brake fluid FORD KUGA 2011 1.G Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 2011, Model line: KUGA, Model: FORD KUGA 2011 1.GPages: 2057
Page 1850 of 2057

To exactly determine the activation points of the
gear shifts and torque converter lockup on the
basis of the type of driving mode chosen, the TCM
receives the following information:
• Selected transmission range (TR sensor)
• Selected driving mode (normal/sport/select-shift)
• Transmission input shaft speed (TSS sensor)
• Transmission output shaft speed (OSS sensor)
• Transmission fluid temperature (TFT sensor)
• The engine speed and the torque as well as thethrottle plate opening - from the PCM via the
CAN databus
• Actuation of accelerator – from the PCM via the CAN databus
• The coolant temperature – from the PCM via the CAN databus
• Road speed – from the ABS module via the CAN databus
• Actuation of brake pedal – from the PCM via the CAN databus
Gearshift control
Adaptation
The TCM monitors every shift operation in all
driving conditions to make even and smooth gear
shifts possible. This is done by the control module,
which either lowers or increases the hydraulic line
pressure during gearshifts.
The changed pressure values are stored in the
control module memory after the engine is switched
off and retrieved during engine starting. This
improves the shift comfort and extends the service
life.
Full adaptability occurs when the following criteria
are met:
• Throttle plate opening is constant.
• Transmission fluid temperature between 65 °Cand 110 °C.
Shifting from 'P' to another transmission
range
To be able to move the selector lever from 'P' into
another transmission range, the ignition must be
switched on and the brake pedal pressed (stoplamp
switch on). The TCM detects the position of the
brake pedal via the CAN data bus and the engaged
transmission range from the TR sensor. Based on this information, the TCM transmits a
signal to the select-shift switch module. This
activates the brake shift interlock actuator in the
selector lever assembly.
When the brake shift interlock actuator is activated,
the locking pin is retracted so that another
transmission range can be selected.
The brake shift interlock actuator is deactivated
when the ignition is switched off. It is mechanically
locked when the gear selector lever is in 'P'.
Automatic transmission, selector lever in
position "D".
The TCM adapts the shift points to match the
driving conditions. Normally the TCM is in adaptive
mode and gear changes take place adapted to the
driving conditions. If special driving conditions are
detected, the TCM switches to predefined
characteristics.
When driving with normal acceleration, the TCM
uses a preset shift program which is optimized for
economical driving.
This shift program is suitable for "normal" driving
and delivers early upward changes and torque
converter lockup. Furthermore, the transmission
fluid pressure is adapted to make smooth
engagement of the gears possible.
Sport mode, selector lever in position "S"
The transmission switches from automatic
operation into sport mode. In this mode the TCM
switches to another set of characteristic curves.
These characteristic curves for control of the gear
changes are adapted to sporting calculations (e.g.
gear change at higher engine speed).
In the sport mode shift program the shift points are
set so that good performance is offered. Changing
down occurs at lower engine speeds.
Manual gear changes (select-shift mode) can be
made in sport mode by moving the selector lever
in the (+) or (-) direction.
Changing gear in select-shift mode
If you move the selector lever to 'S', the automatic
transaxle remains hydraulically in 'D' position. If
you move the gear selector lever forwards (-), the
G1163605en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
307-01-
29
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
— Vehicles With:
5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55 AWD
307-01- 29
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1851 of 2057

select-shift switch module transmits a downshift
signal to the TCM.
If you move the gear selector lever backwards (+),
an upshift signal is transmitted to the TCM. In the
instrument cluster, the symbol when the selector
lever is in the 'S' position changes from 'D' to the
current gear, for example 3.
The TCM transmits a signal to the select-shift
switch module to switch on the light emitting diode
for 'S' and to switch off all other light emitting
diodes. The TCM decides whether the shift process
is possible.
If the shift process is permitted, then the various
valves are activated according to the intended
combination for each gear.
In certain situations however, the TCM determines
the gear shifting. The following applies:
• If the vehicle is stationary, only 1st, 2nd and 3rdgears can be selected. 4th gear can be selected
at speeds over 30 km/h and 5th gear at speeds
over 40 km/h.
• The kickdown function is only available in the automatic transmission range 'D'
• Automatic gear changes into the next higher or next lower gear occur at fixed vehicle speeds
and fixed engine speeds
• The permitted engine speed for manual change down agree with that for the kickdown change
up, i.e. an engine speed of approximately 6000
rpm.
• If the temperature inside the transmission rises too high, the TCM takes control of the shift
decisions in order to select a gear in which
activation of torque converter lockup at the
current speed is possible
• Torque converter lockup is possible in 3rd, 4th and 5th gear. (1st and 2nd gears do not have
torque converter lockup)
The signal that specifies the position of the lever
to the select-shift switch module is generated as
follows in the selector lever position 'S': there is a
Hall sensor at the printed circuit board for the
module for each of the three selector lever
positions. A permanent magnet on the cover in the
selector lever affects the output signals to the
control module from the sensors. The control
module recognizes the position of the lever by the
differences in the signal properties.Selector lever from 'N' to 'R' position
The TCM only permits shifting to reverse gear if
the vehicle speed is less than 4.35 mph.
If the vehicle speed is greater than 7 km/h (approx.
4.35 mph), the clutch (C2) and the multi-plate brake
(B3) are not activated and the gearshift is thus
prevented.
Self-test and Diagnosis
The TCM monitors all the transaxle sensors and
electronic components including the PCM. If a fault
occurs, the driver is informed via a warning
indicator and a text message in the instrument
cluster. Faults are stored as DTCs in the fault
memory of the TCM and can be read out and
cleared using the IDS.
Temperature controlled torque converter
lockup
If heavy load and high ambient temperatures cause
an abnormal rise in the transmission temperature,
torque converter lockup is activated as often as
possible (temperature controlled lockup).
This reduces the slip and the heat developed in
the transmission. When the temperature drops
below +20 °C, torque converter lockup is not used.
Slip locking
When changing gear this function makes it possible
for the gears to engage more smoothly with
reduced vibration and less noise. In this mode, the
torque converter clutch is activated but not fully
locked.
The following conditions must be met for the
function to activate:
• Gear selector lever in position D or S.
• Gear 3, 4 or 5.
• The transmission input speed is 1100 rpm or more and the throttle plate opening 20 - 35%.
• The transmission fluid temperature is 40 - 120 °C.
Hill climbing
The TCM can change the shift pattern slightly when
driving uphill to avoid changing gear too often.
G1163605en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
307-01- 30
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
— Vehicles With:
5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55 AWD
307-01- 30
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1870 of 2057
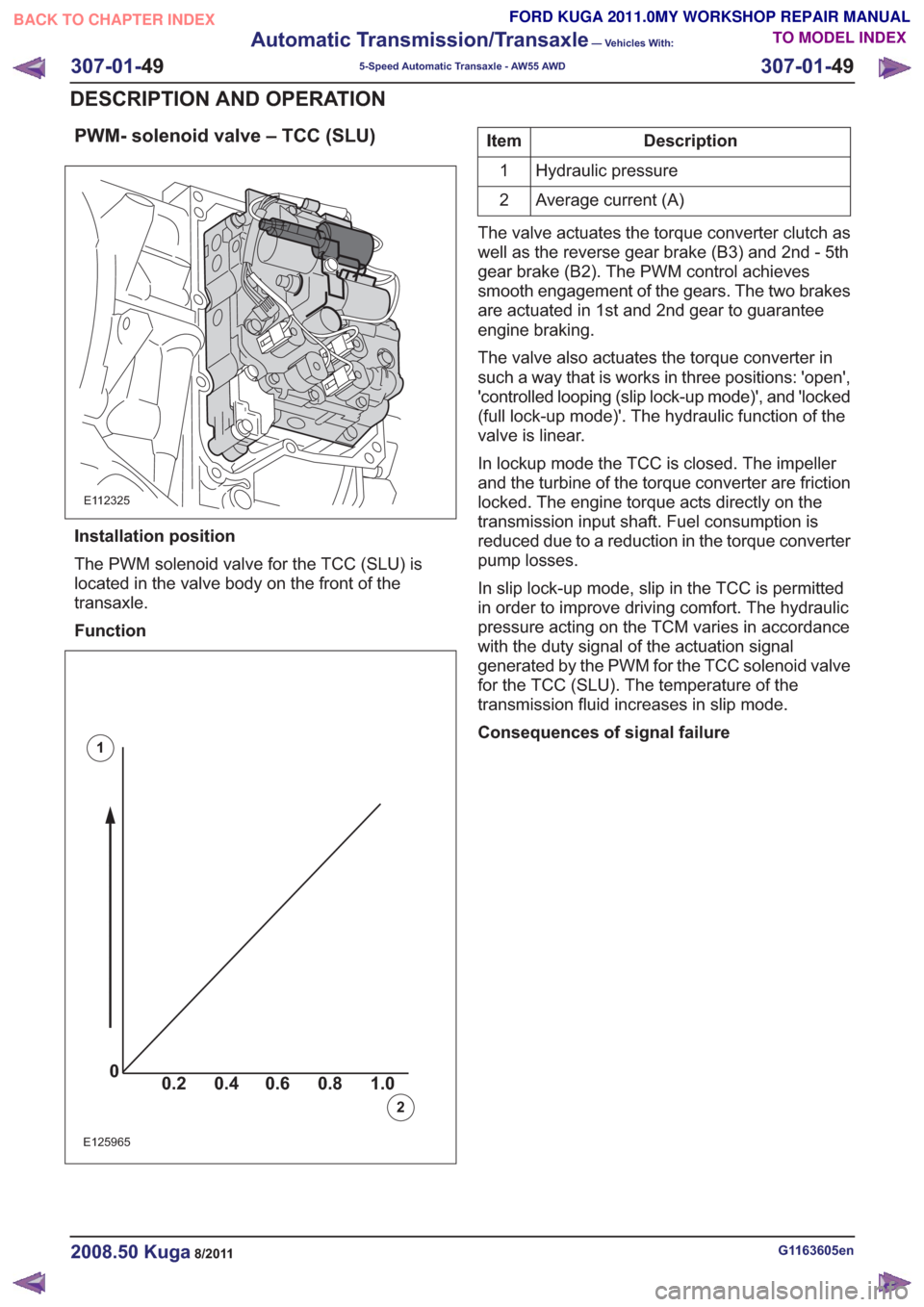
PWM- solenoid valve – TCC (SLU)
E112325
Installation position
The PWM solenoid valve for the TCC (SLU) is
located in the valve body on the front of the
transaxle.
Function
00.2 1.0 0.80.60.4
0
0.2 1.0
0.80.60.4
0
0.2 1.0
0.80.60.40
0.2 1.0 0.80.60.4
E125965
1
2
Description
Item
Hydraulic pressure
1
Average current (A)
2
The valve actuates the torque converter clutch as
well as the reverse gear brake (B3) and 2nd - 5th
gear brake (B2). The PWM control achieves
smooth engagement of the gears. The two brakes
are actuated in 1st and 2nd gear to guarantee
engine braking.
The valve also actuates the torque converter in
such a way that is works in three positions: 'open',
'controlled looping (slip lock-up mode)', and 'locked
(full lock-up mode)'. The hydraulic function of the
valve is linear.
In lockup mode the TCC is closed. The impeller
and the turbine of the torque converter are friction
locked. The engine torque acts directly on the
transmission input shaft. Fuel consumption is
reduced due to a reduction in the torque converter
pump losses.
In slip lock-up mode, slip in the TCC is permitted
in order to improve driving comfort. The hydraulic
pressure acting on the TCM varies in accordance
with the duty signal of the actuation signal
generated by the PWM for the TCC solenoid valve
for the TCC (SLU). The temperature of the
transmission fluid increases in slip mode.
Consequences of signal failure
G1163605en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
307-01- 49
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
— Vehicles With:
5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55 AWD
307-01- 49
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1882 of 2057
Transmission Fluid Level Check
General EquipmentFord Diagnostic Equipment
Materials
Specification
Name
WSS-M2C924-A / 4U7J-
M2C924-AA
Automatic Transmission
Oil E-AW
Inspection
1.
Refer to: Health and Safety Precautions (100-00
General Information, Description and
Operation).
2. Connect the Ford diagnostic equipment.
General Equipment: Ford Diagnostic Equipment
3. Make sure that the transmission is not in
emergency operation mode.
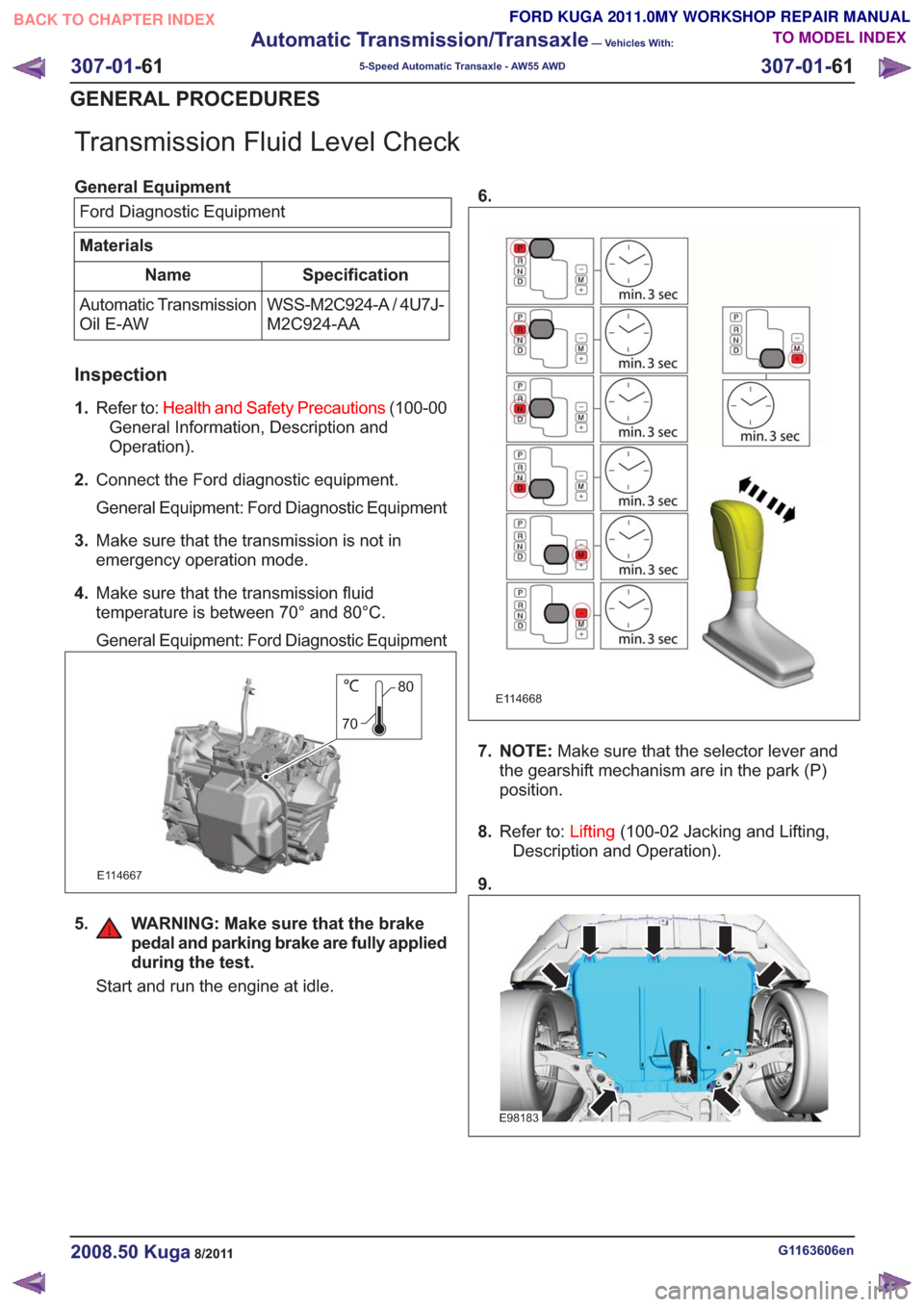
4. Make sure that the transmission fluid
temperature is between 70° and 80°C.
General Equipment: Ford Diagnostic Equipment
80
70
E114667
5. WARNING: Make sure that the brake pedal and parking brake are fully applied
during the test.
Start and run the engine at idle. 6.
E114668
7. NOTE:
Make sure that the selector lever and
the gearshift mechanism are in the park (P)
position.
8. Refer to: Lifting(100-02 Jacking and Lifting,
Description and Operation).
9.
E98183
G1163606en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
307-01- 61
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
— Vehicles With:
5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55 AWD
307-01- 61
GENERAL PROCEDURES
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1970 of 2057

Fuel System — Vehicles With: Fuel Additive Tank
General EquipmentFord diagnostic equipment
Principles of Operation
WARNINGS:
This procedure involves fuel additive
handling. Be prepared for fuel additive
spillage at all times and always observe
fuel handling precautions. Failure to follow
these instructions may result in personal
injury.
Eye, hand, ear protection and protective
clothing are required to be worn during
any general service or removal and
installation service procedure of fuel
additive system components. Failure to
follow this instruction may result in
personal injury.
In case of fuel additive fluid contact with
the skin or the eyes, flush immediately with
water for a minimum of 15 minutes and
seek prompt medical attention. Failure to
follow these instructions may result in
personal injury.
If fuel additive fluid is swallowed, call a
physician immediately. Rinse mouth
immediately with water, do not induce
vomiting. Failure to follow these
instructions may result in personal injury.
Always provide adequate ventilation when
working on the fuel additive fluid system
or related components. Failure to follow
these instructions may result in personal
injury.
Do not smoke or carry lighted tobacco or
open flame of any type when working on
or near any fuel related components.
Highly flammable vapors are always
present and may ignite. Failure to follow
these instructions may result in personal
injury.
CAUTION: Make sure the workshop area
in which the vehicle is being worked on is
as clean and as dust free as possible.
Foreign matter from working on clutches,
brakes or from machining or welding
operations can contaminate the fuel
system and may result in later malfunction. The fuel additive system is an on-board system
that allows the injection of an additive at each
refueling operation by the customer. The additive
quantity is proportional to the fuel quantity that has
been added. The fuel additive system module
controls the amount of additive fluid entering the
fuel tank at each refueling, A switch mounted on
the fuel filler flap is used to detect the start of the
refueling event and the fuel gauge that is mounted
within the fuel tank informs the fuel additive tank
module the quantity of actual fuel added.
Inspection and Verification
1. Verify the customer concern.
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of leakage
and mechanical or electrical damage.
Visual Inspection Chart
Electrical
Mechanical
– Fuse(s)
– Fuel filler switch andmagnet
– Wiring harness(s)
– Electrical connector(s)
– Fuel additive system module
– Fuel additive tank module
– Instrument cluster
– Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
– Fuel level sensor
– Fuel additive tank
– Fuel additive tank
line(s)
– Fuel additive tank pipe(s)
– Fuel additive tank connector(s)
– Fuel tank filler cap
3. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported concern is found, correct the cause (if possible)
before proceeding to the next step
4. If the cause is not visually evident, REFER to the Ford diagnostic equipment.
G1080718en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
310-00- 2
Fuel System - General Information
310-00- 2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL