
if the outside temperature is below 0°C (32°F).
Note:Do not perform this operation if the rear wheels are slipping.
Shifting to/from 4X4 LOW (4WD Low)
1. Bring the vehicle to a complete stop
2. Depress the brake
3. Place the transmission in N (Neutral).
4. Move the 4WD control to the desired position.
•If shifting into 4X4 LOW (4WD Low), wait for the LOW RANGE light
in the instrument cluster to turnonindicating the shift is complete.
•If shifting out of 4X4 LOW (4WD Low), wait for the LOW RANGE light
in the instrument cluster turn turnoffindicating the shift is complete.
Driving off-road with truck and utility vehicles
4WD vehicles are specially equipped for driving on sand, snow, mud and
rough terrain and have operating characteristics that are somewhat
different from conventional vehicles, both on and off the road.
How your vehicle differs from other vehicles
Truck and utility vehicles can differ from some other vehicles. Your
vehicle may be higher to allow it to travel over rough terrain without
getting hung up or damaging underbody components.
The differences that make your vehicle so versatile also make it handle
differently than an ordinary passenger car.
Maintain steering wheel control at all times, especially in rough terrain.
Since sudden changes in terrain can result in abrupt steering wheel
motion, make sure you grip the steering wheel from the outside. Do not
grip the spokes.
Driving
138
Page 140 of 240

If your vehicle gets stuck
If your vehicle gets stuck in mud or snow it may be rocked out by
shifting between forward and reverse gears, stopping between shifts, in a
steady pattern. Press lightly on the accelerator in each gear.
Do not rock the vehicle if the engine is not at normal operating
temperature or damage to the transmission may occur.
Do not rock the vehicle for more than a few minutes or damage
to the transmission and tires may occur or the engine may
overheat.
Always set the parking brake fully and make sure the gearshift is
latched in P (Park). Turn the ignition to the LOCK position and
remove the key whenever you leave your vehicle.
If the parking brake is fully released, but the brake warning lamp
remains illuminated, the brakes may not be working properly.
See your dealer or a qualified service technician.
Do not spin the wheels at over 56 km/h (35 mph). The tires may
fail and injure a passenger or bystander.
Refer toTransmission temperature gaugein theInstrument cluster
chapter for transmission fluid temperature information.
Emergency maneuvers
•In an unavoidable emergency situation where a sudden sharp turn
must be made, remember to avoid “over-driving” your vehicle, i.e.,
turn the steering wheel only as rapidly and as far as required to avoid
the emergency. Excessive steering will result in less vehicle control,
not more. Additionally, smooth variations of the accelerator and/or
brake pedal pressure should be utilized if changes in vehicle speed are
called for. Avoid abrupt steering, acceleration or braking which could
result in an increased risk of loss of vehicle control, vehicle rollover
and/or personal injury. Use all available road surface to return the
vehicle to a safe direction of travel.
•In the event of an emergency stop, avoid skidding the tires and do not
attempt any sharp steering wheel movements.
Driving
140
Page 142 of 240

sounds. This is the front drivetrain coming up to speed and the
automatic locking hubs engaging and is not cause for concern.
Sand
When driving over sand, try to keep all four wheels on the most solid
area of the trail. Avoid reducing the tire pressures but shift to a lower
gear and drive steadily through the terrain. Apply the accelerator slowly
and avoid spinning the wheels.
If you must reduce the tire pressure for whatever reason in sand, make
sure you re-inflate the tires as soon as possible.
Avoid excessive speed because vehicle momentum can work against you
and cause the vehicle to become stuck to the point that assistance may
be required from another vehicle. Remember, you may be able to back
out the way you came if you proceed with caution.
Mud and water
If you must drive through high
water, drive slowly. Traction or
brake capability may be limited.
When driving through water,
determine the depth; avoid water
higher than the bottom of the hubs
(if possible) and proceed slowly. If
the ignition system gets wet, the vehicle may stall.
Once through water, always try the brakes. Wet brakes do not stop the
vehicle as effectively as dry brakes. Drying can be improved by moving
your vehicle slowly while applying light pressure on the brake pedal.
Be cautious of sudden changes in vehicle speed or direction when you
are driving in mud. Even 4WD vehicles can lose traction in slick mud. As
when you are driving over sand, apply the accelerator slowly and avoid
spinning your wheels. If the vehicle does slide, steer in the direction of
the slide until you regain control of the vehicle.
If the transmission, transfer case or front axle are submerged in water,
their fluids should be checked and changed, if necessary.
Driving through deep water may damage the transmission.
Refer toTransmission temperature gaugein theInstrument cluster
chapter for transmission fluid temperature information.
If the front or rear axle is submerged in water, the axle lubricant should
be replaced.
Driving
142
Page 143 of 240

After driving through mud, clean off residue stuck to rotating driveshafts
and tires. Excess mud stuck on tires and rotating driveshafts causes an
imbalance that could damage drive components.
“Tread Lightly” is an educational
program designed to increase public
awareness of land-use regulations
and responsibilities in our nations
wilderness areas. Ford Motor
Company joins the U.S. Forest Service and the Bureau of Land
Management in encouraging you to help preserve our national forest and
other public and private lands by “treading lightly.”
Driving on hilly or sloping terrain
Although natural obstacles may make it necessary to travel diagonally up
or down a hill or steep incline, you should always try to drive straight up
or straight down.Avoid driving crosswise or turning on steep
slopes or hills. A danger lies in losing traction, slipping sideways and
possibly rolling over. Whenever driving on a hill, determine beforehand
the route you will use. Do not drive over the crest of a hill without
seeing what conditions are on the other side. Do not drive in reverse
over a hill without the aid of an observer.
When climbing a steep slope or hill,
start in a lower gear rather than
downshifting to a lower gear from a
higher gear once the ascent has
started. This reduces strain on the
engine and the possibility of stalling.
If you do stall out, do not try to
turn around because you might roll
over. It is better to back down to a
safe location.
Apply just enough power to the wheels to climb the hill. Too much
power will cause the tires to slip, spin or lose traction, resulting in loss of
vehicle control.
Driving
143
Page 147 of 240

that is higher than the bottom of the hubs (for trucks) or the bottom of
the wheel rims (for cars). Traction or brake capability may be limited
and your vehicle may stall. Water may also enter your engine’s air intake
and severely damage your engine.
Once through the water, always dry the brakes by moving your vehicle
slowly while applying light pressure on the brake pedal. Wet brakes do
not stop the vehicle as quickly as dry brakes.Driving through deep
water where the transmission vent tube is submerged may allow
water into the transmission and cause internal transmission
damage.
VEHICLE LOADING
Before loading a vehicle, familiarize yourself with the following terms:
•Base Curb Weight:Weight of the vehicle including any standard
equipment, fluids, lubricants, etc. It does not include occupants or
aftermarket equipment.
•Payload:Combined maximum allowable weight of cargo, occupants
and optional equipment. The payload equals the gross vehicle weight
rating minus base curb weight.
•GVW (Gross Vehicle Weight):Base curb weight plus payload
weight.
•GVWR (Gross Vehicle Weight Rating):Maximum allowable total
weight of the base vehicle, occupants, optional equipment and cargo.
The GVWR is specific to each vehicle and is listed on the Safety
Certification Label on the driver’s door pillar.
•GAWR (Gross Axle Weight Rating):Carrying capacity for each axle
system. The GAWR is specific to each vehicle and is listed on the
Safety Certification Label on the driver’s door pillar.
•GCW (Gross Combined Weight):The combined weight of the
towing vehicle (including occupants and cargo) and the loaded trailer.
•GCWR (Gross Combined Weight Rating):Maximum allowable
combined weight of towing vehicle (including occupants and cargo)
and the loaded trailer.
•Maximum Trailer Weight Rating:Maximum weight of a trailer the
vehicle is permitted to tow. The maximum trailer weight rating is
determined by subtracting the vehicle curb weight for each
engine/transmission combination, any required option weight for trailer
towing and the weight of the driver from the GCWR for the towing
vehicle.
Driving
147
Page 159 of 240
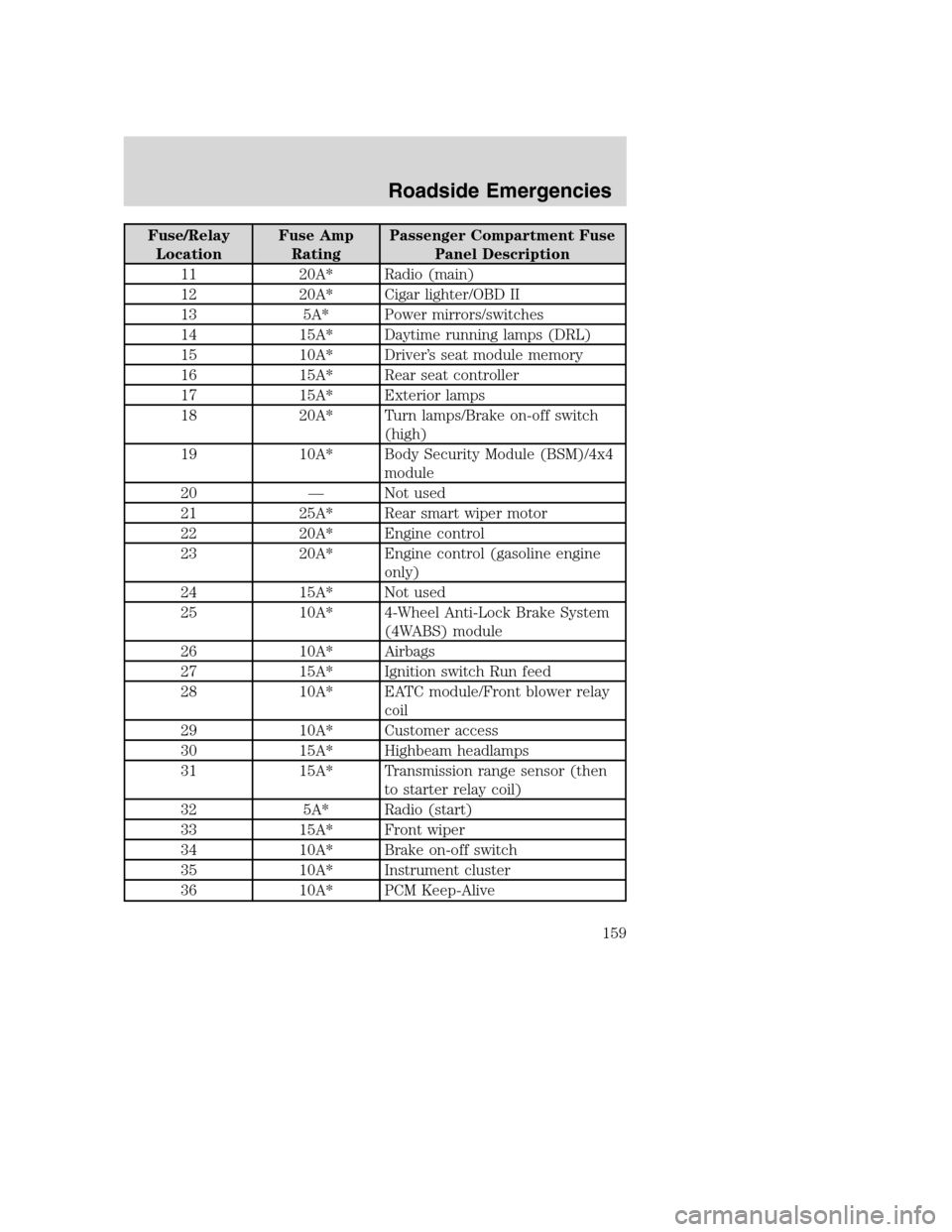
Fuse/Relay
LocationFuse Amp
RatingPassenger Compartment Fuse
Panel Description
11 20A* Radio (main)
12 20A* Cigar lighter/OBD II
13 5A* Power mirrors/switches
14 15A* Daytime running lamps (DRL)
15 10A* Driver’s seat module memory
16 15A* Rear seat controller
17 15A* Exterior lamps
18 20A* Turn lamps/Brake on-off switch
(high)
19 10A* Body Security Module (BSM)/4x4
module
20 — Not used
21 25A* Rear smart wiper motor
22 20A* Engine control
23 20A* Engine control (gasoline engine
only)
24 15A* Not used
25 10A* 4-Wheel Anti-Lock Brake System
(4WABS) module
26 10A* Airbags
27 15A* Ignition switch Run feed
28 10A* EATC module/Front blower relay
coil
29 10A* Customer access
30 15A* Highbeam headlamps
31 15A* Transmission range sensor (then
to starter relay coil)
32 5A* Radio (start)
33 15A* Front wiper
34 10A* Brake on-off switch
35 10A* Instrument cluster
36 10A* PCM Keep-Alive
Roadside Emergencies
159
Page 167 of 240
1.Use only a 12–volt supply to start your vehicle.
2. Do not disconnect the battery of the disabled vehicle as this could
damage the vehicle’s electrical system.
3. Park the booster vehicle close to the hood of the disabled vehicle
making sure the two vehiclesdo nottouch. Set the parking brake on
both vehicles and stay clear of the engine cooling fan and other moving
parts.
4. Check all battery terminals and remove any excessive corrosion before
you attach the battery cables. Ensure that vent caps are tight and level.
5. Turn the heater fan on in both vehicles to protect any electrical
surges. Turn all other accessories off.
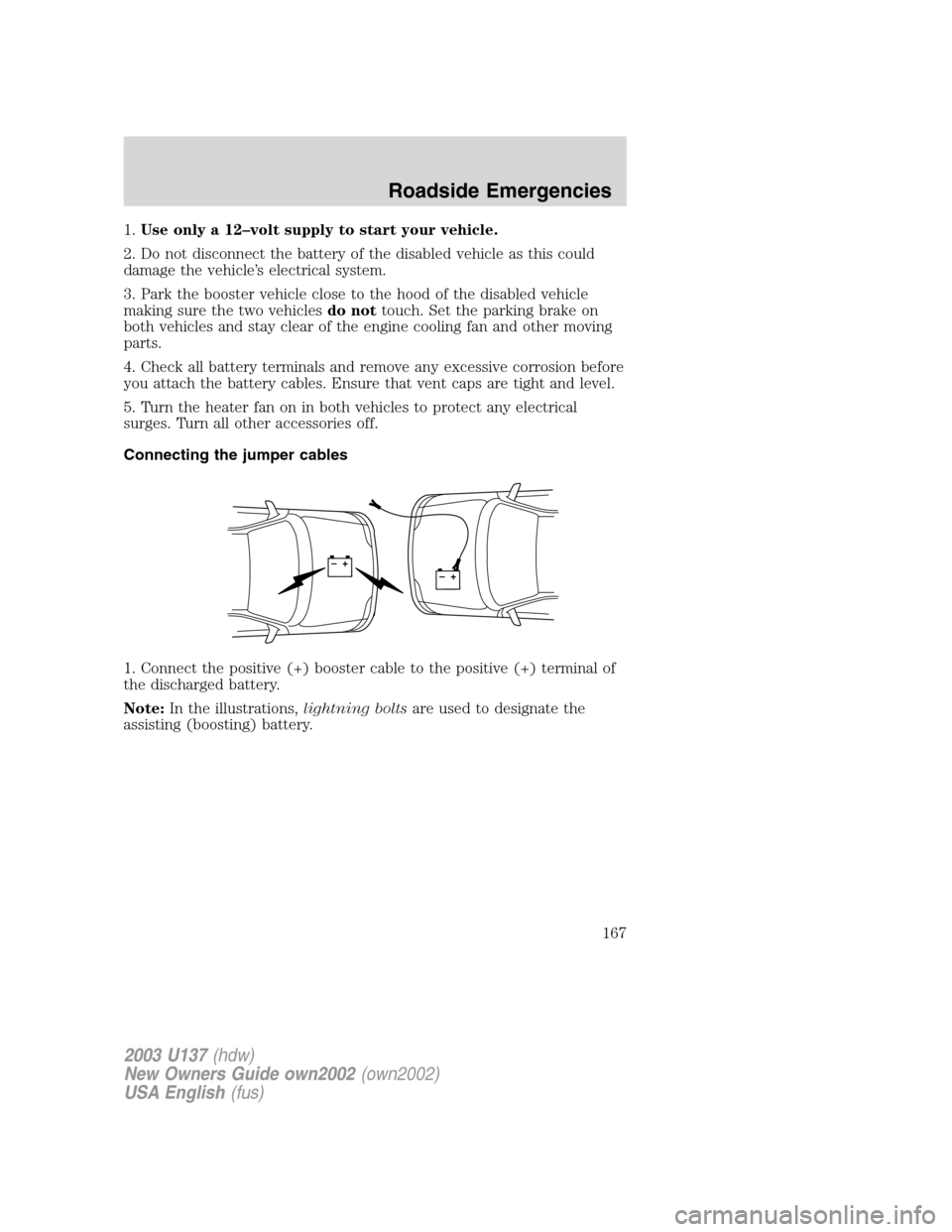
Connecting the jumper cables
1. Connect the positive (+) booster cable to the positive (+) terminal of
the discharged battery.
Note:In the illustrations,lightning boltsare used to designate the
assisting (boosting) battery.
+–+–
2003 U137(hdw)
New Owners Guide own2002(own2002)
USA English(fus)
Roadside Emergencies
167