lights FORD FESTIVA 1991 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 1991, Model line: FESTIVA, Model: FORD FESTIVA 1991Pages: 454, PDF Size: 9.53 MB
Page 68 of 454
Shift Lock ActuatorShift Interlock Systems
Side Marker LightsExterior Lights
SIR Coil Assembly (Clockspring)Air Bag Restraint System
Slip Ring (Clockspring)Air Bag Restraint System; Steering Column Switches
SRS Control ModuleAir Bag Restraint System
Starter MotorStarters
Starter Interrupt RelayStarters
Starter SolenoidStarters
Starter RelayStarters
Steering Wheel Position SensorAnti-Lock Brakes
StoplightsExterior Lights
Stoplight SwitchEngine Performance; Cruise Control Systems; Anti-Lock Brakes
Sun Roof ECUPower Sun Roof
Sun Roof MotorPower Sun Roof
Sun Roof Position SensorPower Sun Roof
TaillightsExterior Lights
Throttle Position (TP) SensorEngine Performance
Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid/SwitchEngine Performance
Traction Control SwitchAnti-Lock Brakes
Trailer Tow ConnectorExterior Lights
Trailer Tow RelayExterior Lights
Transmission/TransaxleEngine Performance
Transmission Control Module (TCM)Engine Performance; Starters
Transmission Range SensorStarters; Back-Up Lights; Engine Performance
Transmission Range SwitchBack-Up Lights; Engine Performance; Anti-Theft System
Turn Signal FlasherExterior Lights
Tu r n S ign a l Ligh t sExterior Lights
Twilight Sentinel SwitchHeadlight Systems; Daytime Running Lights
Vapor Canister Leak Detection PumpEngine Performance
Vehicle Control Module (VCM)Engine Performance
Vehicle Dynamic ModuleElectronic Suspension
Vehicle Speed Control ServoCruise Control Systems
Vehicle Speed SensorData Link Connectors; Analog Instrument Panels; Cruise Control
Systems; Electronic Suspension
Voltage RegulatorGenerators & Regulators
Water-In-Fuel SensorEngine Performance; Analog Instrument Panels
Wheel Speed SensorsAnti-Lock Brakes
Window Timer ModulePower Convertible Top
Windshield Intermittent Wiper RelayWiper/Washer Systems
Windshield Washer MotorWiper/Washer Systems
Wiper MotorWiper/Washer Systems
Copyr ight 2009 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC. All Rights Reserved.
Article GUID: A00130983
Page 6 of 6 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - GENERAL INFORMATION Using Mitchell1's Wiring Diagrams
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B959286D2%2D3A85%2D4BFC%2D9C5C%2D
...
Page 70 of 454
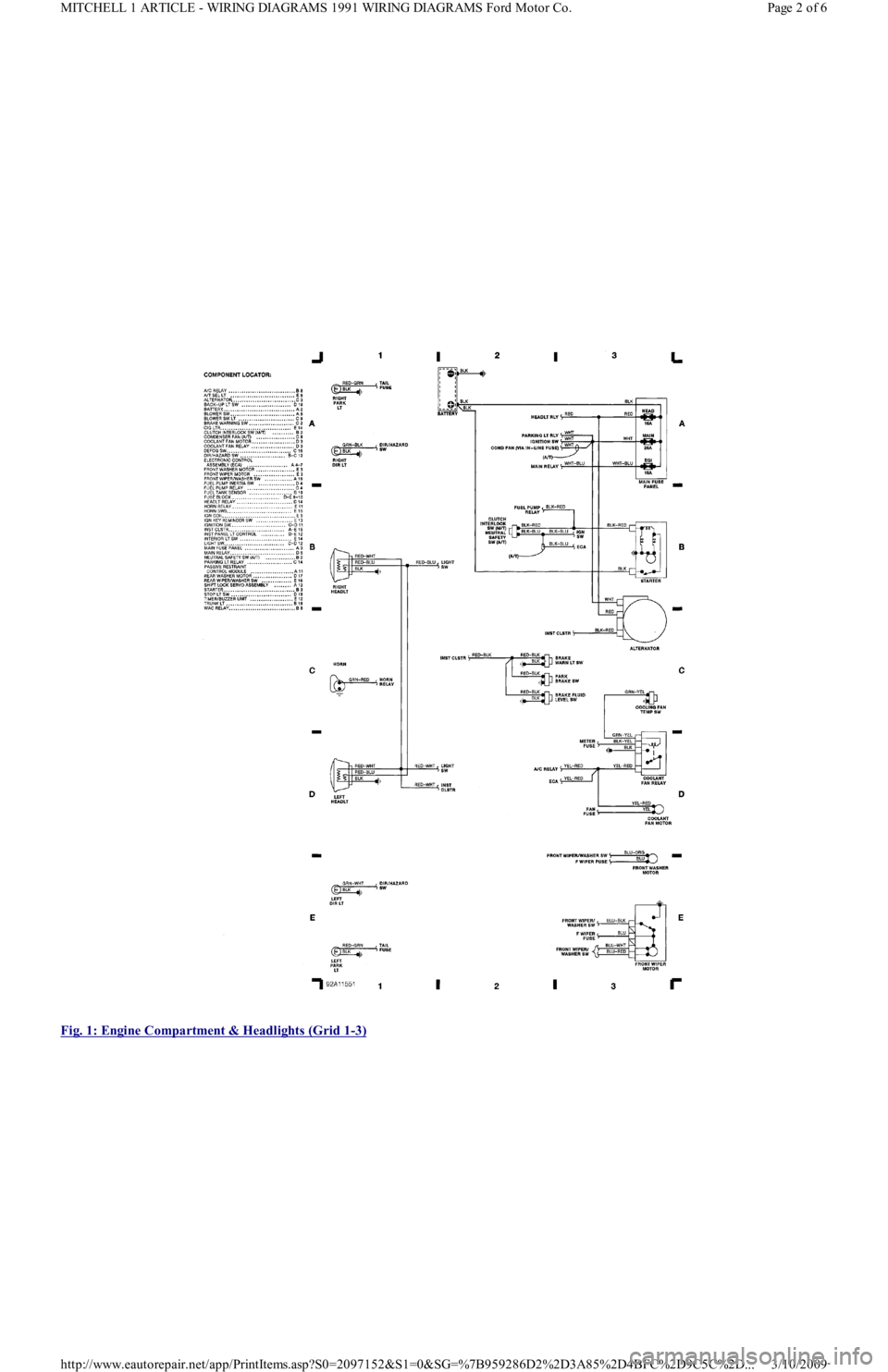
Fig. 1: Engine Compartment & Headlights (Grid 1
-3)
Page 2 of 6 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - WIRING DIAGRAMS 1991 WIRING DIAGRAMS Ford Motor Co.
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B959286D2%2D3A85%2D4BFC%2D9C5C%2D
...
Page 74 of 454
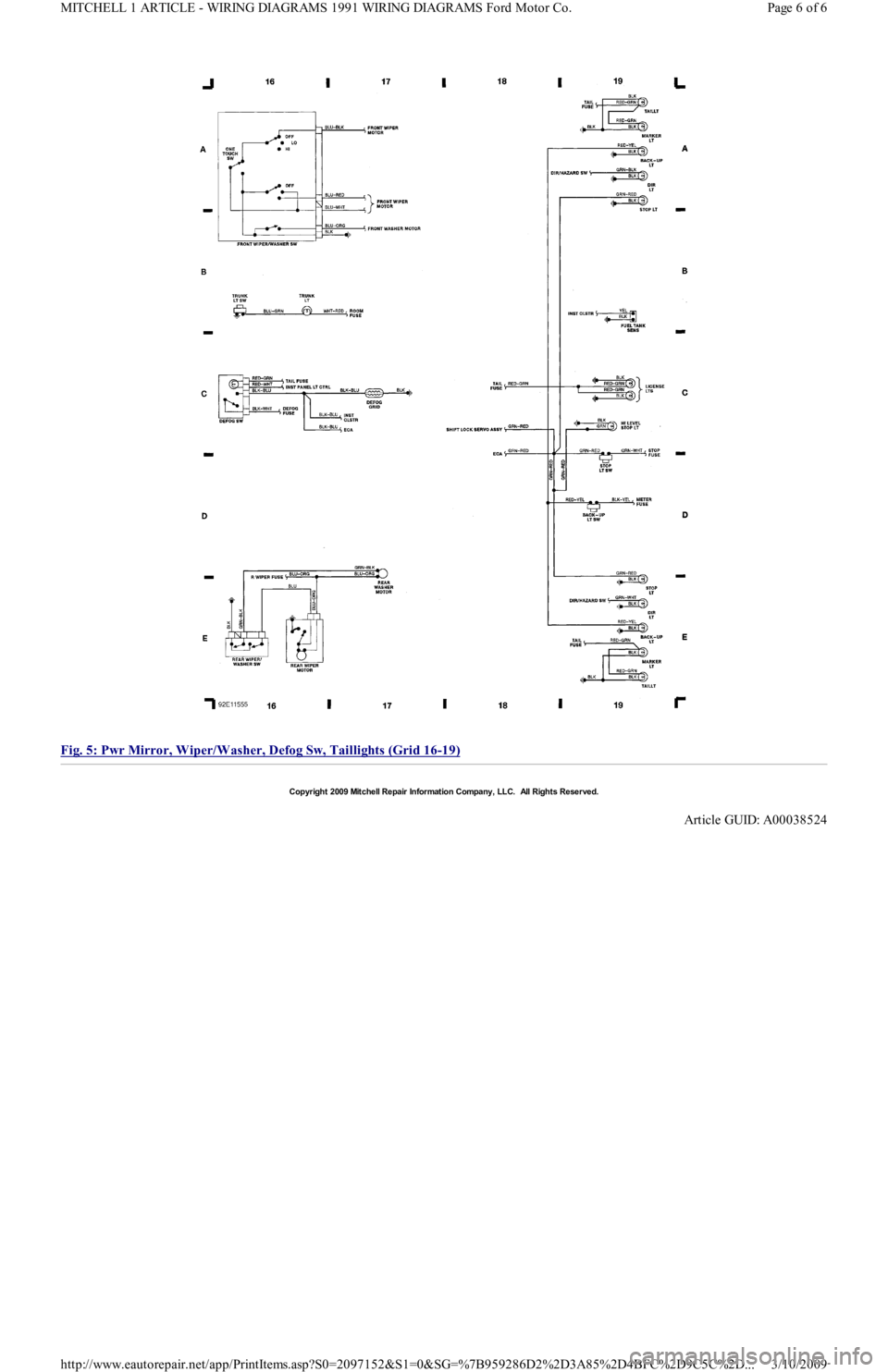
Fig. 5: Pwr Mirror, Wiper/Washer, Defog Sw, Taillights (Grid 16
-19)
Copyr ight 2009 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC. All Rights Reserved.
Article GUID: A00038524
Page 6 of 6 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - WIRING DIAGRAMS 1991 WIRING DIAGRAMS Ford Motor Co.
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B959286D2%2D3A85%2D4BFC%2D9C5C%2D
...
Page 169 of 454
memory. Intermittent failures may be caused by a sensor, connector, or wiring. See INTERMITTENTS in TESTS W/O CODES article in the
ENGINE PERFORMANCE Section.
VISUAL CHECK & VEHICLE PREPARATION
Before connecting any equipment to diagnose EEC system, perform following preparatory procedures:
Verify condition of air cleaner and air ducts.
Check all vacuum hoses for leaks, restrictions, or improper routing.
Check EEC system wiring harness electrical connections for corrosion, bent or broken pins, loose wires or terminals, or improper
routing.
Check ECA, sensors, and actuators for physical damage.
Check engine oil and coolant level.
Perform all necessary safety precautions to prevent personal injury or vehicle damage.
Set parking brake. Place shift lever in Park for automatic transmissions, or Neutral for manual transmissions. DO NOT move shift lever
during test unless specifically directed.
Turn off all lights and accessories. Ensure vehicle doors are closed when measuring voltage or resistance.
Start engine. Run at idle until upper radiator hose is hot and pressurized and engine is off fast idle. Check for leaks around exhaust
manifold, exhaust gas oxygen sensor, and vacuum hose connections.
Turn ignition off. Service items as required. Go to EQUIPMENT HOOK-UP .
EQUIPMENT HOOK-UP
VOM
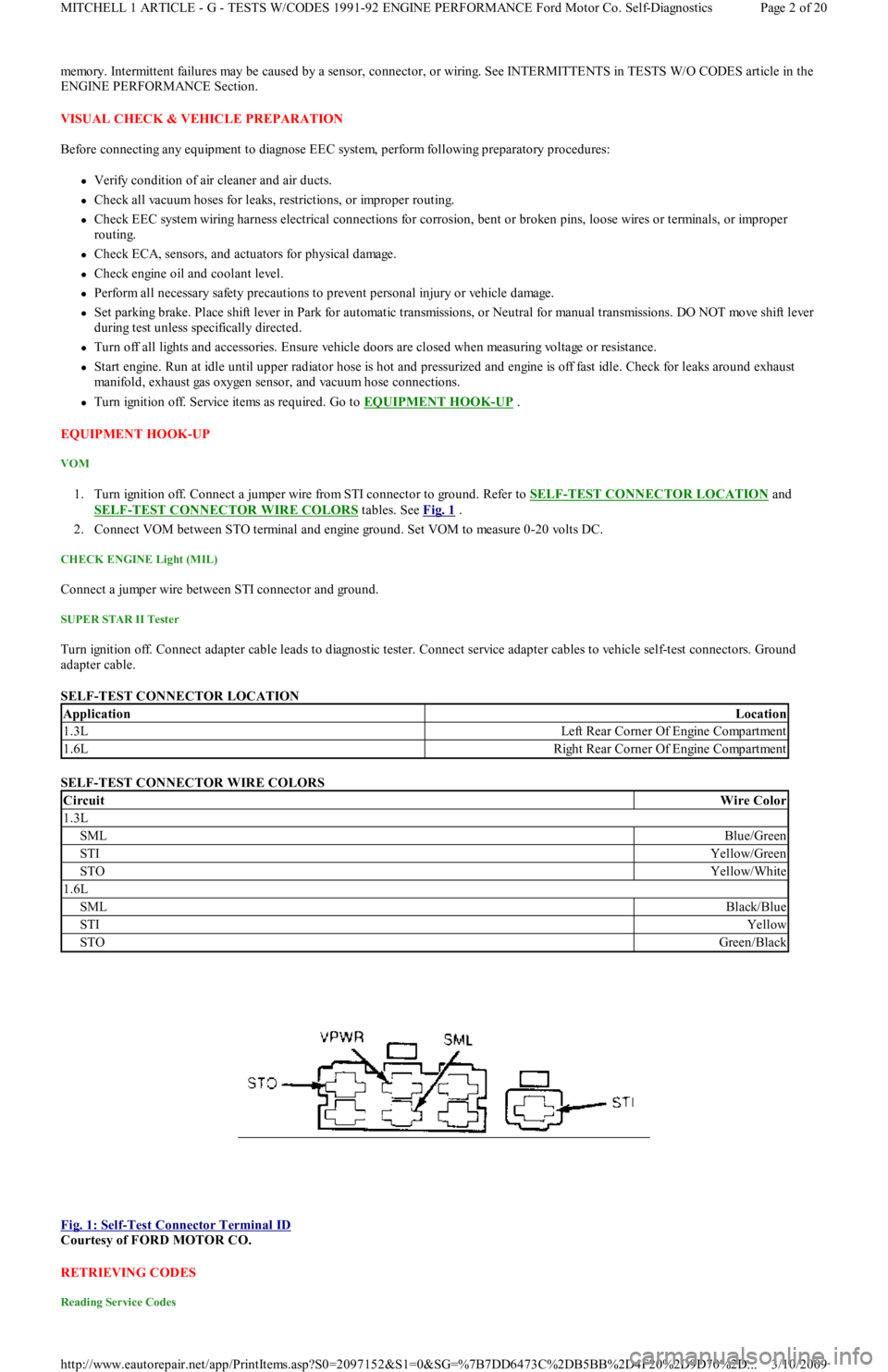
1. Turn ignition off. Connect a jumper wire from STI connector to ground. Refer to SELF-TEST CONNECTOR LOCATION and
SELF
-TEST CONNECTOR WIRE COLORS tables. See Fig. 1 .
2. Connect VOM between STO terminal and engine ground. Set VOM to measure 0-20 volts DC.
CHECK ENGINE Light (MIL)
Connect a jumper wire between STI connector and ground.
SUPER STAR II Tester
Turn ignition off. Connect adapter cable leads to diagnostic tester. Connect service adapter cables to vehicle self-test connectors. Ground
adapter cable.
SELF-TEST CONNECTOR LOCATION
SELF-TEST CONNECTOR WIRE COLORS
Fig. 1: Self
-Test Connector Terminal ID
Courtesy of FORD MOTOR CO.
RETRIEVING CODES
Reading Service Codes
ApplicationLocation
1.3LLeft Rear Corner Of Engine Compartment
1.6LRight Rear Corner Of Engine Compartment
CircuitWire Color
1.3L
SMLBlue/Green
STIYellow/Green
STOYellow/White
1.6L
SMLBlack/Blue
STIYellow
STOGreen/Black
Page 2 of 20 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - G - TESTS W/CODES 1991-92 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Ford Motor Co. Self-Diagnostics
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B7DD6473C%2DB5BB%2D4F20%2D9D70%2D
...
Page 214 of 454
Back To Article
GENERAL INFORMATION
T rouble Shooting - Basic Procedures
* PLEASE READ THIS FIRST *
ACCESSORIES & ELECTRICAL
CHARGING SYSTEM TROUBLE SHOOTING
BASIC CHARGING SYSTEM TROUBLE SHOOTING CHART NOTE:This is GENERAL inform ation. This article is not intended to be specific to any unique situation or
individual vehicle configuration. T he purpose of this T rouble Shooting inform ation is to provide a list
of com m on causes to problem sym ptom s. For m odel-specific T rouble Shooting, refer to SUBJECT ,
DIAGNOST IC, or T EST ING articles available in the section(s) you are accessing.
NOTE:This is GENERAL inform ation. This article is not intended to be specific to any unique situation or
individual vehicle configuration. T he purpose of this T rouble Shooting inform ation is to provide a list
of com m on causes to problem sym ptom s. For m odel-specific T rouble Shooting, refer to SUBJECT ,
DIAGNOST IC, or T EST ING articles available in the section(s) you are accessing.
NOTE:This is GENERAL inform ation. This article is not intended to be specific to any unique situation or
individual vehicle configuration. T he purpose of this T rouble Shooting inform ation is to provide a list
of com m on causes to problem sym ptom s. For m odel-specific T rouble Shooting, refer to SUBJECT ,
DIAGNOST IC, or T EST ING articles available in the section(s) you are accessing.
CONDITION & POSSIBLE CAUSECORRECTION
Vehicle Will Not Start
Dead batteryCheck battery cells, alternator
belt tension and alternator
output
Loose or corroded battery connectionsCheck all charging system
connections
Ignition circuit or switch malfunctionCheck and replace as necessary
Alternator Light Stays On With Engine Running
Loose or worn alternator drive beltCheck alternator drive tension
and condition, See Belt
Adjustment in TUNE-UP article
in the TUNE-UP section
Loose alternator wiring connectionsCheck all charging system
connections
Short in alternator light wiringSee Indicator Warning Lights in
STANDARD INSTRUMENTS
in the ACCESSORIES &
EQUIPMENT section
Defective alternator stator or diodesSee Bench Tests in
ALTERNATOR article
Defective regulatorSee Regulator Check in
ALTERNATOR article
Alternator Light Stays Off With Ignition Switch ON
Blown fuseSee WIRING DIAGRAMS
Defective alternatorSee Testing in ALTERNATOR
article
Defective indicator light bulb or socketSee Indicator Warning Lights in
STANDARD INSTRUMENTS
in the ACCESSORIES &
EQUIPMENT section
Alternator Light Stays OFF With Ignition Switch ON
Short in alternator wiringSee On-Vehicle Tests in
ALTERNATOR article
Defective rectifier bridgeSee Bench Tests in
ALTERNATOR article
Lights or Fuses Burn Out Frequently
Defective alternator wiringSee On-Vehicle Tests in
ALTERNATOR article
Defective regulatorSee Regulator Check in
ALTERNATOR article
Defective batteryCheck and replace as necessary
Ammeter Gauge Shows Discharge
Loose or worn drive beltCheck alternator drive belt
tension and condition. See Belt
Adjustment in TUNE-UP article
in the TUNE-UP section
Defective wiringCheck all wires and wire
Page 1 of 36 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - GENERAL INFORMATION Trouble Shooting - Basic Procedures
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B9B990D68%2D660A%2D45E9%2D8F46%2DE
...
Page 217 of 454
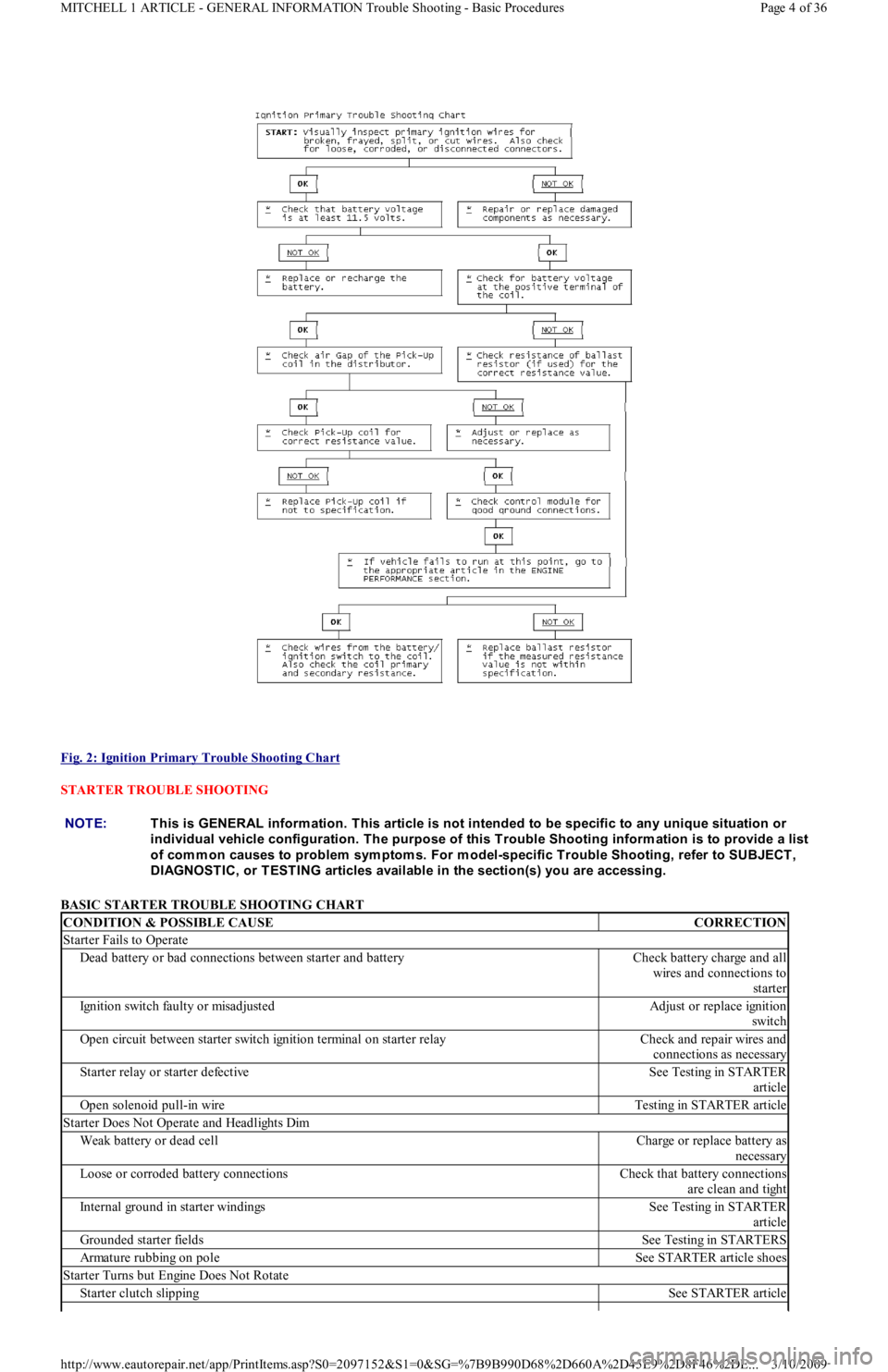
Fig. 2: Ignition Primary Trouble Shooting Chart
STARTER TROUBLE SHOOTING
BASIC STARTER TROUBLE SHOOTING CHART
NOTE:This is GENERAL inform ation. This article is not intended to be specific to any unique situation or
individual vehicle configuration. T he purpose of this T rouble Shooting inform ation is to provide a list
of com m on causes to problem sym ptom s. For m odel-specific T rouble Shooting, refer to SUBJECT ,
DIAGNOST IC, or T EST ING articles available in the section(s) you are accessing.
CONDITION & POSSIBLE CAUSECORRECTION
Starter Fails to Operate
Dead battery or bad connections between starter and batteryCheck battery charge and all
wires and connections to
starter
Ignition switch faulty or misadjustedAdjust or replace ignition
switch
Open circuit between starter switch ignition terminal on starter relayCheck and repair wires and
connections as necessary
Starter relay or starter defectiveSee Testing in STARTER
article
Open solenoid pull-in wireTesting in STARTER article
Starter Does Not Operate and Headlights Dim
Weak battery or dead cellCharge or replace battery as
necessary
Loose or corroded battery connectionsCheck that battery connections
are clean and tight
Internal ground in starter windingsSee Testing in STARTER
article
Grounded starter fieldsSee Testing in STARTERS
Armature rubbing on poleSee STARTER article shoes
Starter Turns but Engine Does Not Rotate
Starter clutch slippingSee STARTER article
Page 4 of 36 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - GENERAL INFORMATION Trouble Shooting - Basic Procedures
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B9B990D68%2D660A%2D45E9%2D8F46%2DE
...
Page 232 of 454
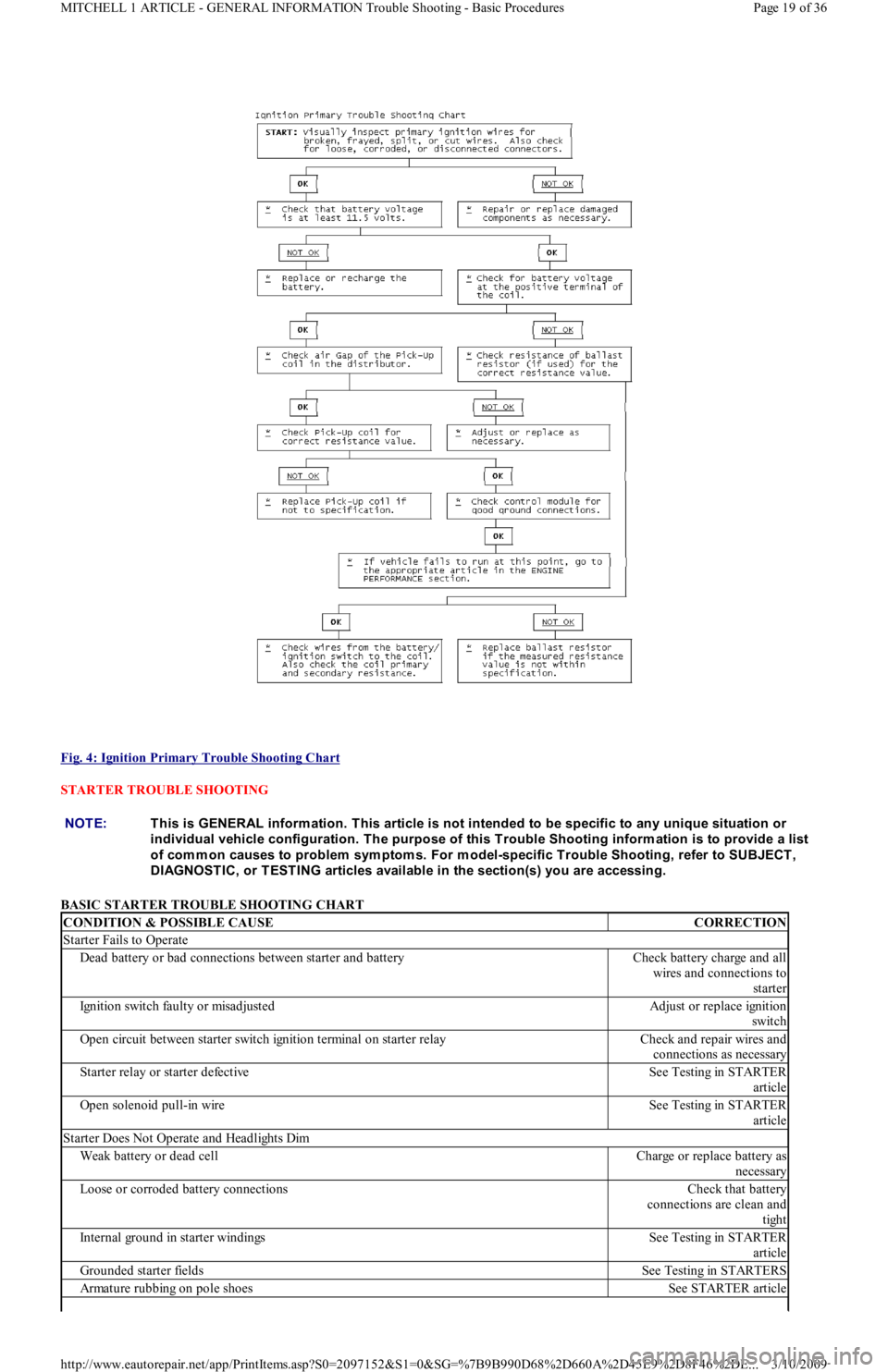
Fig. 4: Ignition Primary Trouble Shooting Chart
STARTER TROUBLE SHOOTING
BASIC STARTER TROUBLE SHOOTING CHART
NOTE:This is GENERAL inform ation. This article is not intended to be specific to any unique situation or
individual vehicle configuration. T he purpose of this T rouble Shooting inform ation is to provide a list
of com m on causes to problem sym ptom s. For m odel-specific T rouble Shooting, refer to SUBJECT ,
DIAGNOST IC, or T EST ING articles available in the section(s) you are accessing.
CONDITION & POSSIBLE CAUSECORRECTION
Starter Fails to Operate
Dead battery or bad connections between starter and batteryCheck battery charge and all
wires and connections to
starter
Ignition switch faulty or misadjustedAdjust or replace ignition
switch
Open circuit between starter switch ignition terminal on starter relayCheck and repair wires and
connections as necessary
Starter relay or starter defectiveSee Testing in STARTER
article
Open solenoid pull-in wireSee Testing in STARTER
article
Starter Does Not Operate and Headlights Dim
Weak battery or dead cellCharge or replace battery as
necessary
Loose or corroded battery connectionsCheck that battery
connections are clean and
tight
Internal ground in starter windingsSee Testing in STARTER
article
Grounded starter fieldsSee Testing in STARTERS
Armature rubbing on pole shoesSee STARTER article
Page 19 of 36 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - GENERAL INFORMATION Trouble Shooting - Basic Procedures
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B9B990D68%2D660A%2D45E9%2D8F46%2DE
...
Page 272 of 454
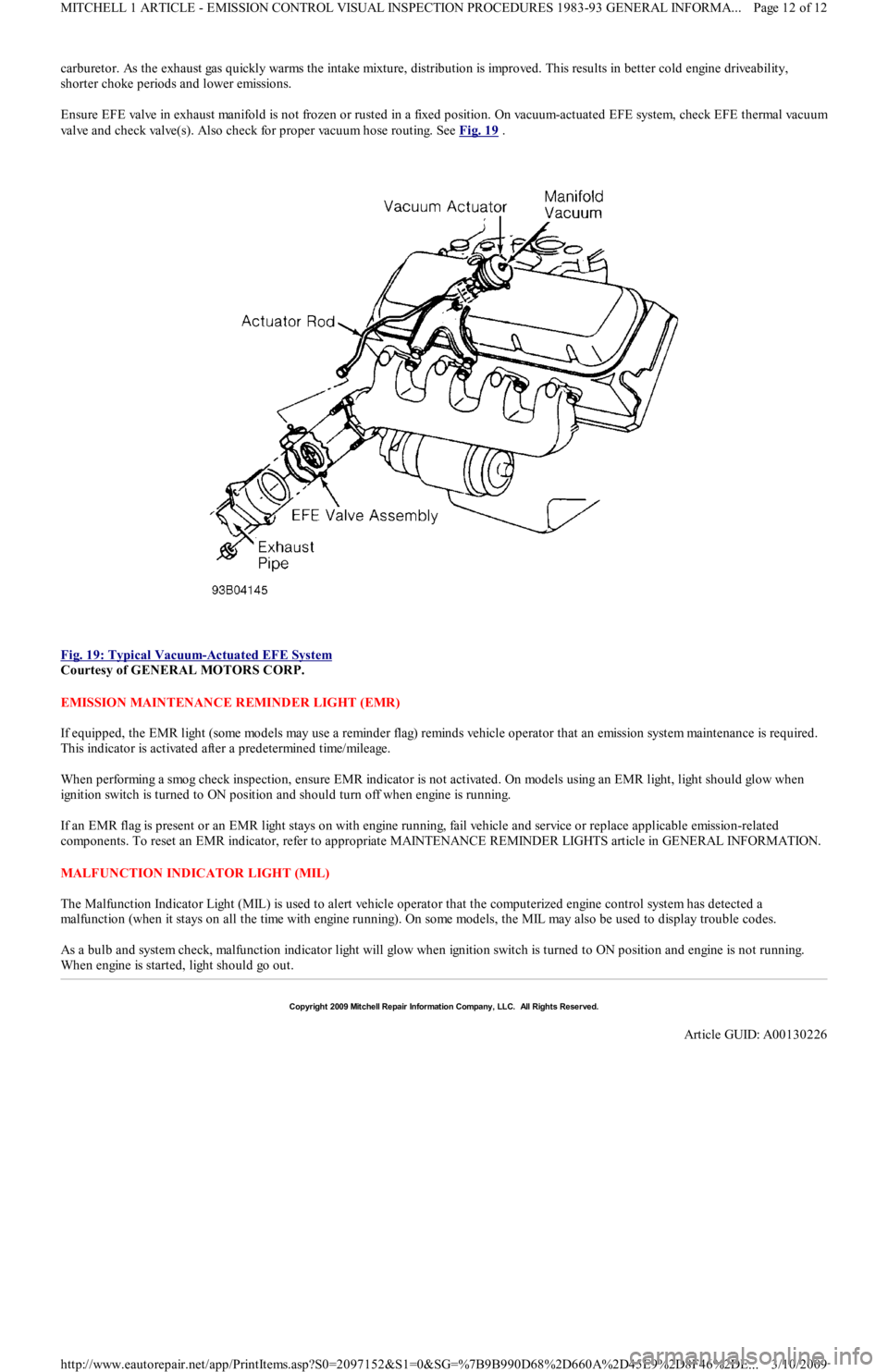
carburetor. As the exhaust gas quickly warms the intake mixture, distribution is improved. This results in better cold engine driveability,
shorter choke periods and lower emissions.
Ensure EFE valve in exhaust manifold is not frozen or rusted in a fixed position. On vacuum-actuated EFE system, check EFE thermal vacuu
m
valve and check valve(s). Also check for proper vacuum hose routing. See Fig. 19
.
Fig. 19: Typical Vacuum
-Actuated EFE System
Courtesy of GENERAL MOTORS CORP.
EMISSION MAINTENANCE REMINDER LIGHT (EMR)
If equipped, the EMR light (some models may use a reminder flag) reminds vehicle operator that an emission system maintenance is required.
This indicator is activated after a predetermined time/mileage.
When performing a smog check inspection, ensure EMR indicator is not activated. On models using an EMR light, light should glow when
ignition switch is turned to ON position and should turn off when engine is running.
If an EMR flag is present or an EMR light stays on with engine running, fail vehicle and service or replace applicable emission-related
components. To reset an EMR indicator, refer to appropriate MAINTENANCE REMINDER LIGHTS article in GENERAL INFORMATION.
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR LIGHT (MIL)
The Malfunction Indicator Light (MIL) is used to alert vehicle operator that the computerized engine control system has detected a
malfunction (when it stays on all the time with engine running). On some models, the MIL may also be used to display trouble codes.
As a bulb and system check, malfunction indicator light will glow when ignition switch is turned to ON position and engine is not running.
When engine is started, light should go out.
Copyr ight 2009 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC. All Rights Reserved.
Article GUID: A00130226
Page 12 of 12 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - EMISSION CONTROL VISUAL INSPECTION PROCEDURES 1983-93 GENERAL INFORMA...
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B9B990D68%2D660A%2D45E9%2D8F46%2DE
...
Page 278 of 454

Back To Article
GENERAL INFORMATION
Parasitic Load Explanation & T est Procedures
* PLEASE READ THIS FIRST *
GENERAL INFORMATION
The term Parasitic Load refers to electrical devices that continue to use or draw current after the ignition switch is turned to OFF position. This
small amount of continuous battery draw is expressed in milliamps (mA). On Chrysler vehicles, a typical Parasitic Load should be no more
than 30 milliamps (0.030 amps). On Ford Motor Co. and General Motors vehicles produced after 1980, a typical Parasitic Load should be no
more than 50 milliamps (0.050 amps).
Vehicles produced since 1980 have memory devices that draw current with ignition off for as long as 20 minutes before shutting down the
Parasitic Drain. When Parasitic Load exceeds normal specifications, the vehicle may exhibit dead battery and no-start condition.
Follow test procedure for checking Parasitic Loads to completion. A brief overview of a suggested test procedure is included along with some
typical Parasitic Load specifications. Refer to GENERAL MOTORS PARASITIC LOAD TABLE chart.
TESTING FOR PARASITIC LOAD
The battery circuit must be opened to connect test switch (shunt) and ammeter into the circuit. When a battery cable is removed, timer circuits
within the vehicle computer are interrupted and immediately begin to discharge. If in doubt about the condition of the ammeter fuse, test it
with an ohmmeter prior to beginning test. An open fuse will show the same reading (00.00) as no parasitic drain. Begin test sequence with the
meter installed and on the 10-amp scale. Select lower scale to read parasitic draw.
CHRYSLER IGNITION OFF DRAW (IOD) TEST
To test for excessive IOD, verify that all electrical accessories are OFF. Turn off all lights, remove ignition key, and close all doors and decklid.
If the vehicle is equipped with electronic accessories (illuminated entry, automatic load leveler, body computer, or high line radio), allow the
system to automatically shut off (time out), up to 3 minutes.
1. Raise the hood and disconnect both battery cables, negative first.
2. Reconnect the negative cable and connect a typical 12-volt test light (low wattage bulb) between the positive cable clamp and the
positive battery post. Remove the engine compartment lamp bulb. If the test light does not light, proceed to step 3
. If the test light does
light, proceed to step, 4
. The test light will indicate IOD greater than 3 amps. After higher amperage IOD has been corrected, proceed to
step 3
.
3. ith 12-volt test light still connected (not lit), connect an ammeter (milliampere scale) between the positive cable clamp and the positive
battery post, disconnect test light, refer to instructions provided with ammeter being used. A reading of 30 milliamperes or less indicates
normal electrical draw. If ammeter reads more than 30 milliamperes, excessive IOD must be corrected.
4. Locate the fuse panel and remove fuses or circuit breakers one at a time, and observe ammeter after each fuse or circuit breaker is
removed. If test light goes out and the reading drops below 30 milliamperes when a certain fuse or circuit breaker is removed, that circuit
may have a defect.
5. If IOD is detected after all fuses and circuit breakers have been removed, disconnect the 60-way connector at the Single Module Engine
Control (SMEC), located outboard of the battery.
6. If excessive IOD is detected after all fused circuits and SMEC have been verified, disconnect the B+ terminal from the alternat o r. If
reading drops below 30 milliamperes, reinstall all fuses and circuit breakers, reconnect B+ terminal at alternator, reconnect battery, and
perform alternator diagnostics.
7. Install engine compartment lamp bulb.
TEST PROCEDURE USING TEST SWITCH
1. Turn ignition off. Remove negative battery terminal cable. Install Disconnect Tool (J-38758) test switch male end to negative battery
cable. Turn test switch knob to OFF position (current through meter). Install negative battery cable to the female end of test switch. NOTE:This is GENERAL inform ation. This article is not intended to be specific to any unique situation or
individual vehicle configuration. For m odel-specific inform ation see appropriate articles where
available.
NOTE:This is GENERAL inform ation. This article is not intended to be specific to any unique situation or
individual vehicle configuration. For m odel-specific inform ation see appropriate articles where
available.
NOTE:This is GENERAL inform ation. This article is not intended to be specific to any unique situation or
individual vehicle configuration. For m odel-specific inform ation see appropriate articles where
available.
CAUT ION: Always turn ignition off when connecting or disconnecting battery cables, battery chargers or jum per
cables. DO NOT turn test switch to OFF position (which causes current to run through am m eter or
vehicle electrical system ).
NOTE:Mem ory functions of various accessories m ust be reset after the battery is reconnected.
CAUT ION: IOD greater than 3 am ps m ay dam age m illam pm eter.
Page 1 of 4 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - GENERAL INFORMATION Parasitic Load Explanation & Test Procedures
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B9B990D68%2D660A%2D45E9%2D8F46%2DE
...
Page 279 of 454
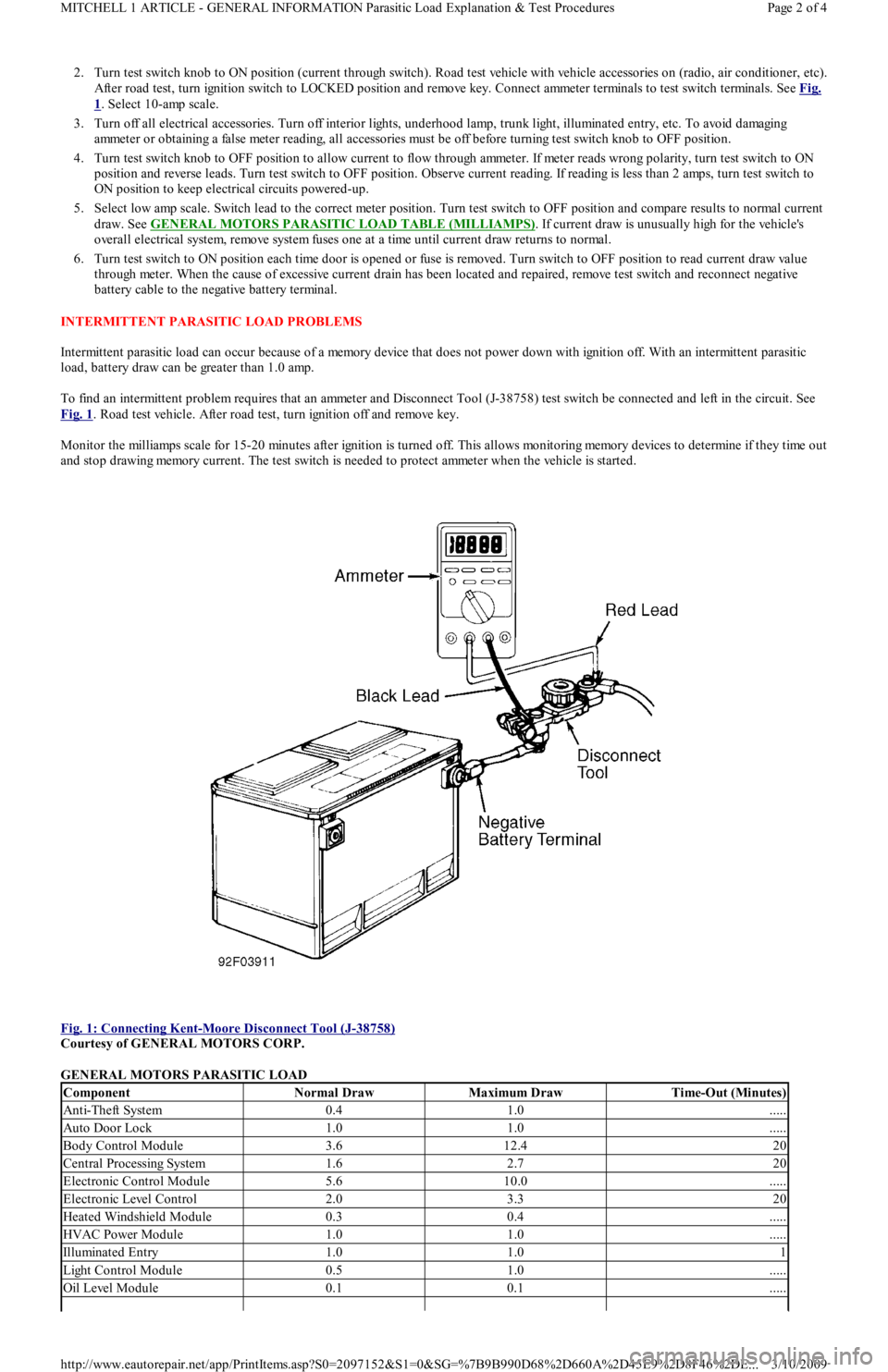
2. Turn test switch knob to ON position (current through switch). Road test vehicle with vehicle accessories on (radio, air conditioner, etc).
After road test, turn ignition switch to LOCKED position and remove key. Connect ammeter terminals to test switch terminals. See Fig.
1. Select 10-amp scale.
3. Turn off all electrical accessories. Turn off interior lights, underhood lamp, trunk light, illuminated entry, etc. To avoid damaging
ammeter or obtaining a false meter reading, all accessories must be off before turning test switch knob to OFF position.
4. Turn test switch knob to OFF position to allow current to flow through ammeter. If meter reads wrong polarity, turn test switch to ON
position and reverse leads. Turn test switch to OFF position. Observe current reading. If reading is less than 2 amps, turn test switch to
ON position to keep electrical circuits powered-up.
5. Select low amp scale. Switch lead to the correct meter position. Turn test switch to OFF position and compare results to normal current
draw. See GENERAL MOTORS PARASITIC LOAD TABLE (MILLIAMPS)
. If current draw is unusually high for the vehicle's
overall electrical system, remove system fuses one at a time until current draw returns to normal.
6. Turn test switch to ON position each time door is opened or fuse is removed. Turn switch to OFF position to read current draw va l u e
through meter. When the cause of excessive current drain has been located and repaired, remove test switch and reconnect negative
battery cable to the negative battery terminal.
INTERMITTENT PARASITIC LOAD PROBLEMS
Intermittent parasitic load can occur because of a memory device that does not power down with ignition off. With an intermittent parasitic
load, battery draw can be greater than 1.0 amp.
To find an intermittent problem requires that an ammeter and Disconnect Tool (J-38758) test switch be connected and left in the circuit. See
Fig. 1
. Road test vehicle. After road test, turn ignition off and remove key.
Monitor the milliamps scale for 15-20 minutes after ignition is turned off. This allows monitoring memory devices to determine if they time out
and stop drawing memory current. The test switch is needed to protect ammeter when the vehicle is started.
Fig. 1: Connecting Kent
-Moore Disconnect Tool (J-38758)
Courtesy of GENERAL MOTORS CORP.
GENERAL MOTORS PARASITIC LOAD
ComponentNormal DrawMaximum DrawTime-Out (Minutes)
Anti-Theft System0.41.0.....
Auto Door Lock1.01.0.....
Body Control Module3.612.420
Central Processing System1.62.720
Electronic Control Module5.610.0.....
Electronic Level Control2.03.320
Heated Windshield Module0.30.4.....
HVAC Power Module1.01.0.....
Illuminated Entry1.01.01
Light Control Module0.51.0.....
Oil Level Module0.10.1.....
Page 2 of 4 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - GENERAL INFORMATION Parasitic Load Explanation & Test Procedures
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B9B990D68%2D660A%2D45E9%2D8F46%2DE
...