weight FORD FIESTA 1989 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 1989, Model line: FIESTA, Model: FORD FIESTA 1989Pages: 296, PDF Size: 10.65 MB
Page 37 of 296

(see illustration). Centralise the seal on the
shaft, then insert and tighten the housing
retaining bolts to the specified torque setting.
Refit the sump with reference to Section 11.
12 Check that the crankshaft rear flange
and the flywheel mating faces are clean, then
refit the flywheel as described in Section 16.
15 Engine/transmission mountings - inspection and
renewal
2
Inspection
1 The engine/transmission mountings seldom
require attention, but broken or deteriorated
mountings should be renewed immediately, or
the added strain placed on the driveline
components may cause damage or wear.
2 During the check, the engine/transmission
must be raised slightly, to remove its weight
from the mountings.
3 Chock the rear wheels then jack up the
front of the car and support it on axle stands
(see “Jacking and Vehicle Support” ). Position
a jack under the sump, with a large block of
wood between the jack head and the sump,
then carefully raise the engine/transmission
just enough to take the weight off the
mountings.
4 Check the mountings to see if the rubber is
cracked, hardened or separated from the metal components. Sometimes, the rubber
will split right down the centre.
5
Check for relative movement between each
mounting’s brackets and the
engine/transmission or body (use a large
screwdriver or lever to attempt to move the
mountings). If movement is noted, lower the
engine and check-tighten the mounting
fasteners.
Renewal
6 The engine mountings can be removed if
the weight of the engine/transmission is
supported by one of the following alternative
methods.
7 Either support the weight of the assembly
from underneath using a jack and a suitable
piece of wood between the jack saddle and
the sump or transmission (to prevent
damage), or from above by attaching a hoist
to the engine. A third method is to use a
suitable support bar with end pieces which
will engage in the water channel each side of
the bonnet lid aperture. Using an adjustable hook and chain connected to the engine, the
weight of the engine and transmission can
then be taken from the mountings.
Engine right-hand mounting
8
Unscrew and remove the mounting side
bolt from under the right-hand wheel arch
(see illustration) .
9 Unscrew and remove the mounting
retaining nut and washer from the suspension
strut cup retaining plate (see illustration).
10 Undo the three bolts securing the
mounting unit to the cylinder block. The
mounting unit and bracket can then be
lowered from the engine (see illustration).
11 Unbolt and remove the mounting from its
support bracket.
Transmission bearer and mountings
12 Unscrew and remove the two nuts
securing the mountings (front and rear) to the
transmission bearer (see illustration).
13 Support the transmission bearer, then
undo and remove the four retaining bolts from
the floorpan, two at the front and two at the
2A•10 HCS engine in-car repair procedures
15.12 Exploded view of the transmission bearer mountings
15.10 Undo the three bolts securing the
mounting assembly to the cylinder block
and withdraw the mounting
15.9 Unscrew and remove the mountingretaining nut and washer from the
suspension strut cup retaining plate15.8 Unscrew and remove the engine
mounting side bolt (arrowed) from under the wheel arch14.11b Fitting the rear oil seal housing
with a new gasket in position on the rear face of the cylinder block
1595Ford Fiesta Remakeprocarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su
Page 57 of 296

clamp brackets and disconnect the pipe joint
union over the top of the cylinder head cover.
Place absorbent rags beneath the union as it
is disconnected to soak up escaping fluid and
plug the open unions to prevent dirt entry and
further fluid loss. Move the pipe(s) clear just
sufficiently to allow removal of the cylinder
head cover.
5Remove the timing belt upper cover (see
Section 7).
6 Disconnect the crankcase breather hose
from the cylinder head cover union (see
illustration) .
7 Unplug the HT leads from the spark plugs
and withdraw them, unclipping the leads from
the cover.
8 Working progressively, unscrew the
cylinder head cover retaining bolts, noting the
spacer sleeve and rubber seal at each, then
withdraw the cover (see illustration).
9 Discard the cover gasket; this mustbe
renewed whenever it is disturbed. Check that
the sealing faces are undamaged, and that the
rubber seal at each retaining bolt is
serviceable; renew any worn or damaged
seals.
Refitting
10 On refitting, clean the cover and cylinder
head gasket faces carefully, then fit a new
gasket to the cover, ensuring that it locates
correctly in the cover grooves (see illustration).
11 Refit the cover to the cylinder head, then
insert the rubber seal and spacer sleeve at
each bolt location (see illustration). Start allbolts finger-tight, ensuring that the gasket
remains seated in its groove.
12
Working in a diagonal sequence from the
centre outwards, and in two stages (see
Specifications), tighten the cover bolts to the
specified torque wrench setting.
13 Refit the HT leads, clipping them into
place so that they are correctly routed; each is
numbered, and can also be identified by the
numbering on its respective coil terminal.
14 Reconnect the crankcase breather hose,
and refit the timing belt upper cover.
Reconnect and adjust the accelerator cable,
then refit the air inlet components (see
Chapter 4B).
15 On models with power steering,
reconnect the high pressure fluid pipe then
bleed the system as described in Chapter 10.
5 Valve clearances -
general information
Refer to Section 5 in Part B of this Chapter.
6 Crankshaft pulley -
removal and refitting
1
Removal
1 Remove the auxiliary drivebelt - either
remove the drivebelt completely, or just secure it clear of the crankshaft pulley,
depending on the work to be carried out (see
Chapter 1).
2
If necessary, rotate the crankshaft until the
timing marks align (see Section 3).
3 The crankshaft must now be locked to
prevent its rotation while the pulley bolt is
unscrewed. To do this, remove the starter
motor (Chapter 5A) and lock the starter ring
gear teeth using a suitable screwdriver.
4 It should now just be possible to reach
between the crankshaft pulley and the body
side member to undo and remove the pulley
bolt and withdraw the pulley. However, if
additional working clearance is needed,
proceed as follows.
5 If not already done, chock the rear wheels
then jack up the front of the car and support it
on axle stands (see “Jacking and Vehicle
Support” ). Remove the front right-hand
roadwheel.
6 Support the weight of the
engine/transmission using a trolley jack, with
a wooden spacer to prevent damage to the
sump.
7 From above, unscrew the three bolts
securing the engine’s front right-hand (Y-
shaped) mounting bracket to the alternator
mounting bracket. Unfasten the engine’s rear
right-hand mounting from the body by
unscrewing first the single nut (and washer)
immediately to the rear of the timing belt
cover, then the bolt in the wheel arch
8 With the engine’s right-hand mountings
unfastened from the body, lower the
engine/transmission on the jack until a socket
spanner can be fitted to the crankshaft pulley
bolt.
9 With the starter ring gear teeth locked,
unscrew the crankshaft pulley bolt and
withdraw the pulley (see illustration).
Refitting
10Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure; ensure that the pulley’s keyway is
aligned with the crankshaft’s locating key, and
tighten the pulley bolt to the specified torque
wrench setting. If the engine mountings were
disturbed, use the jack to adjust the height of
the engine/transmission until the bolts (and
nut, with washer) can be refitted and screwed
2C•4 Zetec engine in-car repair procedures
6.9 Unscrew pulley bolt to release
crankshaft pulley4.11 Ensure rubber seal is fitted to eachcover bolt spacer, as shown
4.10 Ensure gasket is located correctly in cover groove4.8 Removing cylinder head cover
1595Ford Fiesta Remake
4.6 Disconnecting crankcase breather
hose from cylinder head cover unionprocarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su
Page 64 of 296

5Disconnect the accelerator cable from the
throttle linkage as described in Chapter 4D.
Secure the cable clear of the engine/
transmission.
6 Remove the auxiliary drivebelt (see Chap-
ter 1).
7 Remove the three screws securing the
wiring “rail” to the rear of the manifold.
Releasing its wire clip, unplug the large
electrical connector (next to the fuel pressure
regulator) to disconnect the engine wiring from
the main loom (see illustration) . Unplug the
electrical connectors on each side of the
ignition coil, and the single connector from
beneath the front of the thermostat housing, to
disconnect the coil and coolant temperature
gauge sender wiring (see illustration).
8 Marking or labelling them as they are
unplugged, disconnect the vacuum hoses as
follows:
a) One from the rear of the throttle housing
(only the one hose - there is no need to
disconnect the second hose running to
the fuel pressure regulator).
b) One from the union on the inlet manifold’s
left-hand end.
c) The braking system vacuum servo unit hose (see Chapter 9 for details).
9 Unbolt the engine earth lead from the
cylinder head lifting eye.
10 Unbolt both parts of the exhaust manifold
heat shield. Either remove the dipstick and
tube, or swing them out of the way.
11 Unscrew the pulse-air filter housing
retaining bolt, then disconnect its vacuum
hose.
12 Drain the cooling system (see Chapter 1).
13 Disconnect all coolant hoses from the
thermostat housing (see illustration).14
Unscrew the two nuts to disconnect the
exhaust system front downpipe from the
manifold (Chapter 4B); disconnect the oxygen
sensor wiring, so that it is not strained by the
weight of the exhaust system.
15 Remove the timing belt and both
camshafts (see Sections 8 and 11); if the
cylinder head is to be dismantled, withdraw
the hydraulic tappets.
16 Remove the timing belt inner shield (see
Section 7.
17 Working in the reverseof the sequence
shown in illustration 12.28a, slacken the ten
cylinder head bolts progressively and by one
turn at a time; a Torx key (TX 55 size) will be
required. Remove each bolt in turn, and
ensure that new replacements are obtained
for reassembly; these bolts are subjected to
severe stresses and so mustbe renewed,
regardless of their apparent condition,
whenever they are disturbed.
18 Lift the cylinder head away; use
assistance if possible, as it is a heavy
assembly. If necessary, grip the manifolds
and rock it free from the location dowels on
the top face of the cylinder block. Do not
attempt to tap it sideways or lever between
the head and the block top face. Remove the
gasket, noting the two dowels, and discard it.
Preparation for refitting
19 The mating faces of the cylinder head and
cylinder block must be perfectly clean before refitting the head. Use a hard plastic or wood
scraper to remove all traces of gasket and
carbon; also clean the piston crowns. Take
particular care during the cleaning operations,
as aluminium alloy is easily damaged. Also,
make sure that the carbon is not allowed to
enter the oil and water passages - this is
particularly important for the lubrication
system, as carbon could block the oil supply
to the engine’s components. Using adhesive
tape and paper, seal the water, oil and bolt
holes in the cylinder block.
20
Check the mating surfaces of the cylinder
block and the cylinder head for nicks, deep
scratches and other damage. If slight, they
may be removed carefully with a file, but if
excessive, machining may be the only
alternative to renewal.
21 If warpage of the cylinder head gasket
surface is suspected, use a straight-edge to
check it for distortion. Refer to Part D of this
Chapter if necessary.
Refitting
22 Wipe clean the mating surfaces of the
cylinder head and cylinder block. Check that
the two locating dowels are in position in the
cylinder block, and that all cylinder head bolt
holes are free from oil.
23 Position a new gasket over the dowels on
the cylinder block surface, so that the
“TOP/OBEN” mark is uppermost, and with the
tooth (or teeth, according to engine size)
protruding from the front edge (see
illustration) .
24 Temporarily refit the crankshaft pulley,
and rotate the crankshaft anti-clockwise so
that No 1 cylinder’s piston is lowered to
approximately 20 mm before TDC, thus
avoiding any risk of valve/piston contact and
damage during reassembly.
Zetec engine in-car repair procedures 2C•11
12.13 Disconnect all coolant hoses from thermostat housing12.7b Unplug connectors (arrowed) todisconnect ignition coil wiring12.7a Unplug engine wiring loom
connector alongside the inlet manifold
12.23 Ensuring protruding tooth (or teeth) “A” are at front and marking “B” is
upwards, locate new cylinder head gasket on dowels “C”
2C
1595Ford Fiesta Remake
Whenever you disconnect
any vacuum lines, coolant or
emissions hoses, wiring
connectors and fuel lines,
always label them clearly, so that they
can be correctly reassembled. Masking
tape and/or a touch-up paint applicator
work well for marking items. Take
instant photos, or sketch the locations
of components and brackets.
To prevent carbon entering
the gap between the pistons
and bores, smear a little
grease in the gap. After
cleaning each piston, use a small brush
to remove all traces of grease and
carbon from the gap, then wipe away
the remainder with a clean rag.
procarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su
Page 68 of 296
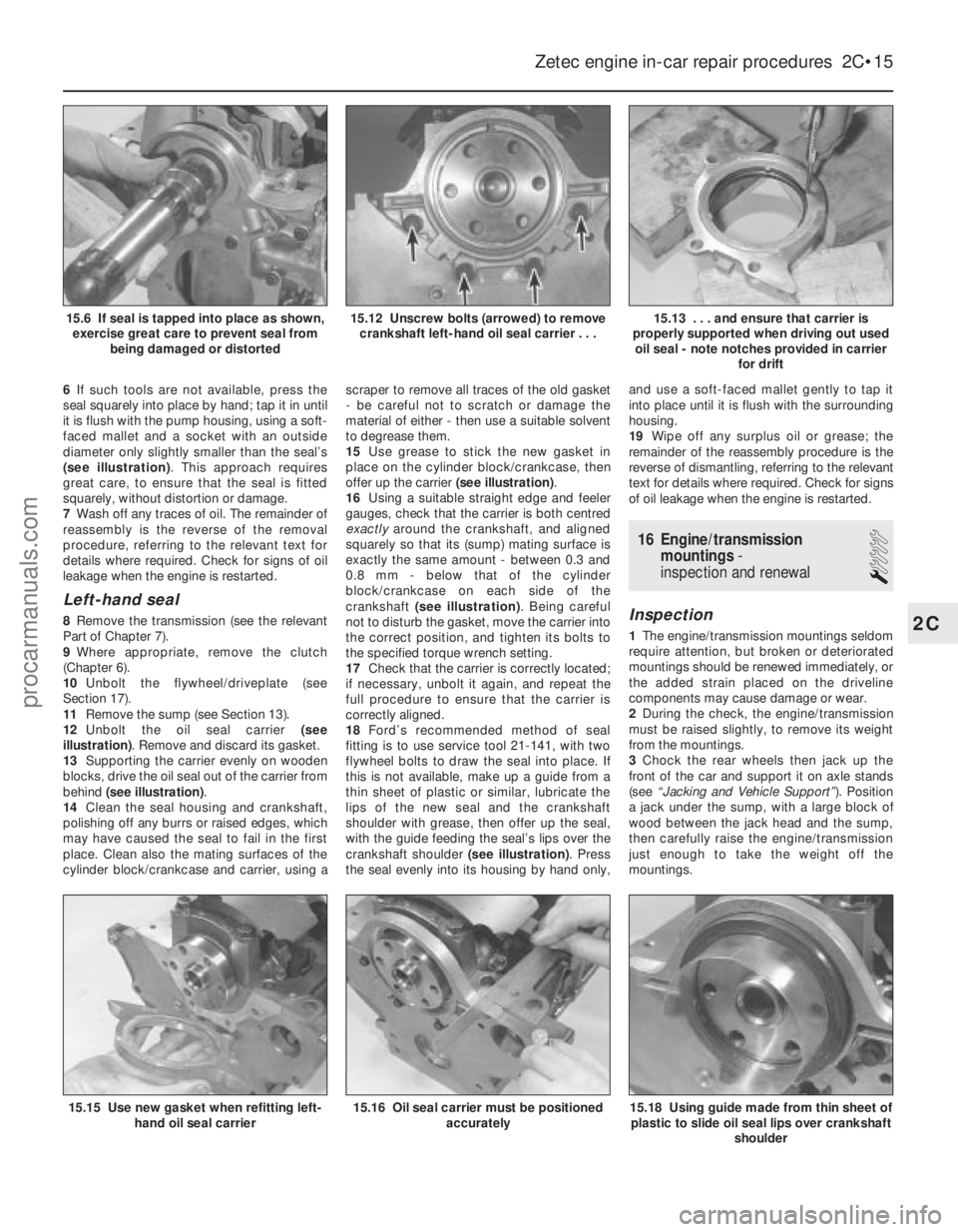
6If such tools are not available, press the
seal squarely into place by hand; tap it in until
it is flush with the pump housing, using a soft-
faced mallet and a socket with an outside
diameter only slightly smaller than the seal’s
(see illustration) . This approach requires
great care, to ensure that the seal is fitted
squarely, without distortion or damage.
7 Wash off any traces of oil. The remainder of
reassembly is the reverse of the removal
procedure, referring to the relevant text for
details where required. Check for signs of oil
leakage when the engine is restarted.
Left-hand seal
8 Remove the transmission (see the relevant
Part of Chapter 7).
9 Where appropriate, remove the clutch
(Chapter 6).
10 Unbolt the flywheel/driveplate (see
Section 17).
11 Remove the sump (see Section 13).
12 Unbolt the oil seal carrier (see
illustration) . Remove and discard its gasket.
13 Supporting the carrier evenly on wooden
blocks, drive the oil seal out of the carrier from
behind (see illustration) .
14 Clean the seal housing and crankshaft,
polishing off any burrs or raised edges, which
may have caused the seal to fail in the first
place. Clean also the mating surfaces of the
cylinder block/crankcase and carrier, using a scraper to remove all traces of the old gasket
- be careful not to scratch or damage the
material of either - then use a suitable solvent
to degrease them.
15
Use grease to stick the new gasket in
place on the cylinder block/crankcase, then
offer up the carrier (see illustration).
16 Using a suitable straight edge and feeler
gauges, check that the carrier is both centred
exactly around the crankshaft, and aligned
squarely so that its (sump) mating surface is
exactly the same amount - between 0.3 and
0.8 mm - below that of the cylinder
block/crankcase on each side of the
crankshaft (see illustration) . Being careful
not to disturb the gasket, move the carrier into
the correct position, and tighten its bolts to
the specified torque wrench setting.
17 Check that the carrier is correctly located;
if necessary, unbolt it again, and repeat the
full procedure to ensure that the carrier is
correctly aligned.
18 Ford’s recommended method of seal
fitting is to use service tool 21-141, with two
flywheel bolts to draw the seal into place. If
this is not available, make up a guide from a
thin sheet of plastic or similar, lubricate the
lips of the new seal and the crankshaft
shoulder with grease, then offer up the seal,
with the guide feeding the seal’s lips over the
crankshaft shoulder (see illustration) . Press
the seal evenly into its housing by hand only, and use a soft-faced mallet gently to tap it
into place until it is flush with the surrounding
housing.
19
Wipe off any surplus oil or grease; the
remainder of the reassembly procedure is the
reverse of dismantling, referring to the relevant
text for details where required. Check for signs
of oil leakage when the engine is restarted.
16 Engine/transmission mountings -
inspection and renewal
1
Inspection
1 The engine/transmission mountings seldom
require attention, but broken or deteriorated
mountings should be renewed immediately, or
the added strain placed on the driveline
components may cause damage or wear.
2 During the check, the engine/transmission
must be raised slightly, to remove its weight
from the mountings.
3 Chock the rear wheels then jack up the
front of the car and support it on axle stands
(see “Jacking and Vehicle Support” ). Position
a jack under the sump, with a large block of
wood between the jack head and the sump,
then carefully raise the engine/transmission
just enough to take the weight off the
mountings.
Zetec engine in-car repair procedures 2C•15
15.13 . . . and ensure that carrier is
properly supported when driving out used oil seal - note notches provided in carrier for drift15.12 Unscrew bolts (arrowed) to removecrankshaft left-hand oil seal carrier . . .15.6 If seal is tapped into place as shown,exercise great care to prevent seal from being damaged or distorted
15.18 Using guide made from thin sheet ofplastic to slide oil seal lips over crankshaft
shoulder15.16 Oil seal carrier must be positionedaccurately15.15 Use new gasket when refitting left-hand oil seal carrier
2C
1595Ford Fiesta Remakeprocarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su
Page 69 of 296

4Check the mountings to see if the rubber is
cracked, hardened or separated from the
metal components. Sometimes, the rubber
will split right down the centre.
5 Check for relative movement between each
mounting’s brackets and the engine/
transmission or body (use a large screwdriver
or lever to attempt to move the mountings). If
movement is noted, lower the engine and
check-tighten the mounting fasteners.
Renewal
6 The engine mountings can be removed if
the weight of the engine/transmission is
supported by one of the following alternative
methods.
7 Either support the weight of the assembly
from underneath using a jack and a suitable
piece of wood between the jack saddle and
the sump or transmission (to prevent
damage), or from above by attaching a hoist
to the engine. A third method is to use a
suitable support bar with end pieces which
will engage in the water channel each side of
the bonnet lid aperture. Using an adjustable
hook and chain connected to the engine, the
weight of the engine and transmission can
then be taken from the mountings.
Engine front right-hand mounting
8 This mounting consists of a two-piece
bracket bolted to the inner wing panel,
connected by the bonded-rubber mounting
itself to a (Y-shaped) bracket, bolted (via the
alternator mounting bracket) to the cylinder
block (see illustration) .
9 Unscrew the three bolts securing the front
right-hand mounting bracket to the alternator
mounting bracket.
10 Unscrew the bolts securing the mounting
bracket to the inner wing panel and chassis
rail and withdraw the mounting assembly.
Engine rear right-hand mounting
11 This mounting consists of the bonded-
rubber mounting secured to the inner wing
panel by a (horizontal) bolt, accessible from
within the wheel arch, and a (vertical) stud, the
retaining nut of which is accessible from the
engine compartment. The mounting is bolted
to a bracket, which is in turn bolted to the
cylinder block.
12 Unbolt the mounting from the body by
unscrewing first the single nut (and washer)
immediately to the rear of the timing belt
cover, then the bolt in the wheel arch.
13 Unbolt the mounting from the cylinder
block bracket and withdraw the mounting
assembly.
Transmission bearer and mountings
14 On XR2i models, remove the front
suspension crossmember as described in
Chapter 10.
15 Unscrew and remove the two nuts
securing the mountings (front and rear) to the
transmission bearer
16 Support the transmission bearer, then
undo and remove the four retaining bolts from
the floorpan, two at the front and two at the
rear, and lower the transmission bearer from
the vehicle. Note plate fitment, as applicable,
for reassembly.
17 To remove the mountings from the
transmission, unscrew the upper bolt and
lower stud (front mounting) or the three nuts
(rear mounting) and withdraw the relevant
mounting and bracket assembly from the
transmission.
All mountings
18 Refitting of all mountings is a reversal of
removal. Make sure that the original sequence
of assembly of washers and plates is
maintained.
19 Do not fully tighten any mounting bolts
until they are all located. As the mounting
bolts and nuts are tightened, check that the
mounting rubbers do not twist.
17 Flywheel/driveplate -
removal, inspection and
refitting
3
Removal
1 Remove the transmission (see the relevant
Part of Chapter 7).
2 Where appropriate, remove the clutch
(Chapter 6).
3 Use a centre-punch or paint to make alignment marks on the flywheel/driveplate
and crankshaft, to ensure correct alignment
during refitting.
4
Prevent the flywheel/driveplate from turning
by locking the ring gear teeth, or by bolting a
strap between the flywheel/driveplate and the
cylinder block/crankcase. Slacken the bolts
evenly until all are free.
5 Remove each bolt in turn, and ensure that
new replacements are obtained for
reassembly; these bolts are subjected to
severe stresses, and so must be renewed,
regardless of their apparent condition,
whenever they are disturbed.
6 Noting the reinforcing plate (automatic
transmission models only), withdraw the
flywheel/driveplate; do not drop it - it is very
heavy.
Inspection
7 Clean the flywheel/driveplate to remove
grease and oil. Inspect the surface for cracks,
rivet grooves, burned areas and score marks.
Light scoring can be removed with emery
cloth. Check for cracked and broken ring gear
teeth. Lay the flywheel/driveplate on a flat
surface, and use a straight edge to check for
warpage.
8 Clean and inspect the mating surfaces of
the flywheel/driveplate and the crankshaft. If
the crankshaft left-hand seal is leaking, renew
it (see Section 15) before refitting the
flywheel/driveplate.
9 While the flywheel/driveplate is removed,
clean carefully its inboard (right-hand) face,
particularly the recesses which serve as the
reference points for the crankshaft speed/
position sensor. Clean the sensor’s tip, and
check that the sensor is securely fastened.
Refitting
10 On refitting, ensure that the engine/
transmission adapter plate is in place (where
necessary), then fit the flywheel/driveplate to
the crankshaft so that all bolt holes align - it
will fit only one way - check this using the
marks made on removal. Do not forget the
reinforcing plate (automatic transmission
models).
11 Lock the flywheel/driveplate by the
method used on dismantling. Working in a
diagonal sequence to tighten them evenly,
and increasing to the final amount in two or
three stages, tighten the new bolts to the
specified torque wrench setting.
12 The remainder of reassembly is the
reverse of the removal procedure, referring to
the relevant text for details where required.
2C•16 Zetec engine in-car repair procedures
16.8 Engine front right-hand mounting
1595Ford Fiesta Remakeprocarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su
Page 75 of 296

Torque wrench settingsNmlbf ft
Main bearing cap bolts and nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8059
Crankpin (big-end) bearing cap bolts: Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . . . . . 1813
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . . . . . Angle-tighten a further 90º
Piston-cooling oil jet/blanking plug Torx screws . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9 7
Cylinder block and head oilway blanking plugs:
M6 x 10 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . . . . . 9 7
M10 x 11.5 - in block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. 2317
1/4 PTF plug - in block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
2418
Engine-to-transmission bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4130
Note: Refer to Part C of this Chapter for remaining torque wrench settings.
2D•6 Engine removal and overhaul procedures
1595Ford Fiesta Remake
1 General information
Included in this Part of Chapter 2 are details
of removing the engine/transmission from the
car and general overhaul procedures for the
cylinder head, cylinder block/crankcase and
all other engine internal components.
The information given ranges from advice
concerning preparation for an overhaul and
the purchase of replacement parts, to detailed
step-by-step procedures covering removal,
inspection, renovation and refitting of engine
internal components.
After Section 6, all instructions are based
on the assumption that the engine has been
removed from the car. For information
concerning in-car engine repair, as well as the
removal and refitting of those external
components necessary for full overhaul, refer
to Part A, B or C of this Chapter (as
applicable) and to Section 6. Ignore any
preliminary dismantling operations described
in Part A, B or C that are no longer relevant
once the engine has been removed from the
car.
2 Engine/transmission removal - preparation and
precautions
If you have decided that an engine must be
removed for overhaul or major repair work,
several preliminary steps should be taken.
Locating a suitable place to work is
extremely important. Adequate work space,
along with storage space for the car, will be
needed. If a workshop or garage is not
available, at the very least, a flat, level, clean
work surface is required. If possible, clear some shelving close to the
work area and use it to store the engine
components and ancillaries as they are
removed and dismantled. In this manner the
components stand a better chance of staying
clean and undamaged during the overhaul.
Laying out components in groups together
with their fixing bolts, screws etc will save
time and avoid confusion when the engine is
refitted. Clean the engine compartment and
engine/transmission before beginning the
removal procedure; this will help visibility and
help to keep tools clean. On three of the engines covered in this
manual (CVH, PTE, and Zetec), the unit can
only be withdrawn by removing it complete
with the transmission; the vehicle’s body must
be raised and supported securely, sufficiently
high that the engine/transmission can be
unbolted as a single unit and lowered to the
ground; the engine/transmission unit can then
be withdrawn from under the vehicle and
separated. On all engines, an engine hoist or
A- frame will be necessary. Make sure the
equipment is rated in excess of the combined
weight of the engine and transmission. The help of an assistant should be
available; there are certain instances when
one person cannot safely perform all of the
operations required to remove the engine
from the vehicle. Safety is of primary
importance, considering the potential hazards
involved in this kind of operation. A second
person should always be in attendance to
offer help in an emergency. If this is the first
time you have removed an engine, advice and
aid from someone more experienced would
also be beneficial. Plan the operation ahead of time. Before
starting work, obtain (or arrange for the hire
of) all of the tools and equipment you will
need. Access to the following items will allow
the task of removing and refitting the
engine/transmission to be completed safely
and with relative ease: an engine hoist - rated
in excess of the combined weight of the
engine/transmission, a heavy-duty trolley
jack, complete sets of spanners and sockets
as described in “ Tools and working facilities ”
at the rear this manual, wooden blocks, and
plenty of rags and cleaning solvent for
mopping up spilled oil, coolant and fuel. A
selection of different sized plastic storage bins
will also prove useful for keeping dismantled
components grouped together. If any of the
equipment must be hired, make sure that you
arrange for it in advance, and perform all of
the operations possible without it beforehand;
this may save you time and money. Plan on the vehicle being out of use for
quite a while, especially if you intend to carry
out an engine overhaul. Read through the
whole of this Section and work out a strategy based on your own experience and the tools,
time and workspace available to you. Some of
the overhaul processes may have to be
carried out by a Ford dealer or an engineering
works - these establishments often have busy
schedules, so it would be prudent to consult
them before removing or dismantling the
engine, to get an idea of the amount of time
required to carry out the work.
When removing the engine from the vehicle,
be methodical about the disconnection of
external components. Labelling cables and
hoses as they removed will greatly assist the
refitting process.
Always be extremely careful when lifting the
engine/transmission assembly from the
engine bay. Serious injury can result from
careless actions. If help is required, it is better
to wait until it is available rather than risk
personal injury and/or damage to components
by continuing alone. By planning ahead and
taking your time, a job of this nature, although
major, can be accomplished successfully and
without incident.
3 Engine - removal and
refitting (HCS engines)
3
Warning: Petrol is extremely
flammable, so take extra
precautions when disconnecting
any part of the fuel system.
Don’t smoke, or allow naked flames or bare
light bulbs, in or near the work area, and
don’t work in a garage where a natural-gas
appliance (such as a clothes dryer or water
heater) is installed. If you spill petrol on
your skin, rinse it off immediately. Have a
fire extinguisher rated for petrol fires
handy, and know how to use it.
Note: Read through the entire Section, as well
as reading the advice in the preceding
Section, before beginning this procedure. The
engine is removed separately from the
transmission and is lifted upwards and out of
the engine compartment.
Removal
1 On fuel injection engines, refer to Chap-
ter 4B and depressurise the fuel system.
2 Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead
(refer to Chapter 5A, Section 1).
procarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su
Page 77 of 296

transmission flange attachment bolts (see
illustration) .
19 Check that the appropriate underside
attachments are disconnected and out of the
way, then lower the vehicle to the ground.
20 Unbolt and remove the heat shield from
the exhaust manifold.
21 Attach a suitable hoist to the engine. It is
possible to fabricate lifting eyes to connect
the hoist to the engine, but make sure that
they are strong enough, and connect them to
the inlet and exhaust manifold at diagonally-
opposite ends of the engine.
22 With the hoist securely connected, take
the weight of the engine. Unscrew and
remove the right-hand engine mounting side
bolt from under the right-hand wheel arch.
Unscrew and remove the mounting retaining
nut and washer from the suspension strut cup
retaining plate, and the three bolts securing
the mounting unit to the cylinder block.
23 Locate a jack under the transmission, and
raise it to take the weight of the transmission.
24 Unscrew and remove the remaining
engine-to-transmission retaining bolts on the
upper flange.
25 Check around the engine to ensure that all
of the relevant fixings and attachments are
disconnected and out of the way for the
removal.
26 Enlist the aid of an assistant, then move
the engine sideways and away from the
transmission, whilst simultaneously raising
the transmission. When the engine is
separated from the transmission, carefully
guide it up and out of the engine
compartment. Do not allow the weight of the
engine to hang on the transmission input shaft
at any point during the removal (or refitting) of
the engine. When the engine sump is clear
of the vehicle, swing the power unit out of the
way, and lower it onto a trolley (if available).
Unless a mobile hoist is being used, it will be
necessary to move the vehicle rearwards and
out of the way in order to allow the engine to
be lowered for removal. In this instance,
ensure that the weight of the transmission is
well supported as the vehicle is moved.
27 While the engine is removed, check the
mountings; renew them if they are worn or
damaged. Similarly, check the condition of all
coolant and vacuum hoses and pipes (see Chapter 1); components that are normally
hidden can now be checked properly, and
should be renewed if there is any doubt at all
about their condition. Also, take the
opportunity to overhaul the clutch
components (see Chapter 6). It is regarded by
many as good working practice to renew the
clutch assembly as a matter of course,
whenever major engine overhaul work is
carried out. Check also the condition of all
components disturbed on removal, and renew
any that are damaged or worn.
Refitting
28
Refitting is in general, a reversal of the
removal procedure, but the following special
points should be noted.
29 Before coupling the engine to the
transmission, apply a thin smear of high-
melting-point grease onto the transmission
input shaft splines. If the clutch has been
removed, ensure that the clutch disc is
centralised, and disconnect the clutch cable
from the release lever on the transmission
casing.
30 Tighten all fixings to their recommended
torque wrench settings.
31 Check that the mating faces are clean,
and fit a new exhaust downpipe-to-manifold
gasket and self-locking nuts when
reconnecting this joint.
32 Ensure that all wiring connections are
correctly and securely made.
33 Remove the plugs from the fuel lines
before reconnecting them correctly and
securely.
34 Reconnect and adjust the accelerator and
choke cables as described in the relevant Part
of Chapter 4. The refitting details for the air
cleaner components are also given in that
Chapter.
35 Renew any coolant hoses (and/or
retaining clips) that are not in good condition.
36 Refer to Chapter 6 for details on
reconnecting the clutch cable.
37 When the engine is fully refitted, check
that the various hoses are connected, and
then top-up the engine oil and coolant levels
as described in Chapter 1 and “Weekly
Checks”.
38 When engine refitting is completed, refer to
Section 19 for the engine start-up procedures.
4 Engine/transmission -
removal and refitting (CVH and
PTE engines)
3
Warning: Petrol is extremely
flammable, so take extra
precautions when disconnecting
any part of the fuel system.
Don’t smoke, or allow naked flames or bare
light bulbs, in or near the work area, and
don’t work in a garage where a natural-gas
appliance (such as a clothes dryer or water
heater) is installed. If you spill petrol on
your skin, rinse it off immediately. Have a
fire extinguisher rated for petrol fires
handy, and know how to use it.
Note: Read through the entire Section, as well
as reading the advice in Section 2, before
beginning this procedure. The engine and
transmission are removed as a unit, lowered to
the ground and removed from underneath,
then separated outside the vehicle.
Removal
1 On all fuel injection engines, refer to
Chapter 4B, C or D as applicable and
depressurise the fuel system.
2 Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead
(refer to Chapter 5A, Section 1).
3 Referring to Chapter 1 for details, drain the
coolant and the engine oil. Refit the drain plug
to the sump on completion.
4 Refer to Chapter 11 for details, and remove
the bonnet.
5 Remove the air cleaner assembly and air
inlet components as described in the relevant
Part of Chapter 4.
6 Release the retaining clips and detach the
coolant top hose, the heater hose and the
radiator overflow hose from the thermostat
housing. Disconnect the coolant hose from
the inlet manifold, and the bottom hose from
the water pump and/or the radiator (see
illustrations) . On 1.4 litre CFi fuel injection
models, also disconnect the coolant hose
from the injection unit. On EFi and SEFi fuel
injection models, detach the heater hose
Y-connector. Allow for coolant spillage as the
hoses are detached. On turbocharged
engines, disconnect the coolant return hose
from the turbocharger connecting pipe.
2D•8 Engine removal and overhaul procedures
4.6b Heater coolant hoses and Y-connector on 1.6 litre EFi fuel injection models4.6a Coolant hose connections to the thermostat (arrowed)
3.18 Engine-to-transmission flangeattachment bolts (arrowed)
1595Ford Fiesta Remakeprocarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su
Page 79 of 296

25Unscrew the retaining bolt, and detach
the shift rod stabiliser from the transmission.
As it is detached, note the washer located
between the stabiliser and the transmission.
Tie the stabiliser and the shift rod up out of
the way.
Automatic transmission models
26 Unclip and detach the wiring connector
from the starter inhibitor switch (on the
transmission housing).
27 Referring to the relevant Part of Chapter 4
for details, unhook the accelerator (cam plate)
cable from the carburettor or fuel injection unit
(as applicable) at the transmission end of
the cable. Undo the retaining bolt and
detach the cable sheath bracket from the
transmission. Detach the cam plate cable
from the link.
28 Undo the two nuts from the selector cable
bracket which connects it to the lever on the
selector shaft. Disconnect the yoke from the
lever on the selector shaft and the cable from
the lever.
29 Unscrew the union nuts, and disconnect
the oil cooler feed and return pipes from the
transmission. Allow for a certain amount of
spillage, and plug the connections to prevent
the ingress of dirt.
All models
30 Unscrew the retaining nut and withdraw
the Torx-type clamp bolt securing the lower
suspension arm to the spindle carrier on each
side.
31 Refer to Chapter 10 for details, and
detach the right-hand and left-hand track rod
end balljoints from the spindle carriers.
32 On vehicles fitted with the anti-lock
braking system, refer to Chapter 9 and release
the right-hand modulator from its mounting
bracket without disconnecting the rigid brake
pipes or return hose. Tie the modulator
securely to the bulkhead. Additionally, undo
the three bolts securing the modulator
bracket.
33 Insert a suitable lever between the right-
hand driveshaft inner joint and the
transmission housing, and prise free the
driveshaft from the transmission; be prepared
for oil spillage from the transmission case
through the vacated driveshaft aperture. As it
is being prised free, simultaneously pull the
roadwheel outwards on that side, to enable
the driveshaft inboard end to separate
from the transmission. Once it is free,
suspend and support the driveshaft from the
steering gear, to prevent unnecessary strain
being placed on the driveshaft joints.
34 Insert a suitable plastic plug (or if
available, an old driveshaft joint), into the
transmission driveshaft aperture, to
immobilise the gears of the differential unit.
35 Proceed as described above in
paragraphs 33 and 34, and disconnect the
left-hand driveshaft from the transmission.
36 Connect a suitable lift hoist and sling to
the engine, connecting to the lifting eyes. When securely connected, take the weight of
the engine/transmission unit so that the
tension is relieved from the mountings.
37
Undo the retaining bolts and nuts and
detach the right-hand engine mounting from
the vehicle body.
38 Undo the four bolts securing the
transmission bearer to the underside of the
vehicle body. The transmission bearer is
removed with the engine/transmission
assembly.
39 Unscrew the three retaining bolts, and
remove the auxiliary drivebelt cover from
under the crankshaft pulley.
40 The engine/transmission unit should now
be ready for removal from the vehicle. Check
that all of the associated connections and
fittings are disconnected from the engine and
transmission, and positioned out of the way.
41 Enlist the aid of an assistant to help
steady and guide the power unit down
through the engine compartment as it is
removed. If available, position a suitable
engine trolley or crawler board under the
engine/transmission so that when lowered,
the power unit can be withdrawn from the
front end of the vehicle, and then moved to
the area where it is to be cleaned and
dismantled. On automatic transmission
models, particular care must be taken not to
damage the transmission fluid pan (sump)
during the removal and subsequent refitting
processes.
42 Carefully lower the engine and
transmission unit, ensuring that no fittings
become snagged. Detach the hoist and
remove the power unit from under the vehicle.
43 Referring to the relevant Part of Chapter 7,
separate the transmission from the engine.
44 While the engine/transmission is removed,
check the mountings; renew them if they are
worn or damaged. Similarly, check the
condition of all coolant and vacuum hoses
and pipes (see Chapter 1). Components that
are normally hidden can now be checked
properly, and should be renewed if there is
any doubt at all about their condition. Where
the vehicle is fitted with manual transmission,
take the opportunity to inspect the clutch
components (see Chapter 6). It is regarded by
many as good working practice to renew the
clutch assembly as a matter of course,
whenever major engine overhaul work is
carried out. Check also the condition of all
components (such as the transmission oil
seals) disturbed on removal, and renew any
that are damaged or worn.
Refitting
45 Refitting is a reversal of removal, however
note the following additional points:
a) Refer to the applicable Chapters and Sections as for removal.
b) Fit new spring clips to the grooves in the
inboard end of the right- and left-hand
driveshaft joints. Lubricate the splines
with transmission oil prior to fitting. c) Renew the exhaust flange gasket when
reconnecting the exhaust. Ensure that all
wires are routed clear of the exhaust
system and, on catalytic converter
models, ensure that the heat shields are
securely and correctly fitted.
d) Ensure that all earth lead connections are
clean and securely made.
e) Tighten all nuts and bolts to the specified torque.
f) Fit a new oil filter, and refill the engine and transmission with oil, with reference to
Chapter 1.
g) Refill the cooling system with reference to Chapter 1.
h) Refit the alternator and starter motor with reference to Chapter 5A.
i) Where applicable, refit the power steering pump with reference to Chapter 10.
46 When engine and transmission refitting is
complete, refer to the procedures described
in Section 19 before restarting the engine.
5 Engine/transmission -
removal and refitting
(Zetec engines)
3
Warning: Petrol is extremely
flammable, so take extra
precautions when disconnecting
any part of the fuel system.
Don’t smoke, or allow naked flames or
bare light bulbs, in or near the work area,
and don’t work in a garage where a
natural-gas appliance (such as a clothes
dryer or water heater) is installed. If you
spill petrol on your skin, rinse it off
immediately. Have a fire extinguisher rated
for petrol fires handy, and know how to
use it.
Note: Read through the entire Section, as well
as reading the advice in Section 2, before
beginning this procedure. The engine and
transmission are removed as a unit, lowered to
the ground and removed from underneath,
then separated outside the vehicle.
Removal
1 Park the vehicle on firm, level ground, apply
the handbrake firmly, and slacken the nuts
securing both front roadwheels.
2 Depressurise the fuel system as described
in Chapter 4D.
3 Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead
(refer to Chapter 5A, Section 1).
4 Place protective covers on the wings, then
remove the bonnet (see Chapter 11).
5 Drain the cooling system and the engine oil
(see Chapter 1).
6 Remove the air inlet components and the
complete air cleaner assembly as described in
Chapter 4D.
7 Equalise the pressure in the fuel tank by
removing the filler cap, then release the fuel
feed and return quick-release couplings, and
pull the hoses off the fuel pipes. Plug or cap
all open fittings.
2D•10 Engine removal and overhaul procedures
1595Ford Fiesta Remakeprocarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su
Page 81 of 296

25On automatic transmission models, clean
around the unions, then disconnect the fluid
pipes from the transmission. Plug the
openings in the transmission and the pipe
unions after removal.
26 Refer to Chapter 10 and remove the front
suspension crossmember.
27 Unscrew the nuts to disconnect the
exhaust system front downpipe from the
manifold. Undo the nuts securing the catalytic
converter to the rear part of the exhaust
system, and remove the converter and
downpipe assembly.
28 On vehicles fitted with the anti-lock braking
system, refer to Chapter 9 and release the
right-hand modulator from its mounting
bracket without disconnecting the rigid brake
pipes or return hose. Tie the modulator
securely to the bulkhead. Additionally, undo
the three bolts securing the modulator bracket.
29 Disconnect both anti-roll bar links from
their respective suspension struts, and both
track rod end ball joints from their spindle
carriers (see Chapter 10).
30 Unscrew the retaining nut and withdraw
the Torx-type clamp bolt securing the lower
suspension arm to the spindle carrier on each
side.
31 Insert a suitable lever between the right-
hand driveshaft inner joint and the
transmission housing, and prise free the
driveshaft from the transmission; be prepared
for oil spillage from the transmission case
through the vacated driveshaft aperture. As it
is being prised free, simultaneously pull the
roadwheel outwards on that side to enable the
driveshaft inboard end to separate from the
transmission. Once it is free, suspend and
support the driveshaft from the steering gear,
to prevent unnecessary strain being placed on
the driveshaft joints.
32 Insert a suitable plastic plug (or if
available, an old driveshaft joint), into the
transmission driveshaft aperture, to
immobilise the gears of the differential unit.
33 Proceed as described above in
paragraphs 31 and 32, and disconnect the
left-hand driveshaft from the transmission.
34 Remove the oil filter, referring to Chapter 1
if necessary.
35 Connect a suitable lift hoist and sling to
the engine, connecting to the lift eyes. When
securely connected, take the weight of the
engine/transmission unit so that the tension is
relieved from the mountings.
36 Unbolt the engine rear right-hand
mounting from the body (one bolt in the wheel
arch, one nut in the engine compartment),
then unbolt the engine front right-hand
mounting from the alternator mounting
bracket. Unbolt the transmission bearer from
the underbody.
37 The engine/transmission unit should now
be hanging on the hoist only, with all
components which connect it to the rest of
the vehicle disconnected or removed, and
secured well clear of the unit. Make a final
check that this is the case. 38
Lower the engine/transmission to the
ground, and withdraw it from under the
vehicle.
39 Referring to the relevant Part of Chapter 7,
separate the transmission from the engine.
40 While the engine/transmission is removed,
check the mountings; renew them if they are
worn or damaged. Similarly, check the
condition of all coolant and vacuum hoses
and pipes (see Chapter 1); components that
are normally hidden can now be checked
properly, and should be renewed if there is
any doubt at all about their condition. Where
the vehicle is fitted with manual transmission,
take the opportunity to overhaul the clutch
components (see Chapter 6). It is regarded by
many as good working practice to renew the
clutch assembly as a matter of course,
whenever major engine overhaul work is
carried out. Check also the condition of all
components (such as the transmission oil
seals) disturbed on removal, and renew any
that are damaged or worn.
Refitting
41 Refitting is a reversal of removal, however
note the following additional points:
a) Refer to the applicable Chapters and Sections as for removal.
b) Fit new spring clips to the grooves in the
inboard end of the right- and left-hand
driveshaft joints. Lubricate the splines
with transmission oil prior to fitting.
c) Renew the exhaust flange gaskets when reconnecting the exhaust. Ensure that all
wires are routed clear of the exhaust
system, and that the heat shields are
securely and correctly fitted.
d) Ensure that all earth lead connections are
clean and securely made.
e) Tighten all nuts and bolts to the specified
torque.
f) Fit a new oil filter, and refill the engine and transmission with oil, with reference to
Chapter 1.
g) Refill the cooling system with reference to
Chapter 1.
h) Bleed the power steering system with reference to Chapter 10.
42 When engine and transmission refitting is
complete, refer to the procedures described
in Section 19 before restarting the engine.
6 Engine overhaul - preliminary information
It is much easier to dismantle and work on
the engine if it is mounted on a portable
engine stand. These stands can often be hired
from a tool hire shop. Before the engine is
mounted on a stand, the flywheel/driveplate
should be removed so that the stand bolts
can be tightened into the end of the cylinder
block/crankcase. If a stand is not available, it is possible to
dismantle the engine with it suitably supported on a sturdy, workbench or on the
floor. Be careful not to tip or drop the engine
when working without a stand.
If you intend to obtain a reconditioned
engine, all ancillaries must be removed first, to
be transferred to the replacement engine (just
as they will if you are doing a complete engine
overhaul yourself). These components include
the following:
a) Alternator/power steering pump and
mounting brackets.
b) DIS/E-DIS ignition coil unit (and mounting
bracket), distributor, HT leads and spark
plugs.
c) The thermostat and housing cover.
d) Carburettor/fuel injection system
components.
e) Inlet and exhaust manifolds.
f) Oil filter.
g) Fuel pump.
h) Engine mountings.
i) Flywheel/driveplate.
j) Water pump.
Note: When removing the external
components from the engine, pay close
attention to details that may be helpful or
important during refitting. Note the fitted
positions of gaskets, seals, washers, bolts and
other small items. If you are obtaining a “short” engine
(cylinder block/crankcase, crankshaft, pistons
and connecting rods all assembled), then the
cylinder head, timing chain/belt (together with
tensioner, tensioner and idler pulleys and
covers) sump and oil pump will have to be
removed also. If a complete overhaul is planned, the
engine can be dismantled in the order given
below, referring to Part A, B or C of this
Chapter unless otherwise stated.
a) Inlet and exhaust manifolds.
b) Timing chain/belt, tensioner and
sprockets.
c) Cylinder head.
d) Flywheel/driveplate.
e) Sump.
f) Oil pump.
g) Pistons (with connecting rods).
h) Crankshaft.
i) Camshaft and tappets (HCS engines).
7 Cylinder head - dismantling
4
Note:New and reconditioned cylinder heads
are available from the manufacturers, and from
engine overhaul specialists. Due to the fact
that some specialist tools are required for the
dismantling and inspection procedures, and
new components may not be readily available,
it may be more practical and economical for
the home mechanic to purchase a
reconditioned head, rather than to dismantle,
inspect and recondition the original head.
1 Remove the cylinder head as described in
Part A, B or C of this Chapter (as applicable).
2D•12 Engine removal and overhaul procedures
1595Ford Fiesta Remakeprocarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su
Page 111 of 296

container which can be sealed (see
illustration) . Where quick-release couplings
are used on the fuel hoses, release the
protruding locking lugs on each union, by
squeezing them together and carefully pulling
the coupling apart. Note that the fuel supply
hose couplings are identified by a white
colour band and the return hose couplings by
a yellow colour band.
6 Disconnect the filler neck sensing pipe
connection from the rear of the tank (see
illustration) .
7 Support beneath the tank to hold it in
position and remove its four securing bolts
(see illustration) .
8 Partially lower the fuel tank and disconnect
the ventilation tube from the tank top surface
and also disconnect the sender unit multi-
plug. The filler pipe should release from its
fuel tank seal location as the tank is
withdrawn.
Inspection
9 Whilst removed, the fuel tank can be
inspected for damage or deterioration.
Removal of the sender unit (see Section 9) will
allow a partial inspection of the interior. If the
tank is contaminated with sediment or water,
swill it out with clean petrol. Do not under any
circumstances undertake any repairs on a
leaking or damaged fuel tank; this work must
be carried out by a professional who has
experience in this critical and potentially-
dangerous work.
10 Whilst the fuel tank is removed from the
vehicle, it should not be placed in an area
where sparks or open flames could ignite the
fumes coming out of the tank. Be especially
careful inside garages where a natural-gas
type appliance is located, because the pilot
light could cause an explosion.
11 Check the condition of the filler pipe seal
in the fuel tank, and renew it if necessary.
Refitting
All models
12 Refitting is a reversal of the removal
procedure. Apply a light smear of grease to the
filler pipe seal, to ease fitting. Ensure that all
connections are securely fitted. Where quick-
release fuel couplings are fitted, press them together until the locking lugs snap into their
groove. If evidence of contamination was
found, do not return any previously-drained
fuel to the tank unless it is carefully filtered first.
9
Fuel gauge sender unit -
removal and refitting
3
Note: Ford specify the use of their service tool
23-014 (a large box spanner with projecting
teeth to engage the fuel gauge sender unit
retaining ring’s slots) for this task. While
alternatives are possible, in view of the difficulty
experienced in removing and refitting the
sender unit, owners are strongly advised to
obtain the correct tool before starting work. The
help of an assistant will be required. Refer to the
warning note in Section 1 before proceeding.
Removal
1 Remove the fuel tank as described in
Section 8.
2 Engage the special tool into the sender unit
then carefully turn the sender unit and release
it from the top of the tank.
Refitting
3 Refit the sender unit in the reverse order of
removal. Be sure to fit a new seal, and
lubricate it with a smear of grease to prevent it
from distorting when fitting the sender unit.
10 Fuel tank ventilation tube -
removal and refitting
3
Note: Refer to the warning note in Section 1
before proceeding.
Removal
1 The fuel tank ventilation tube runs from the
top surface of the fuel tank to the combined roll-
over/anti-trickle-fill valve assembly mounted in
the left-hand rear wheelarch (see illustration).
Its purpose is to eliminate any possibility of
vacuum or pressure build-up in the fuel tank.
2 Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead
(refer to Chapter 5A, Section 1).
3 Chock the front wheels then jack up the
rear of the car and support it on axle stands
(see “Jacking and vehicle support” ). Remove
the left-hand rear roadwheel.
4 Support the fuel tank from underneath on a
suitable jack, using a large thick sheet of
board to spread the weight, then undo and
remove the four fuel tank securing bolts.
5 Lower the fuel tank slightly in such a manner
so as to allow access to disconnect the
ventilation tube from the tank top surface.
Ensure that the fuel tank does not foul or strain
any adjacent components as it is lowered;
take appropriate action, as necessary.
6 Disconnect the ventilation tube from the
combined roll-over/anti-trickle-fill valve, release
the tube from its retaining clips and remove.
Refitting
7 Refitting is a reversal of the removal
procedure, ensuring that the fuel tank filler
pipe is located correctly with the tank.
11 Fuel tank filler pipe -
removal and refitting
3
Note: Refer to the warning note in Section 1
before proceeding.
Removal
1 Remove the fuel tank as described in
Section 8.
4A•6 Fuel system – carburettor engines
10.1 Combined roll-over anti-trickle-fill valve assembly
A Tube ventilating to atmosphere
B Ventilation tube from fuel tank
8.7 Fuel tank securing bolts (arrowed)8.6 Filler neck sensing pipe connection at the rear of the fuel tank
1595Ford Fiesta Remake
8.5 Fuel feed and return pipe connections
(arrowed)procarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su