mileage FORD FESTIVA 1991 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 1991, Model line: FESTIVA, Model: FORD FESTIVA 1991Pages: 454, PDF Size: 9.53 MB
Page 238 of 454
VACUUM PUMP - DIESEL TROUBLE SHOOTING
VACUUM PUMP (DIESEL) TROUBLE SHOOTING CHART
MANUAL TRANSMISSION
MANUAL TRANSMISSION TROUBLE SHOOTING
MANUAL TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE TROUBLE SHOOTING
Clogged air bleedsRemove restriction
EGR valve malfunctionReplace EGR valve
Restricted air cleaner filterReplace air filter
Cracked or broken vacuum hosesReplace vacuum hoses
Cracked or broken ignition wiresReplace ignition wires
Vacuum advance malfunctionCheck unit and replace as
necessary
Defective or fouled spark plugsReplace spark plugs
Ping or Spark Knock
Incorrect ignition timingReset ignition timing see
ENGINE PERFORMANCE
Distributor centrifugal or vacuum advance malfunctionCheck operation and replace
as necessary
Carburetor setting too leanReadjust mixture setting, see
ENGINE PERFORMANCE
Vacuum leakEliminate vacuum leak
EGR valve malfunctionReplace EGR valve
Poor Gasoline Mileage
Cracked or broken vacuumReplace vacuum hoses hoses
Vacuum leaksRepair vacuum leaks
Defective ignition wiresReplace wires
Incorrect choke settingReadjust setting, see ENGINE
PERFORMANCE
Defective vacuum advanceReplace vacuum advance
Defective spark plugsReplace spark plugs
Binding carburetor power pistonEliminate binding
Dirt in carburetor jetsClean and/or replace jets
Incorrect float adjustmentReadjust float setting, see
FUEL
Defective power valveReplace power valve, see
ENGINE PERFORMANCE
Incorrect idle speedReadjust idle speed
Engine Stalls
Improper float levelReadjust float level
Leaking needle valve and seatReplace needle valve and seat
Vacuum leaksEliminate vacuum leaks
NOTE:This is GENERAL inform ation. This article is not intended to be specific to any unique situation or
individual vehicle configuration. T he purpose of this T rouble Shooting inform ation is to provide a list
of com m on causes to problem sym ptom s. For m odel-specific T rouble Shooting, refer to SUBJECT ,
DIAGNOST IC, or T EST ING articles available in the section(s) you are accessing.
NOTE:Diesel engines m echanical diagnosis is the sam e as gasoline engines for item s such as noisy valves,
bearings, pistons, etc. T he following trouble shooting covers only item s pertaining to diesel engines.
CONDITION & POSSIBLE CAUSECORRECTION
Excessive Noise
Loose pump-to-drive assembly screwsTighten screws
Loose tube on pump assemblyTighten tube
Valves not functioning properlyReplace valves
Oil Leakage
Loose end plugTighten end plug
Bad seal crimpRemove and re-crimp
seal
NOTE:This is GENERAL inform ation. This article is not intended to be specific to any unique situation or
individual vehicle configuration. T he purpose of this T rouble Shooting inform ation is to provide a list
of com m on causes to problem sym ptom s. For m odel-specific T rouble Shooting, refer to SUBJECT ,
DIAGNOST IC, or T EST ING articles available in the section(s) you are accessing.
ConditionPossible Cause
Noisy In Forward GearsLow gear oil level, Loose bell housing bolts, Worn bearings or
gears
Clunk On Deceleration (FWD Only)Loose engine mounts, Worn inboard CV joints, Worn differential
pinion shaft, Side gear hub counterbore in case worn oversize
Page 25 of 36 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - GENERAL INFORMATION Trouble Shooting - Basic Procedures
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B9B990D68%2D660A%2D45E9%2D8F46%2DE
...
Page 252 of 454

Back To Article
GENERAL INFORMATION
Com puter Relearn Procedures
COMPUTER RELEARN PROCEDURES
Vehicles equipped with engine or transmission computers may require a relearn procedure after vehicle battery is disconnected. Many vehicle
computers memorize and store vehicle operation patterns for optimum driveability and performance. When vehicle battery is disconnected,
this memory is lost. The computer will use default data until new data from each key start is stored. As computer memorizes vehicle operation
for each new key start, driveability is restored. Vehicle computers may memorize vehicles operation patterns for 40 of more key starts.
Customers often complain of driveability problems during relearn stage because vehicle acts differently then before being serviced. Depending
on type and make of vehicle and how it is equipped, the following complaints (driveability problems) may exist:
Harsh Or Poor Shift Quality
Rough Or Unstable Idle
Hesitation Or Stumble
Rich Or Lean Running
Poor Fuel Mileage
These symptoms and complaints should disappear after a number of drive cycles have been memorized. To reduce the possibility of
complaints, after any service which requires battery power to be disconnected, vehicle should be road tested.
GENERIC COMPUTER RELEARN PROCEDURES
Some manufacturers identify a specific relearn procedure which will help establish suitable driveability during relearn stage. These procedures
are especially important if vehicle is equipped with and electronically controlled automatic transmission or transaxle. Always complete
procedure before returning vehicle to customer. The following general procedures are to be used if driveability problems are encountered after
power loss or battery has been disconnected. These procedures may provide an aid in eliminating these problems.
Automatic Transmission
Set parking brake, start engine in "P" or "N" position. Warm-up vehicle to normal operating temperature or until cooling fan cycles.
Allow vehicle to idle for one minute in "N" position. Select "D" and allow engine to idle for one minute.
Accelerate at normal throttle position (20-50%) until vehicle shifts into top gear.
Cruise at light to medium throttle.
Decelerate to a stop, allowing vehicle to downshift, and use brakes normally.
Process may be repeated as necessary.
Manual Transmission
Place transmission in Neutral position.
Ensure emergency brake has been set and all accessories are turned off.
Start engine and bring to normal operating temperature.
Allow vehicle to idle in Neutral for one minute.
Initial relearn is complete, and process will be completed during normal driving.
Copyr ight 2009 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC. All Rights Reserved.
Article GUID: A00012612
Page 1 of 1 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - GENERAL INFORMATION Computer Relearn Procedures
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B9B990D68%2D660A%2D45E9%2D8F46%2DE
...
Page 272 of 454
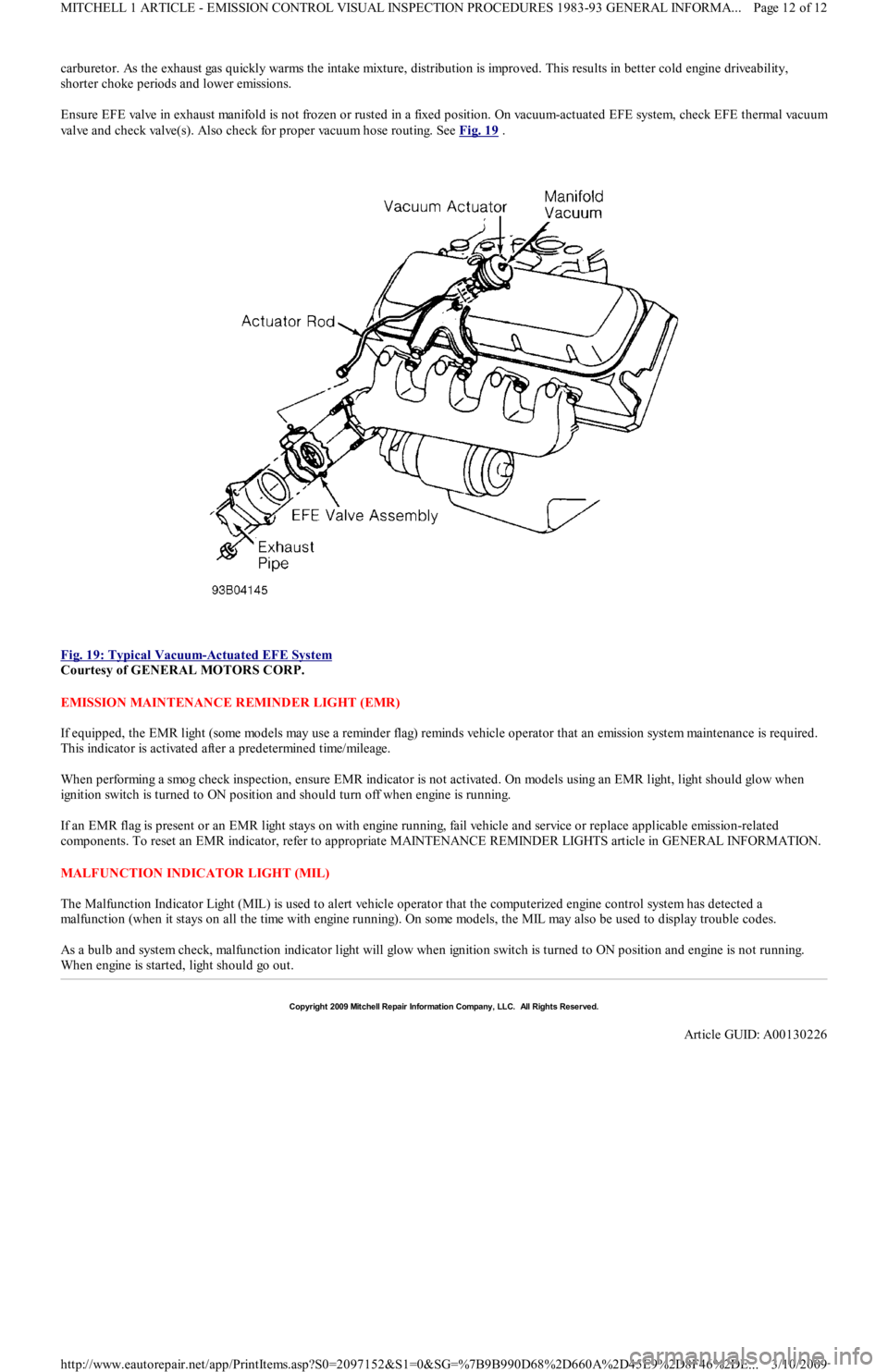
carburetor. As the exhaust gas quickly warms the intake mixture, distribution is improved. This results in better cold engine driveability,
shorter choke periods and lower emissions.
Ensure EFE valve in exhaust manifold is not frozen or rusted in a fixed position. On vacuum-actuated EFE system, check EFE thermal vacuu
m
valve and check valve(s). Also check for proper vacuum hose routing. See Fig. 19
.
Fig. 19: Typical Vacuum
-Actuated EFE System
Courtesy of GENERAL MOTORS CORP.
EMISSION MAINTENANCE REMINDER LIGHT (EMR)
If equipped, the EMR light (some models may use a reminder flag) reminds vehicle operator that an emission system maintenance is required.
This indicator is activated after a predetermined time/mileage.
When performing a smog check inspection, ensure EMR indicator is not activated. On models using an EMR light, light should glow when
ignition switch is turned to ON position and should turn off when engine is running.
If an EMR flag is present or an EMR light stays on with engine running, fail vehicle and service or replace applicable emission-related
components. To reset an EMR indicator, refer to appropriate MAINTENANCE REMINDER LIGHTS article in GENERAL INFORMATION.
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR LIGHT (MIL)
The Malfunction Indicator Light (MIL) is used to alert vehicle operator that the computerized engine control system has detected a
malfunction (when it stays on all the time with engine running). On some models, the MIL may also be used to display trouble codes.
As a bulb and system check, malfunction indicator light will glow when ignition switch is turned to ON position and engine is not running.
When engine is started, light should go out.
Copyr ight 2009 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC. All Rights Reserved.
Article GUID: A00130226
Page 12 of 12 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - EMISSION CONTROL VISUAL INSPECTION PROCEDURES 1983-93 GENERAL INFORMA...
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B9B990D68%2D660A%2D45E9%2D8F46%2DE
...
Page 365 of 454

Back To Article
MAINTENANCE INFORMATION
1988-93 MAINT ENANCE Ford Motor Co. Maintenance Inform ation
MODEL IDENTIFICATION
VIN LOCATION
The Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) is located on the left side of the dash panel at the base of the windshield. The VIN chart explains the
code characters.
VIN CODE ID EXPLANATION
Numbers preceding the explanations in the legend below refer to the sequence of characters as listed on VIN identification label. See VIN
example below.
Fig. 1: VIN Code ID Explanation
MAINTENANCE SERVICE INFORMATION
SEVERE & NORMAL SERVICE DEFINITIONS
Service is recommended at mileage intervals based on vehicle operation. Service schedules are based on the following primary operating
conditions:
Severe Service
Short Trips (About 10 Miles) In Freezing Temperatures
Towing Or Heavily Loaded
Severe Dust Conditions
Hot Weather, Stop-And-Go Driving
Extensive Idling Conditions (Taxi Or Delivery Type Service)
Normal Service
NOTE:For scheduled m aintenance intervals and the related fluid capacities, fluid specifications and labor
tim es for m ajor service intervals, see SCHEDULED SERVICES article in this section. Warranty
inform ation and specifications for fluid capacities, lubrication specifications, wheel and tire size, and
battery type are covered in this article.
NOTE:Use the Severe Service schedule if the vehicle to be serviced is operated under ANY (one or m ore) of
these conditions:
Page 1 of 9 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - MAINTENANCE INFORMATION 1988-93 MAINTENANCE Ford Motor Co. Maintenance Inform...
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B9B990D68%2D660A%2D45E9%2D8F46%2DE
...
Page 366 of 454
Driven More Than 10 Miles Daily
No Operating Conditions From Severe Service Schedule
CAMSHAFT TIMING BELT
The condition of camshaft drive belts should always be checked on vehicles which have more than 50,000 miles. Although some
manufacturers do not recommend belt replacement at a specified mileage, others require it at 60,000-100,000 miles. A camshaft drive belt
failure may cause extensive damage to internal engine components on most engines, although some designs do not allow piston-to-va l ve
contact. These designs are often called "Free Wheeling".
Many manufacturers changed their maintenance and warranty schedules in the mid-1980's to reflect timing belt inspection and/or replacement
at 50,000-60,000 miles. Most service interval schedules in this manual reflect these changes.
Belts or components should be inspected and replaced if any of the following conditions exist:
Cracks Or Tears In Belt Surface
Missing, Damaged, Cracked Or Rounded Teeth
Oil Contamination
Damaged Or Faulty Tensioners
Incorrect Tension Adjustment
Replace camshaft timing belt every 60,000 miles.
COOLING SYSTEM
Replace engine coolant every 36 months or 30,000 miles. Check condition of hoses and clamps every 12 months or 15,000 miles, whichever
comes first. Replace hoses and clamps if necessary.
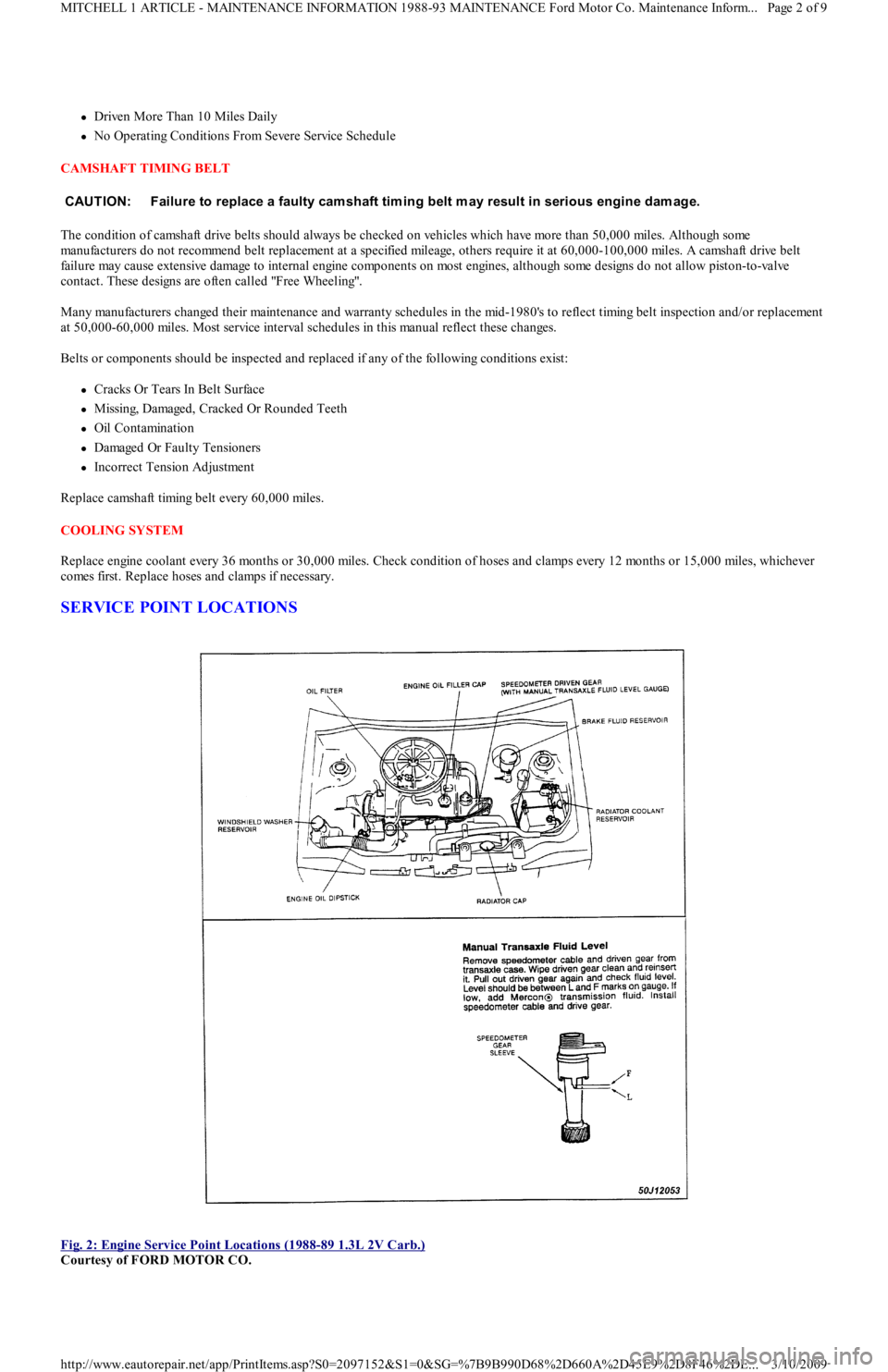
SERVICE POINT LOCATIONS
Fig. 2: Engine Service Point Locations (1988
-89 1.3L 2V Carb.)
Courtesy of FORD MOTOR CO. CAUT ION: Failure to replace a faulty cam shaft tim ing belt m ay result in serious engine dam age.
Page 2 of 9 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - MAINTENANCE INFORMATION 1988-93 MAINTENANCE Ford Motor Co. Maintenance Inform...
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B9B990D68%2D660A%2D45E9%2D8F46%2DE
...