weight FORD EXPLORER 2016 5.G Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 2016, Model line: EXPLORER, Model: FORD EXPLORER 2016 5.GPages: 541, PDF Size: 6.51 MB
Page 244 of 541

*Suppose your vehicle has a
1400-pound (635-kilogram) cargo
and luggage capacity. You decide
to go golfing. Is there enough load
capacity to carry you, four of your
friends and all the golf bags? You
and four friends average 220
pounds (99 kilograms) each and
the golf bags weigh approximately
30 pounds (13.5 kilograms) each.
The calculation would be: 1400 -
(5 x 220) - (5 x 30) = 1400 - 1100
- 150 = 150 pounds. Yes, you have
enough load capacity in your
vehicle to transport four friends
and your golf bags. In metric units,
the calculation would be: 635
kilograms - (5 x 99 kilograms) -
(5 x 13.5 kilograms) = 635 - 495 -
67.5 = 72.5 kilograms.
*Suppose your vehicle has a
1400-pound (635-kilogram) cargo
and luggage capacity. You and
one of your friends decide to pick
up cement from the local home
improvement store to finish that
patio you have been planning for
the past two years. Measuring the
inside of the vehicle with the rear
seat folded down, you have room
for twelve 100-pound
(45-kilogram) bags of cement. Do
you have enough load capacity to
transport the cement to your
home? If you and your friend each
weigh 220 pounds (99 kilograms),
the calculation would be: 1400 -
(2 x 220) - (12 x 100) = 1400 - 440
- 1200 = - 240 pounds. No, you do
not have enough cargo capacity
to carry that much weight. In
metric units, the calculation would
be: 635 kilograms - (2 x 99
kilograms) - (12 x 45 kilograms) =
635 - 198 - 540 = -103 kilograms.
You will need to reduce the load
weight by at least 240 pounds
(104 kilograms). If you remove
three 100-pound (45-kilogram)
cement bags, then the load
calculation would be: 1400 - (2 x
220) - (9 x 100) = 1400 - 440 -
900 = 60 pounds. Now you have
the load capacity to transport the
cement and your friend home. In
metric units, the calculation would
be: 635 kilograms - (2 x 99
kilograms) - (9 x 45 kilograms) =
635 - 198 - 405 = 32 kilograms.
The above calculations also
assume that the loads are
positioned in your vehicle in a
manner that does not overload
the Front or the Rear Gross Axle
Weight Rating specified for your
vehicle on the Safety Compliance
Certification Label. The label shall
be affixed to either the door hinge
pillar, door-latch post, or the door
edge that meets the door-latch
post, next to the driver seating
position.
241
Explorer (TUB), enUSA, First Printing Load Carrying
Page 246 of 541

TOWING A TRAILER
WARNINGS
Do not exceed the GVWR or
the GAWR specified on the
certification label. Towing trailers beyond the
maximum recommended
gross trailer weight exceeds the
limit of the vehicle and could
result in engine damage,
transmission damage, structural
damage, loss of vehicle control,
vehicle rollover and personal
injury. Your vehicle may have electrical
items, such as fuses or relays,
related to towing. See the Fuses
chapter.
Your vehicle's load capacity
designation is by weight, not by
volume, so you cannot necessarily
use all available space when
loading a vehicle or trailer.
Towing a trailer places an extra
load on your vehicle's engine,
transmission, axle, brakes, tires
and suspension. Inspect these
components periodically during,
and after, any towing operation. Load Placement
To help minimize how trailer
movement affects your vehicle
when driving:
•
Load the heaviest items closest
to the trailer floor.
• Load the heaviest items
centered between the left and
right side trailer tires.
• Load the heaviest items above
the trailer axles or just slightly
forward toward the trailer
tongue. Do not allow the final
trailer tongue weight to go
above or below 10-15% of the
loaded trailer weight.
• Select a tow bar with the
correct rise or drop. When both
the loaded vehicle and trailer
are connected, the trailer frame
should be level, or slightly
angled down toward your
vehicle, when viewed from the
side.
When driving with a trailer or
payload, a slight takeoff vibration
or shudder may be present due to
the increased payload weight.
Additional information regarding
proper trailer loading and setting
your vehicle up for towing is
located in another chapter of this
manual. See
Load Limit (page
235).
You can also find information in
the
RV & Trailer Towing Guide
available at your authorized
dealer, or online.
243
Explorer (TUB), enUSA, First Printing Towing
Page 247 of 541

RV & Trailer Towing Guide Online
http://www.fleet.ford.com/towing-guides/
Website
TRAILER SWAY CONTROL (If
Equipped) WARNING
Turning off trailer sway control
increases the risk of loss of vehicle
control, serious injury or death. Ford
does not recommend disabling this feature
except in situations where speed reduction
may be detrimental (such as hill climbing),
the driver has significant trailer towing
experience, and can control trailer sway
and maintain safe operation. Note:
This feature does not prevent trailer
sway, but reduces it when it begins.
Note: This feature cannot stop all trailers
from swaying.
Note: In some cases, if your vehicle speed
is too high, the system may turn on multiple
times, gradually reducing your vehicle speed.
The system applies the brakes to the
individual wheels and reduces engine
torque to aid vehicle stability. If the trailer
begins to sway, the stability control
warning lamp flashes and a message
appears in the information display. See
Information Messages
(page 115). Slow
your vehicle down, pull safely to the side
of the road and check for correct load
distribution. See
Load Carrying (page
233).
You can switch this feature off in the
information display. When you switch the
ignition on, the system automatically turns
on. RECOMMENDED TOWING
WEIGHTS
Note:
Do not exceed the trailer
weight for your vehicle
configuration listed in the chart
below.
Note: Be sure to take into
consideration trailer frontal area.
Do not exceed 20 feet² (1.86
meters²) if your vehicle can tow a
class I trailer or 40 feet² (3.72
meters²) if your vehicle can tow a
class III trailer.
Note: For high altitude operation,
reduce the gross combined weight
by 2% per 1000 feet (300 meters)
starting at the 1000 foot (300
meter) elevation point.
Note: Certain states require
electric trailer brakes for trailers
over a specified weight. Be sure to
check state regulations for this
specified weight. The maximum
trailer weights listed may be limited
to this specified weight, as the
vehicle ’s electrical system may not
include the wiring connector
needed to activate electric trailer
brakes.
244
Explorer (TUB), enUSA, First Printing Towing
Page 248 of 541
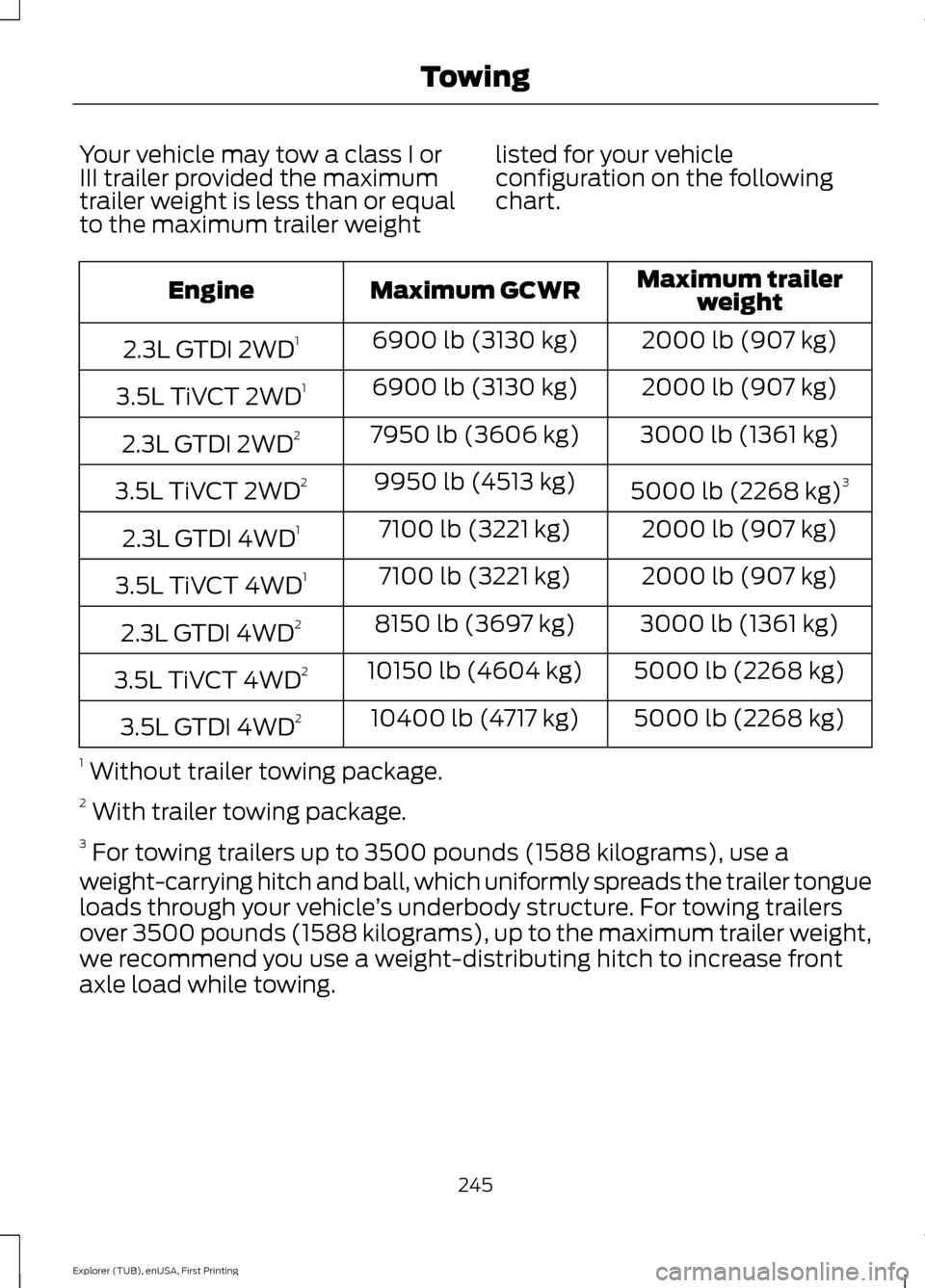
Your vehicle may tow a class I or
III trailer provided the maximum
trailer weight is less than or equal
to the maximum trailer weight
listed for your vehicle
configuration on the following
chart. Maximum trailer
weight
Maximum GCWR
Engine
2000 lb (907 kg)
6900 lb (3130 kg)
2.3L GTDI 2WD 1
2000 lb (907 kg)
6900 lb (3130 kg)
3.5L TiVCT 2WD 1
3000 lb (1361 kg)
7950 lb (3606 kg)
2.3L GTDI 2WD 2
5000 lb (2268 kg)3
9950 lb (4513 kg)
3.5L TiVCT 2WD 2
2000 lb (907 kg)
7100 lb (3221 kg)
2.3L GTDI 4WD 1
2000 lb (907 kg)
7100 lb (3221 kg)
3.5L TiVCT 4WD 1
3000 lb (1361 kg)
8150 lb (3697 kg)
2.3L GTDI 4WD 2
5000 lb (2268 kg)
10150 lb (4604 kg)
3.5L TiVCT 4WD 2
5000 lb (2268 kg)
10400 lb (4717 kg)
3.5L GTDI 4WD 2
1 Without trailer towing package.
2 With trailer towing package.
3 For towing trailers up to 3500 pounds (1588 kilograms), use a
weight-carrying hitch and ball, which uniformly spreads the trailer tongue
loads through your vehicle ’s underbody structure. For towing trailers
over 3500 pounds (1588 kilograms), up to the maximum trailer weight,
we recommend you use a weight-distributing hitch to increase front
axle load while towing.
245
Explorer (TUB), enUSA, First Printing Towing
Page 249 of 541

ESSENTIAL TOWING CHECKS
Follow these guidelines for safe towing:
•
Do not tow a trailer until you drive your
vehicle at least 1000 miles (1600
kilometers).
• Consult your local motor vehicle laws
for towing a trailer.
• See the instructions included with
towing accessories for the proper
installation and adjustment
specifications.
• Service your vehicle more frequently if
you tow a trailer. See your scheduled
maintenance information.
• If you use a rental trailer, follow the
instructions the rental agency gives
you.
You can find information on load
specification terms found on the tire label
and Safety Compliance label as well as
instructions on calculating your vehicle's
load in the Load Carrying chapter. See
Load Limit (page 235).
Remember to account for the trailer
tongue weight as part of your vehicle load
when calculating the total vehicle weight.
Hitches
Do not use a hitch that either clamps onto
the bumper or attaches to the axle.
Distribute the trailer load so 10-15% of the
total trailer weight is on the tongue. Weight-distributing Hitches WARNING
Do not adjust a weight-distributing
hitch to any position where the rear
bumper of the vehicle is higher than
it was before attaching the trailer. Doing
so will defeat the function of the
weight-distributing hitch, which may cause
unpredictable handling, and could result
in serious personal injury. When hooking-up a trailer using a
weight-distributing hitch, always use the
following procedure:
1. Park the loaded vehicle, without the
trailer, on a level surface.
2. Measure the height to the top of your vehicle's front wheel opening on the
fender. This is H1.
3. Attach the loaded trailer to your vehicle
without the weight-distributing bars
connected.
4. Measure the height to the top of your vehicle's front wheel opening on the
fender a second time. This is H2.
5. Install and adjust the tension in the weight-distributing bars so that the
height of your vehicle's front wheel
opening on the fender is approximately
half the way down from H2, toward H1.
6. Check that the trailer is level or slightly
nose down toward your vehicle. If not,
adjust the ball height accordingly and
repeat Steps 2-6.
When the trailer is level or slightly nose
down toward the vehicle:
• Lock the bar tension adjuster in place.
• Check that the trailer tongue securely
attaches and locks onto the hitch.
• Install safety chains, lighting, and trailer
brake controls as required by law or the
trailer manufacturer.
246
Explorer (TUB), enUSA, First Printing Towing
Page 250 of 541

Safety Chains
Note:
Never attach safety chains to the
bumper.
Always connect the safety chains to the
hook retainers of your vehicle hitch.
To connect the trailer ’s safety chains, cross
them under the trailer tongue and allow
enough slack for turning tight corners. Do
not allow the chains to drag on the ground.
Trailer Brakes WARNING
Do not connect a trailer's hydraulic
brake system directly to your
vehicle's brake system. Your vehicle
may not have enough braking power and
your chances of having a collision greatly
increase. Electric brakes and manual, automatic or
surge-type trailer brakes are safe if you
install them properly and adjust them to
the manufacturer's specifications. The
trailer brakes must meet local and federal
regulations.
The rating for the tow vehicle's braking
system operation is at the gross vehicle
weight rating, not the gross combined
weight rating.
Separate functioning brake systems
are required for safe control of towed
vehicles and trailers weighing more
than 1500 pounds (680 kilograms)
when loaded. Trailer Lamps WARNING
Never connect any trailer lamp wiring
to the vehicle's tail lamp wiring; this
may damage the electrical system
resulting in fire. Contact your authorized
dealer as soon as possible for assistance
in proper trailer tow wiring installation.
Additional electrical equipment may be
required. Trailer lamps are required on most towed
vehicles. Make sure all running lights, brake
lights, turn signals and hazard lights are
working.
Before Towing a Trailer
Practice turning, stopping and backing up
to get the feel of your vehicle-trailer
combination before starting on a trip.
When turning, make wider turns so the
trailer wheels clear curbs and other
obstacles.
When Towing a Trailer
•
Do not drive faster than 70 mph (113
km/h) during the first 500 miles (800
kilometers).
• Do not make full-throttle starts.
• Check your hitch, electrical connections
and trailer wheel lug nuts thoroughly
after you have traveled 50 miles (80
kilometers).
• When stopped in congested or heavy
traffic during hot weather, place the
gearshift in position P to aid engine and
transmission cooling and to help A/C
performance.
• Turn off the speed control with heavy
loads or in hilly terrain. The speed
control may turn off automatically
when you are towing on long, steep
grades.
247
Explorer (TUB), enUSA, First Printing Towing
Page 255 of 541

BREAKING-IN
You need to break in new tires for
approximately 300 miles (480
kilometers). During this time, your vehicle
may exhibit some unusual driving
characteristics.
Avoid driving too fast during the first 1000
miles (1600 kilometers). Vary your speed
frequently and change up through the
gears early. Do not labor the engine.
Do not tow during the first 1000 miles
(1600 kilometers).
ECONOMICAL DRIVING
Your fuel economy is affected by several
things, such as how you drive, the
conditions you drive under, and how you
maintain your vehicle.
You may improve your fuel economy by
keeping these things in mind:
•
Accelerate and slow down in a smooth,
moderate fashion.
• Drive at steady speeds without
stopping.
• Anticipate stops; slowing down may
eliminate the need to stop.
• Combine errands and minimize
stop-and-go driving.
• Close the windows for high-speed
driving.
• Drive at reasonable speeds (traveling
at 55 mph [88 km/h] uses 15% less
fuel than traveling at 65 mph [105
km/h]).
• Keep the tires properly inflated and use
only the recommended size.
• Use the recommended engine oil.
• Perform all regularly scheduled
maintenance. Avoid these actions; they reduce your fuel
economy:
•
Sudden accelerations or hard
accelerations.
• Revving the engine before turning it off.
• Idle for periods longer than one minute.
• Warm up your vehicle on cold
mornings.
• Use the air conditioner or front
defroster.
• Use the speed control in hilly terrain.
• Rest your foot on the brake pedal while
driving.
• Drive a heavily loaded vehicle or tow a
trailer.
• Carry unnecessary weight
(approximately 1 mpg [0.4 km/L] is
lost for every 400 lb [180 kilogram] of
weight carried).
• Driving with the wheels out of
alignment.
Conditions
• Heavily loading a vehicle or towing a
trailer may reduce fuel economy at any
speed.
• Adding certain accessories to your
vehicle (for example bug deflectors,
rollbars, light bars, running boards, ski
racks or luggage racks) may reduce
fuel economy.
• To maximize the fuel economy, drive
with the tonneau cover installed (if
equipped).
• Using fuel blended with alcohol may
lower fuel economy.
• Fuel economy may decrease with lower
temperatures during the first 8– 10
miles (12 –16 kilometers) of driving.
• Driving on flat terrain offers improved
fuel economy as compared to driving
on hilly terrain.
252
Explorer (TUB), enUSA, First Printing Driving Hints
Page 280 of 541
4.
Open the hood. Support the hood with
the strut.
Closing the Hood
1. Remove the hood strut from the catch
and secure it correctly after use.
2. Lower the hood and allow it to drop under its own weight for the last
8–12 in (20– 30 cm).
Note: Make sure that the hood is correctly
closed.
277
Explorer (TUB), enUSA, First Printing Maintenance4
E203320
Page 314 of 541

The traction grades, from highest
to lowest are AA, A, B, and C. The
grades represent the tire
’s ability
to stop on wet pavement as
measured under controlled
conditions on specified
government test surfaces of
asphalt and concrete. A tire
marked C may have poor traction
performance.
Temperature A B C WARNING
The temperature grade for
this tire is established for a
tire that is properly inflated and
not overloaded. Excessive speed,
underinflation, or excessive
loading, either separately or in
combination, can cause heat
buildup and possible tire failure. The temperature grades are A
(the highest), B and C,
representing the tire
’s resistance
to the generation of heat and its
ability to dissipate heat when
tested under controlled conditions
on a specified indoor laboratory
test wheel. Sustained high
temperature can cause the
material of the tire to degenerate
and reduce tire life, and excessive
temperature can lead to sudden
tire failure. The grade C
corresponds to a level of
performance which all passenger
car tires must meet under the Federal Motor Vehicle Safety
Standard No. 139. Grades B and A
represent higher levels of
performance on the laboratory
test wheel than the minimum
required by law.
Glossary of Tire Terminology
*Tire label: A label showing the
original equipment tire sizes,
recommended inflation pressure
and the maximum weight the
vehicle can carry.
*
Tire Identification Number
(TIN): A number on the sidewall
of each tire providing information
about the tire brand and
manufacturing plant, tire size and
date of manufacture. Also referred
to as DOT code.
*
Inflation pressure: A measure
of the amount of air in a tire.
*
Standard load: A class of
P-metric or Metric tires designed
to carry a maximum load at set
pressure. For example: For
P-metric tires
35 psi (2.4 bar) or
36 psi (2.5 bar) depending on tires
size and for Metric tires
36 psi
(2.5 bar). Increasing the inflation
pressure beyond this pressure will
not increase the tire ’s load
carrying capability.
*
Extra load: A class of P-metric
or Metric tires designed to carry a
heavier maximum load at
42 psi
(2.9 bar). Increasing the inflation
pressure beyond this pressure will
not increase the tire ’s load
carrying capability.
311
Explorer (TUB), enUSA, First Printing Wheels and Tires
Page 316 of 541

A.
P: Indicates a tire, designated
by the Tire and Rim Association,
that may be used for service on
cars, sport utility vehicles,
minivans and light trucks. Note:
If
your tire size does not begin with
a letter this may mean it is
designated by either the European
Tire and Rim Technical
Organization or the Japan Tire
Manufacturing Association.
B. 215:
Indicates the nominal
width of the tire in millimeters
from sidewall edge to sidewall
edge. In general, the larger the
number, the wider the tire.
C. 65:
Indicates the aspect ratio
which gives the tire's ratio of
height to width.
D. R:
Indicates a radial type tire.
E. 15:
Indicates the wheel or rim
diameter in inches. If you change
your wheel size, you will have to
purchase new tires to match the
new wheel diameter.
F. 95:
Indicates the tire's load
index. It is an index that relates to
how much weight a tire can carry.
You may find this information in
your owner ’s manual. If not,
contact a local tire dealer.
Note: You may not find this
information on all tires because it
is not required by federal law. G.
H:
Indicates the tire's speed
rating. The speed rating denotes
the speed at which a tire is
designed to be driven for extended
periods of time under a standard
condition of load and inflation
pressure. The tires on your vehicle
may operate at different
conditions for load and inflation
pressure. These speed ratings may
need to be adjusted for the
difference in conditions. The
ratings range from
81 mph
(130 km/h) to 186 mph
(299 km/h). These ratings are
listed in the following chart.
Note: You may not find this
information on all tires because it
is not required by federal law. Speed rating
Letter
rating
81 mph (130 km/h)
M
87 mph (140 km/h)
N
99 mph (159 km/h)
Q
106 mph (171 km/h)
R
112 mph (180 km/h)
S
118 mph (190 km/h)
T
124 mph (200 km/h)
U
130 mph (210 km/h)
H
149 mph (240 km/h)
V
313
Explorer (TUB), enUSA, First Printing Wheels and Tires