FORD EXPLORER 2002 3.G Owners Manual
Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 2002, Model line: EXPLORER, Model: FORD EXPLORER 2002 3.GPages: 312, PDF Size: 3.28 MB
Page 181 of 312
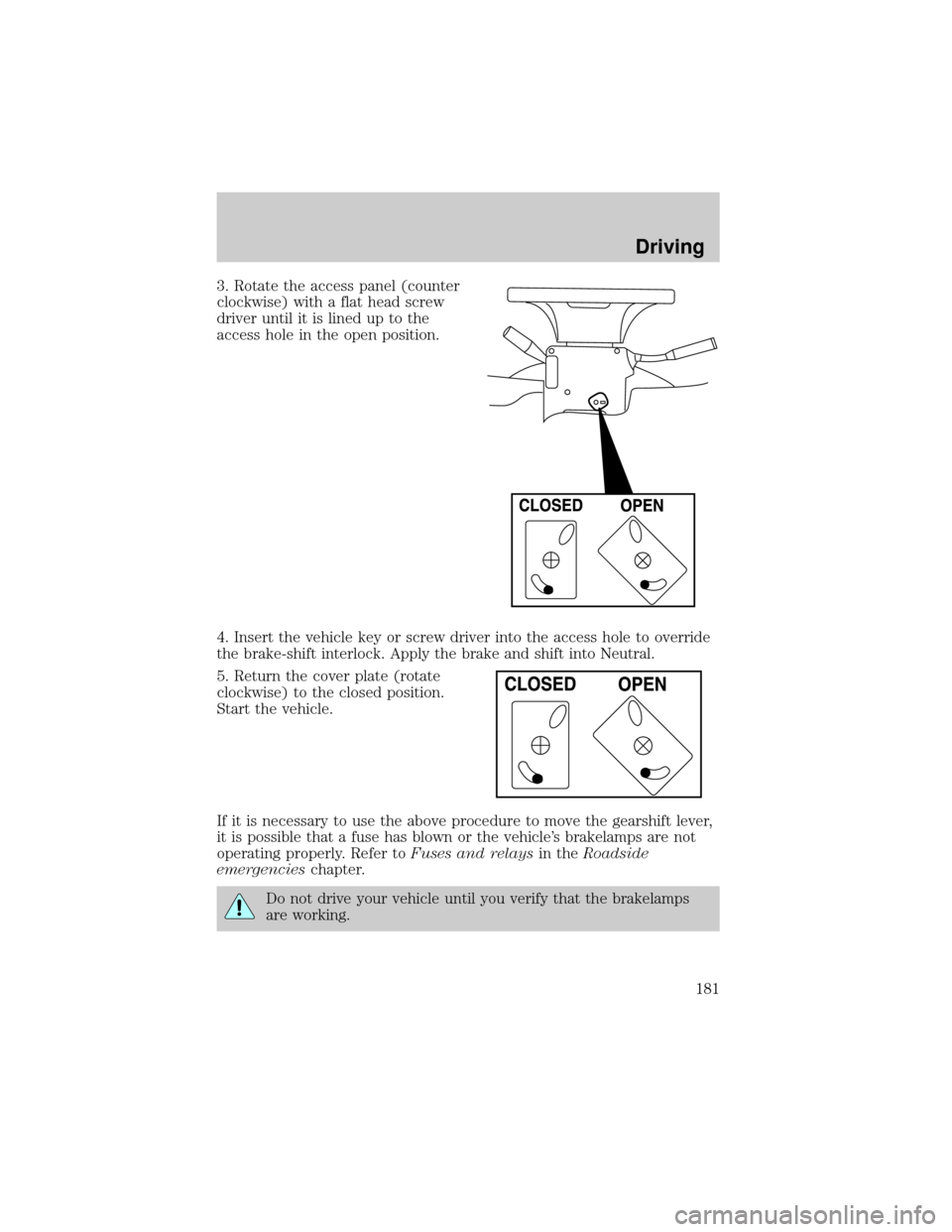
3. Rotate the access panel (counter
clockwise) with a flat head screw
driver until it is lined up to the
access hole in the open position.
4. Insert the vehicle key or screw driver into the access hole to override
the brake-shift interlock. Apply the brake and shift into Neutral.
5. Return the cover plate (rotate
clockwise) to the closed position.
Start the vehicle.
If it is necessary to use the above procedure to move the gearshift lever,
it is possible that a fuse has blown or the vehicle's brakelamps are not
operating properly. Refer toFuses and relaysin theRoadside
emergencieschapter.
Do not drive your vehicle until you verify that the brakelamps
are working.
Driving
181
Page 182 of 312

If your vehicle gets stuck in mud or snow it may be rocked out by
shifting between forward and reverse gears, stopping between shifts, in a
steady pattern. Press lightly on the accelerator in each gear.
Do not rock the vehicle if the engine is not at normal operating
temperature or damage to the transmission may occur.
Do not rock the vehicle for more than a few minutes or damage
to the transmission and tires may occur or the engine may
overheat.
Always set the parking brake fully and make sure the gearshift is
latched in P (Park). Turn off the ignition whenever you leave
your vehicle.
If the parking brake is fully released, but the brake warning lamp
remains illuminated, the brakes may not be working properly.
See your dealer or a qualified service technician.
Driving with a 5±speed automatic transmission (if equipped)
Your automatic transmission electronically controls the shift feel by using
an adaptive learning strategy. This feature is designed to increase
durability, and provide consistent shift feel over the life of the vehicle. It
is normal for a new transmission to shift firmly. This operation is
considered normal and will not affect function or durability of the
transmission. Once the vehicle is at operating temperature it may take
several shifts at the same operating condition for the transmission to
properly adapt. Over time the adaptive learning process will fully update
transmission operation. The more varied the driving habits, speed and
torque, the longer it may take to adapt but the more complete the
process will be.
When the battery is disconnected or a new battery installed, the
transmission must relearn its adaptive strategy. As a result of this, the
transmission may shift firmly. This operation is considered normal and
will fully update transmission operation to its optimum shift feel.
Driving
182
Page 183 of 312

Understanding gearshift positions
Hold the brake pedal down while you move the gearshift lever
from P (Park) to another position. If you do not hold the brake
pedal down, your vehicle may move unexpectedly and injure someone.
P (Park)
To put your vehicle in gear, start the engine, depress the brake pedal,
then move gearshift lever out of P (Park).
Always come to a complete stop
before shifting into P (Park). Make
sure the gearshift lever is securely
latched in P (Park). This position locks the transmission and prevents
the rear wheels from turning.
Always set the parking brake fully and make sure the gearshift is
latched in P (Park). Turn off the ignition whenever you leave
your vehicle.
R (Reverse)
With the gearshift lever in R
(Reverse), the vehicle will move
backward. Always come to a
complete stop before shifting into and out of R (Reverse).
N (Neutral)
With the gearshift lever in N
(Neutral), the vehicle can be started
and is free to roll. Hold the brake
pedal down while in this position.
D (Overdrive)
(Overdrive) can be deactivated by
pressing the transmission control
switch on the end of the gearshift
lever.
O/D OFF
Driving
183
Page 184 of 312

The transmission control indicator
light (TCIL) will illuminate on the
instrument cluster.
Drive (overdrive deactivated)
Activate by pressing the
transmission control switch on the
end of the gearshift lever with the
gearshift in the D(Drive) position. The transmission with overdrive off
operates in gears one through four, providing more engine braking than
D(Drive) with Overdrive ON and is useful whenever driving conditions
(i.e., city traffic, hilly terrain, etc.) cause the transmission to excessively
shift between D (Overdrive) and other gears. Deactivate D (Overdrive)
when:
²driving with a heavy load.
²towing a trailer up or down steep hills.
²additional engine braking is desired. If towing a trailer, refer to
Driving while you towin theTrailer Towingchapter.
To return to D (Overdrive) mode, press the transmission control switch.
The TCIL will no longer be illuminated.
Each time the vehicle is started, the transmission will automatically
return to normal D (Overdrive) mode.
3 (Third)
Transmission operates in third gear
only.
Used from improved traction on
slippery roads. Slecting 3 (Third) provides engine braking.
2 (Second)
Use 2 (Second) to start-up on
slippery roads or to provide
additional engine braking on
downgrades.
O/ D
OFF
Driving
184
Page 185 of 312
1 (First)
Use 1 (First) to provide maximum
engine braking on steep
downgrades. Upshifts can be made
by shifting to 2 (Second) or to (Overdrive). Selecting 1 (Low) at higher
speeds causes the transmission to shift to a lower gear and will shift to 1
(First) after the vehicle decelerates to the proper vehicle speed.
Forced Downshifts
To gain acceleration in (Overdrive) or Drive (O/D OFF) when passing
another vehicle, push the accelerator to the floor. The transmission will
downshift to the appropriate gear: fourth, third, second or first gear.
Driving a manual transmission (if equipped)
Using the clutch
Vehicles equipped with a manual
transmission have a starter interlock
that prevents starting the engine
unless the clutch pedal is fully
depressed.
When starting a vehicle with a
manual transmission:
1. Hold down the brake pedal.
2. Put the gearshift lever in N
(Neutral).
3. Depress the clutch pedal.
4. Start the engine and let it idle for a few seconds.
²Put the gearshift lever in 1 (First) or R (Reverse).
5. Move foot from brake to accelerator and begin to release the clutch
slowly while gradually pressing down on the accelerator.
²Do not drive with your foot resting on the clutch pedal. Do not use
the clutch to hold your vehicle at a standstill while waiting on a hill.
These actions may reduce clutch life.
Driving
185
Page 186 of 312

Parking
1. Apply the brake and shift into N
(Neutral).
2. Engage the parking brake.
3. Shift into 1 (First).
4. Turn the ignition to Off.
Do not park your vehicle in Neutral, it may move unexpectedly
and injure someone. Use 1 (First) gear and set the parking brake
fully.
Recommended shift speeds
Upshifts when accelerating (recommended for best fuel economy)
Shift from: Transfer case position (if equipped)
AUTO or HIGH LOW
1 - 2 14 km/h (9 mph) 5 km/h (3 mph)
2 - 3 32 km/h (20 mph) 11 km/h (7 mph)
3 - 4 50 km/h (31 mph) 19 km/h (12 mph)
4 -5 (Overdrive) 71 km/h (44 mph) 27 km/h (17 mph)
Driving
186
Page 187 of 312
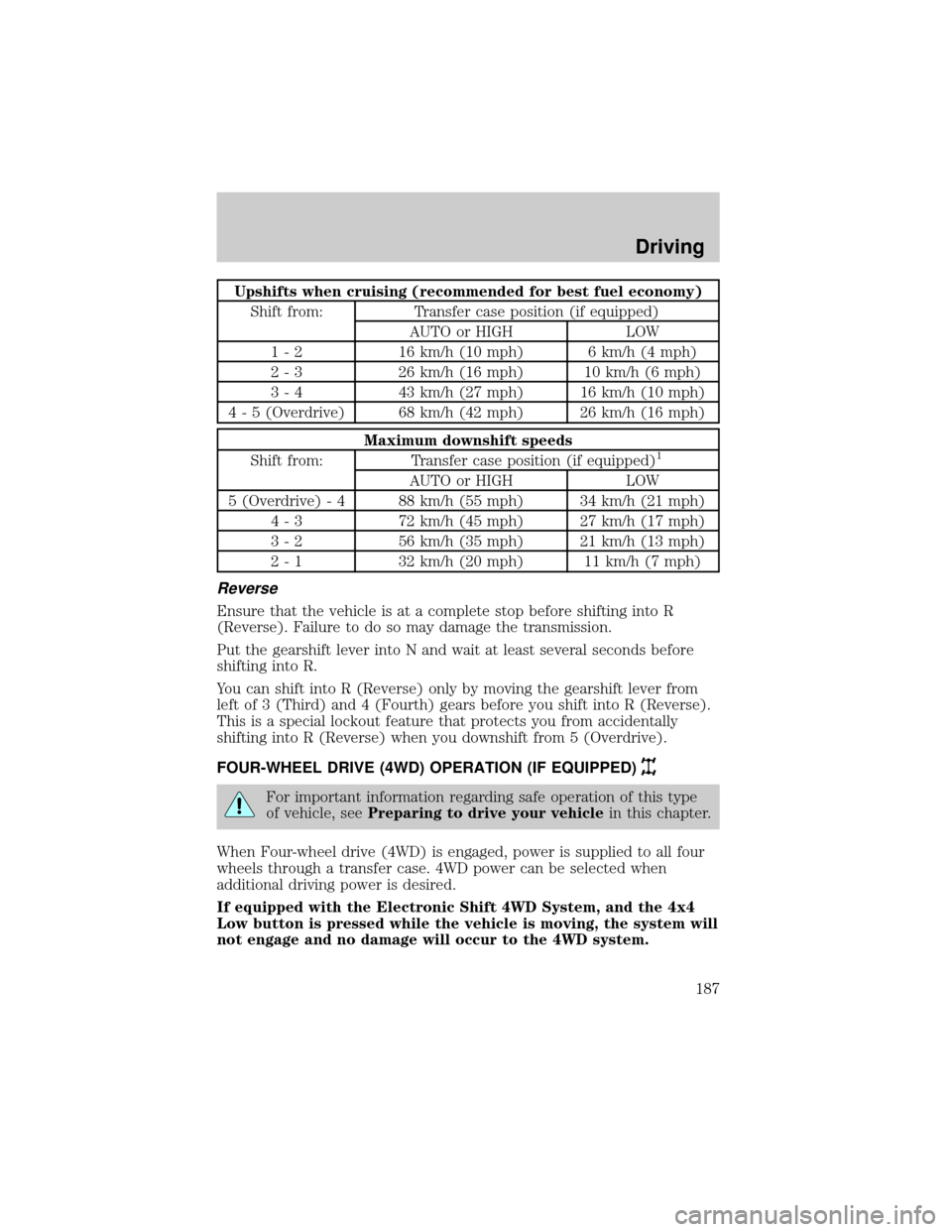
Upshifts when cruising (recommended for best fuel economy)
Shift from: Transfer case position (if equipped)
AUTO or HIGH LOW
1 - 2 16 km/h (10 mph) 6 km/h (4 mph)
2 - 3 26 km/h (16 mph) 10 km/h (6 mph)
3 - 4 43 km/h (27 mph) 16 km/h (10 mph)
4 - 5 (Overdrive) 68 km/h (42 mph) 26 km/h (16 mph)
Maximum downshift speeds
Shift from: Transfer case position (if equipped)1
AUTO or HIGH LOW
5 (Overdrive) - 4 88 km/h (55 mph) 34 km/h (21 mph)
4 - 3 72 km/h (45 mph) 27 km/h (17 mph)
3 - 2 56 km/h (35 mph) 21 km/h (13 mph)
2 - 1 32 km/h (20 mph) 11 km/h (7 mph)
Reverse
Ensure that the vehicle is at a complete stop before shifting into R
(Reverse). Failure to do so may damage the transmission.
Put the gearshift lever into N and wait at least several seconds before
shifting into R.
You can shift into R (Reverse) only by moving the gearshift lever from
left of 3 (Third) and 4 (Fourth) gears before you shift into R (Reverse).
This is a special lockout feature that protects you from accidentally
shifting into R (Reverse) when you downshift from 5 (Overdrive).
FOUR-WHEEL DRIVE (4WD) OPERATION (IF EQUIPPED)
For important information regarding safe operation of this type
of vehicle, seePreparing to drive your vehiclein this chapter.
When Four-wheel drive (4WD) is engaged, power is supplied to all four
wheels through a transfer case. 4WD power can be selected when
additional driving power is desired.
If equipped with the Electronic Shift 4WD System, and the 4x4
Low button is pressed while the vehicle is moving, the system will
not engage and no damage will occur to the 4WD system.
Driving
187
Page 188 of 312
4x4 High and 4x4 Low operation is not recommended on dry
pavement. Doing so could result in difficult disengagement of the
transfer case, increased tire wear and decreased fuel economy.
Control-Trac automatic four-wheel drive system (if equipped)
The 4WD system uses all four wheels to power the vehicle. This
increases traction, enabling you to drive your 4x4 over terrain and road
conditions not normally traveled by two-wheel drive vehicles.
Power is supplied to all four wheels through a transfer case that allows
you to select a four-wheel drive mode best suited for your current
driving conditions.
Positions of the Control-Trac system
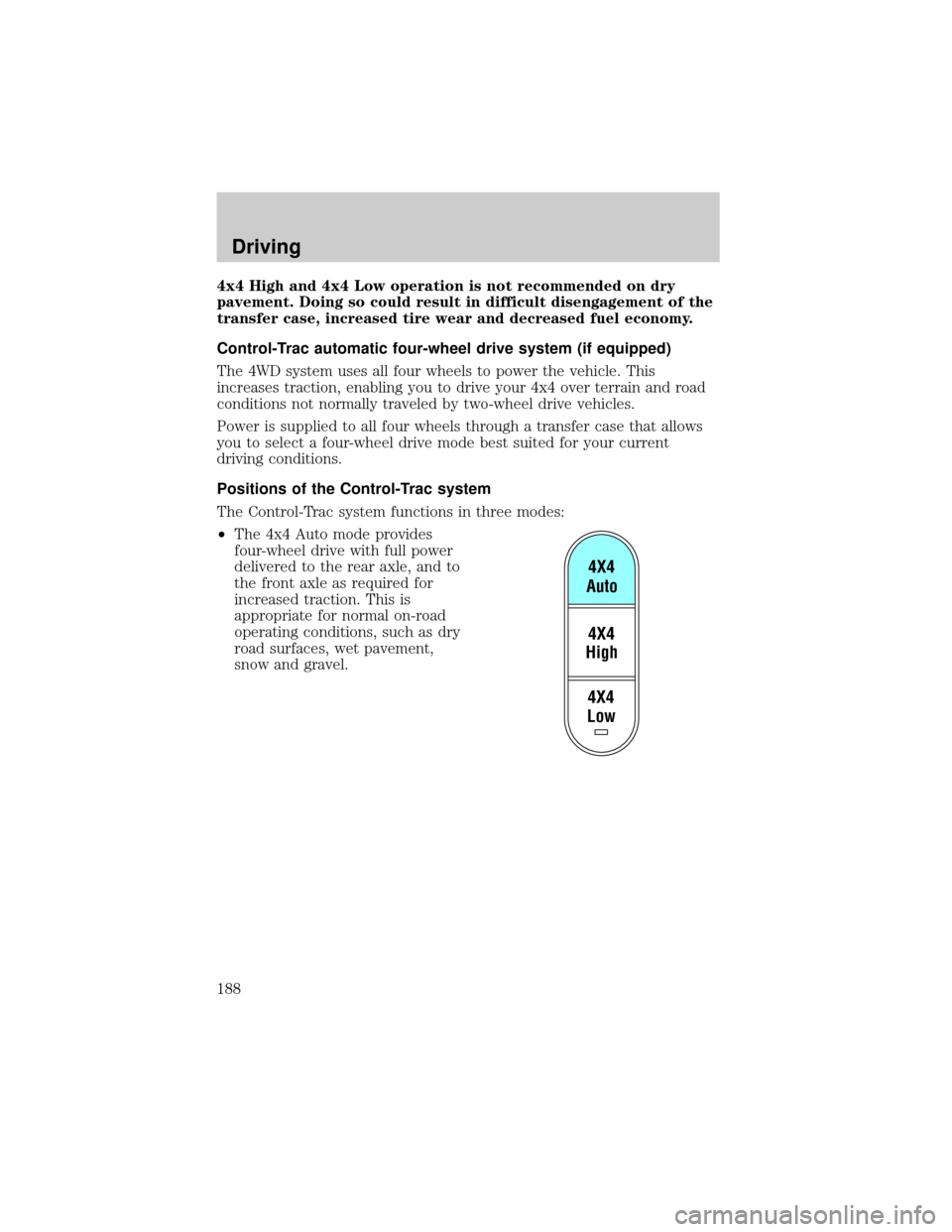
The Control-Trac system functions in three modes:
²The 4x4 Auto mode provides
four-wheel drive with full power
delivered to the rear axle, and to
the front axle as required for
increased traction. This is
appropriate for normal on-road
operating conditions, such as dry
road surfaces, wet pavement,
snow and gravel.
4X4
Low4X4
High4X4
Auto
Driving
188
Page 189 of 312
²The 4x4 High mode provides
four-wheel drive with full power
to both axles. It is only intended
for severe winter or off-road
conditions, such as deep snow
and ice (where no dry or wet
pavement remains uncovered),
and shallow sand.
²The 4x4 Low mode supplies
four-wheel drive with full power
to both axles and includes a
lower gear ratio for low-speed. It
is only intended for off-road
applications that require extra
power including deep sand, steep
grades and pulling a boat and
trailer out of the water.
The vehicle should not be operated in 4x4 High and 4x4 Low on
dry or merely wet pavement. Doing so will produce excessive
noise, increase tire wear and may damage driveline components.
These modes are intended for use only on consistently slippery or
loose surfaces.
If your vehicle is equipped with 4WD, a spare tire of a different
size than the road tires should never be used. Such a tire could
result in damage to driveline components and make the vehicle
difficult to control.
4X4
Low4X4
High4X4
Auto
4X4
Low4X4
High4X4
Auto
Driving
189
Page 190 of 312
Utility and four-wheel drive vehicles arenotdesigned for
cornering at speeds as high as passenger cars any more than
low-slung sports cars are designed to perform satisfactorily under
off-road conditions. Avoid sharp turns or abrupt maneuvers in these
vehicles.
Using the Control-Trac system
Shifting between 4x4 Auto and 4x4 High
When you press the 4x4 High
button, the indicator light will
illuminate in the instrument cluster.
When you press the 4x4 Auto
button, the indicator light will turn
off.
Either shift can be done at a stop or
while driving at any speed.
Shifting from 4x4 Auto or 4x4 High to 4x4 Low
1. Bring the vehicle to a stop.
2. Depress the brake.
3. Place the gearshift in N (Neutral)
(automatic transmission) or depress
the clutch (manual transmission).
4. Press the 4x4 Low button. When
engaged the 4x4 Low instrument
cluster light and the 4x4 Low button
will illuminate.
4X4
Low4X4
High4X4
Auto
4X4
Low4X4
High4X4
Auto
Driving
190