gas type FORD FESTIVA 1991 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 1991, Model line: FESTIVA, Model: FORD FESTIVA 1991Pages: 454, PDF Size: 9.53 MB
Page 234 of 454
TUNE-UP TROUBLE SHOOTING - GAS ENGINE VEHICLES
BASIC SPARK PLUG TROUBLE SHOOTING CHARTS
Faulty solenoid switch, switch connections or relayCheck all wiring between
relay and solenoid or replace
relay or solenoid as necessary
Broken lead or loose soldered connectionsRepair wire or wire
connections as necessary
Solenoid Plunger Vibrates When Switch is Engaged
Weak batteryCharge or replace battery as
necessary
Solenoid contacts corrodedClean contacts or replace
solenoid
Faulty wiringCheck all wiring leading to
solenoid
Broken connections inside switch coverRepair connections or replace
solenoid
Open hold-in wireReplace solenoid
Low Current Draw
Worn brushes or weakReplace brushes or brush
springs as necessary
High Pitched Whine During Cranking Before Engine Fires but Engine Fires and Cranks Normally
Distance too great between starter pinion and flywheelAlign starter or check that
correct starter and flywheel
are being used
High Pitched Whine After Engine Fires With Key released. Engine Fires and Cranks Normally
Distance too small between starter pinion and flywheelFlywheel runout contributes
to the intermittent nature
NOTE:This is GENERAL inform ation. This article is not intended to be specific to any unique situation or
individual vehicle configuration. T he purpose of this T rouble Shooting inform ation is to provide a list
of com m on causes to problem sym ptom s. For m odel-specific T rouble Shooting, refer to SUBJECT ,
DIAGNOST IC, or T EST ING articles available in the section(s) you are accessing.
CONDITION & POSSIBLE CAUSECORRECTION
Normal Spark Plug Condition
Light Tan or Gray depositsNo Action
Electrode not burned or fouledNo Action
Gap tolerance not changedNo Action
Cold Fouling or Carbon Deposits
Overrich air/fuel mixtureAdjust air/fuel mixture, see
ENGINE PERFORMANCE
section
Faulty chokeReplace choke assembly, see
ENGINE PERFORMANCE
section
Clogged air filterClean and/or replace air filter
Incorrect idle speed or dirty carburetorReset idle speed and/ or clean
carburetor
Faulty ignition wiresReplace ignition wiring
Prolonged operation at idleShut engine off during long
idle
Sticking valves or worn valve guide sealsCheck valve train
Wet Fouling or Oil Deposits
Worn rings and pistonsInstall new rings and pistons
Excessive cylinder wearRebore or replace block
Excessive valve guide clearanceWorn or loose bearing
Gap Bridged
Deposits in combustion chamber becoming fused to electrodeClean combustion chamber of
deposits
Blistered Electrode
Engine overheatingCheck cooling system
Wrong type of fuelReplace with correct fuel
Loose spark plugsRetighten spark plugs
Over-advanced ignition timingReset ignition timing see
ENGINE PERFORMANCE
Pre-Ignition or Melted Electrodes
Incorrect type of fuelReplace with correct fuel
Incorrect ignition timingReset ignition timing see
ENGINE PERFORMANCE
Burned valvesReplace valves
Engine OverheatingCheck cooling system
Wrong type of spark plug, too hotReplace with correct spark
Page 21 of 36 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - GENERAL INFORMATION Trouble Shooting - Basic Procedures
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B9B990D68%2D660A%2D45E9%2D8F46%2DE
...
Page 263 of 454

Fig. 5: Identifying Vehicle Calibration Label (1989
-93 Ford Models)
Courtesy of FORD MOTOR CO.
EMISSION CONTROL VISUAL INSPECTION
A visual inspection is made to determine if any required emission control devices are missing, modified or disconnected. Missing, mo d ifie d o r
disconnected systems must be made fully operational before a vehicle can be certified.
POSITIVE CRANKCASE VENTILATION (PCV)
PCV controls the flow of crankcase fumes into the intake manifold while preventing gases and flames from traveling in the opposite direction.
PCV is either an open or closed system. See Fig. 4
.
Ensure PCV system is installed as required. Verify valve, required hoses, connections, flame arresters, etc., are present, routed properly and in
serviceable condition.
Fig. 6: Typical Open & Closed Type PCV System
THERMOSTATIC AIR CLEANER (TAC)
The TAC supplies warm air to air intake during cold engine operation. This system is active during cold engine warm-up only. Under all other
operating conditions, air cleaner function is the same as any non-thermostatic unit.
Ensure required exhaust shroud, hot air duct, vacuum hoses and air cleaner components are present and installed properly. See Fig. 7
. Ensure
any required thermostatic vacuum switches are in place and vacuum hoses are installed and in serviceable condition. Also ensure air cleaner
lid is installed right side up. Check for oversized air filter elements and for additional holes in the air cleaner housing.
NOTE:T he following em ission control visual inspection procedures should be used as a guide only. When
perform ing a visual inspection, always follow your state's recom m ended inspection procedures.
Page 3 of 12 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - EMISSION CONTROL VISUAL INSPECTION PROCEDURES 1983-93 GENERAL INFORMATI
...
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B9B990D68%2D660A%2D45E9%2D8F46%2DE
...
Page 265 of 454

Fig. 9: Typical Oxidation Catalytic Converter (Pellet Type) Shown; Typical Three
-Way Catalytic Converter Is Similar
Courtesy of GENERAL MOTORS CORP.
Three-Way Catalyst (TWC)
This type of converter is nearly identical to a conventional converter with the exception of the catalyst. See Fig. 9 . The TWC converter uses
rhodium, with or without platinum, as its catalyst. Rhodium helps reduce NOx emissions, as well as HC and CO.
Visually check for presence of catalytic converter(s). Also check for presence of any required air supply system for the oxidizing section of the
converter. Check for external damage such as severe dents, removed or damaged heat shields, etc. Check for pellets or pieces of converter in
the tailpipe.
Three-Way Catalyst + Oxidation Catalyst (TWC + OC)
This system contains a TWC converter and an OC converter in a common housing, separated by a small air space. See Fig. 10. The 2 catalysts
are referred to as catalyst beds. Exhaust gases pass through the TWC first. The TWC bed performs the same function as it would as a separate
device, reducing all 3 emissions. As exhaust gases leave the bed, they pass through the air space and into the second (OC) converter catalyst
bed.
Visually check for presence of catalytic converter(s). Check for external damage such as severe dents, removed or damaged heat shields, etc.
Check for pellets or pieces of converter in the tailpipe.
Fig. 10: Typical Three
-Way + Oxidation Catalytic Converter
Courtesy of GENERAL MOTORS CORP.
FILL PIPE RESTRICTOR (FR)
A fuel tank fill pipe restrictor is used to prohibit the introduction of leaded fuel into the fuel tank. Unleaded gasoline pump dispensers have a
smaller diameter nozzle to fit fuel tank of vehicle requiring the use of unleaded fuel (vehicles equipped with catalytic converter).
Visually inspect fill pipe restrictor(s) for tampering, i.e., restrictor is oversize or the flapper is non-functional. If vehicle is equipped with an
auxiliary fuel tank, ensure auxiliary fuel tank is also equipped with a fill pipe restrictor.
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR) SYSTEM
Single Diaphragm EGR Valve
This type uses a single diaphragm connected to the valve by a shaft. Diaphragm is spring-loaded to keep valve closed in the absence of
vacuum. As throttle valves open and engine speed increases, vacuum is applied to the EGR vacuum diaphragm, opening the EGR valve. This
vacuum signal comes from a ported vacuum source. Variations in the vacuum signal control the amount of exhaust gas that is recirculated. See
Fig. 11
.
Verify EGR valve is present and not modified or purposely damaged. Ensure thermal vacuum switches, pressure transducers, speed switches,
Page 5 of 12 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - EMISSION CONTROL VISUAL INSPECTION PROCEDURES 1983-93 GENERAL INFORMATI
...
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B9B990D68%2D660A%2D45E9%2D8F46%2DE
...
Page 271 of 454
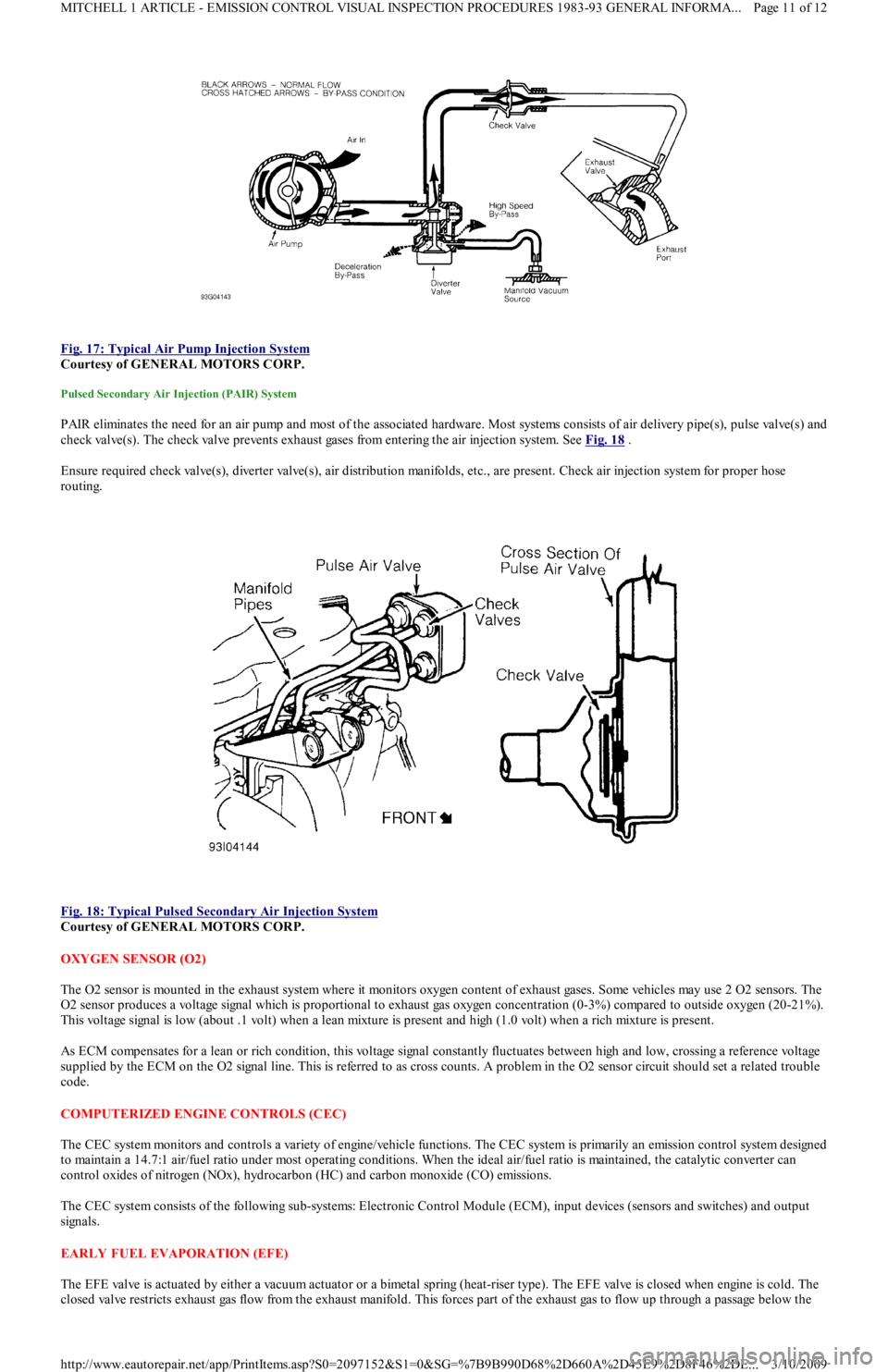
Fig. 17: Typical Air Pump Injection System
Courtesy of GENERAL MOTORS CORP.
Pulsed Secondary Air Injection (PAIR) System
PAIR eliminates the need for an air pump and most of the associated hardware. Most systems consists of air delivery pipe(s), pulse valve(s) and
check valve(s). The check valve prevents exhaust gases from entering the air injection system. See Fig. 18
.
Ensure required check valve(s), diverter valve(s), air distribution manifolds, etc., are present. Check air injection system for proper hose
routing.
Fig. 18: Typical Pulsed Secondary Air Injection System
Courtesy of GENERAL MOTORS CORP.
OXYGEN SENSOR (O2)
The O2 sensor is mounted in the exhaust system where it monitors oxygen content of exhaust gases. Some vehicles may use 2 O2 sensors. The
O2 sensor produces a voltage signal which is proportional to exhaust gas oxygen concentration (0-3%) compared to outside oxygen (20-21%).
This voltage signal is low (about .1 volt) when a lean mixture is present and high (1.0 volt) when a rich mixture is present.
As ECM compensates for a lean or rich condition, this voltage signal constantly fluctuates between high and low, crossing a reference voltage
supplied by the ECM on the O2 signal line. This is referred to as cross counts. A problem in the O2 sensor circuit should set a related trouble
code.
COMPUTERIZED ENGINE CONTROLS (CEC)
The CEC system monitors and controls a variety of engine/vehicle functions. The CEC system is primarily an emission control system designed
to maintain a 14.7:1 air/fuel ratio under most operating conditions. When the ideal air/fuel ratio is maintained, the catalytic converter can
control oxides of nitrogen (NOx), hydrocarbon (HC) and carbon monoxide (CO) emissions.
The CEC system consists of the following sub-systems: Electronic Control Module (ECM), input devices (sensors and switches) and output
signals.
EARLY FUEL EVAPORATION (EFE)
The EFE valve is actuated by either a vacuum actuator or a bimetal spring (heat-riser type). The EFE valve is closed when engine is cold. The
closed valve restricts exhaust gas flow from the exhaust manifold. This forces part of the exhaust gas to flow up through a passage below the
Page 11 of 12 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - EMISSION CONTROL VISUAL INSPECTION PROCEDURES 1983-93 GENERAL INFORMA...
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B9B990D68%2D660A%2D45E9%2D8F46%2DE
...
Page 306 of 454

Back To Article
1991 GENERAL SERVICING
A/C Com pressor Refrigerant Oil Checking
ISOLATING COMPRESSOR
1. Connect service gauge set to the compressor service valves and open compressor valves slightly (turn in clockwise). Start engine and
operate air conditioning. Slowly turn compressor suction valve clockwise toward closed (front-seated) position.
2. When suction pressure is reduced to zero or less, turn off engine and compressor and quickly turn suction valve stem in to full front-
seated position. Suction pressure should be slightly above zero. Turn discharge valve into front-seated position.
3. To check oil level, slowly open compressor crankcase plug to relieve any remaining pressure. After oil level is corrected, cap service
gauge ports on both valves. Back-seat suction service valve to allow refrigerant to enter compressor. Open discharge valve halfway.
4. Loosen discharge service valve cap, allowing refrigerant pressure to force air out of compressor. Back-seat service valve and tighten cap.
Compressor is now ready for operation.
REFRIGERANT OIL
Only new, pure, moisture-free refrigerant oil should be used in the air conditioning system. This oil is highly refined and dehydrated to a point
where moisture content is less than 10 parts per million. The oil container must be tightly closed at all times when not in use, or moisture will
be absorbed into the refrigerant oil from the air.
SERVICING PRECAUTIONS
DISCHARGING SYSTEM PRECAUTIONS
If compressor has stem-type service valves, it can be isolated and removed without discharging entire system. See ISOLATING
COMPRESSOR at the beginning of this article. Otherwise, discharge system completely before loosening any fittings.
DISCONNECTING LINES & FITTINGS TEST
After system is discharged, carefully clean area around all fittings to be opened. Always use 2 wrenches when tightening or loosening fittings
to avoid twisting or distorting lines. Cap or plug all openings as soon as lines are removed. DO NOT remove caps until immediately before
connections are made. This will keep entry of air and moisture to a minimum.
CONNECTING LINES AND FITTINGS
A new gasket or "O" ring should be used in all instances when connecting lines or fittings. Dip "O" ring in new refrigerant oil and ensure it is
not twisted during installation. Always use 2 wrenches to prevent damage to lines and fittings.
PLACING SYSTEM IN OPERATION
After component service or replacement has been completed and all connections have been made, evacuate system thoroughly with a vacuum
pump. Charge system with proper amount of refrigerant and perform a leak test. See REFRIGERANT OIL & R-12 SPECIFICATIONS chart in
this section for system capacities. Be sure to check all fittings that have been opened. After system has been leak tested, make a system
performance check.
ATSUGI ROTARY VANE DRAIN & REFILL
1. Before checking and adjusting oil level, operate compressor at engine idling speed, with controls set for maximum cooling and high
blower speed, for 20 to 30 minutes to return oil to compressor.
2. Stop engine, discharge refrigerant and remove compressor from vehicle. See SERVICING PRECAUTIONS at beginning of article. Drain
compressor oil from compressor discharge port and measure the amount. Oil is sometimes hard to drain when compressor is cool.
Remove oil while compressor is warm.
3. If the amount drained is less than 3 ounces, conduct leak tests at system connections, and if necessary, repair or replace faulty parts.
Check purity of oil and adjust oil level as follows.
4. If amount drained was above 3 ounces, oil level is right. Pour in same amount as was drained. If amount drained was below 3 ounces,
pour in 3 ounces of new refrigerant oil.
BOSCH 6-CYL DRAIN & REFILL
1. Before checking and adjusting oil level, operate compressor at engine idling speed, with controls set for maximum cooling and high
blower speed, for 20 to 30 minutes to return oil to compressor.
2. Stop engine and discharge refrigerant. Remove refrigerant oil level inspection plug on side of compressor. Oil should be at lower lip of
threaded hole. Add necessary new refrigerant oil (if low). Replace inspection plug and tighten to 10-12 ft. lbs. (14-16 N.m). NOTE:Only com pressors with stem -type service valves can be isolated.
NOTE:Recent findings by the EPA indicate that refrigerant is harm ful to the earth's protective Ozone layer.
When discharging refrigerant, DO NOT allow refrigerant to enter the atm osphere. If available, use
refrigerant recovery/recycle system s when discharging system . Always follow m anufacturer's
instructions.
NOTE:Air conditioning system s will not norm ally need addition of refrigerant oil unless definite oil loss has
occurred due to ruptured lines, leaking com pressor seals, com pressor overhaul or com ponent
replacem ent.
Page 1 of 4 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - 1991 GENERAL SERVICING A/C Compressor Refrigerant Oil Checking
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B9B990D68%2D660A%2D45E9%2D8F46%2DE
...
Page 317 of 454

Back To Article
A/C COMPRESSOR SERVICING
1991 GENERAL SERVICING Com pressor Service
ISOLATING COMPRESSOR
1. Connect service gauge set to the compressor service valves and open compressor valves slightly (turn in clockwise). Start engine and
operate air conditioning. Slowly turn compressor suction valve clockwise toward closed (front-seated) position.
2. When suction pressure is reduced to zero or less, turn off engine and compressor and quickly turn suction valve stem in to full front-
seated position. Suction pressure should be slightly above zero. Turn discharge valve into front-seated position.
3. To check oil level, slowly open compressor crankcase plug to relieve any remaining pressure. After oil level is corrected, cap service
gauge ports on both valves. Back-seat suction service valve to allow refrigerant to enter compressor. Open discharge valve halfway.
4. Loosen discharge service valve cap, allowing refrigerant pressure to force air out of compressor. Back-seat service valve and tighten cap.
Compressor is now ready for operation.
REFRIGERANT OIL
Only new, pure, moisture-free refrigerant oil should be used in the air conditioning system. This oil is highly refined and dehydrated to a point
where moisture content is less than 10 parts per million. The oil container must be tightly closed at all times when not in use, or moisture will
be absorbed into the refrigerant oil from the air.
DISCHARGING SYSTEM PRECAUTIONS
If compressor has stem-type service valves, it can be isolated and removed without discharging entire system. Otherwise, discharge system
completely using approved refrigerant recovery/recycling equipment before loosening any fittings.
DISCONNECTING LINES & FITTINGS TEST
After system is discharged, carefully clean area around all fittings to be opened. Always use 2 wrenches when tightening or loosening fittings
to avoid twisting or distorting lines. Cap or plug all openings as soon as lines are removed. Do not remove caps until immediately before
connections are made. This will keep entry of air and moisture to a minimum.
CONNECTING LINES AND FITTINGS
A new gasket or "O" ring should be used in all instances when connecting lines or fittings. Dip "O" ring in new refrigerant oil and ensure it is
not twisted during installation. Always use 2 wrenches to prevent damage to lines and fittings.
PLACING SYSTEM IN OPERATION
After component service or replacement has been completed and all connections have been made, evacuate system thoroughly with a vacuum
pump. Charge system with proper amount of refrigerant and perform a leak test. See REFRIGERANT OIL & R-12 SPECIFICATIONS chart in
this section for system capacities. Be sure to check all fittings that have been opened. After system has been leak tested, make a system
performance check.
ATSUGI ROTARY VANE CLUTCH R & I
Removal
When replacing compressor clutch, be careful not to scratch shaft or bend pulley. When removing center bolt, hold clutch disc with Clutch
Holder (KV99231010). Using Hub Puller (KV998VR001 & KV99231010), remove clutch disc. When removing pulley, remove lock nut with
Hub Socket (KV99235160).
Installation
Wipe oil off clutch surface. Adjust disc pulley clearance to .012-.024" (.3-.6 mm). Tighten center bolt to 80-104 INCH lbs. (9.1-11.8 N.m).
Tighten clutch lock nut to 22-29 ft. lbs. (29-39 N.m). See Fig. 1
. CAUT ION: When discharging air conditioning system , use only approved refrigerant recovery/recycling
equipm ent. Make every attem pt to avoid discharging refrigerant into the atm osphere.
NOTE:Only com pressors with stem -type service valves can be isolated.
CAUT ION: When discharging air conditioning system , use only approved refrigerant recovery/recycling
equipm ent. Make every attem pt to avoid discharging refrigerant into the atm osphere.
NOTE:Air conditioning system s will not norm ally need addition of refrigerant oil unless definite oil loss has
occurred due to ruptured lines, leaking com pressor seals, com pressor overhaul or com ponent
replacem ent.
Page 1 of 18 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - A/C COMPRESSOR SERVICING 1991 GENERAL SERVICING Compressor Service
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B9B990D68%2D660A%2D45E9%2D8F46%2DE
...
Page 341 of 454

Back To Article
A/C SYST EM PRECAUT IONS
A/C GENERAL SERVICING A/C System Servicing cautions
BEFORE OPENING THE SYSTEM
Before disconnecting any lines or fittings, the system must be completely discharged using approved refrigerant recovery/recycling equipment.
DISCHARGING A/C SYSTEM
1. Remove service valve caps and install gauges. For high side gauge hose, Adapter (D81L-19703-A) must be used to connect to high side
service valve.
2. Place open end of center hose in garage exhaust outlet or in a well ventilated area. Slightly open low side gauge valve and let refrigerant
escape slowly without loosing refrigerant oil.
3. When system is nearly discharged, using approved refrigerant recovery/recycling equipment, open high side gauge valve to release any
pressure trapped in compressor. Close valves immediately after discharging to prevent entry of moisture.
DISCONNECTING LINES & FITTINGS
1. After system is discharged, using approved refrigerant recovery/recycling equipment, carefully clean entire area around coupling nut to
prevent dirt entering system. Always use two wrenches to avoid twisting or distorting lines and fittings (hold fitting with one wrench
while loosening coupling nut with second wrench).
2. Ford spring-coupling fittings require a special coupling tool (Motorcraft YT-1056) to open or close. See procedure under Connecting
Lines and Fittings.
3. Cap or plug all LINES and FITTINGS immediately to prevent entry of air and moisture into system. Do not remove these caps until
connections are being made.
COMPONENT REPLACEMENT
When components are replaced, system oil level must be adjusted. Add refrigeration oil to replacement component. See Compressor oil Check
article, as well as COMPONENT OIL REPLACEMENT QUANTITIES chart under A/C SYSTEM SPECS article in this section.
USING R-12 REFRIGERANT - SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
1. Always work in a well-ventilated, clean area. Refrigerant (R-12) is heavier than oxygen, and will displace oxygen in a confined area.
Always wear eye protection when working around air conditioning systems and R-12. The system's high pressure can cause severe injury
to eyes and skin if a hose were to burst. R-12 evaporates quickly when exposed to atmosphere, freezing anything it contacts.
2. Use care when handling refrigerant containers. DO NOT drop or strike containers or expose refrigerant containers to excessive heat.
Containers must never be heated more than 125°F (52°C). Never expose R-12 directly to open flame.
USING INDIVIDUAL R-12 CANS
Disposable refrigerant cans (referred to as one pound cans) have a flat type seal or a screw type seal, and proper can tap must be used for each
type. Be sure sealing gasket on can tap is in good condition. A proper safety can tap will prevent refrigerant from flowing back into open can,
as tap has a one-way flow control.
MULTI-CAN DISPENSING VALVES
A multi-can dispensing valve allows attachment of several cans of refrigerant, and is a good substitute when a bulk container is not available.
Cans are installed onto each leg of multi-can dispensing valve in the same manner as the individual cans, and each leg has its own can tap.
CAN TAP INSTALLATION FLAT TYPE SEAL CANS
On cam-lock or one-piece can taps, first turn the handle outward to the fully open position. Securely engage locking lugs over the can flange,
and lock them in place by turning cam lock or locking nut. Screw tap assembly into adapter so sealing gasket is fully seated against the can
top. Turn tap inward to pierce the can and close the tap. DO NOT open tap until ready to purge the service hose or dispense refrigerant into
the system.
On 2-piece can taps, be certain tap handle is turned fully inward to the closed position. Check that locking base is turned to its outer limit.
Securely engage locking lugs over the can flange. Turn entire tap assembly (without disturbing the closed setting) downward into the locking
base to pierce the can. DO NOT open tap until ready to dispense into system. CAUT ION: When discharging air conditioning system , use only approved refrigerant recovery/recycling
equipm ent. Make every attem pt to avoid discharging refrigerant into the atm osphere.
NOTE:Recent findings by the EPA indicate that R-11, R-12 and R-113 are harm ful to the Earths' protective
Ozone layer. Make every attem pt possible, to avoid discharging R-11, R-12 or R-113 into the
atm osphere.
CAUT ION: When R-12 is exposed to an open flam e, drawn into a running engine, or detected with a Halide
(propane) leak tester, poisonous phosgene gas is form ed. Keep work areas ventilated and avoid
running engines near work area.
NOTE:Recent findings by the EPA indicate that refrigerant is harm ful to the Earth's protective Ozone layer.
When discharging refrigerant avoid allowing refrigerant to enter the atm osphere. Refrigerant recovery
system should be used when discharging the system .
Page 1 of 2 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - A/C SYSTEM PRECAUTIONS A/C GENERAL SERVICING A/C System Servicing cautions
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B9B990D68%2D660A%2D45E9%2D8F46%2DE
...
Page 342 of 454
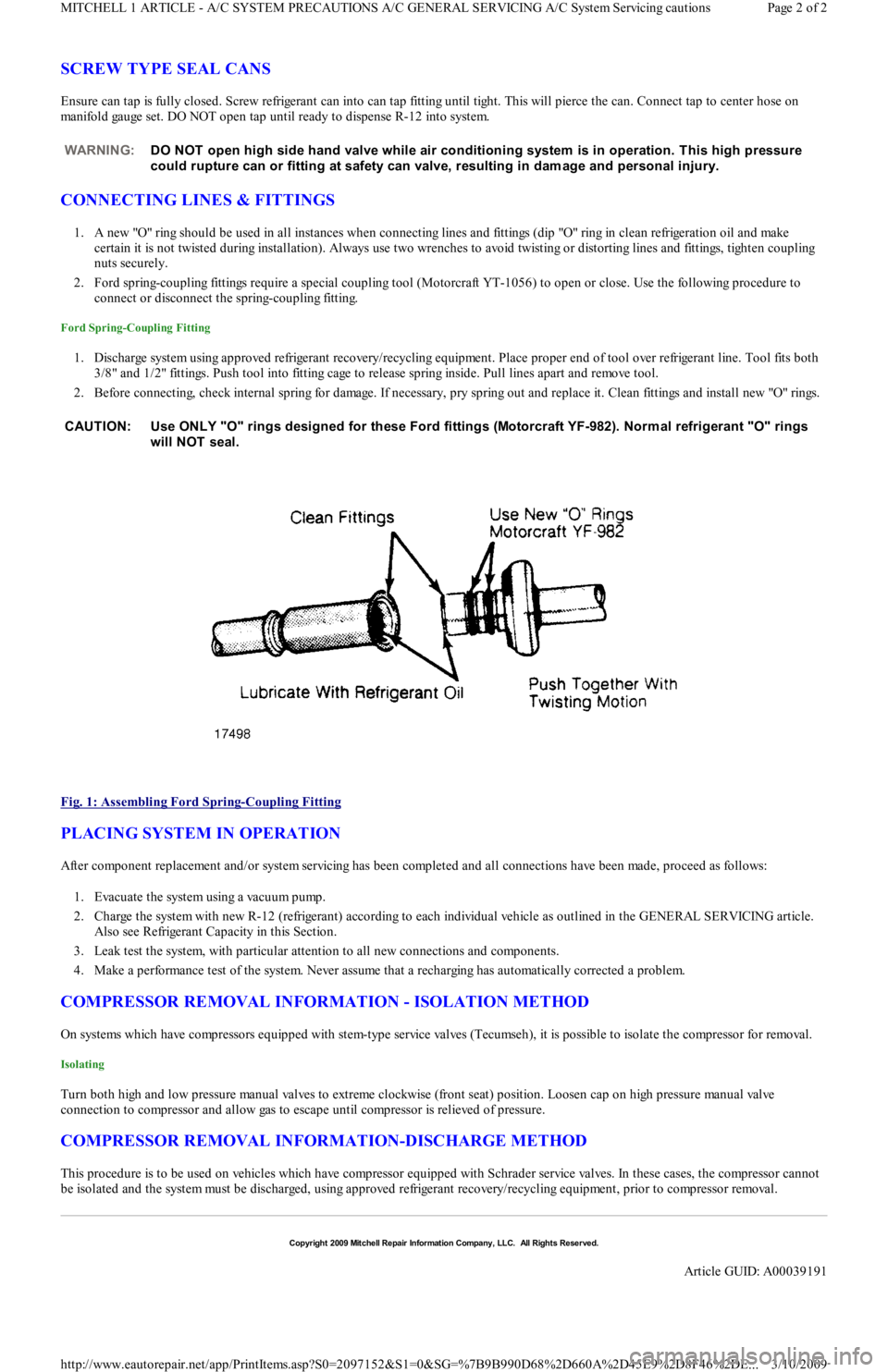
SCREW TYPE SEAL CANS
Ensure can tap is fully closed. Screw refrigerant can into can tap fitting until tight. This will pierce the can. Connect tap to center hose on
manifold gauge set. DO NOT open tap until ready to dispense R-12 into system.
CONNECTING LINES & FITTINGS
1. A new "O" ring should be used in all instances when connecting lines and fittings (dip "O" ring in clean refrigeration oil and make
certain it is not twisted during installation). Always use two wrenches to avoid twisting or distorting lines and fittings, tighten coupling
nuts securely.
2. Ford spring-coupling fittings require a special coupling tool (Motorcraft YT-1056) to open or close. Use the following procedure to
connect or disconnect the spring-coupling fitting.
Ford Spring-Coupling Fitting
1. Discharge system using approved refrigerant recovery/recycling equipment. Place proper end of tool over refrigerant line. Tool fits both
3/8" and 1/2" fittings. Push tool into fitting cage to release spring inside. Pull lines apart and remove tool.
2. Before connecting, check internal spring for damage. If necessary, pry spring out and replace it. Clean fittings and install new "O" rings.
Fig. 1: Assembling Ford Spring
-Coupling Fitting
PLACING SYSTEM IN OPERATION
After component replacement and/or system servicing has been completed and all connections have been made, proceed as follows:
1. Evacuate the system using a vacuum pump.
2. Charge the system with new R-12 (refrigerant) according to each individual vehicle as outlined in the GENERAL SERVICING article.
Also see Refrigerant Capacity in this Section.
3. Leak test the system, with particular attention to all new connections and components.
4. Make a performance test of the system. Never assume that a recharging has automatically corrected a problem.
COMPRESSOR REMOVAL INFORMATION - ISOLATION METHOD
On systems which have compressors equipped with stem-type service valves (Tecumseh), it is possible to isolate the compressor for removal.
Isolating
Turn both high and low pressure manual valves to extreme clockwise (front seat) position. Loosen cap on high pressure manual valve
connection to compressor and allow gas to escape until compressor is relieved of pressure.
COMPRESSOR REMOVAL INFORMATION-DISCHARGE METHOD
This procedure is to be used on vehicles which have compressor equipped with Schrader service valves. In these cases, the compressor cannot
be isolated and the system must be discharged, using approved refrigerant recovery/recycling equipment, prior to compressor removal. WARNING:DO NOT open high side hand valve while air conditioning system is in operation. T his high pressure
could rupture can or fitting at safety can valve, resulting in dam age and personal injury.
CAUT ION: Use ONLY "O" rings designed for these Ford fittings (Motorcraft YF-982). Norm al refrigerant "O" rings
will NOT seal.
Copyr ight 2009 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC. All Rights Reserved.
Article GUID: A00039191
Page 2 of 2 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - A/C SYSTEM PRECAUTIONS A/C GENERAL SERVICING A/C System Servicing cautions
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B9B990D68%2D660A%2D45E9%2D8F46%2DE
...
Page 436 of 454

Back To Article
T RANSMISSION SERVICING - A/T
1988-93 T RANSMISSION SERVICING Ford Motor Co. Autom atic T ransm ission
IDENTIFICATION
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION APPLICATIONS
LUBRICATION
SERVICE INTERVALS
Check fluid level at every engine oil change. Fluid, filter changes and band adjustments are not required under normal operation. Under severe
service operating conditions, change fluid every 30 months or 30,000 miles. Adjust band when fluid is changed.
CHECKING FLUID LEVEL
With transmission at normal operating temperature, place vehicle on level surface. Apply parking brake and run engine at idle. Run gearshift
lever through all positions, ending in Park. With engine running, fluid level should be between "F" and "L" marks. DO NOT overfill.
RECOMMENDED FLUID
Use Dexron-II ATF.
FLUID CAPACITIES
TRANSMISSION REFILL CAPACITIES
DRAINING & REFILLING
1. Remove undercover and side cover to gain access to transaxle oil pan. Remove drain plug and drain fluid. Remove oil pan and discard
gasket. Clean or replace filter screen as necessary. Tighten screen bolts to 71-97 INCH lbs. (8-11 N.m).
2. Install oil pan bolts. Tighten bolts to 44-71 INCH lbs. (5-8 N.m). On all models, install drain plug with NEW washer. Tighten plug to
29-40 ft. lbs. (39-54 N.m).
3. Install undercover and side cover. Add about 3 qts. of specified ATF through dipstick guide tube. DO NOT overfill. Run engine to
normal operating temperature and check fluid level.
ADJUSTMENTS
NEUTRAL SAFETY SWITCH
Combination neutral safety and back-up light switch is screwed into transaxle case. No adjustments are necessary.
SHIFT CONTROL CABLE
1. Disconnect negative battery cable. Remove shift console. Place shift lever in Park. Remove shift lever knob and lock nut. Remove 4 shift
quadrant attaching screws.
2. Loosen shift cable adjuster nuts until they reach end of cable threads. See Fig. 1
. Place shift lever in Park. Tighten lower adjustment
nut until it lightly touches "T" joint, then tighten upper adjustment nut to 80-97 INCH lbs. (9-11 N.m).
3. Lightly press selector push rod and make sure guide pin clearance is correct. See Fig. 2
. Check guide pin clearance when shift lever is
in Neutral and Drive. Readjust shift cable as necessary.
4. Install 4 shift quadrant attaching screws, shift lever knob, lock nut and shift console. Connect negative battery cable.
ModelTransmission
FestivaATX/3HAT
NOTE:Capacities given are approxim ate refill am ounts that apply to overhaul situation. Correct fluid level
should be determ ined by m ark on dipstick.
ApplicationQts. (L)
ATX/3HAT5.6 (5.3)
CAUT ION: DO NOT use any type of gasket sealer or RT V on oil pan gasket. DO NOT overtighten.
CAUT ION: After com pleting linkage adjustm ents, be sure neutral safety switch operates properly. With parking
brake and service brakes applied, try to start engine in each gear position. Engine m ust crank only
when gearshift lever is in Neutral and Park.
Page 1 of 4 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - TRANSMISSION SERVICING - A/T 1988-93 TRANSMISSION SERVICING Ford Motor Co. Aut
...
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B9B990D68%2D660A%2D45E9%2D8F46%2DE
...