ECU FORD GRANADA 1985 Service Owners Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 1985, Model line: GRANADA, Model: FORD GRANADA 1985Pages: 255, PDF Size: 14.98 MB
Page 142 of 255

3If the servo unit still fails to operate
satisfactorily the fault lies within the unit itself.
Repairs to the unit are not possible.
4Remove the master cylinder (Section 27).
5Disconnect the vacuum hose from the servo
unit taking care not to displace the rubber
sealing grommet. Disconnect the wiring plug
from the Pedal Travel Sensor (PTS) which is
situated on the front of the servo.
6Working from inside the vehicle, remove the
servo pushrod retaining clip from the brake
pedal. If necessary, to improve access to the
brake pedal remove the right-hand lower facia
panel .
7Slacken and remove the four nuts securing
the servo unit to the bulkhead, then return to
the engine compartment and remove the
servo unit from the vehicle. Remove the
gasket from the rear of the unit and discard it.
8Note that the vacuum servo unit is a sealed
assembly with no spare parts available
separately. Therefore if it is faulty it must be
renewed as a unit. Inspect the vacuum servo
vacuum hose sealing grommet for damage or
deterioration and renew if necessary.
9Remove all traces of dirt from the servo unit
and bulkhead mating surfaces and fit a new
gasket onto the rear of the servo.
10Manoeuvre the servo unit into position,
ensuring that the servo unit pushrod is
correctly located with the hole in the pedal.
Refit the servo unit retaining nuts and tighten
them to the specified torque setting. Secure
the pushrod in position with the retaining clip
11Carefully refit the vacuum hose to the servo
unit taking great care not to damage or displace
the sealing grommet. Reconnect the wiring
connector to the Pedal Travel Sensor (PTS).
12Refit the master cylinder as described
above. On completion start the engine and
check the operation of the servo unit.
1Disconnect the vacuum hose from the servo
unit taking care not to displace the rubber
sealing grommet.
2To disconnect the hose from the inlet
manifold, use a small flat-bladed screwdriver
to carefully press the flange of the collet into
the manifold then pull the hose out and
remove it from the vehicle (see illustration).
3Examine the vacuum hose and sealing
grommet for damage, splits, cracks or general
deterioration and renew as necessary. Make
sure that the check valve is working correctly
by blowing through the hose from the servo
unit end. Air should flow in this direction, but
not when blown through from the inlet
manifold hose end. Renew the check valve if it
is at all suspect.
4Ensure that the check valve is fitted the
correct way around then push the connector
into the manifold and check that it is securely
held by the retaining collet.5Carefully refit the vacuum hose to the servo
unit taking great care not to damage or
displace the sealing grommet.
6On completion start the engine and check
the operation of the servo unit.
1Disconnect the battery negative terminal.
2Carry out the operations described in
paragraphs 2 to 4 of Section 27.
3Remove all traces of dirt from the exterior of
the block then disconnect the motor and valve
block wiring plugs and free the diagnostic test
wiring plug from the mounting bracket.
4Position some absorbent rag beneath the
valve block then unscrew the three brake pipe
outlet unions whilst avoiding getting surplus
brake fluid in the wiring plugs. Plug the block
ports and pipe ends to minimise the loss of
fluid and prevent the entry of dirt into the
system. Wash off any spilt fluid immediately
with cold water.
5Slacken and remove the three valve block
and pump assembly mounting nuts and
remove the unit from the engine compartment.
6Note that the valve block and pump
assembly is a sealed unit and cannot be
overhauled. If it is faulty it must be renewed.
Note that if the low pressure hoses are
disconnected from the assembly, great care
must be taken when reconnecting them to
ensure that the valve block filter is not
damaged.
7Manoeuvre the assembly into position then
refit the mounting nuts and tighten them by
hand only. Taking into account the amount of
movement in the mounting rubbers, position
the assembly so that it will not contact the
mounting bracket then tighten the mounting
nuts to the specified torque setting.
8Remove the plugs then reconnect the outlet
pipes to the assembly and tighten the union
nuts securely.
9Ensure that the wiring is correctly routed
and reconnect the wiring plugs to the valve
block and pump assembly. Refit thediagnostic test wiring connector to the
mounting bracket.
10Wipe clean the brake pipe/hose unions
and the master cylinder ports. Refit the pipes
to the master cylinder ports and securely
tighten the union nuts. Push the low pressure
hoses into position and check they are
securely held by their retaining collets.
11Reconnect the battery negative terminal,
then fill the master cylinder and bleed the
complete hydraulic system using the
information given earlier in this Section.
1The anti-lock braking control module is
located behind the glovebox. To remove the
module first disconnect the battery negative
terminal.
2Open up the glovebox then, using a small
flat-bladed screwdriver, carefully prise up the
retaining clip and disconnect the glovebox
hinge arms. Withdraw the glovebox assembly
from the facia noting the plastic bushes which
are fitted to the glovebox pivot points.
3Lift the wiring plug retaining clip and
disconnect the plug to the control module. The
ABS module is the upper of the two control
modules mounted horizontally.
4Release the retaining clips and slide the
module out of the mounting bracket (see
illustration).
5Commence refitting by sliding the module
into the mounting bracket until it clips into
position.
6Connect the wiring connector to the
module, ensuring that the wiring is correctly
routed, and secure it in position with the
retaining clip.
7Ensure that the plastic bushes are correctly
fitted to the glovebox then refit the glovebox
assembly, locating the pivots in the correct
locations on the facia panel. Clip the hinge
arms onto the glovebox and check that it
opens and closes smoothly.
8Reconnect the battery negative terminal.
31Control module (April 1992
on) - removal and refitting
30Valve block and pump
assembly (April 1992 on) -
removal and refitting
29 Vacuum servo unit check
valve (April 1992 on) -
removal, testing and refitting
Braking system 10•13
10
29.2 Disconnecting brake servo vacuum
hose from the inlet manifold (DOHC engine
shown)31.4 Removing the ABS control module -
models from April 1992
procarmanuals.com
Page 143 of 255

1Disconnect the battery negative terminal
then deplete the vacuum in the braking system
servo unit by depressing the footbrake several
times.
2Disconnect the wiring plug from the sensor
which is situated on the front of the vacuum
servo unit.
3Using a small flat-bladed screwdriver, prise
off the retaining circlip, then carefully withdraw
the sensor from the servo unit taking great
care not to displace the sealing O-ring (see
illustration).Note:If the O-ring becomes
displaced and falls into the servo unit it must
be recovered before the sensor is refitted.
4If the sensor is to be renewed, ensure that
the tip of the new sensor pushrod is the same
colour as that of the original.
5Fit a new O-ring to the sensor and apply asmear of clean engine oil to it to ease
installation.
6Ease the sensor into position in the servo
unit, taking care not to displace the O-ring,
and secure it in position with the circlip.
7Reconnect the sensor wiring connector and
the battery negative terminal.1Remove the driver’s seat as described in
Chapter 12.
2Carefully peel back the carpet from
immediately behind the crossmember to
reveal the G switch.
3Disconnect the wiring connector then undo
the two retaining screws and remove the
switch from the vehicle.
4Refitting is a reversal of the removal
procedure.
33G (gravity) switch (April 1992
on) - removal and refitting32Pedal Travel Sensor (PTS)
(April 1992 on) - removal and
refitting
10•14Braking system
32.3 Removing the Pedal Travel Sensor
(PTS) circlip - models from April 1992
procarmanuals.com
Page 146 of 255

The steering gear is of rack-and-pinion type.
Power assistance is standard on V6 models
and optional on others. The power-assisted
steering gear has a “variable ratio” effect
which increases the steering ratio about the
straight-ahead position: this provides quick
lock-to-lock action without the penalty of
over-responsiveness in open road driving.
The steering wheel is adjustable both up-
and-down and fore-and-aft. Both steering
column and shaft are designed to collapse
under impact. The steering shaft is connected
to the pinion by an intermediate shaft, which
has a universal joint at its upper end and a
flexible coupling at the lower end.
Front suspension is independent, of the
MacPherson strut type, with coil springs and
concentric telescopic shock absorbers. The
struts are attached to the tops of the stub axle
carriers, which are located at their lower ends
by balljoints incorporated in the lower
suspension arms. The lower suspension arms
pivot at their inner ends, where they are
attached to a central crossmember. The anti-
roll bar is attached to the rear of the arms and
serves to control fore-and-aft movement as
well as reducing roll.
Suspension geometry has been designed to
give good steering “feel”, resistance to pulling
caused by uneven braking effort or tyre
deflation, and (in the case of manual steering)
acceptably low steering wheel effort at parking
speeds. Only toe is adjustable in service.
The rear suspension is also independent. It
is of the semi-trailing arm type, with coil
springs and separate telescopic shock
absorbers. An optionally-available ride height
control system keeps the rear suspension
height constant, regardless of vehicle load.
Both front and rear wheel bearings are of a
special taper-roller type and require no
periodic adjustment in service.1Refer to Chapter 1, Section 35, to check the
power steering fluid level.
2If the fluid level falls so low that air enters
the pump, or after component renewal, the
system must be bled as follows.
3Remove the reservoir filler cap. Top-up with
clean fluid to the appropriate “cold” level. It is
important that the fluid is free of air bubbles,
so do not shake the container when topping-
up, and pour the fluid slowly.
4Disconnect the negative LT lead from the
ignition coil. Have an assistant crank the
engine on the starter in two second bursts, at
the same time turning the steering wheel from
lock to lock. Keep the reservoir topped up
whilst this is going on.
5When air bubbles no longer appear in the
fluid, stop the cranking. Reconnect the coil
negative lead and run the engine for a few
seconds, then stop it and check the level
again. Refit the filler cap.
6Run the vehicle for a few miles to warm up
the fluid and expel any remaining air, then stop
the engine and make a final fluid level check.
Manual steering
1Position the steering in the straight-ahead
position, then remove the ignition key so that
the steering is locked.
2Slacken the front wheel nuts. Raise and
support the front of the vehicle and remove
the front wheels.
3Remove the pinch-bolt and nut which
secure the intermediate shaft flexible coupling
to the pinion shaft (see illustration).
4Slacken the track rod end locknuts by half a
turn each (see illustration).
5Remove the split pin from the track rod
balljoint nuts. Unscrew the nuts, break the
balljoint tapers using a separator tool anddisengage the track rod ends from the
steering arms.
6Remove the two bolts which secure the
steering gear to the crossmember. Lift out the
steering gear.
7Mark the positions of the track rod ends on
the track rods, using paint or sticky tape, so
that they can be refitted in approximately the
same positions. Unscrew the track rod ends
and locknuts.
8Commence refitting by screwing on the
locknuts and track rod ends, observing the
previously made position marks when
applicable.
9Bring the rack to the straight-ahead
position. Do this by counting the number of
turns of the pinion needed to go from lock to
lock, then applying half that number of turns
from full lock on one side.
10Offer the steering gear to the vehicle,
engaging the flexible coupling and loosely
fitting the securing bolts. Note that the master
spline on the pinion shaft mates with the
corresponding groove in the flexible coupling.
11Tighten the two steering gear-to-
crossmember bolts to the specified Stage 1
torque. Slacken the bolts and retighten to the
Stage 2 torque. Finally tighten the bolts
through the angle specified for Stage 3.
12Make sure that the flexible coupling and
pinion shaft are properly engaged, then fit the
pinch-bolt and nut. Tighten the pinch-bolt to
the specified torque.
3Steering gear - removal and
refitting
2Power steering fluid - level
check and bleeding1General information
Steering and suspension 11•3
11
3.3 Master spline and groove on pinion
shaft and coupling
Torque wrench settings (continued)Nmlbf ft
Rear suspension
Driveshaft stub axle nut . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .250 to 290180 to 210
Final drive mounting to floor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20 to 2515 to 18
Final drive mounting to rear cover . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40 to 5030 to 37
Guide plate-to-floor bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41 to 5130 to 38
Guide plate insulator bolt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .69 to 8851 to 65
Lower arm to crossmember . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .80 to 9559 to 70
Brake anchor plate to lower arm . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .52 to 6438 to 47
Anti-roll bar bracket bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20 to 2515 to 18
Shock absorber mountings:
Top . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .73 to 9754 to 72
Bottom . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .68 to 9250 to 68
Rear hub bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .80 to 10059 to 74
Wheels
Wheel nuts (steel or alloy wheels) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .70 to 10052 to 74
procarmanuals.com
Page 147 of 255
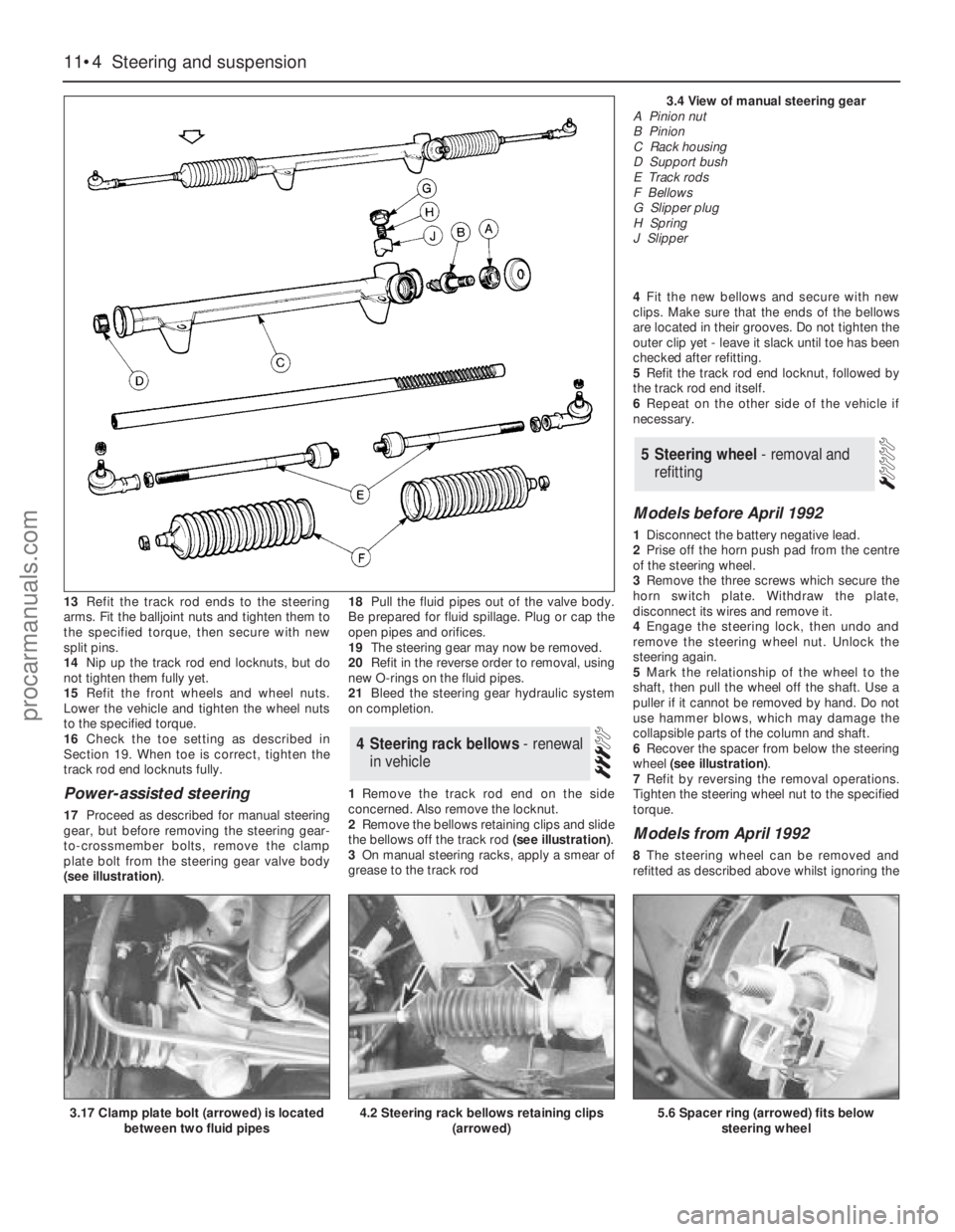
13Refit the track rod ends to the steering
arms. Fit the balljoint nuts and tighten them to
the specified torque, then secure with new
split pins.
14Nip up the track rod end locknuts, but do
not tighten them fully yet.
15Refit the front wheels and wheel nuts.
Lower the vehicle and tighten the wheel nuts
to the specified torque.
16Check the toe setting as described in
Section 19. When toe is correct, tighten the
track rod end locknuts fully.
Power-assisted steering
17Proceed as described for manual steering
gear, but before removing the steering gear-
to-crossmember bolts, remove the clamp
plate bolt from the steering gear valve body
(see illustration).18Pull the fluid pipes out of the valve body.
Be prepared for fluid spillage. Plug or cap the
open pipes and orifices.
19The steering gear may now be removed.
20Refit in the reverse order to removal, using
new O-rings on the fluid pipes.
21Bleed the steering gear hydraulic system
on completion.
1Remove the track rod end on the side
concerned.Also remove the locknut.
2Remove the bellows retaining clips and slide
the bellows off the track rod (see illustration).
3On manual steering racks, apply a smear of
grease to the track rod 4Fit the new bellows and secure with new
clips. Make sure that the ends of the bellows
are located in their grooves. Do not tighten the
outer clip yet - leave it slack until toe has been
checked after refitting.
5Refit the track rod end locknut, followed by
the track rod end itself.
6Repeat on the other side of the vehicle if
necessary.
Models before April 1992
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Prise off the horn push pad from the centre
of the steering wheel.
3Remove the three screws which secure the
horn switch plate. Withdraw the plate,
disconnect its wires and remove it.
4Engage the steering lock, then undo and
remove the steering wheel nut. Unlock the
steering again.
5Mark the relationship of the wheel to the
shaft, then pull the wheel off the shaft. Use a
puller if it cannot be removed by hand. Do not
use hammer blows, which may damage the
collapsible parts of the column and shaft.
6Recover the spacer from below the steering
wheel (see illustration).
7Refit by reversing the removal operations.
Tighten the steering wheel nut to the specified
torque.
Models from April 1992
8The steering wheel can be removed and
refitted as described above whilst ignoring the
5Steering wheel - removal and
refitting
4Steering rack bellows - renewal
in vehicle
11•4Steering and suspension
3.17 Clamp plate bolt (arrowed) is located
between two fluid pipes4.2 Steering rack bellows retaining clips
(arrowed)5.6 Spacer ring (arrowed) fits below
steering wheel
3.4 View of manual steering gearA Pinion nut
B Pinion
C Rack housing
D Support bush
E Track rods
F Bellows
G Slipper plug
H Spring
J Slipper
procarmanuals.com
Page 148 of 255

reference to horn switch plate retaining
screws. Note that the wheel is retained by a
bolt, not a nut as on earlier models. To gain
access to the bolt, prise out the horn button
and disconnect the wiring connectors.
1This operation is for correcting small errors
in steering wheel centralisation - up to 60°. For
larger errors, remove the steering wheel and
make a rough correction by repositioning the
wheel on refitting.
2Drive the vehicle in a straight line on a level
surface. Note the angle by which the steering
wheel deviates from the desired straight-
ahead position.
3Raise the front of the vehicle by driving it
onto ramps, or with a jack and axle stands
(see “Jacking”).
4Slacken both track rod end locknuts. Also
slacken the steering rack bellows outer clips.
5Make alignment marks between each track
rod end and its rod, so that the amount of
rotation applied can be accurately determined.
6Turn both track rodsin the same direction
to correct the steering wheel position. As a
rough guide, 19°of track rod rotation will
change the steering wheel position by 1°. To
correct error at the steering wheel, rotate both
track rods anti-clockwise (viewed from the
left-hand side of the vehicle), and the reverse
to correct as anti-clockwise errors. Both track
rods must be rotated by the same amount.
7Tighten the bellows clips and the track rod
end locknuts when adjustment is correct.
Lower the vehicle.
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Position the steering in the straight-ahead
position.
3Remove the steering wheel. This is not
essential, but will improve access.
4Working under the bonnet, disconnect the
intermediate shaft universal joint from the
steering column shaft.5Remove the steering column shrouds and
disconnect the switch multi-plugs. Do not
forget the ignition/starter switch.
6Disconnect the bonnet release cable from the
operating lever on the underside of the column.
7Prise out the driver’s side air vent. Remove
the under-dash insulation and trim panel on
the driver’s side, unclipping the bulb failure
module, where applicable.
8Remove the three nuts which secure the
column height adjuster to the mounting bracket
(see illustration). Remove the column assembly
by drawing it into the vehicle. Do not drop it or
otherwise mistreat it if it is to be re-used.9When refitting, have an assistant guide the
column shaft into the intermediate shaft
universal joint. Secure the column with the
three nuts inside the vehicle and adjust it to
the minimum length position, then tighten the
coupling pinch-bolt.
10Complete refitting by reversing the
removal operations.
1Remove the steering column (see
illustration).
2Insert the key into the lock and turn it to
position 1. (If the lock has failed so that the key
will not enter, destructive methods will have to
be used.)
8Steering column lock - removal
and refitting
7Steering column - removal and
refitting
6Steering wheel - centralising
Steering and suspension 11•5
11
7.8 Two of the three nuts (arrowed) which
secure the column height adjuster
8.1 View of steering wheel and column
A Steering wheel
B Mounting bracket and
spring
C Thrust washer and spring
D Lower bearingE Height adjuster
F Column shaft and spire
washer
G Multi-function switchH Ignition/steering lock
I Horn brush unit
J Upper bearing
K Multi-function switch
Make alignment marks
between the two shafts for
reference when reassembling.
procarmanuals.com
Page 149 of 255

3Depress the locking button with a small
screwdriver. Draw the lock barrel out of its
housing using the key (see illustration).
4Refit by reversing the removal operations.
1The intermediate shaft and flexible coupling
are not available separately, and so must be
renewed as a unit.
2Disconnect the battery negative lead.
3Position the steering straight-ahead.
4Remove the pinch-bolts which secure the
upper and lower ends of the intermediate
shaft. Free the universal joint from the column
shaft, then pull the flexible coupling off the
pinion shaft.
5When refitting, engage the master spline on
the pinion shaft with the groove in the flexible
coupling.
6Tighten the pinch-bolts to the specified
torque.
7Reconnect the battery.
Refer to Chapter 1, Section 21.
All engines except DOHC
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Wipe clean around the unions, then
disconnect the high pressure and return pipes
from the pump and the reservoir. Be prepared
for fluid spillage; take steps to keep fluid out of
the alternator.
3Remove the pump drivebelt(s).
4Remove the pump mounting, pivot and
adjustment bolts (as applicable) and lift the
pump from the engine (see illustration).
5If a new pump is to be fitted, recover the
pulley and mounting plate from the old pump.6Refit by reversing the removal operations.
Adjust the drivebelt tension on completion and
bleed the steering hydraulic system.
DOHC engines
7The pump is mounted on a bracket on the
front right-hand side of the cylinder block. To
improve access to the pump, firmly apply the
handbrake then jack up the front of the car
and support it securely on axle stands (see
“Jacking”).
8Place a suitable container under the pump,
unscrew the fluid pipe unions, and drain the
fluid.
9Remove the drivebelt with reference to
Chapter 1.
10Prevent the pulley from rotating using a
strap wrench (which can be improvised using
an old drivebelt and a large socket and
wrench), and unscrew the three pulley
securing bolts (see illustration). Withdraw the
pulley.
11Unscrew the three pump securing bolts
from the front of the pump bracket, and the
single bolt from the rear of the bracket, and
withdraw the pump (see illustration).
12Refitting is a reversal of removal, bearing
in mind the following points:
a)Reconnect the fluid unions using new O-
rings.
b)On completion, top-up and bleed the
power steering fluid circuit.1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Clean around the hose unions on the
steering gear. Remove the single securing
bolt, withdraw the hoses and catch the fluid
which will drain from the reservoir.
3Clean around the hose unions on the pump.
Disconnect the unions and remove the hoses.
4Refit in the reverse order to removal, using
new O-rings.
5Top-up the steering fluid and bleed the
system.
1Slacken the front wheel nuts, raise and
support the vehicle and remove the front
wheel on the side concerned.
2Slacken the track rod end locknut by half a
turn.
3Remove the split pin from the track rod end
balljoint nut. Unscrew the nut a few turns (see
illustration).
4Break the balljoint taper with a proprietary
balljoint separator (see illustration). Remove
the separator and the nut and disengage the
track rod end from the steering arm.
5Unscrew the track rod end from the track
rod, being careful not to disturb the locknut.
13Track rod end - removal and
refitting
12Power steering hoses -
removal and refitting
11Power steering pump -
removal and refitting
10Power steering pump
drivebelt - removal, refitting
and tensioning
9Steering intermediate shaft
and flexible coupling - removal
and refitting
11•6Steering and suspension
8.3 Depress the column lock locking button
11.11 . . . for access to the front pump
securing bolts (arrowed)13.3 Track rod end balljoint nut unscrewed
11.4 Steering pump pivot bolt (arrowed) -
V6 model shown11.10 Unbolt the power steering pump
pulley . . .
procarmanuals.com
Page 150 of 255

6When refitting, screw the track rod end onto
the track rod as far as the locknut, then back it
off half a turn.
7Insert the ball-pin into the steering arm.
Tighten the balljoint nut to the specified torque
and secure with a new split pin. Nip up the
track rod end locknut, but do not tighten it fully
yet.
8Refit the roadwheel, lower the vehicle and
tighten the wheel nuts to the specified torque.
9Check the toe setting as described in the
following Section. (This may not be strictly
necessary if the same track rod end has been
refitted, but is certainly advisable if any
components have been renewed.)
10Tighten the track rod end locknut when
toe is correct.
1Front wheel alignment is defined by camber,
castor, steering axis inclination and toe
setting. The first three factors are determined
in production; only toe can be adjusted in
service. Incorrect toe will cause rapid tyre
wear (see illustration).
2Toe is defined as the amount by which the
distance between the front wheels, measured
at hub height, differs from the front edges to
the rear edges. If the distance between the
front edges is less than that at the rear, the
wheels are said to toe-in; the opposite case is
known as toe-out.3To measure toe, it will be necessary to
obtain or make a tracking gauge. These are
available in motor accessory shops, or one
can be made from a length of rigid pipe or bar
with some kind of threaded adjustment facility
at one end. Many tyre specialists will also
check toe free, or for a nominal sum.
4Before measuring toe, check that all
steering and suspension components are
undamaged and that tyre pressures are
correct. The vehicle must be at approximately
kerb weight, with the spare wheel and jack in
their normal positions and any abnormal loads
removed.
5Park the vehicle on level ground and bounce
it a few times to settle the suspension.
6Use the tracking gauge to measure the
distance between the inside faces of the front
wheel rims, at hub height, at the rear of the
front wheels. Record this distance; call it
measurement A.
7Push the vehicle forwards or backwards so
that the wheels rotate exactly 180°(half a turn).
Measure the distance between the front wheel
rims again, this time at the front of the wheels.
Record this distance; call it measurement B.
8Subtract measurement B from
measurement A. If the answer is positive it is
the amount of toe-in; if negative it is the
amount of toe-out. Permissible values are
given in the Specifications.
9If adjustment is necessary loosen the track
rod end locknuts and the outer bellows clips,
then rotate each track rod by equal amounts
until the setting is correct. Hold the track rod
ends in their horizontal position with a spanner
while making the adjustment.
10Tighten the locknuts and outer bellows
clips.
11Provided the track rods have been
adjusted by equal amounts the steering wheel
should be central when moving straight-
ahead. The amount of visible thread on each
track rod should also be equal.
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Raise and securely support the front of the
vehicle.
3Remove the suspension lower arm pivot
nuts and bolts (see illustration). Disengage
the arms from the crossmember.
4Disconnect the steering column shaft from
the intermediate shaft universal joint.
5Remove the two bolts which secure the
steering gear to the crossmember. Draw the
steering gear forwards so that it is clear of the
crossmember and support it by wiring it to the
frame rails.
6It is now necessary to support the engine,
preferably from above, using a hoist or an
adjustable support bar resting on the wings or
suspension turrets. Alternatively a jack and
some wooden blocks may be used frombelow, but this is bound to obstruct access to
some extent.
7Remove the engine mounting lower
securing nuts. Raise the engine until the
mountings are just clear of the crossmember.
8Release the brake pipe clips from the
crossmember and slide the brake pipes from
their slots. Be careful not to strain the pipes.
9Support the crossmember and remove its
four securing bolts. Lower the crossmember
and remove it from the vehicle.
10Commence refitting by offering the
crossmember to the frame rails. Insert the four
securing bolts and tighten them to the
specified torque.
11Secure the brake pipes to the
crossmember.
12Refit the steering gear to the
crossmember. Tighten its securing bolts to the
specified torque.
13Insert the suspension arms into the
crossmember and secure them with the pivot
bolts and nuts. Do not tighten the nuts and
bolts yet, just nip them up.
14Lower the engine onto the crossmember.
Make sure that the engine mountings locate
correctly into the holes in the crossmember.
Tighten the engine mounting nuts. The engine
support bar or hoist can now be removed.
15Reconnect the steering column shaft to
the intermediate shaft. Tighten the pinch-bolt
to the specified torque.
16Lower the vehicle onto its wheels, then
tighten the lower arm pivot bolts to the
specified torque.
17Reconnect the battery.
1Slacken the front wheel nuts. Raise and
support the front of the vehicle and remove
the front wheel.
2Separate the track rod end from the steering
arm.
3Unbolt the brake caliper, pull it off the disc
and tie it up out of the way. Do not allow it to
hang by its hose.
4Remove the split pin from the suspension
lower arm balljoint nut. Slacken the nut a few
16Front stub axle carrier -
removal and refitting
15Front suspension
crossmember - removal and
refitting
14Front wheel alignment -
checking and adjusting
Steering and suspension 11•7
11
13.4 Using a balljoint separator
14.1 Front wheel toe-in (greatly
exaggerated)15.3 Front suspension lower arm pivot bolt
procarmanuals.com
Page 152 of 255

1Raise the vehicle on ramps or on a hoist, so
that the weight is still on the wheels.
2Remove the lower arm pivot nut and bolt
(see illustration).
3Remove the anti-roll bar end nut, dished
washer and plastic cover. Note which way
round these components are fitted.
4Now raise and support the vehicle so that
the front wheels are off the ground.
5Remove the split pin from the lower arm
balljoint nut. Back off the nut a few turns,
break the taper with a balljoint separator, then
remove the nut and free the balljoint from the
stub axle carrier.
6Pull the lower arm off the anti-roll bar and
remove it.
7If the balljoint is defective, the whole arm
must be renewed. The dust boot can be
renewed separately if required.
8The anti-roll bar bushes (compliance
bushes) can be removed by cutting off their
flanges with a chisel, then pressing or tapping
out the remains. Fit new bushes by tapping
them home with a tube or socket.
9The pivot bush can be pressed out using a
bench vice and a couple of large sockets or
suitable pieces of tube. The new pivot bush
should be lubricated with soap or glycerine
(notoil or grease) before being fitted in a
similar fashion. Do not keep the new bush
compressed in the tube for longer than
necessary, in case it becomes permanently
distorted.
10Commence refitting by offering the arm to
the anti-roll bar. Make sure that the shallow
dished washer and the plastic cover are fitted
on the inboard side of the bar (furthest from
the nut).
11Refit the balljoint to the stub axle carrier.
Tighten the castellated nut to the specified
torque and secure it with a new split pin.
12Fit the pivot end of the arm into the
crossmember and secure it with the pivot nut
and bolt. Jacking the vehicle up or down to
vary the loading on the wheels may help to get
the holes lined up. Do not tighten the pivot nut
and bolt yet.
13Lower the vehicle back onto its wheels.14Fit the deep dished washer and the plastic
cover over the end of the anti-roll bar. Fit the
nut and tighten it to the specified torque.
15Tighten the lower arm pivot nut and bolt to
the specified torque.
1Raise the vehicle on ramps or a hoist, so
that the weight is still on the wheels.
2Unbolt the two anti-roll bar clamps (see
illustration).
3Now raise and support the vehicle with the
wheels free.
4Remove the two nuts which hold the ends
of the anti-roll bar to the lower arms. Recover
the plastic covers and deep dished washers.
5Remove one lower arm pivot nut and bolt.
Prise the lower arm out of the crossmember
and work the anti-roll bar free from it.
6Pull the anti-roll bar out of the other lower
arm and remove it. Recover the other
compliance bush covers and washers.
7Refit by reversing the removal operations,
but do not finally tighten any fastenings until
the weight of the vehicle is back on the
wheels. Tighten in the following order:
a)Anti-roll bar clamps
b)Anti-roll bar-to lower arm nuts
c)Lower arm pivot nut and bolt
8Make sure that the anti-roll bar clamp
bushes are not twisted on completion.
Compliance bushes
1These are described in Section 18. It is not
strictly necessary to remove the lower arms to
renew these bushes, though obviously access
is not good with the arms installed.
Clamp bushes
2Although it is possible to remove and refit
the clamp bushes without removing the anti-
roll bar, since the bushes are split, this is not
recommended by the makers.
3Remove the anti-roll bar as described in the
previous Section.4Slide the clamp bushes off the anti-roll bar,
if necessary prising them open a little first.
5Lubricate the new bushes with glycerine or
soap and slide them into position with the split
facing forwards.
6Refit the anti-roll bar.
1Slacken the front wheel nuts, raise and
support the vehicle and remove the front
wheel.
2Disconnect the battery negative lead.
3Unbolt the brake caliper and suspend it
nearby so that the flexible hose is not strained.
4Remove the ABS sensor from the stub axle
carrier.
5Separate the track rod end and suspension
lower arm balljoints from the stub axle carrier.
6Unclip the ABS/brake pad wear wiring from
the strut.
7Remove the dust cover from the top of the
strut.
8Have an assistant support the strut.
Remove the three nuts which secure the strut
to the turret (see illustration).Do notundo
the centre nut.
9Lower the strut out of the turret and remove
it.
10Refit by reversing the removal operations.
Do not fully tighten the strut-to-turret nuts until
the weight of the vehicle is back on its wheels.
21Front suspension strut -
removal and refitting
20Front anti-roll bar bushes -
renewal
19Front anti-roll bar - removal
and refitting
18Front suspension lower arm -
removal, overhaul and refitting
Steering and suspension 11•9
11
19.2 A front anti-roll bar clamp
21.8 Two of the three nuts (arrowed)
securing the suspension strut to the turret
18.2 Front suspension lower arm components
A Anti-roll bar
B Rear dished washer and cover
C Bushes
D Balljoint
E Front dished washer and cover
F Locknut
G Pivot bush
procarmanuals.com
Page 153 of 255
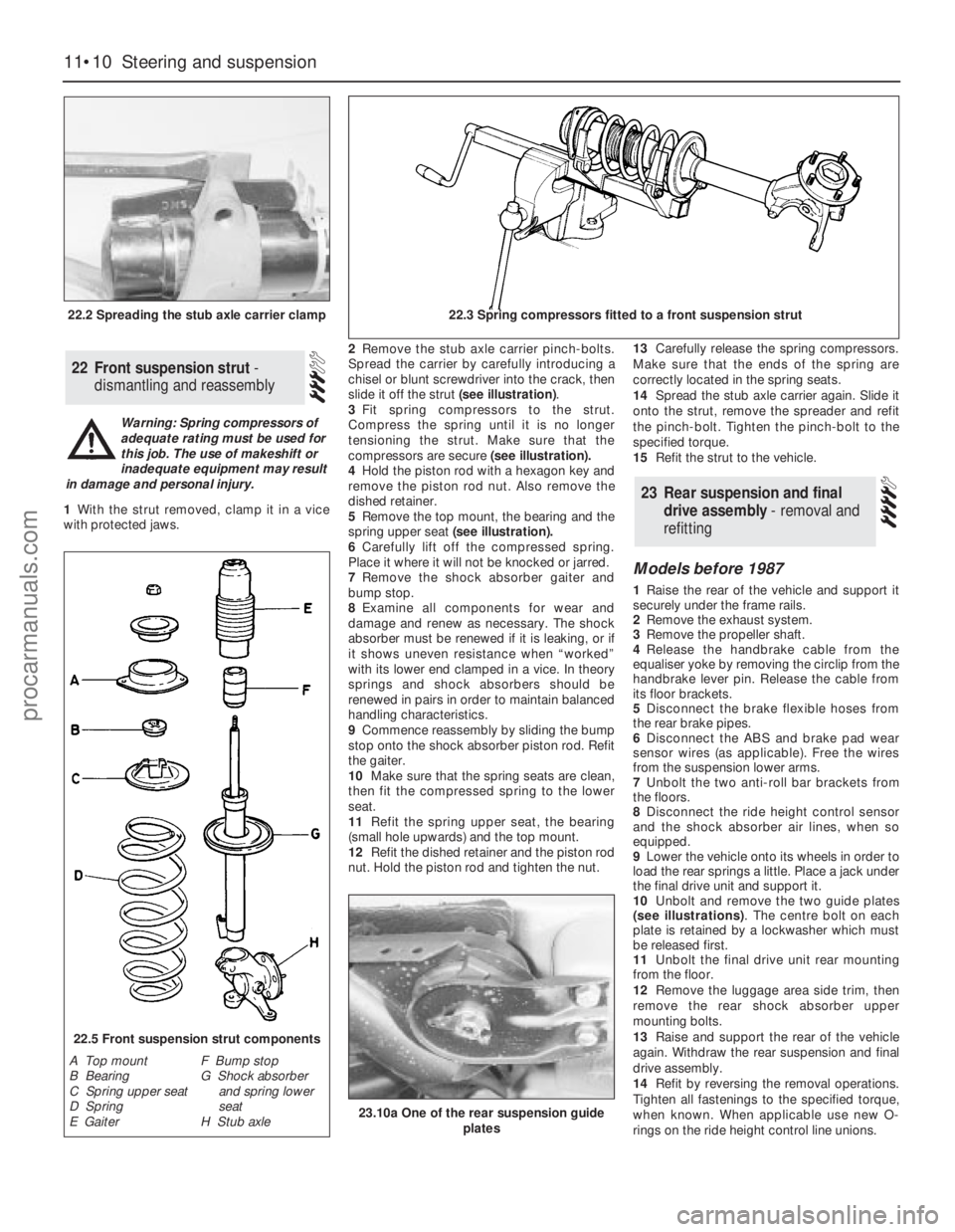
1With the strut removed, clamp it in a vice
with protected jaws.2Remove the stub axle carrier pinch-bolts.
Spread the carrier by carefully introducing a
chisel or blunt screwdriver into the crack, then
slide it off the strut (see illustration).
3Fit spring compressors to the strut.
Compress the spring until it is no longer
tensioning the strut. Make sure that the
compressors are secure (see illustration).
4Hold the piston rod with a hexagon key and
remove the piston rod nut. Also remove the
dished retainer.
5Remove the top mount, the bearing and the
spring upper seat(see illustration).
6Carefully lift off the compressed spring.
Place it where it will not be knocked or jarred.
7Remove the shock absorber gaiter and
bump stop.
8Examine all components for wear and
damage and renew as necessary. The shock
absorber must be renewed if it is leaking, or if
it shows uneven resistance when “worked”
with its lower end clamped in a vice. In theory
springs and shock absorbers should be
renewed in pairs in order to maintain balanced
handling characteristics.
9Commence reassembly by sliding the bump
stop onto the shock absorber piston rod. Refit
the gaiter.
10Make sure that the spring seats are clean,
then fit the compressed spring to the lower
seat.
11Refit the spring upper seat, the bearing
(small hole upwards) and the top mount.
12Refit the dished retainer and the piston rod
nut. Hold the piston rod and tighten the nut.13Carefully release the spring compressors.
Make sure that the ends of the spring are
correctly located in the spring seats.
14Spread the stub axle carrier again. Slide it
onto the strut, remove the spreader and refit
the pinch-bolt. Tighten the pinch-bolt to the
specified torque.
15Refit the strut to the vehicle.
Models before 1987
1Raise the rear of the vehicle and support it
securely under the frame rails.
2Remove the exhaust system.
3Remove the propeller shaft.
4Release the handbrake cable from the
equaliser yoke by removing the circlip from the
handbrake lever pin. Release the cable from
its floor brackets.
5Disconnect the brake flexible hoses from
the rear brake pipes.
6Disconnect the ABS and brake pad wear
sensor wires (as applicable). Free the wires
from the suspension lower arms.
7Unbolt the two anti-roll bar brackets from
the floors.
8Disconnect the ride height control sensor
and the shock absorber air lines, when so
equipped.
9Lower the vehicle onto its wheels in order to
load the rear springs a little. Place a jack under
the final drive unit and support it.
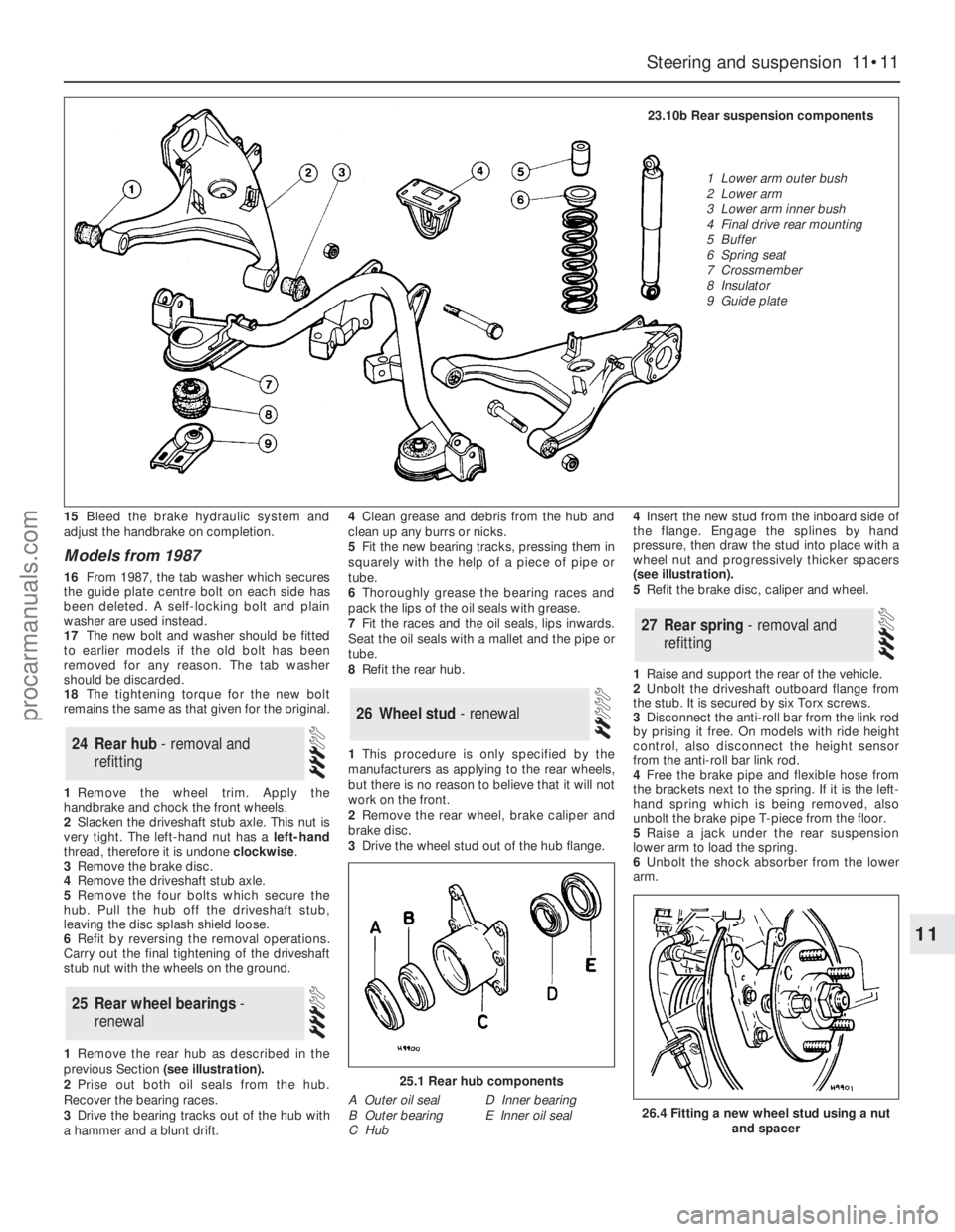
10Unbolt and remove the two guide plates
(see illustrations). The centre bolt on each
plate is retained by a lockwasher which must
be released first.
11Unbolt the final drive unit rear mounting
from the floor.
12Remove the luggage area side trim, then
remove the rear shock absorber upper
mounting bolts.
13Raise and support the rear of the vehicle
again. Withdraw the rear suspension and final
drive assembly.
14Refit by reversing the removal operations.
Tighten all fastenings to the specified torque,
when known. When applicable use new O-
rings on the ride height control line unions.
23Rear suspension and final
drive assembly - removal and
refitting
22Front suspension strut -
dismantling and reassembly
11•10Steering and suspension
22.2 Spreading the stub axle carrier clamp22.3 Spring compressors fitted to a front suspension strut
22.5 Front suspension strut components
A Top mount
B Bearing
C Spring upper seat
D Spring
E GaiterF Bump stop
G Shock absorber
and spring lower
seat
H Stub axle
Warning: Spring compressors of
adequate rating must be used for
this job. The use of makeshift or
inadequate equipment may result
in damage and personal injury.
23.10a One of the rear suspension guide
plates
procarmanuals.com
Page 154 of 255
15Bleed the brake hydraulic system and
adjust the handbrake on completion.
Models from 1987
16From 1987, the tab washer which secures
the guide plate centre bolt on each side has
been deleted. A self-locking bolt and plain
washer are used instead.
17The new bolt and washer should be fitted
to earlier models if the old bolt has been
removed for any reason. The tab washer
should be discarded.
18The tightening torque for the new bolt
remains the same as that given for the original.
1Remove the wheel trim. Apply the
handbrake and chock the front wheels.
2Slacken the driveshaft stub axle. This nut is
very tight. The left-hand nut has aleft-hand
thread, therefore it is undone clockwise.
3Remove the brake disc.
4Remove the driveshaft stub axle.
5Remove the four bolts which secure the
hub. Pull the hub off the driveshaft stub,
leaving the disc splash shield loose.
6Refit by reversing the removal operations.
Carry out the final tightening of the driveshaft
stub nut with the wheels on the ground.
1Remove the rear hub as described in the
previous Section (see illustration).
2Prise out both oil seals from the hub.
Recover the bearing races.
3Drive the bearing tracks out of the hub with
a hammer and a blunt drift.4Clean grease and debris from the hub and
clean up any burrs or nicks.
5Fit the new bearing tracks, pressing them in
squarely with the help of a piece of pipe or
tube.
6Thoroughly grease the bearing races and
pack the lips of the oil seals with grease.
7Fit the races and the oil seals, lips inwards.
Seat the oil seals with a mallet and the pipe or
tube.
8Refit the rear hub.
1This procedure is only specified by the
manufacturers as applying to the rear wheels,
but there is no reason to believe that it will not
work on the front.
2Remove the rear wheel, brake caliper and
brake disc.
3Drive the wheel stud out of the hub flange. 4Insert the new stud from the inboard side of
the flange. Engage the splines by hand
pressure, then draw the stud into place with a
wheel nut and progressively thicker spacers
(see illustration).
5Refit the brake disc, caliper and wheel.
1Raise and support the rear of the vehicle.
2Unbolt the driveshaft outboard flange from
the stub. It is secured by six Torx screws.
3Disconnect the anti-roll bar from the link rod
by prising it free. On models with ride height
control, also disconnect the height sensor
from the anti-roll bar link rod.
4Free the brake pipe and flexible hose from
the brackets next to the spring. If it is the left-
hand spring which is being removed, also
unbolt the brake pipe T-piece from the floor.
5Raise a jack under the rear suspension
lower arm to load the spring.
6Unbolt the shock absorber from the lower
arm.
27Rear spring - removal and
refitting
26Wheel stud - renewal
25Rear wheel bearings -
renewal
24Rear hub - removal and
refitting
Steering and suspension 11•11
11
25.1 Rear hub components
A Outer oil seal
B Outer bearing
C HubD Inner bearing
E Inner oil seal26.4 Fitting a new wheel stud using a nut
and spacer
23.10b Rear suspension components
1 Lower arm outer bush
2 Lower arm
3 Lower arm inner bush
4 Final drive rear mounting
5 Buffer
6 Spring seat
7 Crossmember
8 Insulator
9 Guide plate
procarmanuals.com