ignition FORD MONDEO 1993 Service Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 1993, Model line: MONDEO, Model: FORD MONDEO 1993Pages: 279, PDF Size: 12.71 MB
Page 135 of 279

Chapter 6 Emissions control systems
Catalytic converter - general information, checking
and component renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Diagnosis system - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Electronic control system - description and precautions . . . . . . . . . 2
Engine compartment wiring check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
EVAPorative emissions control (EVAP) system - general
information, checking and component renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system - general
information, checking and component renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Exhaust system check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1General information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Information sensors - general information, testing,
removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) system - general
information, checking and component renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) system check
and filter cleaning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Pulse-air system - general information, checking
and component renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Underbonnet hose check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Crankshaft speed/position sensor
Resistance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 200 to 450 ohms
Camshaft position sensor
Resistance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 200 to 900 ohms
Intake air temperature sensor
Resistance:
At -40°C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 860 to 900 k ohms
At 20°C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35 to 40 k ohms
At 100°C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.9 to 2.5 k ohms
At 120°C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.0 to 1.3 k ohms
Throttle potentiometer
Resistance - see text . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 400 to 6000 ohms
Power steering pressure switch
Operating pressure - green switch body:
Contacts open - infinite resistance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31.5 ± 3.5 bars
Contacts close - 0 to 2.5 ohms resistance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Between 13.5 and 24.0 bars
Charcoal canister-purge solenoid valve
Resistance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50 to 120 ohms
Pulse-air solenoid valve
Resistance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50 to 120 ohms
Torque wrench settingsNm lbf ft
Camshaft position sensor screw . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18 to 23 13 to 17
Intake air temperature sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23 17
Oxygen sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60 44
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system components:
Valve-to-inlet manifold bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9 6
Pipe-to-ignition coil screws . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 7
Pulse-air system components:
Filter housing mounting bolt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47 35
Piping-to-exhaust manifold sleeve nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32 24
6•1
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,suitable
for competent DIY
mechanicDifficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert DIY
or professional
Degrees of difficulty
Specifications Contents
6
procarmanuals.com
Page 136 of 279
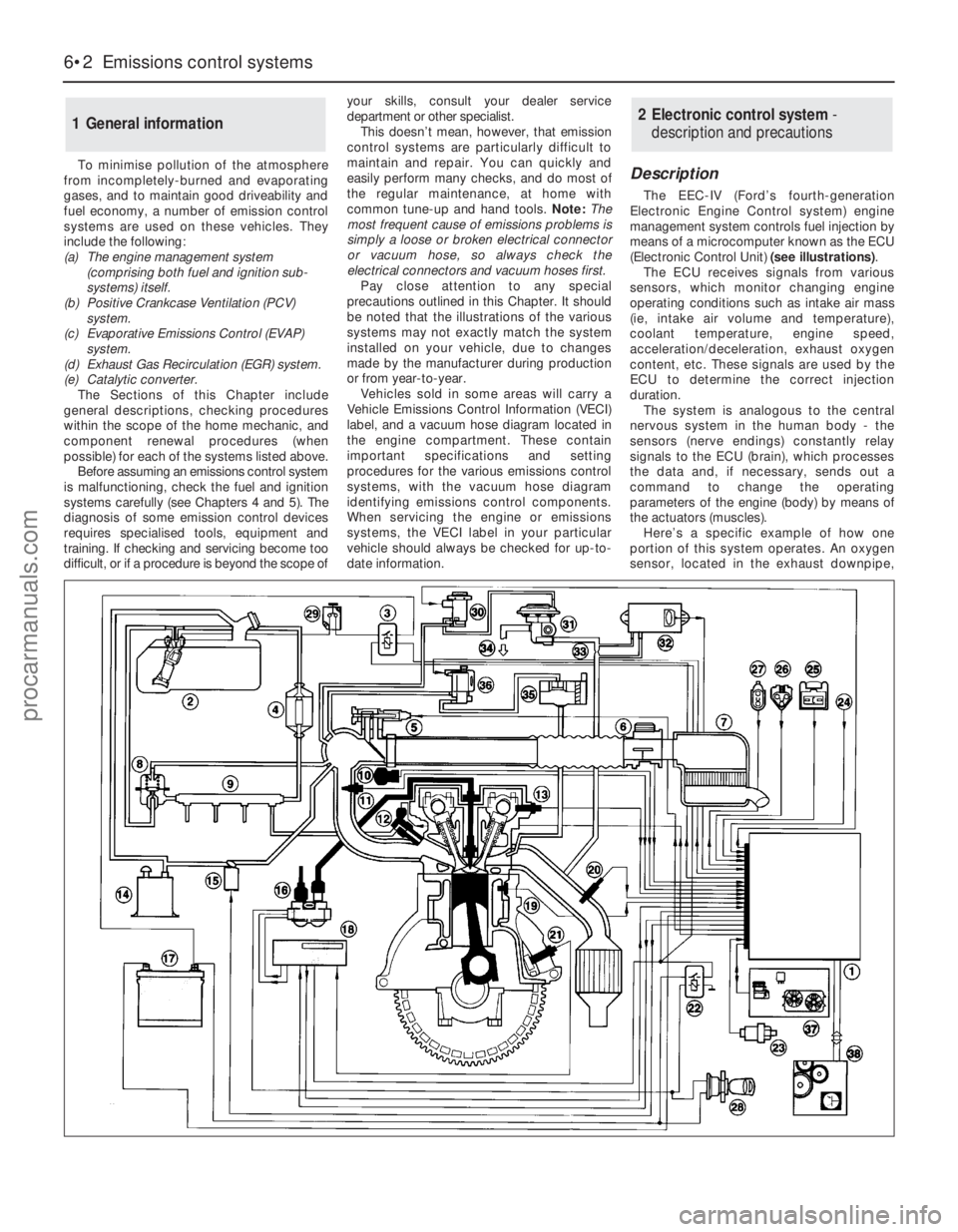
To minimise pollution of the atmosphere
from incompletely-burned and evaporating
gases, and to maintain good driveability and
fuel economy, a number of emission control
systems are used on these vehicles. They
include the following:
(a) The engine management system
(comprising both fuel and ignition sub-
systems) itself.
(b) Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV)
system.
(c) Evaporative Emissions Control (EVAP)
system.
(d) Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system.
(e) Catalytic converter.
The Sections of this Chapter include
general descriptions, checking procedures
within the scope of the home mechanic, and
component renewal procedures (when
possible) for each of the systems listed above.
Before assuming an emissions control system
is malfunctioning, check the fuel and ignition
systems carefully (see Chapters 4 and 5). The
diagnosis of some emission control devices
requires specialised tools, equipment and
training. If checking and servicing become too
difficult, or if a procedure is beyond the scope ofyour skills, consult your dealer service
department or other specialist.
This doesn’t mean, however, that emission
control systems are particularly difficult to
maintain and repair. You can quickly and
easily perform many checks, and do most of
the regular maintenance, at home with
common tune-up and hand tools. Note:The
most frequent cause of emissions problems is
simply a loose or broken electrical connector
or vacuum hose, so always check the
electrical connectors and vacuum hoses first.
Pay close attention to any special
precautions outlined in this Chapter. It should
be noted that the illustrations of the various
systems may not exactly match the system
installed on your vehicle, due to changes
made by the manufacturer during production
or from year-to-year.
Vehicles sold in some areas will carry a
Vehicle Emissions Control Information (VECI)
label, and a vacuum hose diagram located in
the engine compartment. These contain
important specifications and setting
procedures for the various emissions control
systems, with the vacuum hose diagram
identifying emissions control components.
When servicing the engine or emissions
systems, the VECI label in your particular
vehicle should always be checked for up-to-
date information.Description
The EEC-IV (Ford’s fourth-generation
Electronic Engine Control system) engine
management system controls fuel injection by
means of a microcomputer known as the ECU
(Electronic Control Unit) (see illustrations).
The ECU receives signals from various
sensors, which monitor changing engine
operating conditions such as intake air mass
(ie, intake air volume and temperature),
coolant temperature, engine speed,
acceleration/deceleration, exhaust oxygen
content, etc. These signals are used by the
ECU to determine the correct injection
duration.
The system is analogous to the central
nervous system in the human body - the
sensors (nerve endings) constantly relay
signals to the ECU (brain), which processes
the data and, if necessary, sends out a
command to change the operating
parameters of the engine (body) by means of
the actuators (muscles).
Here’s a specific example of how one
portion of this system operates. An oxygen
sensor, located in the exhaust downpipe,
2 Electronic control system -
description and precautions1 General information
6•2 Emissions control systems
procarmanuals.com
Page 137 of 279
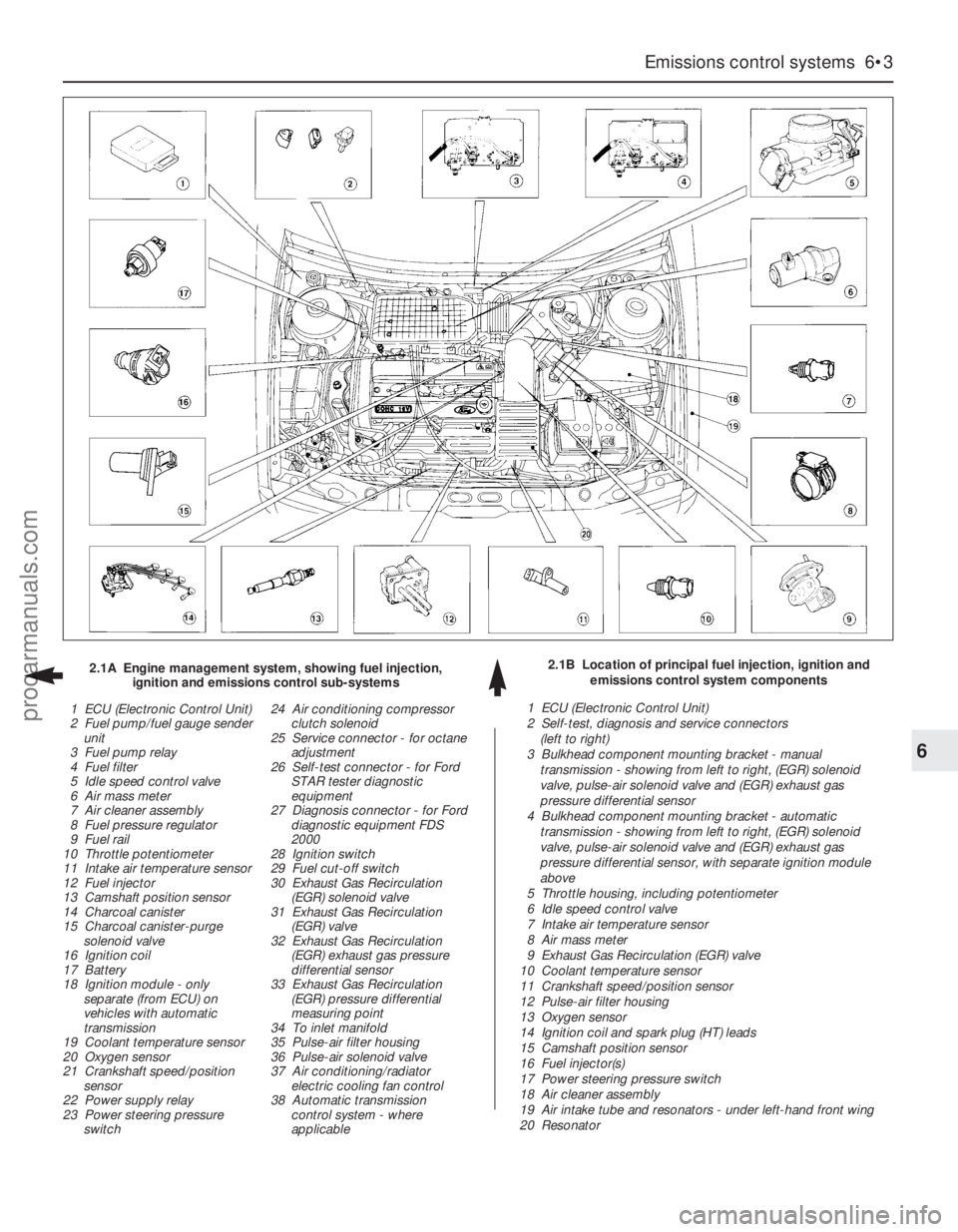
Emissions control systems 6•3
6
2.1B Location of principal fuel injection, ignition and
emissions control system components 2.1A Engine management system, showing fuel injection,
ignition and emissions control sub-systems
1 ECU (Electronic Control Unit)
2 Fuel pump/fuel gauge sender
unit
3 Fuel pump relay
4 Fuel filter
5 Idle speed control valve
6 Air mass meter
7 Air cleaner assembly
8 Fuel pressure regulator
9 Fuel rail
10 Throttle potentiometer
11 Intake air temperature sensor
12 Fuel injector
13 Camshaft position sensor
14 Charcoal canister
15 Charcoal canister-purge
solenoid valve
16 Ignition coil
17 Battery
18 Ignition module - only
separate (from ECU) on
vehicles with automatic
transmission
19 Coolant temperature sensor
20 Oxygen sensor
21 Crankshaft speed/position
sensor
22 Power supply relay
23 Power steering pressure
switch24 Air conditioning compressor
clutch solenoid
25 Service connector - for octane
adjustment
26 Self-test connector - for Ford
STAR tester diagnostic
equipment
27 Diagnosis connector - for Ford
diagnostic equipment FDS
2000
28 Ignition switch
29 Fuel cut-off switch
30 Exhaust Gas Recirculation
(EGR) solenoid valve
31 Exhaust Gas Recirculation
(EGR) valve
32 Exhaust Gas Recirculation
(EGR) exhaust gas pressure
differential sensor
33 Exhaust Gas Recirculation
(EGR) pressure differential
measuring point
34 To inlet manifold
35 Pulse-air filter housing
36 Pulse-air solenoid valve
37 Air conditioning/radiator
electric cooling fan control
38 Automatic transmission
control system - where
applicable1 ECU (Electronic Control Unit)
2 Self-test, diagnosis and service connectors
(left to right)
3 Bulkhead component mounting bracket - manual
transmission - showing from left to right, (EGR) solenoid
valve, pulse-air solenoid valve and (EGR) exhaust gas
pressure differential sensor
4 Bulkhead component mounting bracket - automatic
transmission - showing from left to right, (EGR) solenoid
valve, pulse-air solenoid valve and (EGR) exhaust gas
pressure differential sensor, with separate ignition module
above
5 Throttle housing, including potentiometer
6 Idle speed control valve
7 Intake air temperature sensor
8 Air mass meter
9 Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) valve
10 Coolant temperature sensor
11 Crankshaft speed/position sensor
12 Pulse-air filter housing
13 Oxygen sensor
14 Ignition coil and spark plug (HT) leads
15 Camshaft position sensor
16 Fuel injector(s)
17 Power steering pressure switch
18 Air cleaner assembly
19 Air intake tube and resonators - under left-hand front wing
20 Resonator
procarmanuals.com
Page 138 of 279

constantly monitors the oxygen content of the
exhaust gas. If the percentage of oxygen in
the exhaust gas is incorrect, an electrical
signal is sent to the ECU. The ECU processes
this information, and then sends a command
to the fuel injection system, telling it to change
the air/fuel mixture; the end result is an air/fuel
mixture ratio which is constantly maintained
at a predetermined ratio, regardless of driving
conditions. This happens in a fraction of a
second, and goes on almost all the time while
the engine is running - the exceptions are that
the ECU cuts out the system and runs the
engine on values pre-programmed
(“mapped”) into its memory both while the
oxygen sensor is reaching its normal
operating temperature after the engine has
been started from cold, and when the throttle
is fully open for full acceleration.
In the event of a sensor malfunction, a
back-up circuit will take over, to provide
driveability until the problem is identified and
fixed.
Precautions
(a) Always disconnect the power by
uncoupling the battery terminals - see
Section 1 of Chapter 5 - before removing
any of the electronic control system’s
electrical connectors.
(b) When installing a battery, be particularly
careful to avoid reversing the positive and
negative battery leads.
(c) Do not subject any components of the
system (especially the ECU) to severe
impact during removal or installation.
(d) Do not be careless during fault diagnosis.
Even slight terminal contact can invalidate
a testing procedure, and damage one of
the numerous transistor circuits.
(e) Never attempt to work on the ECU, to test
it (with any kind of test equipment), or to
open its cover.
(f) If you are inspecting electronic control
system components during rainy weather,
make sure that water does not enter any
part. When washing the engine
compartment, do not spray these parts or
their electrical connectors with water.
General
The various components of the fuel, ignition
and emissions control systems (not forgetting
the same ECU’s control of sub-systems such
as the radiator cooling fan, air conditioning
and automatic transmission, where
appropriate) are so closely interlinked that
diagnosis of a fault in any one component is
virtually impossible using traditional methods.
Working on simpler systems in the past, the
experienced mechanic may well have been
able to use personal skill and knowledge
immediately to pinpoint the cause of a fault, or
quickly to isolate the fault, by elimination;however, with an engine management system
integrated to this degree, this is not likely to
be possible in most instances, because of the
number of symptoms that could arise from
even a minor fault.
So that the causes of faults can be quickly
and accurately traced and rectified, the ECU
is provided with a built-in self-diagnosis
facility, which detects malfunctions in the
system’s components. When a fault occurs,
three things happen: the ECU identifies the
fault, stores a corresponding code in its
memory, and (in most cases) runs the system
using back-up values pre-programmed
(“mapped”) into its memory; some form of
driveability is thus maintained, to enable the
vehicle to be driven to a garage for attention.
Any faults that may have occurred are
indicated in the form of three-digit codes
when the system is connected (via the built-in
diagnosis or self-test connectors, as
appropriate) to special diagnostic equipment -
this points the user in the direction of the
faulty circuit, so that further tests can pinpoint
the exact location of the fault.
Given below is the procedure that would be
followed by a Ford technician to trace a fault
from scratch. Should your vehicle’s engine
management system develop a fault, read
through the procedure and decide how much
you can attempt, depending on your skill and
experience and the equipment available to
you, or whether it would be simpler to have
the vehicle attended to by your local Ford
dealer. If you are concerned about the
apparent complexity of the system, however,
remember the comments made in the fourth
paragraph of Section 1 of this Chapter; the
preliminary checks require nothing but care,
patience and a few minor items of equipment,
and may well eliminate the majority of faults.
(a) Preliminary checks
(b) Fault code read-out *
(c) Check ignition timing and base idle
speed. Recheck fault codes to establish
whether fault has been cured or not *
(d) Carry out basic check of ignition system
components. Recheck fault codes to
establish whether fault has been cured or
not *
(e) Carry out basic check of fuel system
components. Recheck fault codes to
establish whether fault has been cured or
not *
(f) If fault is still not located, carry out system
test *
Note:Operations marked with an asterisk
require special test equipment.
Preliminary checks
Note:When carrying out these checks to
trace a fault, remember that if the fault has
appeared only a short time after any part of
the vehicle has been serviced or overhauled,
the first place to check is where that work was
carried out, however unrelated it may appear,
to ensure that no carelessly-refitted
components are causing the problem.If you are tracing the cause of a “partial”
engine fault, such as lack of performance, in
addition to the checks outlined below, check
the compression pressures (see Part A of
Chapter 2) and bear in mind the possibility
that one of the hydraulic tappets might be
faulty, producing an incorrect valve clearance.
Check also that the fuel filter has been
renewed at the recommended intervals.
If the system appears completely dead,
remember the possibility that the
alarm/inhibitor system may be responsible.
1The first check for anyone without special
test equipment is to switch on the ignition,
and to listen for the fuel pump (the sound of
an electric motor running, audible from
beneath the rear seats); assuming there is
sufficient fuel in the tank, the pump should
start and run for approximately one or two
seconds, then stop, each time the ignition is
switched on. If the pump runs continuously all
the time the ignition is switched on, the
electronic control system is running in the
back-up (or “limp-home”) mode referred to by
Ford as “Limited Operation Strategy” (LOS).
This almost certainly indicates a fault in the
ECU itself, and the vehicle should therefore be
taken to a Ford dealer for a full test of the
complete system using the correct diagnostic
equipment; do not waste time trying to test
the system without such facilities.
2If the fuel pump is working correctly (or not
at all), a considerable amount of fault
diagnosis is still possible without special test
equipment. Start the checking procedure as
follows.
3Open the bonnet and check the condition
of the battery connections - remake the
connections or renew the leads if a fault is
found (Chapter 5). Use the same techniques
to ensure that all earth points in the engine
compartment provide good electrical contact
through clean, metal-to-metal joints, and that
all are securely fastened. (In addition to the
earth connection at the engine lifting eye and
that from the transmission to the
body/battery, there is one earth connection
behind each headlight assembly, and one
below the power steering fluid reservoir.)
4Referring to the information given in
Chapter 12 and in the wiring diagrams at the
back of this manual, check that all fuses
protecting the circuits related to the engine
management system are in good condition.
Fit new fuses if required; while you are there,
check that all relays are securely plugged into
their sockets.
5Next work methodically around the engine
compartment, checking all visible wiring, and
the connections between sections of the
wiring loom. What you are looking for at this
stage is wiring that is obviously damaged by
chafing against sharp edges, or against
moving suspension/transmission components
and/or the auxiliary drivebelt, by being
trapped or crushed between carelessly-
refitted components, or melted by being
forced into contact with hot engine castings,
3 Diagnosis system -
general information
6•4 Emissions control systems
procarmanuals.com
Page 140 of 279

back again, as an assistant depresses the
accelerator pedal. If the valve shows any sign
of stiffness, sticking or otherwise-inhibited
movement (and the accelerator cable is
known from the previous check to be in good
condition), spray the throttle linkage with
penetrating lubricant, allow time for it to work,
and repeat the check; if no improvement is
obtained, the complete throttle housing must
be renewed (Chapter 4).
15Unclip the air cleaner cover, and check
that the air filter element and the crankcase
ventilation system filter are not clogged or
soaked. (A clogged air filter will obstruct the
intake air flow, causing a noticeable effect on
engine performance; a clogged crankcase
ventilation system filter will inhibit crankcase
“breathing”). Renew or clean the filter(s) as
appropriate; refer to the relevant Sections of
Chapter 1 for further information, if required.
Before refitting the air cleaner cover, check
that the air intake (located under the front left-
hand wing, opening behind the direction
indicator/headlight assembly) is clear. It
should be possible to blow through the intake,
or to probe it (carefully) as far as the rear of
the direction indicator light.
16Start the engine and allow it to idle.
Note:Working in the engine compartment
while the engine is running requires great care
if the risk of personal injury is to be avoided;
among the dangers are burns from contact
with hot components, or contact with moving
components such as the radiator cooling fan
or the auxiliary drivebelt. Refer to “Safety
first!” at the front of this manual before
starting, and ensure that your hands, and long
hair or loose clothing, are kept well clear of hot
or moving components at all times.
17Working from the air intake junction at the
inner wing panel, via the air cleaner assembly
and air mass meter, to the resonator, plenum
chamber, throttle housing and inlet manifold
(and including the various vacuum hoses and
pipes connected to these), check for air leaks.
Usually, these will be revealed by sucking or
hissing noises, but minor leaks may be traced
by spraying a solution of soapy water on to
the suspect joint; if a leak exists, it will be
shown by the change in engine note and the
accompanying air bubbles (or sucking-in of
the liquid, depending on the pressure
difference at that point). If a leak is found at
any point, tighten the fastening clamp and/or
renew the faulty components, as applicable.
18Similarly, work from the cylinder head, via
the manifold (and not forgetting the related
EGR and pulse-air system components) to the
tailpipe, to check that the exhaust system is
free from leaks. The simplest way of doing
this, if the vehicle can be raised and
supported safely and with complete security
while the check is made, is to temporarily
block the tailpipe while listening for the sound
of escaping exhaust gases; any leak should
be evident. If a leak is found at any point,
tighten the fastening clamp bolts and/or nuts,
renew the gasket, and/or renew the faultysection of the system, as necessary, to seal
the leak.
19It is possible to make a further check of
the electrical connections by wiggling each
electrical connector of the system in turn as
the engine is idling; a faulty connector will be
immediately evident from the engine’s
response as contact is broken and remade. A
faulty connector should be renewed to ensure
the future reliability of the system; note that
this may mean the renewal of that entire
section of the loom - see your local Ford
dealer for details.
20Switch off the engine. If the fault is not yet
identified, the next step is to check the
ignition voltages, using an engine analyser
with an oscilloscope - without such
equipment, the only tests possible are to
remove and check each spark plug in turn, to
check the spark plug (HT) lead connections
and resistances, and to check the
connections and resistances of the ignition
coil. Refer to the relevant Sections of
Chapters 1 and 5.
21The final step in these preliminary checks
would be to use an exhaust gas analyser to
measure the CO level at the exhaust tailpipe.This check cannot be made without special
test equipment - see your local Ford dealer for
details.
Fault code read-out
22As noted in the general comments at the
beginning of this Section, the preliminary
checks outlined above should eliminate the
majority of faults from the engine
management system. If the fault is not yet
identified, the next step is to connect a fault
code reader to the ECU, so that its self-
diagnosis facility can be used to identify the
faulty part of the system; further tests can
then be made to identify the exact cause of
the fault.
23In their basic form, fault code readers are
simply hand-held electronic devices, which
take data stored within an ECU’s memory and
display it when required as two- or three-digit
fault codes. The more sophisticated versions
now available can also control sensors and
actuators, to provide more effective testing;
some can store information, so that a road
test can be carried out, and any faults
encountered during the test can be displayed
afterwards.
6•6 Emissions control systems
3.26 Location and terminal identification of engine management system self-test,
diagnosis and service connectors
1 Power steering fluid reservoir
2 Diagnosis connector - for Ford diagnostic equipment FDS 2000
3 Self-test connector - for fault code read-out - pin 17 is output terminal, pin 48 is input
terminal, pin 40/60 is earth
4 Service connector - for octane adjustment
5 Plug-in bridge - to suit 95 RON fuel
procarmanuals.com
Page 141 of 279

24Ford specify the use of their STAR (Self-
Test Automatic Readout) tester; most Ford
dealers should have such equipment, and the
staff trained to use it effectively. The only
alternatives are as follows:
(a) To obtain one of those proprietary readers
which can interpret EEC-IV three-digit
codes - at present, such readers are too
expensive for the DIY enthusiast, but are
becoming more popular with smaller
specialist garages.
(b) To use an analogue voltmeter, whereby
the stored codes are displayed as sweeps
of the voltmeter needle. This option limits
the operator to a read-out of any codes
stored - ie, there is no control of sensors
and/or actuators - but can still be useful in
pinpointing the faulty part of the engine
management system. The display is
interpreted as follows. Each code
(whether fault code or
command/separator) is marked by a
three-to-four second pause - code “538”
would therefore be shown as long (3 to
4 seconds) pause, five fast sweeps of the
needle, slight (1 second) pause, three fast
sweeps, slight pause, eight fast sweeps,
long pause.
(c) Owners without access to such
equipment must take the vehicle to a Ford
dealer, or to an expert who has similar
equipment and the skill to use it.
25Because of the variations in the design of
fault code readers, it is not possible to give
exact details of the sequence of tests; the
manufacturer’s instructions must be followed,
in conjunction with the codes given below.
The following ten paragraphs outline the
procedure to be followed using a version of
the Ford STAR tester, to illustrate the general
principles, as well as notes to guide the owner
using only a voltmeter.
26The vehicle must be prepared by applying
the handbrake, switching off the air
conditioning (where fitted) and any other
electrical loads (lights, heated rear window,
etc), then selecting neutral (manual
transmission) or the “P” position (automatic
transmission). Where the engine is required to
be running, it must be fully warmed-up to
normal operating temperature before the test
is started. Using any adaptors required,
connect the fault code reader to the system
via the (triangular, three-pin) self-test
connector on the right-hand end of the engine
compartment bulkhead (see illustration). If a
voltmeter is being used, connect its positive
lead to the battery positive terminal, and its
negative lead to the self-test connector’s
output terminal, pin 17. Have a pen and paper
ready to write down the codes displayed.
27Set the tester in operation. For the Ford
STAR tester, a display check will be carried
out and the test mode requirements must be
entered. If a voltmeter is being used, connect
a spare length of wire to earth the self-test
connector’s input terminal, pin 48. Be very
careful to ensure that you earth the correctterminal - the one with the white/green wire.
The first part of the test starts, with the
ignition switched on, but with the engine off.
On pressing the “Mem/test” button, the tester
displays “TEST” and the ready code “000”,
followed by a command code “010” - the
accelerator pedal must be fully depressed
within 10 seconds of the command code
appearing, or fault codes “576” or “577” will
appear when they are called up later. If a
voltmeter is being used, code “000” will not
appear (except perhaps as a flicker of the
needle) and “010” will appear as a single
sweep - to ensure correct interpretation of the
display, watch carefully for the interval
between the end of one code and the
beginning of the next, otherwise you will
become confused and misinterpret the read-
out.
28The tester will then display the codes for
any faults in the system at the time of the test.
Each code is repeated once; if no faults are
present, code “111” will be displayed. If a
voltmeter is being used, the pause between
repetitions will vary according to the
equipment in use and the number of faults in
the system, but was found to be
approximately 3 to 4 seconds - it may be
necessary to start again, and to repeat the
read-out until you are familiar with what you
are seeing.
29Next the tester will display code “010”
(now acting as a separator), followed by the
codes for any faults stored in the ECU’s
memory; if no faults were stored, code “111”
will be displayed.
30When prompted by the tester, the
operator must next depress the accelerator
pedal fully; the tester then checks several
actuators. Further test modes include a
“wiggle test” facility, whereby the operator
can check the various connectors as
described in paragraph 19 above (in this case,
any fault will be logged and the appropriate
code will be displayed), a facility for recalling
codes displayed, and a means for clearing the
ECU’s memory at the end of the test
procedure when any faults have been
rectified.
31The next step when using the Ford STAR
tester is to conduct a test with the engine
running. With the tester set in operation (see
paragraph 26 above) the engine is started and
allowed to idle. On pressing the “Mem/test”
button, the tester displays “TEST”, followed
by one of two codes, as follows.
32If warning code “998” appears, followed
by the appropriate fault code, switch off and
check as indicated the coolant temperature
sensor, the intake air temperature sensor, the
air mass meter, the throttle potentiometer
and/or their related circuits, then restart the
test procedure.
33If command code “020” appears, carry
out the following procedure within ten
seconds:
(a) Depress the brake pedal fully.
(b) Turn the steering to full-lock (either way)and centre it again, to produce a signal
from the power steering pressure switch -
if no signal is sent, fault code “521” will
be displayed.
(c) If automatic transmission is fitted, switch
the overdrive cancel button on and off,
then do the same for the
“Economy/Sport” mode switch.
(d) Wait for separator code “010” to be
displayed, then within 10 seconds,
depress the accelerator pedal fully,
increasing engine speed rapidly above
3000 rpm - release the pedal.
34Any faults found in the system will be
logged and displayed. Each code is repeated
once; if no faults are present, code “111” will
be displayed.
35When the codes have been displayed for
all faults logged, the ECU enters its “Service
Adjustment Programme”, as follows:
(a) The programme lasts for 2 minutes.
(b) The idle speed control valve is
deactivated, and the idle speed is set to
its pre-programmed (unregulated) value. If
the appropriate equipment is connected,
the base idle speed can be checked
(note, however, that it is not adjustable).
(c) The ignition timing can be checked if a
timing light is connected (note, however,
that it is not adjustable).
(d) Pressing the accelerator pedal fully at any
time during this period will execute a
cylinder balance test. Each injector in turn
is switched off, and the corresponding
decrease in engine speed is logged -
code “090” will be displayed if the test is
successful.
(e) At the end of the 2 minutes, the
completion of the programme is shown
by the engine speed briefly rising, then
returning to normal idling speed as
the idle speed control valve is
reactivated.
36As with the engine-off test, further test
modes include a “wiggle test” facility,
whereby the operator can check the various
connectors as described in paragraph 19
above (in this case, any fault will be logged
and the appropriate code will be displayed), a
facility for recalling codes displayed, and a
means for clearing the ECU’s memory at the
end of the test procedure when any faults
have been rectified. If equipment other than
the Ford STAR tester is used, the ECU’s
memory can be cleared by disconnecting the
battery - if this is not done, the code will
reappear with any other codes in the event of
subsequent trouble, but remember that other
systems with memory (such as the clock and
audio equipment) will also be affected. Should
it become necessary to disconnect the
battery during work on any other part of the
vehicle, first check to see if any fault codes
have been logged.
37Given overleaf are the possible codes,
their meanings, and where relevant, the action
to be taken as a result of a code being
displayed.
Emissions control systems 6•7
6
procarmanuals.com
Page 142 of 279
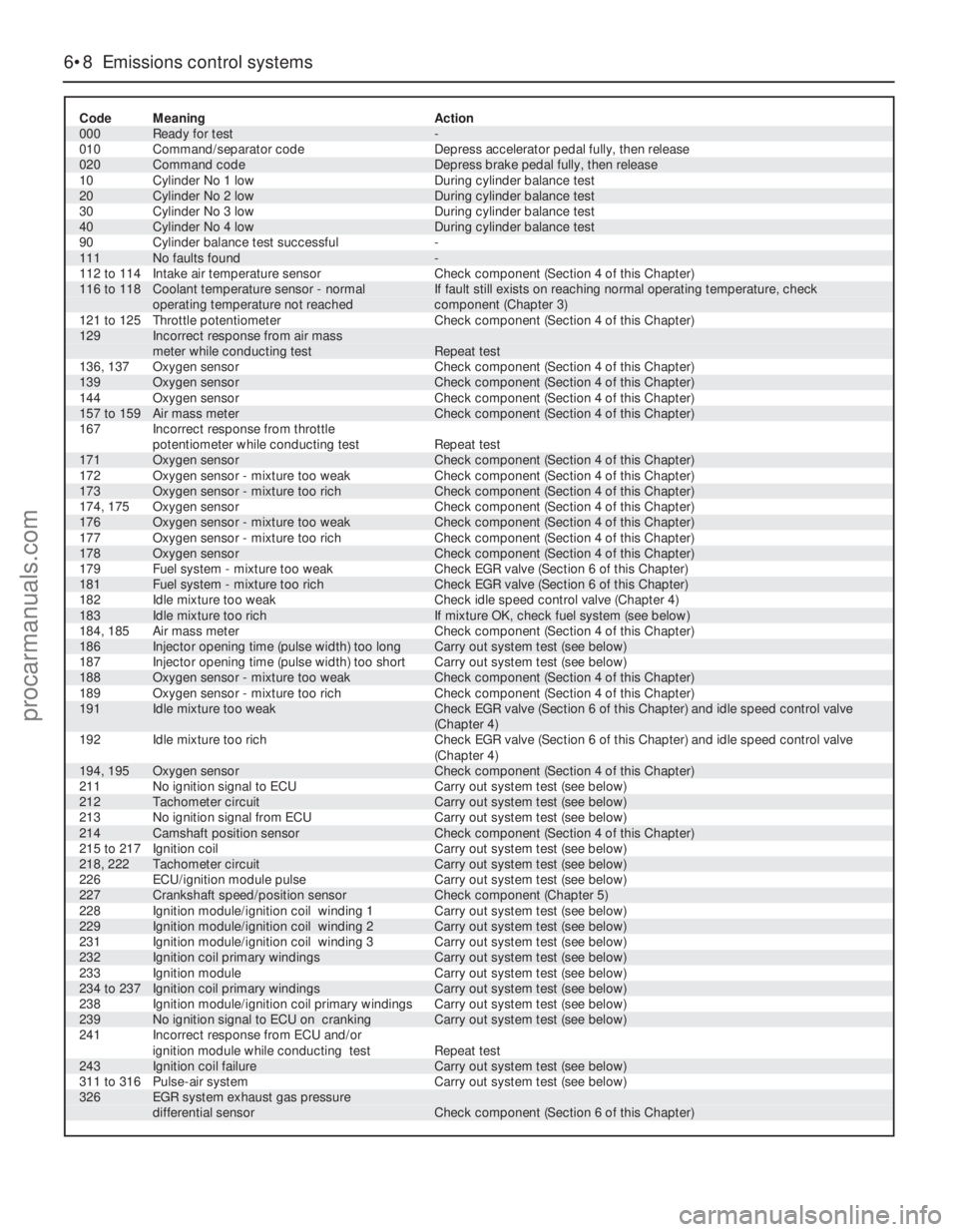
6•8 Emissions control systems
Code Meaning Action
000 Ready for test -
010 Command/separator code Depress accelerator pedal fully, then release
020 Command code Depress brake pedal fully, then release
10 Cylinder No 1 low During cylinder balance test
20 Cylinder No 2 low During cylinder balance test
30 Cylinder No 3 low During cylinder balance test
40 Cylinder No 4 low During cylinder balance test
90 Cylinder balance test successful -
111 No faults found -
112 to 114 Intake air temperature sensor Check component (Section 4 of this Chapter)116 to 118 Coolant temperature sensor - normal If fault still exists on reaching normal operating temperature, check
operating temperature not reached component (Chapter 3)
121 to 125 Throttle potentiometer Check component (Section 4 of this Chapter)129 Incorrect response from air mass
meter while conducting test Repeat test
136, 137 Oxygen sensor Check component (Section 4 of this Chapter)
139 Oxygen sensor Check component (Section 4 of this Chapter)
144 Oxygen sensor Check component (Section 4 of this Chapter)
157 to 159 Air mass meter Check component (Section 4 of this Chapter)
167 Incorrect response from throttle
potentiometer while conducting test Repeat test
171 Oxygen sensor Check component (Section 4 of this Chapter)
172 Oxygen sensor - mixture too weak Check component (Section 4 of this Chapter)
173 Oxygen sensor - mixture too rich Check component (Section 4 of this Chapter)
174, 175 Oxygen sensor Check component (Section 4 of this Chapter)
176 Oxygen sensor - mixture too weak Check component (Section 4 of this Chapter)
177 Oxygen sensor - mixture too rich Check component (Section 4 of this Chapter)
178 Oxygen sensor Check component (Section 4 of this Chapter)
179 Fuel system - mixture too weak Check EGR valve (Section 6 of this Chapter)
181 Fuel system - mixture too rich Check EGR valve (Section 6 of this Chapter)
182 Idle mixture too weak Check idle speed control valve (Chapter 4)
183 Idle mixture too rich If mixture OK, check fuel system (see below)
184, 185 Air mass meter Check component (Section 4 of this Chapter)
186 Injector opening time (pulse width) too long Carry out system test (see below)
187 Injector opening time (pulse width) too short Carry out system test (see below)
188 Oxygen sensor - mixture too weak Check component (Section 4 of this Chapter)
189 Oxygen sensor - mixture too rich Check component (Section 4 of this Chapter)191 Idle mixture too weak Check EGR valve (Section 6 of this Chapter) and idle speed control valve
(Chapter 4)
192 Idle mixture too rich Check EGR valve (Section 6 of this Chapter) and idle speed control valve
(Chapter 4)
194, 195 Oxygen sensor Check component (Section 4 of this Chapter)
211 No ignition signal to ECU Carry out system test (see below)
212 Tachometer circuit Carry out system test (see below)
213 No ignition signal from ECU Carry out system test (see below)
214 Camshaft position sensor Check component (Section 4 of this Chapter)
215 to 217 Ignition coil Carry out system test (see below)
218, 222 Tachometer circuit Carry out system test (see below)
226 ECU/ignition module pulse Carry out system test (see below)
227 Crankshaft speed/position sensor Check component (Chapter 5)
228 Ignition module/ignition coil winding 1 Carry out system test (see below)
229 Ignition module/ignition coil winding 2 Carry out system test (see below)
231 Ignition module/ignition coil winding 3 Carry out system test (see below)
232 Ignition coil primary windings Carry out system test (see below)
233 Ignition module Carry out system test (see below)
234 to 237 Ignition coil primary windings Carry out system test (see below)
238 Ignition module/ignition coil primary windings Carry out system test (see below)
239 No ignition signal to ECU on cranking Carry out system test (see below)
241 Incorrect response from ECU and/or
ignition module while conducting test Repeat test
243 Ignition coil failure Carry out system test (see below)
311 to 316 Pulse-air system Carry out system test (see below)326 EGR system exhaust gas pressure
differential sensor Check component (Section 6 of this Chapter)
procarmanuals.com
Page 144 of 279

Ignition timing and base idle
speed check
Note:The following procedure is a check only,
essentially of the ECU. Both the ignition timing
and the base idle speed are controlled by the
ECU. The ignition timing is not adjustable at
all; the base idle speed is set in production,
and should not be altered.
38If the fault code read-out (with any checks
resulting from it) has not eliminated the fault,
the next step is to check the ECU’s control of
the ignition timing and the base idle speed.
This task requires the use of a Ford STAR
tester (a proprietary fault code reader can be
used only if it is capable of inducing the ECU
to enter its “Service Adjustment Programme”),
coupled with an accurate tachometer and a
good-quality timing light. Without this
equipment, the task is not possible; the
vehicle must be taken to a Ford dealer for
attention.
39To make the check, apply the handbrake,
switch off the air conditioning (where fitted)
and any other electrical loads (lights, heated
rear window, etc), then select neutral (manual
transmission) or the “P” position (automatic
transmission). Start the engine, and warm it
up to normal operating temperature. The
radiator electric cooling fan must be running
continuously while the check is made; this
should be activated by the ECU, when
prompted by the tester. Switch off the engine,
and connect the test equipment as directed
by the manufacturer - refer to paragraph 26
above for details of STAR tester connection.
40Raise and support the front of the vehicle
securely, and remove the auxiliary drivebelt
cover (see Chapter 1). Emphasise the two
pairs of notches in the inner and outer rims of
the crankshaft pulley, using white paint. Note
that an ignition timing reference mark is not
provided on the pulley - in the normal
direction of crankshaft rotation (clockwise,
seen from the right-hand side of the vehicle)
the first pair of notches are irrelevant to the
vehicles covered in this manual, while the
second pair indicate Top Dead Centre (TDC)
when aligned with the rear edge of the raised
mark on the sump; when checking the ignition
timing, therefore, the (rear edge of the) sumpmark should appear just before the TDC
notches (see Part A of Chapter 2, Section 4,
for further information if required).
41Start the engine and allow it to idle. Work
through the engine-running test procedure
until the ECU enters its “Service Adjustment
Programme” - see paragraph 35 above.
42Use the timing light to check that the
timing marks appear approximately as
outlined above at idle speed. Do not spend
too much time on this check; if the timing
appears to be incorrect, the system may have
a fault, and a full system test must be carried
out (see below) to establish its cause.
43Using the tachometer, check that the
base idle speed is as given in the
Specifications Section of Chapter 4.
44If the recorded speed differs significantly
from the specified value, check for air leaks,
as described in the preliminary checks
(paragraphs 15 to 18 above), or any other
faults which might cause the discrepancy.
45The base idle speed is set in production
by means of an air bypass screw (located in
the front right-hand corner of the throttle
housing) which controls the amount of air that
is allowed to pass through a bypass passage,
past the throttle valve when it is fully closed in
the idle position; the screw is then sealed with
a white tamperproof plug (see illustration). In
service, the idle speed is controlled by the
ECU, which has the ability to compensate for
engine wear, build-up of dirt in the throttle
housing, and other factors which might
require changes in idle speed. The air bypass
screw setting should not, therefore, be
altered. If any alterations are made, a blue
tamperproof plug must be fitted, and the
engine should be allowed to idle for at least
five minutes on completion, so that the ECU
can re-learn its idle values.
46When both checks have been made and
the “Service Adjustment Programme” is
completed, follow the tester instructions to
return to the fault code read-out, and
establish whether the fault has been cured or
not.
Basic check of ignition system
47If the checks so far have not eliminated
the fault, the next step is to carry out a basic
check of the ignition system components,
using an engine analyser with an oscilloscope
- without such equipment, the only tests
possible are to remove and check each spark
plug in turn, to check the spark plug (HT) lead
connections and resistances, and to check
the connections and resistances of the
ignition coil. Refer to the relevant Sections of
Chapters 1 and 5.
Basic check of fuel system
48If the checks so far have not eliminated
the fault, the next step is to carry out a basic
check of the fuel system components.
49Assuming that the preliminary checks
have established that the fuel pump is
operating correctly, that the fuel filter isunlikely to be blocked, and also that there are
no leaks in the system, the next step is to
check the fuel pressure (see Chapter 4). If this
is correct, check the injectors (see Chapter 4)
and the Positive Crankcase Ventilation system
(see Chapter 1).
System test
50The final element of the Ford testing
procedure is to carry out a system test, using
a break-out box - this is a device that is
connected between the ECU and its electrical
connector, so that the individual circuits
indicated by the fault code read-out can be
tested while connected to the system, if
necessary with the engine running. In the case
of many of the system’s components, this
enables their output voltages to be measured
- a more accurate means of testing.
51In addition to the break-out box and the
adaptors required to connect it, several items
of specialist equipment are needed to
complete these tests. This puts them quite
beyond the scope of many smaller dealers, let
alone the DIY owner; the vehicle should be
taken to a Ford dealer for attention.
Note:This Section is concerned principally
with the sensors which give the ECU the
information it needs to control the various
engine management sub-systems - for further
details of those systems and their other
components, refer to the relevant Chapter of
this manual.
General
ECU (Electronic Control Unit)
1This component is the heart of the entire
engine management system, controlling the
fuel injection, ignition and emissions control
systems. It also controls sub-systems such as
the radiator cooling fan, air conditioning and
automatic transmission, where appropriate.
Refer to Section 2 of this Chapter for an
illustration of how it works.
Air mass meter
2This uses a “hot-wire” system, sending the
ECU a constantly-varying (analogue) voltage
signal corresponding to the mass of air
passing into the engine. Since air mass varies
with temperature (cold air being denser than
warm), measuring air mass provides the ECU
with a very accurate means of determining the
correct amount of fuel required to achieve the
ideal air/fuel mixture ratio.
Crankshaft speed/position sensor
3This is an inductive pulse generator bolted
(in a separate bracket) to the cylinder
block/crankcase, to scan the ridges between
36 holes machined in the inboard (right-hand)
face of the flywheel/driveplate. As each ridge
4 Information sensors -
general information, testing,
removal and refitting
6•10 Emissions control systems
3.45 Throttle housing air bypass screw is
sealed on production with a white
tamperproof plug (arrowed)
procarmanuals.com
Page 150 of 279

EGR valve, and check the valve and the
inlet manifold for blockage. Clean or
renew parts as necessary, and recheck.
EGR system
6Any further checking of the system requires
special tools and test equipment. Take the
vehicle to a dealer service department for
checking.
Component renewal
Note:These components will be very hot
when the engine is running. Always allow the
engine to cool down fully before starting work,
to prevent the possibility of burns.
EGR valve
7Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead
- see Section 1 of Chapter 5.
8Remove the air mass meter and resonator -
refer to Chapter 4.
9Detach the vacuum hose, unscrew the
sleeve nut securing the EGR pipe to the valve,
remove the two valve mounting bolts, and
withdraw the valve from the inlet manifold
(see illustrations). Ensure that the end of the
pipe is not damaged or distorted as the valve
is withdrawn, and note the valve’s gasket; this
must be renewed whenever the valve is
disturbed.
10Note that the metal pipe from the valve to
the manifold itself should not be disturbed - it
is not available separately from the manifold.However, check whenever the manifold is
removed that the pipe’s end fitting is securely
fastened (see illustration).
11Check the valve for sticking and heavy
carbon deposits. If such is found, clean the
valve or renew it.
12Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure. Apply a smear of anti-seize
compound to the sleeve nut threads, fit a new
gasket, and tighten the valve bolts to the
specified torque wrench setting.
EGR pipe
13Disconnect the battery negative (earth)
lead - see Section 1 of Chapter 5.
14Remove the air mass meter and resonator
- refer to Chapter 4.
15Unbolt the exhaust manifold heat shield
and remove both parts, or move them aside
as required to reach the end of the EGR pipe.
Unscrew the sleeve nut securing the pipe to
the exhaust manifold (see illustration).
16Undo the two screws securing the pipe to
the ignition coil bracket, then disconnect the
two vacuum hoses - note that these are of
different sizes, to ensure that they cannot be
mixed up on reconnection. Unscrew the
sleeve nut securing the EGR pipe to the valve
(see illustration). Withdraw the pipe.
17Check the condition of both hoses, and
renew them if necessary (see Chapter 1). Note
that if the exhaust gases have been backfiring
excessively - eg, due to a blocked exhaust
system - both hoses must be renewed, andtheir connections on the pipe must be cleaned
thoroughly.
18Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure; ensure that the hoses are securely
connected to the correct unions. Apply a
smear of anti-seize compound to the sleeve
nut threads, tighten the nuts securely, and
tighten the two screws to their specified
torque wrench setting.
EGR exhaust gas pressure differential
sensor
19Refer to Section 4 of this Chapter.
EGR solenoid valve
Note:This component can be identified by its
larger top and its two fastening screws. Do not
confuse it with the adjacent pulse-air solenoid
valve, especially when reconnecting vacuum
hoses.
20Disconnect the battery negative (earth)
lead - see Section 1 of Chapter 5.
21Remove the air mass meter and resonator
- refer to Chapter 4. If better access is
required, remove the plenum chamber also
(see illustration).
22Releasing its wire clip, unplug the
electrical connector from the valve. Remove
the two retaining screws, and withdraw the
valve from the bulkhead mounting bracket,
then label and disconnect the two vacuum
hoses.
23Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure; ensure that the hoses are correctly
reconnected.
6•16 Emissions control systems
6.9A Disconnecting vacuum hose from
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) valve . . .6.9B . . . unscrew EGR pipe sleeve nut and
remove bolts (arrowed) to release valve
from inlet manifold6.10 Check end fitting of EGR pipe into
inlet manifold whenever manifold is
removed, but do not disturb
6.15 Unbolt exhaust manifold heat shield,
and unscrew sleeve nut (arrowed) securing
EGR pipe to exhaust manifold . . .6.16 . . . undo screws “A” and sleeve
nut “B”, then disconnect hoses “C” - note
different sizes - to release EGR pipe6.21 EGR solenoid valve “A” and EGR
exhaust gas pressure differential sensor
“B”, located on bulkhead mounting bracket
procarmanuals.com
Page 153 of 279

2The function of these components is to
reduce the emission of unburned
hydrocarbons from the crankcase, and to
minimise the formation of oil sludge. By
ensuring that a depression is created in the
crankcase under most operating conditions,
particularly at idle, and by positively inducing
fresh air into the system, the oil vapours and
“blow-by” gases collected in the crankcase
are drawn from the crankcase, through the oil
separator, into the inlet tract, to be burned by
the engine during normal combustion.
Checking
3Checking procedures for the system
components are included in Chapter 1.
Component renewal
Cylinder head-to-air cleaner hose
4See Chapter 1.
Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV)
valve
5The valve is plugged into the oil separator.
Depending on the tools available, access to
the valve may be possible once the pulse-air
assembly has been removed (see Section 7).
If this is not feasible, proceed as outlined in
paragraph 6 below.
Oil separator
6Remove the exhaust manifold (see Chap-
ter 2, Part A). The Positive Crankcase
Ventilation (PCV) valve can now be unplugged
and flushed, or renewed, as required, as
described in Chapter 1.
7Unbolt the oil separator from the cylinder
block/crankcase, and withdraw it; remove and
discard the gasket.
8Flush out or renew the oil separator, as
required (see Chapter 1).
9On reassembly, fit a new gasket, and
tighten the fasteners to the torque wrench
settings given in the Specifications Section of
Chapter 2, Part B.
10The remainder of the refitting procedure is
the reverse of removal. Refill the cooling
system (see Chapter 1). Run the engine,
check for exhaust leaks, and check the
coolant level when it is fully warmed-up.
General information
1The exhaust gases of any petrol engine
(however efficient or well-tuned) consist
largely (approximately 99 %) of nitrogen (N
2),
carbon dioxide (CO
2), oxygen (O2), other inert
gases and water vapour (H
2O). The remaining
1 % is made up of the noxious materials
which are currently seen (CO
2apart) as the
major polluters of the environment: carbon
monoxide (CO), unburned hydrocarbons (HC),oxides of nitrogen (NO
x) and some solid
matter, including a small lead content.
2Left to themselves, most of these pollutants
are thought eventually to break down naturally
(CO and NO
x, for example, break down in the
upper atmosphere to release CO
2) having first
caused ground-level environmental problems.
The massive increase world-wide in the use of
motor vehicles, and the current popular
concern for the environment has caused the
introduction in most countries of legislation, in
varying degrees of severity, to combat the
problem.
3The device most commonly used to clean
up vehicle exhausts is the catalytic converter.
It is fitted into the vehicle’s exhaust system,
and uses precious metals (platinum and
palladium or rhodium) as catalysts to speed
up the reaction between the pollutants and
the oxygen in the vehicle’s exhaust gases, CO
and HC being oxidised to form H
2O and CO2and (in the three-way type of catalytic
converter) NO
xbeing reduced to N2. Note:
The catalytic converter is not a filter in the
physical sense; its function is to promote a
chemical reaction, but it is not itself affected
by that reaction.
4The converter consists of an element (or
“substrate”) of ceramic honeycomb, coated
with a combination of precious metals in such
a way as to produce a vast surface area over
which the exhaust gases must flow; the whole
being mounted in a stainless-steel box. A
simple “oxidation” (or “two-way”) catalytic
converter can deal with CO and HC only,
while a “reduction” (or “three-way”) catalytic
converter can deal with CO, HC and NO
x.
Three-way catalytic converters are further
sub-divided into “open-loop” (or
“uncontrolled”) converters which can remove
50 to 70 % of pollutants and “closed-loop”
(also known as “controlled” or “regulated”)
converters which can remove over 90 % of
pollutants.
5The catalytic converter fitted to the Mondeo
models covered in this manual is of the three-
way closed-loop type.
6The catalytic converter is a reliable and
simple device, which needs no maintenance
in itself, but there are some facts of which an
owner should be aware if the converter is to
function properly for its full service life.
(a) DO NOT use leaded petrol in a vehicle
equipped with a catalytic converter - the
lead will coat the precious metals,
reducing their converting efficiency, and
will eventually destroy the converter; it will
also affect the operation of the oxygen
sensor, requiring its renewal if lead-
fouled. Opinions vary as to how much
leaded fuel is necessary to affect the
converter’s performance, and whether it
can recover even if only unleaded petrol is
used afterwards; the best course of action
is, therefore, to assume the worst, and to
ensure that NO leaded petrol is used at
any time.
(b) Always keep the ignition and fuel systemswell-maintained in accordance with the
manufacturer’s schedule (Chapter 1) -
particularly, ensure that the air filter
element, the fuel filter and the spark plugs
are renewed at the correct intervals. If the
intake air/fuel mixture is allowed to
become too rich due to neglect, the
unburned surplus will enter and burn in
the catalytic converter, overheating the
element and eventually destroying the
converter.
(c) If the engine develops a misfire, do not
drive the vehicle at all (or at least as little
as possible) until the fault is cured - the
misfire will allow unburned fuel to enter
the converter, which will result in its
overheating, as noted above. For the
same reason, do not persist if the engine
refuses to start - either trace the problem
and cure it yourself, or have the vehicle
checked immediately by a qualified
mechanic.
(d) Avoid allowing the vehicle to run out of
petrol.
(e) DO NOT push- or tow-start the vehicle
unless no other alternative exists,
especially if the engine and exhaust are at
normal operating temperature. Starting
the engine in this way may soak the
catalytic converter in unburned fuel,
causing it to overheat when the engine
does start - see (b) above.
(f) DO NOT switch off the ignition at high
engine speeds, in particular, do not “blip”
the throttle immediately before switching
off. If the ignition is switched off at
anything above idle speed, unburned fuel
will enter the (very hot) catalytic converter,
with the possible risk of its igniting on the
element and damaging the converter.
(g) Avoid repeated successive cold starts
followed by short journeys. If the
converter is never allowed to reach its
proper working temperature, it will gather
unburned fuel, allowing some to pass into
the atmosphere and the rest to soak in
the element, causing it to overheat when
a long journey is made - see (b) above.
(h) DO NOT use fuel or engine oil additives -
these may contain substances harmful to
the catalytic converter. Similarly, DO NOT
use silicone-based sealants on any part of
the engine or fuel system, and do not use
exhaust sealants on any part of the
exhaust system upstream of the catalytic
converter. Even if the sealant itself does
not contain additives harmful to the
converter, pieces of it may break off and
foul the element, causing local
overheating.
(i) DO NOT continue to use the vehicle if the
engine burns oil to the extent of leaving a
visible trail of blue smoke. Unburned
carbon deposits will clog the converter
passages and reduce its efficiency; in
severe cases, the element will overheat.
(j) Remember that the catalytic converter
operates at very high temperatures -
9 Catalytic converter -
general information, checking
and component renewal
Emissions control systems 6•19
6
procarmanuals.com