check engine light FORD GRANADA 1985 Service Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 1985, Model line: GRANADA, Model: FORD GRANADA 1985Pages: 255, PDF Size: 14.98 MB
Page 125 of 255
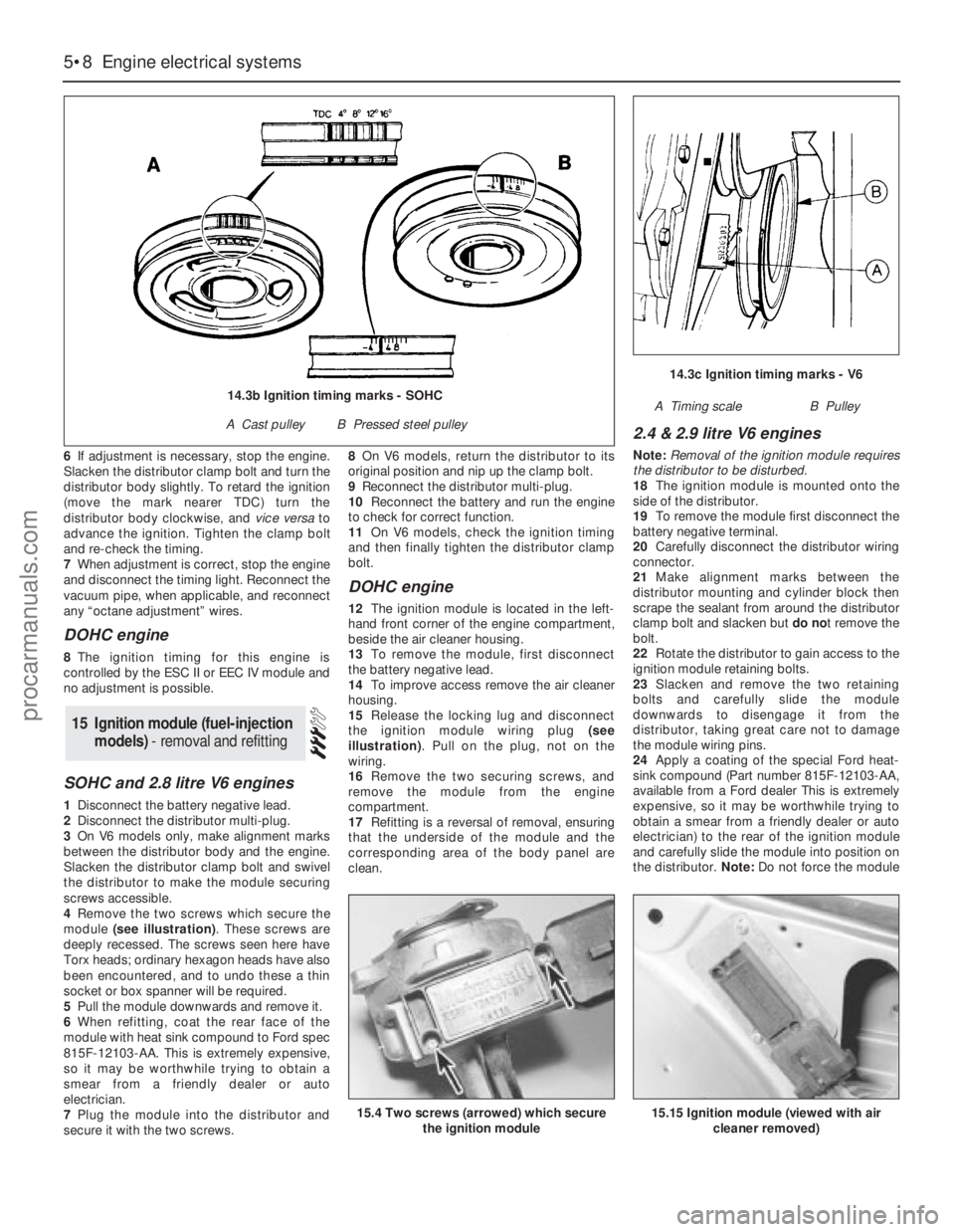
6If adjustment is necessary, stop the engine.
Slacken the distributor clamp bolt and turn the
distributor body slightly. To retard the ignition
(move the mark nearer TDC) turn the
distributor body clockwise, and vice versato
advance the ignition. Tighten the clamp bolt
and re-check the timing.
7When adjustment is correct, stop the engine
and disconnect the timing light. Reconnect the
vacuum pipe, when applicable, and reconnect
any “octane adjustment” wires.
DOHC engine
8The ignition timing for this engine is
controlled by the ESC II or EEC IV module and
no adjustment is possible.
SOHC and 2.8 litre V6 engines
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Disconnect the distributor multi-plug.
3On V6 models only, make alignment marks
between the distributor body and the engine.
Slacken the distributor clamp bolt and swivel
the distributor to make the module securing
screws accessible.
4Remove the two screws which secure the
module (see illustration). These screws are
deeply recessed. The screws seen here have
Torx heads; ordinary hexagon heads have also
been encountered, and to undo these a thin
socket or box spanner will be required.
5Pull the module downwards and remove it.
6When refitting, coat the rear face of the
module with heat sink compound to Ford spec
815F-12103-AA. This is extremely expensive,
so it may be worthwhile trying to obtain a
smear from a friendly dealer or auto
electrician.
7Plug the module into the distributor and
secure it with the two screws.8On V6 models, return the distributor to its
original position and nip up the clamp bolt.
9Reconnect the distributor multi-plug.
10Reconnect the battery and run the engine
to check for correct function.
11On V6 models, check the ignition timing
and then finally tighten the distributor clamp
bolt.
DOHC engine
12The ignition module is located in the left-
hand front corner of the engine compartment,
beside the air cleaner housing.
13To remove the module, first disconnect
the battery negative lead.
14To improve access remove the air cleaner
housing.
15Release the locking lug and disconnect
the ignition module wiring plug (see
illustration). Pull on the plug, not on the
wiring.
16Remove the two securing screws, and
remove the module from the engine
compartment.
17Refitting is a reversal of removal, ensuring
that the underside of the module and the
corresponding area of the body panel are
clean.
2.4 & 2.9 litre V6 engines
Note: Removal of the ignition module requires
the distributor to be disturbed.
18The ignition module is mounted onto the
side of the distributor.
19To remove the module first disconnect the
battery negative terminal.
20Carefully disconnect the distributor wiring
connector.
21Make alignment marks between the
distributor mounting and cylinder block then
scrape the sealant from around the distributor
clamp bolt and slacken but do not remove the
bolt.
22Rotate the distributor to gain access to the
ignition module retaining bolts.
23Slacken and remove the two retaining
bolts and carefully slide the module
downwards to disengage it from the
distributor, taking great care not to damage
the module wiring pins.
24Apply a coating of the special Ford heat-
sink compound (Part number 815F-12103-AA,
available from a Ford dealer This is extremely
expensive, so it may be worthwhile trying to
obtain a smear from a friendly dealer or auto
electrician) to the rear of the ignition module
and carefully slide the module into position on
the distributor. Note: Do not force the module
15Ignition module (fuel-injection
models) - removal and refitting
5•8Engine electrical systems
15.4 Two screws (arrowed) which secure
the ignition module15.15 Ignition module (viewed with air
cleaner removed)
14.3c Ignition timing marks - V6
A Timing scaleB Pulley14.3b Ignition timing marks - SOHC
A Cast pulleyB Pressed steel pulley
procarmanuals.com
Page 127 of 255

16Undo the wiring connector retaining bolt
then carefully disconnect the wiring plug and
remove the module from the car (see
illustration).
17Refitting is a reverse of the removal
procedure ensuring that the wiring plug bolt is
securely tightened. On completion start the
engine and check that it runs correctly.
Note: Irregular idle is not necessarily caused
by a faulty or badly adjusted stepper motor.
Good electrical contact between the stepper
motor plunger and the adjusting screw is
essential. Before attempting adjustment or
renewal of the motor, try the effect of cleaning
the plunger and adjusting screw contact faces
with abrasive paper followed by switch
cleaning fluid. Switch cleaning fluid is available
from electronic component shops.
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Remove the air cleaner.
3Disconnect the multi-plug from the stepper
motor. Release the locking clip and pull on the
plug, not on the wires.
4Remove the four screws which secure the
stepper motor bracket to the carburettor.Remove the motor and bracket and separate
them (see illustration).
5Refit the motor and bracket to the
carburettor and secure with the four screws.
Reconnect the multi-plug.
6Make an initial adjustment to the throttle
lever adjusting screw if necessary so that it
protrudes from the lever by dimension X (see
illustration).
7Reconnect the air cleaner vacuum hose.
Position the air cleaner to one side so that
there is still access to the carburettor and
stepper motor.
8Connect a tachometer (rev. counter) to the
engine as instructed by the manufacturers.
Reconnect the battery.
9Run the engine. Check the idle mixture (CO
level) as described in Chapter 4 and adjust if
necessary.
10Switch off all electrical loads (headlights,
heater blower etc). If the idle speed adjustment
lead is earthed, temporarily isolate it. Make
sure that the automatic transmission selector is
in the N or P position (where applicable).
11Accelerate the engine to a speed greater
then 2500 rpm, allow it to return to idle, then
repeat. Insert a feeler blade of thickness 1.0
mm (0.04 in) between the stepper motor
plunger and the adjusting screw(see
illustration).With the feeler blade in place,
engine speed should be 875 ±25 rpm. 12If adjustment is necessary, remove the
tamperproof cap from the adjusting screw
locknut. Release the locknut, turn the
adjusting screw to achieve the correct speed
and tighten the locknut.
13Repeat paragraph 11 and check that the
speed is still correct. Readjust if necessary.
14Remove the feeler blade. Stop and restart
the engine, observing the stepper motor
plunger. Immediately after switching off, the
plunger should move to the “anti-dieseling”
position; after a few seconds it should extend
to the “vent manifold/start” position (see
illustration).
15Disconnect the test gear and refit the air
cleaner.
16Recheck the idle mixture.
17Fit new tamperproof plugs or caps if
necessary - see Chapter 4,
18Reconnect the idle speed adjustment lead
if it was earthed.
1The engine management system
temperature sensor is located on the underside
of the inlet manifold (SOHC engines), the side
of the manifold (DOHC engines) or on the front
face of the cylinder block (V6 engines).
20Coolant temperature sensor -
removal and refitting
19Carburettor stepper motor
(2.0 litre models) - removal,
refitting and adjustment
5•10Engine electrical systems
18.16 Disconnecting the EEC IV module
A Multi-plugB Securing bolt
19.6 Throttle lever initial adjustment
A Plunger
B Adjusting screw
C CapX 7.5 ±1.0 mm
(0.30 ±0.04 in)
19.11 Stepper motor adjustment
A LocknutB Feeler blade
19.14 Stepper motor plunger positions
A Vent manifold/start
B Anti-dieselingC Idle
19.4 Carburettor stepper motor and
mounting bracket18.15 Removing the engine management
modules (glovebox removed for clarity)
procarmanuals.com
Page 159 of 255

important also to keep watch on those parts of
the vehicle not immediately visible, for
instance the underside, inside all the wheel
arches, and the lower part of the engine
compartment.
The basic maintenance routine for the
bodywork is washing - preferably with a lot of
water, from a hose. This will remove all the
loose solids which may have stuck to the
vehicle. It is important to flush these off in
such a way as to prevent grit from scratching
the finish. The wheel arches and underframe
need washing in the same way, to remove any
accumulated mud, which will retain moisture
and tend to encourage rust. Paradoxically
enough, the best time to clean the underframe
and wheel arches is in wet weather, when the
mud is thoroughly wet and soft. In very wet
weather, the underframe is usually cleaned of
large accumulations automatically, and this is
a good time for inspection.
Periodically, except on vehicles with a wax-
based underbody protective coating, it is a
good idea to have the whole of the underframe
of the vehicle steam-cleaned, engine
compartment included, so that a thorough
inspection can be carried out to see what
minor repairs and renovations are necessary.
Steam-cleaning is available at many garages,
and is necessary for the removal of the
accumulation of oily grime, which sometimes
is allowed to become thick in certain areas. If
steam-cleaning facilities are not available,
there are some excellent grease solvents
available which can be brush-applied; the dirt
can then be simply hosed off. Note that these
methods should not be used on vehicles with
wax-based underbody protective coating, or
the coating will be removed. Such vehicles
should be inspected annually, preferably just
prior to Winter, when the underbody should be
washed down, and any damage to the wax
coating repaired. Ideally, a completely fresh
coat should be applied. It would also be worth
considering the use of such wax-based
protection for injection into door panels, sills,
box sections, etc, as an additional safeguard
against rust damage, where such protection is
not provided by the vehicle manufacturer.
After washing paintwork, wipe off with a
chamois leather to give an unspotted clear
finish. A coat of clear protective wax polish will
give added protection against chemical
pollutants in the air. If the paintwork sheen has
dulled or oxidised, use a cleaner/polisher
combination to restore the brilliance of the
shine. This requires a little effort, but such
dulling is usually caused because regular
washing has been neglected. Care needs to
be taken with metallic paintwork, as special
non-abrasive cleaner/polisher is required to
avoid damage to the finish. Always check that
the door and ventilator opening drain holes
and pipes are completely clear, so that water
can be drained out. Brightwork should be
treated in the same way as paintwork.
Windscreens and windows can be kept clear
of the smeary film which often appears, by theuse of proprietary glass cleaner. Never use
any form of wax or other body or chromium
polish on glass.
Mats and carpets should be brushed or
vacuum-cleaned regularly, to keep them free
of grit. If they are badly stained, remove them
from the vehicle for scrubbing or sponging,
and make quite sure they are dry before
refitting. Seats and interior trim panels can be
kept clean by wiping with a damp cloth. If they
do become stained (which can be more
apparent on light-coloured upholstery), use a
little liquid detergent and a soft nail brush to
scour the grime out of the grain of the material.
Do not forget to keep the headlining clean in
the same way as the upholstery. When using
liquid cleaners inside the vehicle, do not over-
wet the surfaces being cleaned. Excessive
damp could get into the seams and padded
interior, causing stains, offensive odours or
even rot. If the inside of the vehicle gets wet
accidentally, it is worthwhile taking some
trouble to dry it out properly, particularly
where carpets are involved. Do not leave oil or
electric heaters inside the vehicle for this
purpose.
Repairs of minor scratches in
bodywork
If the scratch is very superficial, and does
not penetrate to the metal of the bodywork,
repair is very simple. Lightly rub the area of the
scratch with a paintwork renovator, or a very
fine cutting paste, to remove loose paint from
the scratch, and to clear the surrounding
bodywork of wax polish. Rinse the area with
clean water.
Apply touch-up paint to the scratch using a
fine paint brush; continue to apply fine layers
of paint until the surface of the paint in the
scratch is level with the surrounding
paintwork. Allow the new paint at least two
weeks to harden, then blend it into the
surrounding paintwork by rubbing the scratch
area with a paintwork renovator or a very fine
cutting paste. Finally, apply wax polish.
Where the scratch has penetrated right
through to the metal of the bodywork, causing
the metal to rust, a different repair technique is
required. Remove any loose rust from the
bottom of the scratch with a penknife, then
apply rust-inhibiting paint to prevent the
formation of rust in the future. Using a rubber
or nylon applicator, fill the scratch with
bodystopper paste. If required, this paste can
be mixed with cellulose thinners to provide a
very thin paste which is ideal for filling narrow
scratches. Before the stopper-paste in the
scratch hardens, wrap a piece of smoothcotton rag around the top of a finger. Dip the
finger in cellulose thinners, and quickly sweep
it across the surface of the stopper-paste in
the scratch; this will ensure that the surface of
the stopper-paste is slightly hollowed. The
scratch can now be painted over as described
earlier in this Section.
Repairs of dents in bodywork
When deep denting of the vehicle’s
bodywork has taken place, the first task is to
pull the dent out, until the affected bodywork
almost attains its original shape. There is little
point in trying to restore the original shape
completely, as the metal in the damaged area
will have stretched on impact, and cannot be
reshaped fully to its original contour. It is
better to bring the level of the dent up to a
point which is about 3 mm below the level of
the surrounding bodywork. In cases where the
dent is very shallow anyway, it is not worth
trying to pull it out at all. If the underside of the
dent is accessible, it can be hammered out
gently from behind, using a mallet with a
wooden or plastic head. Whilst doing this,
hold a suitable block of wood firmly against
the outside of the panel, to absorb the impact
from the hammer blows and thus prevent a
large area of the bodywork from being “belled-
out”.
Should the dent be in a section of the
bodywork which has a double skin, or some
other factor making it inaccessible from
behind, a different technique is called for. Drill
several small holes through the metal inside
the area - particularly in the deeper section.
Then screw long self-tapping screws into the
holes, just sufficiently for them to gain a good
purchase in the metal. Now the dent can be
pulled out by pulling on the protruding heads
of the screws with a pair of pliers.
The next stage of the repair is the removal
of the paint from the damaged area, and from
an inch or so of the surrounding “sound”
bodywork. This is accomplished most easily
by using a wire brush or abrasive pad on a
power drill, although it can be done just as
effectively by hand, using sheets of abrasive
paper. To complete the preparation for filling,
score the surface of the bare metal with a
screwdriver or the tang of a file, or
alternatively, drill small holes in the affected
area. This will provide a really good “key” for
the filler paste.
To complete the repair, see the Section on
filling and respraying.
Repairs of rust holes or gashes in
bodywork
Remove all paint from the affected area, and
from an inch or so of the surrounding “sound”
bodywork, using an abrasive pad or a wire
brush on a power drill. If these are not
available, a few sheets of abrasive paper will
do the job most effectively. With the paint
removed, you will be able to judge the severity
of the corrosion, and therefore decide whether
to renew the whole panel (if this is possible) or
4Minor body damage - repair
3Maintenance - upholstery and
carpets
12•2Bodywork and fittings
procarmanuals.com
Page 161 of 255

Where serious damage has occurred or
large areas need renewal due to neglect, it
means certainly that completely new sections
or panels will need welding in and this is best
left to professionals. If the damage is due to
impact, it will also be necessary to completely
check the alignment of the bodyshell
structure. Due to the principle of construction,
the strength and shape of the whole car can
be affected by damage to one part. In such
instances the services of a Ford agent with
specialist checking jigs are essential. If a body
is left misaligned, it is first of all dangerous as
the car will not handle properly, and secondly
uneven stresses will be imposed on the
steering, engine and transmission, causing
abnormal wear or complete failure. Tyre wear
may also be excessive.
1Open and prop the bonnet.
2Mark around the bonnet hinge bolts, using
soft pencil or a washable marker pen, to
provide a guide when refitting (see
illustration).
3Disconnect the windscreen washer hose atthe non-return valve or washer pump. Be
prepared for fluid spillage.
4Disconnect the under-bonnet light (when
fitted).
5Free the insulation from around the left-
hand hinge bolts. With the help of an assistant,
support the bonnet and remove the hinge
bolts. Unhook the bonnet from the pump and
remove it.
6Refit by reversing the removal operations.
Make sure that the gap between the bonnet
and the wings is equal on both sides when the
bonnet is shut; adjust if necessary at the hinge
bolts.
7Adjust the bump stops and bonnet lock
striker if necessary to obtain satisfactory
opening and closing of the bonnet (see
illustration).
Later models
8The operation for later models is essentially
as described above, noting thatit will be
necessary to unclip the insulation panel from
the underside of the bonnet to gain access to
the windscreen washer hose and washer
nozzle heater wiring plugs (see illustration).
9Disconnect the wiring plugs and hose and
free them from the retaining clips on the right-
hand side of the bonnet before removal.
10On refitting ensure that the hose and
wiring are correctly routed and retained by all
the necessary clips before refitting the
insulation panel (see illustrations).1Open the door and disconnect the wiring
multi-plug from the door pillar (see
illustration).
2Unbolt the door check strap.
3Slacken, but do not remove, the hinge
cotter pin nuts (see illustration).
4Open the door to approximately 60°from
the vehicle body and lift it off the hinges. If the
door is reluctant to move, make sure that it is
opened to the correct angle and that the cotter
pin nuts are adequately slackened.
5Refit by reversing the removal operations.
Adjust the door striker plate if necessary as
described in Section 12.
6If a new door is to be fitted, new hinges will
have to be welded to it after trial fitting.
Consult a Ford dealer for details.
Hatchback models
1Open the tailgate and remove the interior
trim panel, which is retained by eleven screws.
2Disconnect the wiring from the heated rear
window, aerial pre-amplifier and lock solenoid.
3Repeat paragraph 2 for the rear wiper motor
and the rear washer tube, and any other
electrical equipment.
8Tailgate - removal and refitting
7Door - removal and refitting
6Bonnet - removal and refitting
5Major body damage - repair
12•4Bodywork and fittings
6.2 Left-hand hinge bolts (arrowed) are
obscured by insulation
6.10 On refitting ensure the wiring and
hoses are correctly routed and secured by
all necessary retaining clips
7.1 Door wiring multi-plug7.3 One of the hinge cotter pins (arrowed)
6.7 Bonnet lock striker and safety catch6.8 On later models disconnect the washer
nozzle heater wiring plugs before removing
the bonnet
procarmanuals.com
Page 181 of 255

the circuit between the relevant connector and
the battery is problem-free.
13Continue to check the remainder of the
circuit in the same fashion.
14When a point is reached at which no
voltage is present, the problem must lie
between that point and the previous test point
with voltage. Most problems can be traced to
a broken, corroded or loose connection.
Finding a short-circuit
15To check for a short-circuit, first disconnect
the load(s) from the circuit (loads are the
components which draw current from a circuit,
such as bulbs, motors, heating elements, etc).
16Remove the relevant fuse from the circuit,
and connect a circuit tester or voltmeter to the
fuse connections.
17Switch on the circuit, bearing in mind that
some circuits are live only when the ignition
switch is moved to a particular position.
18If voltage is present (indicated either by
the tester bulb lighting or a voltmeter reading),
this means that there is a short-circuit.
19If no voltage is present, but the fuse still
blows with the load(s) connected, this
indicates an internal fault in the load(s).
Finding an earth fault
20The battery negative terminal is connected
to “earth” - the metal of the engine/transmission
and the car body - and most systems are wired
so that they only receive a positive feed, the
current returning via the metal of the car body.
This means that the component mounting andthe body form part of that circuit. Loose or
corroded mountings can therefore cause a range
of electrical faults, ranging from total failure of a
circuit, to a puzzling partial fault. In particular,
lights may shine dimly (especially when another
circuit sharing the same earth is in operation),
motors (eg wiper motors or the radiator cooling
fan motor) may run slowly, and the operation of
one circuit may have an apparently-unrelated
effect on another. Note that on many vehicles,
earth straps are used between certain
components, such as the engine/transmission
and the body, usually where there is no metal-to-
metal contact between components, due to
flexible rubber mountings, etc.
21To check whether a component is properly
earthed, disconnect the battery, and connect
one lead of an ohmmeter to a known good
earth point. Connect the other lead to the wire
or earth connection being tested. The
resistance reading should be zero; if not,
check the connection as follows.
22If an earth connection is thought to be
faulty, dismantle the connection, and clean
back to bare metal both the bodyshell and the
wire terminal, or the component’s earth
connection mating surface. Be careful to
remove all traces of dirt and corrosion, then
use a knife to trim away any paint, so that a
clean metal-to-metal joint is made. On
reassembly, tighten the joint fasteners
securely; if a wire terminal is being refitted, use
serrated washers between the terminal and
the bodyshell, to ensure a clean and secure
connection. When the connection is remade,
prevent the onset of corrosion in the future byapplying a coat of petroleum jelly or silicone-
based grease, or by spraying on (at regular
intervals) a proprietary ignition sealer, or a
water-dispersant lubricant.
Headlight
1Open and prop the bonnet. Remove the
cover from the rear of the headlight unit by
twisting it anti-clockwise.
2Disconnect the wiring plug from the
headlight bulb. Release the spring clip by
squeezing its legs together and move it clear
of the bulb (see illustration).
3Remove the headlight bulb (see
illustration). Caution: If the lights have just
been in use, the bulb may be extremely hot.
4When handling the new bulb, use a tissue or
clean cloth to avoid touching the glass with
the fingers. If the glass is accidentally touched,
wipe it clean using methylated spirit. Moisture
and grease from the skin can cause
blackening and rapid failure of the new bulb.
5Fit the new bulb, making sure that the legs
and cut-outs in the bulb base and the reflector
match up. Secure with the spring clip.
6Reconnect the wiring plug. Check the
headlight for correct operation, then refit and
secure the rear cover.
Front parking light (sidelight)
7Gain access as for the headlight bulb, then
pull the parking light bulbholder from the
headlight reflector.
8Extract the wedge base bulb from the
holder (see illustration). Fit the new bulb, refit
the bulbholder and check for correct
operation.
Auxiliary driving light (when fitted)
9From above the auxiliary light unit, release
the cover spring clip and remove the cover
(see illustration).
10Release the spring clip from the bulb.
Withdraw the bulb and unplug its wiring
connector (see illustration). Caution: If the
lights have just been in use, the bulb may be
extremely hot.
11Do not touch the glass of the new bulb
with the fingers.
3Exterior lights - bulb renewal
13•4Body electrical system
3.2 Squeeze the spring clip legs (arrowed)
to remove the headlight bulb3.3 Removing a headlight bulb
3.8 Removing the front parking light bulb
from the holder3.9 Auxiliary driving light cover3.10 Removing the auxiliary driving light
bulb
procarmanuals.com
Page 185 of 255
Footwell lights
11Free the light unit by carefully prising with
a screwdriver(see illustration).
12Extract the bulbholder by twisting and
pulling. Renew the bulb, refit the holder and
press the light unit home.
Luggage area light
13Carefully prise free the light unit (see
illustration).
14Pull out the old bulb, press in the new one
and refit the light unit.
Engine bay light
15This light bulb is directly accessible once
the bonnet is opened. It is of the bayonet type.
Instrument panel lights
16Remove the instrument cluster.
17Extract the appropriate bulb and holder by
twisting it 90°anti-clockwise (see
illustration).
18Large bulbs are of the wedge base typeand can be pulled out of their holders. Small
bulbs and holders cannot be separated, but
must be renewed complete.
19Refit the bulbs and holder, then refit the
instrument panel.
Switch illumination lights
20The pilot lights in the minor switches cannot
be renewed independently of the switch.
21The bulbs which illuminate the lighting
master switch and the heater blower switch
can be renewed after pulling off the switch
knob (see illustration).
22The switch symbols in the instrument
panel surround are illuminated by a single
bulb. To gain access to the bulb, remove the
instrument panel surround, which is secured
by four screws. The bulb is of the wedge base
type (see illustration).
Glovebox light
23Open the glovebox. Remove the
combined switch/light unit, which is secured
by two screws (see illustration).
24Prise out the switch, renew the bayonet
fitting bulb and refit the switch
25Refit and secure the light unit with the two
screws.
Ashtray light
26Remove the storage box or audio unit
from just above the ashtray (see illustration).
27Free the bulbholder from above the ashtray,
either by pulling it outwards (low series trim) or
by carefully prising it away from its housing
using a screwdriver (high series trim).28Renew the wedge base bulb. Refit the
bulbholder and the other disturbed
components.
Radio fader light
29Carefully prise off the fader surround.
30Extract the bulbholder by twisting it anti-
clockwise. Disconnect its wiring plug and
remove it.
31The bulb and holder cannot be separated.
Fit the new bulbholder unit, check for correct
operation, then refit the fader surround.
Heater control light
32Remove the instrument panel surround.
33Pull off the heater control knobs, then
prise the display panel off the heater controls
to expose the bulb.
13•8Body electrical system
6.21 Pull off the switch knob to expose the
bulb
6.26 Ashtray light bulb seen through radio
aperture6.22 Removing the switch symbol
illumination light6.23 The glovebox light unit
6.13 Luggage area light unit6.17 Instrument panel lights
6.11 Footwell light bulb renewal - front (A)
and rear (B)
procarmanuals.com
Page 189 of 255

20When refitting, check the switch for
correct operation before refitting the shrouds
and steering wheel centre cover. When fitting
the shrouds, be careful not to trap the switch
rubber gaiter.
Models from April 1992
21Note that if access to the switch retaining
screws cannot be gained with the steering
wheel in position, then the steering wheel
must first be removed.
Windscreen wipe/wash switch
Models before April 1992
22Proceed as described in the previous sub-
section for the direction indicator switch.
Depending on equipment, the wipe/wash
switch may have more than one multi-plug
connected to it.
Models from April 1992
23Note that if access to the switch retaining
screws cannot be gained with the steering
wheel in position, then the steering wheel
must first be removed.
Door pillar switch (for courtesy
light)
24Remove the single securing screw and pull
the switch from its location (see illustration).
25Retain the wiring with (for instance) string
or a clothes peg, so that it cannot fall into the
door pillar, then disconnect the switch.
26Lubricate the plunger of the switch with a
little petroleum jelly when refitting
Reversing light switch (manual
gearbox)
27Raise the front of the vehicle and support
it securely.
28Locate the reversing light switch, which is
located on the right-hand side of the gearbox.
29Disconnect the wiring from the switch,
wipe clean around it and unscrew it.
30When refitting, make sure that the switch
wiring is routed sufficiently far from the
exhaust system to avoid damage due to heat.
Window operating switch
31The window operating switch is removed
from the armrest or console in the same way
as the mirror control switch previously
described (see illustration).
Sliding roof switch
32Carefully prise the switch from the overhead
console using a thin-bladed screwdriver.
33Disconnect the multi-plug and remove the
switch.
Tailgate lock switch
34The tailgate lock switch controls the
luggage area lights. When appropriate, it also
provides inputs to the auxiliary warning and
anti-theft systems.
35To avoid damage to other components,
the battery must be disconnected before the
tailgate lock switch is removed.
36Remove the tailgate interior trim panel,
which is secured by eleven screws.37Release the switch locking tab, pivot the
switch away from the lock and disconnect it.
38When refitting, make sure that the slot on
the switch engages with the operating lug on
the lock barrel.
Handbrake “ON” switch
39Gain access to the base of the handbrake
lever by removing the rubber gaiter and (if
necessary) the centre console or switch panel
(see illustration).
40Disconnect the wiring from the handbrake
switch. Undo the two screws and remove the
switch, noting how the screws do not pass
through holes in the lever but engage in slots.
41After refitting the switch, check for correct
operation before refitting the surrounding trim.
Stop-light switch
42Remove the under-dash trim on the
driver’s side. The trim is secured by plastic
clips.
43Disconnect the wiring from the switch.
Turn the switch 90°anti-clockwise and
remove it from the brake pedal bracket (see
illustration).
44When refitting, hold the pedal in the fully
raised position, push in the switch and turn it
clockwise to lock it. Release the pedal and
check that at least 2 mm (0.08 in) of the switch
plunger is visible (see illustration).
Oil pressure warning switch
All engines except DOHC
45This switch is located on the left-hand side
of the cylinder block. Access may be impeded
by one of the manifolds and associated
equipment.
46Disconnect the wire from the switch, then
unscrew the switch and remove it.
47Clean the switch and its seat before
refitting. Apply a little sealant to the switch
threads if wished.
48Run the engine and check that there are
no oil leaks from the switch. Stop the engine
and check the oil level.
DOHC engines
49On these engines the switch is located on
the right-hand side of the cylinder block
between the core plugs.
13•12Body electrical system
15.24 Door pillar switch securing screws
(arrowed)
15.43 Stop-light switch fitted to brake
pedal bracket
15.44 Fitting the stop-light switch (A)
Plunger protrusion (between arrows) must be
at least 2 mm (0.08 in)
15.31 Removing a window operating switch15.39 Handbrake “On” switch
procarmanuals.com
Page 242 of 255

Engine misfires throughout the driving speed range
m mFuel filter choked (Chapter 1).
m mFuel pump faulty, or delivery pressure low (Chapter 4).
m mFuel tank vent blocked, or fuel pipes restricted (Chapter 4).
m mVacuum leak at the throttle body, inlet manifold or associated hoses
(Chapter 4).
m mWorn, faulty or incorrectly-gapped spark plugs (Chapter 1).
m mFaulty spark plug HT leads (Chapter 5).
m mDistributor cap cracked or tracking internally (Chapter 5).
m mFaulty ignition coil (Chapter 5).
m mUneven or low cylinder compressions (Chapter 2).
m mFuel injection system fault (Chapter 4).
Engine hesitates on acceleration
m
mWorn, faulty or incorrectly-gapped spark plugs (Chapter 1).
m mVacuum leak at the throttle body, inlet manifold or associated hoses
(Chapter 4).
m mFuel injection system fault (Chapter 4).
Engine stalls
m
mVacuum leak at the throttle body, inlet manifold or associated hoses
(Chapter 4).
m mFuel filter choked (Chapter 1).
m mFuel pump faulty, or delivery pressure low (Chapter 4).
m mFuel tank vent blocked, or fuel pipes restricted (Chapter 4).
m mFuel injection system fault (Chapter 4).
Engine lacks power
m
mFuel filter choked (Chapter 1).
m mFuel pump faulty, or delivery pressure low (Chapter 4).
m mUneven or low cylinder compressions (Chapter 2).
m mWorn, faulty or incorrectly-gapped spark plugs (Chapter 1).
m mVacuum leak at the throttle body, inlet manifold or associated hoses
(Chapter 4).
m mFuel injection system fault (Chapter 4).
m mBrakes binding (Chapters 1 and 10).
m mClutch slipping (Chapter 6).
Engine backfires
m
mVacuum leak at the throttle body, inlet manifold or associated hoses
(Chapter 4).
m mFuel injection system fault (Chapter 4).
Oil pressure warning light illuminated with engine
running
m mLow oil level, or incorrect oil grade (Chapter 1).
m mFaulty oil pressure sensor (Chapter 2).
m mWorn engine bearings and/or oil pump (Chapter 2).
m mExcessively high engine operating temperature (Chapter 3).
m mOil pressure relief valve defective (Chapter 2).
m mOil pick-up strainer clogged (Chapter 2).
Note:Low oil pressure in a high-mileage engine at tickover is not
necessarily a cause for concern. Sudden pressure loss at speed is far
more significant. In any event, check the gauge or warning light sender
before condemning the engine.
Engine runs-on after switching off
m mExcessive carbon build-up in engine (Chapter 2).
m mExcessively high engine operating temperature (Chapter 3).
Engine noises
Pre-ignition (pinking) or knocking during acceleration or
under load
m mIgnition timing incorrect/ignition system fault (Chapters 1 and 5).
m mIncorrect grade of spark plug (Chapter 1).
m mIncorrect grade of fuel (Chapter 1).
m mVacuum leak at throttle body, inlet manifold or associated hoses
(Chapter 4).
m mExcessive carbon build-up in engine (Chapter 2).
m mFuel injection system fault (Chapter 4).
Whistling or wheezing noises
m
mLeaking inlet manifold or throttle body gasket (Chapter 4).
m mLeaking exhaust manifold gasket (Chapter 4).
m mLeaking vacuum hose (Chapters 4 and 10).
m mBlowing cylinder head gasket (Chapter 2).
Tapping or rattling noises
m
mWorn valve gear, timing chain, camshaft or hydraulic tappets
(Chapter 2).
m mAncillary component fault (water pump, alternator, etc) (Chapters 3,
5, etc).
Knocking or thumping noises
m mWorn big-end bearings (regular heavy knocking, perhaps less under
load) (Chapter 2).
m mWorn main bearings (rumbling and knocking, perhaps worsening
under load) (Chapter 2).
m mPiston slap (most noticeable when cold) (Chapter 2).
m mAncillary component fault (water pump, alternator, etc) (Chapters 3,
5, etc).
REF•7Fault Finding
2Cooling system
Overheating
m
mAuxiliary drivebelt broken or incorrectly adjusted (Chapter 1).
m mInsufficient coolant in system (Chapter 1).
m mThermostat faulty (Chapter 3).
m mRadiator core blocked, or grille restricted (Chapter 3).
m mElectric cooling fan or thermostatic switch faulty (Chapter 3).
m mViscous-coupled fan faulty (Chapter 3).
m mIgnition timing incorrect, or ignition system fault (Chapters 1 and 5).
m mInaccurate temperature gauge sender unit (Chapter 3).
m mAirlock in cooling system (Chapter 3).
Overcooling
m
mThermostat faulty (Chapter 3).
m mInaccurate temperature gauge sender unit (Chapter 3).
External coolant leakage
m
mDeteriorated or damaged hoses or hose clips (Chapter 1).
m mRadiator core or heater matrix leaking (Chapter 3).
m mPressure cap faulty (Chapter 3).
m mWater pump internal seal leaking (Chapter 3).
m mWater pump-to-block seal leaking (Chapter 3).
m mBoiling due to overheating (Chapter 3).
m mCore plug leaking (Chapter 2).
Internal coolant leakage
m
mLeaking cylinder head gasket (Chapter 2).
m mCracked cylinder head or cylinder block (Chapter 2).
Corrosion
m
mInfrequent draining and flushing (Chapter 1).
m mIncorrect coolant mixture or inappropriate coolant type (Chapter 1).
procarmanuals.com
Page 252 of 255

A
ABS module - 10•11
Accelerator pump diaphragm renewal - 4•12
Accessory shops - 0•8
Acknowledgements - 0•4
Aerial pre-amplifier - 13•22
Air bags - 0•5
Air charge temperature sensor - 5•12
Air cleaner - 1•16, 4•4
Air conditioner - 1•14, 1•15, 3•2, 3•9
Air temperature sensor - 13•18
Alarm signal buzzer - 13•23
Alarm system horn - 13•23
Alternator - 3•7, 5•4
Anti-roll bar - 11•9, 11•12
Anti-theft alarm - 13•22, 13•23
Antifreeze mixture - 3•2
Asbestos - 0•5
Ashtray light - 13•8
Automatic choke - 1•16, 4•10, 4•12
Automatic transmission- 1•11, 1•15, 2B•6,
2B•7, 7B•1et seq, REF•8
Automatic transmission brake band
adjustment - 1•19
Automatic transmission selector light - 13•9
Auxiliary drivebelt - 1•12
Auxiliary driving light - 13•4, 13•6
Auxiliary shaft - 2A•9, 2A•14, 2A•16
Auxiliary warning system components - 13•18
B
Backrests - 12•19, 12•18
Battery - 0•5, 1•8, 1•13, 5•3, 5•4
Battery will not hold a charge for more than
a few days - REF•11
Bleeding the brakes - 10•3
Bleeding the power steering - 11•3
Body corrosion - 0•14
Body damage - 12•2, 12•4
Body electrical system- 13•1et seq
Bodywork and fittings- 12•1et seq
Bodywork repairs - 12•3
Bonnet - 12•4, 12•9
Bonnet release cable - 12•6
Booster battery (jump) starting - 0•10
Boot lid - 12•5
Boot lid lock barrel - 12•7
Brake band adjustment - 1•19, 7B•3
Brake fluid - 1•7, 1•19
Brake hydraulic system - 10•3
Brake pedal effort high to stop vehicle - REF•9
Brake pedal feels spongy when depressed
- REF•9
Brake pedal pulsates when braking hard -
REF•10
Brake pedal travel excessive - REF•9
Brake pipe and hoses - 1•15, 10•10
Brakes binding - REF•10
Braking system- 0•13, 10•1et seq, REF•9
Bulb failure module - 13•19
Bulbs - 13•4, 13•7
Bumper - 12•10, 12•11
Burning - 0•5
C
Cables - 3•8, 4•7, 6•3, 7B•3, 10•11
Caliper - 10•5, 10•6
Camshaft - 2A•7, 2A•14, 2A•17, 2B•14,
2C•12, 2C•13, 2C•15
Camshaft drivebelt - 1•20
Capacities - 1•3
Carbon canister - 4•23
Carburettor stepper motor - 5•10
Catalytic converter - 4•4
Central locking motor - 13•13
Central locking system inoperative, or
unsatisfactory in operation - REF•11
Centre console - 12•15
Cigarette lighter - 13•10
Clock - 13•9, 13•10
Clutch- 6•1et seq, REF•8
Clutch fails to disengage (unable to select
gears) - REF•8
Clutch pedal travels to floor - REF•8
Clutch release bearing and arm - 6•4
Clutch slips (engine speed increases, with
no increase in vehicle speed) - REF•8
CO emissions (mixture) - 0•14
Compliance bushes - 11•9
Compression test - 2A•20, 2B•18, 2C•21
Compressor drivebelt - 3•9
Computer module and bulb - 13•18
Condenser fan and motor - 3•10
Connecting rods - 2A•11, 2A•13, 2A•15,
2B•17, 2C•12, 2C•14, 2C•16
Console light - 13•9
Contents - 0•2
Control assembly - 13•19
Control module - 10•13
Control switches - 13•19
Control units - 13•13
Conversion factors - REF•16
Coolant - 1•6, 1•20
Coolant hoses - 2C•7
Coolant leakage - REF•7
Coolant level switch - 13•18
Coolant temperature sensor - 5•10
Cooling, heating and ventilation systems-
3•1 et seq, REF•7
Corrosion - REF•7
Courtesy light - 13•7
Crankcase ventilation system - 1•19,
2A•12, 2B•3, 2C•15
Crankshaft and bearings - 2A•11, 2A•12,
2A•15, 2B•17, 2B•18, 2C•12, 2C•14,
2C•15
Crankshaft oil seals - 2A•10, 2B•15, 2C•12
Crankshaft speed/position sensor - 5•11
Crossmember insulator - 11•12
Crushing - 0•5
Cushion - 12•18
Cylinder block and bores - 2A•13
Cylinder bores - 2C•14
Cylinder head - 2A•6, 2A•8, 2A•14, 2A•17,
2B•10, 2B•11, 2B•14, 2C•8, 2C•13,
2C•19
D
De-ice thermostat - 3•10
Decarbonising - 2A•14
Dents in bodywork - 12•2
Direction indicator - 13•5, 13•11
Discs - 10•3, 10•4, 10•8
Distributor - 5•5
Door exterior handle - 12•6
Door interior trim panel - 12•7
Door latch assembly - 12•6
Door lights - 13•7
Door lock barrel - 12•6
Door pillar switch - 13•12
Door speakers - 13•21
Door striker plate - 12•6
Door switch - 13•18
Door weatherstrip - 12•7
Door window - 12•8, 12•9
Doors - 0•12, 12•4, 12•7, 12•8, 12•9, 12•10
Downshift mechanism - 7B•3
Drivebelts - 1•12, 1•20, 3•7, 3•9, 11•6
Driveshaft - 1•15, 9•3
Drivetrain - 1•16
E
Earth fault - 13•4
EEC IV module - 5•9
Electric shock - 0•5
Electric windows inoperative, or
unsatisfactory in operation - REF•11
Electrical system - 0•12, 1•8, REF•10
Electronic ignition systems - 5•3
Engine- 2A•1 et seq, 2B•1 et seq, 2C•1 et
seq, REF•6
Engine backfires - REF•7
Engine bay light - 13•8
Engine difficult to start - REF•6
Engine dismantling - 2B•8
Engine electrical systems- 5•1et seq
Engine fails to rotate when attempting to
start - REF•6
Engine hesitates on acceleration - REF•7
Engine idles erratically - REF•6
Engine lacks power - REF•7
Engine management control module - 5•9
Engine management system relays - 5•11
Engine misfires - REF•6, REF•7
Engine mountings - 2A•11, 2B•8, 2C•12
Engine oil and filter - 1•6, 1•9
Engine rotates, but will not start - REF•6
Engine runs-on after switching off - REF•7
Engine stalls - REF•7
Engine starts, but stops immediately -
REF•6
Engine will not start in any gear, or starts in
gears other than Park or Neutral -
REF•9
Entertainment console - 13•22
Environmental considerations - REF•4
ESC II module - 5•3, 5•9
Exhaust emission checks - 0•14
Exhaust gas oxygen (HEGO) sensor - 4•22
Exhaust manifold(s) - 4•21
Exhaust system - 0•13, 1•10, 4•22
Expansion tank - 3•7
IND•1Index
Note: References throughout this index are in the form - “Chapter number” • “page number”
procarmanuals.com
Page 253 of 255

IND•2
F
Facia panels and trim - 12•12
Fast idle speed adjustment - 4•13
Fault finding- REF•5et seq
Fault-finding - electrical system - 5•3, 13•3
Final drive and driveshafts- 1•15, 9•1et
seq, 11•10, REF•9
Fire - 0•5
Flasher switch and unit - 13•11
Fluid leakage - REF•8
Fluid level checks - 1•6
Flywheel ring gear - 2A•14, 2C•15
Flywheel/driveplate - 2A•9, 2A•16, 2B•15,
2C•11, 2C•17
Foglight - 13•5,13•13
Footbrake - 0•11, 0•12
Footwell lights - 13•8
Fuel and exhaust systems- 0•14, 4•1et seq,
REF•8
Fuel computer components - 13•17
Fuel consumption high - REF•8
Fuel filler lock barrel - 12•7
Fuel filler switch - 13•18
Fuel filter - 1•19, 4•14
Fuel flow sensor - 13•18
Fuel gauge gives false reading - REF•11
Fuel odour - REF•8
Fuel pressure regulator - 4•18
Fuel temperature sensor - 5•12
Fuel trap (carburettor models) - 5•9
Fume or gas intoxication - 0•5
Fumes from exhaust system - REF•8
Fuses - 13•13
G
G (gravity) switch - 10•14
Gaskets - REF•4
Gear linkage - 7A•4
Gear selection problems - REF•8, REF•9
Glossary of technical terms - REF•12
Glovebox light - 13•8
Graphic display module - 13•18
Graphic equaliser - 13•21
Grille - 12•9
H
Handbrake “ON” switch - 13•12
Handbrake - 0•11, 10•11
Handles - 12•6
Hazard warning switch - 13•9, 13•13
HC emissions - 0•14
Headlight - 13•4, 13•6, 13•7, 13•11
Headlining - 12•11
Headphone relay - 13•22
Heated rear window switch - 13•13
Heated seat control switches - 13•13
Heater assembly - 3•7, 3•8, 3•9, 3•10,
13•11, 13•20
High frequency units - 13•22
High pressure hose - 10•10
Hinges - 1•12
Horn - 13•10
Horn emits intermittent or unsatisfactory
sound - REF•11Horn fails to operate - REF•11
Horn inoperative, or unsatisfactory in
operation - REF•11
Horn operates all the time - REF•11
Horn switch plate, slip rings and brushes -
13•10
HT leads - 5•5
HT voltage - 5•3
Hub - 11•11
Hydraulic system seals and hoses - 1•19
Hydraulic unit - 10•8, 10•9, 10•10
Hydrofluoric acid - 0•5
I
Idle mixture - 1•10
Idle speed - 1•10, 4•7, 4•9, 4•11, 4•14, 5•11
Idle speed control valve - 4•15
Idle speed linkage - 1•15
Ignition coil - 5•9
Ignition module - 5•8
Ignition system - 1•17
Ignition timing - 5•7, 5•11
Ignition/no-charge warning light fails to
come on - REF•11
Ignition/no-charge warning light remains
illuminated with engine running - REF•11
Ignition/starter switch - 13•11
Inlet manifold - 1•14, 4•19
Instrument cluster - 13•9, 13•10
Instrument illumination dimmer switch - 13•11
Instrument panel lights - 13•8
Instrument readings inaccurate or erratic -
REF•11
Instruments and electrical equipment - 1•16
Intensive maintenance - 1•6
Interior lights - 13•7
Introduction to the Ford Granada - 0•4
J
Jacking - 0•6
Joint mating faces - REF•4
Joystick fader control - 13•22
Jump starting - 0•10
Jumps out of gear - REF•8
L
Latch locks but will not unlock, or unlocks
but will not lock - REF•11
Leaks - 0•8, 1•10
Lighter - 13•10
Lighting master switch - 13•11
Lights - 13•4, 13•6
Lights inoperative - REF•10
Locknuts, locktabs and washers - REF•4
Locks - 1•12, 12•6, 12•7
Loudspeakers - 13•21, 13•22
Low pressure hose - 10•10
Lower arm - 11•9, 11•12
Lubricant leaks - REF•8
Lubricants and fluids - 1•2
Luggage area light - 13•8
M
Main bearings - 2A•11, 2A•15, 2B•17,
2C•12, 2C•15
Maintenance - bodywork and underframe -
12•1
Maintenance - upholstery and carpets -
12•2
Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor -
5•12
Manifold heater - 5•11
Manual gearbox- 1•11, 2B•6, 2B•7, 7A•1et
seq, REF•8
Manual steering - 11•3
Master cylinder - 10•12
Mirror - 0•11, 12•12, 13•11
Mixture adjustment potentiometer - 4•19
Mixture adjustments - 4•7, 4•9, 4•11, 4•14
Motifs and emblems - 12•10
Motor factors - 0•9
Mountings - 2A•11, 2B•8, 2C•12
N
Needle valve and float - 4•11
Number plate light - 13•5
O
Oil - 1•6, 1•9
Oil filler cap - 1•10
Oil filter - 1•9, 2A•11
Oil leakage from final drive - REF•9
Oil pressure warning light illuminated with
engine running - REF•7
Oil pressure warning switch - 13•12
Oil pump - 2A•10, 2A•12, 2A•16, 2B•16,
2B•17, 2C•11, 2C•14, 2C•17
Oil seals - 2A•10, 2B•15, 2C•12, 9•2, 9•3,
REF•4
On load voltage check - 5•5
Open-circuit - 13•3
Overcooling - REF•7
Overhead console - 12•17
Overheating - REF•7
P
Pads - 1•10, 10•4, 10•5
Parcel shelf - 12•19
Parking light - 13•4
Pedal Travel Sensor (PTS) - 10•14
Pedals - 6•2, 4•6, 10•8
Pierburg 2V carburettor - 4•7, 4•9
Pistons and connecting rods - 2A•11, 2A•13,
2A•15, 2B•17, 2C•12, 2C•14, 2C•16
Pitching and/or rolling around corners, or
during braking - REF•10
Plastic components - 12•3
Poisonous or irrirant substances - 0•5
Power steering - 1•16, 11•3, 11•4, 11•6
Power valve diaphragm - 4•12
Pre-ignition (pinking) or knocking during
acceleration or under load - REF•7
Printed circuit board - 13•20
Propeller shaft- 8•1et seq, REF•9
Pushrods - 2C•13
Index
procarmanuals.com